STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 4 SCIENCE
|
|
|
- Maria Ford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 4 SCIENCE Administered December 2005
2
3 DIRECTIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. SAMPLE A Objects That Conduct Heat Objects That Do Not Conduct Heat Silver spoon Plastic fork Copper pan Glass block Iron nail Wooden handle Gold ring??? The chart shows some objects that conduct heat and some that do not conduct heat. Which of these would complete the column of objects that do not conduct heat? A Electrical wire B Water drop C Cotton glove D Horseshoe magnet Page 1
4 SAMPLE B Plant Growth vs. Time Plant Growth (cm) Day The graph shows how much a plant grew over four days. According to the graph, how many centimeters did the plant grow between Day 1 and Day 4? A 17 cm B 6 cm C 15 cm D 14 cm Page 2
5 1 Students are working with salt water in the science lab. They are dropping different items into the salt water in an effort to determine which items will sink and which items will float. Which of the following would be the most important piece of safety equipment that the students should use for this lab activity? A Eye goggles to keep the salt water from splashing into their eyes B Aprons to keep the salt water off of their clothes C Face masks to keep from inhaling the salt water D A fire extinguisher nearby in case the salt water spills on to the floor 2 If the materials shown above were used in an investigation along with a light bulb, some wires, and a battery, which hypothesis below could be tested? F A nail will conduct electricity, but a wooden block will not. G A wooden block will float, but a nail will not. H Paper is a source of energy, but string is not. J String costs more to buy than wood, paper or a nail. Page 3
6 Beef Soup Mix Some images 2005 JupiterImages Corporation 3 A student wants to determine the mass of a new box of soup mix that he purchased at the store. He uses the triple beam balance shown above. What is the student measuring? A The mass of the soup inside the box B The mass of the box without the soup C The mass of the box and the soup combined D The mass of the soup and the triple beam balance 4 A small ball of clay immediately sinks when dropped into a tub of water. When the clay is flattened and curved so that it resembles a boat, the clay floats in the same tub of water. What can we conclude about the clay from this investigation? F The clay became lighter when we shaped it into a boat. G The clay became heavier when we shaped it into a boat. H The clay was able to float once it was wet. J The clay will sink or float, depending on how it is shaped. Page 4
7 Results of Series Circuit Tests Number of Number of D- Brightness of the Lights Light Bulbs Cell Batteries 1 1 brightest 2 1 fairly bright 3 1 not very bright 4 1 dim 5 Using the table shown above, what conclusion can be made from the information given? A The more light bulbs in a series circuit, the brighter those light bulbs will be. B The less light bulbs in a series circuit, the brighter those light bulbs will be. C The circuits that used C-Cells burned brighter than those that used D-Cells. D All the circuits tested had light bulbs that glowed with the same brightness. In the stream tables shown below, the white circle is a cup with a hole in the bottom. Water is poured into the cup and flows across the land to the ocean. 6 Which stream table model below shows the formation of a delta? F Ocean Land G Ocean Land H Ocean Land J Ocean Land Page 5
8 7 During a science lab, a group of students tested different items in both saltwater and freshwater to see which items would float and which items would sink. After seeing a plastic bead sink in the freshwater and float in the saltwater, one student remarked, "The bead is heavier in the freshwater." Her classmate pointed out that - A there was not enough buoyant force in the freshwater to keep the bead afloat B there was not enough buoyant force in the saltwater to keep the bead afloat C the buoyant force in the freshwater is equal to the buoyant force in the saltwater D the bead is heavier in the saltwater than it is in the freshwater 8 Suppose you conduct an experiment using batteries in a flashlight. You record the data in the chart below. Brand of Battery Brand A Brand B How long did the flashlight produce light? 3 hours 4 hours Which of the following inferences can you draw from your experiment? F The light bulbs used with Brand A are brightest. G The light bulbs used with Brand B are brightest. H Brand A batteries last longer than Brand B batteries. J Brand B batteries last longer than Brand A batteries. Page 6
9 Use the diagram below to answer questions 9, 10, and 11. North Cup West East South 9 A teacher uses the stream table shown above to show erosion and deposition as the stream flows. Which of the following is an example of a limitation of this model? A It does not have any fish in the stream or water. B It does not show how water can flow uphill. C It does not show the different temperatures of erosion. D It does not show how two rivers can join together. 11 What is the role of the cup in the stream table model pictured above? A The sound source B The light source C The river source D The ocean source 10 A stream table like the one shown above was used to show the flow of soil when water is poured on it. In which direction did the soil move? Towards the - F North G South H East J West Page 7
10 Temperature in C C 14 In the science lab, a student conducted an experiment to see what would happen when a small amount of hot, blue colored water was added to a large cup of clear water at room temperature. She noticed that the blue water floated on top of the clear water. This happened because F the blue water got hotter after it was poured in the cup G the water in the cup got colder after the blue water was added H the hot, blue water is denser than the clear water in the cup J the clear water in the cup is denser than the hot, blue water 12 The above Celsius thermometer represents a good temperature for F swimming in July G harvesting pumpkins in October H building a snowman in January J planting tulip bulbs in February 2005 JupiterImages 13 An electric circuit consists of a battery, wire, and a motor that spins. When the wire is removed, the motor will - A stop spinning B start buzzing C spin faster D burn out 15 You make a glass of lemonade and add some ice cubes to it so that the glass is completely full. What states of matter are contained in your glass? A Solid and gas B Gas and liquid C Gas and solid D Liquid and solid Page 8
11 Magnetic Compass Bar Magnet Some images 2005 JupiterImages Corporation 16 A student was working with a bar magnet and a compass like the ones pictured above during science class. When he points one end of the bar magnet at the E on the compass, and then brings the magnet near the compass, the needle on the compass will F move towards the E or the W G move towards the S H start to spin in a circle J stay on the N Page 9
12 17 You are on an airplane going over a mountain range in Colorado. You notice the large, pointed horn of a mountain. You remember reading in science class about valley glaciers. You know that the horn of the mountain was formed when - A the glaciers moved the mountain towards the east and erode away the surfaces B the glaciers melted next to the mountain's side C the glaciers push up against the mountain's sides and erode away the surfaces D the glaciers move up and over the top of the mountain 19 How does the planet Jupiter compare to the planet Earth? A The Earth is closer to the Sun than Jupiter is. B Jupiter is a hot ball of gas, and we use a lot of gas on Earth. C Jupiter and the Earth both rotate around a moon. D Jupiter and the Earth are the same distance from the sun. 18 In the ocean, there are tides. The tides are a result of the moon's continual pull on the oceans. Because of this, we can say that the ocean tides are - F renewable G recyclable H nonrenewable J inexhaustible 20 Which statement best describes the Sun? F The Sun is about the same size as some of the planets. G The Sun is located in the center of the solar system. H Some of the planets are bigger than the Sun. J The Sun s light is dimmer on Mercury than other planets. Page 10
13 Some images copyright 2004 JupiterImages 21 Look at the picture above. What would happen if the sun was taken out of this system? A The water would get hot. B There would be more clouds. C The clouds would not form. D It would rain a lot more. Page 11
14 Use the information in the following paragraph to answer questions 22 and 23. You and your friends are out on the playground after a short rain shower. On the sidewalk, you notice a puddle of water. You decide to draw a circle around the puddle of water with a piece of chalk. When your class comes out for P.E. later in the day, you notice that the puddle is smaller than the circle you drew, so you draw a new circle around the smaller puddle of water. After school, you check the puddle again. You see that the puddle has gotten smaller again. 22 The pattern you have observed in the puddle of water is caused by - F evaporation G condensation H melting J weathering 23 What source of energy caused the changes that you observed in the pattern of circles you drew on the sidewalk? A Sound B Electricity C The Sun D Chemicals Page 12
15 24 What characteristic of the Earth remains constant as it travels around the Sun? F The season of the year G The hours of daylight H The Sun rising in the east J The Earth s distance from the Sun 25 The rock formation below is a famous one on the side of a mountain in New Hampshire. It was called "The Old Man On The Mountain." One day, it just collapsed. Which of the following processes most likely contributed to its fall? A Evaporation B Condensation C Weathering D Flooding Page 13
16 sand clay loam clay and sand mixture Sample J Sample K Sample L Sample M 26 Which of the following would be a good test to find out which of the soil samples will grow the healthiest plants? F Shake the samples and allow the soils to settle back to the bottom. G Place the samples in the sunlight and see if anything grows. H Measure the thickness and the weight of each soil sample. J Plant 5 bean seeds in each soil sample and observe the plants growing. 27 On a recent trip to the beach along the Gulf of Mexico, you saw the rock formation pictured above. What could have caused this large rock to be shaped the way it is? A Wave action B Electricity C Buoyancy D Magnetism Page 14
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 5 SCIENCE
 STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 5 SCIENCE Administered December 2005 DIRECTIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. SAMPLE A Objects That Objects That Do Conduct
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 5 SCIENCE Administered December 2005 DIRECTIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. SAMPLE A Objects That Objects That Do Conduct
STUDENT NAME. Science Grade 4. Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. Switch Lightbulb Battery
 FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS Third Grading Period 2009-10 February 1-5 STUDENT NAME DATE Science Grade 4 Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. + Switch Lightbulb
FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS Third Grading Period 2009-10 February 1-5 STUDENT NAME DATE Science Grade 4 Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. + Switch Lightbulb
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 3 SCIENCE
 STUENT NME TE I GRE 3 SIENE dministered ecember 2005 IRETIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. e sure to mark all of your answers. SMPLE Objects That onduct Heat Objects That o Not onduct
STUENT NME TE I GRE 3 SIENE dministered ecember 2005 IRETIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. e sure to mark all of your answers. SMPLE Objects That onduct Heat Objects That o Not onduct
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 5 SCIENCE
 STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 5 SCIENCE Administered October 2007 DIRECTIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark your answers. SAMPLE A Objects That Conduct Heat Silver spoon Copper
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 5 SCIENCE Administered October 2007 DIRECTIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark your answers. SAMPLE A Objects That Conduct Heat Silver spoon Copper
STUDENT NAME. Science Grade 5. Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers.
 FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS First Grading Period 2010-11 September 21-24 STUDENT NAME DATE Science Grade 5 Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. 1 Which is
FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS First Grading Period 2010-11 September 21-24 STUDENT NAME DATE Science Grade 5 Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. 1 Which is
Science - 4th grade practice test
 Name: Instructions: Bubble the correct answer. Read each choice before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : Use the picture below to answer question 1. 1. A
Name: Instructions: Bubble the correct answer. Read each choice before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : Use the picture below to answer question 1. 1. A
Embedded Assessment Notes
 Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
2 nd Grade Science Fair Ideas
 2 nd Grade Science Fair Ideas Science Rocks! Suggested Science Fair Project Ideas Reporting Category 1 Matter & Energy (2 nd Grade) Physical Properties: shape, relative mass, relative temperature, texture,
2 nd Grade Science Fair Ideas Science Rocks! Suggested Science Fair Project Ideas Reporting Category 1 Matter & Energy (2 nd Grade) Physical Properties: shape, relative mass, relative temperature, texture,
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 4 SCIENCE
 STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 4 SCIENCE Administered March 2004 Page 2 DIRECTIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. SAMPLE A Objects That Conduct Heat Silver
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 4 SCIENCE Administered March 2004 Page 2 DIRECTIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. SAMPLE A Objects That Conduct Heat Silver
STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA
 1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
STUDENT NAME. Science Grade 3. Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers.
 FORMTIVE MINI SSESSMENTS First Grading Period 2009-10 October 20-23 STUENT NME TE Science Grade 3 Read each question and choose the best answer. e sure to mark all of your answers. opyright 2004, Texas
FORMTIVE MINI SSESSMENTS First Grading Period 2009-10 October 20-23 STUENT NME TE Science Grade 3 Read each question and choose the best answer. e sure to mark all of your answers. opyright 2004, Texas
Bottle-and-Pipe System
 Bottle-and-Pipe System Record and label water levels here. Part 1 Where did you put the bottle system? What did you observe? Part 2 Where did you put the bottle system? What did you observe? Explain your
Bottle-and-Pipe System Record and label water levels here. Part 1 Where did you put the bottle system? What did you observe? Part 2 Where did you put the bottle system? What did you observe? Explain your
Science CRCT question pool
 Name: Instructions: Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 1. How often can a full moon be seen? A. once each year B. once each season of the year C. about once each month D. about
Name: Instructions: Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 1. How often can a full moon be seen? A. once each year B. once each season of the year C. about once each month D. about
Air Is There. What can air do? balloon cotton ball feather flex straw foam ball piece of paper plastic bag
 What can air do? Air Is There balloon cotton ball feather flex straw foam ball piece of paper plastic bag Investigation 1: Exploring Air No. 1 Notebook Master Parachutes How does a parachute use air? Investigation
What can air do? Air Is There balloon cotton ball feather flex straw foam ball piece of paper plastic bag Investigation 1: Exploring Air No. 1 Notebook Master Parachutes How does a parachute use air? Investigation
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: 05 5th Grade Science May Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: 05 5th Grade Science May 2010 Student name: Author: Ohio District: Ohio Released Tests Printed: Monday July 02, 2012 1 Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What
Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: 05 5th Grade Science May 2010 Student name: Author: Ohio District: Ohio Released Tests Printed: Monday July 02, 2012 1 Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy
 Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
The Sun and Water Cycle
 Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
Royal International School. Revision Booklet FINAL EXAMINATION. 2nd Semester Science - Grade 3A. Name: Prepared by: Ms.
 Royal International School Revision Booklet FINAL EXAMINATION 2nd Semester 2016-2017 Science - Grade 3A Name: Prepared by: Ms. Marvy 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS TOPIC Page How Does Earth s Surface Change Slowly?
Royal International School Revision Booklet FINAL EXAMINATION 2nd Semester 2016-2017 Science - Grade 3A Name: Prepared by: Ms. Marvy 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS TOPIC Page How Does Earth s Surface Change Slowly?
RELEASED. Spring 2013 North Carolina Measures of Student Learning: NC s Common Exams. Grade 6 Science Form A
 Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Grade 6 Science Form RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction
Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Grade 6 Science Form RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction
SCI-5 Deane_Units1_2_SOL_Practice_Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-5 Deane_Units1_2_SOL_Practice_Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1PEFE2 1 Directions: Type your answer in the box. Use a whole number. What is the mass of the rock shown? g
SCI-5 Deane_Units1_2_SOL_Practice_Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1PEFE2 1 Directions: Type your answer in the box. Use a whole number. What is the mass of the rock shown? g
Year 7 Recall Booklet. Name: Class:
 Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
Comparing the Surfaces of the Moon and Earth
 Chapter 4 Stars and the Solar System Chapter Science Investigation Comparing the Surfaces of the Moon and Earth two clear plastic shoe boxes, one with lid one cup of gravel two file folder labels or masking
Chapter 4 Stars and the Solar System Chapter Science Investigation Comparing the Surfaces of the Moon and Earth two clear plastic shoe boxes, one with lid one cup of gravel two file folder labels or masking
ASSESSMENT CHART FOR INVESTIGATIONS 1 AND 2 STUDENT NAME
 ASSESSMENT CHART FOR INVESTIGATIONS 1 AND 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. STUDENT NAME Weather Measurements (TO)
ASSESSMENT CHART FOR INVESTIGATIONS 1 AND 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. STUDENT NAME Weather Measurements (TO)
S (2.1)2.a Using an illustration, measure a physical property (e.g., length, temperature).
 Morgan County School District Re-3 Science Fourth ***Not all units will be taught in the order suggested on this plan. August Measurement S (2.1)2 Measuring common physical properties of objects (for example,
Morgan County School District Re-3 Science Fourth ***Not all units will be taught in the order suggested on this plan. August Measurement S (2.1)2 Measuring common physical properties of objects (for example,
4th Grade Science Practice Test
 4th Grade Science Practice Name: Instructions: Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 4th Grade Science Practice 1. Which planet has gases, land masses, and large amounts of surface
4th Grade Science Practice Name: Instructions: Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 4th Grade Science Practice 1. Which planet has gases, land masses, and large amounts of surface
STUDENT NAME. Science Grade 3. Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers.
 FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS First Grading Period 10-11 October 18-21 STUDENT NAME DATE Science Grade 3 Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. Copyright 04, Texas
FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS First Grading Period 10-11 October 18-21 STUDENT NAME DATE Science Grade 3 Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers. Copyright 04, Texas
The map shows ocean currents in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Which location most likely has the warmest climate?
 6 th Grade Final Exam Study Guide 1. Use the map below to answer this question. The map shows ocean currents in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Which location most likely has the warmest climate? 2. Daylight
6 th Grade Final Exam Study Guide 1. Use the map below to answer this question. The map shows ocean currents in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Which location most likely has the warmest climate? 2. Daylight
Making Sense of Matter Study Guide. Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass.
 Making Sense of Matter Study Guide Matter is all around us everything is made of matter. Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. We can classify objects by their physical properties. Physical
Making Sense of Matter Study Guide Matter is all around us everything is made of matter. Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. We can classify objects by their physical properties. Physical
The Sun s center is much hotter than the surface. The Sun looks large and bright in the sky. Other stars look much smaller.
 The Sun A star is a huge ball of hot, glowing gases. The Sun is a star. The width of the Sun is equal to the width of 100 Earths placed side by side. The Sun is extremely hot. The surface of the Sun has
The Sun A star is a huge ball of hot, glowing gases. The Sun is a star. The width of the Sun is equal to the width of 100 Earths placed side by side. The Sun is extremely hot. The surface of the Sun has
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8
 The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
Land and Water Study Guide
 Land and Water Study Guide Answer Key Part 1 States of Matter 1. What are the three states of matter for water? Give several examples for each. Solid Ice cube (non water examples = candy bar and a log).
Land and Water Study Guide Answer Key Part 1 States of Matter 1. What are the three states of matter for water? Give several examples for each. Solid Ice cube (non water examples = candy bar and a log).
Fill in the blank with the word that completes the sentence. Then, find that work in the puzzle.
 Classwork #1 Name: 2 nd Grade PSI Fill in the blank with the word that completes the sentence. Then, find that work in the puzzle. 1. When the Earth is facing the sun, it is time. 2. Another word for spins
Classwork #1 Name: 2 nd Grade PSI Fill in the blank with the word that completes the sentence. Then, find that work in the puzzle. 1. When the Earth is facing the sun, it is time. 2. Another word for spins
1st Nine Weeks Midterm Study Guide
 Name: ate: 1. Which statement correctly describes a property of a type of matter?. ir is a mixture of gases.. Ice is a mixture of gases.. ir is a liquid.. Ice is a liquid. 4. Why is cobalt (o) placed before
Name: ate: 1. Which statement correctly describes a property of a type of matter?. ir is a mixture of gases.. Ice is a mixture of gases.. ir is a liquid.. Ice is a liquid. 4. Why is cobalt (o) placed before
FOSS Earth, Cycles, and Change Module The Regents of the University of California Can be duplicated for classroom or workshop use.
 Shadow Challenges 1. Work in pairs. Take turns tracing the outline of your partner s shadow, including his or her feet. 2. Label each shadow with the owner s name and time of day it was drawn. 3. Try to
Shadow Challenges 1. Work in pairs. Take turns tracing the outline of your partner s shadow, including his or her feet. 2. Label each shadow with the owner s name and time of day it was drawn. 3. Try to
STUDENT NAME DATE ID. 6 th Grade Science
 STUDENT NAME DATE ID 6 th Grade Science Administered December 2003 Page 2 Page 3 SAMPLE A SAMPLE A Page 4 The graph shows how much a plant grew over four days. According to the graph, how many centimeters
STUDENT NAME DATE ID 6 th Grade Science Administered December 2003 Page 2 Page 3 SAMPLE A SAMPLE A Page 4 The graph shows how much a plant grew over four days. According to the graph, how many centimeters
1. (a) Methane can be a gas, a liquid or a solid. In the diagram below, arrows P, Q, R and S represent changes of state.
 1. (a) Methane can be a gas, a liquid or a solid. In the diagram below, arrows P, Q, R and S represent changes of state. The boxes on the right show the arrangement of particles of methane in the three
1. (a) Methane can be a gas, a liquid or a solid. In the diagram below, arrows P, Q, R and S represent changes of state. The boxes on the right show the arrangement of particles of methane in the three
5thscience physical (5thscience_physical)
 5thscience physical (5thscience_physical) Name: Date: 1. Which circuit would turn the light bulb on? A. B. C. D. 2. Which item would conduct electricity? A. a glass cup B. a chicken feather C. a plastic
5thscience physical (5thscience_physical) Name: Date: 1. Which circuit would turn the light bulb on? A. B. C. D. 2. Which item would conduct electricity? A. a glass cup B. a chicken feather C. a plastic
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint SCIENCE 0846/02 Paper 2 October 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 50 This document consists of 11 printed pages and 1 blank page. IB16 10_0846_02/4RP
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint SCIENCE 0846/02 Paper 2 October 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 50 This document consists of 11 printed pages and 1 blank page. IB16 10_0846_02/4RP
Grade 5 FCAT 2.0 Science Sample Questions
 Grade FCAT 2.0 Science Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT 2.0 tests. By using these materials, students will
Grade FCAT 2.0 Science Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT 2.0 tests. By using these materials, students will
K-5 Physical Science Overview with Activities
 K-5 Physical Science Overview with Activities The physical science strand encourages the basic observations of what our physical reality is made of and how it interacts matter, energy, forces, atoms and
K-5 Physical Science Overview with Activities The physical science strand encourages the basic observations of what our physical reality is made of and how it interacts matter, energy, forces, atoms and
Al-Omam International School
 Term 2 Test 1- Review Sheet Class: 2 B / C Subject: Science Lessons: Unit.6 Lesson.1 What changes Earth? Unit.6 Lesson.2 What are natural resources? Unit.7 Lesson.1 How does weather change? Unit.7 Lesson.3
Term 2 Test 1- Review Sheet Class: 2 B / C Subject: Science Lessons: Unit.6 Lesson.1 What changes Earth? Unit.6 Lesson.2 What are natural resources? Unit.7 Lesson.1 How does weather change? Unit.7 Lesson.3
Hopkins 8th Benchmark Review (Hopkin8BenchmarkReview1)
 Name: Date: 1. Based on the following characteristics, classify the state of matter. A. gas B. solid C. plasma D. liquid high energy found in stars consists of freely moving charged particles 2. What is
Name: Date: 1. Based on the following characteristics, classify the state of matter. A. gas B. solid C. plasma D. liquid high energy found in stars consists of freely moving charged particles 2. What is
I can classify objects by two of their properties. I can classify objects or events in sequential order.
 I can classify objects by two of their properties (attributes). S.C. Science 3-1.1 I can classify objects or events in sequential order. S.C. Science 3-1.2 I can generate questions such as what if? or
I can classify objects by two of their properties (attributes). S.C. Science 3-1.1 I can classify objects or events in sequential order. S.C. Science 3-1.2 I can generate questions such as what if? or
Name: Date: Class: 2. The diagram below shows the Moon revolving around Earth as viewed from space. (6.L.2.1)
 Name: Date: Class: 6 th Grade Science MSL Practice 1. The diagram below shows the rock cycle. (6.E.2.3) Which two processes result in the formation of igneous rocks? A. melting and solidification B. sedimentation
Name: Date: Class: 6 th Grade Science MSL Practice 1. The diagram below shows the rock cycle. (6.E.2.3) Which two processes result in the formation of igneous rocks? A. melting and solidification B. sedimentation
2018 Version. Separating Mixtures Junior Science
 2018 Version Separating Mixtures Junior Science 6a Solutions are made from a solute dissolved in a solvent Solution (saltwater) Solute (salt) Solvent (water) A solution is made up of a solvent and a solute.
2018 Version Separating Mixtures Junior Science 6a Solutions are made from a solute dissolved in a solvent Solution (saltwater) Solute (salt) Solvent (water) A solution is made up of a solvent and a solute.
Lesson 1 Matter and Its Properties
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 Math Skills 15 School to Home 16 Key Concept Builders
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 Math Skills 15 School to Home 16 Key Concept Builders
School Year. Ecological Framework for the back of your science journal.
 2017-2018 School Year Ecological Framework for the back of your science journal. Life Science = Biosphere slide Physical Science = Nature of Science and Physical Science slides Earth Science = Lithosphere/Geosphere
2017-2018 School Year Ecological Framework for the back of your science journal. Life Science = Biosphere slide Physical Science = Nature of Science and Physical Science slides Earth Science = Lithosphere/Geosphere
Earth Boot Camp. 3.7B: Investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and landslides.
 Earth Boot Camp 3.7B: Investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and landslides. Release Questions 2006 #21 (65%) 1. In which of these ways can volcanoes help
Earth Boot Camp 3.7B: Investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and landslides. Release Questions 2006 #21 (65%) 1. In which of these ways can volcanoes help
PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1. Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? What phase change is this?
 PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1 Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? What phase change is this? PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 2 Make a copy of this graph on your paper. Label
PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1 Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? What phase change is this? PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 2 Make a copy of this graph on your paper. Label
Name Class Date. What are three kinds of energy transfer? What are conductors and insulators? What makes something a good conductor of heat?
 CHAPTER 14 SECTION Heat and Temperature 2 Energy Transfer KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are three kinds of energy transfer? What are conductors and insulators?
CHAPTER 14 SECTION Heat and Temperature 2 Energy Transfer KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are three kinds of energy transfer? What are conductors and insulators?
Earth Space EOC Review Test #1
 Earth Space EOC Review Test #1 NAME: Use test for questions 1 and 2 Jack studied the effects of light pollution on turtles and their offspring. He observed that areas with a high amounts of light pollution
Earth Space EOC Review Test #1 NAME: Use test for questions 1 and 2 Jack studied the effects of light pollution on turtles and their offspring. He observed that areas with a high amounts of light pollution
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 4 SCIENCE
 STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 4 SCIENCE Administered May 2005 Page 1 1. Hand Lens 2. Dry Cell 3. Gloves 4. Magnet N S 5. Goggles 6. Metric Ruler 7. Microscope 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 METRIC 8. Eye Dropper 9. Thermometer
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 4 SCIENCE Administered May 2005 Page 1 1. Hand Lens 2. Dry Cell 3. Gloves 4. Magnet N S 5. Goggles 6. Metric Ruler 7. Microscope 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 METRIC 8. Eye Dropper 9. Thermometer
I/R/M THIRD GRADE Religious Values I. Life Science
 I/R/M THIRD GRADE Religious Values Life Science M. M. R. A. Invertebrates 1. Invertebrates vs. Vertebrates a. Describe the diversity of invertebrate life forms supported by different environments. b. Investigate
I/R/M THIRD GRADE Religious Values Life Science M. M. R. A. Invertebrates 1. Invertebrates vs. Vertebrates a. Describe the diversity of invertebrate life forms supported by different environments. b. Investigate
6th Grade Science Final Exam Practice
 6th Grade Science Final Exam Practice Name: Date: Class: 1. Which of these animals is least likely a member of the pond community? (6.L.2.3) A. C. B. D. 2. Which of these is a natural resource of North
6th Grade Science Final Exam Practice Name: Date: Class: 1. Which of these animals is least likely a member of the pond community? (6.L.2.3) A. C. B. D. 2. Which of these is a natural resource of North
1 Earth s Oceans. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify What are the five main oceans?
 CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
Conceptual Understandings for K-2 Teachers
 AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Ideas ESS1: Earth s Place in the Universe What is the universe, and what is Earth s place in it? ESS1. A: The Universe and Its Stars What is the universe, and what
AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Ideas ESS1: Earth s Place in the Universe What is the universe, and what is Earth s place in it? ESS1. A: The Universe and Its Stars What is the universe, and what
Unit 2. Phases of Matter and Density
 Name Pd Unit 2 Phases of Matter and Density Name Pd Name Pd Homework for Unit 2 1. Vocab for Unit 2; due: 2. Pg 17 (1-5), pg 19 (1-5), pg21 (1-5) complete sentences; due: 3. Pg 23 (1-6), pg 27 (1-6) complete
Name Pd Unit 2 Phases of Matter and Density Name Pd Name Pd Homework for Unit 2 1. Vocab for Unit 2; due: 2. Pg 17 (1-5), pg 19 (1-5), pg21 (1-5) complete sentences; due: 3. Pg 23 (1-6), pg 27 (1-6) complete
CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST GRADE 5 SCIENCE (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 10/02)
 CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 0/02) Physical Sciences 8 30 Physical Sciences Grade 5. Elements and their combinations account for all the varied types of
CALIFORNIA STANDARDS TEST (Blueprint adopted by the State Board of Education 0/02) Physical Sciences 8 30 Physical Sciences Grade 5. Elements and their combinations account for all the varied types of
Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas
 P H Y S I C A L S C I E N C E Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas National Institute for Direct Instruction (NIFDI) Academic Core Level A Lesson 1 a. (Display 3 Phases of Matter chart:)
P H Y S I C A L S C I E N C E Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas National Institute for Direct Instruction (NIFDI) Academic Core Level A Lesson 1 a. (Display 3 Phases of Matter chart:)
This Rocks! Author: Sara Kobilka Institute for Chemical Education and Nanoscale Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison
 This Rocks! Author: Sara Kobilka Institute for Chemical Education and Nanoscale Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison Purpose: To learn about the rock cycle and the role that weather
This Rocks! Author: Sara Kobilka Institute for Chemical Education and Nanoscale Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison Purpose: To learn about the rock cycle and the role that weather
6 th Grade TEKS. Whacha-gotta-no!
 6 th Grade TEKS Whacha-gotta-no! (1) Scientific investigation and reasoning. 1(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards; and 1(B)
6 th Grade TEKS Whacha-gotta-no! (1) Scientific investigation and reasoning. 1(A) demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards; and 1(B)
1. What makes plants different than animals?
 1. What makes plants different than animals? tiger lily tiger 1. Plants are producers, which means they make their own food (through photosynthesis). 2. While plants can move certain structures, they cannot
1. What makes plants different than animals? tiger lily tiger 1. Plants are producers, which means they make their own food (through photosynthesis). 2. While plants can move certain structures, they cannot
Primary Curriculum 2014
 Primary Curriculum 2014 Suggested Key Objectives for Science at Key Stages 1 and 2 www.primarycurriculum.me.uk , 2014 Year 1 Science Key Objectives 1 Asking simple questions and recognising that they can
Primary Curriculum 2014 Suggested Key Objectives for Science at Key Stages 1 and 2 www.primarycurriculum.me.uk , 2014 Year 1 Science Key Objectives 1 Asking simple questions and recognising that they can
A. tornadoes. B. earthquakes. C. tsunamis. D. landslides
 Questions 1 through 30 are science questions. Read each question carefully. Choose the best answer and then go on to the next question. Do not skip any questions. 1. In the atmosphere, warm air tends to
Questions 1 through 30 are science questions. Read each question carefully. Choose the best answer and then go on to the next question. Do not skip any questions. 1. In the atmosphere, warm air tends to
Ocean s Influence on Weather and Climate
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Thermal Energy and Temperature Lab. Experiment Question: How can the difference between thermal energy and temperature be experimentally observed?
 Thermal Energy and Temperature Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Grade / 20 Experiment Question: How can the difference between thermal energy and temperature be experimentally observed? Hypothesis Starters: 1.
Thermal Energy and Temperature Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Grade / 20 Experiment Question: How can the difference between thermal energy and temperature be experimentally observed? Hypothesis Starters: 1.
1. The diagram below shows Earth, four different positions of the Moon, and the direction of incoming sunlight.
 G8 Semester I MCAS Pre-Test Please answer on Scantron Card; not on this test form Standard: 9 - Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and tides. Relate them to the relative positions
G8 Semester I MCAS Pre-Test Please answer on Scantron Card; not on this test form Standard: 9 - Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and tides. Relate them to the relative positions
Geology Rocks Minerals Earthquakes Natural Resources. Meteorology. Oceanography. Astronomy. Weather Storms Warm fronts Cold fronts
 Geology Rocks Minerals Earthquakes Natural Resources Meteorology Weather Storms Warm fronts Cold fronts Oceanography Mid ocean ridges Tsunamis Astronomy Space Stars Planets Moon Prologue 1 Prologue I.
Geology Rocks Minerals Earthquakes Natural Resources Meteorology Weather Storms Warm fronts Cold fronts Oceanography Mid ocean ridges Tsunamis Astronomy Space Stars Planets Moon Prologue 1 Prologue I.
Thermal Energy. Thermal Energy Transfers
 Thermal Energy Thermal Energy Transfers Key Concepts What is the effect of having a small specific heat? What happens to a material when it is heated? In what ways can thermal energy be transferred? What
Thermal Energy Thermal Energy Transfers Key Concepts What is the effect of having a small specific heat? What happens to a material when it is heated? In what ways can thermal energy be transferred? What
PROPERTIES OF MATTER Review Stations
 PROPERTIES OF MATTER Review Stations PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1 Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? Answer: The droplets came from the air surrounding the cup. What phase
PROPERTIES OF MATTER Review Stations PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1 Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? Answer: The droplets came from the air surrounding the cup. What phase
Second Grade GPS Standards
 Second Grade GPS Standards Earth Science S2E1. Students will understand that stars have different sizes, brightness, and patterns. a. Describe the physical attributes of stars size, brightness, and patterns.
Second Grade GPS Standards Earth Science S2E1. Students will understand that stars have different sizes, brightness, and patterns. a. Describe the physical attributes of stars size, brightness, and patterns.
Grade 5 FCAT 2.0 Science Sample Questions
 Grade FCAT 2.0 Science Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT 2.0 tests. By using these materials, students will
Grade FCAT 2.0 Science Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT 2.0 tests. By using these materials, students will
Chapter 2 Planet Earth
 Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Hurricanes. Where's the Really Bad Weather 1. What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide
 Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
Georgia Milestones 5TH GRADE PRE-TEST. Rabieh Hafza ATLANTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS ALL QUESTIONS ARE PROPERTY OF THE STATE OF GEORGIA
 Georgia Milestones 5TH GRADE PRE-TEST Rabieh Hafza ATLANTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS ALL QUESTIONS ARE PROPERTY OF THE STATE OF GEORGIA 1 1. Students identified the nucleus in an animal cell and a plant cell. Nucleus
Georgia Milestones 5TH GRADE PRE-TEST Rabieh Hafza ATLANTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS ALL QUESTIONS ARE PROPERTY OF THE STATE OF GEORGIA 1 1. Students identified the nucleus in an animal cell and a plant cell. Nucleus
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint SCIENCE 0846/01 Paper 1 October 2015 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional Materials: Pen Calculator Pencil Ruler 45 minutes
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint SCIENCE 0846/01 Paper 1 October 2015 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional Materials: Pen Calculator Pencil Ruler 45 minutes
Land and Water Summative Assessment. Name Date
 Land and Water Summative Assessment Name Date Read each question carefully and select the best answer. 1. Abby built a model to study how rain changes the land. She shaped the land into single, smooth
Land and Water Summative Assessment Name Date Read each question carefully and select the best answer. 1. Abby built a model to study how rain changes the land. She shaped the land into single, smooth
Kindergarten Science. Scope and Sequence. Quarter 1
 Kindergarten Science Scope and Sequence Unit of Study 1.1: Weather, 7 days Quarter 1 ESS 1 - The earth and earth materials as we know them today have developed over long periods of time, through continual
Kindergarten Science Scope and Sequence Unit of Study 1.1: Weather, 7 days Quarter 1 ESS 1 - The earth and earth materials as we know them today have developed over long periods of time, through continual
Classifying Matter. What is matter?
 What do ice cream, root beer, and carbon dioxide gas have in common? Not only do these ingredients combine to make a good treat on a hot, summer day, but they are also made of matter. Matter can be found
What do ice cream, root beer, and carbon dioxide gas have in common? Not only do these ingredients combine to make a good treat on a hot, summer day, but they are also made of matter. Matter can be found
Chapter 2: Physical Geography
 Chapter 2: Physical Geography Pg. 39-68 Learning Goals for Chp2: q q q q q Explain how the Earth moves in space and why seasons change. Outline the factors that influence climate and recognize different
Chapter 2: Physical Geography Pg. 39-68 Learning Goals for Chp2: q q q q q Explain how the Earth moves in space and why seasons change. Outline the factors that influence climate and recognize different
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint SCIENCE 0846/02 Paper 2 October 2016 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional Materials: Pen Calculator Pencil Ruler 45 minutes
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary Checkpoint SCIENCE 0846/02 Paper 2 October 2016 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional Materials: Pen Calculator Pencil Ruler 45 minutes
Tips for Success on a Test
 Number of Incorrect: Final Grade: Parent Signature: Top Tips for Success on a Test 1. Read the following statements at least two times. 2. Circle the key words in each question/ or statement. (*Remember
Number of Incorrect: Final Grade: Parent Signature: Top Tips for Success on a Test 1. Read the following statements at least two times. 2. Circle the key words in each question/ or statement. (*Remember
5 th Inquiry Review 2010, 2009, 2008, 2007, , 2004, 2003
 1 A student examined a rock sample and described it as having particles of various colors that were 1 millimeter to 12 millimeters in size. The student was making (1) an inference (3) a prediction (2)
1 A student examined a rock sample and described it as having particles of various colors that were 1 millimeter to 12 millimeters in size. The student was making (1) an inference (3) a prediction (2)
Activity 4: The Electric-Circuit Interaction
 RECORD SHEET Activity 4: The Electric-Circuit Interaction Name Date Class Key Questions 1. 2. Explore Your Ideas Experiment 1: When does an electric-circuit interaction occur? 1. Draw a picture of the
RECORD SHEET Activity 4: The Electric-Circuit Interaction Name Date Class Key Questions 1. 2. Explore Your Ideas Experiment 1: When does an electric-circuit interaction occur? 1. Draw a picture of the
Chapter 2 Geography. Getting to know Earth
 Chapter 2 Geography Getting to know Earth Our Solar System Sun is at the center of our solar system Contains a lot of Mass» Mass gives the Sun gravitational pull» This keeps the planets in our solar system
Chapter 2 Geography Getting to know Earth Our Solar System Sun is at the center of our solar system Contains a lot of Mass» Mass gives the Sun gravitational pull» This keeps the planets in our solar system
Physical Science written by Mr. Franklin
 Physical Science written by Mr. Franklin 1 In normal air, which of the following substances is most common? (1 point) carbon dioxide nitrogen oxygen carbon monoxide 2 Which of the following is a chemical
Physical Science written by Mr. Franklin 1 In normal air, which of the following substances is most common? (1 point) carbon dioxide nitrogen oxygen carbon monoxide 2 Which of the following is a chemical
Energy and Seasons A B1. 9. Which graph best represents the general relationship between latitude and average surface temperature?
 Energy and Seasons A B1 1. Which type of surface absorbs the greatest amount of electromagnetic energy from the Sun? (1) smooth, shiny, and light colored (2) smooth, shiny, and dark colored (3) rough,
Energy and Seasons A B1 1. Which type of surface absorbs the greatest amount of electromagnetic energy from the Sun? (1) smooth, shiny, and light colored (2) smooth, shiny, and dark colored (3) rough,
Lesson 2 The Inner Planets
 Lesson 2 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 School to Home 32 Key Concept Builders 33 Enrichment
Lesson 2 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 School to Home 32 Key Concept Builders 33 Enrichment
TUNKHANNOCK AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT SCIENCE CURRIULUM GRADE 2
 TUNKHANNOCK AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT SCIENCE CURRIULUM GRADE 2 Chapter 4 (How Living Things Grow and Change) 3.1.2.C.2. Explain that living things can only survive if their needs are being met. 3.1.2.A.3.
TUNKHANNOCK AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT SCIENCE CURRIULUM GRADE 2 Chapter 4 (How Living Things Grow and Change) 3.1.2.C.2. Explain that living things can only survive if their needs are being met. 3.1.2.A.3.
The Sun and Water Cycle
 The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time in the
The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time in the
The sun and water cycle
 reflect The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time
reflect The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time
Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2
 Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2 Multiple Choice (30 marks) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What percentage represents the amount of fresh
Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2 Multiple Choice (30 marks) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What percentage represents the amount of fresh
ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST
 4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK SPRING 2006 GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK SPRING 2006 GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
Guide to Exploratorium Activities That Align with California Science Content Standards
 Guide to Exploratorium Activities That Align with California Science Content Standards The following activities are recommended by the Exploratorium Field Trips program as Exploratorium activities that
Guide to Exploratorium Activities That Align with California Science Content Standards The following activities are recommended by the Exploratorium Field Trips program as Exploratorium activities that
The grade 5 English science unit, Weather, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 Among the diverse meteorological elements, this area focuses on humidity, dew, fog, clouds, rain, snow, wind and atmospheric pressure. Weather influences not only our daily outdoor activities, but also
Among the diverse meteorological elements, this area focuses on humidity, dew, fog, clouds, rain, snow, wind and atmospheric pressure. Weather influences not only our daily outdoor activities, but also
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic
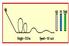 Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
Changes to Land 5.7B. landforms: features on the surface of Earth such as mountains, hills, dunes, oceans and rivers
 All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
Date: / Page #: 4. The diagram below show an enlarged view of the beams of a triple-beam balance.
 Name: Review Packet - Unit 2 1. Two objects A and B were placed in two vials with different liquids C and D in them. This diagram shows what happened to each object when placed in the vial. Date: / Page
Name: Review Packet - Unit 2 1. Two objects A and B were placed in two vials with different liquids C and D in them. This diagram shows what happened to each object when placed in the vial. Date: / Page
Grade 5 Science Practice Test
 Grade 5 Science Practice Test Nebraska Department of Education 2012 Directions: On the following pages of your test booklet are multiple-choice questions for Session 1 of the Grade 5 Nebraska State Accountability
Grade 5 Science Practice Test Nebraska Department of Education 2012 Directions: On the following pages of your test booklet are multiple-choice questions for Session 1 of the Grade 5 Nebraska State Accountability
1. The Sun directly provides. A water energy B wind energy C heat energy D electrical energy
 1. The Sun directly provides A water energy B wind energy C heat energy D electrical energy 2. What is the Sun doing in this picture? F Burning away the clouds in the sky G Drying up the plant roots H
1. The Sun directly provides A water energy B wind energy C heat energy D electrical energy 2. What is the Sun doing in this picture? F Burning away the clouds in the sky G Drying up the plant roots H
