Parameterization of Lakes in NWP and Climate Models
|
|
|
- Anthony Crawford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parameterization of Lakes in NWP and Climate Models Dmitrii Mironov and Jürgen Helmert German Weather Service, Offenbach am Main, Germany Hermann Asensio, Erdmann Heise, Ekaterina Machulskaya, Bodo Ritter (German Weather Service, Offenbach am Main, Germany) Sergey Golosov (Institute for Lake Research, Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg, Russia) Georgy Kirillin (Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries, Berlin, Germany) Ekaterina Kourzeneva (Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland, and Russian State Hydrometeorological University, St. Petersburg, Russia) Arkady Terzhevik (Northern Water Problems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Petrozavodsk, Russia)
2 Outline Parameterization of lakes in NWP and climate models the problem The lake parameterization scheme FLake FLake in COSMO (ICON) FLake performance Conclusions and outlook
3 Parameterization of Lakes in NWP and Climate Models A Twofold Problem (1a) The interaction of the atmosphere with the underlying surface is strongly dependent on the surface temperature and its time-rate-of-change. (Most) NWP models assume that the water surface temperature can be kept constant over the entire forecast period. The assumption is doubtful for small-to-medium size relatively shallow lakes, where the diurnal variations of the surface temperature reach several degrees. A large number of such lakes will become resolved-scale features as the horizontal resolution is increased. (1b) Apart from forecasting the lake surface temperature, its initialization is also an issue. (2) Lakes strongly modify the structure and the transport properties of the atmospheric surface layer. A major outstanding question is the parameterization of the water-surface roughness with respect to wind (e.g. limited fetch) and to scalar quantities.
4 Lake Regions: Finland, Karelia
5 Lake Regions: Khanty-Mansiisk region (middle Ob river) Lake Regions: Canada
6 Schematic lake temperature stratification Summer θ (t) θ (t) b s θ S (t) Snow Ice Winter θ I (t) θ s (t) θ b (t) -H(t)-H I -H(t) I h(t) Water h(t) D θ H (t) D H(t) Sediment H(t) L θ H (t) θ L θ L L
7 Lake Parameterization Schemes for NWP and Climate Models (e.g. Croley 1989, 1992, Croley and Assel 1994, Hostetler and Bartlein 1990, Hostetler 1991, Hostetler et al. 1993, 1994, Barrette and Laprise 2005, Bates et al. 1993, 1995, Ljungemir et al. 1996, Goyette et al. 2000, Tsuang et al. 2001, Song et al. 2004, León et al. 2005, 2007, Long et al. 2007, Mackay 2005, Mackay et al. 2009, Stepanenko and Lykosov 2005, Stepanenko 2007, Stepanenko et al. 2010, Subin et al. 2012) One-layer models, complete mixing down to the bottom Neglect stratification large errors in the surface temperature Turbulence closure models, multi-layer (finite-difference) Describe the lake thermocline better expensive computationally A compromise between physical realism and computational economy is required A two layer-model with a parameterized vertical temperature structure
8 The Concept Put forward by Kitaigorodskii and Miropolsky (1970) to describe the temperature structure of the oceanic seasonal thermocline. The essence of the concept is that the temperature profile in the thermocline can be fairly accurately parameterized through a universal function of dimensionless depth, using the temperature difference across the thermocline, θ=θ s -θ b, and its thickness, h, as appropriate scales of temperature and depth: θ s ( t) θ ( z, t) = ϑ ( ς ), ς = z h( t). θ ( t) h( t)
9 Analogy with the Mixed-Layer Concept Using θ s (t) and h(t) as appropriate scales of temperature and depth, the temperature profile in the upper mixed layer is represented as θ ( z, t) θ ( t) s = Φ( ξ ), ξ = z. h( t) Since the layer is well mixed, the universal function Φ(ξ) is simply a constant equal to 1. Then, integrating the heat transfer equation (partial differential equation in z, t) θ t w θ = z over z from 0 to h(t), reduces the problem to the solution of an ordinary differential equation for θ s (t), dθs Qs Q( h) = dt h
10 The Lake Model FLake The model is based on the idea of self-similarity (assumed shape) of the evolving temperature profile. That is, instead of solving partial differential equations (in z, t) for the temperature and turbulence quantities (e.g. TKE), the problems is reduced to solving ordinary differential equations for time-dependent parameters (variables) that specify the temperature profile. These are (optional, modules can be switched off) the mean temperature of the water column, the surface temperature, the bottom temperature, the mixed-layer depth, the shape factor with respect to the temperature profile in the thermocline, the depth within bottom sediments penetrated by the thermal wave, and the temperature at that depth. In case of ice-covered lake, additional prognostic variables are the ice depth, the temperature at the ice upper surface, the snow depth, and the temperature at the snow upper surface. Important! The model does not require (re-)tuning.
11 Schematic representation of the evolving temperature profile θ b (t) θ s (t) h(t) C θ (t) D H(t) L θ H (t) θ L (a) (a) The evolving temperature profile is characterised by several time-dependent variables, namely, the temperature θ s (t) of the mixed layer, its depth h(t), the bottom temperature θ b (t), and the temperature-profile shape factor C θ (t). Optionally, the depth H(t) within bottom sediments penetrated by the thermal wave and the temperature θ H (t) at that depth can be computed.
12 θ S (t) Snow θ I (t) θ s (t) θ b (t) -H (t)-h (t) I S -H (t) I Ice h(t) Water C θ (t) Sediment (b) θ H (t) θ L D H(t) L (b) For ice-covered lakes, additional variables are the temperature θ I (t) at the ice upper surface and the ice thickness H I (t), and (optionally) the temperature θ S (t) at the snow upper surface and the snow thickness H S (t).
13 FLake in NWP and Climate Models: External Parameters geographical latitude (easy) lake fraction of the NWP model grid-box (not so easy) lake depth (not easy at all, e.g. for lack of data) typical wind fetch optical characteristics of lake water (extinction coefficients with respect to solar radiation) depth of the thermally active layer of bottom sediments, temperature at that depth (cf. soil model parameters) Default values of the last four parameters can be used.
14 Lake Fraction Lake-fraction external-parameter field for the COSMO-EU numerical domain of the COSMO model (ca. 7 km horizontal mesh size).
15 Lake Depth Lake depths for Northern Europe region of the COSMO-EU numerical domain (ca. 7 km horizontal mesh size).
16 Lake Depth Lake depths based on COSMO-DE external-parameter field (ca. 2.8 km horizontal mesh size).
17 FLake in COSMO (ICON): Configuration bottom sediment module is switched off (heat flux through the waterbottom sediment interface is zero) snow above the lake ice is not considered explicitly, the effect of snow is accounted for implicitly through the temperature dependence of the ice surface albedo (Mironov and Ritter 2003, 2004, Mironov et al. 2012) turbulent fluxes at the surface are computed with the current COSMO/ICON surface-layer scheme (Raschendorfer 2001); optionally, the new surface-layer scheme (Mironov et al. 2003) can be used 2D fields of lake fraction and of lake depth based on data (Kourzeneva 2009, 2010, Kourzeneva et al. 2012), default values of other lake-specific parameters
18 FLake in COSMO: Results from Parallel Experiment January 31 December 2006 Lake Hjälmaren, Sweden (mean depth = 6.1 m) Black lake surface temperature from the COSMO SST analysis Green lake surface temperature computed with FLake
19 FLake in COSMO: Results from Parallel Experiment January 31 December 2006 Lake Balaton, Hungary (mean depth = 3.3 m) Black lake surface temperature from the COSMO SST analysis Green lake surface temperature computed with FLake
20 FLake in COSMO: Results from Parallel Experiment January 31 December 2006 Freeze-up: 10 January Ice melting: very beginning of March Lake Balaton, Hungary (mean depth = 3.3 m). Ice thickness computed with COSMO-FLake.
21 FLake in COSMO: Results from Parallel Experiment January 31 December 2006 Lough Neagth, UK (mean depth = 8.9 m) Black lake surface temperature from the COSMO SST analysis Green lake surface temperature computed with FLake
22 FLake in NWP and Climate Models As a lake parameterization scheme, FLake is implemented, or on the way, into a number of NWP and climate models (COSMO, ICON, HIRLAM, UK Met Office Unified Model, NWP model suite of Meteo France, ECMWF IFS, CLM, RCA, Canadian Regional Climate Model), used as a lake parameterization module in the surface schemes TESSEL, SURFEX, and JULES, used operationally at the German Weather Service within COSMO-UE/DE, implemented into ICON, used operationally at the Finish Meteorological Institute within HIRLAM
23 Conclusions and Outlook FLake is implemented into the COSMO model (set llake=.false. to run without FLake) Since / Flake is operational at DWD within COSMO- EU/DE (ca. 7 km and ca. 2.8 km mesh size, respectively) Documentation and synopsis of FLake routines are ready FLake is implemented into ICON Monitor operational results, assess the effect of lake parameterization scheme on the overall NWP/climate model performance Update external-parameter fields Use FLake within a tiled surface scheme Long term prospective: explicit treatment of snow over lake ice, three-layer temperature profile, salinity, data on optical properties of lake water
24 Info FLake Web Page (mirror c/o Georgiy Kirillin and Arkady Terzhevik Online FLake version at (take a look and have fun!) References Kirillin, G., J. Hochschild, D.Mironov, A. Terzhevik, S.Golosov, and G. Nützmann, 2011: FLake-Global: Online lake model with worldwide coverage. Environ. Modell. Softw., 26, Kourzeneva, E., 2010: External data for lake parameterization in Numerical Weather Prediction and climate modeling. Boreal Env. Res., 15, Kourzeneva, E., H. Asensio, E. Martin, and S. Faroux, 2012: Global gridded dataset of lake coverage and lake depth for use in numerical weather prediction and climate modelling. Tellus A, 64, doi: /tellusa.v64i Mironov, D. V., 2008: Parameterization of lakes in numerical weather prediction. Description of a lake model. COSMO Technical Report, No. 11, Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach am Main, Germany, 41 pp. Mironov, D., E. Heise, E. Kourzeneva, B. Ritter, N. Schneider, and A. Terzhevik, 2010: Implementation of the lake parameterisation scheme FLake into the numerical weather prediction model COSMO. Boreal Env. Res., 15, Mironov, D., B. Ritter, J.-P. Schulz, M. Buchhold, M. Lange, and E. Machulskaya, 2012: Parameterization of sea and lake ice in numerical weather prediction modelsof the German Weather Service. Accepted for publication in Tellus A. Further references at
25 Thank you for your attention! Acknowledgements: Frank Beyrich, Michael Buchhold, Ulrich Damrath, Günther Doms, Jochen Förstner, Helmut Frank, Thomas Hanisch, Jürgen Helmert, Peter Meyring, Van Tan Nguyen, Ulrich Schättler, Christoph Schraff (DWD), Andrey Martynov (UQAM), Burkhardt Rockel (GKSS), Patrick Samuelsson (SMHI), Laura Rontu (FMI), Zachary Subin (UC Berkeley). EU Commissions, Projects INTAS and INTAS ; Nordic Research Board through the Nordic Networks on Fine-Scale Atmospheric Modelling (NetFAM) and Towards Multi- Scale Modelling of the Atmospheric Environment (MUSCATEN).
Implementation of the lake parameterisation scheme FLake into the numerical weather prediction model COSMO
 Boreal Environment Research 15: 218 230 2010 ISSN 1239-6095 (print) ISSN 1797-2469 (online) helsinki 30 April 2010 Implementation of the lake parameterisation scheme FLake into the numerical weather prediction
Boreal Environment Research 15: 218 230 2010 ISSN 1239-6095 (print) ISSN 1797-2469 (online) helsinki 30 April 2010 Implementation of the lake parameterisation scheme FLake into the numerical weather prediction
Parameterisation of sea and lake ice in numerical weather prediction models of the German Weather Service
 PUBLISHED BY THE INTERNATIONAL METEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE IN STOCKHOLM SERIES A DYNAMIC METEOROLOGY AND OCEANOGRAPHY Parameterisation of sea and lake ice in numerical weather prediction models of the German
PUBLISHED BY THE INTERNATIONAL METEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE IN STOCKHOLM SERIES A DYNAMIC METEOROLOGY AND OCEANOGRAPHY Parameterisation of sea and lake ice in numerical weather prediction models of the German
Interactive lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM): present state and perspectives
 44th Annual CMOS Congress May 31 June 4, 21, Ottawa Interactive lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM): present state and perspectives A. Martynov, L. Sushama, R. Laprise Centre ESCER Université
44th Annual CMOS Congress May 31 June 4, 21, Ottawa Interactive lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM): present state and perspectives A. Martynov, L. Sushama, R. Laprise Centre ESCER Université
Interactive lakes in NWP
 2nd ALADIN Forecasters meeting Interactive lakes in NWP Rui Salgado Instituto de Ciências da Terra (ICT) Universidade de Évora 22 October 2015 IPMA, Lisboa Authorship This short presentation aims to be
2nd ALADIN Forecasters meeting Interactive lakes in NWP Rui Salgado Instituto de Ciências da Terra (ICT) Universidade de Évora 22 October 2015 IPMA, Lisboa Authorship This short presentation aims to be
Representing inland water bodies and coastal areas in global numerical weather prediction
 Representing inland water bodies and coastal areas in global numerical weather prediction Gianpaolo Balsamo, Anton Beljaars, Souhail Boussetta, Emanuel Dutra Outline: Introduction lake and land contrasts
Representing inland water bodies and coastal areas in global numerical weather prediction Gianpaolo Balsamo, Anton Beljaars, Souhail Boussetta, Emanuel Dutra Outline: Introduction lake and land contrasts
Lake parameters climatology for cold start runs (lake initialization) in the ECMWF forecast system
 2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Lake parameters climatology for cold start runs (lake initialization) in the ECMWF forecast system R. Salgado(1),
2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Lake parameters climatology for cold start runs (lake initialization) in the ECMWF forecast system R. Salgado(1),
An intercomparison model study of Lake Valkea-Kotinen (in a framework of LakeMIP)
 Third Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Finnish Meteorological Insitute, Helsinki, September 18-20 2012 An intercomparison model study of Lake
Third Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Finnish Meteorological Insitute, Helsinki, September 18-20 2012 An intercomparison model study of Lake
Introducing inland water bodies and coastal areas in ECMWF forecasting system:
 Introducing inland water bodies and coastal areas in ECMWF forecasting system: Outline: Introduction lake and land contrasts forecasts impact when considering lakes Summary & outlook Gianpaolo Balsamo
Introducing inland water bodies and coastal areas in ECMWF forecasting system: Outline: Introduction lake and land contrasts forecasts impact when considering lakes Summary & outlook Gianpaolo Balsamo
External data for lake parameterization in Numerical Weather Prediction and climate modeling
 Boreal Environment Research 15: 165 177 2010 ISSN 1239-6095 (print) ISSN 1797-2469 (online) helsinki 30 April 2010 External data for lake parameterization in Numerical Weather Prediction and climate modeling
Boreal Environment Research 15: 165 177 2010 ISSN 1239-6095 (print) ISSN 1797-2469 (online) helsinki 30 April 2010 External data for lake parameterization in Numerical Weather Prediction and climate modeling
Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction models
 Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction models Dmitri Mironov, Laura Rontu, Ekaterina Kurzeneva & 26 participants of the Lake12 workshop SRNWP-EWGLAM meeting Helsinki 8-11 October 2012
Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction models Dmitri Mironov, Laura Rontu, Ekaterina Kurzeneva & 26 participants of the Lake12 workshop SRNWP-EWGLAM meeting Helsinki 8-11 October 2012
COSMO / CLM Training Course
 COSMO / CLM Training Course DWD and the CLM-Community DWD Training and Conference Center (BTZ) in Langen 02-06 March 2009 Introduction The COSMO-model together with the preprocessing package is a state
COSMO / CLM Training Course DWD and the CLM-Community DWD Training and Conference Center (BTZ) in Langen 02-06 March 2009 Introduction The COSMO-model together with the preprocessing package is a state
Validation of 2-meters temperature forecast at cold observed conditions by different NWP models
 Validation of 2-meters temperature forecast at cold observed conditions by different NWP models Evgeny Atlaskin Finnish Meteorological Institute / Russian State Hydrometeorological University OUTLINE Background
Validation of 2-meters temperature forecast at cold observed conditions by different NWP models Evgeny Atlaskin Finnish Meteorological Institute / Russian State Hydrometeorological University OUTLINE Background
An effective lake depth for FLAKE model
 An effective lake depth for FLAKE model Gianpaolo Balsamo, Emanuel Dutra, Victor Stepanenko, Pedro Viterbo, Pedro Miranda and Anton Beljaars thanks to: Dmitrii Mironov, Arkady Terzhevik, Yuhei Takaya,
An effective lake depth for FLAKE model Gianpaolo Balsamo, Emanuel Dutra, Victor Stepanenko, Pedro Viterbo, Pedro Miranda and Anton Beljaars thanks to: Dmitrii Mironov, Arkady Terzhevik, Yuhei Takaya,
Coupling of the Canadian Regional Climate Model with lake models
 Workshop on Parametrization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling 18-2 September 28, St. Petersburg (Zelenogorsk), Russia Coupling of the Canadian Regional Climate Model with lake
Workshop on Parametrization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling 18-2 September 28, St. Petersburg (Zelenogorsk), Russia Coupling of the Canadian Regional Climate Model with lake
The HIGHTSI ice model and plans in SURFEX
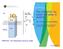 Air Snow T in Ice with snow cover T sfc x T snow Q si F si h s h s The HIGHTSI ice model and plans in SURFEX Bin Cheng and Laura Rontu Water Ice T ice h i Finnish Meteorological Institute, FI-11 Helsinki,
Air Snow T in Ice with snow cover T sfc x T snow Q si F si h s h s The HIGHTSI ice model and plans in SURFEX Bin Cheng and Laura Rontu Water Ice T ice h i Finnish Meteorological Institute, FI-11 Helsinki,
Introduction : Scientific context : SRNWP Expert Team on Surface Processes (model and data assimilation) Draft of a workplan for
 SRNWP Expert Team on Surface Processes (model and data assimilation) Draft of a workplan for 2008-2009 Revised version (05 September 2008) Introduction : The Expert Team on Surface Processes will focus
SRNWP Expert Team on Surface Processes (model and data assimilation) Draft of a workplan for 2008-2009 Revised version (05 September 2008) Introduction : The Expert Team on Surface Processes will focus
Interactive Lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model, versions 4 and 5
 2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Norrköping, Sweden, September 15-17 21 Interactive Lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model, versions
2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Norrköping, Sweden, September 15-17 21 Interactive Lakes in the Canadian Regional Climate Model, versions
Overview of COSMO WG3a activities Upper air physical aspects. Federico Grazzini, ARPA Emilia-Romagna Servizio Idro Meteo Clima (SIMC)
 Overview of COSMO WG3a activities Upper air physical aspects Federico Grazzini, ARPA Emilia-Romagna Servizio Idro Meteo Clima (SIMC) The former WG3 has been split: wg coordinator Federico Grazzini Scientists
Overview of COSMO WG3a activities Upper air physical aspects Federico Grazzini, ARPA Emilia-Romagna Servizio Idro Meteo Clima (SIMC) The former WG3 has been split: wg coordinator Federico Grazzini Scientists
A study on lake temperature and ice cover in HIRLAM
 A study on lake temperature and ice cover in HIRLAM Kalle Eerola 1, Laura Rontu 1, Ekaterina Kourzeneva 2, and Ekaterina Scherbak 2 1 Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 2 Russian State
A study on lake temperature and ice cover in HIRLAM Kalle Eerola 1, Laura Rontu 1, Ekaterina Kourzeneva 2, and Ekaterina Scherbak 2 1 Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 2 Russian State
Report of the Scientific Project Manager
 Report of the Scientific Project Manager G. Doms, DWD, 4th COSMO General Meeting, Warsaw, Poland Status of the LM LM Version 2.13 (18 January 2002) - Option for use of Wind profiler/rass reports - Adjustments
Report of the Scientific Project Manager G. Doms, DWD, 4th COSMO General Meeting, Warsaw, Poland Status of the LM LM Version 2.13 (18 January 2002) - Option for use of Wind profiler/rass reports - Adjustments
Global database for the parameterization of lakes in NWP and climate modelling
 2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Ekaterina Kurzeneva Global database for the parameterization of lakes in NWP and climate modelling 2 contents
2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Ekaterina Kurzeneva Global database for the parameterization of lakes in NWP and climate modelling 2 contents
State of the art of wind forecasting and planned improvements for NWP Helmut Frank (DWD), Malte Mülller (met.no), Clive Wilson (UKMO)
 State of the art of wind forecasting and planned improvements for NWP Helmut Frank (DWD), Malte Mülller (met.no), Clive Wilson (UKMO) thanks to S. Bauernschubert, U. Blahak, S. Declair, A. Röpnack, C.
State of the art of wind forecasting and planned improvements for NWP Helmut Frank (DWD), Malte Mülller (met.no), Clive Wilson (UKMO) thanks to S. Bauernschubert, U. Blahak, S. Declair, A. Röpnack, C.
Tuesday the 18th of September Auditorium Brainstorm / Lecture room Aqua
 Tuesday the 18th of September 2012. Auditorium Brainstorm / Lecture room Aqua 09.00 09.10 Opening Sylvain Joffre, head of Meteorological Research of FMI 09.10 09.20 Practical arrangements Lake data assimilation
Tuesday the 18th of September 2012. Auditorium Brainstorm / Lecture room Aqua 09.00 09.10 Opening Sylvain Joffre, head of Meteorological Research of FMI 09.10 09.20 Practical arrangements Lake data assimilation
Parameterization of Convection in the Global NWP System GME of the German Weather Service
 Parameterization of Convection in the Global NWP System GME of the German Weather Service Dmitrii Mironov and Bodo Ritter German Weather Service, Offenbach am Main, Germany (dmitrii.mironov@dwd.de, bodo.ritter@dwd.de)
Parameterization of Convection in the Global NWP System GME of the German Weather Service Dmitrii Mironov and Bodo Ritter German Weather Service, Offenbach am Main, Germany (dmitrii.mironov@dwd.de, bodo.ritter@dwd.de)
The Lake Model Intercomparison Project (LakeMIP): present state and perspectives
 2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Norrköping, Sweden, September 15-17 2010 The Lake Model Intercomparison Project (LakeMIP): present state
2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Norrköping, Sweden, September 15-17 2010 The Lake Model Intercomparison Project (LakeMIP): present state
Deutscher Wetterdienst
 Deutscher Wetterdienst Modelling the Volcanic Ash Episode: Experiences with COSMO-ART Detlev Majewski (FE1) Bernhard Vogel, Heike Vogel (KIT) Thomas Hanisch, Jochen Förstner (FE13), Ulrich Pflüger (FE15)
Deutscher Wetterdienst Modelling the Volcanic Ash Episode: Experiences with COSMO-ART Detlev Majewski (FE1) Bernhard Vogel, Heike Vogel (KIT) Thomas Hanisch, Jochen Förstner (FE13), Ulrich Pflüger (FE15)
Current status of lake modelling and initialisation at ECMWF
 Current status of lake modelling and initialisation at ECMWF G Balsamo, A Manrique Suñen, E Dutra, D. Mironov, P. Miranda, V Stepanenko, P Viterbo, A Nordbo, R Salgado, I Mammarella, A Beljaars, H Hersbach
Current status of lake modelling and initialisation at ECMWF G Balsamo, A Manrique Suñen, E Dutra, D. Mironov, P. Miranda, V Stepanenko, P Viterbo, A Nordbo, R Salgado, I Mammarella, A Beljaars, H Hersbach
On the use of FLAKE in SURFEX coupled to Meso-NH. Rui Salgado
 On the use of FLAKE in SURFEX coupled to Meso-NH Rui Salgado with M. Potes, M. Yakunin, A. Penha and M.J. Costa Institute of Earth Sciences (ICT), University of Évora, Portugal 1/23 Motivation Return to
On the use of FLAKE in SURFEX coupled to Meso-NH Rui Salgado with M. Potes, M. Yakunin, A. Penha and M.J. Costa Institute of Earth Sciences (ICT), University of Évora, Portugal 1/23 Motivation Return to
Variational soil assimilation at DWD
 Variational soil assimilation at DWD Werner Wergen, Reinhold Hess and Martin Lange Deutscher Wetterdienst Offenbach am Main, Germany The soil moisture assimilation scheme (SMA) at DWD Full description
Variational soil assimilation at DWD Werner Wergen, Reinhold Hess and Martin Lange Deutscher Wetterdienst Offenbach am Main, Germany The soil moisture assimilation scheme (SMA) at DWD Full description
ICON. The Icosahedral Nonhydrostatic modelling framework
 ICON The Icosahedral Nonhydrostatic modelling framework Basic formulation, NWP and high-performance computing aspects, and its perspective towards a unified model for seamless prediction Günther Zängl,
ICON The Icosahedral Nonhydrostatic modelling framework Basic formulation, NWP and high-performance computing aspects, and its perspective towards a unified model for seamless prediction Günther Zängl,
ICON. Limited-area mode (ICON-LAM) and updated verification results. Günther Zängl, on behalf of the ICON development team
 ICON Limited-area mode (ICON-LAM) and updated verification results Günther Zängl, on behalf of the ICON development team COSMO General Meeting, Offenbach, 07.09.2016 Outline Status of limited-area-mode
ICON Limited-area mode (ICON-LAM) and updated verification results Günther Zängl, on behalf of the ICON development team COSMO General Meeting, Offenbach, 07.09.2016 Outline Status of limited-area-mode
Model Output Statistics (MOS)
 Model Output Statistics (MOS) Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models calculate the future state of the atmosphere at certain points of time (forecasts). The calculation of these forecasts is based on
Model Output Statistics (MOS) Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models calculate the future state of the atmosphere at certain points of time (forecasts). The calculation of these forecasts is based on
A MULTI-LAYER SNOW COVER MODEL FOR NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION AND CLIMATE MODELS
 A MULTI-LAYER SNOW COVER MODEL FOR NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION AND CLIMATE MODELS Sascha Bellaire 1 and Michael Lehning 1,2 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland 2 Labaratory
A MULTI-LAYER SNOW COVER MODEL FOR NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION AND CLIMATE MODELS Sascha Bellaire 1 and Michael Lehning 1,2 1 WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF, Davos, Switzerland 2 Labaratory
COSMO WG3b: Activity Review
 Eidgenössisches Departement des Innern EDI Bundesamt für Meteorologie und Klimatologie MeteoSchweiz COSMO WG3b: Activity Review Jean-Marie Bettems / MeteoSwiss Offenbach, COSMO GM, September 2016 PP and
Eidgenössisches Departement des Innern EDI Bundesamt für Meteorologie und Klimatologie MeteoSchweiz COSMO WG3b: Activity Review Jean-Marie Bettems / MeteoSwiss Offenbach, COSMO GM, September 2016 PP and
The Model SNOW 4. A Tool to Operationally Estimate Precipitation Supply
 The Model SNOW 4 A Tool to Operationally Estimate Precipitation Supply Uwe BöhmB hm,, Thomas Reich, Gerold Schneider Deutscher Wetterdienst, Dep. Hydrometeorology, Germany Conceptual Design of SNOW 4 Conceptual
The Model SNOW 4 A Tool to Operationally Estimate Precipitation Supply Uwe BöhmB hm,, Thomas Reich, Gerold Schneider Deutscher Wetterdienst, Dep. Hydrometeorology, Germany Conceptual Design of SNOW 4 Conceptual
Deutscher Wetterdienst. MeteoSwiss. Ufficio Generale Spacio Aero e Meteorologia. Instytucie Meteorogii i Gospodarki Wodnej
 ! "# "$ %'&)(+*-,-./(1032546&+798;:=@8BADCEC F"GIH=GKJ LBMNL;HPORQ GSMOUTIV TW!XGIY5L[Z O\V ] ^KJ L[HPOU_`GIacb LdGMfe9L[HgFH[LEh5Oi_jMOUTIV k L[Z[_lHPOnmoMOUTIV TBW!G XGIY5Lqp TrhDL[a st uwv.u
! "# "$ %'&)(+*-,-./(1032546&+798;:=@8BADCEC F"GIH=GKJ LBMNL;HPORQ GSMOUTIV TW!XGIY5L[Z O\V ] ^KJ L[HPOU_`GIacb LdGMfe9L[HgFH[LEh5Oi_jMOUTIV k L[Z[_lHPOnmoMOUTIV TBW!G XGIY5Lqp TrhDL[a st uwv.u
HIRLAM/HARMONIE work on surface data assimilation and modelling
 HIRLAM/HARMONIE work on surface data assimilation and modelling Ekaterina Kourzeneva *, Laura Rontu, Trygve Aspelien, Maria Diez, Mariken Homleid, Kalle Eerola, Suleiman Mostamandi, Patrick Samuelsson,
HIRLAM/HARMONIE work on surface data assimilation and modelling Ekaterina Kourzeneva *, Laura Rontu, Trygve Aspelien, Maria Diez, Mariken Homleid, Kalle Eerola, Suleiman Mostamandi, Patrick Samuelsson,
A hierarchy of one- and two-moment microphysical parameterizations in the COSMO model
 Deutscher Wetterdienst GB Forschung und Entwicklung A hierarchy of one- and two-moment microphysical parameterizations in the COSMO model Axel Seifert German Weather Service Offenbach, Germany Ulrich Blahak
Deutscher Wetterdienst GB Forschung und Entwicklung A hierarchy of one- and two-moment microphysical parameterizations in the COSMO model Axel Seifert German Weather Service Offenbach, Germany Ulrich Blahak
Can the Baltic Sea be parameterized as fresh or salt water lake?
 2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in NWP and Climate Modelling, Norrköping 2010 Can the Baltic Sea be parameterized as fresh or salt water lake? First results from COSMO-CLM FLake simulation Frederik
2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in NWP and Climate Modelling, Norrköping 2010 Can the Baltic Sea be parameterized as fresh or salt water lake? First results from COSMO-CLM FLake simulation Frederik
Snow and ice on Bear Lake (Alaska) - sensitivity experiments with two lake ice models
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Snow and ice on Bear Lake (Alaska) - sensitivity experiments with two lake ice models Semmler, Tido 212 Semmler, T, Cheng, B, Yang, Y & Rontu, L 212, ' Snow and ice on Bear Lake
https://helda.helsinki.fi Snow and ice on Bear Lake (Alaska) - sensitivity experiments with two lake ice models Semmler, Tido 212 Semmler, T, Cheng, B, Yang, Y & Rontu, L 212, ' Snow and ice on Bear Lake
Andrey Martynov 1, René Laprise 1, Laxmi Sushama 1, Katja Winger 1, Bernard Dugas 2. Université du Québec à Montréal 2
 CMOS-2012, Montreal, 31 May 2012 Reanalysis-driven climate simulation over CORDEX North America domain using the Canadian Regional Climate Model, version 5: model performance evaluation Andrey Martynov
CMOS-2012, Montreal, 31 May 2012 Reanalysis-driven climate simulation over CORDEX North America domain using the Canadian Regional Climate Model, version 5: model performance evaluation Andrey Martynov
Development and applications of regional reanalyses for Europe and Germany based on DWD s NWP models: Status and outlook
 Development and applications of regional reanalyses for Europe and Germany based on DWD s NWP models: Status and outlook Frank Kaspar 1, Michael Borsche 1, Natacha Fery 1, Andrea K. Kaiser-Weiss 1, Jan
Development and applications of regional reanalyses for Europe and Germany based on DWD s NWP models: Status and outlook Frank Kaspar 1, Michael Borsche 1, Natacha Fery 1, Andrea K. Kaiser-Weiss 1, Jan
Assimilation of Snow and Ice Data (Incomplete list)
 Assimilation of Snow and Ice Data (Incomplete list) Snow/ice Sea ice motion (sat): experimental, climate model Sea ice extent (sat): operational, U.S. Navy PIPs model; Canada; others? Sea ice concentration
Assimilation of Snow and Ice Data (Incomplete list) Snow/ice Sea ice motion (sat): experimental, climate model Sea ice extent (sat): operational, U.S. Navy PIPs model; Canada; others? Sea ice concentration
HARMONIE physics plans Laura Rontu, FMI
 HARMONIE physics plans Laura Rontu, FMI with contributions by Imanol Guerrero, Timo Vihma and others ALARO working days 13-15 June 2012 Ljubljana A FEW STRATEGIC COMMENTS Towards scale-adaptive, cross-package
HARMONIE physics plans Laura Rontu, FMI with contributions by Imanol Guerrero, Timo Vihma and others ALARO working days 13-15 June 2012 Ljubljana A FEW STRATEGIC COMMENTS Towards scale-adaptive, cross-package
Sami Niemelä and Carl Fortelius Finnish Meteorological Institute
 6B.6 APPLICABILITY OF GRID-SIZE-DEPENDENT CONVECTION PARAMETERIZATION TO MESO-γ-SCALE HIRLAM. Sami Niemelä and Carl Fortelius Finnish Meteorological Institute. INTRODUCTION The representation of convective
6B.6 APPLICABILITY OF GRID-SIZE-DEPENDENT CONVECTION PARAMETERIZATION TO MESO-γ-SCALE HIRLAM. Sami Niemelä and Carl Fortelius Finnish Meteorological Institute. INTRODUCTION The representation of convective
Implementation and validation of the. ECMWF IFS convection scheme. in COSMO-CLM. Peter Brockhaus. Daniel Lüthi. Christoph Schär
 Implementation and validation of the ECMWF IFS convection scheme in COSMO-CLM Peter Brockhaus Peter Bechtold Daniel Lüthi Oliver Fuhrer Christoph Schär (ETH) (ECMWF) (ETH) (MeteoSwiss) (ETH) COSMO/CLM
Implementation and validation of the ECMWF IFS convection scheme in COSMO-CLM Peter Brockhaus Peter Bechtold Daniel Lüthi Oliver Fuhrer Christoph Schär (ETH) (ECMWF) (ETH) (MeteoSwiss) (ETH) COSMO/CLM
EUMETSAT SAF NETWORK. Lothar Schüller, EUMETSAT SAF Network Manager
 1 EUMETSAT SAF NETWORK Lothar Schüller, EUMETSAT SAF Network Manager EUMETSAT ground segment overview METEOSAT JASON-2 INITIAL JOINT POLAR SYSTEM METOP NOAA SATELLITES CONTROL AND DATA ACQUISITION FLIGHT
1 EUMETSAT SAF NETWORK Lothar Schüller, EUMETSAT SAF Network Manager EUMETSAT ground segment overview METEOSAT JASON-2 INITIAL JOINT POLAR SYSTEM METOP NOAA SATELLITES CONTROL AND DATA ACQUISITION FLIGHT
Convection-Resolving Model Simulations: Process-Based Comparison of LM Results with Observations
 Convection-Resolving Model Simulations: Process-Based Comparison of LM Results with Observations Jörg Trentmann, Britta Wecker, Marcus Paulat, Heini Wernli, Ulrich Corsmeier, Jan Handwerker Goal Improve
Convection-Resolving Model Simulations: Process-Based Comparison of LM Results with Observations Jörg Trentmann, Britta Wecker, Marcus Paulat, Heini Wernli, Ulrich Corsmeier, Jan Handwerker Goal Improve
Deutscher Wetterdienst
 Deutscher Wetterdienst Limited-area ensembles: finer grids & shorter lead times Susanne Theis COSMO-DE-EPS project leader Deutscher Wetterdienst Thank You Neill Bowler et al. (UK Met Office) Andras Horányi
Deutscher Wetterdienst Limited-area ensembles: finer grids & shorter lead times Susanne Theis COSMO-DE-EPS project leader Deutscher Wetterdienst Thank You Neill Bowler et al. (UK Met Office) Andras Horányi
Consortium for Small- Scale Modelling
 Consortium for Small- Scale Modelling Michał Ziemiański Consortia presentations 34 th EWGLAM and 19 th SRNWP meeting 8 October 2012, Helsinki Outline COSMO Organisation: News COSMO Model: Changes since
Consortium for Small- Scale Modelling Michał Ziemiański Consortia presentations 34 th EWGLAM and 19 th SRNWP meeting 8 October 2012, Helsinki Outline COSMO Organisation: News COSMO Model: Changes since
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Bolli Pálmason and Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Bolli Pálmason and Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts
Cluster analysis results of regional climate model simulations in the PIDCAP period
 BOREAL ENVIRONMENT RESEARCH 7: 219 223 ISSN 1239-6095 Helsinki 2 October 2002 2002 Cluster analysis results of regional climate model simulations in the PIDCAP period Martin Kücken, Friedrich-Wilhelm Gerstengarbe
BOREAL ENVIRONMENT RESEARCH 7: 219 223 ISSN 1239-6095 Helsinki 2 October 2002 2002 Cluster analysis results of regional climate model simulations in the PIDCAP period Martin Kücken, Friedrich-Wilhelm Gerstengarbe
PP COLOBOC. Status Report
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss PP COLOBOC Status Report Jean-Marie Bettems MeteoSwiss COLOBOC/SOILVEG Workshop 01 March 2010, Langen Review
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss PP COLOBOC Status Report Jean-Marie Bettems MeteoSwiss COLOBOC/SOILVEG Workshop 01 March 2010, Langen Review
COLOBOC Project Status
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss COLOBOC Project Status Jean-Marie Bettems / MeteoSwiss COLOBOC/SOILVEG Workshop Langen, February 28th, 2011
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss COLOBOC Project Status Jean-Marie Bettems / MeteoSwiss COLOBOC/SOILVEG Workshop Langen, February 28th, 2011
Simulations of Lake Processes within a Regional Climate Model
 Simulations of Lake Processes within a Regional Climate Model Jiming Jin Departments of Watershed Sciences and Plants, Soils, and Climate Utah State University, Logan, Utah Utah State University 850 Faculty
Simulations of Lake Processes within a Regional Climate Model Jiming Jin Departments of Watershed Sciences and Plants, Soils, and Climate Utah State University, Logan, Utah Utah State University 850 Faculty
Optimal combination of NWP Model Forecasts for AutoWARN
 ModelMIX Optimal combination of NWP Model Forecasts for AutoWARN Tamas Hirsch, Reinhold Hess, Sebastian Trepte, Cristina Primo, Jenny Glashoff, Bernhard Reichert, Dirk Heizenreder Deutscher Wetterdienst
ModelMIX Optimal combination of NWP Model Forecasts for AutoWARN Tamas Hirsch, Reinhold Hess, Sebastian Trepte, Cristina Primo, Jenny Glashoff, Bernhard Reichert, Dirk Heizenreder Deutscher Wetterdienst
Improvement of objective analysis of lake surface state in HIRLAM using satellite observations
 HIRLAM ASM 2013 & ALADIN 23 rd Workshop Reykjavik, Iceland 15-19 April, 2013 Improvement of objective analysis of lake surface state in HIRLAM using satellite observations H. Kheyrollah Pour, C.R. Duguay
HIRLAM ASM 2013 & ALADIN 23 rd Workshop Reykjavik, Iceland 15-19 April, 2013 Improvement of objective analysis of lake surface state in HIRLAM using satellite observations H. Kheyrollah Pour, C.R. Duguay
The Climate mode of the Local Model and the CLM-Community
 The Climate mode of the Local Model and the CLM-Community Community A.Will (BTU Cottbus) Developed Developed by the by CLM-Community the CLM-Community in cooperation with the German weather German service
The Climate mode of the Local Model and the CLM-Community Community A.Will (BTU Cottbus) Developed Developed by the by CLM-Community the CLM-Community in cooperation with the German weather German service
The Rossby Centre Ocean model applied to the Arctic Ocean using ERA-40
 The Ocean model applied to the Arctic Ocean using ERA-40 H.E. Markus Meier, R. Döscher, K. Wyser /SMHI, Norrköping and K. Döös MISU, Stockholm University, Stockholm Ocean model (RCO) based on the BRYAN-COX-SEMTNER
The Ocean model applied to the Arctic Ocean using ERA-40 H.E. Markus Meier, R. Döscher, K. Wyser /SMHI, Norrköping and K. Döös MISU, Stockholm University, Stockholm Ocean model (RCO) based on the BRYAN-COX-SEMTNER
Direct and semi-direct radiative effects of absorbing aerosols in Europe: Results from a regional model
 GEOPHYSICAL SEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl050994, 2012 Direct and semi-direct radiative effects of absorbing aerosols in Europe: Results from a regional model J. Meier, 1 I. Tegen, 1 B. Heinold,
GEOPHYSICAL SEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl050994, 2012 Direct and semi-direct radiative effects of absorbing aerosols in Europe: Results from a regional model J. Meier, 1 I. Tegen, 1 B. Heinold,
Deutscher Wetterdienst
 Deutscher Wetterdienst NUMEX Numerical Experiments and NWP-development at DWD 14th Workshop on Meteorological Operational Systems ECMWF 18-20 November 2013 Thomas Hanisch GB Forschung und Entwicklung (FE)
Deutscher Wetterdienst NUMEX Numerical Experiments and NWP-development at DWD 14th Workshop on Meteorological Operational Systems ECMWF 18-20 November 2013 Thomas Hanisch GB Forschung und Entwicklung (FE)
Operational and research activities at ECMWF now and in the future
 Operational and research activities at ECMWF now and in the future Sarah Keeley Education Officer Erland Källén Director of Research ECMWF An independent intergovernmental organisation established in 1975
Operational and research activities at ECMWF now and in the future Sarah Keeley Education Officer Erland Källén Director of Research ECMWF An independent intergovernmental organisation established in 1975
Simulation studies for Lake Taihu effect on local meteorological environment. Ren Xia
 Simulation studies for Lake Taihu effect on local meteorological environment Ren Xia 2017.05.12 1 Outline Background Experimental design Result and discussion Next work Background Taihu Lake is the largest
Simulation studies for Lake Taihu effect on local meteorological environment Ren Xia 2017.05.12 1 Outline Background Experimental design Result and discussion Next work Background Taihu Lake is the largest
Centre report - DWD. 27 th WGNE meeting Oct. 2011, Boulder. M. Baldauf, M. Lange, H. Frank, G. Zängl, B. Früh (DWD)
 Centre report - DWD 27 th WGNE meeting 17-21 Oct. 2011, Boulder M. Baldauf, M. Lange, H. Frank, G. Zängl, B. Früh (DWD) Supercomputing environment at DWD (Sept. 2011) One production and one research computer
Centre report - DWD 27 th WGNE meeting 17-21 Oct. 2011, Boulder M. Baldauf, M. Lange, H. Frank, G. Zängl, B. Früh (DWD) Supercomputing environment at DWD (Sept. 2011) One production and one research computer
Evaluation and Assimilation of Remotely- Sensed Lake Surface Temperature in the HIRLAM Weather Forecasting System
 Evaluation and Assimilation of Remotely- Sensed Lake Surface Temperature in the HIRLAM Weather Forecasting System H. Kheyrollah Pour 1, C.R. Duguay 1, L. Rontu 2 with contributions from Kalle Eerola 2,
Evaluation and Assimilation of Remotely- Sensed Lake Surface Temperature in the HIRLAM Weather Forecasting System H. Kheyrollah Pour 1, C.R. Duguay 1, L. Rontu 2 with contributions from Kalle Eerola 2,
Improving the use of satellite winds at the Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD)
 Improving the use of satellite winds at the Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD) Alexander Cress Deutscher Wetterdienst, Frankfurter Strasse 135, 63067 Offenbach am Main, Germany alexander.cress@dwd.de Ø Introduction
Improving the use of satellite winds at the Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD) Alexander Cress Deutscher Wetterdienst, Frankfurter Strasse 135, 63067 Offenbach am Main, Germany alexander.cress@dwd.de Ø Introduction
Towards the Fourth GEWEX Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model Inter-Comparison Study (GABLS4)
 Towards the Fourth GEWEX Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model Inter-Comparison Study (GABLS4) Timo Vihma 1, Tiina Nygård 1, Albert A.M. Holtslag 2, Laura Rontu 1, Phil Anderson 3, Klara Finkele 4, and Gunilla
Towards the Fourth GEWEX Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model Inter-Comparison Study (GABLS4) Timo Vihma 1, Tiina Nygård 1, Albert A.M. Holtslag 2, Laura Rontu 1, Phil Anderson 3, Klara Finkele 4, and Gunilla
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra
 Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Title. Author(s)Leppäranta, Matti; Shirasawa, Kunio. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information.
 Title Influence of the ice-ocean heat flux on the ice thic Author(s)Leppäranta, Matti; Shirasawa, Kunio Issue Date 7 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/115/38937 Type proceedings (author version) Note 16th
Title Influence of the ice-ocean heat flux on the ice thic Author(s)Leppäranta, Matti; Shirasawa, Kunio Issue Date 7 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/115/38937 Type proceedings (author version) Note 16th
Surface data assimilation activities in the HIRLAM consortium
 Surface data assimilation activities in the HIRLAM consortium LACE DA Working Days 016 September, 016 Magnus Lindskog and Patrick Samuelsson Outline Introduction Surface data assimilation for nature tile
Surface data assimilation activities in the HIRLAM consortium LACE DA Working Days 016 September, 016 Magnus Lindskog and Patrick Samuelsson Outline Introduction Surface data assimilation for nature tile
Climate change projections for Ontario: an updated synthesis for policymakers and planners
 Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry Climate change projections for Ontario: an updated synthesis for policymakers and planners Shannon Fera and Adam Hogg Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources and
Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry Climate change projections for Ontario: an updated synthesis for policymakers and planners Shannon Fera and Adam Hogg Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources and
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2017
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2017 Finnish Meteorological Institute compiled by Weather and Safety Centre with help of several experts 1. Summary of major highlights FMI s forecasts are
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2017 Finnish Meteorological Institute compiled by Weather and Safety Centre with help of several experts 1. Summary of major highlights FMI s forecasts are
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2009
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2009 Hungarian Meteorological Service 1. Summary of major highlights The objective verification of ECMWF forecasts have been continued on all the time ranges
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2009 Hungarian Meteorological Service 1. Summary of major highlights The objective verification of ECMWF forecasts have been continued on all the time ranges
MARINE BOUNDARY-LAYER HEIGHT ESTIMATED FROM NWP MODEL OUTPUT BULGARIA
 MARINE BOUNDARY-LAYER HEIGHT ESTIMATED FROM NWP MODEL OUTPUT Sven-Erik Gryning 1 and Ekaterina Batchvarova 1, 1 Wind Energy Department, Risø National Laboratory, DK-4 Roskilde, DENMARK National Institute
MARINE BOUNDARY-LAYER HEIGHT ESTIMATED FROM NWP MODEL OUTPUT Sven-Erik Gryning 1 and Ekaterina Batchvarova 1, 1 Wind Energy Department, Risø National Laboratory, DK-4 Roskilde, DENMARK National Institute
The importance of long-term Arctic weather station data for setting the research stage for climate change studies
 The importance of long-term Arctic weather station data for setting the research stage for climate change studies Taneil Uttal NOAA/Earth Systems Research Laboratory Boulder, Colorado Things to get out
The importance of long-term Arctic weather station data for setting the research stage for climate change studies Taneil Uttal NOAA/Earth Systems Research Laboratory Boulder, Colorado Things to get out
SENSITIVITY STUDY OF SIMULATED WIND PROFILES TO MODEL RESOLUTION, LAND COVER AND CLIMATE FORCING DATA
 5A.1 SENSITIVITY STUDY OF SIMULATED WIND PROFILES TO MODEL RESOLUTION, LAND COVER AND CLIMATE FORCING DATA Janna Lindenberg* (1), Heinz-Theo Mengelkamp (1) and Wei Yu (2) (1) Institute for Coastal Research,
5A.1 SENSITIVITY STUDY OF SIMULATED WIND PROFILES TO MODEL RESOLUTION, LAND COVER AND CLIMATE FORCING DATA Janna Lindenberg* (1), Heinz-Theo Mengelkamp (1) and Wei Yu (2) (1) Institute for Coastal Research,
Experiences from implementing GPS Radio Occultations in Data Assimilation for ICON
 Experiences from implementing GPS Radio Occultations in Data Assimilation for ICON Harald Anlauf Research and Development, Data Assimilation Section Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach, Germany IROWG 4th
Experiences from implementing GPS Radio Occultations in Data Assimilation for ICON Harald Anlauf Research and Development, Data Assimilation Section Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach, Germany IROWG 4th
Regional Climate Centre Network (RCC) in RA VI as a GFCS contribution
 Regional Climate Centre Network (RCC) in RA VI as a GFCS contribution Stefan Rösner and Peter Bissolli Deutscher Wetterdienst (German Meteorological Service) Dep. Climate Monitoring, Offenbach, Germany
Regional Climate Centre Network (RCC) in RA VI as a GFCS contribution Stefan Rösner and Peter Bissolli Deutscher Wetterdienst (German Meteorological Service) Dep. Climate Monitoring, Offenbach, Germany
ERA-CLIM: Developing reanalyses of the coupled climate system
 ERA-CLIM: Developing reanalyses of the coupled climate system Dick Dee Acknowledgements: Reanalysis team and many others at ECMWF, ERA-CLIM project partners at Met Office, Météo France, EUMETSAT, Un. Bern,
ERA-CLIM: Developing reanalyses of the coupled climate system Dick Dee Acknowledgements: Reanalysis team and many others at ECMWF, ERA-CLIM project partners at Met Office, Météo France, EUMETSAT, Un. Bern,
ICON-ESM MPI-M s next-generation Earth system model
 ICON-ESM MPI-M s next-generation Earth system model Climate and Earth system models are applied to simulate the past, present, and projected future climate, and to advance understanding of processes that
ICON-ESM MPI-M s next-generation Earth system model Climate and Earth system models are applied to simulate the past, present, and projected future climate, and to advance understanding of processes that
Sea ice charts and SAR for sea ice classification. Patrick Eriksson Juha Karvonen Jouni Vainio
 Sea ice charts and SAR for sea ice classification Patrick Eriksson Juha Karvonen Jouni Vainio ECMWF Ocean Workshop, 22-25 January 2018 Ice service from past to present Finland has long experience in ice
Sea ice charts and SAR for sea ice classification Patrick Eriksson Juha Karvonen Jouni Vainio ECMWF Ocean Workshop, 22-25 January 2018 Ice service from past to present Finland has long experience in ice
Modelling approaches for MOSAiC. Klaus Dethloff, A. Rinke, A. Sommerfeld, D. Klaus T. Vihma, M. Müller, J. Inoue, W. Maslowski & modelling team
 Modelling approaches for MOSAiC Klaus Dethloff, A. Rinke, A. Sommerfeld, D. Klaus T. Vihma, M. Müller, J. Inoue, W. Maslowski & modelling team Why do we need MOSAiC? High quality co-observations of A-O-I-BGC-E
Modelling approaches for MOSAiC Klaus Dethloff, A. Rinke, A. Sommerfeld, D. Klaus T. Vihma, M. Müller, J. Inoue, W. Maslowski & modelling team Why do we need MOSAiC? High quality co-observations of A-O-I-BGC-E
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT
 SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change. Renguang Wu
 The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
Austria (ZAMG) Implementation and development of AROME. Upgrade ALADIN-LAEF. Research on land surface data assimilation, e.g. ASCAT.
 Austria (ZAMG) Implementation and development of AROME Upgrade ALADIN-LAEF Research on land surface data assimilation, e.g. ASCAT. Belgium (RMI) Multi-scale behavior of ALARO-0 for extreme summer precipitation
Austria (ZAMG) Implementation and development of AROME Upgrade ALADIN-LAEF Research on land surface data assimilation, e.g. ASCAT. Belgium (RMI) Multi-scale behavior of ALARO-0 for extreme summer precipitation
EUMETSAT SAF NETWORK. Lothar Schüller, EUMETSAT SAF Network Manager
 1 EUMETSAT SAF NETWORK Lothar Schüller, EUMETSAT SAF Network Manager EUMETSAT ground segment overview METEOSAT JASON-2 INITIAL JOINT POLAR SYSTEM METOP NOAA SATELLITES CONTROL AND DATA ACQUISITION FLIGHT
1 EUMETSAT SAF NETWORK Lothar Schüller, EUMETSAT SAF Network Manager EUMETSAT ground segment overview METEOSAT JASON-2 INITIAL JOINT POLAR SYSTEM METOP NOAA SATELLITES CONTROL AND DATA ACQUISITION FLIGHT
COLD REGION SCIENCE AND MARINE TECHNOLOGY - Seasonal Lake Ice - Matti Leppäranta
 SEASONAL LAKE ICE Matti Leppäranta Department of Physics, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland Keywords: ice formation, ice type, ice thickness, heat budget, ice drift, lake ecology Contents 1. Introduction
SEASONAL LAKE ICE Matti Leppäranta Department of Physics, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland Keywords: ice formation, ice type, ice thickness, heat budget, ice drift, lake ecology Contents 1. Introduction
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting
 Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
ICON. The Icosahedral Nonhydrostatic model: Formulation of the dynamical core and physics-dynamics coupling
 ICON The Icosahedral Nonhydrostatic model: Formulation of the dynamical core and physics-dynamics coupling Günther Zängl and the ICON deelopment team PDEs on the sphere 2012 Outline Introduction: Main
ICON The Icosahedral Nonhydrostatic model: Formulation of the dynamical core and physics-dynamics coupling Günther Zängl and the ICON deelopment team PDEs on the sphere 2012 Outline Introduction: Main
M.Sc. in Meteorology. Physical Meteorology Prof Peter Lynch. Mathematical Computation Laboratory Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield.
 M.Sc. in Meteorology Physical Meteorology Prof Peter Lynch Mathematical Computation Laboratory Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Climate Change???????????????? Tourists run through a swarm of pink
M.Sc. in Meteorology Physical Meteorology Prof Peter Lynch Mathematical Computation Laboratory Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Climate Change???????????????? Tourists run through a swarm of pink
Seasonal Forecast for the area of the east Mediterranean, Products and Perspectives
 Seasonal Forecast for the area of the east Mediterranean, Products and Perspectives Dr Kleanthis Nicolaides Senior Meteorological Officer Department of Meteorology The need for weather forecasts from where
Seasonal Forecast for the area of the east Mediterranean, Products and Perspectives Dr Kleanthis Nicolaides Senior Meteorological Officer Department of Meteorology The need for weather forecasts from where
New soil physical properties implemented in the Unified Model
 New soil physical properties implemented in the Unified Model Imtiaz Dharssi 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 3, Anne Verhoef 3, Bruce Macpherson 1, Clive Jones 1 and Martin Best 2 1 Met Office (Exeter, UK) 2 Met
New soil physical properties implemented in the Unified Model Imtiaz Dharssi 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 3, Anne Verhoef 3, Bruce Macpherson 1, Clive Jones 1 and Martin Best 2 1 Met Office (Exeter, UK) 2 Met
Storm surge forecasting and other Met Office ocean modelling
 Storm surge forecasting and other Met Office ocean modelling EMODnet stakeholder meeting Clare O Neill + many others Outline Ocean modelling at the Met Office Storm surge forecasting Current operational
Storm surge forecasting and other Met Office ocean modelling EMODnet stakeholder meeting Clare O Neill + many others Outline Ocean modelling at the Met Office Storm surge forecasting Current operational
Regional climate modelling in the future. Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden
 Regional climate modelling in the future Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden The chain Global H E H E C ( m 3/s ) Regional downscaling 120 adam 3 C HAM 4 adam 3 C HAM 4 trl A2 A2 B2 B2 80 40 0 J F M A M J J A S
Regional climate modelling in the future Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden The chain Global H E H E C ( m 3/s ) Regional downscaling 120 adam 3 C HAM 4 adam 3 C HAM 4 trl A2 A2 B2 B2 80 40 0 J F M A M J J A S
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007
 Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
The convection-permitting COSMO-DE-EPS and PEPS at DWD
 Deutscher Wetterdienst The convection-permitting COSMO-DE-EPS and PEPS at DWD Detlev Majewski based on Chr. Gebhardt, S. Theis, M. Paulat, M. Buchhold and M. Denhard Deutscher Wetterdienst The model COSMO-DE
Deutscher Wetterdienst The convection-permitting COSMO-DE-EPS and PEPS at DWD Detlev Majewski based on Chr. Gebhardt, S. Theis, M. Paulat, M. Buchhold and M. Denhard Deutscher Wetterdienst The model COSMO-DE
GEWEX Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model
 GEWEX Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model Inter-comparison Studies Timo Vihma 1, Tiina Kilpeläinen 1, Albert A.M. Holtslag 2, Laura Rontu 1, Phil Anderson 3, Klara Finkele 4, and Gunilla Svensson 5 1 Finnish
GEWEX Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model Inter-comparison Studies Timo Vihma 1, Tiina Kilpeläinen 1, Albert A.M. Holtslag 2, Laura Rontu 1, Phil Anderson 3, Klara Finkele 4, and Gunilla Svensson 5 1 Finnish
Added Value of Convection Resolving Climate Simulations (CRCS)
 Added Value of Convection Resolving Climate Simulations (CRCS) Prein Andreas, Gobiet Andreas, Katrin Lisa Kapper, Martin Suklitsch, Nauman Khurshid Awan, Heimo Truhetz Wegener Center for Climate and Global
Added Value of Convection Resolving Climate Simulations (CRCS) Prein Andreas, Gobiet Andreas, Katrin Lisa Kapper, Martin Suklitsch, Nauman Khurshid Awan, Heimo Truhetz Wegener Center for Climate and Global
ENSEMBLES multimodel simulations forced by ERA40: Analysis of CLM results
 ENSEMBLES multimodel simulations forced by ERA40: Analysis of CLM results Ivonne Anders, Burkhardt Rockel Contents ENSEMBLES Project Model Simulation Subregions Simulation Results Conclusion Outlook ENSEMBLES
ENSEMBLES multimodel simulations forced by ERA40: Analysis of CLM results Ivonne Anders, Burkhardt Rockel Contents ENSEMBLES Project Model Simulation Subregions Simulation Results Conclusion Outlook ENSEMBLES
Seasonal variations of vertical structure in the deep waters of the Southern Caspian Sea
 278 Research in Marine Sciences Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018 Pages 278-286 Seasonal variations of vertical structure in the deep waters of the Southern Caspian Sea Somayeh Nahavandian 1,*, and Alireza Vasel
278 Research in Marine Sciences Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018 Pages 278-286 Seasonal variations of vertical structure in the deep waters of the Southern Caspian Sea Somayeh Nahavandian 1,*, and Alireza Vasel
