E & P SERV/US-SUB/ISBM INSTALLATION OF SUBSEA FACILITIES AREA: INDEX OF REVISIONS
|
|
|
- Kristian Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E&P-SERV US-SUB/ISBM TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Nº: I-ET PMU de 48 PROJECT: INSTALLATION OF SUBSEA FACILITIES AREA: SUBSEA FACILITIES INDEX OF REVISIONS REV DESCRIPTION AND/OR AFFECTED PAGES 0 This document substitute ET PSE-001 Rev.H A Emission for use Rev 0 Rev A Rev B Rev C Rev D Rev E Rev F Rev G Rev H DATE 31/07/07 31/07/07 EXECUTED BY JMLF JMLF CHECKED BY - - APPROVED BY João Manoel João Manoel THE DATA OR PARTS THEREOF ARE PETROBRAS PROPERTY AND THUS MUST NOT BE USED IN ANY WAY WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION.
2 2 de 48 I N D E X LAYING SYSTEM VERTICAL LAYING SPREAD (VLS) HORIZONTAL LAYING SPREAD 1 (HLS 1) HORIZONTAL LAYING SPREAD 2 (HLS 2) UMBILICAL WINCH LAYING SPREAD (ULS 1) UMBILICAL TENSIONER LAYING SPREAD (ULS 2) FLEXIBLE PIPE AND UMBILICAL STORAGE FIGURES RAO AND PHASE ANGLES
3 3 de LAYING SYSTEM The complete laying system is composed of 3 (three) independent laying spreads that permit a simultaneous deployment of the 3 (three) lines of a bundle (i.e. production pipe, annulus pipe and control umbilical): I. Vertical Laying Spread (VLS); II. III. Horizontal laying Spread (HLS): Composed of 2 (two) distinct laying spreads: A. HORIZONTAL TENSIONER LAYING SPREAD 1 (HLS 1); B. HORIZONTAL TENSIONER LAYING SPREAD 2 (HLS 2); Umbilical Laying Spread (ULS): Composed of 2 (two) distinct laying spreads: A. UMBILICAL WINCH LAYING SPREAD 1(ULS 1); B. UMBILICAL TENSIONER LAYING SPREAD 2(ULS 2); See attachment 1 for additional information about VLS and others appurtenances. 1.1 VERTICAL LAYING SPREAD(VLS) Vertical spread designed for heavy loads and large diameter pipe. Maximum capacity: 270 t. Figures 2,3,6 and 8.The spread is installed on the stern starboard side of the vessel and is composed of 3 (three) stacked elements: 1. Working table, above sea level. The working table is designed to support a maximum catenary load of 270 t. It is composed of movable parts, hydraulicallly operated, which can clamp the pipe fitting and hold the catenary tension, for a connection in a vertical configuration of 2 (two) pipe segments; 2. 2 (two) modules of 4-belt tensioners (i.e. quad-cartepillars), installed over the table on foundation structure; 3. Top module supporting a pipe deflector, a 10 t service crane and the 270 t winch (i.e. load transfer system). The VLS system also allows the passage of previously connected and intermediate connections. Table 1 condenses the VLS capacities: Table 1 - VLS Capacities Maximum Pull (kn - t) (See note 1) Maximum Break Capacity (kn - t) (See note 2) Laying Speed Range (m/ s) 0-16/ 60 Diameter of the Tensioner Passage (m) 1.20 Gutter radius/width(m) 3.00/1.16 Maximum pipe outside diameter (mm - inch) Minimum pipe outside diameter (mm - inch) (See note 3) Static Friction Coefficient (pipe - belt) 0.10 NOTES :
4 4 de In quad mode, with a 100 t/ m clamping load; 2. In quad mode, with a 150 t/ m clamping load; 3. In quad mode. In a 2-belt mode, the minimum pipe diameter is 80 mm (3.1 ) HORIZONTAL LAYING SPREAD 1 (HLS 1) The horizontal laying spread permits handling of flexible pipes from 2.5 up to 4 (nominal diameter). Maximum capacity: 3 x 33.3 = 100t.See Figures 1,2,3 and 6. The HLS 1 is located on the port side of the vessel, and its track is parallel to the Umbilical Laying Spread 1 (ULS 1). The spread equipment permits 100T maximum dynamic laying tension. The flexible pipes can be deployed from a stern laying wheel of 6 m diameter and the laying tension is handled by 3 (three) tensioners with a maximum capacity of 33t each, located in a horizontal configuration, on the working deck. The 1.2 m passage, in fully open position, permits the transfer of large end fittings or connectors. The distance adjacent tensioners is approximately 1.44 m.` The spread has been designed for a maximum pipe diameter of 4 (nominal diameter). However, in order to offer the best facilities during the pipe loading and transfer operations, the tensioners are able to handle a higher diameter pipe (up to 12 - nominal diameter), under reduced tension. Table 2 - Condenses the HLS 1 capacities Maximum Pull (kn - t) (See note 1) Maximum Break Capacity (kn - t) 1471,5 150 (See note 2) Laying Speed Range (m/min) 0-15 Diameter of the passage through tensioner(mm) 1200 Maximum pipe outside diameter (mm - inch) (See note 3) Minimum pipe outside diameter (mm - inch) Static Friction Coefficient (pipe - belt) 0.10 NOTES: 1. *With a 40 t/ m clamping load; 2. With a 60 t/ m clamping load; 3. Under a 75 t tension load. Under a tensile load of 25 t, the correspondent value is 350 mm (13.8 ). In addition, for loading operation on shore or during transfer between storage baskets on board, the correspondent value is 400 mm (15.7 ). The maximum pipe outside diameter versus tension is determined by the limit capacity of the safety clamp (pipe diameters < 220 mm) and the limit capacity of the chinese finger (for higher pipe diameters); HORIZONTAL LAYING SPREAD 2 (HLS 2)
5 5 de 48 The horizontal laying spread permits handling of flexible pipes from 2.5 up to 6 (nominal diameter) and Umbilical. Maximum capacity: 2 x 40 = 80T.See Figures 1,2,3 and 6. The HLS 2 is located on the starboard side of the vessel, and its track is parallel to the Umbilical Laying Spread 1 (ULS 1). The spread equipment permits 80T maximum dynamic laying tension. The flexible pipes can be deployed from a stern laying wheel of 6 m diameter and the laying tension is handled by 2 (three) tensioners with a maximum capacity of 40T each, located in a horizontal configuration, on the working deck. The 1.2 m passage, in fully open position, permits the transfer of large end fittings or connectors. The distance adjacent tensioners is approximately 1.44 m.` The pipe is deployed and overboarded from a stern laying wheel with a similar system and methods as used for the HLS 1. The stern laying wheel has similar dimension and grove shape. The transfer of intermediate connection, or end of line fittings, throughout the tensioner and the subsequent stern wheel overboarding, is performed with the help of a hold back collar fitted onto the connection and connected to a 80T winch, which holds the catenary tension and controls the transfer while the tensioners are opened to let the connection go through. The intermediate connections are performed on the deck area immediately before the tensioners entrance. : Table 3 - Condenses the HLS 2 capacities Maximum Pull (kn - t) 784,4-80 (See note 1) Maximum Break Capacity (kn - t) 1128,15 115(See note 2) Laying Speed Range (m/ min) 0-15 Diameter of the passage through (mm) 1200 Maximum pipe outside diameter (mm - inch) (See note 3) Minimum pipe outside diameter (mm - inch) Static Friction Coefficient (pipe - belt) 0.10 NOTES : 1. With a 40 t/ m clamping load; 2. With a 60 t/ m clamping load; 3. Under a 75 t tension load. Under a tensile load of 25 t, the correspondent value is 350 mm (13.8 ). In addition, for loading operation on shore or during transfer between storage baskets on board, the correspondent value is 400 mm (15.7 ). The maximum pipe outside diameter versus tension is determined by the limit capacity of the safety clamp (pipe diameters < 220 mm) and the limit capacity of the chinese finger (for higher pipe diameters); UMBILICAL WINCH LAYING SPREAD (ULS 1) Direct laying from a storage winch (rated for a maximum laying tension of 25 t at its outermost layer). Figures 2,3,6 and 9.
6 6 de 48 The umbilical is laid directly from the storage winch (see item FLEXIBLE PIPE AND UMBILICAL STORAGE). Table 4 condenses the ULS 1 capacities: Table 4 - ULS 1 Capacities Maximum Pull (kn - t) Maximum Break Capacity (kn - t) Laying Speed Range (m/ s) 0-16/ UMBILICAL TENSIONER LAYING SPREAD (ULS-2) Horizontal spread for umbilical. Maximum capacity: 4 x 7.5 = 25.0 t. Figures 2,3,6 and 7. The system is composed of 4 (four) individual 2-belts tensioners (bicaterpillars), configured on line, over the working deck of the vessel. It is designed for deploying umbilical diameter from 2 up to 11.8 (outside diameter), with a laying tension up to 25.It can also recover umbilical within a range from 2 up to 11.8 (outside diameter). The umbilical is laid by means of 4 (four) individual bi-caterpillars. The umbilical is stored into rotative basket 1 (see item FLEXIBLE PIPE AND UMBILICAL STORAGE). Table 5 condenses the ULS 2 capacities. Table 5 - ULS 2 Capacities Maximum Pull (kn - t) (See note 1) Maximum radial clamping load (t/m) 10.0 Minimum radial clamping load (t/m) 5.0 Maximum Break Capacity (kn - t) Laying Speed Range (m/ s) 0-16/ 60 Diameter of the Tensioner Passage (m) 0.5 Maximum umbilical outside diameter (mm - inch) Minimum umbilical outside diameter (mm - inch) Static Friction Coefficient (pipe - belt) 0.10 NOTES: 1. With maximum clamping load; FLEXIBLE PIPES AND UMBILICAL STORAGE Flexible pipes and umbilicals are stored by 3 (threee) storage and rotating baskets, and a storage reel (ULS 1). Table 6 condenses the characteristics of the 3 (three) baskets (for flexible pipes and umbilicals). Table 6-A condenses the storage capacity of the vessel (baskets and reel). Figures 1,2,3,4 and 5.
7 7 de 48 Table 6 - Storage baskets characteristics BASKET ---> Basket 1 Baskets 2 and 3 (Internal Partition) (See note 1) Application Umbilical up to 60 hoses and flexible pipe up to 4 (nominal diameter) 2.5 and 4 Flexible pipe (nominal diameter) Baskets 2 and 3 (External Partition) (See note 1) 6 and up to 12 Flexible pipe (nominal diameter) Maximum Capacity (t) 600 See note 2 Storage Volume (m 3 ) 350 Storage Capacity (m) 20,000(See note See Table 6-A See Table 6-A 3) Outside Storage Diameter (m) Internal Storage Diameter (m) Storage Height (m) Rotation Speed (m/ s) 16/ 60 16/ 60 16/ 60 NOTES : 1. Baskets 2 and 3 are divided into 2 (two) storage partitions (internal and external) for best operation and sequence flexibility, each partition being fitted with an individual spooling system; 2. Baskets 2 and 3 have a maximum capacity and a total storage volume of 1,500 t and 833 m 3 ; 3. Referred to an umbilical with an outside diameter of 100 mm. Basket/ Winch Table 6-A - Storage capacity (m) of the vessel 12 pipe 6 pipe 4 pipe (nominal (nominal (nominal diameter) diameter) diameter) Maximum Capacity (t) 2.5 pipe (nominal diameter) Umbilical (see note3 - Table 6) ,000 20,000 20, External 1,500 3,000 9,600 21,000 38, Internal ,000 11, External 1,500 3,000 9,600 21,000 38, Internal ,000 11, S. Reel (see note 1) x 3,500 NOTES: 1. The storage reel can hold 2 (two) umbilicals segments, and a central separator arrangement is provided to store the two segment first end fittings FIGURES FIGURE 1 FIGURE 2 HLS-1 AND HLS-2 DETAILS SUNRISE 2000 TOP VIEW
8 8 de 48 FIGURE 3 SUNRISE 2000 PROFILE VIEW FIGURE 4 BASKET 2 AND 3 FLEXIBLE PIPES STORAGE FIGURE 5 BASKET 1 UMBILICALS STORAGE FIGURE 6 ULS-2,HLS-1,HL-2 AND VLS TENSIONER SHOES CHARACTERISTS FIGURE 7 ULS-2 DETAILS FIGURE 8 VLS DETAILS FIGURE 9 ULS-1 WINCH DETAILS FIGURE 10 FLEXIBLE PIPE AND UMBILICAL STERN LAYING WHEEL ATTACHMENTS Attachment 1 - NOTA TÉCNICA No B 065 Rev 3 DIMENSÕES MÁXIMAS PARA ACESSÓRIOS DE LINHAS A SEREM LANÇADAS PELO PLSV CSO SUNRISE-2000.
9 9 de 48 FIGURE 1 HLS-1 AND HLS-2 TENSIONER DETAILS
10 10 de 48 FIGURE 2 SUNRISE TOP VIEW
11 11 de 48 FIGURE 3 SUNRISE PROFILE VIEW
12 12 de 48 FIGURE 4 BASKET 2 AND 3 FLEXIBLE PIPES STORAGE
13 13 de 48 FIGURE 5 BASKET 1 UMBILICALS STORAGE
14 14 de 48 FIGURE 6 ULS-2,HLS-1,HLS-2 AND VLS TENSIONER SHOES CHARACTERISTS
15 15 de 48 FIGURE 7 ULS-2 DETAILS
16 16 de 48 FIGURE 8 VLS DETAILS
17 17 de 48 FIGURE 9 ULS-1 WINCH DETAIL
18 18 de 48 FIGURE 10 FLEXIBLE PIPE AND UMBILICAL STERN LAYING WHEEL
19 19 de RAO AND PHASE ANGLES RAO and Phase Angles curves attached. 1 The movements shown in the tables) are refered to the vessel SUNRISE 2000 at conditions of Ballast,Arrival (vessel draft of 5.29 m), and Operation, Full Load (vessel draft of 6.28 m), respectively; 2 The coordinate system for carrying out the movements has its origin in the vessel center of gravity (CG), which is positioned with the following coordinates: Loading Condition 1 (Ballast, Arrival) - Vessel draft of 5.29 m - (57.39 ; 0.01 ; 7.12); Loading Condition 2 (Operation, Full load) - Vessel draft of 6.28 m - (57.90 ; ;8.75) The origin of cartesian reference system is taken as the point situated at the Frame 0 (rudder shaft), at the center line and at the base line (keel), considering the following orientation for the coordinate axis: X is forward, Y is port and Z is upward. 3 Other remarkable points coordinates: * Coordinates of VLS Working Table Deck(to be considered as the top point of riser deployed by thevls): (-6.40 ; ; 10.1) * Coordinates for stern laying wheels: F Wheel nr. 1 (starboard) (-2.60 ; 8.39 ; 14.80) wheel radius=2.70m Wheel nr. 2 (center)(-2.60 ; 4.70 ; 14.80) wheel radius=2.70m Wheel nr. 3 (portside) (-2.60 ; ; 14.80) wheel radius=2.70m The origin of cartesian reference system is taken as the point situated at the Frame 0 (rudder shaft), at the center line and at the base line (keel), considering the following orientation for the coordinate axis: X is forward, Y is port and Z is upward. Z Y 0(rudder shaft,center X * A 0 wave incidence means waves coming from the stern towards the bow of the vessel; * A 180 wave incidence means waves coming from the bow towards the stern of the vessel;
20 20 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 5.29m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +000 deg off stern WAV ENC SURGE SURGE SWAY SWAY HEAVE HEAVE ROLL ROLL PITCH PITCH YAW YAW E SQRT FREQ SL / WL FREQ AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE ( r / s) ( - ) ( r / s ) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg)
21 21 de
22 22 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 5.29m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +090 deg off stern WAV SQRT ENC...SURGE...SURGE...SWAY...SWAY...HEAVE...HEAVE...ROLL....ROLL. E FREQ SL / WL...PITCH.....PITCH...YAW FREQ AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL ( r / s) ( - ) ( r / s ) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) YAW. PHAS E
23 23 de
24 24 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 5.29m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +120 deg off stern WAV SQRT ENC...SURGE...SURGE...SWAY...SWAY....HEAVE..HEAVE...ROLL....ROLL....PITCH.....PITCH...YAW.....YAW FREQ AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHAS E E FREQ SL / WL ( r / s) ( - ) ( r / s ) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg)
25 25 de
26 26 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 5.29m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +150 deg off stern WAV ENC...SURGE...SURGE...SWAY...SWAY...HEAVE...HEAVE...ROLL....ROLL. E SQRT FREQ SL / WL...PITCH.....PITCH...YAW.. YAW FREQ AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHAS E ( r / s) ( - ) ( r / s ) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg)
27 27 de
28 28 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 5.29m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +180 deg off stern WAV ENC...SURGE...SURGE...SWAY...SWAY...HEAVE...HEAVE...ROLL....ROLL....PITCH.....PITCH...YAW.....YAW E SQRT FREQ SL / WL FREQ AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHAS E ( r / s) ( - ) ( r / s ) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg) (deg/m)
29 29 de
30 30 de
31 31 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 6.28m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +000 deg off stern WAV ENC...SURGE...SURGE...SWAY...SWAY...HEAVE...HEAVE...ROLL....ROLL....PITCH.....PITCH...YAW....YAW. E SQRT FREQ SL / FREQ AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHASE AMPL PHAS ( r / s ) WL ( - ) E ( r / s ) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg) (deg/m) (deg/m)
32 32 de
33 33 de
34 34 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 6.28m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +090 deg off stern WAV E SQRT FREQ SL / WL ( r / s ) ) ( - ENC...SURGE...SURGE...SWAY...SWAY...HEAVE...HEAVE...ROLL....ROLL....PITCH......PITC...YAW H. FREQ AMPL PHASE AMPL AMPL PHASE AMPL AMPL AMPL PHASE PHASE PHAS E ( r / s ) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg/m) (deg/m) YAW... PHAS E (deg)
35 35 de
36 36 de
37 37 de
38 38 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 6.28m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +120 deg off stern WAV SQRT ENC...SURGE...SURGE..SWAY..SWAY.....HEAVE...HEAVE...ROLL....ROLL....PITCH.....PITCH...YAW....YAW. E FREQ SL / AMPL PHASE AMPL AMPL PHASE AMPL AMPL PHASE AMPL WL FREQ PHASE PHASE PHAS E ( r / s ( - ) ( r / s (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg) ) ) (deg/m) (deg/m)
39 39 de
40 40 de
41 41 de
42 42 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 6.28m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +150 deg off stern WAV E SQRT FREQ SL / WL ( r / s ) ) ( - ENC...SURGE...SURGE..SWAY...SWAY....HEAVE...HEAVE...ROLL....ROLL....PITCH.....PITCH...YAW....YAW FREQ AMPL PHASE AMPL AMPL PHASE AMPL AMPL AMPL PHASE PHASE PHASE PHAS E ( r / s ) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) (deg) (deg/m) (deg/m)
43 43 de
44 44 de
45 45 de 48 Calculation of Shipmotions by Program SEAWAY SUNRISE - calado de 6.28m FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIC MOTIONS FORWARD SPEED =.00 kn WAVE DIRECTION = +180 deg off stern WAV E FREQ SL / WL SQRT ENC...SURGE...SURGE..SWAY...SWAY....HEAVE...HEAVE...ROLL....ROLL....PITCH.....PITCH...YAW AMPL PHASE AMPL AMPL PHASE AMPL AMPL AMPL FREQ PHASE PHASE PHASE ( r / s ( - ) ( r / s (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (m/m) (deg) (deg) (deg/m) (deg) ) ) (deg/m) (deg/m) YAW... PHAS E (deg)
46 46 de
47 47 de
48 48 de
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION. Ships. Part 3 Hull Chapter 4 Loads. Edition January 2017 DNV GL AS
 RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION Ships Edition January 2017 Part 3 Hull Chapter 4 The content of this service document is the subject of intellectual property rights reserved by ("DNV GL"). The user accepts that
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION Ships Edition January 2017 Part 3 Hull Chapter 4 The content of this service document is the subject of intellectual property rights reserved by ("DNV GL"). The user accepts that
Reel-lay Installation of Steel Catenary Risers and Inline Sleds in High Surface Currents
 NH GRAND HOTEL KRASNAPOLSKY AMSTERDAM 3-5 APRIL 2017 Reel-lay Installation of Steel Catenary Risers and Inline Sleds in High Surface Currents D. Jacob Fannon, P.E. EMAS CHIYODA Subsea Problem Statement:
NH GRAND HOTEL KRASNAPOLSKY AMSTERDAM 3-5 APRIL 2017 Reel-lay Installation of Steel Catenary Risers and Inline Sleds in High Surface Currents D. Jacob Fannon, P.E. EMAS CHIYODA Subsea Problem Statement:
Wuchang Shipbuilding Industry Co., Ltd. China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation
 Safety Assessments for Anchor Handling Conditions of Multi-purpose Platform Work Vessels Reporter:Yu Wang Wuchang Shipbuilding Industry Co., Ltd. China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation 2009.12.04 0 Outline
Safety Assessments for Anchor Handling Conditions of Multi-purpose Platform Work Vessels Reporter:Yu Wang Wuchang Shipbuilding Industry Co., Ltd. China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation 2009.12.04 0 Outline
Emerging Subsea Networks
 OPTIMIZING DESIGN OF A DYNAMIC FIBER OPTIC RISER CABLE USING CROSS SECTION ANALYSIS Bjørn Konradsen 1 Magnus Komperød 1 Email: bjorn.konradsen@nexans.com 1 Technological Analyses Centre, Nexans Norway
OPTIMIZING DESIGN OF A DYNAMIC FIBER OPTIC RISER CABLE USING CROSS SECTION ANALYSIS Bjørn Konradsen 1 Magnus Komperød 1 Email: bjorn.konradsen@nexans.com 1 Technological Analyses Centre, Nexans Norway
SOLUTION 8 7. To hold lever: a+ M O = 0; F B (0.15) - 5 = 0; F B = N. Require = N N B = N 0.3. Lever,
 8 3. If the coefficient of static friction at is m s = 0.4 and the collar at is smooth so it only exerts a horizontal force on the pipe, determine the minimum distance x so that the bracket can support
8 3. If the coefficient of static friction at is m s = 0.4 and the collar at is smooth so it only exerts a horizontal force on the pipe, determine the minimum distance x so that the bracket can support
Sample 5. Determine the tension in the cable and the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at the pin A. Neglect the size of the pulley.
 Sample 1 The tongs are designed to handle hot steel tubes which are being heat-treated in an oil bath. For a 20 jaw opening, what is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the jaws and the
Sample 1 The tongs are designed to handle hot steel tubes which are being heat-treated in an oil bath. For a 20 jaw opening, what is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the jaws and the
On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
 International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 1 March 28 On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 1 March 28 On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
7.6 Journal Bearings
 7.6 Journal Bearings 7.6 Journal Bearings Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving Frictional Forces on Journal Bearings For problems involving a
7.6 Journal Bearings 7.6 Journal Bearings Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving Frictional Forces on Journal Bearings For problems involving a
The basic dynamic load rating C is a statistical number and it is based on 90% of the bearings surviving 50 km of travel carrying the full load.
 Technical data Load Rating & Life Under normal conditions, the linear rail system can be damaged by metal fatigue as the result of repeated stress. The repeated stress causes flaking of the raceways and
Technical data Load Rating & Life Under normal conditions, the linear rail system can be damaged by metal fatigue as the result of repeated stress. The repeated stress causes flaking of the raceways and
SAFEHULL-DYNAMIC LOADING APPROACH FOR VESSELS
 Guide for SafeHull- Dynamic Loading Approach for Vessels GUIDE FOR SAFEHULL-DYNAMIC LOADING APPROACH FOR VESSELS DECEMBER 2006 (Updated February 2014 see next page) American Bureau of Shipping Incorporated
Guide for SafeHull- Dynamic Loading Approach for Vessels GUIDE FOR SAFEHULL-DYNAMIC LOADING APPROACH FOR VESSELS DECEMBER 2006 (Updated February 2014 see next page) American Bureau of Shipping Incorporated
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Transport Analysis Report Full Stability Analysis. Project EXAMPLE PROJECT DEMO RUN FOR REVIEW. Client ORCA OFFSHORE
 ONLINE MARINE ENGINEERING Transport Analysis Report Full Stability Analysis Project EXAMPLE PROJECT DEMO RUN FOR REVIEW Client ORCA OFFSHORE Issue Date 18/11/2010 Report reference number: Herm-18-Nov-10-47718
ONLINE MARINE ENGINEERING Transport Analysis Report Full Stability Analysis Project EXAMPLE PROJECT DEMO RUN FOR REVIEW Client ORCA OFFSHORE Issue Date 18/11/2010 Report reference number: Herm-18-Nov-10-47718
Optimal Design of FPSO Vessels
 November 2, 201 Optimal Design of FPSO Vessels Ezebuchi Akandu PhD, MTech, BTech, COREN, RINA, MNSE Department of Marine Engineering, Rivers State University, Port Harcourt, Nigeria akandu.ezebuchi@ust.edu.ng
November 2, 201 Optimal Design of FPSO Vessels Ezebuchi Akandu PhD, MTech, BTech, COREN, RINA, MNSE Department of Marine Engineering, Rivers State University, Port Harcourt, Nigeria akandu.ezebuchi@ust.edu.ng
Chain Conveyors Practical Calculations
 PDHonline Course M360 (1PDH) Chain Conveyors Practical Calculations (Metric and US Systems) Jurandir Primo, PE 2009 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
PDHonline Course M360 (1PDH) Chain Conveyors Practical Calculations (Metric and US Systems) Jurandir Primo, PE 2009 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
3D Force Couple System and Resultant. Q.No.1: Replace the force system by an equivalent force and couple moment at point A.
 3D Force Couple System and Resultant Q.No.1: Replace the force system by an equivalent force and couple moment at point A. Q.No.2: Handle forces F1 and F2 are applied to the electric drill. Replace this
3D Force Couple System and Resultant Q.No.1: Replace the force system by an equivalent force and couple moment at point A. Q.No.2: Handle forces F1 and F2 are applied to the electric drill. Replace this
SOLUTION 8 1. a+ M B = 0; N A = 0. N A = kn = 16.5 kn. Ans. + c F y = 0; N B = 0
 8 1. The mine car and its contents have a total mass of 6 Mg and a center of gravity at G. If the coefficient of static friction between the wheels and the tracks is m s = 0.4 when the wheels are locked,
8 1. The mine car and its contents have a total mass of 6 Mg and a center of gravity at G. If the coefficient of static friction between the wheels and the tracks is m s = 0.4 when the wheels are locked,
Identification system for short product names. Changes/amendments at a glance. 2 Bosch Rexroth AG OBB omega modules R ( )
 Omega Modules OBB 2 OBB omega modules R9990079 (206-05) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example: O B B - 085 - N N - System = Omega module Guideway = Ball Rail System Drive
Omega Modules OBB 2 OBB omega modules R9990079 (206-05) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example: O B B - 085 - N N - System = Omega module Guideway = Ball Rail System Drive
Matlab Sheet 2. Arrays
 Matlab Sheet 2 Arrays 1. a. Create the vector x having 50 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10 and ending at 1000. b. Create the vector x having 20 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10
Matlab Sheet 2 Arrays 1. a. Create the vector x having 50 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10 and ending at 1000. b. Create the vector x having 20 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10
HEAVE DAMPING EFFECTS DUE TO CIRCULAR PLATES ATTACHED AT KEEL TO SPAR HULL
 HEAVE DAMPING EFFECTS DUE TO CIRCULAR PLATES ATTACHED AT KEEL TO SPAR HULL P.Uma 1 1 M.TECH Civil Engineering Dadi Institute of Engineering and Technology College Abstract Single point Anchor Reservoir
HEAVE DAMPING EFFECTS DUE TO CIRCULAR PLATES ATTACHED AT KEEL TO SPAR HULL P.Uma 1 1 M.TECH Civil Engineering Dadi Institute of Engineering and Technology College Abstract Single point Anchor Reservoir
Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3
 Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 2 3 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR = F1 + F2 and its direction, measured counterclockwise from the
Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 2 3 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR = F1 + F2 and its direction, measured counterclockwise from the
Linear guide drives. Synchronous shafts The use of synchronous shafts enables several linear axes to be operated with one drive.
 Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
Moments practice exam questions
 Moments practice exam questions Name - 50 minutes 48 marks Page 1 of 13 Q1. A waiter holds a tray horizontally in one hand between fingers and thumb as shown in the diagram. P, Q and W are the three forces
Moments practice exam questions Name - 50 minutes 48 marks Page 1 of 13 Q1. A waiter holds a tray horizontally in one hand between fingers and thumb as shown in the diagram. P, Q and W are the three forces
STATICS. Friction VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Eighth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
Inclined Plane Dynamics Set
 Instruction Manual 012-10874A *012-10874* Inclined Plane Dynamics Set ME-6966 Table of Contents Included Equipment..................................................... 3 Related Equipment.....................................................
Instruction Manual 012-10874A *012-10874* Inclined Plane Dynamics Set ME-6966 Table of Contents Included Equipment..................................................... 3 Related Equipment.....................................................
SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE
 N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
Example of Calculating the Nominal Life
 Condition (Horizontal Installation) Assumed model number : KR 5520A LM Guide unit (C = 800N, C 0 = 6900N) Ball Screw unit (C a = 620N, C 0a = 9290N) Bearing unit(fixed Side) (C a = 7600N, P 0a = 990N)
Condition (Horizontal Installation) Assumed model number : KR 5520A LM Guide unit (C = 800N, C 0 = 6900N) Ball Screw unit (C a = 620N, C 0a = 9290N) Bearing unit(fixed Side) (C a = 7600N, P 0a = 990N)
Investigation of basic elements loading and tension of heavy hydraulic presses for metallurgical production
 Investigation of basic elements loading and tension of heavy hydraulic presses for metallurgical production Ganush V. I. National metallurgical academe of Ukraine Ostroverhov N. P., Sultan A. V., Dzichkovky
Investigation of basic elements loading and tension of heavy hydraulic presses for metallurgical production Ganush V. I. National metallurgical academe of Ukraine Ostroverhov N. P., Sultan A. V., Dzichkovky
Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association
 Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association 567 Strand Ct., Suite, Naples, Florida 34110 Tel: (39) - 514-3441 Fax: (39) - 514-3470 Web Site: http://www.cemanet.org Belt Book, 7th Edition Errata items
Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association 567 Strand Ct., Suite, Naples, Florida 34110 Tel: (39) - 514-3441 Fax: (39) - 514-3470 Web Site: http://www.cemanet.org Belt Book, 7th Edition Errata items
After publication, this Indian Standard will supersede the following Indian Standards:
 For Comments Only Doc: PGD 26(1110)W Draft Indian Standard SPECIFICATION FOR NON-AUTOMATIC WEIGHING INSTRUMENTS PART 1 TERMINOLOGY AND DEFINITIONS ICS No. 01.040.17; 17.100 Not to be reproduced without
For Comments Only Doc: PGD 26(1110)W Draft Indian Standard SPECIFICATION FOR NON-AUTOMATIC WEIGHING INSTRUMENTS PART 1 TERMINOLOGY AND DEFINITIONS ICS No. 01.040.17; 17.100 Not to be reproduced without
THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY
 THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY D. Peschel 1, D. Mauersberger 1, D. Schwind 2, U. Kolwinski 2 1 Solid mechanics department, PTB, Germany 2 Gassmann Theiss Messtechnik
THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY D. Peschel 1, D. Mauersberger 1, D. Schwind 2, U. Kolwinski 2 1 Solid mechanics department, PTB, Germany 2 Gassmann Theiss Messtechnik
MECHANICAL TESTS FOR UMBILICALS
 Escola Politécnica da Universidade de São Paulo Laboratório de Estruturas e Materiais Estruturais ( LEM ) MECHANICAL TESTS FOR UMBILICALS Semi-submersible Escola Politécnica da Universidade de São Paulo
Escola Politécnica da Universidade de São Paulo Laboratório de Estruturas e Materiais Estruturais ( LEM ) MECHANICAL TESTS FOR UMBILICALS Semi-submersible Escola Politécnica da Universidade de São Paulo
Q1. The figure below shows an apparatus used to locate the centre of gravity of a non-uniform metal rod.
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. The figure below shows an apparatus used to locate the centre of gravity of a non-uniform metal rod. The rod is supported horizontally by two wires, P and Q and is in equilibrium.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. The figure below shows an apparatus used to locate the centre of gravity of a non-uniform metal rod. The rod is supported horizontally by two wires, P and Q and is in equilibrium.
BAUER MeBo Sea Bed Drill Rig
 BAUER MeBo Sea Bed Drill Rig Spotlights BAUER Maritime Experiences 1993 Diamond deposit exploration with a BC cutter in water depth of 160 m (South Africa) Atlantic Ocean 2005 Drilling inside of a monopile
BAUER MeBo Sea Bed Drill Rig Spotlights BAUER Maritime Experiences 1993 Diamond deposit exploration with a BC cutter in water depth of 160 m (South Africa) Atlantic Ocean 2005 Drilling inside of a monopile
Seminar Container Securing on Container Vessels Part 1. May 11, 2012 Portoroz
 Seminar Container Securing on Container Vessels Part 1 University of Ljubljana May 11, 2012 Portoroz Why pay keen attention to container securing? Forces acting on container stack Wind load (only for wind
Seminar Container Securing on Container Vessels Part 1 University of Ljubljana May 11, 2012 Portoroz Why pay keen attention to container securing? Forces acting on container stack Wind load (only for wind
DOCUMENTATION PAGE. REPORT NUMBER NRC REPORT NUMBER DATE LM January, 2008 REPORT SECURITY CLASSIFICATION UNCLASSIFIED
 DOCUMENTATION PAGE REPORT NUMBER NRC REPORT NUMBER DATE LM-2008-04 January, 2008 REPORT SECURITY CLASSIFICATION DISTRIBUTION UNCLASSIFIED UNLIMITED TITLE Thrust Allocation Techniques for Dynamically Positioned
DOCUMENTATION PAGE REPORT NUMBER NRC REPORT NUMBER DATE LM-2008-04 January, 2008 REPORT SECURITY CLASSIFICATION DISTRIBUTION UNCLASSIFIED UNLIMITED TITLE Thrust Allocation Techniques for Dynamically Positioned
2. Identify other PIs associated with the cruise: 3. Identify the at-sea Chief Scientist: Charles Langmuir
 Pre-Cruise Meeting April 17, 2014 AT26-19, Charles Langmuir, Aug 28 Sept 11, 2014. RV Atlantis with OSU Coring Facility General Program Overview: 1. Scientific Objectives: Our aim is to obtain as many
Pre-Cruise Meeting April 17, 2014 AT26-19, Charles Langmuir, Aug 28 Sept 11, 2014. RV Atlantis with OSU Coring Facility General Program Overview: 1. Scientific Objectives: Our aim is to obtain as many
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 6B: Applications of Friction in Machines Wedges Used to produce small position adjustments of a body or to apply large forces When sliding is impending, the resultant
Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 6B: Applications of Friction in Machines Wedges Used to produce small position adjustments of a body or to apply large forces When sliding is impending, the resultant
Equilibrium of a Particle
 ME 108 - Statics Equilibrium of a Particle Chapter 3 Applications For a spool of given weight, what are the forces in cables AB and AC? Applications For a given weight of the lights, what are the forces
ME 108 - Statics Equilibrium of a Particle Chapter 3 Applications For a spool of given weight, what are the forces in cables AB and AC? Applications For a given weight of the lights, what are the forces
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 6B: Applications of Friction in Machines Wedges Used to produce small position adjustments of a body or to apply large forces When sliding is impending, the resultant
Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 6B: Applications of Friction in Machines Wedges Used to produce small position adjustments of a body or to apply large forces When sliding is impending, the resultant
Operating Instructions Validation Tool Kit, KT2 For use with USP Apparatus #1 & #2
 Operating Instructions Validation Tool Kit, KT2 For use with USP Apparatus #1 & #2 P/N VALTOL-KT2 Revision 2.0 October 7, 2014 Prepared by: Quality Lab Accessories, LLC 100 Emlen Way, Suite 108 Telford,
Operating Instructions Validation Tool Kit, KT2 For use with USP Apparatus #1 & #2 P/N VALTOL-KT2 Revision 2.0 October 7, 2014 Prepared by: Quality Lab Accessories, LLC 100 Emlen Way, Suite 108 Telford,
STATE OF COLORADO DESIGN CRITERIA FOR POTABLE WATER SYSTEMS WATER QUALITY CONTROL DIVISION. Price: $5.00. Revised March 31, 1997
 STATE OF COLORADO DESIGN CRITERIA FOR POTABLE WATER SYSTEMS WATER QUALITY CONTROL DIVISION Revised March 31, 1997 Price: $5.00 a. an arrangement where the water pipe to be injected with chlorine enters
STATE OF COLORADO DESIGN CRITERIA FOR POTABLE WATER SYSTEMS WATER QUALITY CONTROL DIVISION Revised March 31, 1997 Price: $5.00 a. an arrangement where the water pipe to be injected with chlorine enters
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER /13
 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 2012/13 COURSE NAME: ENGINEERING MECHANICS - STATICS CODE: ENG 2008 GROUP: AD ENG II DATE: May 2013 TIME: DURATION: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 2012/13 COURSE NAME: ENGINEERING MECHANICS - STATICS CODE: ENG 2008 GROUP: AD ENG II DATE: May 2013 TIME: DURATION: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
SPECIAL CONDITION. Water Load Conditions. SPECIAL CONDITION Water Load Conditions
 Doc. No. : SC-CVLA.051-01 Issue : 1d Date : 04-Aug-009 Page : 1 of 13 SUBJECT : CERTIFICATION SPECIFICATION : VLA.51 PRIMARY GROUP / PANEL : 03 (Structure) SECONDARY GROUPE / PANEL : -- NATURE : SCN VLA.51
Doc. No. : SC-CVLA.051-01 Issue : 1d Date : 04-Aug-009 Page : 1 of 13 SUBJECT : CERTIFICATION SPECIFICATION : VLA.51 PRIMARY GROUP / PANEL : 03 (Structure) SECONDARY GROUPE / PANEL : -- NATURE : SCN VLA.51
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05010302 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, February 2008 ENGINEERING MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Metallurgy & Material Technology, Production Engineering,
Code No: R05010302 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, February 2008 ENGINEERING MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Metallurgy & Material Technology, Production Engineering,
CARGO STOWAGE AND SECURING
 Resolutions from the 17th Session of the Assembly of IMO, November 1991, as amended CODE OF SAFE PRACTICE FOR CARGO STOWAGE AND SECURING CARGO STOWAGE AND SECURING ANNEX 13. Til bruk i maritime fagskoler
Resolutions from the 17th Session of the Assembly of IMO, November 1991, as amended CODE OF SAFE PRACTICE FOR CARGO STOWAGE AND SECURING CARGO STOWAGE AND SECURING ANNEX 13. Til bruk i maritime fagskoler
Pullout Tests of Geogrids Embedded in Non-cohesive Soil
 Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 51 (2004), No. 2, pp. 135 147 Pullout Tests of Geogrids Embedded in Non-cohesive Soil Angelika Duszyńska, Adam F. Bolt Gdansk University of
Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 51 (2004), No. 2, pp. 135 147 Pullout Tests of Geogrids Embedded in Non-cohesive Soil Angelika Duszyńska, Adam F. Bolt Gdansk University of
Effect of Tethers Tension Force in the Behavior of a Tension Leg Platform Subjected to Hydrodynamic Force Amr R. El-Gamal, Ashraf Essa, Ayman Ismail
 Vol:7, No:1, 13 Effect of Tethers Tension Force in the Behavior of a Tension Leg Platform Subjected to Hydrodynamic Force Amr R. El-Gamal, Ashraf Essa, Ayman Ismail International Science Index, Bioengineering
Vol:7, No:1, 13 Effect of Tethers Tension Force in the Behavior of a Tension Leg Platform Subjected to Hydrodynamic Force Amr R. El-Gamal, Ashraf Essa, Ayman Ismail International Science Index, Bioengineering
Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships
 (August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
(August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION. Ships. Part 3 Hull Chapter 6 Hull local scantling. Edition January 2017 DNV GL AS
 RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION Ships Edition January 2017 Part 3 Hull Chapter 6 The content of this service document is the subject of intellectual property rights reserved by ("DNV GL"). The user accepts that
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION Ships Edition January 2017 Part 3 Hull Chapter 6 The content of this service document is the subject of intellectual property rights reserved by ("DNV GL"). The user accepts that
Classification of Cranes and Components
 Classification of Cranes and Components Why there is no need for M-Classes Cranes move loads the mass of which is within their rated capacity. However there are wide variations in their duty. The crane
Classification of Cranes and Components Why there is no need for M-Classes Cranes move loads the mass of which is within their rated capacity. However there are wide variations in their duty. The crane
Selection Calculations For Linear & Rotary Actuators
 H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods
 ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
Eng Sample Test 4
 1. An adjustable tow bar connecting the tractor unit H with the landing gear J of a large aircraft is shown in the figure. Adjusting the height of the hook F at the end of the tow bar is accomplished by
1. An adjustable tow bar connecting the tractor unit H with the landing gear J of a large aircraft is shown in the figure. Adjusting the height of the hook F at the end of the tow bar is accomplished by
Ship Control in Manoeuvring Situations with Fuzzy Logic Controllers
 International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number March 28 Ship Control in Manoeuvring Situations with Fuzzy Logic Controllers L. Morawski Gnia Maritime University,
International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number March 28 Ship Control in Manoeuvring Situations with Fuzzy Logic Controllers L. Morawski Gnia Maritime University,
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF A NEW TYPE OF DEEP DRAFT MULTI-COLUMN FDPSO
 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 5, No. 3, pp. 39-3 (17) 39 DOI: 1.6119/JMST-17-15-1 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF A NEW TYPE OF DEEP DRAFT MULTI-COLUMN FDPSO Jia-Yang
Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 5, No. 3, pp. 39-3 (17) 39 DOI: 1.6119/JMST-17-15-1 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF A NEW TYPE OF DEEP DRAFT MULTI-COLUMN FDPSO Jia-Yang
SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy
 SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy Research Paper January 2011 Vol.54 No.1: 26 34 Hydrodynamics in Ocean Engineering doi: 10.1007/s11433-010-4200-1 Full scale measurement for FPSO on motions
SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy Research Paper January 2011 Vol.54 No.1: 26 34 Hydrodynamics in Ocean Engineering doi: 10.1007/s11433-010-4200-1 Full scale measurement for FPSO on motions
Product Description. Further highlights. Outstanding features. 4 Bosch Rexroth Corporation Miniature Linear Modules R310A 2418 (2009.
 4 Bosch Rexroth orporation Miniature Linear Modules R310A 2418 (2009.05) Product Description Outstanding features Rexroth Miniature Linear Modules are precise, ready-to-install linear motion systems that
4 Bosch Rexroth orporation Miniature Linear Modules R310A 2418 (2009.05) Product Description Outstanding features Rexroth Miniature Linear Modules are precise, ready-to-install linear motion systems that
2.2 Mechanical Equilibrium WALKING THE PLANK. Purpose
 Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 2.2 Mechanical Equilibrium WALKING THE PLANK Thanx to Howie Brand Purpose In this activity, you will measure and interpret the forces acting on an object
Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 2.2 Mechanical Equilibrium WALKING THE PLANK Thanx to Howie Brand Purpose In this activity, you will measure and interpret the forces acting on an object
Selection Calculations For Motorized Actuators
 Selection Calculations/ Selection Calculations For Linear Slides and Cylinders Select from the EZS Series, EZS Series for Cleanroom Use, EZC Series First determine your series, then select your model.
Selection Calculations/ Selection Calculations For Linear Slides and Cylinders Select from the EZS Series, EZS Series for Cleanroom Use, EZC Series First determine your series, then select your model.
VIBRATION MEASUREMENT OF TSING MA BRIDGE DECK UNITS DURING ERECTION
 VIBRATION MEASUREMENT OF TSING MA BRIDGE DECK UNITS DURING ERECTION Tommy CHAN Assistant Professor The Polytechnic University Ching Kwong LAU Deputy Director Highways Dept., Government Jan Ming KO Chair
VIBRATION MEASUREMENT OF TSING MA BRIDGE DECK UNITS DURING ERECTION Tommy CHAN Assistant Professor The Polytechnic University Ching Kwong LAU Deputy Director Highways Dept., Government Jan Ming KO Chair
Sailing Performance and Maneuverability of a Traditional Ryukyuan Tribute Ship
 sia Navigation Conference 009 ailing Performance and Maneuverability of a Traditional Ryukyuan Tribute hip by Yutaka MUYM (Kanazawa Institute of Technology) Hikaru YGI (Tokai University ) Yutaka TERO (Tokai
sia Navigation Conference 009 ailing Performance and Maneuverability of a Traditional Ryukyuan Tribute hip by Yutaka MUYM (Kanazawa Institute of Technology) Hikaru YGI (Tokai University ) Yutaka TERO (Tokai
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION. Ships. Part 3 Hull Chapter 10 Special requirements. Edition January 2017 DNV GL AS
 RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION Ships Edition January 2017 Part 3 Hull Chapter 10 The content of this service document is the subject of intellectual property rights reserved by ("DNV GL"). The user accepts that
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION Ships Edition January 2017 Part 3 Hull Chapter 10 The content of this service document is the subject of intellectual property rights reserved by ("DNV GL"). The user accepts that
Back to Basics: Realizing Cabling Determines Design. F. Patrick Mahoney, CSI CDT, RCDD Direct Supply - Aptura
 Back to Basics: Realizing Cabling Determines Design F. Patrick Mahoney, CSI CDT, RCDD Direct Supply - Aptura Back to Basics: Realizing Cabling Determines Design Cabling distribution design implementation
Back to Basics: Realizing Cabling Determines Design F. Patrick Mahoney, CSI CDT, RCDD Direct Supply - Aptura Back to Basics: Realizing Cabling Determines Design Cabling distribution design implementation
Study Questions/Problems Week 4
 Study Questions/Problems Week 4 Chapter 6 treats many topics. I have selected on average less than three problems from each topic. I suggest you do them all. Likewise for the Conceptual Questions and exercises,
Study Questions/Problems Week 4 Chapter 6 treats many topics. I have selected on average less than three problems from each topic. I suggest you do them all. Likewise for the Conceptual Questions and exercises,
Product description. Compact Modules. Characteristic features. Further highlights
 4 Compact Modules Product description Characteristic features Five fine-tuned sizes based on a compact precision aluminum profile with two integrated pre-tensioned ball rail systems Identical external
4 Compact Modules Product description Characteristic features Five fine-tuned sizes based on a compact precision aluminum profile with two integrated pre-tensioned ball rail systems Identical external
AP Q1 Practice Questions Kinematics, Forces and Circular Motion
 AP Q1 Practice Questions Kinematics, Forces and Circular Motion Q1 1999B1. (REDUCED 9 mins) The Sojourner rover vehicle shown in the sketch above was used to explore the surface of Mars as part of the
AP Q1 Practice Questions Kinematics, Forces and Circular Motion Q1 1999B1. (REDUCED 9 mins) The Sojourner rover vehicle shown in the sketch above was used to explore the surface of Mars as part of the
Page 1. A Grieg Group Company
 Page 1 ECDIS PAST, PRESENT & Future 2000-2010 Past Present 2010-2015 2015... Future Page 2 History Page 3 DEEPLY - Past What is going on there????? I am Checking now Sir Page 4 ECDIS History ECDIS has
Page 1 ECDIS PAST, PRESENT & Future 2000-2010 Past Present 2010-2015 2015... Future Page 2 History Page 3 DEEPLY - Past What is going on there????? I am Checking now Sir Page 4 ECDIS History ECDIS has
Forces. A Force is a push or a pull on an object. Forces can cause a resting object to move
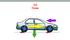 13.2 Forces Forces A Force is a push or a pull on an object Forces can cause a resting object to move Forces can cause a moving object to accelerate by changing its speed or its direction Measuring Force
13.2 Forces Forces A Force is a push or a pull on an object Forces can cause a resting object to move Forces can cause a moving object to accelerate by changing its speed or its direction Measuring Force
Real-Time Measurement of Sea Ice Thickness, Keel Sizes and Distributions and Ice Velocities Using Upward Looking Sonar Instruments
 Real-Time Measurement of Sea Ice Thickness, Keel Sizes and Distributions and Ice Velocities Using Upward Looking Sonar Instruments David Fissel, Rene Chave and Jan Buermans ASL Environmental Sciences Inc.
Real-Time Measurement of Sea Ice Thickness, Keel Sizes and Distributions and Ice Velocities Using Upward Looking Sonar Instruments David Fissel, Rene Chave and Jan Buermans ASL Environmental Sciences Inc.
Ice Class Regulations and the Application Thereof
 1 (65) Date of issue: 14 Nov. 2017 Entry into force: 1 Dec. 2017 Validity: indefinitely Legal basis: Act on the Ice Classes of Ships and Icebreaker Assistance (1121/2005), section 4.1 Implemented EU legislation:
1 (65) Date of issue: 14 Nov. 2017 Entry into force: 1 Dec. 2017 Validity: indefinitely Legal basis: Act on the Ice Classes of Ships and Icebreaker Assistance (1121/2005), section 4.1 Implemented EU legislation:
INF.7. Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee. Working Party on the Transport of Dangerous Goods 23 July 2012
 Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee Working Party on the Transport of Dangerous Goods 23 July 2012 Joint Meeting of the RID Committee of Experts and the Working Party on the Transport
Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee Working Party on the Transport of Dangerous Goods 23 July 2012 Joint Meeting of the RID Committee of Experts and the Working Party on the Transport
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF FREE STANDING HYBRID RISERS. A Thesis TIANCONG HOU
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF FREE STANDING HYBRID RISERS A Thesis by TIANCONG HOU Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF FREE STANDING HYBRID RISERS A Thesis by TIANCONG HOU Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Forces. A Force is a push or a pull on an object. Forces can cause a resting object to move
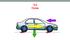 13.2 Forces Forces A Force is a push or a pull on an object Forces can cause a resting object to move Forces can cause a moving object to accelerate by changing its speed or its direction Measuring Force
13.2 Forces Forces A Force is a push or a pull on an object Forces can cause a resting object to move Forces can cause a moving object to accelerate by changing its speed or its direction Measuring Force
AP Physics Free Response Practice Dynamics
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Dynamics 14) In the system shown above, the block of mass M 1 is on a rough horizontal table. The string that attaches it to the block of mass M 2 passes over a frictionless
AP Physics Free Response Practice Dynamics 14) In the system shown above, the block of mass M 1 is on a rough horizontal table. The string that attaches it to the block of mass M 2 passes over a frictionless
Visit any one of our 30 locations or visit us on line at
 TYPE IA ALUMINUM 2886509079 2886501870 2886510013 2886510010 2886510014 2886504441 AS3002 2' TYPE IA AS3003 3' TYPE IA AS3004 4' TYPE IA AS3006 6' TYPE IA AS3008 8' TYPE IA AS3010 10' TYPE IA 34.99 57.99
TYPE IA ALUMINUM 2886509079 2886501870 2886510013 2886510010 2886510014 2886504441 AS3002 2' TYPE IA AS3003 3' TYPE IA AS3004 4' TYPE IA AS3006 6' TYPE IA AS3008 8' TYPE IA AS3010 10' TYPE IA 34.99 57.99
Rubber- and cellular buffers
 Rubber- and cellular buffers Rubber- and cellular buffers Industrial Brakes Thrusters Pressure Oil Pumps Couplings Hydraulic Buffers Cellular Buffers Rail Pliers Sheaves Hook Blocks Crane Rail Wheels Rail
Rubber- and cellular buffers Rubber- and cellular buffers Industrial Brakes Thrusters Pressure Oil Pumps Couplings Hydraulic Buffers Cellular Buffers Rail Pliers Sheaves Hook Blocks Crane Rail Wheels Rail
Compendium Screw Jacks
 Compendium Screw Jacks Screw Jack Technology Overview of chapters Useful information Project planning Screw jacks Bevel gear boxes Lifting screw protective covers Couplings and connecting shafts Accessories
Compendium Screw Jacks Screw Jack Technology Overview of chapters Useful information Project planning Screw jacks Bevel gear boxes Lifting screw protective covers Couplings and connecting shafts Accessories
RULES FOR THE CONSTRUCTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF SHIPS IDENTIFIED BY THEIR MISSIONS DREDGERS AND MUD BARGES CHAPTERS CHAPTERS SCOPE
 PARTE II RULES FOR THE CONSTRUCTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF SHIPS IDENTIFIED BY THEIR MISSIONS TÍTULO 43 DREDGERS AND MUD BARGES SECTION 2 STRUCTURE CHAPTERS SECTION 2 STRUCTURE CHAPTERS A B C SCOPE DOCUMENTS,
PARTE II RULES FOR THE CONSTRUCTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF SHIPS IDENTIFIED BY THEIR MISSIONS TÍTULO 43 DREDGERS AND MUD BARGES SECTION 2 STRUCTURE CHAPTERS SECTION 2 STRUCTURE CHAPTERS A B C SCOPE DOCUMENTS,
Investigation of Drill Bit Heave Response to Drill Rig Heave Excitation
 Investigation of Drill Bit Heave Response to Drill Rig Heave Excitation Liqing Huang, Galin V. Tahchiev and Yusong Cao MARINTEK USA Inc 263 Augusta Drive, Suite 2, Houston, Texas, 7757, USA ABSTRACT Managing
Investigation of Drill Bit Heave Response to Drill Rig Heave Excitation Liqing Huang, Galin V. Tahchiev and Yusong Cao MARINTEK USA Inc 263 Augusta Drive, Suite 2, Houston, Texas, 7757, USA ABSTRACT Managing
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling.
 SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
Engineering Forecasts and Monitoring for Offshore Construction Operations
 Engineering Forecasts and Monitoring for Offshore Construction Operations Peter Lai 1 (M), Anton Slozkin 1 (AM) 1. Saipem Limited, Engineering Department A successful offshore construction operation such
Engineering Forecasts and Monitoring for Offshore Construction Operations Peter Lai 1 (M), Anton Slozkin 1 (AM) 1. Saipem Limited, Engineering Department A successful offshore construction operation such
Pre-owned - 8 colour press FA-Line: FA-4* NEXT CLEANINKING #F4733 MODULAR 16" MULTI-SUBSTRATE FLEXO PRESS
 Pre-owned - colour press FA-Line: FA-4* NEXT CLEANINKING #F4733 MODULAR 6" MULTI-SUBSTRATE FLEXO PRESS Press Specification Number: Date: Our ref.: 60270 9.06.20 JAL/kis U N W I N D M O D U L E Motorized
Pre-owned - colour press FA-Line: FA-4* NEXT CLEANINKING #F4733 MODULAR 6" MULTI-SUBSTRATE FLEXO PRESS Press Specification Number: Date: Our ref.: 60270 9.06.20 JAL/kis U N W I N D M O D U L E Motorized
1. Two forces are applied to a wooden box as shown below. Which statement best describes the effect these forces have on the box?
 1. Two forces are applied to a wooden box as shown below. Which statement best describes the effect these forces have on the box? A. The box does not move. B. The box moves to the right. C. The box moves
1. Two forces are applied to a wooden box as shown below. Which statement best describes the effect these forces have on the box? A. The box does not move. B. The box moves to the right. C. The box moves
Lab Section Date. ME4751 Air Flow Rate Measurement
 Name Lab Section Date ME4751 Air Flow Rate Measurement Objective The objective of this experiment is to determine the volumetric flow rate of air flowing through a pipe using a Pitot-static tube and a
Name Lab Section Date ME4751 Air Flow Rate Measurement Objective The objective of this experiment is to determine the volumetric flow rate of air flowing through a pipe using a Pitot-static tube and a
Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses
 (Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
(Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
Client RSK Environment Ltd Job No. J387 Date 19/11/2016. Project: Environmental Survey Location: Otranto Vessel: RV Atlante
 FUGRO OCEANSISMICA S.p.A. GEODETIC PARAMETERS Client RSK Environment Ltd Job No. J387 Date 19/11/216 Project: Environmental Survey Location: Otranto Vessel: RV Atlante WGS-84 Geodetic Parameters Datum
FUGRO OCEANSISMICA S.p.A. GEODETIC PARAMETERS Client RSK Environment Ltd Job No. J387 Date 19/11/216 Project: Environmental Survey Location: Otranto Vessel: RV Atlante WGS-84 Geodetic Parameters Datum
Cooperative Control Applied to Multi-Vessel DP Operations - Numerical and Experimental Analysis
 Author s Name Name of the Paper Session DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 15-1, 213 RISK SESSION Cooperative Control Applied to Multi-Vessel DP Operations - Numerical and Experimental Analysis By
Author s Name Name of the Paper Session DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 15-1, 213 RISK SESSION Cooperative Control Applied to Multi-Vessel DP Operations - Numerical and Experimental Analysis By
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT
 Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
Wake fraction and thrust deduction during ship astern manoeuvres
 Wake fraction and thrust deduction during ship astern manoeuvres J. Artyszuk Maritime University of Szczecin, Poland Abstract A relatively small amount of data concerning the behaviour of propulsion coefficients,
Wake fraction and thrust deduction during ship astern manoeuvres J. Artyszuk Maritime University of Szczecin, Poland Abstract A relatively small amount of data concerning the behaviour of propulsion coefficients,
FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTIONS PREAMBLE. There are two types of vibrations: resonance and instability.
 FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTIONS PREAMBLE There are two types of vibrations: resonance and instability. Resonance occurs when a structure is excited at a natural frequency. When damping is low, the structure
FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTIONS PREAMBLE There are two types of vibrations: resonance and instability. Resonance occurs when a structure is excited at a natural frequency. When damping is low, the structure
Overview. Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance
 Friction Chapter 8 Overview Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance Dry Friction Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents slipping of the body
Friction Chapter 8 Overview Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance Dry Friction Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents slipping of the body
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
RULES PUBLICATION NO. 17/P ZONE STRENGTH ANALYSIS OF HULL STRUCTURE OF ROLL ON/ROLL OFF SHIP
 RULES PUBLICATION NO. 17/P ZONE STRENGTH ANALYSIS OF HULL STRUCTURE OF ROLL ON/ROLL OFF SHIP 1995 Publications P (Additional Rule Requirements), issued by Polski Rejestr Statków, complete or extend the
RULES PUBLICATION NO. 17/P ZONE STRENGTH ANALYSIS OF HULL STRUCTURE OF ROLL ON/ROLL OFF SHIP 1995 Publications P (Additional Rule Requirements), issued by Polski Rejestr Statków, complete or extend the
IODP Expedition 341S: SCIMPI and 858G ReCORK. Week 1 Report (19 27 May 2013) Operations. Victoria Port Call and Transit to Hole 858G
 IODP Expedition 341S: SCIMPI and 858G ReCORK Week 1 Report (19 27 May 2013) Operations Victoria Port Call and Transit to Hole 858G IODP SCIMPI and 858G ReCORK Expedition (341S) officially began when the
IODP Expedition 341S: SCIMPI and 858G ReCORK Week 1 Report (19 27 May 2013) Operations Victoria Port Call and Transit to Hole 858G IODP SCIMPI and 858G ReCORK Expedition (341S) officially began when the
Physics. Chapter 8 Rotational Motion
 Physics Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Circular Motion Tangential Speed The linear speed of something moving along a circular path. Symbol is the usual v and units are m/s Rotational Speed Number of revolutions
Physics Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Circular Motion Tangential Speed The linear speed of something moving along a circular path. Symbol is the usual v and units are m/s Rotational Speed Number of revolutions
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION Inland navigation vessels. Part 3 Structures, equipment Chapter 2 Design load principles. Edition December 2015 DNV GL AS
 RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION Inland navigation vessels Edition December 2015 Part 3 Structures, equipment Chapter 2 s The content of this service document is the subject of intellectual property rights reserved
RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION Inland navigation vessels Edition December 2015 Part 3 Structures, equipment Chapter 2 s The content of this service document is the subject of intellectual property rights reserved
DYNAMIC LOADING APPROACH FOR FLOATING PRODUCTION, STORAGE AND OFFLOADING (FPSO) INSTALLATIONS
 Guide for Dynamic Loading Approach for Floating Production, Storage and Offloading (FPSO) Installations GUIDE FOR DYNAMIC LOADING APPROACH FOR FLOATING PRODUCTION, STORAGE AND OFFLOADING (FPSO) INSTALLATIONS
Guide for Dynamic Loading Approach for Floating Production, Storage and Offloading (FPSO) Installations GUIDE FOR DYNAMIC LOADING APPROACH FOR FLOATING PRODUCTION, STORAGE AND OFFLOADING (FPSO) INSTALLATIONS
DYNAMICS ME HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS
 DYNAMICS ME 34010 HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS Mahmoud M. Safadi 1, M.B. Rubin 2 1 safadi@technion.ac.il, 2 mbrubin@technion.ac.il Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Spring
DYNAMICS ME 34010 HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS Mahmoud M. Safadi 1, M.B. Rubin 2 1 safadi@technion.ac.il, 2 mbrubin@technion.ac.il Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Spring
VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 Proceedings of COBEM 2007 Copyright 2007 by ABCM 19th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 5-9, 2007, Brasília, DF VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Luiz
Proceedings of COBEM 2007 Copyright 2007 by ABCM 19th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 5-9, 2007, Brasília, DF VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Luiz
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results
 Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
