INTERFEROMETERS. There are 4 principal types of measurements that can be made with this type of interferometer.
|
|
|
- Jesse Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front surface aluminized. Do not touch the surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. Introduction This experiment provides three techniques for observing interference phenomena in light, and enables you to make various measurements using interference. A. Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is fully described in references 1, 2 and 3. Light from an extended source is separated into 2 paths by partial reflection from a semi-silvered mirror, and then recombined by the same mechanism, so that interference occurs. The particularly useful feature of this interferometer is the extend of separation of the paths, so that comparison of two very different types of optical paths may be made. There are 4 principal types of measurements that can be made with this type of interferometer. 1. Width and fine structure of spectral lines, 2. Lengths or displacements in terms of wavelengths of light, 3. Refractive indices, 4. Differences in the velocity of light along 2 different directions. In this experiment, several such measurements are suggested. You may try out whatever is of interest to you. Experiment 1 - Circular Fringes Set up the interferometer as described in references 1 and 3. Using either a Sodium or a Mercury vapour lamp (observe the fringes from both) adjust the mirror tilt screws and the micrometer position control so that the images of the two mirrors are parallel and so that circular fringes are observed. Move the micrometer position control so that the diameter of the fringes become largest. This implies that you are close to zero optical path difference between the two light paths. (Recall that zero difference produces a bright fringe across the whole field of view). Now using a white light source, observe white light fringes. The dark centre of the white light fringes will tell you the position of zero path difference. (Note the white light fringes are only observable over a region of about 20 fringes, corresponding to a total rotation of about 20 of the micrometer screw, so they are easy to miss).
2 Experiment 2 - Localized Fringes Starting with the adjusted apparatus of Experiment 1, and using first Mercury and Sodium light, and then white light, observe localized fringes by slightly changing the adjustment on the tillable mirror and then varying the micrometer position control. Experiment 3 - To Measure a Distance in Terms of the Mean Wavelength of Sodium Light View the circular or nearly circular fringes of sodium light. Traverse the mirror slowly by means of the micrometer screw counting the fringes which pass the edge of the field of view. Record the micrometer screw reading every 50 fringes and continue until about 1000 fringes have been counted. NOTE: The mirror carriage should always be driven towards the observer when making readings. Overshoot cannot easily be corrected by reversing the direction of rotation of the micrometer screw because of backlash between the screw thread and the carriage. Ask the demonstrator to explain this point if it is not clear to you. Plot a graph of the micrometer reading against number of fringes n passing the field. From this graph, and the mean value of the wavelength of the sodium lines you can obtain a calibration curve of micrometer reading against actual distance moved by the mirror. Comment on the uniformity of the micrometer screw thread. (See Reference 1 for the theory of this measurement). Experiment 4 - To Determine the Wavelength Difference for the Two Lines The sodium `line' is really a doublet of 2 wavelengths λ 1 and λ 2 having a small wavelength separation and different but comparable intensities. A fringe pattern is formed for each wavelength and the resultant seen is that produced by the superposition of these two patterns. For certain path differences (i.e. positions of the mirror) the bright fringes of the two patterns coincide and the resultant fringes pattern has good fringe visibility. For other path differences (intermediate between those for maximum fringe visibility) the bright fringes of one pattern coincide with the dark fringes of the other and the resultant fringe pattern has rather low visibility. Thus on moving the mirror back slowly, successive positions of the mirror for about 12 of each of these situations should be measured. From these readings the average distance between adjacent positions of the mirror giving maximum fringe visibility is obtained, and a similar value can be found for the positions of minimum visibility. Although each setting for maximum (or minimum) fringe visibility is probably not very accurate (since it is subjective) by making a large number of settings the probable error can be reduced. To calculate, the wavelength separation of the 2 sodium yellow spectral lines, consider λ 1 and λ 2 to be the 2 sodium wavelengths where λ 1 > λ 2. 2
3 Then if m is the change in order number at the centre of the field of view between consecutive positions of maximum fringe visibility for λ 1, then ( m + 1) is the corresponding change in order number for wavelength λ 2. If t is the average distance between the positions of the mirror for maximum fringe visibility. Then so 2t = m1 = ( m + 1) t( - ) = = 12 = t m 2 /2t = 1 1 m Experiment 5 - To Determine the Refractive Index of a Transparent Solid If a thin plate of thickness `d' of the transparent substance is placed in one beam of an interferometer the optical path difference is changed by ( - 1)d. (The refractive index of air being taken as unity). As a result the interference pattern moves through n fringes where Note that n is not necessarily a whole number. n = ( -1)d/ Unfortunately since all monochromatic fringes look the same we cannot recognise a sudden jump in the fringe pattern. This can be overcome by using white light fringes to locate the whole number of fringes moved. Set the moving mirror to give equal path lengths for the interfering beams using the mercury and then white light source. Note the reading of the micrometer for the mirror on the carriage. Interpose the transparent solid in one of the interfering beams, and compensate for this change in optical path difference by moving the mirror back or forward until white light fringes are central in the field of view again. Measure the new position of the mirror. 3
4 Experiment 6 - To Determine the Refractive Index of Air The principle of this experiment is the same as in Experiment 5. In this case the gas cell is placed in one beam path and the two compensating glass discs are placed in the other beam path to compensate for path differences introduced by the windows of the gas cell. By connecting the gas cell to a manometer and a vacuum pump and valves, the pressure of air in the gas cell can be measured. By counting fringes passing as the pressure is changed, the refractive index of air as a function of pressure can be measured. Experiment 7 - An Exercise in Appreciating the Michelson - Morley Experiment Considering the accuracy of measurement you were able to achieve in the above experiments, deduce what improvements in the performance of the apparatus would be needed to detect the moving aether effect in a Michelson-Morley experiment, assuming the aether theory were valid. Suggest ways you could obtain this improvement. B. Fabry-Perot Interferometer The Fabry-Perot interferometer is fully described in references 2, 3, 4 and 5. In this case, the interferometer consists of parallel semi-silvered glass plates, so that multiple reflections take place. This results in very narrow sharp interference fringes, allowing small wavelength differences to be measured. In particular, this interferometer has been used in the measurement of Zeeman effect and hyperfine structure os spectra. No set experiment will be described here. You are free to set-up the apparatus as described in reference 3, to observe the interference fringes, and if you wish, work out further experiments. C. Twyman - Green Interferometer This interferometer configuration provides a means of testing the true-ness and optical perfection of prisms and lenses. The technique, which uses a modification of the Michelson interferometer, is fully described in references 1, 2 and 3. We suggest that you set-up the interferometer as described in reference 3. Mercury light is convenient for this set-up. Test out one or two prisms and evaluate their optical uniformity. If you wish to see what a bad prism looks like, you can simulate this by placing a common slide glass in front of a good prism References 1. F.A. Jenkins and H.E. White, "Fundamentals of Optics 4th Edition",
5 2. R.W. Ditchburn, "Light". 3. Ealing/Beck "Instructions for the description of the `Universal' Interferometer", (available at the wicket). 4. F.A. Jenkins and H.E. White, "Fundamentals of Optics 4th Edition", A.C. Melissinos, "Experiments in Modern Physics", J.V. 6/82 Rev. 5
The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER:
 LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
ABSTRACT. The following values for the wavelength of the sodium doublet lines were calculated:
 Determination of the wavelengths of the Sodium doublet lines and the measurement of the thickness of a thin transparent film using a Michelson interferometer Luke Pomfrey Tutor: Dr. P. Doel March 22, 2007
Determination of the wavelengths of the Sodium doublet lines and the measurement of the thickness of a thin transparent film using a Michelson interferometer Luke Pomfrey Tutor: Dr. P. Doel March 22, 2007
Measurments with Michelson interferometers
 Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Measurments with Michelson interferometers Objectives In this experiment you will: Understand the
Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Measurments with Michelson interferometers Objectives In this experiment you will: Understand the
Interferometers. PART 1: Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the most useful of all optical instru
 Interferometers EP421 Lab Interferometers Introduction: Interferometers are the key to accurate distance measurement using optics. Historically, when mechanical measurements dominated, interferometers
Interferometers EP421 Lab Interferometers Introduction: Interferometers are the key to accurate distance measurement using optics. Historically, when mechanical measurements dominated, interferometers
(M.I. - F.P.) Michelson and Fabry Perot Interferometers and Study of Channeled Spectra
 Michelson and Fabry Perot Interferometers and Channeled Spectra (M.I. - F.P.) Michelson and Fabry Perot Interferometers and Study of Channeled Spectra References. ** Jenkins and White. Fundamentals of
Michelson and Fabry Perot Interferometers and Channeled Spectra (M.I. - F.P.) Michelson and Fabry Perot Interferometers and Study of Channeled Spectra References. ** Jenkins and White. Fundamentals of
Experiment 3 1. The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado
 Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
Introduction. Procedure. In this experiment, you'll use the interferometer to EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Lens 18mm FL. Component holder.
 12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
Experiment 8 Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment 8 Michelson Interferometer Introduction This week s experiment utilizes the Michelson interferometer. You are to measure the wavelength of the green mercury light, the wavelength of the sodium
Experiment 8 Michelson Interferometer Introduction This week s experiment utilizes the Michelson interferometer. You are to measure the wavelength of the green mercury light, the wavelength of the sodium
Chapter 1. Optical Interferometry. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Optical Interferometry Experiment objectives: Assemble and align Michelson and Fabry-Perot interferometers, calibrate them using a laser of known wavelength, and then use them characterize the
Chapter 1 Optical Interferometry Experiment objectives: Assemble and align Michelson and Fabry-Perot interferometers, calibrate them using a laser of known wavelength, and then use them characterize the
PS210 - Optical Techniques. Section VI
 PS210 - Optical Techniques Section VI Section I Light as Waves, Rays and Photons Section II Geometrical Optics & Optical Instrumentation Section III Periodic and Non-Periodic (Aperiodic) Waves Section
PS210 - Optical Techniques Section VI Section I Light as Waves, Rays and Photons Section II Geometrical Optics & Optical Instrumentation Section III Periodic and Non-Periodic (Aperiodic) Waves Section
Experiment 4. Michelson Interferometer. 4.1 Introduction. References
 Experiment 4 Michelson Interferometer References Optics by E. Hecht, Section 9.4.2 Fundamentals of Optics by F. Jenkins & H. White, Chapter 13, Sections 8 through 15, and Chapter 14, Section 13 An Introduction
Experiment 4 Michelson Interferometer References Optics by E. Hecht, Section 9.4.2 Fundamentals of Optics by F. Jenkins & H. White, Chapter 13, Sections 8 through 15, and Chapter 14, Section 13 An Introduction
Speed of Light in Air
 Speed of Light in Air Electromagnetic waves represent energy in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate through vacuum with a speed c = 2.9979246x10 8 m/s. Electromagnetic
Speed of Light in Air Electromagnetic waves represent energy in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate through vacuum with a speed c = 2.9979246x10 8 m/s. Electromagnetic
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
The Michelson Interferometer and the He-Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado
 Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He-Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado In the experiment, two different types of measurements will be made with
Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He-Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado In the experiment, two different types of measurements will be made with
8. The Michelson Interferometer
 M 8. The Michelson Interferometer 8.1 Introduction Interference patterns from superposed coherent waves may be used for precise determination of wavelength or, if the wavelength is known, time-of-flight,
M 8. The Michelson Interferometer 8.1 Introduction Interference patterns from superposed coherent waves may be used for precise determination of wavelength or, if the wavelength is known, time-of-flight,
THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER
 Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
THE ZEEMAN EFFECT PHYSICS 359E
 THE ZEEMAN EFFECT PHYSICS 359E INTRODUCTION The Zeeman effect is a demonstration of spatial quantization of angular momentum in atomic physics. Since an electron circling a nucleus is analogous to a current
THE ZEEMAN EFFECT PHYSICS 359E INTRODUCTION The Zeeman effect is a demonstration of spatial quantization of angular momentum in atomic physics. Since an electron circling a nucleus is analogous to a current
EXPERIMENT NO. 8. OBJECT: To determine the wavelength of sodium light by method.
 EXPERIMENT NO. 8 OBJECT: To determine the wavelength of sodium light by method. Fresnel s APPARATUS: Optical bench with four uprights, a sodium lamp, Fresnel s, a convex lens and micrometer eyepiece. DIAGRAM:
EXPERIMENT NO. 8 OBJECT: To determine the wavelength of sodium light by method. Fresnel s APPARATUS: Optical bench with four uprights, a sodium lamp, Fresnel s, a convex lens and micrometer eyepiece. DIAGRAM:
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers
 Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
The Anomalous Zeeman Splitting of the Sodium 3P States
 Advanced Optics Laboratory The Anomalous Zeeman Splitting of the Sodium 3P States David Galey Lindsay Stanceu Prasenjit Bose April 5, 010 Objectives Calibrate Fabry-Perot interferometer Determine the Zeeman
Advanced Optics Laboratory The Anomalous Zeeman Splitting of the Sodium 3P States David Galey Lindsay Stanceu Prasenjit Bose April 5, 010 Objectives Calibrate Fabry-Perot interferometer Determine the Zeeman
Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting
 Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting PHYS 3330: Experiments in Optics Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30602 (Dated: Revised
Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting PHYS 3330: Experiments in Optics Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30602 (Dated: Revised
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Michelson Interferometer. crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity.
 Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
Chapter 4. Dispersion of Glass. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Apparatus
 Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
Coherence and width of spectral lines with Michelson interferometer
 Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION
 E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION References for Fraunhofer Diffraction 1. Jenkins and White Fundamentals of Optics. Chapters on Fraunhofer diffraction and
E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION References for Fraunhofer Diffraction 1. Jenkins and White Fundamentals of Optics. Chapters on Fraunhofer diffraction and
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings. Abstract
 Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
DRONACHARYA COLLEGE OF ENEGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED SCEINCE AND HUMANITIES SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS: Unit-I. Chapter I: Interference
 DRONACHARYA COLLEGE OF ENEGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED SCEINCE AND HUMANITIES SUBJECT: PHYSICS-I CODE: PHY-101-F SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS: Unit-I Chapter I: Interference 1. State the condition for sustained
DRONACHARYA COLLEGE OF ENEGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED SCEINCE AND HUMANITIES SUBJECT: PHYSICS-I CODE: PHY-101-F SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS: Unit-I Chapter I: Interference 1. State the condition for sustained
Zeeman Effect - Lab exercises 24
 Zeeman Effect - Lab exercises 24 Pieter Zeeman Franziska Beyer August 2010 1 Overview and Introduction The Zeeman effect consists of the splitting of energy levels of atoms if they are situated in a magnetic
Zeeman Effect - Lab exercises 24 Pieter Zeeman Franziska Beyer August 2010 1 Overview and Introduction The Zeeman effect consists of the splitting of energy levels of atoms if they are situated in a magnetic
Department of Physics, Colorado State University PH 425 Advanced Physics Laboratory The Zeeman Effect. 1 Introduction. 2 Origin of the Zeeman Effect
 Department of Physics, Colorado State University PH 425 Advanced Physics Laboratory The Zeeman Effect (a) CAUTION: Do not look directly at the mercury light source. It is contained in a quartz tube. The
Department of Physics, Colorado State University PH 425 Advanced Physics Laboratory The Zeeman Effect (a) CAUTION: Do not look directly at the mercury light source. It is contained in a quartz tube. The
LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I
 OPTI 202L - Geometrical and Instrumental Optics Lab LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I 10-1 Measuring the refractive index of a material is one of the most fundamental optical measurements, and
OPTI 202L - Geometrical and Instrumental Optics Lab LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I 10-1 Measuring the refractive index of a material is one of the most fundamental optical measurements, and
Interference- Michelson Interferometer. Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam
 Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Experiment 6: Interferometers
 Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
DIFFRACTION GRATING. OBJECTIVE: To use the diffraction grating in the formation of spectra and in the measurement of wavelengths.
 DIFFRACTION GRATING OBJECTIVE: To use the diffraction grating in the formation of spectra and in the measurement of wavelengths. THEORY: The operation of the grating is depicted in Fig. 1 on page Lens
DIFFRACTION GRATING OBJECTIVE: To use the diffraction grating in the formation of spectra and in the measurement of wavelengths. THEORY: The operation of the grating is depicted in Fig. 1 on page Lens
THE ZEEMAN EFFECT v3 R. A. Schumacher, May 2017 B. B. Luokkala, January 2001
 THE ZEEMAN EFFECT v3 R. A. Schumacher, May 2017 B. B. Luokkala, January 2001 I. INTRODUCTION The goal of this experiment is to measure the Bohr magneton using the normal Zeeman effect of the 643.8 nm (red)
THE ZEEMAN EFFECT v3 R. A. Schumacher, May 2017 B. B. Luokkala, January 2001 I. INTRODUCTION The goal of this experiment is to measure the Bohr magneton using the normal Zeeman effect of the 643.8 nm (red)
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE426F Optical Engineering. Final Exam. Dec. 17, 2003.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
The Michelson Interferometer as a Device for Measuring the Wavelength of a Helium-Neon Laser
 Journal of Advanced Undergraduate Physics Laboratory Investigation Volume 3 2017-2018 Article 2 2018 The Michelson Interferometer as a Device for Measuring the Wavelength of a Helium-Neon Laser Carly E.
Journal of Advanced Undergraduate Physics Laboratory Investigation Volume 3 2017-2018 Article 2 2018 The Michelson Interferometer as a Device for Measuring the Wavelength of a Helium-Neon Laser Carly E.
Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra
 Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra Background Reading: Tipler, Llewellyn pp. 163-165 Apparatus: Spectrometer, sodium lamp, hydrogen lamp, mercury lamp, diffraction grating, watchmaker eyeglass,
Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra Background Reading: Tipler, Llewellyn pp. 163-165 Apparatus: Spectrometer, sodium lamp, hydrogen lamp, mercury lamp, diffraction grating, watchmaker eyeglass,
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Farooq Hassan Roll no: 2012-10-0101 LUMS School of Science and Engineering November 13, 2010 1 Abstract Michelson Interferometer was first used in the classic experiment in 1887
Michelson Interferometer Farooq Hassan Roll no: 2012-10-0101 LUMS School of Science and Engineering November 13, 2010 1 Abstract Michelson Interferometer was first used in the classic experiment in 1887
Chapter 8 Optical Interferometry
 Chapter 8 Optical Interferometry Lecture Notes for Modern Optics based on Pedrotti & Pedrotti & Pedrotti Instructor: Nayer Eradat Spring 009 4/0/009 Optical Interferometry 1 Optical interferometry Interferometer
Chapter 8 Optical Interferometry Lecture Notes for Modern Optics based on Pedrotti & Pedrotti & Pedrotti Instructor: Nayer Eradat Spring 009 4/0/009 Optical Interferometry 1 Optical interferometry Interferometer
The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom
 Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM. Student Number. The last two pages of the exam have some equations and some physical constants.
 PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY
 Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY When atoms of a gas are excited (by high voltage, for instance) they will give off light. Each element (in fact, each isotope) gives off a characteristic atomic spectrum,
Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY When atoms of a gas are excited (by high voltage, for instance) they will give off light. Each element (in fact, each isotope) gives off a characteristic atomic spectrum,
JRE Group of Institutions ASSIGNMENT # 1 Special Theory of Relativity
 ASSIGNMENT # 1 Special Theory of Relativity 1. What was the objective of conducting the Michelson-Morley experiment? Describe the experiment. How is the negative result of the experiment interpreted? 2.
ASSIGNMENT # 1 Special Theory of Relativity 1. What was the objective of conducting the Michelson-Morley experiment? Describe the experiment. How is the negative result of the experiment interpreted? 2.
THE MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER Intermediate ( first part) to Advanced (latter parts)
 THE MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER Intermediate ( first part) to Advanced (latter parts) Goal: There is a progression of goals for this experiment but you do not have to do the last goal. The first goal is to
THE MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER Intermediate ( first part) to Advanced (latter parts) Goal: There is a progression of goals for this experiment but you do not have to do the last goal. The first goal is to
Dispersion and resolving power of the prism and grating spectroscope (Item No.: P )
 Dispersion and resolving power of the prism and grating spectroscope (Item No.: P2210300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Light and Optics Subtopic: Diffraction
Dispersion and resolving power of the prism and grating spectroscope (Item No.: P2210300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Light and Optics Subtopic: Diffraction
Determination of Cauchy s Contants
 8. Determination of Cauchy s Contants 8.1 Objective: To determine Cauchy s Constants using a prism and spectrometer. Apparatus: Glass prism, spectrometer and mercury vapour lamp. 8. Theory: The wavelength
8. Determination of Cauchy s Contants 8.1 Objective: To determine Cauchy s Constants using a prism and spectrometer. Apparatus: Glass prism, spectrometer and mercury vapour lamp. 8. Theory: The wavelength
2. OPERATIONAL CONDITIONS
 1. INTRODUCTION This device was designed for modern physics labs of colleges and graduate schools. It demonstrates the influence of a magnetic field on light, known as Zeeman Effect, and reveals the behavior
1. INTRODUCTION This device was designed for modern physics labs of colleges and graduate schools. It demonstrates the influence of a magnetic field on light, known as Zeeman Effect, and reveals the behavior
EXPERIMENT 5:Determination of the refractive index (µ) of the material of a prism using sprectometer
 EXPERIMENT 5:Determination of the refractive index (µ) of the material of a prism using sprectometer Debangshu Mukherjee B.Sc Physics,1st year Chennai Mathematical Institute 17.10.008 1 Aim of Experiment
EXPERIMENT 5:Determination of the refractive index (µ) of the material of a prism using sprectometer Debangshu Mukherjee B.Sc Physics,1st year Chennai Mathematical Institute 17.10.008 1 Aim of Experiment
A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth.
 Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer
 Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 19, 2018 Last time diffraction patterns diffraction and interference resolution and Raleigh s criterion
Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 19, 2018 Last time diffraction patterns diffraction and interference resolution and Raleigh s criterion
Atomic emission spectra experiment
 Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
Optics. Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer. LD Physics Leaflets P
 Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
WHITE-LIGHT INTERFERENCE FRINGES WITH A THICK GLASS PLA TE IN ONE PA TH. PART II
 216 PHYSICS: W. N. BIRCHB Y PROC. N. A. S. 1 Th. Lyman, Astrophys. J., 60, No. 1, July, 1924. 2 H. B. Dorgelo and T. H. Abbink, Zeitschr. Physik, 37, 667, 1926. 3 A. Fowler, Proc. Roy. Soc., A91, 208,
216 PHYSICS: W. N. BIRCHB Y PROC. N. A. S. 1 Th. Lyman, Astrophys. J., 60, No. 1, July, 1924. 2 H. B. Dorgelo and T. H. Abbink, Zeitschr. Physik, 37, 667, 1926. 3 A. Fowler, Proc. Roy. Soc., A91, 208,
Any first year text, sections on atomic structure, spectral lines and spectrometers
 Physics 33 Experiment 5 Atomic Spectra References Any first year text, sections on atomic structure, spectral lines and spectrometers Any modern physics text, eg F.K. Richtmeyer, E.H. Kennard and J.N.
Physics 33 Experiment 5 Atomic Spectra References Any first year text, sections on atomic structure, spectral lines and spectrometers Any modern physics text, eg F.K. Richtmeyer, E.H. Kennard and J.N.
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Varma Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee
 Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Varma Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-03 Lecture-01 Interference of Light Part 01 Myself, Dr. JD Varma, Associate Professor in Department
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Varma Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-03 Lecture-01 Interference of Light Part 01 Myself, Dr. JD Varma, Associate Professor in Department
Dispersion of Glass Introduction Apparatus Theory
 Dispersion of Glass Introduction This experiment will develop skills in aligning and using a spectrometer to measure dispersion of glass, and choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting
Dispersion of Glass Introduction This experiment will develop skills in aligning and using a spectrometer to measure dispersion of glass, and choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting
Protokoll. Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy
 Protokoll Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy 1 Elaboration 1.1 Optical Spectroscopy Student: Hauke Rasch, Martin Borchert Tutor: Madsen Date: 22.October2014 This experiment is about the fundamental
Protokoll Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy 1 Elaboration 1.1 Optical Spectroscopy Student: Hauke Rasch, Martin Borchert Tutor: Madsen Date: 22.October2014 This experiment is about the fundamental
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee
 Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
PHYA5/2D. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June Unit 5D Turning Points in Physics Section B
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examinerʼs Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examinerʼs Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2012 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examinerʼs Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examinerʼs Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2012 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
Double Slit is VERY IMPORTANT because it is evidence of waves. Only waves interfere like this.
 Double Slit is VERY IMPORTANT because it is evidence of waves. Only waves interfere like this. Superposition of Sinusoidal Waves Assume two waves are traveling in the same direction, with the same frequency,
Double Slit is VERY IMPORTANT because it is evidence of waves. Only waves interfere like this. Superposition of Sinusoidal Waves Assume two waves are traveling in the same direction, with the same frequency,
Atomic and nuclear physics
 Atomic and nuclear physics Atomic shell Normal Zeeman effect LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Observing the normal Zeeman effect in transverse and longitudinal configuration Spectroscopy with a Fabry-Perot etalon
Atomic and nuclear physics Atomic shell Normal Zeeman effect LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Observing the normal Zeeman effect in transverse and longitudinal configuration Spectroscopy with a Fabry-Perot etalon
The science of light. P. Ewart
 The science of light P. Ewart Oxford Physics: Second Year, Optics Parallel reflecting surfaces t images source Extended source path difference xcos 2t=x Fringes localized at infinity Circular fringe constant
The science of light P. Ewart Oxford Physics: Second Year, Optics Parallel reflecting surfaces t images source Extended source path difference xcos 2t=x Fringes localized at infinity Circular fringe constant
Optics Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Lab
 Optics 513 - Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Lab Lab #6 - Interference Microscopes The purpose of this lab is to observe the samples provided using two different interference microscopes --
Optics 513 - Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Lab Lab #6 - Interference Microscopes The purpose of this lab is to observe the samples provided using two different interference microscopes --
Zeeman Effect. Alex Povilus Physics 441- Fall 2003 December 20, 2003
 Zeeman Effect Alex Povilus Physics 441- Fall 2003 December 20, 2003 Abstract The Zeeman Effect is observed by application of a strong magnetic field to a mercury vapor cell and exciting transitions by
Zeeman Effect Alex Povilus Physics 441- Fall 2003 December 20, 2003 Abstract The Zeeman Effect is observed by application of a strong magnetic field to a mercury vapor cell and exciting transitions by
Laboratory #29: Spectrometer
 INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, P309 LABORATORY Laboratory #29: Spectrometer Goal: Learn to adjust an optical spectrometer, use a transmission grating to measure known spectral lines of mercury,
INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, P309 LABORATORY Laboratory #29: Spectrometer Goal: Learn to adjust an optical spectrometer, use a transmission grating to measure known spectral lines of mercury,
Michelson Interferometer
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum O10e Michelson Interferometer Tasks 1. Adjust a Michelson interferometer and determine the wavelength of a He-Ne laser. 2. Measure
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum O10e Michelson Interferometer Tasks 1. Adjust a Michelson interferometer and determine the wavelength of a He-Ne laser. 2. Measure
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
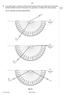 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
Downloaded from
 Question 10.1: Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. What are the wavelength, frequency and speed of (a) reflected, and (b) refracted light? Refractive index
Question 10.1: Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. What are the wavelength, frequency and speed of (a) reflected, and (b) refracted light? Refractive index
Interference. Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website
 Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 6 Jul 2009
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 6 Jul 2009 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 6 Jul 2009](/thumbs/90/104151225.jpg) v8 Measuring the Molecular Polarizability of Air M.J. Madsen, D.R. Brown, S.R. Krutz, and M.J. Milliman Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated: July 7, 2009) Abstract arxiv:0907.0782v1
v8 Measuring the Molecular Polarizability of Air M.J. Madsen, D.R. Brown, S.R. Krutz, and M.J. Milliman Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated: July 7, 2009) Abstract arxiv:0907.0782v1
PHYS 450 Spring semester Lecture 10: Interferometers. Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University.
 3/10/017 PHYS 450 Spring semester 017 Lecture 10: Interferometers Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purue University Lecture 10 1 Brief History Interferometry uses superposition of coherent
3/10/017 PHYS 450 Spring semester 017 Lecture 10: Interferometers Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purue University Lecture 10 1 Brief History Interferometry uses superposition of coherent
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light
 Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F)
 B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Determination of Young s modulus of glass by Cornu s apparatus
 Determination of Young s modulus of glass b Cornu s apparatus Objective To determine Young s modulus and Poisson s ratio of a glass plate using Cornu s method. Theoretical Background Young s modulus, also
Determination of Young s modulus of glass b Cornu s apparatus Objective To determine Young s modulus and Poisson s ratio of a glass plate using Cornu s method. Theoretical Background Young s modulus, also
DISPERSION OF A GLASS PRISM
 PH2 page 1 DISPERSION OF A GLASS PRISM OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to analyze the emission spectrum of helium and to analyze the dispersion of a glass prism by measuring the index of
PH2 page 1 DISPERSION OF A GLASS PRISM OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to analyze the emission spectrum of helium and to analyze the dispersion of a glass prism by measuring the index of
Lab #13: Polarization
 Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT
 1 INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT In the year 1678, Christian Huygens proposed the wave theory of light. According to this, a Luminous body is a source of disturbance in hypothetical medium called ether
1 INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT In the year 1678, Christian Huygens proposed the wave theory of light. According to this, a Luminous body is a source of disturbance in hypothetical medium called ether
Atomic Spectra. d sin θ = mλ (1)
 Atomic Spectra Objectives: To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify that the measured wavelengths obey the empirical Rydberg formula. To observe emission spectra
Atomic Spectra Objectives: To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify that the measured wavelengths obey the empirical Rydberg formula. To observe emission spectra
Unit 2 - Particles and Waves - Part 2
 WAVE-PARTICLE DUALITY Unit - Particles and Waves - Part 8. The photoelectric effect and wave particle duality Photoelectric effect as evidence for the particulate nature of light. Photons of sufficient
WAVE-PARTICLE DUALITY Unit - Particles and Waves - Part 8. The photoelectric effect and wave particle duality Photoelectric effect as evidence for the particulate nature of light. Photons of sufficient
Optical Shop Testing
 Optical Shop Testing nd Edition (199 ) Edited by Daniel Malacara 1 OUTLINE Chapter 1. Newton, Fizeau, and Haidinger Interferometer 1.1 1. Fizeau Interferometer 1.3 Haidinger Interferometer 1.4 Absolute
Optical Shop Testing nd Edition (199 ) Edited by Daniel Malacara 1 OUTLINE Chapter 1. Newton, Fizeau, and Haidinger Interferometer 1.1 1. Fizeau Interferometer 1.3 Haidinger Interferometer 1.4 Absolute
Waves Part 3B: Interference
 Waves Part 3B: Interference Last modified: 31/01/2018 Contents Links Interference Path Difference & Interference Light Young s Double Slit Experiment What Sort of Wave is Light? Michelson-Morley Experiment
Waves Part 3B: Interference Last modified: 31/01/2018 Contents Links Interference Path Difference & Interference Light Young s Double Slit Experiment What Sort of Wave is Light? Michelson-Morley Experiment
high energy state for the electron in the atom low energy state for the electron in the atom
 Atomic Spectra Objectives The objectives of this experiment are to: 1) Build and calibrate a simple spectroscope capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light. 2) Measure several wavelengths of light
Atomic Spectra Objectives The objectives of this experiment are to: 1) Build and calibrate a simple spectroscope capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light. 2) Measure several wavelengths of light
Background The power radiated by a black body of temperature T, is given by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law
 Phys316 Exploration 2: Verifying Stefan-Boltzmann Relationship Background The power radiated by a black body of temperature T, is given by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Where A is the effective radiating area,
Phys316 Exploration 2: Verifying Stefan-Boltzmann Relationship Background The power radiated by a black body of temperature T, is given by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Where A is the effective radiating area,
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves As the chart shows, the electromagnetic spectrum covers an extremely wide range of wavelengths and frequencies. Though the names indicate that these waves have a number of sources,
Electromagnetic Waves As the chart shows, the electromagnetic spectrum covers an extremely wide range of wavelengths and frequencies. Though the names indicate that these waves have a number of sources,
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps
 Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
The new physiology of vision-chapter The colours of interference. SIR C V RAMAN Received October 14, 1965
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. A62 243-248 (1965) The new physiology of vision-chapter The colours of interference XXVII. SIR C V RAMAN Received October 14, 1965 The characteristic features and properties of
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. A62 243-248 (1965) The new physiology of vision-chapter The colours of interference XXVII. SIR C V RAMAN Received October 14, 1965 The characteristic features and properties of
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps
 Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
Lecture 09: Interferometers
 1/31/16 PHYS 45 Fall semester 16 Lecture 9: Interferometers Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purue University Lecture 9 1 Two Types of Interference Division of Wavefront primary wavefront emits
1/31/16 PHYS 45 Fall semester 16 Lecture 9: Interferometers Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purue University Lecture 9 1 Two Types of Interference Division of Wavefront primary wavefront emits
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 3 Coherence and Interferometry
Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 3 Coherence and Interferometry
Science Lab I Properties of Light
 Art & Science of Light Fall 2007 Science Lab I Properties of Light Prepared by: Dr. Dharshi Bopegedera 1 Using the Filtergraph (15 minutes) 1. Turn on the filtergraph, place a card on it and look at the
Art & Science of Light Fall 2007 Science Lab I Properties of Light Prepared by: Dr. Dharshi Bopegedera 1 Using the Filtergraph (15 minutes) 1. Turn on the filtergraph, place a card on it and look at the
To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating.
 12. Diffraction grating OBJECT To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating. INTRODUCTION: Consider a light beam transmitted through an aperture
12. Diffraction grating OBJECT To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating. INTRODUCTION: Consider a light beam transmitted through an aperture
Atomic Emission Spectra
 Atomic Emission Spectra Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are as follows: To build and calibrate a simple meter-stick spectroscope that is capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light.
Atomic Emission Spectra Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are as follows: To build and calibrate a simple meter-stick spectroscope that is capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light.
[2] [2] Fig. 4.1
![[2] [2] Fig. 4.1 [2] [2] Fig. 4.1](/thumbs/79/80000819.jpg) 1 (a) (i) Explain what is meant by a progressive wave.... [2] (ii) State two differences between a progressive and a stationary wave. 1... 2... [2] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows, at time t = 0, the shape of a section
1 (a) (i) Explain what is meant by a progressive wave.... [2] (ii) State two differences between a progressive and a stationary wave. 1... 2... [2] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows, at time t = 0, the shape of a section
