Michelson Interferometer
|
|
|
- Lisa Berry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum O10e Michelson Interferometer Tasks 1. Adjust a Michelson interferometer and determine the wavelength of a He-Ne laser. 2. Measure the change in the length of a piezoelectric actor when a voltage is applied. Plot the length change as a function of voltage and determine the sensitivity of the sensor. 3. Measure the dependence of the refractive index of air as a function of the air pressure p. Plot Δn(p) and calculate the index of refraction n 0 at standard conditions. 4. Measure the length of a ferromagnetic rod as a function of an applied magnetic field. Plot the relative length change versus the applied field. 5. Determine the relative change in the length of a metal rod as a function of temperature and calculate the linear expansion coefficient. Literature Physics, P.A. Tipler 3. Ed., Vol. 2, Chap University Physics, H. Benson, Chap Physikalisches Praktikum, 13. Auflage, Hrsg. W. Schenk, F. Kremer, Optik, 2.0.1, 2.0.2, 2.4 Accessories He-Ne laser, various optical components for the setup of a Michelson interferometer, piezoelectric actor with mirror, laboratory power supply, electromagnet, ferromagnetic rod with mirror, metal rod with heating filament and mirror, vacuum chamber with hand pump. Keywords for preparation - Interference, coherence - Basic principle of the Michelson interferometer - Generation and properties of laser light - Index of refraction, standard conditions - Piezoelectricity, magnetostriction, thermal expansion 1
2 In this experiment you will work with high quality optical components. Work with great care! While operating the LASER do not look directly into the laser beam or its reflections! Basics The time and position dependence of a plane wave travelling in the positive (negative) z-direction is given by ψ = ψ exp 0 [ i( ωtm kz+ ϕ) ], (1) where ψ might denote e.g. a component of the electric field. The phase of the wave is given by the expression ( ωtm kz+ ϕ), the wave vector by k = 2π/λ, the angular frequency by ω = 2π/T. ϕ denotes the phase angle at zero. The phase velocity of the wave, v ph, which in vacuum is equal to the velocity of light c 0, follows from the condition of constant phase to dz / dt = vph = ω / k. Interference occurs, when two (or more) wave fronts superimpose at a given position. During superposition the resulting wave is either amplified or weakened, depending on the relative phases. The most important precondition for the observability of interference is that the superimposing waves are coherent, i.e. have a fixed phase relation. The phase difference of two waves is taking the presence of two media 1 and 2 into account given by ΔΦ = ( k1δ z1 + ϕ1) ( k2δ z2 + ϕ2), where Δz 1 and Δz 2 are the etric path differences along which the two waves have travelled. If the pairwise occurring phase jumps due to reflection at a fixed end compensate, as is the case in the present experiment, the phase difference is caused by a difference in kz or nz, respectively. The latter quantity is called the optical path length (n: refractive index). The optical path difference is then given by Δ= n1δz1 n2δ z2 = ( ΔΦ /2 πλ ) 0, where λ 0 denotes the vacuum wave length. When two waves ψ 1 (z, t) and ψ 2 (z, t) with phase difference ΔΦ superimpose, the resulting intensity is given by I= I1 + I2 + 2 I1I2 cos( ΔΦ ). One obtains constructive interference for ΔΦ = 2nπ and destructive interference for ΔΦ = (2n + 1) π. For the considerations so far, ideal, i.e. monochromatic as well as infinite waves in both time and space, were assumed. However, every wave, as well as every spectral line, has due to its finite bandwidth Δf (resp. spectral width Δλ ) a finite length of its wave train, namely the coherence length L k, or equivalently, the coherence time Δt = L k /c 0. The uncertainty principle for waves leads to ΔΔ k z 1/2 and ΔΔ f t 1/(4 π ). Therefore one has 2 1 λ0 L k 2Δk 4πΔ λ. (2) The finite coherence length determines the maximally possible optical path difference in interference instruments. In many setups the coherence of the superimposing waves is generated by beam splitting using halftransparent mirrors or other devices. This does only work in case of spatially extended light sources (with a typical spatial extension of a), if the coherence condition is fulfilled (θ: denotes the angle of the beam spread): 2asin( θ) λ/2. (3) 2
3 Laser light is especially coherent with coherence lengths of the order of 1 m. It is generated by stimulated emission. The excited atoms emit the light frequency that is determined by the mirror distance coherently with equal phases. In the He/Ne gas mixture an electric discharge is sustained between two electrodes and the He atoms are excited by electron collisions. The excitation of the Ne atoms into the relevant 3s state occurs by He-Ne collisions with simultaneous energy transfer (collisions of the second kind). At standard operation the He-Ne-LASER emits light with a wavelength λ = nm. Fig. 1 He-Ne energy diagram Adjustment The He-Ne laser beam is split by a half-transparent mirror (Fig. 2 b, in our setup a beam-splitter cube is used) into two partial beams of approximately the same intensity. One resultant beam is guided towards the planar mirror d and will be reflected from there through the beam divider directly onto the screen h. The second beam is reflected by the adjustable mirror c (coupled with the fineadjustment mechanism) and arrives at the screen h after being reflected again by the beam divider b. The diffraction pattern is clearly visible, if the two beams superimpose, if the surfaces of the optical components are rather flat and if the optical path lengths of the two beams do not differ more than half the coherence length from each other. A spherical lens e is used for a better observation of the diffraction pattern. If the setup is well adjusted, a diffraction pattern as shown in Fig. 3 should be observable on the screen. The width and quality of the line fringes are dependent on the setup. The better the adjustment, the wider are the fringes. This is due to the fact that a sloppy adjustment leads to a larger optical path difference between the two interfering rays and therefore to a bigger number of interference fringes in the interference pattern. A very dense diffraction pattern is not of advantage, because counting the number of light-dark fringes is more difficult. When the optical path length is continuously changed, the fringes should move slowly across the screen. 3
4 Fig. 2 Michelson interferometer with fine adjustment drive Fig. 3 Interference pattern with straight line fringes The experimental setup is quite sensitive against vibrations. Therefore the optical components are put up on a massive socket - base plate (a) in Fig. 2 which is seated on a pneumatic dampingsystem in order to damp the vibrations of the table. The base plate is relatively small, so the setup has to be well planned. In a slightly darkened room assemble and adjust the optical components as follows: - Attach the aperture to the opening of the laser beam, switch on laser. - Adjust the laser mount, so that the beam path is parallel to the surface of the base plate. - Adjust the beam divider and the mirrors using the fine adjustment screws, such that the laser beam is reflected back near the laser aperture. The quality of the laser beam is affected, if the reflected split beams fall back right into the aperture of the laser. - Setup beam divider (b) according to Fig. 2, such that one partial beam is reflected at an angle of approximately 90 degrees with respect to the original beam direction. - Setup the fixed mirror (d) in the beam path, such that the reflected beam hits the beam divider in the same spot as the original laser beam. - Setup the adjustable mirror (c), such that the reflected beam hits the beam divider (b) in the same spot as the primary laser beam leaves the half-mirror. -Position screen (h) as shown in Fig. 2, but without the spherical lens with antireflective coating (e, focal length f=2.7 mm). Turn the adjustable mirror (c), such that the split beams superimpose on the screen and that also the points appearing on the half mirror will remain on top of each other. Further partial beams with low intensity will appear beside the major rays; these are due to multiple reflections and will be removed later by the lens holder. - Place the spherical lens (e), such that the overlaid beams hit the lens opening. At the same time check the diffraction pattern. The fringes should not be too wide or too narrow for a sensitive measurement. If necessary, readjust the beams. The micrometer screw which is connected to the fine adjustment mechanism is turned by an electronic motor for easier measurement. The motor voltage supply (1V to 6V) for the engine is supplied by a laboratory voltage supply. The micrometer screw has a gear reduction ratio 100:1 and moves the mirror a well-defined length. The direction of rotation of the motor is equivalent to the 4
5 direction of rotation of the micrometer screw. During the measurement the micrometer screw should act against the pressure of the spring and the sense of rotation of the motor has to be chosen accordingly by the polarity of the voltage. The measurement is started, when the movement of the fringes is continuous. Count the passing fringes using a mark on the screen for at least 10 rotations of the motor. For the determination of the wavelength use the following equation: k λ = 2 (m) (4) 100 z k: number of turns of the micrometer screw, z: number of fringes, : scaling factor relating one turn of the micrometer screw to the displacement of the mirror. Measurements with a piezoelectric sensor The adjustable mirror connected to the micrometer screw and motor is exchanged with the piezoelectric sensor. Readjust the interferometer. Pay attention to the correct polarity of the voltage supply. In principle, a maximum positive voltage of 150 DCV might be applied to the piezoelectric actor, but small negative voltages of -15 DCV might already destroy it! The voltage for the piezoelectric sensor is supplied by a laboratory power supply in the range between 0 and 40 DCV. Measure the hysteresis of the piezoactor for increasing and decreasing voltages. Plot the length change Δl versus the voltage and determine the average slope of the graph (in units of µm/v). Measurement of the index of refraction of air Place the test chamber in one of the beam paths such that the partial beam passes through it axially. Use the hand pump with pressure display to evacuate the chamber. Carry out about eight measurements between atmospheric air pressure and a chamber pressure of approximately 100 hpa. Determine the number z of fringes passing a mark on the screen in dependence on the pressure inside the chamber. Use the following equations for the determination of the index of refraction of air at the atmospheric pressure p = p(air). opt s = n ds n : index of refraction s opt : optical path length s : etric path length d = 50 mm (length of the test chamber) s = 2d (Michelson interferometer) Δ n np ( ) np ( = 0) = p, n(p = 0) = 1 (vacuum refractive index), Δ p Δs opt Δ n = = s Δ zλ s Δz λ np ( ) = 1+ p Δp s with p = p(air). Determine the slope Δz/Δp graphically. Calculate the index of refraction of air at standard conditions. Using the relationship n 1 N (N: number of particles per volume, (5) 5
6 1 1 p N= NA p/ RT assuming an ideal gas, γ = K ) one obtains ( n 1) = ( n0 1) p0 (1 + γ ϑ ) this equation!). (Derive Measurement of the magnetostriction of a ferromagnetic rod For the study of magnetostriction a ferromagnetic rod with given length l is used, with a plane mirror attached to one end. The rod is installed instead of the mirror (c). Place a coil around the rod which creates a magnetic field that in turn leads to a length change Δl of the rod. Coil current should be in the range I = A. In order to avoid strong heating of the coil, the measurements at high currents should be speedily made. To determine the sign of the length change (extension or contraction) the rod is subsequently warmed with a blow-dryer. If the interference fringes move on warming in the same direction as on increase of the coil current, the magnetostriction is positive, i.e. an extension; otherwise it is negative (contraction). Plot the relative length change ε = Δl/l = f(b), where B is the magnetic induction measured with a Teslameter. In order to obtain reproducible values, it would be favourable to demagnetize the rod in a magnetic ac field of decreasing amplitude, before the start of the experiment. Measurement of the linear thermal expansion In this case a metal rod with integrated heater foil is used; again a plane mirror is attached to one end of the rod. The heater current is supplied by a laboratory power supply and the temperature of the rod is measured with an integrated thermal sensor. The thermal expansion coefficient α of the rod (of known length l) can be determined under the assumption of a linear thermal expansion from λ Δ z α = 2l Δ T. (6) The rod should be warmed up to a maximum temperature of 60 C with a maximum heater power of 15 W. Subsequently, the length change is measured on cooling from about 45 C down to room temperature. In the experiment the interference fringes moving across a mark are counted and the dependence z(t) is plotted. Δz/ΔT is determined from the slope of the graph. The length of the rod l is measured with a ruler. 6
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
W 18e Heat Capacity Ratio γ
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum W 8e Heat Capacity Ratio γ Tasks Determine the heat capacity ratio γ of air and carbon dioxide using the method of Clément and Desormes.
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum W 8e Heat Capacity Ratio γ Tasks Determine the heat capacity ratio γ of air and carbon dioxide using the method of Clément and Desormes.
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers
 Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER:
 LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
Speed of Light in Air
 Speed of Light in Air Electromagnetic waves represent energy in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate through vacuum with a speed c = 2.9979246x10 8 m/s. Electromagnetic
Speed of Light in Air Electromagnetic waves represent energy in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate through vacuum with a speed c = 2.9979246x10 8 m/s. Electromagnetic
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment 3 1. The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado
 Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
PS210 - Optical Techniques. Section VI
 PS210 - Optical Techniques Section VI Section I Light as Waves, Rays and Photons Section II Geometrical Optics & Optical Instrumentation Section III Periodic and Non-Periodic (Aperiodic) Waves Section
PS210 - Optical Techniques Section VI Section I Light as Waves, Rays and Photons Section II Geometrical Optics & Optical Instrumentation Section III Periodic and Non-Periodic (Aperiodic) Waves Section
Coherence and width of spectral lines with Michelson interferometer
 Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
Introduction. Procedure. In this experiment, you'll use the interferometer to EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Lens 18mm FL. Component holder.
 12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Experiment 6: Interferometers
 Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
1. Waves and Particles 2. Interference of Waves 3. Wave Nature of Light
 1. Waves and Particles 2. Interference of Waves 3. Wave Nature of Light 1. Double-Slit Eperiment reading: Chapter 22 2. Single-Slit Diffraction reading: Chapter 22 3. Diffraction Grating reading: Chapter
1. Waves and Particles 2. Interference of Waves 3. Wave Nature of Light 1. Double-Slit Eperiment reading: Chapter 22 2. Single-Slit Diffraction reading: Chapter 22 3. Diffraction Grating reading: Chapter
Experiment 8 Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment 8 Michelson Interferometer Introduction This week s experiment utilizes the Michelson interferometer. You are to measure the wavelength of the green mercury light, the wavelength of the sodium
Experiment 8 Michelson Interferometer Introduction This week s experiment utilizes the Michelson interferometer. You are to measure the wavelength of the green mercury light, the wavelength of the sodium
A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth.
 Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Interference- Michelson Interferometer. Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam
 Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Farooq Hassan Roll no: 2012-10-0101 LUMS School of Science and Engineering November 13, 2010 1 Abstract Michelson Interferometer was first used in the classic experiment in 1887
Michelson Interferometer Farooq Hassan Roll no: 2012-10-0101 LUMS School of Science and Engineering November 13, 2010 1 Abstract Michelson Interferometer was first used in the classic experiment in 1887
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Measurments with Michelson interferometers
 Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Measurments with Michelson interferometers Objectives In this experiment you will: Understand the
Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Measurments with Michelson interferometers Objectives In this experiment you will: Understand the
Michelson Interferometry Hassan Mirza
 Michelson Interferometry Hassan Mirza Queen Mary University, Department of Physics Mile End Road, London, England, E1 4NS Introduction Interferometry is a method of experiment in which electromagnetic
Michelson Interferometry Hassan Mirza Queen Mary University, Department of Physics Mile End Road, London, England, E1 4NS Introduction Interferometry is a method of experiment in which electromagnetic
M15e Bending of beams
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum M5e Bending of beams Tasks. Determine Young s modulus E for two metal rods of different material but of the same crosssectional form
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum M5e Bending of beams Tasks. Determine Young s modulus E for two metal rods of different material but of the same crosssectional form
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F)
 B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
Coupled pendulums and degree of coupling
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum Me Coupled pendulums and degree of coupling Tasks. Measure for three different positions of the coupling spring: a) the oscillation
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum Me Coupled pendulums and degree of coupling Tasks. Measure for three different positions of the coupling spring: a) the oscillation
Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1)
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
Interferometers. PART 1: Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the most useful of all optical instru
 Interferometers EP421 Lab Interferometers Introduction: Interferometers are the key to accurate distance measurement using optics. Historically, when mechanical measurements dominated, interferometers
Interferometers EP421 Lab Interferometers Introduction: Interferometers are the key to accurate distance measurement using optics. Historically, when mechanical measurements dominated, interferometers
Homework 1. Property LASER Incandescent Bulb
 Homework 1 Solution: a) LASER light is spectrally pure, single wavelength, and they are coherent, i.e. all the photons are in phase. As a result, the beam of a laser light tends to stay as beam, and not
Homework 1 Solution: a) LASER light is spectrally pure, single wavelength, and they are coherent, i.e. all the photons are in phase. As a result, the beam of a laser light tends to stay as beam, and not
The Michelson Interferometer and the He-Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado
 Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He-Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado In the experiment, two different types of measurements will be made with
Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He-Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado In the experiment, two different types of measurements will be made with
IO3. Modul Optics. Diffraction
 IO3 Modul Optics Diffraction The phenomenon of diffraction is an essential manifestation of the wave properties of light. As a part of geometrical optics, this phenomenon can not be understood because
IO3 Modul Optics Diffraction The phenomenon of diffraction is an essential manifestation of the wave properties of light. As a part of geometrical optics, this phenomenon can not be understood because
INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT
 1 INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT In the year 1678, Christian Huygens proposed the wave theory of light. According to this, a Luminous body is a source of disturbance in hypothetical medium called ether
1 INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT In the year 1678, Christian Huygens proposed the wave theory of light. According to this, a Luminous body is a source of disturbance in hypothetical medium called ether
iprom Optical Interferometry Prof. Dr. -Ing. Rainer Tutsch Institut für Produktionsmesstechnik IPROM Technische Universität Braunschweig
 Optical Interferometry Prof. Dr. -Ing. Rainer Tutsch Institut für Produktionsmesstechnik IPROM Technische Universität Braunschweig Frontiers of Metrology April 1, 01 I P NSTITUT FÜR RODUKTIONSMESSTECHNIK
Optical Interferometry Prof. Dr. -Ing. Rainer Tutsch Institut für Produktionsmesstechnik IPROM Technische Universität Braunschweig Frontiers of Metrology April 1, 01 I P NSTITUT FÜR RODUKTIONSMESSTECHNIK
Physics General Physics II. Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter Wave Optics. Fall 2015 Semester Prof.
 Physics 21900 General Physics II Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter 23.1-2 Wave Optics Fall 2015 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Announcement Exam #2 will be on Thursday, November 5 th (tomorrow)
Physics 21900 General Physics II Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter 23.1-2 Wave Optics Fall 2015 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Announcement Exam #2 will be on Thursday, November 5 th (tomorrow)
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Double Slit is VERY IMPORTANT because it is evidence of waves. Only waves interfere like this.
 Double Slit is VERY IMPORTANT because it is evidence of waves. Only waves interfere like this. Superposition of Sinusoidal Waves Assume two waves are traveling in the same direction, with the same frequency,
Double Slit is VERY IMPORTANT because it is evidence of waves. Only waves interfere like this. Superposition of Sinusoidal Waves Assume two waves are traveling in the same direction, with the same frequency,
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS6012W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 Coherent Light, Coherent Matter Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS6012W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 Coherent Light, Coherent Matter Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries
Chapter 1. Optical Interferometry. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Optical Interferometry Experiment objectives: Assemble and align Michelson and Fabry-Perot interferometers, calibrate them using a laser of known wavelength, and then use them characterize the
Chapter 1 Optical Interferometry Experiment objectives: Assemble and align Michelson and Fabry-Perot interferometers, calibrate them using a laser of known wavelength, and then use them characterize the
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings. Abstract
 Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
INTERFEROMETERS. There are 4 principal types of measurements that can be made with this type of interferometer.
 INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front surface aluminized. Do not touch the surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. Introduction This experiment provides
INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front surface aluminized. Do not touch the surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. Introduction This experiment provides
E13e Switching Processes and Damped Oscillations
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum E13e Switching Processes and Damped Oscillations Tasks 1. To familiarize yourself with the computer-supported setup PA, measure various
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum E13e Switching Processes and Damped Oscillations Tasks 1. To familiarize yourself with the computer-supported setup PA, measure various
WAVE OPTICS GENERAL. Fig.1a The electromagnetic spectrum
 WAVE OPTICS GENERAL - The ray optics cannot explain the results of the two following experimental situations: a) When passing by small openings or illuminating small obstacles, the light bends around borders
WAVE OPTICS GENERAL - The ray optics cannot explain the results of the two following experimental situations: a) When passing by small openings or illuminating small obstacles, the light bends around borders
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light
 Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
PH 222-3A Spring 2010
 PH -3A Spring 010 Interference Lecture 6-7 Chapter 35 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding
PH -3A Spring 010 Interference Lecture 6-7 Chapter 35 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding
2. Determine the surface tension of water with the capillary-rise method.
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum M19e Surface Tension Tasks 1. Determine the surface tension σ of an organic liquid using the anchor-ring method. Use three different
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum M19e Surface Tension Tasks 1. Determine the surface tension σ of an organic liquid using the anchor-ring method. Use three different
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light
 Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
 The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules Breakdown of classical physics: Wave-particle duality Dr Grant Ritchie Electromagnetic waves Remember: The speed of a wave, v, is related to its wavelength, λ,
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules Breakdown of classical physics: Wave-particle duality Dr Grant Ritchie Electromagnetic waves Remember: The speed of a wave, v, is related to its wavelength, λ,
PHYS 229: Experiment 1 Expansion Coefficients of Copper and Invar Bars Through Laser Interferometry
 PHYS 229: Experiment 1 Expansion Coefficients of Copper and Invar Bars Through Laser Interferometry Jack Hong 30935134 Partner: Omar Mrani Zentar January 15, 2015 1 Introduction: When objects are heated,
PHYS 229: Experiment 1 Expansion Coefficients of Copper and Invar Bars Through Laser Interferometry Jack Hong 30935134 Partner: Omar Mrani Zentar January 15, 2015 1 Introduction: When objects are heated,
Chapter 35. Interference
 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding many natural phenomena, ranging from color shifting in butterfly wings to intensity patterns formed by small apertures.
Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding many natural phenomena, ranging from color shifting in butterfly wings to intensity patterns formed by small apertures.
Modern optics Lasers
 Chapter 13 Phys 322 Lecture 36 Modern optics Lasers Reminder: Please complete the online course evaluation Last lecture: Review discussion (no quiz) LASER = Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of
Chapter 13 Phys 322 Lecture 36 Modern optics Lasers Reminder: Please complete the online course evaluation Last lecture: Review discussion (no quiz) LASER = Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of
25 LIGHT INTERFERENCE
 Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics Physics Laboratory I P Politechnika Warszawska Andrzej Kubiaczyk Wydział Fizyki Laboratorium Fizyki I 5 LIGHT INTERFERENCE NEWTON S ZJAWISKO RINGS, MICHELSON
Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics Physics Laboratory I P Politechnika Warszawska Andrzej Kubiaczyk Wydział Fizyki Laboratorium Fizyki I 5 LIGHT INTERFERENCE NEWTON S ZJAWISKO RINGS, MICHELSON
Optics. Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer. LD Physics Leaflets P
 Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
4. Dispersion. The index of refraction of the prism at the input wavelength can be calculated using
 4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
= (fundamental constants c 0, h, k ). (1) k
 Introductory Physics Laboratory, Faculty of Physics and Geosciences, University of Leipzig W 12e Radiation Thermometers Tasks 1 Measure the black temperature T s of a glowing resistance wire at eight different
Introductory Physics Laboratory, Faculty of Physics and Geosciences, University of Leipzig W 12e Radiation Thermometers Tasks 1 Measure the black temperature T s of a glowing resistance wire at eight different
Experiment 4. Michelson Interferometer. 4.1 Introduction. References
 Experiment 4 Michelson Interferometer References Optics by E. Hecht, Section 9.4.2 Fundamentals of Optics by F. Jenkins & H. White, Chapter 13, Sections 8 through 15, and Chapter 14, Section 13 An Introduction
Experiment 4 Michelson Interferometer References Optics by E. Hecht, Section 9.4.2 Fundamentals of Optics by F. Jenkins & H. White, Chapter 13, Sections 8 through 15, and Chapter 14, Section 13 An Introduction
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves As the chart shows, the electromagnetic spectrum covers an extremely wide range of wavelengths and frequencies. Though the names indicate that these waves have a number of sources,
Electromagnetic Waves As the chart shows, the electromagnetic spectrum covers an extremely wide range of wavelengths and frequencies. Though the names indicate that these waves have a number of sources,
Michelson Interferometer. crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity.
 Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
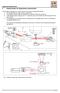 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
Laserphysik. Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu. Fachgebiet Angewandte Nanophysik, Institut für Physik
 Laserphysik Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet Angewandte Nanophysik, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Heisenbergbau V 202, Unterpörlitzer Straße
Laserphysik Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet Angewandte Nanophysik, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Heisenbergbau V 202, Unterpörlitzer Straße
8. The Michelson Interferometer
 M 8. The Michelson Interferometer 8.1 Introduction Interference patterns from superposed coherent waves may be used for precise determination of wavelength or, if the wavelength is known, time-of-flight,
M 8. The Michelson Interferometer 8.1 Introduction Interference patterns from superposed coherent waves may be used for precise determination of wavelength or, if the wavelength is known, time-of-flight,
and the radiation from source 2 has the form. The vector r points from the origin to the point P. What will the net electric field be at point P?
 Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Some properties of waves: Huygens principle Superposition Coherence Interference Young s double-slit experiment Thin-film interference
 Some properties of waves: Huygens principle Superposition Coherence Interference Young s double-slit experiment Thin-film interference Phys 2435: Chap. 35, Pg 1 Geometrical Optics Assumption: the dimensions
Some properties of waves: Huygens principle Superposition Coherence Interference Young s double-slit experiment Thin-film interference Phys 2435: Chap. 35, Pg 1 Geometrical Optics Assumption: the dimensions
Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY
 Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY When atoms of a gas are excited (by high voltage, for instance) they will give off light. Each element (in fact, each isotope) gives off a characteristic atomic spectrum,
Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY When atoms of a gas are excited (by high voltage, for instance) they will give off light. Each element (in fact, each isotope) gives off a characteristic atomic spectrum,
Circular Motion & Oscillations
 A Physics Revision Page 1 of 8 Circular Motion & Oscillations Angular speed, ω = Δθ = πf (assuming angle is a complete revolution, in radians) Δt mv Centripetal Force, F = r Simple Harmonic Motion is a
A Physics Revision Page 1 of 8 Circular Motion & Oscillations Angular speed, ω = Δθ = πf (assuming angle is a complete revolution, in radians) Δt mv Centripetal Force, F = r Simple Harmonic Motion is a
Revision Guide. Chapter 7 Quantum Behaviour
 Revision Guide Chapter 7 Quantum Behaviour Contents CONTENTS... 2 REVISION CHECKLIST... 3 REVISION NOTES... 4 QUANTUM BEHAVIOUR... 4 Random arrival of photons... 4 Photoelectric effect... 5 PHASE AN PHASORS...
Revision Guide Chapter 7 Quantum Behaviour Contents CONTENTS... 2 REVISION CHECKLIST... 3 REVISION NOTES... 4 QUANTUM BEHAVIOUR... 4 Random arrival of photons... 4 Photoelectric effect... 5 PHASE AN PHASORS...
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide
 AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
4. Dispersion. The index of refraction of the prism at the input wavelength can be calculated using
 4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
The Diffraction Grating
 The Diffraction Grating If one extends the double slit to large number of slits very closely spaced, one gets what is called a diffraction grating. d sin θ. Maxima are still at d sin θ m = mλ, m = 0, 1,
The Diffraction Grating If one extends the double slit to large number of slits very closely spaced, one gets what is called a diffraction grating. d sin θ. Maxima are still at d sin θ m = mλ, m = 0, 1,
THE MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER Intermediate ( first part) to Advanced (latter parts)
 THE MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER Intermediate ( first part) to Advanced (latter parts) Goal: There is a progression of goals for this experiment but you do not have to do the last goal. The first goal is to
THE MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER Intermediate ( first part) to Advanced (latter parts) Goal: There is a progression of goals for this experiment but you do not have to do the last goal. The first goal is to
LC circuit: Energy stored. This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters
 Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Lab 2: Mach Zender Interferometer Overview
 Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
The Photoelectric Effect
 Stellar Astrophysics: The Interaction of Light and Matter The Photoelectric Effect Methods of electron emission Thermionic emission: Application of heat allows electrons to gain enough energy to escape
Stellar Astrophysics: The Interaction of Light and Matter The Photoelectric Effect Methods of electron emission Thermionic emission: Application of heat allows electrons to gain enough energy to escape
The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
MODERN OPTICS. P47 Optics: Unit 9
 MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
PAP Physics Spring Exam Review
 Class: Date: PAP Physics Spring Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A container of gas is at a pressure of.3 0 5 Pa
Class: Date: PAP Physics Spring Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A container of gas is at a pressure of.3 0 5 Pa
Interference. Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website
 Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Electromagnetic Waves A.K.A. Light
 Electromagnetic Waves A.K.A. Light When Thomas Edison worked late into the night on the electric light, he had to do it by gas lamp or candle. I'm sure it made the work seem that much more urgent. George
Electromagnetic Waves A.K.A. Light When Thomas Edison worked late into the night on the electric light, he had to do it by gas lamp or candle. I'm sure it made the work seem that much more urgent. George
Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference
 Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference Waves that combine in phase add up to relatively high irradiance. = Constructive interference (coherent) Waves that combine
Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference Waves that combine in phase add up to relatively high irradiance. = Constructive interference (coherent) Waves that combine
P5 Revision Questions
 P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
Revision Guide for Chapter 7
 Revision Guide for Chapter 7 Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes Path of least time... 4 Interference of photons... 5 Quantum behaviour... 5 Photons... 6 Electron diffraction... 7 Probability...
Revision Guide for Chapter 7 Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes Path of least time... 4 Interference of photons... 5 Quantum behaviour... 5 Photons... 6 Electron diffraction... 7 Probability...
The Michelson Interferometer as a Device for Measuring the Wavelength of a Helium-Neon Laser
 Journal of Advanced Undergraduate Physics Laboratory Investigation Volume 3 2017-2018 Article 2 2018 The Michelson Interferometer as a Device for Measuring the Wavelength of a Helium-Neon Laser Carly E.
Journal of Advanced Undergraduate Physics Laboratory Investigation Volume 3 2017-2018 Article 2 2018 The Michelson Interferometer as a Device for Measuring the Wavelength of a Helium-Neon Laser Carly E.
Experiment 2: The Speed of Light
 Experiment 2: The Speed of Light Modern Physics Laboratory Department of Physics and Astronomy Austin Peay State University September 12, 2006 Abstract In this experiment you will determine the value of
Experiment 2: The Speed of Light Modern Physics Laboratory Department of Physics and Astronomy Austin Peay State University September 12, 2006 Abstract In this experiment you will determine the value of
Chapter 35 Physical Optics: Light as a wave
 Chapter 35 Physical Optics: Light as a wave Interference happens when two or more waves combine Examples of no-pigmented color presentation (iridescence): Beautiful oil spills Colors on soap bubble Color
Chapter 35 Physical Optics: Light as a wave Interference happens when two or more waves combine Examples of no-pigmented color presentation (iridescence): Beautiful oil spills Colors on soap bubble Color
Zeeman Effect. Rabia Aslam Chaudary Roll no: LUMS School of Science and Engineering. Friday May 20, 2011
 Zeeman Effect Rabia Aslam Chaudary Roll no: 2012-10-0011 LUMS School of Science and Engineering Friday May 20, 2011 1 Abstract In this experiment, we will observe the Zeeman effect which is defined as
Zeeman Effect Rabia Aslam Chaudary Roll no: 2012-10-0011 LUMS School of Science and Engineering Friday May 20, 2011 1 Abstract In this experiment, we will observe the Zeeman effect which is defined as
SPEED OF SOUND AND SPEED OF LIGHT IN AIR
 University of Oulu Student laboratory in Physics Laboratory Exercises in Physics 1 SPEED OF SOUND AND SPEED OF LIGHT IN AIR 1. Introduction Sound can be determined as a longitudinal, mechanical wave motion
University of Oulu Student laboratory in Physics Laboratory Exercises in Physics 1 SPEED OF SOUND AND SPEED OF LIGHT IN AIR 1. Introduction Sound can be determined as a longitudinal, mechanical wave motion
TA/TI survey. Phy Phy
 TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
P.M. THURSDAY, 21 May hours. Write your name, centre number and candidate number in the spaces at the top of this page.
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1322/01 New AS PHYSICS ASSESSMENT UNIT PH2: WAVES AND PARTICLES P.M. THURSDAY, 21 May 2009 1 1 4 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1322/01 New AS PHYSICS ASSESSMENT UNIT PH2: WAVES AND PARTICLES P.M. THURSDAY, 21 May 2009 1 1 4 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this
1/d o +1/d i =1/f. Chapter 24 Wave Optics. The Lens Equation. Diffraction Interference Polarization. The Nature of Light
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Interference Polarization 2F h o The Lens Equation 1/d o +1/d i =1/f F F O d o f d i h i Geometrical and Physical Optics Geometrical Optics: The study of optical phenomena
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Interference Polarization 2F h o The Lens Equation 1/d o +1/d i =1/f F F O d o f d i h i Geometrical and Physical Optics Geometrical Optics: The study of optical phenomena
Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer
 Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 19, 2018 Last time diffraction patterns diffraction and interference resolution and Raleigh s criterion
Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 19, 2018 Last time diffraction patterns diffraction and interference resolution and Raleigh s criterion
Confocal Microscopy Imaging of Single Emitter Fluorescence and Hanbury Brown and Twiss Photon Antibunching Setup
 1 Confocal Microscopy Imaging of Single Emitter Fluorescence and Hanbury Brown and Twiss Photon Antibunching Setup Abstract Jacob Begis The purpose of this lab was to prove that a source of light can be
1 Confocal Microscopy Imaging of Single Emitter Fluorescence and Hanbury Brown and Twiss Photon Antibunching Setup Abstract Jacob Begis The purpose of this lab was to prove that a source of light can be
RED. BLUE Light. Light-Matter
 1 Light-Matter This experiment demonstrated that light behaves as a wave. Essentially Thomas Young passed a light of a single frequency ( colour) through a pair of closely spaced narrow slits and on the
1 Light-Matter This experiment demonstrated that light behaves as a wave. Essentially Thomas Young passed a light of a single frequency ( colour) through a pair of closely spaced narrow slits and on the
5 TH ERMAL GRADIENT INTERFEROMETRIC MEASUREMENT
 5 TH ERMAL GRADIENT INTERFEROMETRIC MEASUREMENT Gradient Index Measurement with Temperature MODEL OEK-100 PROJECT #4 50 5.1 Introduction It is possible to measure the change in index of refraction of a
5 TH ERMAL GRADIENT INTERFEROMETRIC MEASUREMENT Gradient Index Measurement with Temperature MODEL OEK-100 PROJECT #4 50 5.1 Introduction It is possible to measure the change in index of refraction of a
Vågrörelselära och optik
 Vågrörelselära och optik Harmonic oscillation: Experiment Experiment to find a mathematical description of harmonic oscillation Kapitel 14 Harmonisk oscillator 1 2 Harmonic oscillation: Experiment Harmonic
Vågrörelselära och optik Harmonic oscillation: Experiment Experiment to find a mathematical description of harmonic oscillation Kapitel 14 Harmonisk oscillator 1 2 Harmonic oscillation: Experiment Harmonic
Physics 101 Final Exam Problem Guide
 Physics 101 Final Exam Problem Guide Liam Brown, Physics 101 Tutor C.Liam.Brown@gmail.com General Advice Focus on one step at a time don t try to imagine the whole solution at once. Draw a lot of diagrams:
Physics 101 Final Exam Problem Guide Liam Brown, Physics 101 Tutor C.Liam.Brown@gmail.com General Advice Focus on one step at a time don t try to imagine the whole solution at once. Draw a lot of diagrams:
Atomic and nuclear physics
 Atomic and nuclear physics Atomic shell Normal Zeeman effect LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Observing the normal Zeeman effect in transverse and longitudinal Objects of the experiment Observing the line triplet
Atomic and nuclear physics Atomic shell Normal Zeeman effect LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Observing the normal Zeeman effect in transverse and longitudinal Objects of the experiment Observing the line triplet
A) n 1 > n 2 > n 3 B) n 1 > n 3 > n 2 C) n 2 > n 1 > n 3 D) n 2 > n 3 > n 1 E) n 3 > n 1 > n 2
 55) The diagram shows the path of a light ray in three different materials. The index of refraction for each material is shown in the upper right portion of the material. What is the correct order for
55) The diagram shows the path of a light ray in three different materials. The index of refraction for each material is shown in the upper right portion of the material. What is the correct order for
The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom
 Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting
 Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting PHYS 3330: Experiments in Optics Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30602 (Dated: Revised
Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting PHYS 3330: Experiments in Optics Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30602 (Dated: Revised
Chapter 10. Interference of Light
 Chapter 10. Interference of Light Last Lecture Wave equations Maxwell equations and EM waves Superposition of waves This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton
Chapter 10. Interference of Light Last Lecture Wave equations Maxwell equations and EM waves Superposition of waves This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics. Final Exam. April 16, 2007.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
