@ Lesson(591(Solving(Inequalities(by(Addition(and(Subtraction( 78-12>65
|
|
|
- Rosalind Lamb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
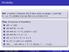
1 182 Page1 AlgebraIUnit2LinearRelationships Chapter5LinearInequalities Lesson591SolvingInequalitiesbyAdditionandSubtraction Objectives: Icansolvelinearequalitiesbyusingaddition Icansolvelinearinequalitiesbyusingsubtraction CCSS: ACED1,AREI3,MP2,MP4 Example1:SolvebyAdding Solvec 12>65Checkyoursolution C > 77 GuidedPractice1:SolvebyAdding 7812>65 66 > 65 SolveeachinequalityCheckyoursolution a 22>m 8 + s Check b d 14 L Check die l9
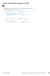
2 ,<o Page2 StandardizedTestExample2:SolvebySubtracting Solvetheinequalityx+23<14 A%%{x x < 9} B{x x < 37} C{x x > 9} D{x x > 39} GuidedPractice2:SolvebySubtracting Solvep+8 18 s 3 23 stg xc 9 F%%{p p 10} G{p p 10} H{p p 26} J{p p 126} 10+23<14 132<14 Example3:VariablesonEachSide Solve12nL4 13nThengraphthesolutionsetonanumberline 12h 12N YEE tgl#i # GuidedPractice3:VariablesonEachSide SolveeachinequalityThengraphthesolutionsetonanumberline, a 9n 1<10n an an b 5h 12+4h 4h 4h HER icn o 4 07 for LIS^ 13
3 Page3 Real9WorldExample4:UseanInequalitytoSolveaProblem PamwantstobuyseasonpassestotwothemeparksIfoneseasonpasscosts$5499andPamhas$100 tospendonbothpasses,thesecondseasonpassmustcostnomorethanwhatamount? 100> ,012 X GuidedPractice4:UseanInequalitytoSolveaProblem $4501 Samhas$65tospendatthemallHeboughtaTLshirtfor$18andabeltfor$14IfSamwantsapairof jeans,howmuchcanhespend? > Lesson592SolvingInequalitiesbyMultiplicationandDivision 33 >_ X Objectives: Icansolvelinearinequalitiesbyusingmultiplication Icansolvelinearinequalitiesbyusingdivision CCSS: ACED1,AREI3,MP1,MP6
4 Page4 Real9WorldExample1:WriteandSolveanInequalityUPSCheck) Mattwalksatarateof¾mileperhourHeknowsthatitisatleast9milestoOnyxLakeHowlongwillit takematttogetthere?writeandsolveaninequalitytofindthetime R 9<30 D= RT MountKinabalueinMalaysiahasthegreatestconcentrationofwildorchidsonEarthItcontainsmore than750species,oraboutonefourthofallorchidspeciesinmalaysiahowmanyorchidspeciesare thereinmalaysia? cheek 9<3*40 ) q4i3q 363<35 9<3403 it < ytm 3000 < M
5 5 Page5 Example2:SolvebyMultiplying 5 Solve 3 5 d 6Graphthesolutiononanumberline 31>30 check =3 =3 d*i0 3g 0>6 o# Nol GuidedPractice2:SolvebyMultiplying D= e 10 4TH SolveeachinequalityGraphthesolutiononanumberline a n 6 8 b r8 3 8 t < 5 ' U 6 nz 48 => is > t< 131/3 th 3t< Example3:DividetoSolveanInequality SolveeachinequalityGraphthesolutiononanumberline a 12k 60 kz5 a a 4 TH
6 Hk ' Page6 b L8q<136 I I GuidedPractice3:DividetoSolveanInequality SolveeachinequalityGraphthesolutiononanumberline a L42 6r q > 17 tis#hqq7zrhyte o b L12h>15 a 72 " tinfo Lesson593SolvingMulti9StepInequalities Objectives: Icansolvelinearinequalitiesinvolvingmorethanoneoperation IcansolvelinearinequalitiesinvolvingtheDistributiveProperty CCSS: ACED1,AREI3,MP7 Real9WorldExample1:SolveaMulti9StepInequality Adrianahasabudgetof$115forfaxesThefaxservicesheusescharges$25toactivateanaccountand $008perpagetosendfaxesHowmanypagescanAdrianafaxandstaywithinherbudget? GuidedPractice1:SolveaMulti9StepInequality ThePrintShopadvertisesaspecialtoprint400flyersforlessthanthecompetitionThepriceincludesa $350setLupfeeIfthecompetitioncharges$3550,whatdoesthePrintShopchargeforeachflyer? Example2:InequalityInvolvingaNegativeCoefficient Solve13 11d 79Graphthesolutiononanumberline p 1 O8p pe s 25 Toy Is ,50 > p 32>40/ Too 66 DE 6 =, Ii 7 GuidedPractice2:InequalityInvolvingaNegativeCoefficient SolveeachinequalityGraphthesolutiononanumberline k PE 1125 p< 108 a w W a a 6,51W > LIFT
7 28L IK 8< 4k Page7 b 43>L4y > If It 11 4y y a 1 as Example3:WriteandSolveanInequality Defineavariable,writeaninequality,andsolvetheproblemThencheckyoursolutionFour%times%a% number%plus%twelve%is%less%than%the%number%minus%three% io/4x+1zcxz 3 1,3<72 B 3X< GuidedPractice3:WriteandSolveandInequality 5 3 Defineavariable,writeaninequality,andsolvetheproblemThencheckyoursolutionTwo%more%than% half%of%a%number%is%greater%than%twenty=seven% Example4:DistributiveProperty Solve6c+32 c) L2c+1Graphthesolutiononanumberline GuidedPractice4:DistributiveProperty SolveeachinequalityGraphthesolutiononanumberline a 65z 3) 36z 3Oz n 60+63=2 b 2h+6)>L38 h) 2h 2h Example5:EmptySetandAllReals SolveeachinequalityCheckyoursolution a L7k+4)+11k 8k 22k+1) n It 'zx > It Zctl texszst > < 5 cz *6>92%+1 5C 25 gte 30218<362 mm n 112> To 13W 12>24 the 2h k >_ 8k n F 18<62 6 F 3 EZ h< jo# k O No he 4k solution 4k 282 4k 2 z at to
8 24C Page8 x b 24r+3) 22+8r 2) m 1 ' R 8r +6<22 + 8r 16 8rt6 E 8r +6 6<6 GuidedPractice5:EmptySetandAllReals SolveeachinequalityCheckyoursolution a 18 38c+4) L64c 1) 18 24C C C 16 b 46 8m 42m+5) +6 #, < m 46=20 8m 20 Lesson594SolvingCompoundInequalities No solution z 4TH Objectives: Icansolvecompoundinequalitiescontainingthewordand,andgraphtheirsolutionset Icansolvecompoundinequalitiescontainingthewordor,andgraphtheirsolutionset CCSS: ACED1,AREI3,MP1,MP8 Example1:SolveandGraphanIntersection Solve7<z+2 11Thengraphthesolutionset GuidedPractice1:SolveandGraphanIntersection SolveeachcompoundinequalityThengraphthesolutionset z =9 tfm a y 3 L11andy 3 L8 ye aia;, tfm# I b 6 r+7<10 z 7 7 ±r< 3 art tmy
9 Page9 Real9WorldExample2:WriteandGraphaCompoundInequality AskiresorthasseveraltypesofhotelroomsandcabinsThehotelroomscostatmost$89pernight,and thecabinscostatleast$109pernightwriteandgraphacompoundinequalitythatdescribesthe amountaguestwouldpaypernightattheresort GuidedPractice2:WriteandGraphaCompoundInequality Acompanyismanufacturinganactionfigurethatmustbeatleast112centimetersandatmost114 centimeterstallwriteandgraphacompoundinequalitythatdescribeshowtalltheactionfigurecanbe 892C OR 109 EC, Example3:SolveandGraphaUnion hit Solve4k 7 25or12 9k 30Thengraphthesolutionset k 8 or n z GuidedPractice3:SolveandGraphaUnion on > lz 4k 32 9k >_ 18 II ZEX AND 11,42 z 0 SolveeachcompoundinequalityThengraphthesolutionset It <i {= 11,4 ' : its ;if p a a%+1<4ora 1 3 too 9<3 or a > 4 fat b x 9or2+4x<10 X±9 or 4x< < 8 2 a o o o THfbtla 'I
Green s Theorem. Fundamental Theorem for Conservative Vector Fields
 Assignment - Mathematics 4(Model Answer) onservative vector field and Green theorem onservative Vector Fields If F = φ, for some differentiable function φ in a domaind, then we say that F is conservative
Assignment - Mathematics 4(Model Answer) onservative vector field and Green theorem onservative Vector Fields If F = φ, for some differentiable function φ in a domaind, then we say that F is conservative
MS 2001: Test 1 B Solutions
 MS 2001: Test 1 B Solutions Name: Student Number: Answer all questions. Marks may be lost if necessary work is not clearly shown. Remarks by me in italics and would not be required in a test - J.P. Question
MS 2001: Test 1 B Solutions Name: Student Number: Answer all questions. Marks may be lost if necessary work is not clearly shown. Remarks by me in italics and would not be required in a test - J.P. Question
An Obligation Regarding. Best Yet
 5 L K N C N LL b b b b b b L L L L L C G N Y C 2 929 L N 929 b L G Y b b Y N NK b b b < C b z b L C b b b Gb G b q b b : x C - Q C b 22 5 b 5 b b 5 2 b K 2 b 3-2 b 6 b Gb b Lb C C -- L - 9 : 999 929 ]
5 L K N C N LL b b b b b b L L L L L C G N Y C 2 929 L N 929 b L G Y b b Y N NK b b b < C b z b L C b b b Gb G b q b b : x C - Q C b 22 5 b 5 b b 5 2 b K 2 b 3-2 b 6 b Gb b Lb C C -- L - 9 : 999 929 ]
Polynomial Functions
 Polynomial Functions Equations and Graphs Characteristics The Factor Theorem The Remainder Theorem http://www.purplemath.com/modules/polyends5.htm 1 A cross-section of a honeycomb has a pattern with one
Polynomial Functions Equations and Graphs Characteristics The Factor Theorem The Remainder Theorem http://www.purplemath.com/modules/polyends5.htm 1 A cross-section of a honeycomb has a pattern with one
A quadratic expression is a mathematical expression that can be written in the form 2
 118 CHAPTER Algebra.6 FACTORING AND THE QUADRATIC EQUATION Textbook Reference Section 5. CLAST OBJECTIVES Factor a quadratic expression Find the roots of a quadratic equation A quadratic expression is
118 CHAPTER Algebra.6 FACTORING AND THE QUADRATIC EQUATION Textbook Reference Section 5. CLAST OBJECTIVES Factor a quadratic expression Find the roots of a quadratic equation A quadratic expression is
PRISON POLICY INITIATIVE ANNUAL REPORT
 PRISON POLICY INITIATIVE 2015-2016 2016-2017 ANNUAL REPORT N 2016 2017 PO Bx 127 N MA 01061 :// (413) 527-0845 1 T Ex D 1 W 3 P k 4 C R - 7 S j 8 B j 10 P x 12 P j 14 P 16 Wk 18 C x 19 Y P Nk S R 15 B
PRISON POLICY INITIATIVE 2015-2016 2016-2017 ANNUAL REPORT N 2016 2017 PO Bx 127 N MA 01061 :// (413) 527-0845 1 T Ex D 1 W 3 P k 4 C R - 7 S j 8 B j 10 P x 12 P j 14 P 16 Wk 18 C x 19 Y P Nk S R 15 B
CHAPTER X. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS.
 CHAPTER X. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS. 140. A SINGLE equation which contains two or more unknown quantities can be satisfied by an indefinite number of values of the unknown quantities. For we can give any
CHAPTER X. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS. 140. A SINGLE equation which contains two or more unknown quantities can be satisfied by an indefinite number of values of the unknown quantities. For we can give any
Ehrhart polynomial for lattice squares, cubes, and hypercubes
 Ehrhart polynomial for lattice squares, cubes, and hypercubes Eugen J. Ionascu UWG, REU, July 10th, 2015 math@ejionascu.ro, www.ejionascu.ro 1 Abstract We are investigating the problem of constructing
Ehrhart polynomial for lattice squares, cubes, and hypercubes Eugen J. Ionascu UWG, REU, July 10th, 2015 math@ejionascu.ro, www.ejionascu.ro 1 Abstract We are investigating the problem of constructing
Calculus With Analytic Geometry by SM. Yusaf & Prof.Muhammad Amin
 The Sphere Definition: The set of all points in space that are equidistant from a fixed point is called a sphere. The constant distance is called the radius of the sphere and the fixed point is called
The Sphere Definition: The set of all points in space that are equidistant from a fixed point is called a sphere. The constant distance is called the radius of the sphere and the fixed point is called
Roots and Coefficients Polynomials Preliminary Maths Extension 1
 Preliminary Maths Extension Question If, and are the roots of x 5x x 0, find the following. (d) (e) Question If p, q and r are the roots of x x x 4 0, evaluate the following. pq r pq qr rp p q q r r p
Preliminary Maths Extension Question If, and are the roots of x 5x x 0, find the following. (d) (e) Question If p, q and r are the roots of x x x 4 0, evaluate the following. pq r pq qr rp p q q r r p
UP and ENTRIES. Farmers and WivUs to Hold Old-Fashioned Meeting Here
 LD : g C L K C Y Y 4 L LLL C 7 944 v g 8 C g 85 Y K D L gv 7 88[ L C 94 : 8 g Cg x C? g v g 5 g g / /»» > v g g :! v! $ g D C v g g g 9 ; v g ] v v v g L v g g 6 g (; C g C C g! v g gg gv v v 8 g g q»v
LD : g C L K C Y Y 4 L LLL C 7 944 v g 8 C g 85 Y K D L gv 7 88[ L C 94 : 8 g Cg x C? g v g 5 g g / /»» > v g g :! v! $ g D C v g g g 9 ; v g ] v v v g L v g g 6 g (; C g C C g! v g gg gv v v 8 g g q»v
APPENDIX : PARTIAL FRACTIONS
 APPENDIX : PARTIAL FRACTIONS Appendix : Partial Fractions Given the expression x 2 and asked to find its integral, x + you can use work from Section. to give x 2 =ln( x 2) ln( x + )+c x + = ln k x 2 x+
APPENDIX : PARTIAL FRACTIONS Appendix : Partial Fractions Given the expression x 2 and asked to find its integral, x + you can use work from Section. to give x 2 =ln( x 2) ln( x + )+c x + = ln k x 2 x+
LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions
 LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions Section 11.4, # 40: This problem was solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 42: This problem was also solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 43: Also solved in class
LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions Section 11.4, # 40: This problem was solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 42: This problem was also solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 43: Also solved in class
Discovery Guide. Beautiful, mysterious woman pursued by gunmen. Sounds like a spy story...
 Dv G W C T Gp, A T Af Hk T 39 Sp. M Mx Hk p j p v, f M P v...(!) Af Hk T 39 Sp, B,,, UNMISSABLE! T - f 4 p v 150 f-p f x v. Bf, k 4 p v 150. H k f f x? D,,,, v? W k, pf p f p? W f f f? W k k p? T p xp
Dv G W C T Gp, A T Af Hk T 39 Sp. M Mx Hk p j p v, f M P v...(!) Af Hk T 39 Sp, B,,, UNMISSABLE! T - f 4 p v 150 f-p f x v. Bf, k 4 p v 150. H k f f x? D,,,, v? W k, pf p f p? W f f f? W k k p? T p xp
Downloaded from pdmag.info at 18: on Friday March 22nd 2019
 2 (- ( ( )*+, )%.!"# $% &" :( ( 2 * -% 345 678-397.) /0 &" &2. ) ( B(
2 (- ( ( )*+, )%.!"# $% &" :( ( 2 * -% 345 678-397.) /0 &" &2. ) ( B(
) = (3.5, 3) 5-3. check it out!
 44. Let be the irumenter of the. Given: = m; so by the properties of -6-9,. So = + = _ 5- = _ () = 4 m. medians and altitudes of Triangles hek it out! 1a. KZ + ZW = KW _ KW + ZW = KW ZW KW 7 KW 1 = KW
44. Let be the irumenter of the. Given: = m; so by the properties of -6-9,. So = + = _ 5- = _ () = 4 m. medians and altitudes of Triangles hek it out! 1a. KZ + ZW = KW _ KW + ZW = KW ZW KW 7 KW 1 = KW
1 (30 pts) Dominant Pole
 EECS C8/ME C34 Fall Problem Set 9 Solutions (3 pts) Dominant Pole For the following transfer function: Y (s) U(s) = (s + )(s + ) a) Give state space description of the system in parallel form (ẋ = Ax +
EECS C8/ME C34 Fall Problem Set 9 Solutions (3 pts) Dominant Pole For the following transfer function: Y (s) U(s) = (s + )(s + ) a) Give state space description of the system in parallel form (ẋ = Ax +
2. Matrix Algebra and Random Vectors
 2. Matrix Algebra and Random Vectors 2.1 Introduction Multivariate data can be conveniently display as array of numbers. In general, a rectangular array of numbers with, for instance, n rows and p columns
2. Matrix Algebra and Random Vectors 2.1 Introduction Multivariate data can be conveniently display as array of numbers. In general, a rectangular array of numbers with, for instance, n rows and p columns
MATH 250 REVIEW TOPIC 3 Partial Fraction Decomposition and Irreducible Quadratics. B. Decomposition with Irreducible Quadratics
 Math 250 Partial Fraction Decomposition Topic 3 Page MATH 250 REVIEW TOPIC 3 Partial Fraction Decomposition and Irreducible Quadratics I. Decomposition with Linear Factors Practice Problems II. A. Irreducible
Math 250 Partial Fraction Decomposition Topic 3 Page MATH 250 REVIEW TOPIC 3 Partial Fraction Decomposition and Irreducible Quadratics I. Decomposition with Linear Factors Practice Problems II. A. Irreducible
3.2 Gaussian Elimination (and triangular matrices)
 (1/19) Solving Linear Systems 3.2 Gaussian Elimination (and triangular matrices) MA385/MA530 Numerical Analysis 1 November 2018 Gaussian Elimination (2/19) Gaussian Elimination is an exact method for solving
(1/19) Solving Linear Systems 3.2 Gaussian Elimination (and triangular matrices) MA385/MA530 Numerical Analysis 1 November 2018 Gaussian Elimination (2/19) Gaussian Elimination is an exact method for solving
A monomial or sum of monomials
 Polynomial: A monomial or sum of monomials Polynomial in x is an expression of the form a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 +. a 1 x 1 + a 0 where n is a positive integer and a n 0 Example: 6x 3 + 2x 8x
Polynomial: A monomial or sum of monomials Polynomial in x is an expression of the form a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 +. a 1 x 1 + a 0 where n is a positive integer and a n 0 Example: 6x 3 + 2x 8x
EE263: Introduction to Linear Dynamical Systems Review Session 2
 EE263: Introduction to Linear Dynamical Systems Review Session 2 Basic concepts from linear algebra nullspace range rank and conservation of dimension EE263 RS2 1 Prerequisites We assume that you are familiar
EE263: Introduction to Linear Dynamical Systems Review Session 2 Basic concepts from linear algebra nullspace range rank and conservation of dimension EE263 RS2 1 Prerequisites We assume that you are familiar
3.2. Built Environment: Land Use and Transportation
 Affc, gfc Ipc, g p, g, pc., f A c c q q f qc b c f pjc p., ffc b c f A cp A 2, bc b f c f p fc. 3.2. : L U Tp 3.2.1. L U T c p xg UGA Kp C. I p cg F I f A pc f cg. T fc f pc c f, cg c, cpb. I cb pc c f
Affc, gfc Ipc, g p, g, pc., f A c c q q f qc b c f pjc p., ffc b c f A cp A 2, bc b f c f p fc. 3.2. : L U Tp 3.2.1. L U T c p xg UGA Kp C. I p cg F I f A pc f cg. T fc f pc c f, cg c, cpb. I cb pc c f
~fw. urning Desire. lean ul. «sw. Final Extinction NEW QUIRK 69, N. Q., TUESDAY, APR^FCX^^W. ted:
 EK» - - - u I» -? NE QUIRK 69 N Q UEDY PRFCX F Ex X!E - - - ; - - - ; & P --?!R» u \ u CCNY -C C j pp N up - [ P-up p upu >j u D CC F 9u - x pu x pp p p p u p & K I? - >
EK» - - - u I» -? NE QUIRK 69 N Q UEDY PRFCX F Ex X!E - - - ; - - - ; & P --?!R» u \ u CCNY -C C j pp N up - [ P-up p upu >j u D CC F 9u - x pu x pp p p p u p & K I? - >
A.dr.rwarded to foreiirti count rie will be f 7 SOperann.. rsri--.-j- -.?- .JULY. 12, lsiii).,11,111. yc:tl crst.iif. lit. J. lor Sale... Kb l.
 E E b g b E x Y b p p g b 2 x $ p 2 p p 6 p x b b p x p pp 5 b x b p Y Yg g pg 2 Dp g pb? xp p g G 2 p p x D D p 59 E 9pp b b x xp D p p? 8 5 2 pp E x z b x? p p Z 2 p p x p 9 p x p p EE E EY E G E p EQ
E E b g b E x Y b p p g b 2 x $ p 2 p p 6 p x b b p x p pp 5 b x b p Y Yg g pg 2 Dp g pb? xp p g G 2 p p x D D p 59 E 9pp b b x xp D p p? 8 5 2 pp E x z b x? p p Z 2 p p x p 9 p x p p EE E EY E G E p EQ
Core Mathematics 3 Algebra
 http://kumarmathsweeblycom/ Core Mathematics 3 Algebra Edited by K V Kumaran Core Maths 3 Algebra Page Algebra fractions C3 The specifications suggest that you should be able to do the following: Simplify
http://kumarmathsweeblycom/ Core Mathematics 3 Algebra Edited by K V Kumaran Core Maths 3 Algebra Page Algebra fractions C3 The specifications suggest that you should be able to do the following: Simplify
Final A. Problem Points Score Total 100. Math115A Nadja Hempel 03/23/2017
 Final A Math115A Nadja Hempel 03/23/2017 nadja@math.ucla.edu Name: UID: Problem Points Score 1 10 2 20 3 5 4 5 5 9 6 5 7 7 8 13 9 16 10 10 Total 100 1 2 Exercise 1. (10pt) Let T : V V be a linear transformation.
Final A Math115A Nadja Hempel 03/23/2017 nadja@math.ucla.edu Name: UID: Problem Points Score 1 10 2 20 3 5 4 5 5 9 6 5 7 7 8 13 9 16 10 10 Total 100 1 2 Exercise 1. (10pt) Let T : V V be a linear transformation.
Dr. Allen Back. Oct. 6, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back Oct. 6, 2014 Distribution Min=48 Max=100 Q1=74 Median=83 Q3=91.5 mean = 81.48 std. dev. = 12.5 Distribution Distribution: (The letters will not be directly used.) Scores Freq. 100 2 98-99
Dr. Allen Back Oct. 6, 2014 Distribution Min=48 Max=100 Q1=74 Median=83 Q3=91.5 mean = 81.48 std. dev. = 12.5 Distribution Distribution: (The letters will not be directly used.) Scores Freq. 100 2 98-99
WORLD MATHS DAY ACTIVITY PACK. Ages worldmathsday.com UNICEF WORLD MATHS DAY Lesson Plans Age 4 10 ACTIVITY RESOURCE
 UNICEF AND WORLD MATHS DAY Hp q WORLD MATHS DAY ACTIVITY PACK A 4-10 UNICEF WORLD MATHS DAY 2018 L P A 4 10 ACTIVITY RESOURCE APPENDIX 1 APPENDIX 2 G S---Bx S E f UNICEF WORLD MATHS DAY 2018 L P A 4-10
UNICEF AND WORLD MATHS DAY Hp q WORLD MATHS DAY ACTIVITY PACK A 4-10 UNICEF WORLD MATHS DAY 2018 L P A 4 10 ACTIVITY RESOURCE APPENDIX 1 APPENDIX 2 G S---Bx S E f UNICEF WORLD MATHS DAY 2018 L P A 4-10
Given a polynomial and one of its factors, find the remaining factors of the polynomial. 4. x 3 6x x 6; x 1 SOLUTION: Divide by x 1.
 Use synthetic substitution to find f (4) and f ( 2) for each function. 2. f (x) = x 4 + 8x 3 + x 2 4x 10 Divide the function by x 4. The remainder is 758. Therefore, f (4) = 758. Divide the function by
Use synthetic substitution to find f (4) and f ( 2) for each function. 2. f (x) = x 4 + 8x 3 + x 2 4x 10 Divide the function by x 4. The remainder is 758. Therefore, f (4) = 758. Divide the function by
P3.C8.COMPLEX NUMBERS
 Recall: Within the real number system, we can solve equation of the form and b 2 4ac 0. ax 2 + bx + c =0, where a, b, c R What is R? They are real numbers on the number line e.g: 2, 4, π, 3.167, 2 3 Therefore,
Recall: Within the real number system, we can solve equation of the form and b 2 4ac 0. ax 2 + bx + c =0, where a, b, c R What is R? They are real numbers on the number line e.g: 2, 4, π, 3.167, 2 3 Therefore,
 Twitter: @Owen134866 www.mathsfreeresourcelibrary.com Prior Knowledge Check 1) Simplify: a) 3x 2 5x 5 b) 5x3 y 2 15x 7 2) Factorise: a) x 2 2x 24 b) 3x 2 17x + 20 15x 2 y 3 3) Use long division to calculate:
Twitter: @Owen134866 www.mathsfreeresourcelibrary.com Prior Knowledge Check 1) Simplify: a) 3x 2 5x 5 b) 5x3 y 2 15x 7 2) Factorise: a) x 2 2x 24 b) 3x 2 17x + 20 15x 2 y 3 3) Use long division to calculate:
Homework Set #6 - Solutions
 EE 15 - Applications of Convex Optimization in Signal Processing and Communications Dr Andre Tkacenko JPL Third Term 11-1 Homework Set #6 - Solutions 1 a The feasible set is the interval [ 4] The unique
EE 15 - Applications of Convex Optimization in Signal Processing and Communications Dr Andre Tkacenko JPL Third Term 11-1 Homework Set #6 - Solutions 1 a The feasible set is the interval [ 4] The unique
P-FACTOR-APPROACH TO DEGENERATE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEMS
 P-FACTOR-APPROACH TO DEGENERATE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEMS 0. A. ~rezhneva,~ and A. A. ~ret'yakov~ ' ~e~artment of Mathematics and Statistics, Miami University, Oxford, OH 45056, USA, Brezhnoa@muohio.edu, 2~enter
P-FACTOR-APPROACH TO DEGENERATE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEMS 0. A. ~rezhneva,~ and A. A. ~ret'yakov~ ' ~e~artment of Mathematics and Statistics, Miami University, Oxford, OH 45056, USA, Brezhnoa@muohio.edu, 2~enter
Differential Groups and Differential Relations. Michael F. Singer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC USA
 Differential Groups and Differential Relations Michael F. Singer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC 27695-8205 USA http://www.math.ncsu.edu/ singer Theorem: (Hölder,
Differential Groups and Differential Relations Michael F. Singer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC 27695-8205 USA http://www.math.ncsu.edu/ singer Theorem: (Hölder,
McGill University Math 325A: Differential Equations LECTURE 12: SOLUTIONS FOR EQUATIONS WITH CONSTANTS COEFFICIENTS (II)
 McGill University Math 325A: Differential Equations LECTURE 12: SOLUTIONS FOR EQUATIONS WITH CONSTANTS COEFFICIENTS (II) HIGHER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (IV) 1 Introduction (Text: pp. 338-367, Chap.
McGill University Math 325A: Differential Equations LECTURE 12: SOLUTIONS FOR EQUATIONS WITH CONSTANTS COEFFICIENTS (II) HIGHER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (IV) 1 Introduction (Text: pp. 338-367, Chap.
Fast Polynomial Reduction. Nikolay Vassiliev Steklov Inst. оf Math. St.Petersburg
 Fast Polynomial Reduction Nikolay Vassiliev Steklov Inst. оf Math. St.Petersburg CADE2009, Papmlona, 2009 30 October Outline of the talk Gröbner bases and normal forms in commutative and differential algebra
Fast Polynomial Reduction Nikolay Vassiliev Steklov Inst. оf Math. St.Petersburg CADE2009, Papmlona, 2009 30 October Outline of the talk Gröbner bases and normal forms in commutative and differential algebra
TRAN S F O R M E R S TRA N SMI S S I O N. SECTION AB Issue 2, March, March,1958, by American Telephone and Telegraph Company
 B B, ch, 9 B h f h c h l f f Bll lh, c chcl l l k l, h, h ch f h f ll ll l f h lh h c ll k f Bll lh, c ck ll ch,9, c lh lh B B c x l l f f f 9 B l f c l f f l 9 f B c, h f c x ch 9 B B h f f fc Bll c f
B B, ch, 9 B h f h c h l f f Bll lh, c chcl l l k l, h, h ch f h f ll ll l f h lh h c ll k f Bll lh, c ck ll ch,9, c lh lh B B c x l l f f f 9 B l f c l f f l 9 f B c, h f c x ch 9 B B h f f fc Bll c f
Integration - Past Edexcel Exam Questions
 Integration - Past Edexcel Exam Questions 1. (a) Given that y = 5x 2 + 7x + 3, find i. - ii. - (b) ( 1 + 3 ) x 1 x dx. [4] 2. Question 2b - January 2005 2. The gradient of the curve C is given by The point
Integration - Past Edexcel Exam Questions 1. (a) Given that y = 5x 2 + 7x + 3, find i. - ii. - (b) ( 1 + 3 ) x 1 x dx. [4] 2. Question 2b - January 2005 2. The gradient of the curve C is given by The point
Quartic Equation. By CH vd Westhuizen A unique Solution assuming Complex roots. Ax^4 + Bx^3 + Cx^2 + Dx + E = 0
 Quartic Equation By CH vd Westhuizen A unique Solution assuming Complex roots The general Quartic is given by Ax^4 + Bx^3 + Cx^ + Dx + E = 0 As in the third order polynomial we are first going to reduce
Quartic Equation By CH vd Westhuizen A unique Solution assuming Complex roots The general Quartic is given by Ax^4 + Bx^3 + Cx^ + Dx + E = 0 As in the third order polynomial we are first going to reduce
2 If ax + bx + c = 0, then x = b) What are the x-intercepts of the graph or the real roots of f(x)? Round to 4 decimal places.
 Quadratic Formula - Key Background: So far in this course we have solved quadratic equations by the square root method and the factoring method. Each of these methods has its strengths and limitations.
Quadratic Formula - Key Background: So far in this course we have solved quadratic equations by the square root method and the factoring method. Each of these methods has its strengths and limitations.
DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON 22ND MARCH, TIME : 9-12 BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE]
![DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON 22ND MARCH, TIME : 9-12 BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON 22ND MARCH, TIME : 9-12 BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE]](/thumbs/90/102188445.jpg) DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON ND MARCH, TIME : 9- BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Let y = cos x (cos x cos x). Then y is (A) 0 only when x 0 (B) 0 for all real x (C) 0 for all real x
DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON ND MARCH, TIME : 9- BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Let y = cos x (cos x cos x). Then y is (A) 0 only when x 0 (B) 0 for all real x (C) 0 for all real x
PRACTICE PAPER -- III
 . PRACTICE PAPER -- III. z + z :::.0, if and only if (a) Re (z) ::: O (b) Im z) = 0 (c) z = 0 (d) none of these 2. zz = 0, if and only if (a) Re(z) = O (b) Im (z) = 0 (c) z = 0 (d) none of these 3. (3
. PRACTICE PAPER -- III. z + z :::.0, if and only if (a) Re (z) ::: O (b) Im z) = 0 (c) z = 0 (d) none of these 2. zz = 0, if and only if (a) Re(z) = O (b) Im (z) = 0 (c) z = 0 (d) none of these 3. (3
FINITE GROUPS AND EQUATIONS OVER FINITE FIELDS A PROBLEM SET FOR ARIZONA WINTER SCHOOL 2016
 FINITE GROUPS AND EQUATIONS OVER FINITE FIELDS A PROBLEM SET FOR ARIZONA WINTER SCHOOL 2016 PREPARED BY SHABNAM AKHTARI Introduction and Notations The problems in Part I are related to Andrew Sutherland
FINITE GROUPS AND EQUATIONS OVER FINITE FIELDS A PROBLEM SET FOR ARIZONA WINTER SCHOOL 2016 PREPARED BY SHABNAM AKHTARI Introduction and Notations The problems in Part I are related to Andrew Sutherland
Divisibility. Def: a divides b (denoted a b) if there exists an integer x such that b = ax. If a divides b we say that a is a divisor of b.
 Divisibility Def: a divides b (denoted a b) if there exists an integer x such that b ax. If a divides b we say that a is a divisor of b. Thm: (Properties of Divisibility) 1 a b a bc 2 a b and b c a c 3
Divisibility Def: a divides b (denoted a b) if there exists an integer x such that b ax. If a divides b we say that a is a divisor of b. Thm: (Properties of Divisibility) 1 a b a bc 2 a b and b c a c 3
VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE
 VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE A line in the xy-plane is determined when a point on the line and the direction of the line (its slope or angle of inclination) are given.
VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE A line in the xy-plane is determined when a point on the line and the direction of the line (its slope or angle of inclination) are given.
Lesson 3: Linear differential equations of the first order Solve each of the following differential equations by two methods.
 Lesson 3: Linear differential equations of the first der Solve each of the following differential equations by two methods. Exercise 3.1. Solution. Method 1. It is clear that y + y = 3 e dx = e x is an
Lesson 3: Linear differential equations of the first der Solve each of the following differential equations by two methods. Exercise 3.1. Solution. Method 1. It is clear that y + y = 3 e dx = e x is an
Lesson 3.4 Exercises, pages
 Lesson 3. Exercises, pages 17 A. Identify the values of a, b, and c to make each quadratic equation match the general form ax + bx + c = 0. a) x + 9x - = 0 b) x - 11x = 0 Compare each equation to ax bx
Lesson 3. Exercises, pages 17 A. Identify the values of a, b, and c to make each quadratic equation match the general form ax + bx + c = 0. a) x + 9x - = 0 b) x - 11x = 0 Compare each equation to ax bx
Lecture 3. Frits Beukers. Arithmetic of values of E- and G-function. Lecture 3 E- and G-functions 1 / 20
 Lecture 3 Frits Beukers Arithmetic of values of E- and G-function Lecture 3 E- and G-functions 1 / 20 G-functions, definition Definition An analytic function f (z) given by a powerseries a k z k k=0 with
Lecture 3 Frits Beukers Arithmetic of values of E- and G-function Lecture 3 E- and G-functions 1 / 20 G-functions, definition Definition An analytic function f (z) given by a powerseries a k z k k=0 with
Math Exam III - Spring
 Math 3 - Exam III - Spring 8 This exam contains 5 multiple choice questions and hand graded questions. The multiple choice questions are worth 5 points each and the hand graded questions are worth a total
Math 3 - Exam III - Spring 8 This exam contains 5 multiple choice questions and hand graded questions. The multiple choice questions are worth 5 points each and the hand graded questions are worth a total
Objective Mathematics
 Multiple choice questions with ONE correct answer : ( Questions No. 1-5 ) 1. If the equation x n = (x + ) is having exactly three distinct real solutions, then exhaustive set of values of 'n' is given
Multiple choice questions with ONE correct answer : ( Questions No. 1-5 ) 1. If the equation x n = (x + ) is having exactly three distinct real solutions, then exhaustive set of values of 'n' is given
Transweb Educational Services Pvt. Ltd Tel:
 . An aeroplane flying at a constant speed, parallel to the horizontal ground, km above it, is observed at an elevation of 6º from a point on the ground. If, after five seconds, its elevation from the same
. An aeroplane flying at a constant speed, parallel to the horizontal ground, km above it, is observed at an elevation of 6º from a point on the ground. If, after five seconds, its elevation from the same
The Sphere OPTIONAL - I Vectors and three dimensional Geometry THE SPHERE
 36 THE SPHERE You must have played or seen students playing football, basketball or table tennis. Football, basketball, table tennis ball are all examples of geometrical figures which we call "spheres"
36 THE SPHERE You must have played or seen students playing football, basketball or table tennis. Football, basketball, table tennis ball are all examples of geometrical figures which we call "spheres"
Algebra. Pang-Cheng, Wu. January 22, 2016
 Algebra Pang-Cheng, Wu January 22, 2016 Abstract For preparing competitions, one should focus on some techniques and important theorems. This time, I want to talk about a method for solving inequality
Algebra Pang-Cheng, Wu January 22, 2016 Abstract For preparing competitions, one should focus on some techniques and important theorems. This time, I want to talk about a method for solving inequality
Def. The euclidian distance between two points x = (x 1,...,x p ) t and y = (y 1,...,y p ) t in the p-dimensional space R p is defined as
 MAHALANOBIS DISTANCE Def. The euclidian distance between two points x = (x 1,...,x p ) t and y = (y 1,...,y p ) t in the p-dimensional space R p is defined as d E (x, y) = (x 1 y 1 ) 2 + +(x p y p ) 2
MAHALANOBIS DISTANCE Def. The euclidian distance between two points x = (x 1,...,x p ) t and y = (y 1,...,y p ) t in the p-dimensional space R p is defined as d E (x, y) = (x 1 y 1 ) 2 + +(x p y p ) 2
Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics (FP1) Required Knowledge Information Sheet. Daniel Hammocks
 Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics (FP1) Required Knowledge Information Sheet FP1 Formulae Given in Mathematical Formulae and Statistical Tables Booklet Summations o =1 2 = 1 + 12 + 1 6 o =1 3 = 1 64
Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics (FP1) Required Knowledge Information Sheet FP1 Formulae Given in Mathematical Formulae and Statistical Tables Booklet Summations o =1 2 = 1 + 12 + 1 6 o =1 3 = 1 64
Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
 Title Integration of Rational Functions by MATH 1700 MATH 1700 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 2 / 11 Rational functions A rational function is one of the form where P and Q are
Title Integration of Rational Functions by MATH 1700 MATH 1700 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 2 / 11 Rational functions A rational function is one of the form where P and Q are
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Overview: 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Properties of Logarithms 3.4 Solving Exponential and
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Overview: 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Properties of Logarithms 3.4 Solving Exponential and
Integral Similarity and Commutators of Integral Matrices Thomas J. Laffey and Robert Reams (University College Dublin, Ireland) Abstract
 Integral Similarity and Commutators of Integral Matrices Thomas J. Laffey and Robert Reams (University College Dublin, Ireland) Abstract Let F be a field, M n (F ) the algebra of n n matrices over F and
Integral Similarity and Commutators of Integral Matrices Thomas J. Laffey and Robert Reams (University College Dublin, Ireland) Abstract Let F be a field, M n (F ) the algebra of n n matrices over F and
Solutions. .5 = e k k = ln(.5) Now that we know k we find t for which the exponential function is = e kt
 MATH 1220-03 Exponential Growth and Decay Spring 08 Solutions 1. (#15 from 6.5.) Cesium 137 and strontium 90 were two radioactive chemicals released at the Chernobyl nuclear reactor in April 1986. The
MATH 1220-03 Exponential Growth and Decay Spring 08 Solutions 1. (#15 from 6.5.) Cesium 137 and strontium 90 were two radioactive chemicals released at the Chernobyl nuclear reactor in April 1986. The
We introduce the third of the classical geometries, hyperbolic geometry.
 Chapter Hyperbolic Geometry We introduce the third of the classical geometries, hyperbolic geometry.. Hyperbolic Geometry Lines are (i) vertical lines in H H = H 2 = {(x, y) R 2 y > 0} = {z C Im(z) > 0}
Chapter Hyperbolic Geometry We introduce the third of the classical geometries, hyperbolic geometry.. Hyperbolic Geometry Lines are (i) vertical lines in H H = H 2 = {(x, y) R 2 y > 0} = {z C Im(z) > 0}
Classification of Algebraic Subgroups of Lower Order Unipotent Algebraic Groups
 Classification of Algebraic Subgroups of Lower Order Unipotent Algebraic Groups AMS Special Session, Boston, MA; Differential Algebraic Geometry and Galois Theory (in memory of J. Kovacic) V. Ravi Srinivasan
Classification of Algebraic Subgroups of Lower Order Unipotent Algebraic Groups AMS Special Session, Boston, MA; Differential Algebraic Geometry and Galois Theory (in memory of J. Kovacic) V. Ravi Srinivasan
7.4: Integration of rational functions
 A rational function is a function of the form: f (x) = P(x) Q(x), where P(x) and Q(x) are polynomials in x. P(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + + a 0. Q(x) = b m x m + b m 1 x m 1 + + b 0. How to express a
A rational function is a function of the form: f (x) = P(x) Q(x), where P(x) and Q(x) are polynomials in x. P(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + + a 0. Q(x) = b m x m + b m 1 x m 1 + + b 0. How to express a
6.3 Partial Fractions
 6.3 Partial Fractions Mark Woodard Furman U Fall 2009 Mark Woodard (Furman U) 6.3 Partial Fractions Fall 2009 1 / 11 Outline 1 The method illustrated 2 Terminology 3 Factoring Polynomials 4 Partial fraction
6.3 Partial Fractions Mark Woodard Furman U Fall 2009 Mark Woodard (Furman U) 6.3 Partial Fractions Fall 2009 1 / 11 Outline 1 The method illustrated 2 Terminology 3 Factoring Polynomials 4 Partial fraction
HOLIDAY GIFT GUIDE. Christmas. Christmas. Christmas. Christmas. Christmas. -C hr is Jones. Christmas. Christmas
 PIKE OUNY DISPAH HURSDAY DEEBER 13 2018 P 11 H G G E O 0 2 F S A R O A A W K A O J K W S W - I K P A H A p H p P N j D 1 1 I p z - p! 2 1 - J p W A K - A A W 2010 p W E p q Pz A L A P P & p S A W P B L
PIKE OUNY DISPAH HURSDAY DEEBER 13 2018 P 11 H G G E O 0 2 F S A R O A A W K A O J K W S W - I K P A H A p H p P N j D 1 1 I p z - p! 2 1 - J p W A K - A A W 2010 p W E p q Pz A L A P P & p S A W P B L
or E ( U(X) ) e zx = e ux e ivx = e ux( cos(vx) + i sin(vx) ), B X := { u R : M X (u) < } (4)
 :23 /4/2000 TOPIC Characteristic functions This lecture begins our study of the characteristic function φ X (t) := Ee itx = E cos(tx)+ie sin(tx) (t R) of a real random variable X Characteristic functions
:23 /4/2000 TOPIC Characteristic functions This lecture begins our study of the characteristic function φ X (t) := Ee itx = E cos(tx)+ie sin(tx) (t R) of a real random variable X Characteristic functions
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 15: Linear transformations (continued). Range and kernel. Matrix transformations.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 15: Linear transformations (continued). Range and kernel. Matrix transformations. Linear mapping = linear transformation = linear function Definition. Given vector spaces
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 15: Linear transformations (continued). Range and kernel. Matrix transformations. Linear mapping = linear transformation = linear function Definition. Given vector spaces
The first order quasi-linear PDEs
 Chapter 2 The first order quasi-linear PDEs The first order quasi-linear PDEs have the following general form: F (x, u, Du) = 0, (2.1) where x = (x 1, x 2,, x 3 ) R n, u = u(x), Du is the gradient of u.
Chapter 2 The first order quasi-linear PDEs The first order quasi-linear PDEs have the following general form: F (x, u, Du) = 0, (2.1) where x = (x 1, x 2,, x 3 ) R n, u = u(x), Du is the gradient of u.
MATHEMATICS SOLUTION
 MATHEMATICS SOLUTION MHT-CET 6 (MATHEMATICS). (A) 5 0 55 5 9 6 5 9. (A) If the school bus does not come) (I will not go to school) ( I shall meet my friend) (I shall go out for a movie) ~ p ~ q r s ~ p
MATHEMATICS SOLUTION MHT-CET 6 (MATHEMATICS). (A) 5 0 55 5 9 6 5 9. (A) If the school bus does not come) (I will not go to school) ( I shall meet my friend) (I shall go out for a movie) ~ p ~ q r s ~ p
ON THE LEAST PRIMITIVE ROOT MODULO p 2
 ON THE LEAST PRIMITIVE ROOT MODULO p 2 S. D. COHEN, R. W. K. ODONI, AND W. W. STOTHERS Let h(p) be the least positive primitive root modulo p 2. Burgess [1] indicated that his work on character sums yields
ON THE LEAST PRIMITIVE ROOT MODULO p 2 S. D. COHEN, R. W. K. ODONI, AND W. W. STOTHERS Let h(p) be the least positive primitive root modulo p 2. Burgess [1] indicated that his work on character sums yields
95 Holt McDougal Geometry
 1. It is given that KN is the perpendicular bisector of J and N is the perpendicular bisector of K. B the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem, JK = K and K =. Thus JK = b the Trans. Prop. of =. B the definition
1. It is given that KN is the perpendicular bisector of J and N is the perpendicular bisector of K. B the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem, JK = K and K =. Thus JK = b the Trans. Prop. of =. B the definition
Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
 Title Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions MATH 1700 December 6, 2016 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions December 6, 2016 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions
Title Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions MATH 1700 December 6, 2016 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions December 6, 2016 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions
: i; ii: i:i: I. : q t:iig l3 [i E. i;issii:i::: r p. ! s:r;e;:e;!f. as Iet5;Fgi. i EiiF;:'+3EI. : :*gsc:li-ii. ; si;;ei:i:g; .
 , / - H f ) - $ H A - --" G \/ - - f \f ff P) G T - ), - ) -..R '' (.) f- w (, AA - Нотная библиотека \ S R.- R \?! -! h )! - X* - Y - J. ** " { B e B Rk * f [He 1e [Y!!-- e *J! *Jee.1!.,1g -!. -! >. j.,
, / - H f ) - $ H A - --" G \/ - - f \f ff P) G T - ), - ) -..R '' (.) f- w (, AA - Нотная библиотека \ S R.- R \?! -! h )! - X* - Y - J. ** " { B e B Rk * f [He 1e [Y!!-- e *J! *Jee.1!.,1g -!. -! >. j.,
y 1 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 ) 2 A circle is a set of points P in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point, called the center.
 Ch 12. Conic Sections Circles, Parabolas, Ellipses & Hyperbolas The formulas for the conic sections are derived by using the distance formula, which was derived from the Pythagorean Theorem. If you know
Ch 12. Conic Sections Circles, Parabolas, Ellipses & Hyperbolas The formulas for the conic sections are derived by using the distance formula, which was derived from the Pythagorean Theorem. If you know
Mathematics of Physics and Engineering II: Homework answers You are encouraged to disagree with everything that follows. P R and i j k 2 1 1
 Mathematics of Physics and Engineering II: Homework answers You are encouraged to disagree with everything that follows Homework () P Q = OQ OP =,,,, =,,, P R =,,, P S = a,, a () The vertex of the angle
Mathematics of Physics and Engineering II: Homework answers You are encouraged to disagree with everything that follows Homework () P Q = OQ OP =,,,, =,,, P R =,,, P S = a,, a () The vertex of the angle
Calculus Method of Solving Quadratic Equations
 International Journal of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 9, Number 2 (2017), pp. 155-159 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Calculus Method of Solving Quadratic
International Journal of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 9, Number 2 (2017), pp. 155-159 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Calculus Method of Solving Quadratic
Kalman Filter Computer Vision (Kris Kitani) Carnegie Mellon University
 Kalman Filter 16-385 Computer Vision (Kris Kitani) Carnegie Mellon University Examples up to now have been discrete (binary) random variables Kalman filtering can be seen as a special case of a temporal
Kalman Filter 16-385 Computer Vision (Kris Kitani) Carnegie Mellon University Examples up to now have been discrete (binary) random variables Kalman filtering can be seen as a special case of a temporal
A UNIQUENESS THEOREM FOR A BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM
 PROCEEDINGS of the AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 77, Number 3, December 1979 A UNIQUENESS THEOREM FOR A BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM RIAZ A. USMANI Abstract. In this paper it is proved that the two-point
PROCEEDINGS of the AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 77, Number 3, December 1979 A UNIQUENESS THEOREM FOR A BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM RIAZ A. USMANI Abstract. In this paper it is proved that the two-point
MA Ordinary Differential Equations
 MA 108 - Ordinary Differential Equations Santanu Dey Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 76 dey@math.iitb.ac.in March 26, 2014 Outline of the lecture Method
MA 108 - Ordinary Differential Equations Santanu Dey Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 76 dey@math.iitb.ac.in March 26, 2014 Outline of the lecture Method
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Overview: 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Properties of Logarithms 3.4 Solving Exponential and
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Overview: 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Properties of Logarithms 3.4 Solving Exponential and
RAJASTHAN P.E.T. MATHS 1997
 RAJASTHAN P.E.T. MATHS 1997 1. The value of k for which the points (0,0), (2,0), (0,1) and (0,k) lies on a circle is : (1) 1,2 (2) -1,2 (3) 0,2 (4) 0, 1 2. The area of the triangle formed by the tangent
RAJASTHAN P.E.T. MATHS 1997 1. The value of k for which the points (0,0), (2,0), (0,1) and (0,k) lies on a circle is : (1) 1,2 (2) -1,2 (3) 0,2 (4) 0, 1 2. The area of the triangle formed by the tangent
General Comparison between AISC LRFD and ASD
 General Comparison between AISC LRFD and ASD 1 General Comparison between AISC LRFD and ASD 2 AISC ASD and LRFD AISC ASD = American Institute of Steel Construction = Allowable Stress Design AISC Ninth
General Comparison between AISC LRFD and ASD 1 General Comparison between AISC LRFD and ASD 2 AISC ASD and LRFD AISC ASD = American Institute of Steel Construction = Allowable Stress Design AISC Ninth
6.3. Nonlinear Systems of Equations
 G. NAGY ODE November,.. Nonlinear Systems of Equations Section Objective(s): Part One: Two-Dimensional Nonlinear Systems. ritical Points and Linearization. The Hartman-Grobman Theorem. Part Two: ompeting
G. NAGY ODE November,.. Nonlinear Systems of Equations Section Objective(s): Part One: Two-Dimensional Nonlinear Systems. ritical Points and Linearization. The Hartman-Grobman Theorem. Part Two: ompeting
PARTIAL FRACTIONS AND POLYNOMIAL LONG DIVISION. The basic aim of this note is to describe how to break rational functions into pieces.
 PARTIAL FRACTIONS AND POLYNOMIAL LONG DIVISION NOAH WHITE The basic aim of this note is to describe how to break rational functions into pieces. For example 2x + 3 1 = 1 + 1 x 1 3 x + 1. The point is that
PARTIAL FRACTIONS AND POLYNOMIAL LONG DIVISION NOAH WHITE The basic aim of this note is to describe how to break rational functions into pieces. For example 2x + 3 1 = 1 + 1 x 1 3 x + 1. The point is that
Final Examination 201-NYC-05 - Linear Algebra I December 8 th, and b = 4. Find the value(s) of a for which the equation Ax = b
 Final Examination -NYC-5 - Linear Algebra I December 8 th 7. (4 points) Let A = has: (a) a unique solution. a a (b) infinitely many solutions. (c) no solution. and b = 4. Find the value(s) of a for which
Final Examination -NYC-5 - Linear Algebra I December 8 th 7. (4 points) Let A = has: (a) a unique solution. a a (b) infinitely many solutions. (c) no solution. and b = 4. Find the value(s) of a for which
MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY TENTH LECTURE
 MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY TENTH LECTURE The subject of this lecture is finite fields. 1. Root Fields Let k be any field, and let f(x) k[x] be irreducible and have positive degree. We want to construct a
MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY TENTH LECTURE The subject of this lecture is finite fields. 1. Root Fields Let k be any field, and let f(x) k[x] be irreducible and have positive degree. We want to construct a
Determinants connected with the Periodic Solutions of Mathieu's Equations. (Read 11th June Received 28th June 1915.)
 122 Determinants connected with the Periodic Solutions of Mathieu's Equations. By A. G. BURGESS, Research Student, Edinburgh University Mathematical Laboratory. (Read 11th June 1915. Received 28th June
122 Determinants connected with the Periodic Solutions of Mathieu's Equations. By A. G. BURGESS, Research Student, Edinburgh University Mathematical Laboratory. (Read 11th June 1915. Received 28th June
CAT. NO /irtl,417~ S- ~ I ';, A RIDER PUBLICATION BY H. A. MIDDLETON
 CAT. NO. 139-3 THIRD SUPPLEMENT I /irtl,417~ S- ~ I ';,... 0 f? BY H. A. MIDDLETON.. A RIDER PUBLICATION B36 B65 B152 B309 B319 B329 B719 D63 D77 D152 DA90 DAC32 DAF96 DC70 DC80 DCC90 DD6 DD7 DF62 DF91
CAT. NO. 139-3 THIRD SUPPLEMENT I /irtl,417~ S- ~ I ';,... 0 f? BY H. A. MIDDLETON.. A RIDER PUBLICATION B36 B65 B152 B309 B319 B329 B719 D63 D77 D152 DA90 DAC32 DAF96 DC70 DC80 DCC90 DD6 DD7 DF62 DF91
Predicate Logic. CSE 191, Class Note 02: Predicate Logic Computer Sci & Eng Dept SUNY Buffalo
 Predicate Logic CSE 191, Class Note 02: Predicate Logic Computer Sci & Eng Dept SUNY Buffalo c Xin He (University at Buffalo) CSE 191 Discrete Structures 1 / 22 Outline 1 From Proposition to Predicate
Predicate Logic CSE 191, Class Note 02: Predicate Logic Computer Sci & Eng Dept SUNY Buffalo c Xin He (University at Buffalo) CSE 191 Discrete Structures 1 / 22 Outline 1 From Proposition to Predicate
Name: Partners: PreCalculus. Review 5 Version A
 Name: Partners: PreCalculus Date: Review 5 Version A [A] Circle whether each statement is true or false. 1. 3 log 3 5x = 5x 2. log 2 16 x+3 = 4x + 3 3. ln x 6 + ln x 5 = ln x 30 4. If ln x = 4, then e
Name: Partners: PreCalculus Date: Review 5 Version A [A] Circle whether each statement is true or false. 1. 3 log 3 5x = 5x 2. log 2 16 x+3 = 4x + 3 3. ln x 6 + ln x 5 = ln x 30 4. If ln x = 4, then e
Linear Algebra. Paul Yiu. 6D: 2-planes in R 4. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Fall 2011
 Linear Algebra Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Fall 2011 6D: 2-planes in R 4 The angle between a vector and a plane The angle between a vector v R n and a subspace V is the
Linear Algebra Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Fall 2011 6D: 2-planes in R 4 The angle between a vector and a plane The angle between a vector v R n and a subspace V is the
gpc x All 4i s at gpcx 0CxsfcyjVx.yE Imf 0cg IgE G C H is a Facts HMIEL cxgj it 7 X CG 4 gpc x G Escala c 23 G cyclic G E CZ t G Zaz t
 MidtermRevieir A group is a set G equipped with a G x G G such that x y say c notation binary operation ht x y z e G associative Y Ky 2 x Cyz 7 Be E G s t see ex x tf x c G identity 3 Given see G ye G
MidtermRevieir A group is a set G equipped with a G x G G such that x y say c notation binary operation ht x y z e G associative Y Ky 2 x Cyz 7 Be E G s t see ex x tf x c G identity 3 Given see G ye G
f;g,7k ;! / C+!< 8R+^1 ;0$ Z\ \ K S;4 i!;g + 5 ;* \ C! 1+M, /A+1+> 0 /A+>! 8 J 4! 9,7 )F C!.4 ;* )F /0 u+\ 30< #4 8 J C!
 393/09/0 393//07 :,F! ::!n> b]( a.q 5 O +D5 S ١ ; ;* :'!3Qi C+0;$ < "P 4 ; M V! M V! ; a 4 / ;0$ f;g,7k ;! / C+!< 8R+^ ;0$ Z\ \ K S;4 "* < 8c0 5 *
393/09/0 393//07 :,F! ::!n> b]( a.q 5 O +D5 S ١ ; ;* :'!3Qi C+0;$ < "P 4 ; M V! M V! ; a 4 / ;0$ f;g,7k ;! / C+!< 8R+^ ;0$ Z\ \ K S;4 "* < 8c0 5 *
Sums of distinct divisors
 Oberlin College February 3, 2017 1 / 50 The anatomy of integers 2 / 50 What does it mean to study the anatomy of integers? Some natural problems/goals: Study the prime factors of integers, their size and
Oberlin College February 3, 2017 1 / 50 The anatomy of integers 2 / 50 What does it mean to study the anatomy of integers? Some natural problems/goals: Study the prime factors of integers, their size and
Section A.6. Solving Equations. Math Precalculus I. Solving Equations Section A.6
 Section A.6 Solving Equations Math 1051 - Precalculus I A.6 Solving Equations Simplify 1 2x 6 x + 2 x 2 9 A.6 Solving Equations Simplify 1 2x 6 x + 2 x 2 9 Factor: 2x 6 = 2(x 3) x 2 9 = (x 3)(x + 3) LCD
Section A.6 Solving Equations Math 1051 - Precalculus I A.6 Solving Equations Simplify 1 2x 6 x + 2 x 2 9 A.6 Solving Equations Simplify 1 2x 6 x + 2 x 2 9 Factor: 2x 6 = 2(x 3) x 2 9 = (x 3)(x + 3) LCD
Geometric Steiner Trees
 Geometric Steiner Trees From the book: Optimal Interconnection Trees in the Plane By Marcus Brazil and Martin Zachariasen Part 3: Computational Complexity and the Steiner Tree Problem Marcus Brazil 2015
Geometric Steiner Trees From the book: Optimal Interconnection Trees in the Plane By Marcus Brazil and Martin Zachariasen Part 3: Computational Complexity and the Steiner Tree Problem Marcus Brazil 2015
Mini-Lesson 9. Section 9.1: Relations and Functions. Definitions
 9 Section 9.1: Relations and Functions A RELATION is any set of ordered pairs. Definitions A FUNCTION is a relation in which every input value is paired with exactly one output value. Table of Values One
9 Section 9.1: Relations and Functions A RELATION is any set of ordered pairs. Definitions A FUNCTION is a relation in which every input value is paired with exactly one output value. Table of Values One
Assignment 11 Assigned Mon Sept 27
 Assignment Assigned Mon Sept 7 Section 7., Problem 4. x sin x dx = x cos x + x cos x dx ( = x cos x + x sin x ) sin x dx u = x dv = sin x dx du = x dx v = cos x u = x dv = cos x dx du = dx v = sin x =
Assignment Assigned Mon Sept 7 Section 7., Problem 4. x sin x dx = x cos x + x cos x dx ( = x cos x + x sin x ) sin x dx u = x dv = sin x dx du = x dx v = cos x u = x dv = cos x dx du = dx v = sin x =
B.Sc. MATHEMATICS - II YEAR
 MANONMANIAM SUNDARANAR UNIVERSITY DIRECTORATE OF DISTANCE & CONTINUING EDUCATION TIRUNELVELI 671, TAMIL NADU B.Sc. MATHEMATICS - II YEAR DJMA - ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY D AND VECTOR CALCULUS (From the academic
MANONMANIAM SUNDARANAR UNIVERSITY DIRECTORATE OF DISTANCE & CONTINUING EDUCATION TIRUNELVELI 671, TAMIL NADU B.Sc. MATHEMATICS - II YEAR DJMA - ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY D AND VECTOR CALCULUS (From the academic
5-6 The Remainder and Factor Theorems
 Use synthetic substitution to find f (4) and f ( 2) for each function. 1. f (x) = 2x 3 5x 2 x + 14 58; 20 2. f (x) = x 4 + 8x 3 + x 2 4x 10 758; 46 3. NATURE The approximate number of bald eagle nesting
Use synthetic substitution to find f (4) and f ( 2) for each function. 1. f (x) = 2x 3 5x 2 x + 14 58; 20 2. f (x) = x 4 + 8x 3 + x 2 4x 10 758; 46 3. NATURE The approximate number of bald eagle nesting
