E13e Switching Processes and Damped Oscillations
|
|
|
- Harry Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum E13e Switching Processes and Damped Oscillations Tasks 1. To familiarize yourself with the computer-supported setup PA, measure various time dependent output voltages from a function generator. Determine the frequency and amplitude of the voltages using the cursor measurement-system.. Measure the time dependence of currents and voltages when switching on or off various R and RL series circuits. alculate the characteristic parameters of the circuit elements from the measured time constants. 3. Measure the free oscillations of a RL series circuit. Determine frequency f and damping of the oscillation. By using a variable ohmic resistor tune to the aperiodic limiting case. Literature Physics, P. A. Tipler, 3rd Edition, Vol., 3-, 6-8, 8-4 Physikalisches Praktikum, 14. Auflage, Hrsg. W. Schenk, F. remer, Elektrizitätslehre, 3.3, 4.1 (in German) Accessories Analog-to-digital converter PA with software, connection panel, function generator, laboratory power supply, resistors, capacitors, coils, digital multimeter ey Aspects for Preparation - Time dependence of the charging/discharging of a capacitor - Time dependence of the coil voltage during charging/discharging - Differential equation of the harmonic oscillator, eigenfrequency - Differential equation of the RL series circuit, eigenfrequency, quality factor, damping constant, logarithmic decrement, solutions for the oscillating case, aperiodic limiting case, creep case 1
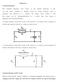
2 Remarks The aim of this experiment is the study of time-resolved switching on/off processes occurring in R and RL series circuits. Moreover, free oscillations of a RL series circuit should be investigated. The latter circuit is modelled by a linear homogeneous differential equation of. order that is known from the mechanics of the damped harmonic oscillator, but has also broad applications in optics, atomic and molecular physics. For preparation, use irchhoff s laws to set up the relevant differential equations describing the circuits and verify the following solutions for switching on/off processes as well as damped oscillations. Switching on/off of a R series circuit (see circuits below) Switch-on time-function (charging) [time constant τ R = R] U ( ) exp t I t = R R, t U ( t) = U 1 exp R Switch-off time-function (discharging) I (t) = U exp t R R, U ( t ) = U exp t R Switching on/off of a RL series circuit (see circuits below) Switch-on time-function [time constant τ RLE = L/(R+R Sp)] U + R RSp ISp( t) = 1 exp t, L R USp( t) = U 1 1 exp t R + R Sp L Switch-off time-function [time constant τ RLA = L / ( R+R Sp+R p )] U + + R RSp Rp ISp( t) = exp t, L R + Rp + Rp USp( t) = U exp t L
3 Free damped oscillations Oscillation [ ω o > δ, δ =R/L] - U ( ) = e t t U (cos t + sin t ) or ( ) o - t U sin ( ) t = U e t + with tan Aperiodic limiting case [ω o = δ ] - t U ( t ) = U e ( 1 + t ) reep [ω o < δ ] (U : terminal voltage, : damping constant) tanh - o t - t U ( t) = U e 1 - cosh - o t 1- o / Hints to the experiment All voltages must be limited to a maximum of U < 10 V. The following circuits must be set up in a voltageless state and have to be controlled by the supervisor before use. The time dependent electric voltages are digitized by the PA interface, an analog-to-digital converter (AD). Via an USB interface the data are transmitted to the P and are stored in the software PA. The sampling rate and other settings are adjusted via the software. The measurement conditions are different for the various tasks and various values of the circuit elements. Adjust the measurement parameter in such a way that the time curve can be evaluated with highest precision possible in this experiment. The optoelectronic relay of the PA interface is used to switch the circuits. To this end the numbering of the inputs has to be taken into account (see sketch to the right). In the initial state inputs 0 and 1 are connected, whereas after activation of the relay that occurs automatically in the course of the measurement process, a connection between 0 and is established. Inputs and relay circuit of the PA (schematic) 3
4 Get to know the setup onnect the output (OUTPUT 0-10 V pp, 50 ) of the function generator with the input (H 1) of the PA interface. Measure the time dependence of a sine and a triangular voltage. Determine the frequency (or period) and the amplitude using the cursor system of the PA software. R series circuit Discharging As capacitance an electrolytic capacitor is used; therefore, during setup of the circuit pay attention to the correct polarity. The capacitance X is unknown and should be determined. To this end choose ten values of the resistor decade between R = 0.9 k and R = 9 k, determine the time constants from the time dependent voltage U (t) and find X by linear regression of the time constants. harging In order to determine the unknown value of the resistance R X, use the capacitor from the previous task. Measure the switch-on time-curve I(t)=U R(t)/R. Export the data into Origin and determine the time constant R by linear regression of the linearized graph or by fitting an exponential function to the data. Use the value of the time constant to calculate R X. RL series circuit Switch-on process hoose values R = 100 or R = 00 at the decade resistor for the determination of the inductance (L 1, L or L 3) of one of the available coils. Measure the switch-on time-function of the current I(t)=U R(t)/R using the voltage U R(t). In order to determine RL,in, evaluate the measured curve either with the cursor system in PA or with an appropriate graphic analysis. 4
5 Switch-off process For the circuit to the right use resistances R P = 0 and R = 00 (decade resistor). Evaluate the time function U Sp(t) for the determination of the time constant RL,out graphically or by linear regression. RL series circuit For the measurement of the free oscillations of a RL circuit use two known, but different values of the capacitance (important: Osc). Determine the eigenfrequency and the damping constant with the cursor system of the PA software. From these values calculate the inductance used in the experiment and compare to the result of the previous tasks. Software PA The software PA allows for the adjustment of the measurement parameters of the PA interface, it facilitates the transmission of the recorded values to the P and serves for the analysis and storage of the data. Data are recorded on up to four selectable channels. The measured voltages of these channels are shown on a numerical display. For the measurement the sampling rate (number of measurements per second) and the number of measurement points must be adjusted. Take into account that the UI des Programms PA maximum sampling rate is given by 10 5 /number of channels. The voltage range is fixed to ±10 V. The digital resolution is 16 Bit. The switching of the optoelectronic relay integrated in the PA interface is controllable from the program. The recorded data are shown in a table and in a diagram. The export of the data for further analysis is possible in an ASII format. Within the diagram measurements can be directly made with a cursor system. 5
Coupled pendulums and degree of coupling
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum Me Coupled pendulums and degree of coupling Tasks. Measure for three different positions of the coupling spring: a) the oscillation
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum Me Coupled pendulums and degree of coupling Tasks. Measure for three different positions of the coupling spring: a) the oscillation
W 18e Heat Capacity Ratio γ
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum W 8e Heat Capacity Ratio γ Tasks Determine the heat capacity ratio γ of air and carbon dioxide using the method of Clément and Desormes.
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum W 8e Heat Capacity Ratio γ Tasks Determine the heat capacity ratio γ of air and carbon dioxide using the method of Clément and Desormes.
Inductance, RL and RLC Circuits
 Inductance, RL and RLC Circuits Inductance Temporarily storage of energy by the magnetic field When the switch is closed, the current does not immediately reach its maximum value. Faraday s law of electromagnetic
Inductance, RL and RLC Circuits Inductance Temporarily storage of energy by the magnetic field When the switch is closed, the current does not immediately reach its maximum value. Faraday s law of electromagnetic
Inductance, Inductors, RL Circuits & RC Circuits, LC, and RLC Circuits
 Inductance, Inductors, RL Circuits & RC Circuits, LC, and RLC Circuits Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the timevarying
Inductance, Inductors, RL Circuits & RC Circuits, LC, and RLC Circuits Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the timevarying
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3.
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Handout 10: Inductance. Self-Inductance and inductors
 1 Handout 10: Inductance Self-Inductance and inductors In Fig. 1, electric current is present in an isolate circuit, setting up magnetic field that causes a magnetic flux through the circuit itself. This
1 Handout 10: Inductance Self-Inductance and inductors In Fig. 1, electric current is present in an isolate circuit, setting up magnetic field that causes a magnetic flux through the circuit itself. This
Old Dominion University Physics 112N/227N/232N Lab Manual, 13 th Edition
 RC Circuits Experiment PH06_Todd OBJECTIVE To investigate how the voltage across a capacitor varies as it charges. To find the capacitive time constant. EQUIPMENT NEEDED Computer: Personal Computer with
RC Circuits Experiment PH06_Todd OBJECTIVE To investigate how the voltage across a capacitor varies as it charges. To find the capacitive time constant. EQUIPMENT NEEDED Computer: Personal Computer with
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2003 Experiment 17: RLC Circuit (modified 4/15/2003) OBJECTIVES
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 7: R Circuit (modified 4/5/3) OBJECTIVES. To observe electrical oscillations, measure their frequencies, and verify energy
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 7: R Circuit (modified 4/5/3) OBJECTIVES. To observe electrical oscillations, measure their frequencies, and verify energy
Basic RL and RC Circuits R-L TRANSIENTS: STORAGE CYCLE. Engineering Collage Electrical Engineering Dep. Dr. Ibrahim Aljubouri
 st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
MODULE I. Transient Response:
 Transient Response: MODULE I The Transient Response (also known as the Natural Response) is the way the circuit responds to energies stored in storage elements, such as capacitors and inductors. If a capacitor
Transient Response: MODULE I The Transient Response (also known as the Natural Response) is the way the circuit responds to energies stored in storage elements, such as capacitors and inductors. If a capacitor
Coupled Electrical Oscillators Physics Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 2018 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 5/24/2018
 Coupled Electrical Oscillators Physics 3600 - Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 08 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 5/4/08 I. INTRODUCTION The objectives of this experiment are: () explore the properties
Coupled Electrical Oscillators Physics 3600 - Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 08 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 5/4/08 I. INTRODUCTION The objectives of this experiment are: () explore the properties
Lab 4 RC Circuits. Name. Partner s Name. I. Introduction/Theory
 Lab 4 RC Circuits Name Partner s Name I. Introduction/Theory Consider a circuit such as that in Figure 1, in which a potential difference is applied to the series combination of a resistor and a capacitor.
Lab 4 RC Circuits Name Partner s Name I. Introduction/Theory Consider a circuit such as that in Figure 1, in which a potential difference is applied to the series combination of a resistor and a capacitor.
Lecture 39. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 39 PHYC 161 Fall 016 Announcements DO THE ONLINE COURSE EVALUATIONS - response so far is < 8 % Magnetic field energy A resistor is a device in which energy is irrecoverably dissipated. By contrast,
Lecture 39 PHYC 161 Fall 016 Announcements DO THE ONLINE COURSE EVALUATIONS - response so far is < 8 % Magnetic field energy A resistor is a device in which energy is irrecoverably dissipated. By contrast,
Chapter 32. Inductance
 Chapter 32 Inductance Joseph Henry 1797 1878 American physicist First director of the Smithsonian Improved design of electromagnet Constructed one of the first motors Discovered self-inductance Unit of
Chapter 32 Inductance Joseph Henry 1797 1878 American physicist First director of the Smithsonian Improved design of electromagnet Constructed one of the first motors Discovered self-inductance Unit of
Physics 4 Spring 1989 Lab 5 - AC Circuits
 Physics 4 Spring 1989 Lab 5 - AC Circuits Theory Consider the series inductor-resistor-capacitor circuit shown in figure 1. When an alternating voltage is applied to this circuit, the current and voltage
Physics 4 Spring 1989 Lab 5 - AC Circuits Theory Consider the series inductor-resistor-capacitor circuit shown in figure 1. When an alternating voltage is applied to this circuit, the current and voltage
Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the time-varying current.
 Inductance Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the time-varying current. Basis of the electrical circuit element called an
Inductance Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the time-varying current. Basis of the electrical circuit element called an
Active Figure 32.3 (SLIDESHOW MODE ONLY)
 RL Circuit, Analysis An RL circuit contains an inductor and a resistor When the switch is closed (at time t = 0), the current begins to increase At the same time, a back emf is induced in the inductor
RL Circuit, Analysis An RL circuit contains an inductor and a resistor When the switch is closed (at time t = 0), the current begins to increase At the same time, a back emf is induced in the inductor
Chapter 30. Inductance. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow
 Chapter 30 Inductance PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 30 Looking forward at how a time-varying
Chapter 30 Inductance PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 30 Looking forward at how a time-varying
Physics Investigation 10 Teacher Manual
 Physics Investigation 10 Teacher Manual Observation When a light bulb is connected to a number of charged capacitors, it lights up for different periods of time. Problem What does the rate of discharging
Physics Investigation 10 Teacher Manual Observation When a light bulb is connected to a number of charged capacitors, it lights up for different periods of time. Problem What does the rate of discharging
AC Circuits Homework Set
 Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Chapter 4 Transients. Chapter 4 Transients
 Chapter 4 Transients Chapter 4 Transients 1. Solve first-order RC or RL circuits. 2. Understand the concepts of transient response and steady-state response. 1 3. Relate the transient response of first-order
Chapter 4 Transients Chapter 4 Transients 1. Solve first-order RC or RL circuits. 2. Understand the concepts of transient response and steady-state response. 1 3. Relate the transient response of first-order
University of TN Chattanooga Physics 1040L 8/18/2012 PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 4: R.C. TIME CONSTANT LAB
 PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 4: R.C. TIME CONSTANT LAB OBJECT: To study the discharging of a capacitor and determine the time constant for a simple circuit. APPARATUS: Capacitor (about 24 μf), two resistors (about
PHYSICS 1040L LAB LAB 4: R.C. TIME CONSTANT LAB OBJECT: To study the discharging of a capacitor and determine the time constant for a simple circuit. APPARATUS: Capacitor (about 24 μf), two resistors (about
Slide 1 / 26. Inductance by Bryan Pflueger
 Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
Capacitors. The charge Q on a capacitor s plate is proportional to the potential difference V across the Q = C V (1)
 apacitors THEORY The charge Q on a capacitor s plate is proportional to the potential difference V across the capacitor. We express this with Q = V (1) where is a proportionality constant known as the
apacitors THEORY The charge Q on a capacitor s plate is proportional to the potential difference V across the capacitor. We express this with Q = V (1) where is a proportionality constant known as the
[1] (b) Fig. 1.1 shows a circuit consisting of a resistor and a capacitor of capacitance 4.5 μf. Fig. 1.1
![[1] (b) Fig. 1.1 shows a circuit consisting of a resistor and a capacitor of capacitance 4.5 μf. Fig. 1.1 [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 shows a circuit consisting of a resistor and a capacitor of capacitance 4.5 μf. Fig. 1.1](/thumbs/81/83276652.jpg) 1 (a) Define capacitance..... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 shows a circuit consisting of a resistor and a capacitor of capacitance 4.5 μf. S 1 S 2 6.3 V 4.5 μf Fig. 1.1 Switch S 1 is closed and switch S 2 is left
1 (a) Define capacitance..... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 shows a circuit consisting of a resistor and a capacitor of capacitance 4.5 μf. S 1 S 2 6.3 V 4.5 μf Fig. 1.1 Switch S 1 is closed and switch S 2 is left
Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work Solutions
 Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work s 21.1 Problem 21.11 What is the time constant of the circuit in Figure (21.19). 10 Ω 10 Ω 5.0 Ω 2.0µF 2.0µF 2.0µF 3.0µF Figure 21.19: Given: The circuit
Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work s 21.1 Problem 21.11 What is the time constant of the circuit in Figure (21.19). 10 Ω 10 Ω 5.0 Ω 2.0µF 2.0µF 2.0µF 3.0µF Figure 21.19: Given: The circuit
Lab 08 Capacitors 2. Figure 2 Series RC circuit with SPDT switch to charge and discharge capacitor.
 Lab 08: Capacitors Last edited March 5, 2018 Learning Objectives: 1. Understand the short-term and long-term behavior of circuits containing capacitors. 2. Understand the mathematical relationship between
Lab 08: Capacitors Last edited March 5, 2018 Learning Objectives: 1. Understand the short-term and long-term behavior of circuits containing capacitors. 2. Understand the mathematical relationship between
Inductance, RL Circuits, LC Circuits, RLC Circuits
 Inductance, R Circuits, C Circuits, RC Circuits Inductance What happens when we close the switch? The current flows What does the current look like as a function of time? Does it look like this? I t Inductance
Inductance, R Circuits, C Circuits, RC Circuits Inductance What happens when we close the switch? The current flows What does the current look like as a function of time? Does it look like this? I t Inductance
Chapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance
 hapter 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplex Impedance In this chapter we introduce the concept of complex resistance, or impedance, by studying two reactive circuit elements, the capacitor and the inductor.
hapter 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplex Impedance In this chapter we introduce the concept of complex resistance, or impedance, by studying two reactive circuit elements, the capacitor and the inductor.
M15e Bending of beams
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum M5e Bending of beams Tasks. Determine Young s modulus E for two metal rods of different material but of the same crosssectional form
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum M5e Bending of beams Tasks. Determine Young s modulus E for two metal rods of different material but of the same crosssectional form
= (fundamental constants c 0, h, k ). (1) k
 Introductory Physics Laboratory, Faculty of Physics and Geosciences, University of Leipzig W 12e Radiation Thermometers Tasks 1 Measure the black temperature T s of a glowing resistance wire at eight different
Introductory Physics Laboratory, Faculty of Physics and Geosciences, University of Leipzig W 12e Radiation Thermometers Tasks 1 Measure the black temperature T s of a glowing resistance wire at eight different
EE 242 EXPERIMENT 8: CHARACTERISTIC OF PARALLEL RLC CIRCUIT BY USING PULSE EXCITATION 1
 EE 242 EXPERIMENT 8: CHARACTERISTIC OF PARALLEL RLC CIRCUIT BY USING PULSE EXCITATION 1 PURPOSE: To experimentally study the behavior of a parallel RLC circuit by using pulse excitation and to verify that
EE 242 EXPERIMENT 8: CHARACTERISTIC OF PARALLEL RLC CIRCUIT BY USING PULSE EXCITATION 1 PURPOSE: To experimentally study the behavior of a parallel RLC circuit by using pulse excitation and to verify that
Exercise 1: Capacitors
 Capacitance AC 1 Fundamentals Exercise 1: Capacitors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to describe the effect a capacitor has on dc and ac circuits by using measured
Capacitance AC 1 Fundamentals Exercise 1: Capacitors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to describe the effect a capacitor has on dc and ac circuits by using measured
Experiment 8: Capacitance and the Oscilloscope
 Experiment 8: Capacitance and the Oscilloscope Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Outline Capacitance: Capacitor
Experiment 8: Capacitance and the Oscilloscope Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Outline Capacitance: Capacitor
Switch. R 5 V Capacitor. ower upply. Voltmete. Goals. Introduction
 Switch Lab 6. Circuits ower upply Goals + + R 5 V Capacitor V To appreciate the capacitor as a charge storage device. To measure the voltage across a capacitor as it discharges through a resistor, and
Switch Lab 6. Circuits ower upply Goals + + R 5 V Capacitor V To appreciate the capacitor as a charge storage device. To measure the voltage across a capacitor as it discharges through a resistor, and
Electrical Circuits Lab Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram
 Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
Switch. R 5 V Capacitor. ower upply. Voltmete. Goals. Introduction
 Switch Lab 6. Circuits ower upply Goals + + R 5 V Capacitor V To appreciate the capacitor as a charge storage device. To measure the voltage across a capacitor as it discharges through a resistor, and
Switch Lab 6. Circuits ower upply Goals + + R 5 V Capacitor V To appreciate the capacitor as a charge storage device. To measure the voltage across a capacitor as it discharges through a resistor, and
Michelson Interferometer
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum O10e Michelson Interferometer Tasks 1. Adjust a Michelson interferometer and determine the wavelength of a He-Ne laser. 2. Measure
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum O10e Michelson Interferometer Tasks 1. Adjust a Michelson interferometer and determine the wavelength of a He-Ne laser. 2. Measure
EXPERIMENT 5A RC Circuits
 EXPERIMENT 5A Circuits Objectives 1) Observe and qualitatively describe the charging and discharging (decay) of the voltage on a capacitor. 2) Graphically determine the time constant for the decay, τ =.
EXPERIMENT 5A Circuits Objectives 1) Observe and qualitatively describe the charging and discharging (decay) of the voltage on a capacitor. 2) Graphically determine the time constant for the decay, τ =.
TAP 126-4: Charging capacitors
 TAP 126-4: harging capacitors What to do Answer the questions. They develop a line of thought, so answering them in order is likely to help. uestions In an experiment a capacitor is charged from a constant
TAP 126-4: harging capacitors What to do Answer the questions. They develop a line of thought, so answering them in order is likely to help. uestions In an experiment a capacitor is charged from a constant
An Optimised High Current Impulse Source
 An Optimised High Current Impulse Source S. Kempen, D. Peier Institute of High Voltage Engineering, University of Dortmund, Germany Abstract Starting from a predefined 8/0 µs impulse current, the design
An Optimised High Current Impulse Source S. Kempen, D. Peier Institute of High Voltage Engineering, University of Dortmund, Germany Abstract Starting from a predefined 8/0 µs impulse current, the design
Class #12: Experiment The Exponential Function in Circuits, Pt 1
 Class #12: Experiment The Exponential Function in Circuits, Pt 1 Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to begin to become familiar with the properties and uses of the exponential function in circuits
Class #12: Experiment The Exponential Function in Circuits, Pt 1 Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to begin to become familiar with the properties and uses of the exponential function in circuits
Capacitor in the AC circuit with Cobra3
 Capacitor in the AC circuit with Cobra3 LEP Related Topics Capacitance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, AC impedance, Phase displacement Principle A capacitor is connected in a circuit with a variable-frequency
Capacitor in the AC circuit with Cobra3 LEP Related Topics Capacitance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, AC impedance, Phase displacement Principle A capacitor is connected in a circuit with a variable-frequency
( ) ( ) = q o. T 12 = τ ln 2. RC Circuits. 1 e t τ. q t
 Objectives: To explore the charging and discharging cycles of RC circuits with differing amounts of resistance and/or capacitance.. Reading: Resnick, Halliday & Walker, 8th Ed. Section. 27-9 Apparatus:
Objectives: To explore the charging and discharging cycles of RC circuits with differing amounts of resistance and/or capacitance.. Reading: Resnick, Halliday & Walker, 8th Ed. Section. 27-9 Apparatus:
Laboratory manual : RC circuit
 THE UNIVESITY OF HONG KONG Department of Physics PHYS55 Introductory electricity and magnetism Laboratory manual 55-: C circuit In this laboratory session, CO is used to investigate various properties
THE UNIVESITY OF HONG KONG Department of Physics PHYS55 Introductory electricity and magnetism Laboratory manual 55-: C circuit In this laboratory session, CO is used to investigate various properties
RLC Circuits. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Undriven Systems. 1.2 Driven Systems
 RLC Circuits Equipment: Capstone, 850 interface, RLC circuit board, 4 leads (91 cm), 3 voltage sensors, Fluke mulitmeter, and BNC connector on one end and banana plugs on the other Reading: Review AC circuits
RLC Circuits Equipment: Capstone, 850 interface, RLC circuit board, 4 leads (91 cm), 3 voltage sensors, Fluke mulitmeter, and BNC connector on one end and banana plugs on the other Reading: Review AC circuits
2005 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 2005 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM In the circuit shown above, resistors 1 and 2 of resistance R 1 and R 2, respectively, and an inductor of inductance L are connected to a battery of emf e and
2005 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM In the circuit shown above, resistors 1 and 2 of resistance R 1 and R 2, respectively, and an inductor of inductance L are connected to a battery of emf e and
Switch. R 5 V Capacitor. ower upply. Voltmete. Goals. Introduction
 Switch Lab 9. Circuits ower upply Goals + + R 5 V Capacitor V To appreciate the capacitor as a charge storage device. To measure the voltage across a capacitor as it discharges through a resistor, and
Switch Lab 9. Circuits ower upply Goals + + R 5 V Capacitor V To appreciate the capacitor as a charge storage device. To measure the voltage across a capacitor as it discharges through a resistor, and
ECE 241L Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering. Experiment 5 Transient Response
 ECE 241L Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Experiment 5 Transient Response NAME PARTNER A. Objectives: I. Learn how to use the function generator and oscilloscope II. Measure step response of RC and
ECE 241L Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Experiment 5 Transient Response NAME PARTNER A. Objectives: I. Learn how to use the function generator and oscilloscope II. Measure step response of RC and
Exercise 4 Modeling transient currents and voltages
 Exercise 4 Modeling transient currents and voltages Basic A circuit elements In a D circuit, the electro-motive forces push the electrons along the circuit and resistors remove that energy by conversion
Exercise 4 Modeling transient currents and voltages Basic A circuit elements In a D circuit, the electro-motive forces push the electrons along the circuit and resistors remove that energy by conversion
RLC Series Circuit. We can define effective resistances for capacitors and inductors: 1 = Capacitive reactance:
 RLC Series Circuit In this exercise you will investigate the effects of changing inductance, capacitance, resistance, and frequency on an RLC series AC circuit. We can define effective resistances for
RLC Series Circuit In this exercise you will investigate the effects of changing inductance, capacitance, resistance, and frequency on an RLC series AC circuit. We can define effective resistances for
Name:... Section:... Physics 208 Quiz 8. April 11, 2008; due April 18, 2008
 Name:... Section:... Problem 1 (6 Points) Physics 8 Quiz 8 April 11, 8; due April 18, 8 Consider the AC circuit consisting of an AC voltage in series with a coil of self-inductance,, and a capacitor of
Name:... Section:... Problem 1 (6 Points) Physics 8 Quiz 8 April 11, 8; due April 18, 8 Consider the AC circuit consisting of an AC voltage in series with a coil of self-inductance,, and a capacitor of
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Prepare for this experiment!
 Notes on Experiment #8 Theorems of Linear Networks Prepare for this experiment! If you prepare, you can finish in 90 minutes. If you do not prepare, you will not finish even half of this experiment. So,
Notes on Experiment #8 Theorems of Linear Networks Prepare for this experiment! If you prepare, you can finish in 90 minutes. If you do not prepare, you will not finish even half of this experiment. So,
RC Circuit (Power amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 Object: RC Circuit (Power amplifier, Voltage Sensor) To investigate how the voltage across a capacitor varies as it charges and to find its capacitive time constant. Apparatus: Science Workshop, Power
Object: RC Circuit (Power amplifier, Voltage Sensor) To investigate how the voltage across a capacitor varies as it charges and to find its capacitive time constant. Apparatus: Science Workshop, Power
Laboratory 7: Charging and Discharging a Capacitor Prelab
 Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 7: Charging and Discharging a Capacitor Prelab Consider a capacitor with capacitance C connected in series to a resistor with resistance R as shown in Fig. 1. Theory predicts
Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 7: Charging and Discharging a Capacitor Prelab Consider a capacitor with capacitance C connected in series to a resistor with resistance R as shown in Fig. 1. Theory predicts
Lab #4 Capacitors and Inductors. Capacitor Transient and Steady State Response
 Capacitor Transient and Steady State Response Like resistors, capacitors are also basic circuit elements. Capacitors come in a seemingly endless variety of shapes and sizes, and they can all be represented
Capacitor Transient and Steady State Response Like resistors, capacitors are also basic circuit elements. Capacitors come in a seemingly endless variety of shapes and sizes, and they can all be represented
Name: Lab Partner: Section:
 Chapter 6 Capacitors and RC Circuits Name: Lab Partner: Section: 6.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to investigate the physics of capacitors in circuits. The charging and discharging of a capacitor
Chapter 6 Capacitors and RC Circuits Name: Lab Partner: Section: 6.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to investigate the physics of capacitors in circuits. The charging and discharging of a capacitor
On the axes of Fig. 4.1, carefully sketch a graph to show how the potential difference V across the capacitor varies with time t. Label this graph L.
 1 (a) A charged capacitor is connected across the ends of a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor kept at a fixed temperature. The capacitor discharges through the thermistor. The potential
1 (a) A charged capacitor is connected across the ends of a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor kept at a fixed temperature. The capacitor discharges through the thermistor. The potential
Assessment Schedule 2015 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of electrical systems (91526)
 NCEA Level 3 Physics (91526) 2015 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2015 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of electrical systems (91526) Evidence Q Evidence Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement
NCEA Level 3 Physics (91526) 2015 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2015 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of electrical systems (91526) Evidence Q Evidence Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement
RC Circuit Lab - Discovery PSI Physics Capacitors and Resistors
 1 RC Circuit Lab - Discovery PSI Physics Capacitors and Resistors Name Date Period Purpose The purpose of this lab will be to determine how capacitors behave in R-C circuits. The manner in which capacitors
1 RC Circuit Lab - Discovery PSI Physics Capacitors and Resistors Name Date Period Purpose The purpose of this lab will be to determine how capacitors behave in R-C circuits. The manner in which capacitors
Experiment Guide for RC Circuits
 Guide-P1 Experiment Guide for RC Circuits I. Introduction 1. Capacitors A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field. The unit of capacitance is
Guide-P1 Experiment Guide for RC Circuits I. Introduction 1. Capacitors A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field. The unit of capacitance is
HOMEWORK 4: MATH 265: SOLUTIONS. y p = cos(ω 0t) 9 ω 2 0
 HOMEWORK 4: MATH 265: SOLUTIONS. Find the solution to the initial value problems y + 9y = cos(ωt) with y(0) = 0, y (0) = 0 (account for all ω > 0). Draw a plot of the solution when ω = and when ω = 3.
HOMEWORK 4: MATH 265: SOLUTIONS. Find the solution to the initial value problems y + 9y = cos(ωt) with y(0) = 0, y (0) = 0 (account for all ω > 0). Draw a plot of the solution when ω = and when ω = 3.
Inductance. Slide 2 / 26. Slide 1 / 26. Slide 4 / 26. Slide 3 / 26. Slide 6 / 26. Slide 5 / 26. Mutual Inductance. Mutual Inductance.
 Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
RC, RL, and LCR Circuits
 RC, RL, and LCR Circuits EK307 Lab Note: This is a two week lab. Most students complete part A in week one and part B in week two. Introduction: Inductors and capacitors are energy storage devices. They
RC, RL, and LCR Circuits EK307 Lab Note: This is a two week lab. Most students complete part A in week one and part B in week two. Introduction: Inductors and capacitors are energy storage devices. They
Core Technology Group Application Note 3 AN-3
 Measuring Capacitor Impedance and ESR. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In power system design, capacitors are used extensively for improving noise rejection, lowering power system impedance and power supply
Measuring Capacitor Impedance and ESR. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In power system design, capacitors are used extensively for improving noise rejection, lowering power system impedance and power supply
Physics 4B Chapter 31: Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current
 Physics 4B Chapter 31: Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current People of mediocre ability sometimes achieve outstanding success because they don't know when to quit. Most men succeed because
Physics 4B Chapter 31: Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current People of mediocre ability sometimes achieve outstanding success because they don't know when to quit. Most men succeed because
Capacitors. Example 1
 Physics 30AP Resistors and apacitors I apacitors A capacitor is a device for storing electrical charge that consists of two conducting objects placed near one another but not touching. A A typical capacitor
Physics 30AP Resistors and apacitors I apacitors A capacitor is a device for storing electrical charge that consists of two conducting objects placed near one another but not touching. A A typical capacitor
 Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
Alternating Currents. The power is transmitted from a power house on high voltage ac because (a) Electric current travels faster at higher volts (b) It is more economical due to less power wastage (c)
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 35/Page 1
 PES 0 Spring 04, Spendier Lecture 35/Page Today: chapter 3 - LC circuits We have explored the basic physics of electric and magnetic fields and how energy can be stored in capacitors and inductors. We
PES 0 Spring 04, Spendier Lecture 35/Page Today: chapter 3 - LC circuits We have explored the basic physics of electric and magnetic fields and how energy can be stored in capacitors and inductors. We
Electricity and Light Pre Lab Questions
 Electricity and Light Pre Lab Questions The pre lab questions can be answered by reading the theory and procedure for the related lab. You are strongly encouraged to answers these questions on your own.
Electricity and Light Pre Lab Questions The pre lab questions can be answered by reading the theory and procedure for the related lab. You are strongly encouraged to answers these questions on your own.
Lab 5 AC Concepts and Measurements II: Capacitors and RC Time-Constant
 EE110 Laboratory Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Lab 5 AC Concepts and Measurements II: Capacitors and RC Time-Constant Capacitors Capacitors are devices that can store electric charge
EE110 Laboratory Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Lab 5 AC Concepts and Measurements II: Capacitors and RC Time-Constant Capacitors Capacitors are devices that can store electric charge
Version 001 CIRCUITS holland (1290) 1
 Version CIRCUITS holland (9) This print-out should have questions Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering AP M 99 MC points The power dissipated
Version CIRCUITS holland (9) This print-out should have questions Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering AP M 99 MC points The power dissipated
Physics 401 Classical Physics Laboratory. Experiment 5. Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits. I. Introduction II. Theory...
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Physics 401 Classical Physics Laboratory Department of Physics Experiment 5 Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits I. Introduction... II. Theory... 3 b 0
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Physics 401 Classical Physics Laboratory Department of Physics Experiment 5 Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits I. Introduction... II. Theory... 3 b 0
PHYSICS 171 UNIVERSITY PHYSICS LAB II. Experiment 6. Transient Response of An RC Circuit
 PHYSICS 171 UNIVERSITY PHYSICS LAB II Experiment 6 Transient Response of An RC Circuit Equipment: Supplies: Function Generator, Dual Trace Oscilloscope.002 Microfarad, 0.1 Microfarad capacitors; 1 Kilohm,
PHYSICS 171 UNIVERSITY PHYSICS LAB II Experiment 6 Transient Response of An RC Circuit Equipment: Supplies: Function Generator, Dual Trace Oscilloscope.002 Microfarad, 0.1 Microfarad capacitors; 1 Kilohm,
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits
 Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
RC Circuits. Equipment: Capstone with 850 interface, RLC circuit board, 2 voltage sensors (no alligator clips), 3 leads V C = 1
 R ircuits Equipment: apstone with 850 interface, RL circuit board, 2 voltage sensors (no alligator clips), 3 leads 1 Introduction The 3 basic linear circuits elements are the resistor, the capacitor, and
R ircuits Equipment: apstone with 850 interface, RL circuit board, 2 voltage sensors (no alligator clips), 3 leads 1 Introduction The 3 basic linear circuits elements are the resistor, the capacitor, and
The RC Time Constant
 The RC Time Constant Objectives When a direct-current source of emf is suddenly placed in series with a capacitor and a resistor, there is current in the circuit for whatever time it takes to fully charge
The RC Time Constant Objectives When a direct-current source of emf is suddenly placed in series with a capacitor and a resistor, there is current in the circuit for whatever time it takes to fully charge
ENERGY AND TIME CONSTANTS IN RC CIRCUITS By: Iwana Loveu Student No Lab Section: 0003 Date: February 8, 2004
 ENERGY AND TIME CONSTANTS IN RC CIRCUITS By: Iwana Loveu Student No. 416 614 5543 Lab Section: 0003 Date: February 8, 2004 Abstract: Two charged conductors consisting of equal and opposite charges forms
ENERGY AND TIME CONSTANTS IN RC CIRCUITS By: Iwana Loveu Student No. 416 614 5543 Lab Section: 0003 Date: February 8, 2004 Abstract: Two charged conductors consisting of equal and opposite charges forms
Figure 1: Capacitor circuit
 Capacitors INTRODUCTION The basic function of a capacitor 1 is to store charge and thereby electrical energy. This energy can be retrieved at a later time for a variety of uses. Often, multiple capacitors
Capacitors INTRODUCTION The basic function of a capacitor 1 is to store charge and thereby electrical energy. This energy can be retrieved at a later time for a variety of uses. Often, multiple capacitors
AC analysis. EE 201 AC analysis 1
 AC analysis Now we turn to circuits with sinusoidal sources. Earlier, we had a brief look at sinusoids, but now we will add in capacitors and inductors, making the story much more interesting. What are
AC analysis Now we turn to circuits with sinusoidal sources. Earlier, we had a brief look at sinusoids, but now we will add in capacitors and inductors, making the story much more interesting. What are
PROBLEMS FOR EXPERIMENT ES: ESTIMATING A SECOND Solutions
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department 801X Fall 2002 PROBLEMS FOR EXPERIMENT ES: ESTIMATING A SECOND Solutions Problem 1: Use your calculator or your favorite software program to compute
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department 801X Fall 2002 PROBLEMS FOR EXPERIMENT ES: ESTIMATING A SECOND Solutions Problem 1: Use your calculator or your favorite software program to compute
(d) describe the action of a 555 monostable timer and then use the equation T = 1.1 RC, where T is the pulse duration
 Chapter 1 - Timing Circuits GCSE Electronics Component 2: Application of Electronics Timing Circuits Learners should be able to: (a) describe how a RC network can produce a time delay (b) describe how
Chapter 1 - Timing Circuits GCSE Electronics Component 2: Application of Electronics Timing Circuits Learners should be able to: (a) describe how a RC network can produce a time delay (b) describe how
Lab 5 RC Circuits. What You Need To Know: Physics 212 Lab
 Lab 5 R ircuits What You Need To Know: The Physics In the previous two labs you ve dealt strictly with resistors. In today s lab you ll be using a new circuit element called a capacitor. A capacitor consists
Lab 5 R ircuits What You Need To Know: The Physics In the previous two labs you ve dealt strictly with resistors. In today s lab you ll be using a new circuit element called a capacitor. A capacitor consists
As light level increases, resistance decreases. As temperature increases, resistance decreases. Voltage across capacitor increases with time LDR
 LDR As light level increases, resistance decreases thermistor As temperature increases, resistance decreases capacitor Voltage across capacitor increases with time Potential divider basics: R 1 1. Both
LDR As light level increases, resistance decreases thermistor As temperature increases, resistance decreases capacitor Voltage across capacitor increases with time Potential divider basics: R 1 1. Both
first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date)
 (ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 1 Capacitance In this Experiment you will learn the relationship between the voltage and charge stored on a capacitor;
(ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 1 Capacitance In this Experiment you will learn the relationship between the voltage and charge stored on a capacitor;
P441 Analytical Mechanics - I. RLC Circuits. c Alex R. Dzierba. In this note we discuss electrical oscillating circuits: undamped, damped and driven.
 Lecture 10 Monday - September 19, 005 Written or last updated: September 19, 005 P441 Analytical Mechanics - I RLC Circuits c Alex R. Dzierba Introduction In this note we discuss electrical oscillating
Lecture 10 Monday - September 19, 005 Written or last updated: September 19, 005 P441 Analytical Mechanics - I RLC Circuits c Alex R. Dzierba Introduction In this note we discuss electrical oscillating
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE
 EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 14 121011 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review Steady-State Analysis RC Circuits RL Circuits 3 DC Steady-State
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 14 121011 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review Steady-State Analysis RC Circuits RL Circuits 3 DC Steady-State
RC Studies Relaxation Oscillator
 RC Studies Relaxation Oscillator Introduction A glass tube containing neon gas will give off its characteristic light when the voltage across the tube exceeds a certain value. The value corresponds to
RC Studies Relaxation Oscillator Introduction A glass tube containing neon gas will give off its characteristic light when the voltage across the tube exceeds a certain value. The value corresponds to
Practical 1 RC Circuits
 Objectives Practical 1 Circuits 1) Observe and qualitatively describe the charging and discharging (decay) of the voltage on a capacitor. 2) Graphically determine the time constant for the decay, τ =.
Objectives Practical 1 Circuits 1) Observe and qualitatively describe the charging and discharging (decay) of the voltage on a capacitor. 2) Graphically determine the time constant for the decay, τ =.
Lecture 15. LC Circuit. LC Oscillation - Qualitative. LC Oscillator
 Lecture 5 Phys. 07: Waves and Light Physics Department Yarmouk University 63 Irbid Jordan &KDSWHUElectromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent L ircuit In this chapter you will see how the electric
Lecture 5 Phys. 07: Waves and Light Physics Department Yarmouk University 63 Irbid Jordan &KDSWHUElectromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating urrent L ircuit In this chapter you will see how the electric
Industrial Technology: Electronic Technology Crosswalk to AZ Math Standards
 Page 1 of 1 August 1998 1M-P1 Compare and contrast the real number system and its various subsystems with regard to their structural characteristics. PO 2 PO 3 2.0 Apply mathematics calculations. 2.1 Apply
Page 1 of 1 August 1998 1M-P1 Compare and contrast the real number system and its various subsystems with regard to their structural characteristics. PO 2 PO 3 2.0 Apply mathematics calculations. 2.1 Apply
Laboratory 3 Measuring Capacitor Discharge with the MicroBLIP
 Laboratory 3 page 1 of 6 Laboratory 3 Measuring Capacitor Discharge with the MicroBLIP Introduction In this lab, you will use the MicroBLIP in its Data Acquisition Mode to sample the voltage over time
Laboratory 3 page 1 of 6 Laboratory 3 Measuring Capacitor Discharge with the MicroBLIP Introduction In this lab, you will use the MicroBLIP in its Data Acquisition Mode to sample the voltage over time
Physics 212 Midterm 2 Form A
 1. A wire contains a steady current of 2 A. The charge that passes a cross section in 2 s is: A. 3.2 10-19 C B. 6.4 10-19 C C. 1 C D. 2 C E. 4 C 2. In a Physics 212 lab, Jane measures the current versus
1. A wire contains a steady current of 2 A. The charge that passes a cross section in 2 s is: A. 3.2 10-19 C B. 6.4 10-19 C C. 1 C D. 2 C E. 4 C 2. In a Physics 212 lab, Jane measures the current versus
2.4 Models of Oscillation
 2.4 Models of Oscillation In this section we give three examples of oscillating physical systems that can be modeled by the harmonic oscillator equation. Such models are ubiquitous in physics, but are
2.4 Models of Oscillation In this section we give three examples of oscillating physical systems that can be modeled by the harmonic oscillator equation. Such models are ubiquitous in physics, but are
Electric Circuits Fall 2015 Solution #5
 RULES: Please try to work on your own. Discussion is permissible, but identical submissions are unacceptable! Please show all intermeate steps: a correct solution without an explanation will get zero cret.
RULES: Please try to work on your own. Discussion is permissible, but identical submissions are unacceptable! Please show all intermeate steps: a correct solution without an explanation will get zero cret.
Chapter 26 Direct-Current Circuits
 Chapter 26 Direct-Current Circuits 1 Resistors in Series and Parallel In this chapter we introduce the reduction of resistor networks into an equivalent resistor R eq. We also develop a method for analyzing
Chapter 26 Direct-Current Circuits 1 Resistors in Series and Parallel In this chapter we introduce the reduction of resistor networks into an equivalent resistor R eq. We also develop a method for analyzing
RC & RL Transient Response
 EE 2006 University of Minnesota Duluth ab 8 1. Introduction R & R Transient Response The student will analyze series R and R circuits. A step input will excite these respective circuits, producing a transient
EE 2006 University of Minnesota Duluth ab 8 1. Introduction R & R Transient Response The student will analyze series R and R circuits. A step input will excite these respective circuits, producing a transient
Capacitance Measurement
 Overview The goal of this two-week laboratory is to develop a procedure to accurately measure a capacitance. In the first lab session, you will explore methods to measure capacitance, and their uncertainties.
Overview The goal of this two-week laboratory is to develop a procedure to accurately measure a capacitance. In the first lab session, you will explore methods to measure capacitance, and their uncertainties.
Lab 10: DC RC circuits
 Name: Lab 10: DC RC circuits Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Objectives: 1. To understand current and voltage characteristics of a DC RC circuit 2. To understand the effect of the RC time constant Apparatus:
Name: Lab 10: DC RC circuits Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Objectives: 1. To understand current and voltage characteristics of a DC RC circuit 2. To understand the effect of the RC time constant Apparatus:
