Protean Signature Schemes
|
|
|
- Gillian Hoover
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Protean Signature Schemes Stephan Krenn, Henrich C. Pöhls, Kai Samelin, Daniel Slamanig October 2, 2018 Cryptology And Network Security (CANS 2018), Naples, Italy 1
2 Digital Signatures 2
3 Digital Signatures Establish the origin of a message (bind signer s identity to message) A valid signature guarantees Message integrity (no modifications happened) Identity of the signer 3
4 Digital Signatures Establish the origin of a message (bind signer s identity to message) A valid signature guarantees Message integrity (no modifications happened) Identity of the signer Security (EUF-CMA) Obtain signatures on arbitrary messages Not able to produce valid signature for non-queried message 3
5 Controlled Modification of Signed Messages Modifications? That s what we try to prevent? 4
6 Controlled Modification of Signed Messages Modifications? That s what we try to prevent? Controlled modifications Signer determines how signed message can be altered Think of implicitly signing all possible messages 4
7 Controlled Modification of Signed Messages Modifications? That s what we try to prevent? Controlled modifications Signer determines how signed message can be altered Think of implicitly signing all possible messages Example: Medical documents Anonymization for research/accounting (still want authenticity guarantees) Removing exact diagnosis for sick leave Re-signing after the fact might not be possible (availability, etc.) 4
8 Controlled Modification of Signed Messages Will look at two common schemes: redactable and sanitizable signatures 4
9 Redactable Signatures (RSS) 5
10 Redactable Signatures (RSS) 6
11 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Blacking out/removal of designated parts by everyone 6
12 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Security properties Unforgeability Privacy In EUF-CMA sense: cannot come up with valid signature for a message not derivable from signed ones Redacted signatures leaks no information about redacted parts Transparancy (optional) Not visible if redaction happened or not Unlinkability 7
13 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Originally proposed in [SBZ, ICISC 01] and [JMSW, CT-RSA 02] Various ad-hoc constructions for different message representations (linear, sets, trees) Generic construction from EUF-CMA secure signatures and indistinguishable accumulators [DPSS, ICISC 15] 8
14 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Sketch of RSS for sets (accumulator + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): 9
15 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Sketch of RSS for sets (accumulator + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Accumulator: X = {x 1,..., x n } succinctly represented by acc X 9
16 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Sketch of RSS for sets (accumulator + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Accumulator: X = {x 1,..., x n } succinctly represented by acc X Witnesses wit xi certifying membership of x i in acc X Efficiently computable x X, intractable y / X 9
17 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Sketch of RSS for sets (accumulator + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Accumulator: X = {x 1,..., x n } succinctly represented by acc X Witnesses wit xi certifying membership of x i in acc X Efficiently computable x X, intractable y / X Indistinguishability [DS, CT-RSA 15] Neither acc nor wit leak information about X 9
18 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Sketch of RSS for sets (accumulator + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Accumulator: X = {x 1,..., x n } succinctly represented by acc X Witnesses wit xi certifying membership of x i in acc X Efficiently computable x X, intractable y / X Indistinguishability [DS, CT-RSA 15] Neither acc nor wit leak information about X RSS: To sign m = {m 1,..., m n } 9
19 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Sketch of RSS for sets (accumulator + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Accumulator: X = {x 1,..., x n } succinctly represented by acc X Witnesses wit xi certifying membership of x i in acc X Efficiently computable x X, intractable y / X Indistinguishability [DS, CT-RSA 15] Neither acc nor wit leak information about X RSS: To sign m = {m 1,..., m n } Compute acc m and use Σ to sign acc m 9
20 Redactable Signatures (RSS) Sketch of RSS for sets (accumulator + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Accumulator: X = {x 1,..., x n } succinctly represented by acc X Witnesses wit xi certifying membership of x i in acc X Efficiently computable x X, intractable y / X Indistinguishability [DS, CT-RSA 15] Neither acc nor wit leak information about X RSS: To sign m = {m 1,..., m n } Compute acc m and use Σ to sign acc m As redactable signature provide signature of Σ and {wit mi } 9
21 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) 10
22 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) 11
23 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) 12
24 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Replacement of designated parts by designated entity 12
25 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Security properties Unforgeability Immutability Privacy In EUF-CMA sense: Sanitizer cannot come up with valid signature for a message not derivable from signed ones Signer/Sanitizer accountability Signer/sanitizer cannot blame the other party for having produced a signature Transparancy (optional) Invisibility (optional) Signature does not leak which parts are sanitizable Unlinkability 13
26 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Originally proposed in [ACMT, ESORICS 05] and rigorous security model [BFFLP+, PKC 09] Various constructions with different properties and sanitizing restrictions, e.g., limit sanitizing to defined set Generic construction from EUF-CMA secure signatures and chameleon hash functions [BFFLP+, PKC 09] 14
27 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Sketch of SSS (chameleon hashes + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): 15
28 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Sketch of SSS (chameleon hashes + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Chameleon Hash: Collision resistant hash keyed with (sk, pk) 15
29 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Sketch of SSS (chameleon hashes + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Chameleon Hash: Collision resistant hash keyed with (sk, pk) Hashing: h CHash(pk, m; r) 15
30 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Sketch of SSS (chameleon hashes + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Chameleon Hash: Collision resistant hash keyed with (sk, pk) Hashing: h CHash(pk, m; r) Collision: sk allows for any h, ˆm to compute ˆr s.t. CHash(pk, m; r) = CHash(pk, ˆm;ˆr) 15
31 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Sketch of SSS (chameleon hashes + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Chameleon Hash: Collision resistant hash keyed with (sk, pk) Hashing: h CHash(pk, m; r) Collision: sk allows for any h, ˆm to compute ˆr s.t. CHash(pk, m; r) = CHash(pk, ˆm;ˆr) SSS: To sign m = (m 1,..., m n ) 15
32 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Sketch of SSS (chameleon hashes + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Chameleon Hash: Collision resistant hash keyed with (sk, pk) Hashing: h CHash(pk, m; r) Collision: sk allows for any h, ˆm to compute ˆr s.t. CHash(pk, m; r) = CHash(pk, ˆm;ˆr) SSS: To sign m = (m 1,..., m n ) Use Σ to sign h = (h 1,..., h n ) where CHash(pk, m i ; r i ), h i = m i, else if sanitizable 15
33 Sanitizable Signatures (SSS) Sketch of SSS (chameleon hashes + EUF-CMA signatures Σ): Chameleon Hash: Collision resistant hash keyed with (sk, pk) Hashing: h CHash(pk, m; r) Collision: sk allows for any h, ˆm to compute ˆr s.t. CHash(pk, m; r) = CHash(pk, ˆm;ˆr) SSS: To sign m = (m 1,..., m n ) Use Σ to sign h = (h 1,..., h n ) where CHash(pk, m i ; r i ), h i = m i, else if sanitizable As sanitizable signature provide signature of Σ and r 15
34 Merging the Functionalities Provide a primitive that supports removal and editing at the same time Generalize RSS and SSS into a single primitive having all desired properties of RSS and SSS Motivating example (k-anonymization): Removal of attributes Generalization of attributes 16
35 Using Existing Approaches? We could use SSS to mimic the functionality of RSS Use limited set replacement with a special symbol denoting redaction 17
36 Using Existing Approaches? We could use SSS to mimic the functionality of RSS Use limited set replacement with a special symbol denoting redaction Destroys transparency! 17
37 Using Existing Approaches? We could use SSS to mimic the functionality of RSS Use limited set replacement with a special symbol denoting redaction Destroys transparency! Ideally have efficient construction providing all properties 17
38 Protean Signature Schemes (PSS) 18
39 Protean Signature Schemes (PSS) 19
40 Protean Signature Schemes (PSS) Replacement and removal of designated parts by designated entity 19
41 Protean Signature Schemes (PSS) Security properties Unforgeability Immutability Privacy Signer/Sanitizer accountability Transparancy (optional) Invisibility (optional) 20
42 Sketch of Construction (Ingredients) We provide a black-box construction of a protean signature scheme Ingredients A secure sanitizable signature scheme (SSS) A secure redactable signature scheme (RSS) A CCA2 secure labeled public key encryption scheme Only required if RSS provides auxiliary redaction information RED RED typically makes redactions more efficient 21
43 Sketch of Construction (Keys) Signer keys (keys from SSS and RSS) sk sig (sk SSS sig, skrss ) pk sig (pk SSS sig, pkrss ) Sanitizer keys (keys from SSS) sk san sk SSS san pk san pk SSS san 22
44 Sketch of Construction (Signing) Let us consider a message m = (m 1, m 2, m 3) 23
45 Sketch of Construction (Signing) Let us consider a message m = (m 1, m 2, m 3) Inner SSS (m 1, τ, τ 1, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 1 (m 2, τ, τ 2, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 2 (m 3, τ, τ 3, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 3 23
46 Sketch of Construction (Signing) Let us consider a message m = (m 1, m 2, m 3) Inner SSS (m 1, τ, τ 1, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 1 RSS (τ 1, τ 2, τ 3, τ, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ RSS (m 2, τ, τ 2, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 2 (m 3, τ, τ 3, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 3 23
47 Sketch of Construction (Signing) Let us consider a message m = (m 1, m 2, m 3) Inner SSS (m 1, τ, τ 1, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 1 RSS (τ 1, τ 2, τ 3, τ, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ RSS Outer SSS (m 2, τ, τ 2, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 2 (m 3, τ, τ 3, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 3 ((m 1, m 2, m 3), σ RSS, (τ 1, τ 2, τ 3, σ1 SSS, σ2 SSS, σ3 SSS ), τ, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ0 SSS 23
48 Sketch of Construction (Editing) Edit the message m = (m 1, m 2, m 3) to ˆm = (m 1, ˆm 2) 24
49 Sketch of Construction (Editing) Edit the message m = (m 1, m 2, m 3) to ˆm = (m 1, ˆm 2) Inner SSS (m 1, τ, τ 1, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 1 (m 2, τ, τ 2, pk sig, pk san ) (m 3, τ, τ 3, }{{} σ2 SSS pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ3 SSS 24
50 Sketch of Construction (Editing) Edit the message m = (m 1, m 2, m 3) to ˆm = (m 1, ˆm 2) Inner SSS (m 1, τ, τ 1, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 1 (m 2, τ, τ 2, pk sig, pk san ) (m 3, τ, τ 3, }{{} σ2 SSS pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ3 SSS RSS (τ 1, τ 2, τ3, τ, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} ˆσ RSS 24
51 Sketch of Construction (Editing) Edit the message m = (m 1, m 2, m 3) to ˆm = (m 1, ˆm 2) Inner SSS (m 1, τ, τ 1, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 1 (m 2, τ, τ 2, pk sig, pk san ) (m 3, τ, τ 3, pk }{{} σ2 SSS sig, pk san ) }{{} σ3 SSS RSS (τ 1, τ 2, τ3, τ, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} ˆσ RSS Outer SSS ((m 1, m 2, m 3), σ RSS, (τ 1, τ 2, τ 3, σ1 SSS, σ2 SSS, σ3 SSS ), τ, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ0 SSS 24
52 Sketch of Construction (Editing) Edit the message m = (m 1, m 2, m 3) to ˆm = (m 1, ˆm 2) Inner SSS (m 1, τ, τ 1, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ SSS 1 (m 2, τ, τ 2, pk sig, pk san ) (m 3, τ, τ 3, }{{} σ2 SSS pk sig, pk san ) }{{} σ3 SSS RSS (τ 1, τ 2, τ3, τ, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} ˆσ RSS ((m 1, ˆm 2), ˆσ RSS, (τ 1, τ 2, σ1 SSS, σ2 SSS ), τ, pk sig, pk san ) }{{} ˆσ 0 SSS 24
53 Open Issues and Potential Directions Limiting sets: Integrate features to limit sanitizing to signer-chosen sets of values 25
54 Open Issues and Potential Directions Limiting sets: Integrate features to limit sanitizing to signer-chosen sets of values Block-level: Accountability notions on a block instead of message level 25
55 Open Issues and Potential Directions Limiting sets: Integrate features to limit sanitizing to signer-chosen sets of values Block-level: Accountability notions on a block instead of message level Dependencies: Enforce restrictions such as if block i is redacted, also block j needs to be redacted 25
56 Open Issues and Potential Directions Limiting sets: Integrate features to limit sanitizing to signer-chosen sets of values Block-level: Accountability notions on a block instead of message level Dependencies: Enforce restrictions such as if block i is redacted, also block j needs to be redacted Unlinkability: Seems hard to achieve with our construction paradigm 25
57 Conclusions and Take-Home RSS and SSS allow controlled modifications of signed messages 26
58 Conclusions and Take-Home RSS and SSS allow controlled modifications of signed messages RSS and SSS provide different features (e.g., remove vs. replace) 26
59 Conclusions and Take-Home RSS and SSS allow controlled modifications of signed messages RSS and SSS provide different features (e.g., remove vs. replace) We generalize RSS and SSS into protean signatures (PSS) 26
60 Conclusions and Take-Home RSS and SSS allow controlled modifications of signed messages RSS and SSS provide different features (e.g., remove vs. replace) We generalize RSS and SSS into protean signatures (PSS) PSS provide all features and strong privacy guarantees 26
61 Conclusions and Take-Home RSS and SSS allow controlled modifications of signed messages RSS and SSS provide different features (e.g., remove vs. replace) We generalize RSS and SSS into protean signatures (PSS) PSS provide all features and strong privacy guarantees We provide a generic construction based on RSS and SSS (and labeled PKE) 26
62 Thank you! Supported by EU H2020 and ECSEL
Chameleon-Hashes with Dual Long-Term Trapdoors and Their Applications
 This is the full and revised version of a paper which appears in Progress in Cryptology - AFRICACRYPT 2018-10th International Conference on Cryptology in Africa, Marrakesh, Morocco, May 7-9, 2018, Proceedings.
This is the full and revised version of a paper which appears in Progress in Cryptology - AFRICACRYPT 2018-10th International Conference on Cryptology in Africa, Marrakesh, Morocco, May 7-9, 2018, Proceedings.
Cryptographic Solutions for Data Integrity in the Cloud
 Cryptographic Solutions for Stanford University, USA Stanford Computer Forum 2 April 2012 Homomorphic Encryption Homomorphic encryption allows users to delegate computation while ensuring secrecy. Homomorphic
Cryptographic Solutions for Stanford University, USA Stanford Computer Forum 2 April 2012 Homomorphic Encryption Homomorphic encryption allows users to delegate computation while ensuring secrecy. Homomorphic
Revisiting Cryptographic Accumulators, Additional Properties and Relations to other Primitives
 S C I E N C E P A S S I O N T E C H N O L O G Y Revisiting Cryptographic Accumulators, Additional Properties and Relations to other Primitives David Derler, Christian Hanser, and Daniel Slamanig, IAIK,
S C I E N C E P A S S I O N T E C H N O L O G Y Revisiting Cryptographic Accumulators, Additional Properties and Relations to other Primitives David Derler, Christian Hanser, and Daniel Slamanig, IAIK,
Practical Strongly Invisible and Strongly Accountable Sanitizable Signatures
 This is the full version of a paper which appears in Information Security and Privacy - ACISP 2017-22nd Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy, Auckland, New Zealand, July 3-5, 2017,
This is the full version of a paper which appears in Information Security and Privacy - ACISP 2017-22nd Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy, Auckland, New Zealand, July 3-5, 2017,
Chameleon-Hashes with Ephemeral Trapdoors
 This is the full version of a paper which appears in Public-Key Cryptography - PKC 2017-20th IACR International Conference on Practice and Theory in Public-Key Cryptography, Amsterdam, The Netherlands,
This is the full version of a paper which appears in Public-Key Cryptography - PKC 2017-20th IACR International Conference on Practice and Theory in Public-Key Cryptography, Amsterdam, The Netherlands,
Digital signature schemes
 Digital signature schemes Martin Stanek Department of Computer Science Comenius University stanek@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Cryptology 1 (2017/18) Content Introduction digital signature scheme security of digital
Digital signature schemes Martin Stanek Department of Computer Science Comenius University stanek@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Cryptology 1 (2017/18) Content Introduction digital signature scheme security of digital
Digital Signatures. Adam O Neill based on
 Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited
 From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model. A. Hülsing
 Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signa
 Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants. COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from
 Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Indistinguishability of One-Way Accumulators
 Indistinguishability of One-Way Accumulators Hermann de Meer, Manuel Liedel, Henrich C. Pöhls, Joachim Posegga, Kai Samelin demeer@uni-passau.de, manuel.liedel@wiwi.uni-regensburg.de, {hp,jp,ks}@sec.uni-passau.de,
Indistinguishability of One-Way Accumulators Hermann de Meer, Manuel Liedel, Henrich C. Pöhls, Joachim Posegga, Kai Samelin demeer@uni-passau.de, manuel.liedel@wiwi.uni-regensburg.de, {hp,jp,ks}@sec.uni-passau.de,
Proofs on Encrypted Values in Bilinear Groups and an Application to Anonymity of Signatures
 Proofs on Encrypted Values in Bilinear Groups and an Application to Anonymity of Signatures G. Fuchsbauer D. Pointcheval École normale supérieure Pairing'09, 13.08.2009 Fuchsbauer, Pointcheval (ENS) Proofs
Proofs on Encrypted Values in Bilinear Groups and an Application to Anonymity of Signatures G. Fuchsbauer D. Pointcheval École normale supérieure Pairing'09, 13.08.2009 Fuchsbauer, Pointcheval (ENS) Proofs
Anonymous Signatures Made Easy
 Anonymous Signatures Made Easy Marc Fischlin Darmstadt University of Technology, Germany marc.fischlin @ gmail.com www.fischlin.de Abstract. At PKC 2006, Yang, Wong, Deng and Wang proposed the notion of
Anonymous Signatures Made Easy Marc Fischlin Darmstadt University of Technology, Germany marc.fischlin @ gmail.com www.fischlin.de Abstract. At PKC 2006, Yang, Wong, Deng and Wang proposed the notion of
Ring Group Signatures
 Ring Group Signatures Liqun Chen Hewlett-Packard Laboratories, Long Down Avenue, Stoke Gifford, Bristol, BS34 8QZ, United Kingdom. liqun.chen@hp.com Abstract. In many applications of group signatures,
Ring Group Signatures Liqun Chen Hewlett-Packard Laboratories, Long Down Avenue, Stoke Gifford, Bristol, BS34 8QZ, United Kingdom. liqun.chen@hp.com Abstract. In many applications of group signatures,
Schnorr Signature. Schnorr Signature. October 31, 2012
 . October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
. October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
Short Redactable Signatures Using Random Trees
 Short Redactable Signatures Using Random Trees Ee-Chien Chang Chee Liang Lim Jia Xu Department of Computer Science National University of Singapore {changec, xujia}@comp.nus.edu.sg Abstract. A redactable
Short Redactable Signatures Using Random Trees Ee-Chien Chang Chee Liang Lim Jia Xu Department of Computer Science National University of Singapore {changec, xujia}@comp.nus.edu.sg Abstract. A redactable
The Random Oracle Paradigm. Mike Reiter. Random oracle is a formalism to model such uses of hash functions that abound in practical cryptography
 1 The Random Oracle Paradigm Mike Reiter Based on Random Oracles are Practical: A Paradigm for Designing Efficient Protocols by M. Bellare and P. Rogaway Random Oracles 2 Random oracle is a formalism to
1 The Random Oracle Paradigm Mike Reiter Based on Random Oracles are Practical: A Paradigm for Designing Efficient Protocols by M. Bellare and P. Rogaway Random Oracles 2 Random oracle is a formalism to
Enforcing honesty of certification authorities: Tagged one-time signature schemes
 Enforcing honesty of certification authorities: Tagged one-time signature schemes Information Security Group Royal Holloway, University of London bertram.poettering@rhul.ac.uk Stanford, January 11, 2013
Enforcing honesty of certification authorities: Tagged one-time signature schemes Information Security Group Royal Holloway, University of London bertram.poettering@rhul.ac.uk Stanford, January 11, 2013
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes
 Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
FUNCTIONAL SIGNATURES AND PSEUDORANDOM FUNCTIONS. Elette Boyle Shafi Goldwasser Ioana Ivan
 FUNCTIONAL SIGNATURES AND PSEUDORANDOM FUNCTIONS Elette Boyle Shafi Goldwasser Ioana Ivan Traditional Paradigm: All or Nothing Encryption [DH76] Given SK, can decrypt. Otherwise, can t distinguish encryptions
FUNCTIONAL SIGNATURES AND PSEUDORANDOM FUNCTIONS Elette Boyle Shafi Goldwasser Ioana Ivan Traditional Paradigm: All or Nothing Encryption [DH76] Given SK, can decrypt. Otherwise, can t distinguish encryptions
Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures
 Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures Zhou Sujing Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, zhousujing@pmail.ntu.edu.sg Abstract. Transitive signature, motivated by signing
Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures Zhou Sujing Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, zhousujing@pmail.ntu.edu.sg Abstract. Transitive signature, motivated by signing
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes
 From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Smooth Projective Hash Function and Its Applications
 Smooth Projective Hash Function and Its Applications Rongmao Chen University of Wollongong November 21, 2014 Literature Ronald Cramer and Victor Shoup. Universal Hash Proofs and a Paradigm for Adaptive
Smooth Projective Hash Function and Its Applications Rongmao Chen University of Wollongong November 21, 2014 Literature Ronald Cramer and Victor Shoup. Universal Hash Proofs and a Paradigm for Adaptive
CLASSICAL CRYPTOSYSTEMS IN A QUANTUM WORLD
 CLASSICAL CRYPTOSYSTEMS IN A QUANTUM WORLD Mark Zhandry Stanford University * Joint work with Dan Boneh But First: My Current Work Indistinguishability Obfuscation (and variants) Multiparty NIKE without
CLASSICAL CRYPTOSYSTEMS IN A QUANTUM WORLD Mark Zhandry Stanford University * Joint work with Dan Boneh But First: My Current Work Indistinguishability Obfuscation (and variants) Multiparty NIKE without
Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample
 Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample Fuchun Guo 1, Rongmao Chen 2, Willy Susilo 1, Jianchang Lai 1, Guomin Yang 1, and Yi Mu 1 1 Institute
Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample Fuchun Guo 1, Rongmao Chen 2, Willy Susilo 1, Jianchang Lai 1, Guomin Yang 1, and Yi Mu 1 1 Institute
Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Proofs of Non-Membership
 Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Proofs of Non-Membership O. Blazy, C. Chevalier, D. Vergnaud XLim / Université Paris II / ENS O. Blazy (XLim) Negative-NIZK CT-RSA 2015 1 / 22 1 Brief Overview 2 Building
Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Proofs of Non-Membership O. Blazy, C. Chevalier, D. Vergnaud XLim / Université Paris II / ENS O. Blazy (XLim) Negative-NIZK CT-RSA 2015 1 / 22 1 Brief Overview 2 Building
Group Undeniable Signatures
 Group Undeniable Signatures YUH-DAUH LYUU Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering and Department of Finance National Taiwan University No 1, Sec 4, Roosevelt Rd, Taipei, Taiwan lyuu@csie.ntu.edu.tw
Group Undeniable Signatures YUH-DAUH LYUU Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering and Department of Finance National Taiwan University No 1, Sec 4, Roosevelt Rd, Taipei, Taiwan lyuu@csie.ntu.edu.tw
Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman
 Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman Dan Boneh 1, Emily Shen 1, and Brent Waters 2 1 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA {dabo,emily}@cs.stanford.edu
Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman Dan Boneh 1, Emily Shen 1, and Brent Waters 2 1 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA {dabo,emily}@cs.stanford.edu
Authentication. Chapter Message Authentication
 Chapter 5 Authentication 5.1 Message Authentication Suppose Bob receives a message addressed from Alice. How does Bob ensure that the message received is the same as the message sent by Alice? For example,
Chapter 5 Authentication 5.1 Message Authentication Suppose Bob receives a message addressed from Alice. How does Bob ensure that the message received is the same as the message sent by Alice? For example,
Short Randomizable Signatures
 SESSION ID: CRYP-W02 Short Randomizable Signatures David Pointcheval Senior Researcher ENS/CNRS/INRIA Paris, France Joint work with Olivier Sanders S C I E N C E P A S S I O N
SESSION ID: CRYP-W02 Short Randomizable Signatures David Pointcheval Senior Researcher ENS/CNRS/INRIA Paris, France Joint work with Olivier Sanders S C I E N C E P A S S I O N
March 19: Zero-Knowledge (cont.) and Signatures
 March 19: Zero-Knowledge (cont.) and Signatures March 26, 2013 1 Zero-Knowledge (review) 1.1 Review Alice has y, g, p and claims to know x such that y = g x mod p. Alice proves knowledge of x to Bob w/o
March 19: Zero-Knowledge (cont.) and Signatures March 26, 2013 1 Zero-Knowledge (review) 1.1 Review Alice has y, g, p and claims to know x such that y = g x mod p. Alice proves knowledge of x to Bob w/o
Group Undeniable Signatures
 Group Undeniable Signatures YUH-DAUH LYUU Dept. of Computer Science & Information Engineering and Dept. of Finance National Taiwan University No 1, Sec 4, Roosevelt Rd, Taipei, Taiwan lyuu@csie.ntu.edu.tw
Group Undeniable Signatures YUH-DAUH LYUU Dept. of Computer Science & Information Engineering and Dept. of Finance National Taiwan University No 1, Sec 4, Roosevelt Rd, Taipei, Taiwan lyuu@csie.ntu.edu.tw
Convertible Group Undeniable Signatures
 Convertible Group Undeniable Signatures Yuh-Dauh Lyuu 1 and Ming-Luen Wu 2 1 Dept. of Computer Science & Information Engineering and Dept. of Finance, National Taiwan University, Taiwan lyuu@csie.ntu.edu.tw
Convertible Group Undeniable Signatures Yuh-Dauh Lyuu 1 and Ming-Luen Wu 2 1 Dept. of Computer Science & Information Engineering and Dept. of Finance, National Taiwan University, Taiwan lyuu@csie.ntu.edu.tw
Lecture 16 Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko. 1 Digital Signature Schemes. CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004
 CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
Hash-based signatures & Hash-and-sign without collision-resistance
 Hash-based signatures & Hash-and-sign without collision-resistance Andreas Hülsing 22.12.2016 Hash-based Signature Schemes [Mer89] Post quantum Only secure hash function Security well understood Fast 22-12-2016
Hash-based signatures & Hash-and-sign without collision-resistance Andreas Hülsing 22.12.2016 Hash-based Signature Schemes [Mer89] Post quantum Only secure hash function Security well understood Fast 22-12-2016
Cryptographic Protocols Notes 2
 ETH Zurich, Department of Computer Science SS 2018 Prof. Ueli Maurer Dr. Martin Hirt Chen-Da Liu Zhang Cryptographic Protocols Notes 2 Scribe: Sandro Coretti (modified by Chen-Da Liu Zhang) About the notes:
ETH Zurich, Department of Computer Science SS 2018 Prof. Ueli Maurer Dr. Martin Hirt Chen-Da Liu Zhang Cryptographic Protocols Notes 2 Scribe: Sandro Coretti (modified by Chen-Da Liu Zhang) About the notes:
George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK
 George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
II. Digital signatures
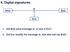 II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
Gentry IBE Paper Reading
 Gentry IBE Paper Reading Y. Jiang 1 1 University of Wollongong September 5, 2014 Literature Craig Gentry. Practical Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles. Advances in Cryptology - EUROCRYPT
Gentry IBE Paper Reading Y. Jiang 1 1 University of Wollongong September 5, 2014 Literature Craig Gentry. Practical Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles. Advances in Cryptology - EUROCRYPT
Multi-Key Homomorphic Signatures Unforgeable under Insider Corruption
 Multi-Key Homomorphic Signatures Unforgeable under Insider Corruption Russell W. F. Lai 1,2, Raymond K. H. Tai 1, Harry W. H. Wong 1, and Sherman S. M. Chow 1 1 Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Multi-Key Homomorphic Signatures Unforgeable under Insider Corruption Russell W. F. Lai 1,2, Raymond K. H. Tai 1, Harry W. H. Wong 1, and Sherman S. M. Chow 1 1 Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
RSA and Rabin Signatures Signcryption
 T-79.5502 Advanced Course in Cryptology RSA and Rabin Signatures Signcryption Alessandro Tortelli 26-04-06 Overview Introduction Probabilistic Signature Scheme PSS PSS with message recovery Signcryption
T-79.5502 Advanced Course in Cryptology RSA and Rabin Signatures Signcryption Alessandro Tortelli 26-04-06 Overview Introduction Probabilistic Signature Scheme PSS PSS with message recovery Signcryption
A Constant-Size Signature Scheme with a Tighter Reduction from the CDH Assumption
 A Constant-Size Signature Scheme with a Tighter Reduction from the CDH Assumption Kaisei Kajita 1, Kazuto Ogawa 1, Eiichiro Fujisaki 2 1 Japan Broadcasting Corporation, Tokyo, Japan {kajita.k-bu, ogawa.k-cm}@nhk.or.jp
A Constant-Size Signature Scheme with a Tighter Reduction from the CDH Assumption Kaisei Kajita 1, Kazuto Ogawa 1, Eiichiro Fujisaki 2 1 Japan Broadcasting Corporation, Tokyo, Japan {kajita.k-bu, ogawa.k-cm}@nhk.or.jp
An update on Hash-based Signatures. Andreas Hülsing
 An update on Hash-based Signatures Andreas Hülsing Trapdoor- / Identification Scheme-based (PQ-)Signatures Lattice, MQ, Coding Signature and/or key sizes Runtimes Secure parameters 9-9-2015 PAGE 2... 1
An update on Hash-based Signatures Andreas Hülsing Trapdoor- / Identification Scheme-based (PQ-)Signatures Lattice, MQ, Coding Signature and/or key sizes Runtimes Secure parameters 9-9-2015 PAGE 2... 1
Digital Signatures. p1.
 Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
Outline. The Game-based Methodology for Computational Security Proofs. Public-Key Cryptography. Outline. Introduction Provable Security
 The Game-based Methodology for Computational s David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA Computational and Symbolic Proofs of Security Atagawa Heights Japan April 6th, 2009 1/39 2/39 Public-Key
The Game-based Methodology for Computational s David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA Computational and Symbolic Proofs of Security Atagawa Heights Japan April 6th, 2009 1/39 2/39 Public-Key
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography
 Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
A Prover-Anonymous and Terrorist-Fraud Resistant Distance-Bounding Protocol
 A Prover-Anonymous and Terrorist-Fraud Resistant Distance-Bounding Protocol Xavier Bultel 1 Sébastien Gambs 2 David Gerault 1 Pascal Lafourcade 1 Cristina Onete 3 Jean-Marc Robert 4 1 University Clermont
A Prover-Anonymous and Terrorist-Fraud Resistant Distance-Bounding Protocol Xavier Bultel 1 Sébastien Gambs 2 David Gerault 1 Pascal Lafourcade 1 Cristina Onete 3 Jean-Marc Robert 4 1 University Clermont
Blind Signature Protocol Based on Difficulty of. Simultaneous Solving Two Difficult Problems
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 202, no. 39, 6903-690 Blind Signature Protocol Based on Difficulty of Simultaneous Solving Two Difficult Problems N. H. Minh, D. V. Binh 2, N. T. Giang 3 and N. A.
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 202, no. 39, 6903-690 Blind Signature Protocol Based on Difficulty of Simultaneous Solving Two Difficult Problems N. H. Minh, D. V. Binh 2, N. T. Giang 3 and N. A.
Practice Final Exam Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017
 Practice Final Exam Name: Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total
Practice Final Exam Name: Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total
On the (In)security of the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm
 On the (In)security of the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Shafi Goldwasser Yael Tauman February 2, 2004 Abstract In 1986, Fiat and Shamir proposed a general method for transforming secure 3-round public-coin identification
On the (In)security of the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Shafi Goldwasser Yael Tauman February 2, 2004 Abstract In 1986, Fiat and Shamir proposed a general method for transforming secure 3-round public-coin identification
Lattice-based DAPS and Generalizations
 Lattice-based DAPS and Generalizations Dan Boneh, Sam Kim, Valeria Nikolaenko Stanford University July 11, 2017 Certificate Authorities Certificate Authorities Certificate Authorities Certificate Authorities
Lattice-based DAPS and Generalizations Dan Boneh, Sam Kim, Valeria Nikolaenko Stanford University July 11, 2017 Certificate Authorities Certificate Authorities Certificate Authorities Certificate Authorities
SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS. CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography
 SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography This is based on Chapter 8 of Trappe and Washington DIGITAL SIGNATURES message sig 1. How do we bind
SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography This is based on Chapter 8 of Trappe and Washington DIGITAL SIGNATURES message sig 1. How do we bind
CIS 6930/4930 Computer and Network Security. Topic 5.2 Public Key Cryptography
 CIS 6930/4930 Computer and Network Security Topic 5.2 Public Key Cryptography 1 Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange 2 Diffie-Hellman Protocol For negotiating a shared secret key using only public communication
CIS 6930/4930 Computer and Network Security Topic 5.2 Public Key Cryptography 1 Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange 2 Diffie-Hellman Protocol For negotiating a shared secret key using only public communication
Accumulators with Applications to Anonymity-Preserving Revocation
 Accumulators with Applications to Anonymity-Preserving Revocation Foteini Baldimtsi 1, Jan Camenisch 2, Maria Dubovitskaya 2, Anna Lysyanskaya 3, Leonid Reyzin 4, Kai Samelin 2,5, and Sophia Yakoubov 4
Accumulators with Applications to Anonymity-Preserving Revocation Foteini Baldimtsi 1, Jan Camenisch 2, Maria Dubovitskaya 2, Anna Lysyanskaya 3, Leonid Reyzin 4, Kai Samelin 2,5, and Sophia Yakoubov 4
Signatures with Flexible Public Key: A Unified Approach to Privacy-Preserving Signatures (Full Version)
 Signatures with Flexible Public Key: A Unified Approach to Privacy-Preserving Signatures (Full Version) Michael Backes 1,3, Lucjan Hanzlik 2,3, Kamil Kluczniak 4, and Jonas Schneider 2,3 1 CISPA Helmholtz
Signatures with Flexible Public Key: A Unified Approach to Privacy-Preserving Signatures (Full Version) Michael Backes 1,3, Lucjan Hanzlik 2,3, Kamil Kluczniak 4, and Jonas Schneider 2,3 1 CISPA Helmholtz
Practice Exam Winter 2018, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2018
 Practice Exam Name: Winter 2018, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2018 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total of
Practice Exam Name: Winter 2018, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2018 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total of
ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011
 ECS 127: Cryptography Handout F UC Davis Phillip Rogaway June 9, 2011 ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011 Hints for success: Good luck on the exam. I don t think it s all that hard (I do believe I
ECS 127: Cryptography Handout F UC Davis Phillip Rogaway June 9, 2011 ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011 Hints for success: Good luck on the exam. I don t think it s all that hard (I do believe I
Secure Signatures and Chosen Ciphertext Security in a Post-Quantum World
 Secure Signatures and Chosen Ciphertext Security in a Post-Quantum World Dan Boneh Mark Zhandry Stanford University {dabo,zhandry}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract We initiate the study of quantum-secure digital
Secure Signatures and Chosen Ciphertext Security in a Post-Quantum World Dan Boneh Mark Zhandry Stanford University {dabo,zhandry}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract We initiate the study of quantum-secure digital
BEYOND POST QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY
 BEYOND POST QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY Mark Zhandry Stanford University Joint work with Dan Boneh Classical Cryptography Post-Quantum Cryptography All communication stays classical Beyond Post-Quantum Cryptography
BEYOND POST QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY Mark Zhandry Stanford University Joint work with Dan Boneh Classical Cryptography Post-Quantum Cryptography All communication stays classical Beyond Post-Quantum Cryptography
Comparing With RSA. 1 ucl Crypto Group
 Comparing With RSA Julien Cathalo 1, David Naccache 2, and Jean-Jacques Quisquater 1 1 ucl Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, b-1348, Belgium julien.cathalo@uclouvain.be, jean-jacques.quisquater@uclouvain.be
Comparing With RSA Julien Cathalo 1, David Naccache 2, and Jean-Jacques Quisquater 1 1 ucl Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, b-1348, Belgium julien.cathalo@uclouvain.be, jean-jacques.quisquater@uclouvain.be
Short Signatures Without Random Oracles
 Short Signatures Without Random Oracles Dan Boneh and Xavier Boyen (presented by Aleksandr Yampolskiy) Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion Why signatures without
Short Signatures Without Random Oracles Dan Boneh and Xavier Boyen (presented by Aleksandr Yampolskiy) Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion Why signatures without
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 11 October 7, 2015 CPSC 467, Lecture 11 1/37 Digital Signature Algorithms Signatures from commutative cryptosystems Signatures from
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 11 October 7, 2015 CPSC 467, Lecture 11 1/37 Digital Signature Algorithms Signatures from commutative cryptosystems Signatures from
Post-Quantum Cryptography & Privacy. Andreas Hülsing
 Post-Quantum Cryptography & Privacy Andreas Hülsing Privacy? Too abstract? How to achieve privacy? Under the hood... Public-key crypto ECC RSA DSA Secret-key crypto AES SHA2 SHA1... Combination of both
Post-Quantum Cryptography & Privacy Andreas Hülsing Privacy? Too abstract? How to achieve privacy? Under the hood... Public-key crypto ECC RSA DSA Secret-key crypto AES SHA2 SHA1... Combination of both
Chapter 8 Public-key Cryptography and Digital Signatures
 Chapter 8 Public-key Cryptography and Digital Signatures v 1. Introduction to Public-key Cryptography 2. Example of Public-key Algorithm: Diffie- Hellman Key Exchange Scheme 3. RSA Encryption and Digital
Chapter 8 Public-key Cryptography and Digital Signatures v 1. Introduction to Public-key Cryptography 2. Example of Public-key Algorithm: Diffie- Hellman Key Exchange Scheme 3. RSA Encryption and Digital
Ring Signatures without Random Oracles
 Ring Signatures without Random Oracles Sherman S. M. Chow 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, Victor K. Wei 3 and Tsz Hon Yuen 3 1 Department of Computer Science Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University,
Ring Signatures without Random Oracles Sherman S. M. Chow 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, Victor K. Wei 3 and Tsz Hon Yuen 3 1 Department of Computer Science Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University,
On the Selective-Opening Security of DHIES
 On the Selective-Opening Security of DHIES and other practical encryption schemes UbiCrypt Research Retreat, Schloss Raesfeld: 29.& 30. Sep. 2014 Felix Heuer, Tibor Jager, Eike Kiltz, Sven Schäge Horst
On the Selective-Opening Security of DHIES and other practical encryption schemes UbiCrypt Research Retreat, Schloss Raesfeld: 29.& 30. Sep. 2014 Felix Heuer, Tibor Jager, Eike Kiltz, Sven Schäge Horst
Computing on Authenticated Data for Adjustable Predicates
 A short version of this work appears at ACNS 2013. This is the full version. Computing on Authenticated Data for Adjustable Predicates Björn Deiseroth Victoria Fehr Marc Fischlin Manuel Maasz Nils Fabian
A short version of this work appears at ACNS 2013. This is the full version. Computing on Authenticated Data for Adjustable Predicates Björn Deiseroth Victoria Fehr Marc Fischlin Manuel Maasz Nils Fabian
XMSS A Practical Forward Secure Signature Scheme based on Minimal Security Assumptions
 XMSS A Practical Forward Secure Signature Scheme based on Minimal Security Assumptions Johannes Buchmann and Andreas Hülsing {buchmann,huelsing}@cdc.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Cryptography and Computeralgebra
XMSS A Practical Forward Secure Signature Scheme based on Minimal Security Assumptions Johannes Buchmann and Andreas Hülsing {buchmann,huelsing}@cdc.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Cryptography and Computeralgebra
Attribute-Based Signatures
 Attribute-Based Signatures Hemanta K. Maji Manoj Prabhakaran Mike Rosulek Abstract We introduce Attribute-Based Signatures (ABS), a versatile primitive that allows a party to sign a message with fine-grained
Attribute-Based Signatures Hemanta K. Maji Manoj Prabhakaran Mike Rosulek Abstract We introduce Attribute-Based Signatures (ABS), a versatile primitive that allows a party to sign a message with fine-grained
A survey on quantum-secure cryptographic systems
 A survey on quantum-secure cryptographic systems Tomoka Kan May 24, 2018 1 Abstract Post-quantum cryptography refers to the search for classical cryptosystems which remain secure in the presence of a quantum
A survey on quantum-secure cryptographic systems Tomoka Kan May 24, 2018 1 Abstract Post-quantum cryptography refers to the search for classical cryptosystems which remain secure in the presence of a quantum
Dr George Danezis University College London, UK
 Dr George Danezis University College London, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
Dr George Danezis University College London, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
1 Number Theory Basics
 ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
Mitigating Multi-Target-Attacks in Hash-based Signatures. Andreas Hülsing joint work with Joost Rijneveld, Fang Song
 Mitigating Multi-Target-Attacks in Hash-based Signatures Andreas Hülsing joint work with Joost Rijneveld, Fang Song A brief motivation Trapdoor- / Identification Scheme-based (PQ-)Signatures Lattice, MQ,
Mitigating Multi-Target-Attacks in Hash-based Signatures Andreas Hülsing joint work with Joost Rijneveld, Fang Song A brief motivation Trapdoor- / Identification Scheme-based (PQ-)Signatures Lattice, MQ,
Improved Security for Linearly Homomorphic Signatures: A Generic Framework
 Improved Security for Linearly Homomorphic Signatures: A Generic Framework Stanford University, USA PKC 2012 Darmstadt, Germany 23 May 2012 Problem: Computing on Authenticated Data Q: How do we delegate
Improved Security for Linearly Homomorphic Signatures: A Generic Framework Stanford University, USA PKC 2012 Darmstadt, Germany 23 May 2012 Problem: Computing on Authenticated Data Q: How do we delegate
Lecture 9 - Symmetric Encryption
 0368.4162: Introduction to Cryptography Ran Canetti Lecture 9 - Symmetric Encryption 29 December 2008 Fall 2008 Scribes: R. Levi, M. Rosen 1 Introduction Encryption, or guaranteeing secrecy of information,
0368.4162: Introduction to Cryptography Ran Canetti Lecture 9 - Symmetric Encryption 29 December 2008 Fall 2008 Scribes: R. Levi, M. Rosen 1 Introduction Encryption, or guaranteeing secrecy of information,
Instructor: Daniele Venturi. Master Degree in Data Science Sapienza University of Rome Academic Year
 Data Privacy and Security Instructor: Daniele Venturi Master Degree in Data Science Sapienza University of Rome Academic Year 2017-2018 Interlude: Number Theory Cubum autem in duos cubos, aut quadratoquadratum
Data Privacy and Security Instructor: Daniele Venturi Master Degree in Data Science Sapienza University of Rome Academic Year 2017-2018 Interlude: Number Theory Cubum autem in duos cubos, aut quadratoquadratum
Short Signatures From Diffie-Hellman: Realizing Short Public Key
 Short Signatures From Diffie-Hellman: Realizing Short Public Key Jae Hong Seo Department of Mathematics, Myongji University Yongin, Republic of Korea jaehongseo@mju.ac.kr Abstract. Efficient signature
Short Signatures From Diffie-Hellman: Realizing Short Public Key Jae Hong Seo Department of Mathematics, Myongji University Yongin, Republic of Korea jaehongseo@mju.ac.kr Abstract. Efficient signature
A Composition Theorem for Universal One-Way Hash Functions
 A Composition Theorem for Universal One-Way Hash Functions Victor Shoup IBM Zurich Research Lab, Säumerstr. 4, 8803 Rüschlikon, Switzerland sho@zurich.ibm.com Abstract. In this paper we present a new scheme
A Composition Theorem for Universal One-Way Hash Functions Victor Shoup IBM Zurich Research Lab, Säumerstr. 4, 8803 Rüschlikon, Switzerland sho@zurich.ibm.com Abstract. In this paper we present a new scheme
A New Paradigm of Hybrid Encryption Scheme
 A New Paradigm of Hybrid Encryption Scheme Kaoru Kurosawa 1 and Yvo Desmedt 2 1 Ibaraki University, Japan kurosawa@cis.ibaraki.ac.jp 2 Dept. of Computer Science, University College London, UK, and Florida
A New Paradigm of Hybrid Encryption Scheme Kaoru Kurosawa 1 and Yvo Desmedt 2 1 Ibaraki University, Japan kurosawa@cis.ibaraki.ac.jp 2 Dept. of Computer Science, University College London, UK, and Florida
The Cramer-Shoup Cryptosystem
 The Cramer-Shoup Cryptosystem Eileen Wagner October 22, 2014 1 / 28 The Cramer-Shoup system is an asymmetric key encryption algorithm, and was the first efficient scheme proven to be secure against adaptive
The Cramer-Shoup Cryptosystem Eileen Wagner October 22, 2014 1 / 28 The Cramer-Shoup system is an asymmetric key encryption algorithm, and was the first efficient scheme proven to be secure against adaptive
Available online at J. Math. Comput. Sci. 6 (2016), No. 3, ISSN:
 Available online at http://scik.org J. Math. Comput. Sci. 6 (2016), No. 3, 281-289 ISSN: 1927-5307 AN ID-BASED KEY-EXPOSURE FREE CHAMELEON HASHING UNDER SCHNORR SIGNATURE TEJESHWARI THAKUR, BIRENDRA KUMAR
Available online at http://scik.org J. Math. Comput. Sci. 6 (2016), No. 3, 281-289 ISSN: 1927-5307 AN ID-BASED KEY-EXPOSURE FREE CHAMELEON HASHING UNDER SCHNORR SIGNATURE TEJESHWARI THAKUR, BIRENDRA KUMAR
Structure-Preserving Signatures on Equivalence Classes and their Application to Anonymous Credentials
 Structure-Preserving Signatures on Equivalence Classes and their Application to Anonymous Credentials Christian Hanser and Daniel Slamanig Institute for Applied Information Processing and Communications
Structure-Preserving Signatures on Equivalence Classes and their Application to Anonymous Credentials Christian Hanser and Daniel Slamanig Institute for Applied Information Processing and Communications
Non-interactive Designated Verifier Proofs and Undeniable Signatures
 Non-interactive Designated Verifier Proofs and Undeniable Signatures Caroline Kudla and Kenneth G. Paterson Information Security Group Royal Holloway, University of London, UK {c.j.kudla,kenny.paterson}@rhul.ac.uk
Non-interactive Designated Verifier Proofs and Undeniable Signatures Caroline Kudla and Kenneth G. Paterson Information Security Group Royal Holloway, University of London, UK {c.j.kudla,kenny.paterson}@rhul.ac.uk
Provable security. Michel Abdalla
 Lecture 1: Provable security Michel Abdalla École normale supérieure & CNRS Cryptography Main goal: Enable secure communication in the presence of adversaries Adversary Sender 10110 10110 Receiver Only
Lecture 1: Provable security Michel Abdalla École normale supérieure & CNRS Cryptography Main goal: Enable secure communication in the presence of adversaries Adversary Sender 10110 10110 Receiver Only
Transitive Signatures based on Factoring and RSA
 An extended abstract of this paper appears in Advances in Cryptology ASIACRYPT 02, Lecture Notes in Computer Science Vol., Y. Zheng ed., Springer-Verlag, 2002. This is the full version. Transitive Signatures
An extended abstract of this paper appears in Advances in Cryptology ASIACRYPT 02, Lecture Notes in Computer Science Vol., Y. Zheng ed., Springer-Verlag, 2002. This is the full version. Transitive Signatures
Practical Verifiable Encryption and Decryption of Discrete Logarithms
 Practical Verifiable Encryption and Decryption of Discrete Logarithms Jan Camenisch IBM Zurich Research Lab Victor Shoup New York University p.1/27 Verifiable encryption of discrete logs Three players:
Practical Verifiable Encryption and Decryption of Discrete Logarithms Jan Camenisch IBM Zurich Research Lab Victor Shoup New York University p.1/27 Verifiable encryption of discrete logs Three players:
Post-Quantum Zero-Knowledge Proofs for Accumulators with Applications to Ring Signatures from Symmetric-Key Primitives
 Post-Quantum Zero-Knowledge Proofs for Accumulators with Applications to Ring Signatures from Symmetric-Key Primitives David Derler 1, Sebastian Ramacher 1, and Daniel Slamanig 2 1 IAIK, Graz University
Post-Quantum Zero-Knowledge Proofs for Accumulators with Applications to Ring Signatures from Symmetric-Key Primitives David Derler 1, Sebastian Ramacher 1, and Daniel Slamanig 2 1 IAIK, Graz University
Sub-linear Blind Ring Signatures without Random Oracles
 Sub-linear Blind Ring Signatures without Random Oracles Essam Ghadafi Dept. Computer Science, University of Bristol, Merchant Venturers Building, Woodland Road, Bristol, BS8 1UB. United Kingdom. ghadafi@cs.bris.ac.uk
Sub-linear Blind Ring Signatures without Random Oracles Essam Ghadafi Dept. Computer Science, University of Bristol, Merchant Venturers Building, Woodland Road, Bristol, BS8 1UB. United Kingdom. ghadafi@cs.bris.ac.uk
John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes. Table of contents
 John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time: Good news and bad There
John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time: Good news and bad There
Practical Round-Optimal Blind Signatures in the Standard Model
 W I S S E N T E C H N I K L E I D E N S C H A F T IAIK Practical Round-Optimal Blind Signatures in the Standard Model Georg Fuchsbauer, Christian Hanser and Daniel Slamanig, Institute of Science and Technology
W I S S E N T E C H N I K L E I D E N S C H A F T IAIK Practical Round-Optimal Blind Signatures in the Standard Model Georg Fuchsbauer, Christian Hanser and Daniel Slamanig, Institute of Science and Technology
TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITEIT EINDHOVEN Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Friday 25 January 2019
 Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Friday 25 January 2019 Name : TU/e student number : Exercise 1 2 3 4 5 total points Notes: Please hand in all sheets at the end of the exam.
Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Friday 25 January 2019 Name : TU/e student number : Exercise 1 2 3 4 5 total points Notes: Please hand in all sheets at the end of the exam.
VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic
 VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic - as already seen signatures can be used and are used in practice to design identification protocols - next we show how we can obtain signatures schemes from - protocols using
VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic - as already seen signatures can be used and are used in practice to design identification protocols - next we show how we can obtain signatures schemes from - protocols using
Hash-based Signatures. Andreas Hülsing
 Hash-based Signatures Andreas Hülsing Post-Quantum Signatures Lattice, MQ, Coding Signature and/or key sizes Runtimes Secure parameters 23-2-2016 PAGE 2... 1 3 1 4 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 1 y x x x x
Hash-based Signatures Andreas Hülsing Post-Quantum Signatures Lattice, MQ, Coding Signature and/or key sizes Runtimes Secure parameters 23-2-2016 PAGE 2... 1 3 1 4 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 1 y x x x x
SPHINCS: practical stateless hash-based signatures
 SPHINCS: practical stateless hash-based signatures D. J. Bernstein, D. Hopwood, A. Hülsing, T. Lange, R. Niederhagen, L. Papachristodoulou, P. Schwabe, and Z. Wilcox O'Hearn Digital Signatures are Important!
SPHINCS: practical stateless hash-based signatures D. J. Bernstein, D. Hopwood, A. Hülsing, T. Lange, R. Niederhagen, L. Papachristodoulou, P. Schwabe, and Z. Wilcox O'Hearn Digital Signatures are Important!
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography. Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017
 COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Previously Digital Signatures Algorithms: Gen() à (sk,pk) Sign(sk,m) à σ Ver(pk,m,σ) à 0/1 Correctness: Pr[Ver(pk,m,Sign(sk,m))=1:
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Previously Digital Signatures Algorithms: Gen() à (sk,pk) Sign(sk,m) à σ Ver(pk,m,σ) à 0/1 Correctness: Pr[Ver(pk,m,Sign(sk,m))=1:
Key-Exposure Free Chameleon Hashing and Signatures Based on Discrete Logarithm Systems
 Key-Exposure Free Chameleon Hashing and Signatures Based on Discrete Logarithm Systems Xiaofeng Chen, Fangguo Zhang, Haibo Tian, Baodian Wei, and Kwangjo Kim 1 School of Information Science and Technology,
Key-Exposure Free Chameleon Hashing and Signatures Based on Discrete Logarithm Systems Xiaofeng Chen, Fangguo Zhang, Haibo Tian, Baodian Wei, and Kwangjo Kim 1 School of Information Science and Technology,
Lecture 1. Crypto Background
 Lecture 1 Crypto Background This lecture Crypto background hash functions random oracle model digital signatures and applications Cryptographic Hash Functions Hash function takes a string of arbitrary
Lecture 1 Crypto Background This lecture Crypto background hash functions random oracle model digital signatures and applications Cryptographic Hash Functions Hash function takes a string of arbitrary
Outline. Provable Security in the Computational Model. III Signatures. Public-Key Encryption. Outline. David Pointcheval.
 Provable Security in the Computational Model III Signatures David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRI Public-Key Encryption Signatures 2 dvanced Security for Signature dvanced Security Notions
Provable Security in the Computational Model III Signatures David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRI Public-Key Encryption Signatures 2 dvanced Security for Signature dvanced Security Notions
Communication-Efficient Non-Interactive Proofs of Knowledge with Online Extractors
 Communication-Efficient Non-Interactive Proofs of Knowledge with Online Extractors Marc Fischlin Institute for Theoretical Computer Science, ETH Zürich, Switzerland marc.fischlin @ inf.ethz.ch http://www.fischlin.de/
Communication-Efficient Non-Interactive Proofs of Knowledge with Online Extractors Marc Fischlin Institute for Theoretical Computer Science, ETH Zürich, Switzerland marc.fischlin @ inf.ethz.ch http://www.fischlin.de/
