Coupling of the Canadian Regional Climate Model with lake models
|
|
|
- Lenard Boyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Workshop on Parametrization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling 18-2 September 28, St. Petersburg (Zelenogorsk), Russia Coupling of the Canadian Regional Climate Model with lake models Andrey Martynov, Laxmi Sushama, René Laprise Canadian regional climate modelling and diagnostics (CRCMD) Network University of Quebec in Ouranos
2 Outline Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM) Land surface modelling in CRCM: a short overview Lakes in Canada: abundance and diversity Lakes in CRCM: mixing layer model (S. Goyette) Lakes in CRCM: coupling with 1D lakes models - Lake models - Off-line lake model tests - Coupled CRCM-lakes simulations: first results Summary and future plans Lake Estérel, Québec, Canada
3 Canadian Regional Climate Model The Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM): A good CRCM review: Laprise R., Regional Climate Modelling, J. Comp. Phys., 227(28) Current version: CRCM 4 Dynamics: fully elastic non-hydrostatic formulation, semi-implicit semi-lagrangian time scheme, based on the Mesoscale Compressible Community MC2 model Physical parameterisation : currently based on the GCMIII package of CCCMa with the surface schema CLASS 2.7. Horizontal resolution: 4 km, single-processor code Towards CRCM : a high-resolution regional model Horizontal resolution: 1-2 km, fit for massively-parallelised computing Based on the existing dynamical core of the Global Environment Multi-scale (GEM) global model of RPN (Recherche en Prévision Numérique, Environment Canada) in the GEM-LAM configuration Physical parameterisation: RPN-GEM physical package with the surface schema ISBA (better suited for the NWP-use) and, alternatively, GCMIV with CLASS 3.3 for climate simulations. GEM configurations: Global Regular Global Variable GEM - LAM
4 Land surface modelling in CRCM Current surface scheme: CLASS 2.7 (Canadian LAnd Surface Scheme: D. L. Verseghy, Atmosphere-Ocean, vol. 38, no. 1, pp. 1-13, 2) Thermally separate vegetation canopy, snow cover and three soil layers (.1,.2, 3.7m). Four main vegetation structural types (needleleaf trees, broadleaf trees, crops and grass) Up to four subareas allowed over each model grid cell: vegetation covered, bare soil, snow with vegetation and snow over bare soil One soil type for each grid cell A simple mixed layer lake model of the Great Lakes CLASS 2.7 to CLASS 3.3: Optional mosaic formulation (subgrid lakes!) Ability to model organic soils Ability to model lateral movement of soil water 4 Enhanced snow density and snow interception New canopy conductance formulation Option for multiple soil layers at depth User-defined soil and vegetation types CLASS2.7 structure (from Verseghy 2) Other advanced land modelling elements in CRCM: Dynamic vegetation: based on the Canadian Terrestrial Ecosystem Model (CTEM). Interactive permafrost: based on the Goodrich model Interactive lakes: coupling with 1D column lake models.
5 Lakes in Canada: abundance and diversity Inland water bodies. Data sources: GLWD 1,2,3 databases, SWBD database (between 6 S and 6 N) 9% of Canada s territory is covered by lakes, especially abundant on the Canadian Shield. Their influence on the regional climate can be substantial in many areas. There are lakes of all kinds and sizes in Canada: from small tundra ponds to the Great Lakes. - Many large and deep lakes are resolved by CRCM (current resolution: 4 km, planned: 1 km) - Numerous small and shallow lakes remain unresolved at the CRCM resolution (subgrid lakes) Lake models have to deal with both resolved and subgrid lakes
6 Lakes in Canada: abundance and diversity Lakes of different kinds: large, medium, small - influence the climate and have to be taken into account by regional climate models. Physical conditions and thermal regimes are different in lakes of different sizes and depths. Some examples: Water convection is often stronger in large, deep lakes because many physical mechanisms that cause water mixing, become important in these lakes. Under-ice convection can become important in such lakes. Deeper mixing layers in deep lakes than in shallow ones, leading to longer spring heating and lower maximum temperatures The sediment layer can be important in shallow lakes, but negligible in deep lakes The ice cover is less homogenous in large lakes, with ice breaking and drifting far from it's origin - influencing the surface albedo, evaporation, latent and sensible heat fluxes Lake Superior, NDBC buoy N, 87.78W Depth: m Area: 1277 km 2 Sparkling Lake 46.N, 89.61W Depth: 2. m Area:.64 km 2 Months of the year 2 It is known that lake models of different kinds (3D,1D,D) suit better to large, medium and small lakes. Coupling different lake models in parallel with the regional climate models can be too complex and computationally expensive. For the sake of simplicity, it is preferable to use a single lake model for all kinds of lakes. It is important to determine, whether such compromise can be achieved. In CRCM, first lake model coupling was realized by S. Goyette: a mixed layer model, using heat flux residuals, is now part of the standard CRCM 4 Coupling with 1D lake models is currently underway. Ice on a small lake Ice on the Lake Erie
7 Lakes in CRCM: mixed layer model of the Great Lakes Goyette, S., N.A. McFarlane, and G. Flato, 2: Application of the Canadian Regional Climate Model to the Laurentian Great Lakes Regions. Implementation of a Lake Model. Atmos. Oc., 38, Lake water temperature: mixed-layer model Thermodynamic ice model with ice leads, simulating the ice redistribution in the Great Lakes Horizontal and vertical heat flux residuals, obtained from uncoupled simulations, are used to adjust the thermal balance in lake water and ice Air-lakes interaction: the same formulation as for the open ocean: - The neutral drag 1m height C D =1.3*1-3, close to experimental estimations over the Great Lakes (adjusted to the actual lowest model level) - The effects of atmospheric stability on surface drag are accounted for by a Richardson number dependence (McFarlane, N.A et al, 1987: J. Clim., (1), ) Main result: good reproduction of annual thermal cycle in Great Lakes Inconveniences: - An uncoupled simulation is required in order to produce residuals - Not applicable to subgrid lakes Average water surface temperature, o C 2 Superior 1 Michigan 2 Huron 1 Ontario 3 Erie 2 1 Observed Goyette/CRCM Months
8 Lakes in CRCM: 1D lake models Two 1D lake models, having water and ice/snow modules, are currently considered for coupling with CRCM: The model of S.W. Hostetler: Hostetler S.W., Bates G.T., Georgi F.,1993: J Geoph. Res., 98(D3), p 4 Water: 1D heat diffusion equation is solved, eddy turbulence is parameterized by the enhanced thermal diffusion coefficient. Thermal convection is taken into account. Zero heat flux on the bottom. Ice/snow: modified Patterson-Hamblin thermal balance model. Patterson, J. C., and P. F. Hamblin Thermal simulation of lakes with winter ice cover. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33: Fractial ice coverage: separate temperature profiles for ice-free and ice-covered tile fractions, then horizontal mixing, weighted by the ice coverage fraction. Simple ice redistribution mechanism is provided; it can be easlily modified or replaced by another mechanism. FLake (Freshwater Lake model): D. Mironov et al., Water: self-similarity based parametric approach. Two explicit layers: the mixed layer and the thermocline Ice/snow, active bottom sediment layer : similar parametric approach. Ice cover: no fractional coverage, the same ice thickness everywhere. The parametric concept of the FLake model makes it more difficult to implement fractional ice cover mechanisms. Before coupling with the CRCM, both lake models were tested in different conditions, representing the variety of Canadian lakes. Two extreme cases: small, shallow and large, deep lakes were studied.
9 Offline tests: small lakes Sparkling Lake, Wisc., USA. Dimictic freezing lake, area:.64 km 2, max depth: 2 m, Sechhi depth: 7.m Data sources: the LTER NTL project buoy measurements and nearby airport's meteorological data Simulation: perpetual year 2, timestep: 1hour, no sediments (FLake), no snow Surface temperature: good for both models - Hostetler s model: rapid temperature changes in autumn and spring Mixing layer depth: higher in FLake in spring (full overturning) Ice thickness and duration: good for both models Small, shallow lakes: good performance of both models Water surface temperature, o C Mixing depth, m Observations Hostetler FLake Ice-free period (observation) Julian day (2) Ice thickness, m
10 Offline tests: the Great Lakes Simulation period: , 1 years spin-up. Timestep: 1hour. Horizontal resolution: 4 km Input data: ERA4 reanalysis at 2.º, interpolated to 144 points over the Great Lakes, simulating the CRCM grid Validation data sources: NDBC buoy observations, NOAA Great Lakes Ice Atlas Observed and simulated water surface temperatures Lake Superior, NDBC buoy 41, depth: m Observations Hostetler offline FLake offline Lake Michigan, NDBC buoy 42, depth: m Lake Erie, NDBC buoy 4, depth: 12.6 m Average water surface temperature, o C Water temperature climatology Superior Michigan Huron Ontario Erie Observed CRCM/Goyette Hostetler FLake Months Offline Great Lakes tests: both models have problems with deep lakes.
11 Coupling with lake models This work is currently in the research phase: debugging and first runs are being carried out. A CLASS/lake models interface was added, forming input and output data for lake models. The switch LAKE in the CRCM input file "PARAMETRES" defines the lake model choice: no interactive lakes LAKE = 1 S. Goyette's model (requires previously calculated residuals) 2 Hostetler's model 3 FLake model New options can be added in future Only lakes, resolved at 4 km, can be dealt with under current CRCM/CLASS versions. Air-lake interactions, water/ice albedo: now as in S. Goyette model. No snow over ice (yet) Hostetler: real bathymetry, FLake: maximum depth: 6 meters. FLake: continuous ice cover, no ice redistribution within tiles Hostetler's model: continuous ice cover or ice redistribution, following McFarlane, N.A. et al, 1992: The Canadian Climate Centre Second-Generation General Circulation Model and Its Equilibrium Climate. J. Climate,,
12 Coupling with lake models First coupled simulation: year 1991, LAKE=2 (Hostetler), driven at the boundaries by the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis Grid: 8 9, horizontal resolution: 4 km. Lakes: only the Great Lakes (other lakes are masked out) Lake Superior, NDBC buoy 41, depth: m Lake Michigan, NDBC buoy 42, depth: m Observations Hostetler offline FLake offline CRCM/Hostetler Lake Michigan, NDBC buoy 47, depth: 16 m Simulation domain Lake Huron, NDBC buoy 48, depth: 4.3 m This coupled simulation reproduces much better the observed temperature patterns, than offline ones. Long spring water warming from C to 4 C in deep lakes is reproduced in coupled simulations. Why? Too high water temperature in summertime: air/lake interactions need to be adjusted. Lake Erie, NDBC buoy 4, depth: 12.6 m
13 Coupling with lake models The initial water temperature profile (the 1 st of January 1991) in the presented coupled simulation was linear, with C at the surface and +4 C at the bottom. This is not an equilibrium profile for the Hostetler s model. In wintertime and in presence of ice, the Hostetler s model would produce an almost neutral equilibrium profile at +4 C, with a thin cold layer close to the surface. The spring water warming is very different in these two cases. Linear temperature profile under the ice: The water surface heats up after the complete ice melting temperature inversion deep convection slow water surface heating from C to 4 C. Constant temperature profile under the ice (equilibrium profile): The water surface heats up after the complete ice melting only the thin upper layer has to be heated up the water column remains stable no convection very rapid water surface heating from C to 4 C, as demonstrated by offline simulations. Linear temperature profile under the ice: impossible with the standard Hostetler s model, but approximating the actual situation in large and deep lakes with mixing, stronger than in the Hostetler s model. An unintentional, but useful insight on possible ways of modelling deep lakes with 1D models. Lake Superior, NDBC buoy 41, depth: m 2 Observations Hostetler offline CRCM/Hostetler 2 1 Surface Bottom 4 T, C
14 Coupling with lake models: FLake First coupled simulation: year 1991, LAKE=3 (FLake), driven at the boundaries by the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis Grid: 8 9, horizontal resolution: 4 km. Lakes: only the Great Lakes (other lakes are masked out) The simulation was not finished because the computer was turned off Lake Superior, NDBC buoy 41, depth: m 18 9 Observations Hostetler offline FLake offline CRCM/Hostetler CRCM/FLake Simulation domain
15 Summary A new version of the Canadian Regional Climate Model will include several advanced land modelling elements, among them interactive lakes. Lakes are a substantial element of the Canadian climate system. Both small, shallow and large, deep lakes are important for the regional climate and have to be taken into account in the Canadian regional climate simulations. Offline tests have shown good performance of 1D lake models in small and shallow lakes. Substantial problems exist, however, with large and deep lakes (the Great Lakes). First coupled CRCM -1D lake model simulations were carried out. The simulation with the Hostetler s model revealed the importance of the correct model initialisation as well an interesting dependence of the model behavior on the initial temperature profile. Future plans Lakes are introduced in the CRCM in a step-by-step manner: - Mixed layer model of Stephan Goyette (the Great Lakes only) - Offline 1D lake model tests and validation - Coupling with 1D lake models Surface schema / lake models interface for resolved lakes (CRCM4/CLASS2.7) - current phase Tests and validation of coupled model - current phase Correction of lake models and of the air-lake interaction parameterization Multi-decadal simulations, climate change simulations - Implementation of lake coupling to subgrid lakes, using the mosaic approach (CRCM4/CLASS3.3, then CRCM/CLASS 3.3 and later versions)
Interactive lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM): present state and perspectives
 44th Annual CMOS Congress May 31 June 4, 21, Ottawa Interactive lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM): present state and perspectives A. Martynov, L. Sushama, R. Laprise Centre ESCER Université
44th Annual CMOS Congress May 31 June 4, 21, Ottawa Interactive lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM): present state and perspectives A. Martynov, L. Sushama, R. Laprise Centre ESCER Université
Interactive Lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model, versions 4 and 5
 2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Norrköping, Sweden, September 15-17 21 Interactive Lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model, versions
2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Norrköping, Sweden, September 15-17 21 Interactive Lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model, versions
Regional offline land surface simulations over eastern Canada using CLASS. Diana Verseghy Climate Research Division Environment Canada
 Regional offline land surface simulations over eastern Canada using CLASS Diana Verseghy Climate Research Division Environment Canada The Canadian Land Surface Scheme (CLASS) Originally developed for the
Regional offline land surface simulations over eastern Canada using CLASS Diana Verseghy Climate Research Division Environment Canada The Canadian Land Surface Scheme (CLASS) Originally developed for the
Andrey Martynov 1, René Laprise 1, Laxmi Sushama 1, Katja Winger 1, Bernard Dugas 2. Université du Québec à Montréal 2
 CMOS-2012, Montreal, 31 May 2012 Reanalysis-driven climate simulation over CORDEX North America domain using the Canadian Regional Climate Model, version 5: model performance evaluation Andrey Martynov
CMOS-2012, Montreal, 31 May 2012 Reanalysis-driven climate simulation over CORDEX North America domain using the Canadian Regional Climate Model, version 5: model performance evaluation Andrey Martynov
The Lake Model Intercomparison Project (LakeMIP): present state and perspectives
 2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Norrköping, Sweden, September 15-17 2010 The Lake Model Intercomparison Project (LakeMIP): present state
2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Norrköping, Sweden, September 15-17 2010 The Lake Model Intercomparison Project (LakeMIP): present state
DESCRIPTION OF THE CANADIAN REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL. 1. Introduction
 DESCRIPTION OF THE CANADIAN REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL D. CAYA ~, R. LAPRISE ~, M. GIGUI~RE ', G. BERGERON ~, J. P. BLANCHET ~, B. J. STOCKS z, G. J. BOER 3 and N. A. McFARLANE 3 1Cooperative Centre for Research
DESCRIPTION OF THE CANADIAN REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL D. CAYA ~, R. LAPRISE ~, M. GIGUI~RE ', G. BERGERON ~, J. P. BLANCHET ~, B. J. STOCKS z, G. J. BOER 3 and N. A. McFARLANE 3 1Cooperative Centre for Research
SIMULATION OF ARCTIC STORMS 7B.3. Zhenxia Long 1, Will Perrie 1, 2 and Lujun Zhang 2
 7B.3 SIMULATION OF ARCTIC STORMS Zhenxia Long 1, Will Perrie 1, 2 and Lujun Zhang 2 1 Fisheries & Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth NS, Canada 2 Department of Engineering Math,
7B.3 SIMULATION OF ARCTIC STORMS Zhenxia Long 1, Will Perrie 1, 2 and Lujun Zhang 2 1 Fisheries & Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth NS, Canada 2 Department of Engineering Math,
Lake and Climate Models Linkage: A 3D Hydrodynamic Contribution
 Lake and Climate Models Linkage: A 3D Hydrodynamic Contribution Luis F. Leon 1a,b, David Lam 2, William Schertzer 2 and David Swayne 1b 1a University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, N2G3L1 (lfleonvi@uwaterloo.ca)
Lake and Climate Models Linkage: A 3D Hydrodynamic Contribution Luis F. Leon 1a,b, David Lam 2, William Schertzer 2 and David Swayne 1b 1a University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, N2G3L1 (lfleonvi@uwaterloo.ca)
The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes
 1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
Interactive lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model, version 5: the role of lakes in the regional climate of North America
 SERIES A DYNAMIC METEOROLOGY AND OCEANOGRAPHY PUBLISHED BY THE INTERNATIONAL METEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE IN STOCKHOLM Interactive lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model, version 5: the role of lakes
SERIES A DYNAMIC METEOROLOGY AND OCEANOGRAPHY PUBLISHED BY THE INTERNATIONAL METEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE IN STOCKHOLM Interactive lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model, version 5: the role of lakes
Current status of lake modelling and initialisation at ECMWF
 Current status of lake modelling and initialisation at ECMWF G Balsamo, A Manrique Suñen, E Dutra, D. Mironov, P. Miranda, V Stepanenko, P Viterbo, A Nordbo, R Salgado, I Mammarella, A Beljaars, H Hersbach
Current status of lake modelling and initialisation at ECMWF G Balsamo, A Manrique Suñen, E Dutra, D. Mironov, P. Miranda, V Stepanenko, P Viterbo, A Nordbo, R Salgado, I Mammarella, A Beljaars, H Hersbach
Lake parameters climatology for cold start runs (lake initialization) in the ECMWF forecast system
 2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Lake parameters climatology for cold start runs (lake initialization) in the ECMWF forecast system R. Salgado(1),
2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Lake parameters climatology for cold start runs (lake initialization) in the ECMWF forecast system R. Salgado(1),
Representing inland water bodies and coastal areas in global numerical weather prediction
 Representing inland water bodies and coastal areas in global numerical weather prediction Gianpaolo Balsamo, Anton Beljaars, Souhail Boussetta, Emanuel Dutra Outline: Introduction lake and land contrasts
Representing inland water bodies and coastal areas in global numerical weather prediction Gianpaolo Balsamo, Anton Beljaars, Souhail Boussetta, Emanuel Dutra Outline: Introduction lake and land contrasts
Simulations of Lake Processes within a Regional Climate Model
 Simulations of Lake Processes within a Regional Climate Model Jiming Jin Departments of Watershed Sciences and Plants, Soils, and Climate Utah State University, Logan, Utah Utah State University 850 Faculty
Simulations of Lake Processes within a Regional Climate Model Jiming Jin Departments of Watershed Sciences and Plants, Soils, and Climate Utah State University, Logan, Utah Utah State University 850 Faculty
A 3D Hydrodynamic Lake Model: Simulation on Great Slave Lake
 A 3D Hydrodynamic Lake Model: Simulation on Great Slave Lake Luis F. León 1, David C.L. Lam 2, William M. Schertzer 2 and David A. Swayne 3 1 University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada: lfleonvi@uwaterloo.ca
A 3D Hydrodynamic Lake Model: Simulation on Great Slave Lake Luis F. León 1, David C.L. Lam 2, William M. Schertzer 2 and David A. Swayne 3 1 University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada: lfleonvi@uwaterloo.ca
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks. Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC
 Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Introducing inland water bodies and coastal areas in ECMWF forecasting system:
 Introducing inland water bodies and coastal areas in ECMWF forecasting system: Outline: Introduction lake and land contrasts forecasts impact when considering lakes Summary & outlook Gianpaolo Balsamo
Introducing inland water bodies and coastal areas in ECMWF forecasting system: Outline: Introduction lake and land contrasts forecasts impact when considering lakes Summary & outlook Gianpaolo Balsamo
Future Great Lakes climatology and water levels simulated using Regional Climate Models
 Future Great Lakes climatology and water levels simulated using Regional Climate Models Frank Seglenieks Environment Canada The St. Clair River Symposium Port Huron, MI 2014-09-18 Summary Great Lakes hydroclimatology
Future Great Lakes climatology and water levels simulated using Regional Climate Models Frank Seglenieks Environment Canada The St. Clair River Symposium Port Huron, MI 2014-09-18 Summary Great Lakes hydroclimatology
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate
 Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
THE CANADIAN CENTRE FOR CLIMATE MODELLING AND ANALYSIS
 THE CANADIAN CENTRE FOR CLIMATE MODELLING AND ANALYSIS As Canada s climate changes, and weather patterns shift, Canadian climate models provide guidance in an uncertain future. CANADA S CLIMATE IS CHANGING
THE CANADIAN CENTRE FOR CLIMATE MODELLING AND ANALYSIS As Canada s climate changes, and weather patterns shift, Canadian climate models provide guidance in an uncertain future. CANADA S CLIMATE IS CHANGING
An Overview of Atmospheric Models
 An Overview of Atmospheric Models MAGS Model Cross-Training Workshop 5-6 September 2002, York University Kit K. Szeto Climate Research Branch, Meteorological Service of Canada 4905 Dufferin Street, Downsview,
An Overview of Atmospheric Models MAGS Model Cross-Training Workshop 5-6 September 2002, York University Kit K. Szeto Climate Research Branch, Meteorological Service of Canada 4905 Dufferin Street, Downsview,
Multiple climate regimes in an idealized lake ice atmosphere model
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) 1 2 Multiple climate regimes in an idealized lake ice atmosphere model 3 4 Noriyuki Sugiyama Sergey Kravtsov Paul Roebber 5 6 January 26, 2017 7 8
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) 1 2 Multiple climate regimes in an idealized lake ice atmosphere model 3 4 Noriyuki Sugiyama Sergey Kravtsov Paul Roebber 5 6 January 26, 2017 7 8
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra
 Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Pierre Gauthier Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Université du Québec à Montréal (UQAM)
 Pierre Gauthier Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Université du Québec à Montréal (UQAM) Contributions: Katja Winger, Kamel Chikhar, René Laprise, Laxmi Sushama Department of Earth and Atmospheric
Pierre Gauthier Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Université du Québec à Montréal (UQAM) Contributions: Katja Winger, Kamel Chikhar, René Laprise, Laxmi Sushama Department of Earth and Atmospheric
Climate Modelling and Scenarios in Canada. Elaine Barrow Principal Investigator (Science) Canadian Climate Impacts Scenarios (CCIS) Project
 Climate Modelling and Scenarios in Canada Elaine Barrow Principal Investigator (Science) Canadian Climate Impacts Scenarios (CCIS) Project Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis (CCCma) http://www.cccma.bc.ec.gc.ca
Climate Modelling and Scenarios in Canada Elaine Barrow Principal Investigator (Science) Canadian Climate Impacts Scenarios (CCIS) Project Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis (CCCma) http://www.cccma.bc.ec.gc.ca
COLOBOC Project Status
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss COLOBOC Project Status Jean-Marie Bettems / MeteoSwiss COLOBOC/SOILVEG Workshop Langen, February 28th, 2011
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss COLOBOC Project Status Jean-Marie Bettems / MeteoSwiss COLOBOC/SOILVEG Workshop Langen, February 28th, 2011
Modelling approaches for MOSAiC. Klaus Dethloff, A. Rinke, A. Sommerfeld, D. Klaus T. Vihma, M. Müller, J. Inoue, W. Maslowski & modelling team
 Modelling approaches for MOSAiC Klaus Dethloff, A. Rinke, A. Sommerfeld, D. Klaus T. Vihma, M. Müller, J. Inoue, W. Maslowski & modelling team Why do we need MOSAiC? High quality co-observations of A-O-I-BGC-E
Modelling approaches for MOSAiC Klaus Dethloff, A. Rinke, A. Sommerfeld, D. Klaus T. Vihma, M. Müller, J. Inoue, W. Maslowski & modelling team Why do we need MOSAiC? High quality co-observations of A-O-I-BGC-E
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Sensitivity of Present Day Arctic Climate Simulations to Snow
 Sensitivity of Present Day Arctic Climate Simulations to Snow Heidrun Matthes, Annette Rinke Alfred-Wegener- Institute for Polar and Marine Research photo: Thomas Opel Motivation - Why do we care? Snow
Sensitivity of Present Day Arctic Climate Simulations to Snow Heidrun Matthes, Annette Rinke Alfred-Wegener- Institute for Polar and Marine Research photo: Thomas Opel Motivation - Why do we care? Snow
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change. Renguang Wu
 The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
The Arctic Ocean's response to the NAM
 The Arctic Ocean's response to the NAM Gerd Krahmann and Martin Visbeck Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University RT 9W, Palisades, NY 10964, USA Abstract The sea ice response of the Arctic
The Arctic Ocean's response to the NAM Gerd Krahmann and Martin Visbeck Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University RT 9W, Palisades, NY 10964, USA Abstract The sea ice response of the Arctic
Wind Flow Modeling The Basis for Resource Assessment and Wind Power Forecasting
 Wind Flow Modeling The Basis for Resource Assessment and Wind Power Forecasting Detlev Heinemann ForWind Center for Wind Energy Research Energy Meteorology Unit, Oldenburg University Contents Model Physics
Wind Flow Modeling The Basis for Resource Assessment and Wind Power Forecasting Detlev Heinemann ForWind Center for Wind Energy Research Energy Meteorology Unit, Oldenburg University Contents Model Physics
A NEMO-based hydrodynamic/hydraulic system for the Great Lakes. F. Dupont, P. Chittibabu, A. Huang, R. Yerubandi, V. Fortin, Y. Lu
 A NEMO-based hydrodynamic/hydraulic system for the Great Lakes F. Dupont, P. Chittibabu, A. Huang, R. Yerubandi, V. Fortin, Y. Lu Objectives: Development of a coupled hydrological forecasting system for
A NEMO-based hydrodynamic/hydraulic system for the Great Lakes F. Dupont, P. Chittibabu, A. Huang, R. Yerubandi, V. Fortin, Y. Lu Objectives: Development of a coupled hydrological forecasting system for
Don't let your PBL scheme be rejected by brine: Parameterization of salt plumes under sea ice in climate models
 Don't let your PBL scheme be rejected by brine: Parameterization of salt plumes under sea ice in climate models Dimitris Menemenlis California Institute of Technology, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Frontiers
Don't let your PBL scheme be rejected by brine: Parameterization of salt plumes under sea ice in climate models Dimitris Menemenlis California Institute of Technology, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Frontiers
Parameterization of Lakes in NWP and Climate Models
 Parameterization of Lakes in NWP and Climate Models Dmitrii Mironov and Jürgen Helmert German Weather Service, Offenbach am Main, Germany Hermann Asensio, Erdmann Heise, Ekaterina Machulskaya, Bodo Ritter
Parameterization of Lakes in NWP and Climate Models Dmitrii Mironov and Jürgen Helmert German Weather Service, Offenbach am Main, Germany Hermann Asensio, Erdmann Heise, Ekaterina Machulskaya, Bodo Ritter
Modeling the Arctic Climate System
 Modeling the Arctic Climate System General model types Single-column models: Processes in a single column Land Surface Models (LSMs): Interactions between the land surface, atmosphere and underlying surface
Modeling the Arctic Climate System General model types Single-column models: Processes in a single column Land Surface Models (LSMs): Interactions between the land surface, atmosphere and underlying surface
M.Sc. in Meteorology. Physical Meteorology Prof Peter Lynch. Mathematical Computation Laboratory Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield.
 M.Sc. in Meteorology Physical Meteorology Prof Peter Lynch Mathematical Computation Laboratory Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Climate Change???????????????? Tourists run through a swarm of pink
M.Sc. in Meteorology Physical Meteorology Prof Peter Lynch Mathematical Computation Laboratory Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Climate Change???????????????? Tourists run through a swarm of pink
The HIGHTSI ice model and plans in SURFEX
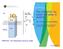 Air Snow T in Ice with snow cover T sfc x T snow Q si F si h s h s The HIGHTSI ice model and plans in SURFEX Bin Cheng and Laura Rontu Water Ice T ice h i Finnish Meteorological Institute, FI-11 Helsinki,
Air Snow T in Ice with snow cover T sfc x T snow Q si F si h s h s The HIGHTSI ice model and plans in SURFEX Bin Cheng and Laura Rontu Water Ice T ice h i Finnish Meteorological Institute, FI-11 Helsinki,
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Update on Coupled Air-Sea-Ice Modelling
 Update on Coupled Air-Sea-Ice Modelling H. Ritchie 1,4, G. Smith 1, J.-M. Belanger 1, J-F Lemieux 1, C. Beaudoin 1, P. Pellerin 1, M. Buehner 1, A. Caya 1, L. Fillion 1, F. Roy 2, F. Dupont 2, M. Faucher
Update on Coupled Air-Sea-Ice Modelling H. Ritchie 1,4, G. Smith 1, J.-M. Belanger 1, J-F Lemieux 1, C. Beaudoin 1, P. Pellerin 1, M. Buehner 1, A. Caya 1, L. Fillion 1, F. Roy 2, F. Dupont 2, M. Faucher
Land Surface Modeling in the Navy Operational Global Atmospheric Prediction System. Timothy F. Hogan Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943
 11.B.1 Land Surface Modeling in the Navy Operational Global Atmospheric Prediction System Timothy F. Hogan Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943 1. INTRODUCTION The Navy Operational Global Atmospheric
11.B.1 Land Surface Modeling in the Navy Operational Global Atmospheric Prediction System Timothy F. Hogan Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943 1. INTRODUCTION The Navy Operational Global Atmospheric
ICRC-CORDEX Sessions A: Benefits of Downscaling Session A1: Added value of downscaling Stockholm, Sweden, 18 May 2016
 ICRC-CORDEX Sessions A: Benefits of Downscaling Session A1: Added value of downscaling Stockholm, Sweden, 18 May 2016 Challenges in the quest for added value of climate dynamical downscaling: Evidence
ICRC-CORDEX Sessions A: Benefits of Downscaling Session A1: Added value of downscaling Stockholm, Sweden, 18 May 2016 Challenges in the quest for added value of climate dynamical downscaling: Evidence
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic
 Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica
 Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Climate Roles of Land Surface
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
SENSITIVITY STUDY FOR SZEGED, HUNGARY USING THE SURFEX/TEB SCHEME COUPLED TO ALARO
 SENSITIVITY STUDY FOR SZEGED, HUNGARY USING THE SURFEX/TEB SCHEME COUPLED TO ALARO Report from the Flat-Rate Stay at the Royal Meteorological Institute, Brussels, Belgium 11.03.2015 01.04.2015 Gabriella
SENSITIVITY STUDY FOR SZEGED, HUNGARY USING THE SURFEX/TEB SCHEME COUPLED TO ALARO Report from the Flat-Rate Stay at the Royal Meteorological Institute, Brussels, Belgium 11.03.2015 01.04.2015 Gabriella
A WATER CYCLE PREDICTION SYSTEM
 A WATER CYCLE PREDICTION SYSTEM FOR THE GREAT LAKES AND ST. LAWRENCE RIVER V. Fortin 1, D. Durnford 2, G. Smith 1, P. Matte 1, M. Mackay 1, N. Bernier 1... and many others 1 Meteorological Research Division,
A WATER CYCLE PREDICTION SYSTEM FOR THE GREAT LAKES AND ST. LAWRENCE RIVER V. Fortin 1, D. Durnford 2, G. Smith 1, P. Matte 1, M. Mackay 1, N. Bernier 1... and many others 1 Meteorological Research Division,
Extreme Weather and Climate Change: the big picture Alan K. Betts Atmospheric Research Pittsford, VT NESC, Saratoga, NY
 Extreme Weather and Climate Change: the big picture Alan K. Betts Atmospheric Research Pittsford, VT http://alanbetts.com NESC, Saratoga, NY March 10, 2018 Increases in Extreme Weather Last decade: lack
Extreme Weather and Climate Change: the big picture Alan K. Betts Atmospheric Research Pittsford, VT http://alanbetts.com NESC, Saratoga, NY March 10, 2018 Increases in Extreme Weather Last decade: lack
An effective lake depth for FLAKE model
 An effective lake depth for FLAKE model Gianpaolo Balsamo, Emanuel Dutra, Victor Stepanenko, Pedro Viterbo, Pedro Miranda and Anton Beljaars thanks to: Dmitrii Mironov, Arkady Terzhevik, Yuhei Takaya,
An effective lake depth for FLAKE model Gianpaolo Balsamo, Emanuel Dutra, Victor Stepanenko, Pedro Viterbo, Pedro Miranda and Anton Beljaars thanks to: Dmitrii Mironov, Arkady Terzhevik, Yuhei Takaya,
An intercomparison model study of Lake Valkea-Kotinen (in a framework of LakeMIP)
 Third Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Finnish Meteorological Insitute, Helsinki, September 18-20 2012 An intercomparison model study of Lake
Third Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Finnish Meteorological Insitute, Helsinki, September 18-20 2012 An intercomparison model study of Lake
Soil Moisture Prediction and Assimilation
 Soil Moisture Prediction and Assimilation Analysis and Prediction in Agricultural Landscapes Saskatoon, June 19-20, 2007 STEPHANE BELAIR Meteorological Research Division Prediction and Assimilation Atmospheric
Soil Moisture Prediction and Assimilation Analysis and Prediction in Agricultural Landscapes Saskatoon, June 19-20, 2007 STEPHANE BELAIR Meteorological Research Division Prediction and Assimilation Atmospheric
Prof. Simon Tett, Chair of Earth System Dynamics & Modelling: The University of Edinburgh
 SAGES Scottish Alliance for Geoscience, Environment & Society Modelling Climate Change Prof. Simon Tett, Chair of Earth System Dynamics & Modelling: The University of Edinburgh Climate Modelling Climate
SAGES Scottish Alliance for Geoscience, Environment & Society Modelling Climate Change Prof. Simon Tett, Chair of Earth System Dynamics & Modelling: The University of Edinburgh Climate Modelling Climate
The Great Lakes' Regional Climate Regimes
 University of Wisconsin Milwaukee UWM Digital Commons Theses and Dissertations December 2015 The Great Lakes' Regional Climate Regimes Noriyuki Sugiyama University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Follow this and
University of Wisconsin Milwaukee UWM Digital Commons Theses and Dissertations December 2015 The Great Lakes' Regional Climate Regimes Noriyuki Sugiyama University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Follow this and
Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere
 Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere Mike Dinniman and John Klinck Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University
Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere Mike Dinniman and John Klinck Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University
Investigating Regional Climate Model - RCM Added-Value in simulating Northern America Storm activity
 Investigating Regional Climate Model - RCM Added-Value in simulating Northern America Storm activity E. D. Poan 1, P. Gachon 1, R. Laprise 1, R. Aider 1,2, G. Dueymes 1 1 Centre d Etude et la Simulation
Investigating Regional Climate Model - RCM Added-Value in simulating Northern America Storm activity E. D. Poan 1, P. Gachon 1, R. Laprise 1, R. Aider 1,2, G. Dueymes 1 1 Centre d Etude et la Simulation
Related Improvements. A DFS Application. Mark A. Bourassa
 Related Improvements in Surface Turbulent Heat Fluxes A DFS Application Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, The Florida State University,
Related Improvements in Surface Turbulent Heat Fluxes A DFS Application Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies & Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, The Florida State University,
Mesoscale meteorological models. Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen
 Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Weather Research and Forecasting Model. Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004
 Weather Research and Forecasting Model Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004 Outline What does WRF model do? WRF Standard Initialization WRF Dynamics Conservation Equations Grid staggering
Weather Research and Forecasting Model Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004 Outline What does WRF model do? WRF Standard Initialization WRF Dynamics Conservation Equations Grid staggering
Arctic Boundary Layer
 Annual Seminar 2015 Physical processes in present and future large-scale models Arctic Boundary Layer Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology and Bolin Centre for Climate Research Stockholm University,
Annual Seminar 2015 Physical processes in present and future large-scale models Arctic Boundary Layer Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology and Bolin Centre for Climate Research Stockholm University,
Characteristics of the night and day time atmospheric boundary layer at Dome C, Antarctica
 Characteristics of the night and day time atmospheric boundary layer at Dome C, Antarctica S. Argentini, I. Pietroni,G. Mastrantonio, A. Viola, S. Zilitinchevich ISAC-CNR Via del Fosso del Cavaliere 100,
Characteristics of the night and day time atmospheric boundary layer at Dome C, Antarctica S. Argentini, I. Pietroni,G. Mastrantonio, A. Viola, S. Zilitinchevich ISAC-CNR Via del Fosso del Cavaliere 100,
Observational validation of an extended mosaic technique for capturing subgrid scale heterogeneity in a GCM
 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2007 The Authors Journal compilation C 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard TELLUS Observational validation of an extended mosaic technique for capturing subgrid scale
Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2007 The Authors Journal compilation C 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard TELLUS Observational validation of an extended mosaic technique for capturing subgrid scale
The Canadian Precipitation Analysis (CaPA) and the Canadian Land Data Assimilation System (CaLDAS)
 The Canadian Precipitation Analysis (CaPA) and the Canadian Land Data Assimilation System (CaLDAS) Vincent Fortin (and many collaborators) Division de la recherche en météorologie Environnement en Changement
The Canadian Precipitation Analysis (CaPA) and the Canadian Land Data Assimilation System (CaLDAS) Vincent Fortin (and many collaborators) Division de la recherche en météorologie Environnement en Changement
RAL Advances in Land Surface Modeling Part I. Andrea Hahmann
 RAL Advances in Land Surface Modeling Part I Andrea Hahmann Outline The ATEC real-time high-resolution land data assimilation (HRLDAS) system - Fei Chen, Kevin Manning, and Yubao Liu (RAL) The fine-mesh
RAL Advances in Land Surface Modeling Part I Andrea Hahmann Outline The ATEC real-time high-resolution land data assimilation (HRLDAS) system - Fei Chen, Kevin Manning, and Yubao Liu (RAL) The fine-mesh
Great Lakes Update. Volume 191: 2014 January through June Summary. Vol. 191 Great Lakes Update August 2014
 Great Lakes Update Volume 191: 2014 January through June Summary The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) monitors the water levels of each of the Great Lakes. This report provides a summary of the Great
Great Lakes Update Volume 191: 2014 January through June Summary The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) monitors the water levels of each of the Great Lakes. This report provides a summary of the Great
A R C T E X Results of the Arctic Turbulence Experiments Long-term Monitoring of Heat Fluxes at a high Arctic Permafrost Site in Svalbard
 A R C T E X Results of the Arctic Turbulence Experiments www.arctex.uni-bayreuth.de Long-term Monitoring of Heat Fluxes at a high Arctic Permafrost Site in Svalbard 1 A R C T E X Results of the Arctic
A R C T E X Results of the Arctic Turbulence Experiments www.arctex.uni-bayreuth.de Long-term Monitoring of Heat Fluxes at a high Arctic Permafrost Site in Svalbard 1 A R C T E X Results of the Arctic
Great Lakes Update. Volume 188: 2012 Annual Summary
 Great Lakes Update Volume 188: 2012 Annual Summary Background The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) tracks the water levels of each of the Great Lakes. This report highlights hydrologic conditions of
Great Lakes Update Volume 188: 2012 Annual Summary Background The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) tracks the water levels of each of the Great Lakes. This report highlights hydrologic conditions of
CLIMATE CHANGE DATA PROJECTIONS FOR ONTARIO AND THE GREAT LAKES BASIN
 CLIMATE CHANGE DATA PROJECTIONS FOR ONTARIO AND THE GREAT LAKES BASIN ECO Climate Data Roundtable, January 8, 2014 Richard Peltier, Physics, U Toronto Regional Data Sets of Climate Change Projections 2
CLIMATE CHANGE DATA PROJECTIONS FOR ONTARIO AND THE GREAT LAKES BASIN ECO Climate Data Roundtable, January 8, 2014 Richard Peltier, Physics, U Toronto Regional Data Sets of Climate Change Projections 2
P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS
 P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS Haruyasu NAGAI *, Takuya KOBAYASHI, Katsunori TSUDUKI, and Kyeongok KIM
P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS Haruyasu NAGAI *, Takuya KOBAYASHI, Katsunori TSUDUKI, and Kyeongok KIM
ICON-ESM MPI-M s next-generation Earth system model
 ICON-ESM MPI-M s next-generation Earth system model Climate and Earth system models are applied to simulate the past, present, and projected future climate, and to advance understanding of processes that
ICON-ESM MPI-M s next-generation Earth system model Climate and Earth system models are applied to simulate the past, present, and projected future climate, and to advance understanding of processes that
GABLS4 Results from NCEP Single Column Model
 GABLS4 Results from NCEP Single Column Model Weizhong Zheng 1,2, Michael Ek 1,Ruiyu Sun 1,2 and Jongil Han 1,2 1 NOAA/NCEP/Environmental Modeling Center(EMC), USA 2 IMSG@NOAA/NCEP/EMC, USA Email: Weizhong.Zheng@noaa.gov
GABLS4 Results from NCEP Single Column Model Weizhong Zheng 1,2, Michael Ek 1,Ruiyu Sun 1,2 and Jongil Han 1,2 1 NOAA/NCEP/Environmental Modeling Center(EMC), USA 2 IMSG@NOAA/NCEP/EMC, USA Email: Weizhong.Zheng@noaa.gov
Climate Modeling and Downscaling
 Climate Modeling and Downscaling Types of climate-change experiments: a preview 1) What-if sensitivity experiments increase the optically active gases and aerosols according to an assumed scenario, and
Climate Modeling and Downscaling Types of climate-change experiments: a preview 1) What-if sensitivity experiments increase the optically active gases and aerosols according to an assumed scenario, and
Electromagnetic Radiation. Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance. Electromagnetic Spectrum of the Sun
 Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Solar radiation warms the planet Conversion of solar energy at the surface Absorption and emission by the atmosphere The greenhouse
Radiation and the Planetary Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Solar radiation warms the planet Conversion of solar energy at the surface Absorption and emission by the atmosphere The greenhouse
Representing land surface heterogeneity with the tiling method: merits and limitations in presence of large contrast
 683 Representing land surface heterogeneity with the tiling method: merits and limitations in presence of large contrast A. Manrique Suñén, A. Nordbo (1), G. Balsamo, A. Beljaars, and I. Mammarella (1)
683 Representing land surface heterogeneity with the tiling method: merits and limitations in presence of large contrast A. Manrique Suñén, A. Nordbo (1), G. Balsamo, A. Beljaars, and I. Mammarella (1)
Don t like the weather? Wait ten minutes. has been a phrase used by many in the Great
 Climate Change in the Great Lakes Michael John Michalek Don t like the weather? Wait ten minutes. has been a phrase used by many in the Great Lakes region. With weather and temperature extremes being pushed
Climate Change in the Great Lakes Michael John Michalek Don t like the weather? Wait ten minutes. has been a phrase used by many in the Great Lakes region. With weather and temperature extremes being pushed
The Canadian Land Data Assimilation System (CaLDAS)
 The Canadian Land Data Assimilation System (CaLDAS) Marco L. Carrera, Stéphane Bélair, Bernard Bilodeau and Sheena Solomon Meteorological Research Division, Environment Canada Dorval, QC, Canada 2 nd Workshop
The Canadian Land Data Assimilation System (CaLDAS) Marco L. Carrera, Stéphane Bélair, Bernard Bilodeau and Sheena Solomon Meteorological Research Division, Environment Canada Dorval, QC, Canada 2 nd Workshop
Some remarks on climate modeling
 Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Earth s Heat Budget. What causes the seasons? Seasons
 Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting
 Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
Modeling of deep currents in the Japan/East Sea
 Modeling of deep currents in the Japan/East Sea Olga Trusenkova V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia PICES 2014 Annual Meeting, 16-26 October 2014, Korea, Yeosu Deep
Modeling of deep currents in the Japan/East Sea Olga Trusenkova V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia PICES 2014 Annual Meeting, 16-26 October 2014, Korea, Yeosu Deep
Introduction to climate modeling. ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008
 Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
FREEZING- RAIN IN THE GREAT LAKES
 About this Work GLISA participated in a winter climate adaptation project focused on Chicago, IL (http://glisaclimate.org/project/indicator-suite-and-winter-adaptation-measures-for-thechicago-climate-action-plan).
About this Work GLISA participated in a winter climate adaptation project focused on Chicago, IL (http://glisaclimate.org/project/indicator-suite-and-winter-adaptation-measures-for-thechicago-climate-action-plan).
Great Lakes Update. Volume 199: 2017 Annual Summary. Background
 Great Lakes Update Volume 199: 2017 Annual Summary Background The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) tracks and forecasts the water levels of each of the Great Lakes. This report is primarily focused
Great Lakes Update Volume 199: 2017 Annual Summary Background The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) tracks and forecasts the water levels of each of the Great Lakes. This report is primarily focused
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions
 ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
1. Current atmospheric DA systems 2. Coupling surface/atmospheric DA 3. Trends & ideas
 1 Current issues in atmospheric data assimilation and its relationship with surfaces François Bouttier GAME/CNRM Météo-France 2nd workshop on remote sensing and modeling of surface properties, Toulouse,
1 Current issues in atmospheric data assimilation and its relationship with surfaces François Bouttier GAME/CNRM Météo-France 2nd workshop on remote sensing and modeling of surface properties, Toulouse,
Modeling Southern Ocean iceberg drift and decay
 Modeling Southern Ocean iceberg drift and decay Thomas Rackow, C. Wesche, R. Timmermann AWI Climate Dynamics Tuesday, July 29 th, 2014 IUP AWI block seminar on Ice Ocean Interaction Overview 1. Role of
Modeling Southern Ocean iceberg drift and decay Thomas Rackow, C. Wesche, R. Timmermann AWI Climate Dynamics Tuesday, July 29 th, 2014 IUP AWI block seminar on Ice Ocean Interaction Overview 1. Role of
IP3 Workshop #3, November 2008, Whitehorse, Yukon
 River and Lake Ice: Quantification, Extremes and Historical i Trends; Advances under IPY cryosphere/hydrology & ArcticNet Terry Prowse Katrina Bennett Rheannon Brooks Laurent de Rham Holly Goulding Simon
River and Lake Ice: Quantification, Extremes and Historical i Trends; Advances under IPY cryosphere/hydrology & ArcticNet Terry Prowse Katrina Bennett Rheannon Brooks Laurent de Rham Holly Goulding Simon
Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model
 Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model Gabriella Zsebeházi Gabriella Zsebeházi and Gabriella Szépszó Hungarian Meteorological Service,
Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model Gabriella Zsebeházi Gabriella Zsebeházi and Gabriella Szépszó Hungarian Meteorological Service,
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Air Pollution Meteorology
 Air Pollution Meteorology Government Pilots Utilities Public Farmers Severe Weather Storm / Hurricane Frost / Freeze Significant Weather Fog / Haze / Cloud Precipitation High Resolution Weather & Dispersion
Air Pollution Meteorology Government Pilots Utilities Public Farmers Severe Weather Storm / Hurricane Frost / Freeze Significant Weather Fog / Haze / Cloud Precipitation High Resolution Weather & Dispersion
Treatment of Land-Use and Urbanization
 Treatment of Land-Use and Urbanization LECTURE 9 Alexander Mahura Danish Meteorological Institute, DMI, Copenhagen, Denmark NetFAM Summer School on Integrated Modelling 7-12 July 2008, Zelenogorsk, Russia
Treatment of Land-Use and Urbanization LECTURE 9 Alexander Mahura Danish Meteorological Institute, DMI, Copenhagen, Denmark NetFAM Summer School on Integrated Modelling 7-12 July 2008, Zelenogorsk, Russia
( ) = 1005 J kg 1 K 1 ;
 Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
Regional Climate Simulations with WRF Model
 WDS'3 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 8 84, 23. ISBN 978-8-737852-8 MATFYZPRESS Regional Climate Simulations with WRF Model J. Karlický Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics
WDS'3 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 8 84, 23. ISBN 978-8-737852-8 MATFYZPRESS Regional Climate Simulations with WRF Model J. Karlický Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics
Seasonal forecast system based on SL-AV model at Hydrometcentre of Russia
 Seasonal forecast system based on SL-AV model at Hydrometcentre of Russia M.A. Tolstykh (2,1) and D.B.Kiktev (1), R.B. Zaripov (1), V.N. Kryjov (1), E.N.Kruglova (1), I.A.Kulikova (1), V.M.Khan (1), V.F.Tischenko
Seasonal forecast system based on SL-AV model at Hydrometcentre of Russia M.A. Tolstykh (2,1) and D.B.Kiktev (1), R.B. Zaripov (1), V.N. Kryjov (1), E.N.Kruglova (1), I.A.Kulikova (1), V.M.Khan (1), V.F.Tischenko
First steps of a Lake Model Intercomparison Project:
 Boreal Environment Research 15: 191 202 2010 ISSN 1239-6095 (print) ISSN 1797-2469 (online) helsinki 30 April 2010 First steps of a Lake Model Intercomparison Project: LakeMIP Victor M. Stepanenko 1),
Boreal Environment Research 15: 191 202 2010 ISSN 1239-6095 (print) ISSN 1797-2469 (online) helsinki 30 April 2010 First steps of a Lake Model Intercomparison Project: LakeMIP Victor M. Stepanenko 1),
Overview of data assimilation in oceanography or how best to initialize the ocean?
 Overview of data assimilation in oceanography or how best to initialize the ocean? T. Janjic Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research Bremerhaven, Germany Outline Ocean observing system Ocean
Overview of data assimilation in oceanography or how best to initialize the ocean? T. Janjic Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research Bremerhaven, Germany Outline Ocean observing system Ocean
Characterization of the solar irradiation field for the Trentino region in the Alps
 Characterization of the solar irradiation field for the Trentino region in the Alps L. Laiti*, L. Giovannini and D. Zardi Atmospheric Physics Group University of Trento - Italy outline of the talk Introduction
Characterization of the solar irradiation field for the Trentino region in the Alps L. Laiti*, L. Giovannini and D. Zardi Atmospheric Physics Group University of Trento - Italy outline of the talk Introduction
