Say Kids, What Time Is It?
|
|
|
- Maria Rogers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Say Kids, What Time Is It? David Malone Thu Apr 19 19:30:00 BST
2 Time What is time all about? second: In the International System of Units (SI), the time interval equal to 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium-133 atom. For scientists that s usually as far as it goes, but what do ordinary people make of time? 2
3 It s that incredibly useful stuff that we all use to stop every thing happening at once. Jeff Rosson Mostly time is used for ordering our lives, not measuring how long has passed between events. I want to look at this while avoiding the profound issues. If a job application must be in by 5pm, how do you know when that is? 3
4 Time In Ireland 1880 GMT in England, DMT in Ireland 1916 assimilated with GB 1925 Western-European Time (minister of justice) 1968 Standard Time (GMT+1) 1971 Changed mind 1986 Order giving effect to EEC directive 1997 EU directive currently in force All in terms of GMT. What is GMT? 4
5 GMT Greenwich Mean Time: Mean solar time at the Greenwich Meridian. Note the word solar days are related to the sun! GMT used to be measured from noon (00:00GMT) to noon. In 1925 they moved to starting the clock at mid-night. 5
6 Universal Times Sidereal Time is measured against a point in the sky, the catalog equinox. You can find out the local sidereal time by measuring where a star is in the sky and then looking it up in a catalog. The sun isn t important here. Universal Time is calculated from sidereal time using a formula T T 2 (A day is usually long). 6
7 TAI and UTC International Atomic Time has been available since 1955 officially since 1972). Uses SI second. Problem is that UT seconds and SI seconds are different. Coordinated Universal Time is a compromise. It ticks once per SI second, in sync with TAI. If UTC is more than one second from UT1 then a leap second is introduced. 7
8 Years Days are kept in sync with sunrise. Years are kept in sync with seasons. The time of year: angle between earth s axis and the line from the earth to the sun. NB: seasons nothing to do with distance to sun. Earth is at it s closest about 2 nd January. Current aim of our calendar: Keep the vernial equinox near 21 st March. 8
9 The length of the year isn t a whole number of days ( ), which causes complications. When Calendar Length???? old roman 45BC Julian AD Gregorian It s hard to get the length right when you can t write it down. 9
10 Counting Years We now count years from the (supposed) birth of Christ. Dionysius Exiguus (AD 523) was asked to produce table of Easter Dates. Unfortunately, Herod died in 4BC, so Dionysius probably got it wrong. BC dating came somewhat later, along with the missing year zero. Before that dates were counted since the founding of Rome. 1AD = 754AUC (ab urbe condita). 10
11 Hours, Minutes and Seconds Pretty arbitrary divisions of a day. They arise by dividing things into 12 and
12 Weeks and Months 7 day week is very old. Used by Romans and Jews (independently?). English French Planet Monday lundi Moon Tuesday mardi Mars Wednesday mercredi Mercury Thursday jeudi Jupiter Friday vendredi Venus Saturday samedi Saturn Sunday dimanche (Sun) Months were probably supposed to keep in sync with the moon ( days). Some other calendars are much better in this respect. 12
13 Easter Easter Sunday is the first Sunday after the first full moon after vernal equinox. But which full moon and which equinox? G = Y mod 19 C = Y 100 H = (C C 4 8 C G + 15) 25 mod 30 I = H H 28 (1 H H G ) 11 J = (Y + Y 4 + I + 2 C + C 4 ) mod 7 L = I J Month = 3 + L Day = L EasterMonth 4 G is the Golden Number, H is Epact. 13
14 Julian Day Number Another way of counting days avoiding BC/AD problems. It is a cycle of 7980 years. JD 0 designates the 24 hours from noon UTC on 1 January 4713 BC to noon UTC on 2 January 4713 BC. Today is Julian Day or MJD Why start then? Why 7980 years? A combination of Indiction, Golden Number and Solar Number (15*19*28=7980). 14
15 Friday the Thirteenth Solar Number counts what part of the 28 year year/weekday cycle we are in for the Julian Calendar. lcm( , 7) = 28years What about the Gregorian Calendar? lcm( , 7) = 400years So there is room for bias! Sunday 687 Monday 685 Tuesday 685 Wednesday 687 Thursday 684 Friday 688 Saturday
16 Daylight Saving Introduced in 1916 to save energy during the war. Double summer time was used during the second world war. Now EC uses last Sunday in March/October. Americans use first Sunday of April and last of October. EU report covering agriculture, environment, energy, health, leisure, road safety, transport and communications. Seems to be quite an emotive issue. 16
17 Computers and Time Computers store time in various ways. Y2K thing was all about ways of storing time. Unix counts the number of UTC seconds since Thu Apr 19 05:25:21 BST Sun Sep 9 02:46:40 BST Tue Jan 19 03:14:07 GMT 2038 Counting is done in various ways: RTC chips, interrupts or special registers. Correct dates are important for sharing files, time-stamping events, certain crypto-protocols and charging people. 17
18 NTP The Network Time Protocol synchronises a computer to a source of UTC (either another computer or a clock). Works by building a tree of servers. Stratum 1 are connected directly to a clock, Stratum 2 are synchronised to a Stratum 1 over the network, Stratum 3 are synchronised to a Stratum 2,... It works by passing time-stamps back and forth across the network and slewing the clock. 18
19 remote st poll delay offset disp =rackety.udel.edu =LOCAL(1) auth1.auth.iol.ie web1.tcd.ie orca.ucd.ie *GPSNMEA(0) rizzo.esat.net =err.ee.ethz.ch burke.cs.tcd.ie salmon.maths.tcd.ie
20 Various ref-clocks are used: Rugby, GPS, Cesium clocks, dialup. One of the best things about NTP is the jargon: PLL, PPS, jitter, epochs, RTT, PPM, false-tickers, chime-heads. 20
Why is it 20:00:00, Wednesday 2 nd November 2011?
 Why is it 20:00:00, Wednesday 2 nd November 2011? David Malone Hamilton Institute, NUI Maynooth. School of Mathematics, TCD. 2011-11-02 20:00:00 GMT 2011: The Year Seasons: Weather
Why is it 20:00:00, Wednesday 2 nd November 2011? David Malone Hamilton Institute, NUI Maynooth. School of Mathematics, TCD. 2011-11-02 20:00:00 GMT 2011: The Year Seasons: Weather
Time in the Modern World
 Time in the Modern World David Malone Hamilton Institute, NUI Maynooth. School of Mathematics, TCD. 2006-01-24 18:30 UTC 1 What is time all about? It s that incredibly useful stuff
Time in the Modern World David Malone Hamilton Institute, NUI Maynooth. School of Mathematics, TCD. 2006-01-24 18:30 UTC 1 What is time all about? It s that incredibly useful stuff
Astronomy = Timekeeping
 Astronomy = Timekeeping Day, month, year Important for seasons - hunter gatherer Annual migrations Seasons important for farmers Heliacal rising of Sirius Important for navigation Longitude & GPS Important
Astronomy = Timekeeping Day, month, year Important for seasons - hunter gatherer Annual migrations Seasons important for farmers Heliacal rising of Sirius Important for navigation Longitude & GPS Important
Astronomy 291. Professor Bradley M. Peterson
 Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates
 PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates Astronomical Clocks Earth s Rotation on its Axis Time between two successive meridian transits of the sun 1 solar day (our adopted clock time) 24 hours (86,400
PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates Astronomical Clocks Earth s Rotation on its Axis Time between two successive meridian transits of the sun 1 solar day (our adopted clock time) 24 hours (86,400
Smalltalk 10/2/15. Dates. Brian Heinold
 Smalltalk 10/2/15 Dates Brian Heinold Leap years Leap years are every four years, right? Leap years Leap years are every four years, right? 2016, 2020, 2024, 2028,...,... Leap years Leap years are every
Smalltalk 10/2/15 Dates Brian Heinold Leap years Leap years are every four years, right? Leap years Leap years are every four years, right? 2016, 2020, 2024, 2028,...,... Leap years Leap years are every
Name: (This only happens every four years or does it?)
 Name: (This only happens every four years or does it?) Calendars: Then and Now Name: 1. What is a leap year? What do you already know about leap years? 2. List at least three questions about leap years
Name: (This only happens every four years or does it?) Calendars: Then and Now Name: 1. What is a leap year? What do you already know about leap years? 2. List at least three questions about leap years
DAILY QUESTIONS 28 TH JUNE 18 REASONING - CALENDAR
 DAILY QUESTIONS 28 TH JUNE 18 REASONING - CALENDAR LEAP AND NON-LEAP YEAR *A non-leap year has 365 days whereas a leap year has 366 days. (as February has 29 days). *Every year which is divisible by 4
DAILY QUESTIONS 28 TH JUNE 18 REASONING - CALENDAR LEAP AND NON-LEAP YEAR *A non-leap year has 365 days whereas a leap year has 366 days. (as February has 29 days). *Every year which is divisible by 4
Cartesian Coordinates Need two dimensional system 2 number lines perpendicular to each other X-axis is horizontal Y-axis is vertical Position relative
 General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky
 Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
Time, coordinates and how the Sun and Moon move in the sky Using the colors and magnitudes of quasars drawn from the SDSS Catalog Archive Server to distinguish quasars from stars using the light they emit
ASTR 1010 Astronomy of the Solar System. Course Info. Course Info. Fall 2006 Mon/Wed/Fri 11:00-11:50AM 430 Aderhold Learning Center
 ASTR 1010 Astronomy of the Solar System Fall 2006 Mon/Wed/Fri 11:00-11:50AM 430 Aderhold Learning Center Instructor: Wes Ryle Course Info In-class Activities/Quizzes (10%) 4 Homework Assignments (15%)
ASTR 1010 Astronomy of the Solar System Fall 2006 Mon/Wed/Fri 11:00-11:50AM 430 Aderhold Learning Center Instructor: Wes Ryle Course Info In-class Activities/Quizzes (10%) 4 Homework Assignments (15%)
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section II
 ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section II Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section II Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course.
 Licensed for Personal Use Only DO NOT DISTRIBUTE These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course. Distributing them in anyway will be considered a breach
Licensed for Personal Use Only DO NOT DISTRIBUTE These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course. Distributing them in anyway will be considered a breach
What Patterns Can Be Observed in a Year?
 LESSON 3 What Patterns Can Be Observed in a Year? From this vantage point, you can see the moon, sun, stars, and Earth. From Earth s surface, there are patterns to how the sun, moon, and stars appear in
LESSON 3 What Patterns Can Be Observed in a Year? From this vantage point, you can see the moon, sun, stars, and Earth. From Earth s surface, there are patterns to how the sun, moon, and stars appear in
Review of previous concepts!! Earth s orbit: Year, seasons, observed constellations, Polaris (North star), day/night lengths, equinoxes
 Review of previous concepts!! Earth s orbit: Year, seasons, observed constellations, Polaris (North star), day/night lengths, equinoxes Celestial poles, celestial equator, ecliptic, ecliptic plane (Fig
Review of previous concepts!! Earth s orbit: Year, seasons, observed constellations, Polaris (North star), day/night lengths, equinoxes Celestial poles, celestial equator, ecliptic, ecliptic plane (Fig
JANUARY MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY SATURDAY SUNDAY
 Vocabulary (01) The Calendar (012) In context: Look at the calendar. Then, answer the questions. JANUARY MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY SATURDAY SUNDAY 1 New 2 3 4 5 6 Year s Day 7 8 9 10 11
Vocabulary (01) The Calendar (012) In context: Look at the calendar. Then, answer the questions. JANUARY MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY SATURDAY SUNDAY 1 New 2 3 4 5 6 Year s Day 7 8 9 10 11
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION Heavenly Mathematics: Cultural Astronomy
 1 GEK1506 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2005 2006 GEK1506 Heavenly Mathematics: Cultural Astronomy April/May 2006 Time allowed: 2 hours 1. After taking
1 GEK1506 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2005 2006 GEK1506 Heavenly Mathematics: Cultural Astronomy April/May 2006 Time allowed: 2 hours 1. After taking
Time frames, leap seconds and GPS
 Time frames, leap seconds and GPS Andy Shearer Centre for Astronomy NUI, Galway How important is absolute timing accuracy... I How important is absolute timing accuracy... II important enough for particle
Time frames, leap seconds and GPS Andy Shearer Centre for Astronomy NUI, Galway How important is absolute timing accuracy... I How important is absolute timing accuracy... II important enough for particle
Astronomical Techniques I
 Astronomical Techniques I Lecture 1 Yogesh Wadadekar Jan-Feb 2015 IUCAA-NCRA Grad School 1 / 23 Course Website http://www.ncra.tifr.res.in:8081/ yogesh/astrotech1_2015/ Best way to reach me is by email
Astronomical Techniques I Lecture 1 Yogesh Wadadekar Jan-Feb 2015 IUCAA-NCRA Grad School 1 / 23 Course Website http://www.ncra.tifr.res.in:8081/ yogesh/astrotech1_2015/ Best way to reach me is by email
Did you Fall Back Today?
 Did you Fall Back Today? Yes this morning at 2AM Daylight Savings Time (DST) we switched to Standard Time (ST) and turned our clocks back 1 hour. Time is basically calculated based on Earth s rotation,
Did you Fall Back Today? Yes this morning at 2AM Daylight Savings Time (DST) we switched to Standard Time (ST) and turned our clocks back 1 hour. Time is basically calculated based on Earth s rotation,
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy
 PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
Chapter S1 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
Coordinates on the Sphere
 Survey Observations Coordinates on the Sphere Any position on the surface of a sphere (such as the Earth or the night sky) can be expressed in terms of the angular coordinates latitude and longitude Latitude
Survey Observations Coordinates on the Sphere Any position on the surface of a sphere (such as the Earth or the night sky) can be expressed in terms of the angular coordinates latitude and longitude Latitude
120 Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky
 120 Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky divisible by 400, were leap years. The average length of this Gregorian year, 365.2425 mean solar days, is correct to about 1 day in 3300 years. The Catholic countries
120 Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky divisible by 400, were leap years. The average length of this Gregorian year, 365.2425 mean solar days, is correct to about 1 day in 3300 years. The Catholic countries
SKYCAL - Sky Events Calendar
 SKYCAL - Sky Events Calendar Your web browser must have Javascript turned on. The following browsers have been successfully tested: Macintosh - Firefox 3.0 (Safari NOT supported) Windows - Firefox 3.0,
SKYCAL - Sky Events Calendar Your web browser must have Javascript turned on. The following browsers have been successfully tested: Macintosh - Firefox 3.0 (Safari NOT supported) Windows - Firefox 3.0,
UNIT 14 Time and Timetables Activities
 UNIT 14 Time and Timetables Activities Activities 14.1 Gregorian Calendar 14.2 Days of the Week 14.3 Easter Day 14.4 A Tour of Scotland Notes and Solutions (2 pages) ACTIVITY 14.1 Gregorian Calendar When
UNIT 14 Time and Timetables Activities Activities 14.1 Gregorian Calendar 14.2 Days of the Week 14.3 Easter Day 14.4 A Tour of Scotland Notes and Solutions (2 pages) ACTIVITY 14.1 Gregorian Calendar When
The Metonic Cycle Made Simple
 The Cycle Made Simple All calendars require some form of intercalation. This means that in order to keep the calendar months aligned with the correct seasons, additional time must occasionally be added.
The Cycle Made Simple All calendars require some form of intercalation. This means that in order to keep the calendar months aligned with the correct seasons, additional time must occasionally be added.
Astronomy Club of Asheville March 2018 Sky Events
 March 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Close Conjunction of Venus and Mercury page 5 The Crescent Moon Joins Venus and Mercury page 6 A Crescent Moon Pairs with Aldebaran page 7 Planet Highlights
March 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Close Conjunction of Venus and Mercury page 5 The Crescent Moon Joins Venus and Mercury page 6 A Crescent Moon Pairs with Aldebaran page 7 Planet Highlights
Passover Days CE
 Passover Days 28-35 CE 1. Introduction There have been various attempts over the years at producing calendars in modern formats for the year of the Crucifixion of the Messaiah. The accuracy of these is
Passover Days 28-35 CE 1. Introduction There have been various attempts over the years at producing calendars in modern formats for the year of the Crucifixion of the Messaiah. The accuracy of these is
Days of the week: - named after 7 Power (moving) objects in the sky (Sun, Moon, 5 planets) Models of the Universe:
 Motions of the Planets ( Wanderers ) Planets move on celestial sphere - change RA, Dec each night - five are visible to naked eye Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn Days of the week: - named after 7
Motions of the Planets ( Wanderers ) Planets move on celestial sphere - change RA, Dec each night - five are visible to naked eye Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn Days of the week: - named after 7
Earth & Beyond Teacher Newsletter
 Paul Floyd s Astronomy & Space Website Earth & Beyond Teacher Newsletter www.nightskyonline.info Earth & Beyond Teaching opportunities for 2012 This special edition has been prepared to assist you with
Paul Floyd s Astronomy & Space Website Earth & Beyond Teacher Newsletter www.nightskyonline.info Earth & Beyond Teaching opportunities for 2012 This special edition has been prepared to assist you with
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Using the Dark Times Calendars
 Using the Dark Times Calendars Purpose My main reason for creating the Dark Times Calendars was to show, in advance, the best times for deep space astronomical observing. If I want to plan a family vacation
Using the Dark Times Calendars Purpose My main reason for creating the Dark Times Calendars was to show, in advance, the best times for deep space astronomical observing. If I want to plan a family vacation
Discovering the Universe
 Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events have defined the cycles of human life They have inspired great religion stories The scientific revolution
Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events have defined the cycles of human life They have inspired great religion stories The scientific revolution
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Astronomy. Unit 2. The Moon
 Astronomy Unit 2 The Moon 1 Traveling on Spaceship Earth Although we imagine ourselves to be at rest, the Earth takes part in the motions outlined below. The Earth spins about its N-S axis, with a period
Astronomy Unit 2 The Moon 1 Traveling on Spaceship Earth Although we imagine ourselves to be at rest, the Earth takes part in the motions outlined below. The Earth spins about its N-S axis, with a period
4.4 The Calendar program
 4.4. THE CALENDAR PROGRAM 109 4.4 The Calendar program To illustrate the power of functions, in this section we will develop a useful program that allows the user to input a date or a month or a year.
4.4. THE CALENDAR PROGRAM 109 4.4 The Calendar program To illustrate the power of functions, in this section we will develop a useful program that allows the user to input a date or a month or a year.
The Earth, Moon, and Sky. Lecture 5 1/31/2017
 The Earth, Moon, and Sky Lecture 5 1/31/2017 From Last Time: Stable Orbits The type of orbit depends on the initial speed of the object Stable orbits are either circular or elliptical. Too slow and gravity
The Earth, Moon, and Sky Lecture 5 1/31/2017 From Last Time: Stable Orbits The type of orbit depends on the initial speed of the object Stable orbits are either circular or elliptical. Too slow and gravity
Key #
 4-3.8. 1. Which of the following instruments is used to directly observe objects in the sky? 4-3.1. 2. Earth is a rocky planet that resides close to the Sun. Recognize the list of planets below that has
4-3.8. 1. Which of the following instruments is used to directly observe objects in the sky? 4-3.1. 2. Earth is a rocky planet that resides close to the Sun. Recognize the list of planets below that has
LETTER TO FAMILY. Science News. Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Family,
 LETTER TO FAMILY Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Family, Science News We are about to begin a study of objects in the sky the Sun, Moon, and planets. We ll start with
LETTER TO FAMILY Cut here and paste onto school letterhead before making copies. Dear Family, Science News We are about to begin a study of objects in the sky the Sun, Moon, and planets. We ll start with
2. Knowing the Heavens
 2. Knowing the Heavens Ancient naked-eye astronomy Eighty-eight constellations The sky s ever-changing appearance The celestial sphere Celestial coordinates Seasons: Earth s axial tilt Precession of Earth
2. Knowing the Heavens Ancient naked-eye astronomy Eighty-eight constellations The sky s ever-changing appearance The celestial sphere Celestial coordinates Seasons: Earth s axial tilt Precession of Earth
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Review of Monday s Class Spherical Trigonometry Review plane trigonometry Concepts in Spherical Trigonometry Distance measures Azimuths and bearings Basic formulas:
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Review of Monday s Class Spherical Trigonometry Review plane trigonometry Concepts in Spherical Trigonometry Distance measures Azimuths and bearings Basic formulas:
Astronomical Events 2019 (edited somewhat) from:
 Astronomical Events 2019 (edited somewhat) from: http://astropixels.com/ephemeris/astrocal/astrocal2019gmt.html January Note: Time column is UT, subtract 5 hours for local EST, 4 hours for DST Jan 1 to
Astronomical Events 2019 (edited somewhat) from: http://astropixels.com/ephemeris/astrocal/astrocal2019gmt.html January Note: Time column is UT, subtract 5 hours for local EST, 4 hours for DST Jan 1 to
Homework Assignment #9: Apparent Motions of the Heavens Due to Actual Motions of Earth
 Name Homework Assignment #9: Apparent Motions of the Heavens Due to Actual Motions of Earth 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico
Name Homework Assignment #9: Apparent Motions of the Heavens Due to Actual Motions of Earth 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation. How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?
 Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
ASTROLOGY CALENDAR 2018
 ASTROLOGY CALENDAR 2018 www.sarahsastrology.com Email: sarahsastrology@googlemail.com Twitter @sarahsastro Google+ sarahsastrology Facebook www.facebook.com/sarahsastrology Linkedin Sarah Cochrane Pinterest
ASTROLOGY CALENDAR 2018 www.sarahsastrology.com Email: sarahsastrology@googlemail.com Twitter @sarahsastro Google+ sarahsastrology Facebook www.facebook.com/sarahsastrology Linkedin Sarah Cochrane Pinterest
Geometry of Earth Sun System
 12S56 Geometry of Earth Sun System Figure below shows the basic geometry Northern Hemisphere Winter ω equator Earth s Orbit Ecliptic ω ω SUN equator Northern Hemisphere Spring Northern Hemisphere Fall
12S56 Geometry of Earth Sun System Figure below shows the basic geometry Northern Hemisphere Winter ω equator Earth s Orbit Ecliptic ω ω SUN equator Northern Hemisphere Spring Northern Hemisphere Fall
ASTR 101L: Motion of the Sun Take Home Lab
 Name: CWID: Section: Introduction Objectives This lab is designed to help you understand the Sun s apparent motion in the sky over the course of the year. In Section 2 you are asked to answer some questions
Name: CWID: Section: Introduction Objectives This lab is designed to help you understand the Sun s apparent motion in the sky over the course of the year. In Section 2 you are asked to answer some questions
UNIVERSAL CONSCIOUS CALENDARS 2017
 UNIVERSAL CONSCIOUS CALENDARS 2017 WHAT DO THE COLORS MEAN? Green Days are Go Days: Commerce, marketing and sales Launches in general Sending newsletters and communications Teaching classes Hosting events
UNIVERSAL CONSCIOUS CALENDARS 2017 WHAT DO THE COLORS MEAN? Green Days are Go Days: Commerce, marketing and sales Launches in general Sending newsletters and communications Teaching classes Hosting events
STANDARD. S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position.
 STANDARD S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. S6E2 b. Explain the alignment of the earth, moon, and sun during solar and lunar eclipses. c. Relate the
STANDARD S6E1 d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. S6E2 b. Explain the alignment of the earth, moon, and sun during solar and lunar eclipses. c. Relate the
The Earth Orbits the Sun Student Question Sheet (Advanced)
 The Earth Orbits the Sun Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge
The Earth Orbits the Sun Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge
Time Zones. Doug Fischer Geog 106 LRS
 Time Zones Doug Fischer Geog 106 LRS Learning goals Students should be able to Explain time zones as a function of longitude Calculate time differences between different locations Demonstrate corrections
Time Zones Doug Fischer Geog 106 LRS Learning goals Students should be able to Explain time zones as a function of longitude Calculate time differences between different locations Demonstrate corrections
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 5 The Motion of the Earth and Moon Time, Precession, Eclipses, Tides
 Observational Astronomy - Lecture 5 The Motion of the Earth and Moon Time, Precession, Eclipses, Tides Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu March 2, 2014 1 / 29 Geosynchronous
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 5 The Motion of the Earth and Moon Time, Precession, Eclipses, Tides Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu March 2, 2014 1 / 29 Geosynchronous
Phases and Motions of the Moon *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m59788 1 Phases and Motions of the Moon * OpenStax Astronomy This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Learning Objectives
OpenStax-CNX module: m59788 1 Phases and Motions of the Moon * OpenStax Astronomy This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Learning Objectives
TIME. Astronomical time Time is defined by astronomical cycles. The day is the average time from noon to noon (the solar day).
 ASTRONOMY READER TIME 2.1 TIME Astronomical time Time is defined by astronomical cycles. The day is the average time from noon to noon (the solar day). The month was originally based on the average time
ASTRONOMY READER TIME 2.1 TIME Astronomical time Time is defined by astronomical cycles. The day is the average time from noon to noon (the solar day). The month was originally based on the average time
Griffith Observatory Field Trip Guide
 To enter the Griffith Observatory you must make a reservation for a seat on a shuttle. There is a cost associated with each shuttle ticket and it is $8.00. There is no other way to enter Griffith Observatory!
To enter the Griffith Observatory you must make a reservation for a seat on a shuttle. There is a cost associated with each shuttle ticket and it is $8.00. There is no other way to enter Griffith Observatory!
John Conway s Doomsday Algorithm
 1 The algorithm as a poem John Conway s Doomsday Algorithm John Conway introduced the Doomsday Algorithm with the following rhyme: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 The last of Feb., or of Jan. will do
1 The algorithm as a poem John Conway s Doomsday Algorithm John Conway introduced the Doomsday Algorithm with the following rhyme: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 The last of Feb., or of Jan. will do
Discovering the Universe
 Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events day and night, seasons -- have defined the rhythms of human life They have inspired great myths and
Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events day and night, seasons -- have defined the rhythms of human life They have inspired great myths and
Discovering the Universe
 Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events day and night, seasons -- have defined the rhythms of human life They have inspired great myths and
Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events day and night, seasons -- have defined the rhythms of human life They have inspired great myths and
4thscience_earth (4thscience_earth)
 Name: Date: 1. The temperature at noon for the last week is shown in the graph. Which day had a lower temperature than Tuesday? A. Monday B. Wednesday C. Thursday D. Saturday 2. Which instrument would
Name: Date: 1. The temperature at noon for the last week is shown in the graph. Which day had a lower temperature than Tuesday? A. Monday B. Wednesday C. Thursday D. Saturday 2. Which instrument would
Discovering the Universe
 Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events define the rhythms of human life and have inspired myths and religion stories Attempts to explain astronomical
Discovering the Universe Astronomy and human culture have always been intertwined Astronomical events define the rhythms of human life and have inspired myths and religion stories Attempts to explain astronomical
TIME & FREQUENCY. Overview from artefact to current definition & Realisation UTC. Frank Coutereel.
 TIME & FREQUENCY Overview from artefact to current definition & Realisation UTC Frank Coutereel Legal Time in Belgium Past: based on GMT or UT (observations in sky) Today: based on UTC (working atomic
TIME & FREQUENCY Overview from artefact to current definition & Realisation UTC Frank Coutereel Legal Time in Belgium Past: based on GMT or UT (observations in sky) Today: based on UTC (working atomic
These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course.
 Licensed for Personal Use Only DO NOT DISTRIBUTE These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course. Distributing them in anyway will be considered a breach
Licensed for Personal Use Only DO NOT DISTRIBUTE These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course. Distributing them in anyway will be considered a breach
Before Reading. Practice. wave. east. west. A. Fill in the blanks using the word list. west east tired wave pull shines. The Lazy Moon.
 Before Reading Practice A. Fill in the blanks using the word list. west east tired wave pull shines wave Pull shines tired east west The Lazy Moon 1 B. Circle the right word. 1. She just (sit, sat) in
Before Reading Practice A. Fill in the blanks using the word list. west east tired wave pull shines wave Pull shines tired east west The Lazy Moon 1 B. Circle the right word. 1. She just (sit, sat) in
HNRS 227 Fall 2007 Chapter 14. Earth in Space presented by Prof. Geller 25 October 2007
 HNRS 227 Fall 2007 Chapter 14 Earth in Space presented by Prof. Geller 25 October 2007 Key Points of Chapter 14 Shape, Size and Motions of the Earth Rotation and Revolution Precession Coordinate Systems
HNRS 227 Fall 2007 Chapter 14 Earth in Space presented by Prof. Geller 25 October 2007 Key Points of Chapter 14 Shape, Size and Motions of the Earth Rotation and Revolution Precession Coordinate Systems
Astronomy Club of Asheville April 2017 Sky Events
 April 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 April 6 th - Regulus and the Gibbous Moon page 5 April 10 th -The Full Moon Joins Jupiter and Spica page 6 Planet Highlights page 7 Moon Phases page
April 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 April 6 th - Regulus and the Gibbous Moon page 5 April 10 th -The Full Moon Joins Jupiter and Spica page 6 Planet Highlights page 7 Moon Phases page
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture.
 Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Syllabus, Semester Project, Scales/Scale Models. Questions? One comment
 Syllabus, Semester Project, Scales/Scale Models Questions? One comment Patterns in the Sky: Traxoline Cardinal Directions (N, S, E, W) Positions in the Sky ( high, low ) Meridian, Zenith, Horizon Noon
Syllabus, Semester Project, Scales/Scale Models Questions? One comment Patterns in the Sky: Traxoline Cardinal Directions (N, S, E, W) Positions in the Sky ( high, low ) Meridian, Zenith, Horizon Noon
Essential Astrophysics
 ASTR 530 Essential Astrophysics Course Notes Paul Hickson The University of British Columbia, Department of Physics and Astronomy January 2015 1 1 Introduction and review Several text books present an
ASTR 530 Essential Astrophysics Course Notes Paul Hickson The University of British Columbia, Department of Physics and Astronomy January 2015 1 1 Introduction and review Several text books present an
Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin. 43 North 89 West. September Daylight
 Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin 43 North 89 West 7 32 September 21 2005 Daylight Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin September 21,2005 7:32 43 North 89 West Names & Planetary Character Luminaries Symbols
Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin 43 North 89 West 7 32 September 21 2005 Daylight Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin September 21,2005 7:32 43 North 89 West Names & Planetary Character Luminaries Symbols
Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, Anne Green / Richard Thompson
 Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, 2006 Anne Green / Richard Thompson http://www.physics.usyd.edu.au/ag/agschome.htm Course Coordinator: Mike Wheatland Course Goals Evaluate & interpret information,
Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, 2006 Anne Green / Richard Thompson http://www.physics.usyd.edu.au/ag/agschome.htm Course Coordinator: Mike Wheatland Course Goals Evaluate & interpret information,
In The Sky This Quarter
 WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY EBERLY COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES THE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS TOMCHIN PLANETARIUM AND OBSERVATORY Volume 11, Issue 1 http://planetarium.wvu.edu/ January - March 2011 On January
WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY EBERLY COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES THE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS TOMCHIN PLANETARIUM AND OBSERVATORY Volume 11, Issue 1 http://planetarium.wvu.edu/ January - March 2011 On January
The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Astronomical Time Periods 9/18/2009
 Astronomical Time Periods 9/18/2009 Opening Discussion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kmegyngwwyc Have you see anything interesting in the news? What did we talk about last class? Checking grades. Minute
Astronomical Time Periods 9/18/2009 Opening Discussion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kmegyngwwyc Have you see anything interesting in the news? What did we talk about last class? Checking grades. Minute
Viewed from Earth's north pole, the rotation of Earth and its moon are counter-clockwise.!
 The Earth rotates around once in 24 hours The time it takes for the Earth to rotate completely around once is what we call a day. It's Earth's rotation that gives us night and day. Viewed from Earth's
The Earth rotates around once in 24 hours The time it takes for the Earth to rotate completely around once is what we call a day. It's Earth's rotation that gives us night and day. Viewed from Earth's
Notes on Moon Calendar 1/21/2015
 Notes on Moon Calendar 1/21/2015 I used Sun and Moon data from http://aa.usno.navy.mil/data/docs/rs_oneyear.php. I chose "District of Columbia" for location, partly because that's what came up on the screen.
Notes on Moon Calendar 1/21/2015 I used Sun and Moon data from http://aa.usno.navy.mil/data/docs/rs_oneyear.php. I chose "District of Columbia" for location, partly because that's what came up on the screen.
The simultaneity of the planets and the simultaneity of time
 Eric Kraeghbod The simultaneity of the planets and the simultaneity of time [ Simultaneity Theory - SIMT ] April 2009 Copyright Eric Kraeghbod 2008-2009 The present English version is an approximative
Eric Kraeghbod The simultaneity of the planets and the simultaneity of time [ Simultaneity Theory - SIMT ] April 2009 Copyright Eric Kraeghbod 2008-2009 The present English version is an approximative
Brock University. Test 1, October 2016 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01 Number of Students: 500 Date of Examination: October 3, 2016
 Brock University Test 1, October 2016 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01 Number of Students: 500 Date of Examination: October 3, 2016 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 17:00 17:50 Instructor:
Brock University Test 1, October 2016 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01 Number of Students: 500 Date of Examination: October 3, 2016 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 17:00 17:50 Instructor:
At Home Phases Demo. Astronomy 210. Section 1 MWF Astronomy Building. Geocentric vs. Heliocentric system. The Motion of the Planets
 Astronomy 210 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astronomy Building This Class (Lecture 4): Early Cosmology HW #1 Due on Friday! Next Class: You missed the first planetarium show. Cosmic Revolution Music: Twilight
Astronomy 210 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astronomy Building This Class (Lecture 4): Early Cosmology HW #1 Due on Friday! Next Class: You missed the first planetarium show. Cosmic Revolution Music: Twilight
2. Modern: A constellation is a region in the sky. Every object in the sky, whether we can see it or not, is part of a constellation.
 6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
6 The Orbit of Mercury
 6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
One sine wave is 7.64 minutes peak to peak variation. Two sine waves is 9.86
 WHY THE SUN IS SOMETIMES FAST AND SOMETIMES SLOW As the earth orbits the sun in an ellipse, it goes faster approaching the sun and slower when receding, just like when you throw a ball up in the air and
WHY THE SUN IS SOMETIMES FAST AND SOMETIMES SLOW As the earth orbits the sun in an ellipse, it goes faster approaching the sun and slower when receding, just like when you throw a ball up in the air and
Astrology in the casebooks
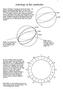 Astrology in the casebooks 1 Forman s and Napier s astrology was based on the zodiac the group of constellations through which the sun moves on its apparent course around the earth. That course is a circle
Astrology in the casebooks 1 Forman s and Napier s astrology was based on the zodiac the group of constellations through which the sun moves on its apparent course around the earth. That course is a circle
Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS
 NAME(S)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ASTRONOMY 25 Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD Overview The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes
NAME(S)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ASTRONOMY 25 Computer Activity #3 SUNRISE AND SUNSET: THE SEASONS SECTION DAY/TIME S. V. LLOYD Overview The seasonal variation in temperature is due to two changes
Remember that for one of your observing projects you can go to a star party (stargazing). This is available at the Lawrence Hall of Science every 1st
 Observing Project Remember that for one of your observing projects you can go to a star party (stargazing). This is available at the Lawrence Hall of Science every 1st and 3rd Saturday of the month. For
Observing Project Remember that for one of your observing projects you can go to a star party (stargazing). This is available at the Lawrence Hall of Science every 1st and 3rd Saturday of the month. For
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon. Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017
 Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Astronomy Club of Asheville June 2018 Sky Events
 June 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 June 14 th Dusk s Venus, Mercury and a Sliver of Moon page 5 June 27 th Conjunction of the Full Moon with Saturn page 6 Planet Highlights - page 7 Moon
June 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 June 14 th Dusk s Venus, Mercury and a Sliver of Moon page 5 June 27 th Conjunction of the Full Moon with Saturn page 6 Planet Highlights - page 7 Moon
Equatorial Telescope Mounting
 Equatorial Telescope Mounting Star Catalogs simbad IRSA The Meridian Every line of celestial longitude is a meridian of longitude, but we recognize the line of longitude, or simply the great circle line,
Equatorial Telescope Mounting Star Catalogs simbad IRSA The Meridian Every line of celestial longitude is a meridian of longitude, but we recognize the line of longitude, or simply the great circle line,
The sun then falls below the horizon, and it is nighttime for our little person:
 Venus Update! Problem 6 on Homework 1 in Physics 2A last September asked you to find the distance from Earth to Venus at that time. I gave you the angle between the sun and Venus at that time; you drew
Venus Update! Problem 6 on Homework 1 in Physics 2A last September asked you to find the distance from Earth to Venus at that time. I gave you the angle between the sun and Venus at that time; you drew
Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
Directed Reading. Section: Viewing the Universe THE VALUE OF ASTRONOMY. Skills Worksheet. 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME. a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system.
 UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
Calculations Equation of Time. EQUATION OF TIME = apparent solar time - mean solar time
 Calculations Equation of Time APPARENT SOLAR TIME is the time that is shown on sundials. A MEAN SOLAR DAY is a constant 24 hours every day of the year. Apparent solar days are measured from noon one day
Calculations Equation of Time APPARENT SOLAR TIME is the time that is shown on sundials. A MEAN SOLAR DAY is a constant 24 hours every day of the year. Apparent solar days are measured from noon one day
Chapter 26 Section 1 pages Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe
 Name: Period: Chapter 26 Section 1 pages 659-666 Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 2. What is the main reason people study the
Name: Period: Chapter 26 Section 1 pages 659-666 Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 2. What is the main reason people study the
FOR DISCUSSION TODAY: THE ANNUAL MOTION OF THE SUN
 ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework #1 due today at end of class. HW #2 due next Thursday. Homework #1 question #1 and Homework #2 meridian slice questions will be discussed in the course of the lecture today. Observing
ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework #1 due today at end of class. HW #2 due next Thursday. Homework #1 question #1 and Homework #2 meridian slice questions will be discussed in the course of the lecture today. Observing
GTAS 2016 Event Planning Calendar
 GTAS 0 Event Planning Calendar This calendar is a PDF print of NASA's SkyCal for 0 with text added for events with Nitro PDF Creator (Reader ), a free program. The official copy is maintained by Bob Moler
GTAS 0 Event Planning Calendar This calendar is a PDF print of NASA's SkyCal for 0 with text added for events with Nitro PDF Creator (Reader ), a free program. The official copy is maintained by Bob Moler
(defun solar-longitude-at-moment (moment) ;; TYPE moment -> angle ;; Longitude of sun at moment. (solar-longitude (jd-from-moment moment))) Finally, w
 Implementing Solar Astronomical Calendars Nachum Dershowitz Edward M. Reingold Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 1304 West Springfield Avenue Urbana, Illinois 61801-2987,
Implementing Solar Astronomical Calendars Nachum Dershowitz Edward M. Reingold Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 1304 West Springfield Avenue Urbana, Illinois 61801-2987,
