VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic
|
|
|
- Rudolf McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic - as already seen signatures can be used and are used in practice to design identification protocols - next we show how we can obtain signatures schemes from - protocols using the Fiat-Shamir heuristic - construction based on hash functions - prove security of resulting signatures in random oracle model - FS heuristic leads to signatures schemes used in practice, i.e. Schnorr signatures - construction can also be used to design signatures schemes with additional functionality - see group signatures as an example in next section 1
2 Relations R {0,1} * {0,1} * binary relation, (x,y) R : R(x,y) = 1 x {0,1} * : W(x) := {w {0,1} * : R(x,w) = 1},w W(x) called called witnesses for x. L R := {x {0,1} * : W(x) } language corresponding to R R polynomially bounded: there is a l N such that for all x {0,1} * and all w W(x) : w x l. In this section assume for simplicity x = x l. - Since we want to formally prove the security of signatures obtained from Fiat-Shamir heuristic need to be more careful - asymptotics - instance generators - hard relations 2
3 Instance generators Defintion 5.4 (restated) An instance generator for relation R is a ppt IG that an input 1 K outputs a pair (x,w) R with x = K. 3
4 Witness finding R Witness finding game WF A,IG 1. Run Gen(1 K ) to obtain ( x,w ). ( K) { } *. 2. A gets as input 1 K and x. A outputs w 0,1 3. Output of experiment is 1, if and only if w W ( x). R Write WF A,IG ( K) = 1, if output is 1. Defintion 6.1 Let R be an relation and IG an instance generator for R. Relation R is called hard for generator IG if for every ppt A there is a negligible function µ such that Pr WF R A,IG ( K ) = 1 = µ ( k ). 4
5 Three round protocols for relation R P with input (x,w) V with input x a α(x,w;k) a c c C r ρ(x,w,k,c) r ϕ(x,a,c,r)? 5
6 Three round protocols for relation R P with input (x,w) { 0,1} K { 0,1} Kc V with input x { 0,1} K a α(x,w;k), k { 0,1} L( K),a A K a c c C K r ρ(x,w,k,c),r R K r ϕ(x,a,c,r)? L( ) polynomial in K, α,ρ,ϕ ppts in K A K,C K,R K sets with size 2 Kl for some fixed l N. 6
7 Soundness and zero-knowledge Definition 3.5 (restated) A three round protocol for relation R has special soundness if there exists a ppt algorithm E (extractor) which given x L R and any two accepting transcripts (a,c,r) and (a,c',r') with c c' computes a witness w satisfying (x,w) R. Definition 3.6 (restated) A three round protocol for relation R is a special honest verifier zero-knowledge protocol if there exists a ppt algorithm S (simulator) which given any x L R and any challenge c produces transcripts (a,c,r) with the same distribution as in the real protocol. - ppts always with respect to x. 7
8 The Fiat-Shamir heuristic Construction 6.2 Let R be a relation, IG an instance generator and Σ R a three round protocol for R with ppts α,ρ,ϕ, announcement spaces A K,challenge spaces C K, and response { } K N,H K : A K { 0,1} * C K be a family of ( ) is spaces R K. Let H K functions. Then signature scheme ϒ = Gen,Sign, Vrfy defined by Gen( 1 K ) : ( x,w ) IG( 1 K ),pk := x,sk := w. Sign sk Vrfy pk ( m) : a α ( pk,sk;k),c := H ( K a,m),r ρ( pk,sk,k,c). Output σ: = ( a,c,r ). ( m,σ) : Output 1, iff ϕ ( pk,a,c,r ) = 1 H ( K a,m) = c. ϒ called Σ R - signature scheme 8
9 Fiat-Shamir and Schnorr Example Schnorr protocol for R DL pk = ( p,g,v ),sk := w such that g w = v mod p. H: Z * { 0,1 } * { 1,,2 l } ( Z p p 1 ) collision-resistant Sign sk Vrfy pk ( m) : k Z p 1,a := g k modp,c := H( a,m), r := k c w mod p 1. Output σ: = ( a,c,r ). ( m,σ) : Output 1, iff a = g r pk c H( a,m) = c. Modification Sign sk Vrfy pk ( m) : just outputs ( c,r ) ( m,σ) : compute a = g r pk c, output 1 iff H( a,m) = c. 9
10 Security of Fiat-Shamir heuristic Definition 6.3 A three round protocol Σ R for relation R is called smooth if for all K N, ( x, w ) R, x = K,a A K we have ( ) Pr k { 0,1 } a = α x,w;k L( K) 2 K 2. Theorem 6.4 If relation R is smooth, IG is hard for R, and Σ R is a Σ- protocol for R, then signature scheme ϒ from Construction 6.2 is existentially unforgeable under chosen message attacks, provided thefunctions H K are modelled as random oracles. 10
11 Outline of proof - will us a proof technique similar to the one used for the proof of Theorem this time use forger to construct two forgeries from which, using the extractor, one can construct witnesses - but forgeries must be on the same message and having the same a in order to apply extractor for R to obtain witnesses - how to do this not obvious since there is additional randomness due to the hash functions H - first show the result for adversaries A without access to signing racle 11
12 Restrictions and extensions for A assume that on input pk of length K, adversaries makes exactly q = q( K)queries assume that A does not repeat queries extend A's original output m,σ 0 J q, where 0 if m, σ J = ( ) i if A's i-th query is for H a,m ( ) = ( m,a,c,r ) to ( m,σ,j) with ( ) is not a valid forgery or A never queried for H a,m ( ) 12
13 From forger A to witness finder A A on input 1 K and x = pk, x = K 1. R 0,1 { } L(K),h = h 1,,h q ( ) C K q 2. Simulate A with randomness R and H K realized by h. ( ) be A's extended output. Let m, σ,i 3. If I = 0, output and abort. ( ) C K q I+1 4. h I,, h q 5. Simulate A with randomness R and H realized by h = ( h 1,,h I 1, h I,, h q ). Let ( m, σ, I ) be A's extended output. 6. If I = I, run extractor E for Σ R with input σ, σ. Output whatever E outputs. 13
14 Two simple lemmata Lemma 6.5 Let Y be a discrte random variable. Then E X 2 E X 2. Lemma 6.6 Let x 1,,x q R. Then q x 2 i 1 i=1 q ( q x ) 2 i=1 i. 14
15 Answering queries to Sign On query m to Sig sk ( ) : 1. if query is the i-th (overall) query, use the simulator for Σ R to obtain σ = ( a,c,r ) 2. if H( a,m) was among the first i 1 queries, then abort 3. else, set H( a,m) = h i and output Sign ( sk m) = σ = ( ) 15
III. Authentication - identification protocols
 III. Authentication - identification protocols Definition 3.1 A cryptographic protocol is a distributed algorithm describing precisely the interaction between two or more parties, achieving certain security
III. Authentication - identification protocols Definition 3.1 A cryptographic protocol is a distributed algorithm describing precisely the interaction between two or more parties, achieving certain security
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography
 Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
II. Digital signatures
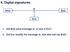 II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
Schnorr Signature. Schnorr Signature. October 31, 2012
 . October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
. October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes. Table of contents
 John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time: Good news and bad There
John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time: Good news and bad There
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model. A. Hülsing
 Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
Lecture 16 Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko. 1 Digital Signature Schemes. CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004
 CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model
 Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt (CASED) - TU Darmstadt, Germany June, 21st, 2012 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt (CASED) - TU Darmstadt, Germany June, 21st, 2012 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Tightly-Secure Signatures From Lossy Identification Schemes
 Tightly-Secure Signatures From Lossy Identification Schemes Michel Abdalla, Pierre-Alain Fouque, Vadim Lyubashevsky, and Mehdi Tibouchi 2 École normale supérieure {michel.abdalla,pierre-alain.fouque,vadim.lyubashevsky}@ens.fr
Tightly-Secure Signatures From Lossy Identification Schemes Michel Abdalla, Pierre-Alain Fouque, Vadim Lyubashevsky, and Mehdi Tibouchi 2 École normale supérieure {michel.abdalla,pierre-alain.fouque,vadim.lyubashevsky}@ens.fr
Block Ciphers/Pseudorandom Permutations
 Block Ciphers/Pseudorandom Permutations Definition: Pseudorandom Permutation is exactly the same as a Pseudorandom Function, except for every key k, F k must be a permutation and it must be indistinguishable
Block Ciphers/Pseudorandom Permutations Definition: Pseudorandom Permutation is exactly the same as a Pseudorandom Function, except for every key k, F k must be a permutation and it must be indistinguishable
Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge
 Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge - interactive protocols formalize what can be recognized by polynomial time restricted verifiers in arbitrary protocols - generalizes NP - zero-knowledge formalizes
Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge - interactive protocols formalize what can be recognized by polynomial time restricted verifiers in arbitrary protocols - generalizes NP - zero-knowledge formalizes
Digital Signatures. Adam O Neill based on
 Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
March 19: Zero-Knowledge (cont.) and Signatures
 March 19: Zero-Knowledge (cont.) and Signatures March 26, 2013 1 Zero-Knowledge (review) 1.1 Review Alice has y, g, p and claims to know x such that y = g x mod p. Alice proves knowledge of x to Bob w/o
March 19: Zero-Knowledge (cont.) and Signatures March 26, 2013 1 Zero-Knowledge (review) 1.1 Review Alice has y, g, p and claims to know x such that y = g x mod p. Alice proves knowledge of x to Bob w/o
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography. Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2018
 COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2018 Identification Identification Non- Repudiation Consider signature- based C- R sk ch=r res = Sig(vk,ch) Bob can prove to police
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2018 Identification Identification Non- Repudiation Consider signature- based C- R sk ch=r res = Sig(vk,ch) Bob can prove to police
Lecture 8 Alvaro A. Cardenas Nicholas Sze Yinian Mao Kavitha Swaminathan. 1 Introduction. 2 The Dolev-Dwork-Naor (DDN) Scheme [1]
![Lecture 8 Alvaro A. Cardenas Nicholas Sze Yinian Mao Kavitha Swaminathan. 1 Introduction. 2 The Dolev-Dwork-Naor (DDN) Scheme [1] Lecture 8 Alvaro A. Cardenas Nicholas Sze Yinian Mao Kavitha Swaminathan. 1 Introduction. 2 The Dolev-Dwork-Naor (DDN) Scheme [1]](/thumbs/82/86919338.jpg) CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography February 19, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 8 Scribe(s): Alvaro A. Cardenas Nicholas Sze Yinian Mao Kavitha Swaminathan 1 Introduction Last time we introduced
CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography February 19, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 8 Scribe(s): Alvaro A. Cardenas Nicholas Sze Yinian Mao Kavitha Swaminathan 1 Introduction Last time we introduced
GQ and Schnorr Identification Schemes: Proofs of Security against Impersonation under Active and Concurrent Attacks
 GQ and Schnorr Identification Schemes: Proofs of Security against Impersonation under Active and Concurrent Attacks [Mihir Bellare, Adriana Palacio] Iliopoulos Fotis School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
GQ and Schnorr Identification Schemes: Proofs of Security against Impersonation under Active and Concurrent Attacks [Mihir Bellare, Adriana Palacio] Iliopoulos Fotis School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge
 Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge - interactive protocols formalize what can be recognized by polynomial time restricted verifiers in arbitrary protocols - generalizes NP - zero-knowledge formalizes
Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge - interactive protocols formalize what can be recognized by polynomial time restricted verifiers in arbitrary protocols - generalizes NP - zero-knowledge formalizes
Digital Signatures from Challenge-Divided Σ-Protocols
 Digital Signatures from Challenge-Divided Σ-Protocols Andrew C. Yao Yunlei Zhao Abstract Digital signature is one of the basic primitives in cryptography. A common paradigm of obtaining signatures, known
Digital Signatures from Challenge-Divided Σ-Protocols Andrew C. Yao Yunlei Zhao Abstract Digital signature is one of the basic primitives in cryptography. A common paradigm of obtaining signatures, known
Outline. Provable Security in the Computational Model. III Signatures. Public-Key Encryption. Outline. David Pointcheval.
 Provable Security in the Computational Model III Signatures David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRI Public-Key Encryption Signatures 2 dvanced Security for Signature dvanced Security Notions
Provable Security in the Computational Model III Signatures David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRI Public-Key Encryption Signatures 2 dvanced Security for Signature dvanced Security Notions
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants. COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from
 Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes
 Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
Short Signatures Without Random Oracles
 Short Signatures Without Random Oracles Dan Boneh and Xavier Boyen (presented by Aleksandr Yampolskiy) Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion Why signatures without
Short Signatures Without Random Oracles Dan Boneh and Xavier Boyen (presented by Aleksandr Yampolskiy) Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion Why signatures without
Constructing secure MACs Message authentication in action. Table of contents
 Constructing secure MACs Message authentication in action Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time Recall the definition of message
Constructing secure MACs Message authentication in action Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time Recall the definition of message
An Identification Scheme Based on KEA1 Assumption
 All rights are reserved and copyright of this manuscript belongs to the authors. This manuscript has been published without reviewing and editing as received from the authors: posting the manuscript to
All rights are reserved and copyright of this manuscript belongs to the authors. This manuscript has been published without reviewing and editing as received from the authors: posting the manuscript to
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited
 From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures
 Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures Zhou Sujing Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, zhousujing@pmail.ntu.edu.sg Abstract. Transitive signature, motivated by signing
Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures Zhou Sujing Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, zhousujing@pmail.ntu.edu.sg Abstract. Transitive signature, motivated by signing
On the (In)security of the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm
 On the (In)security of the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Shafi Goldwasser Yael Tauman February 2, 2004 Abstract In 1986, Fiat and Shamir proposed a general method for transforming secure 3-round public-coin identification
On the (In)security of the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Shafi Goldwasser Yael Tauman February 2, 2004 Abstract In 1986, Fiat and Shamir proposed a general method for transforming secure 3-round public-coin identification
Analysis - "Post-Quantum Security of Fiat-Shamir" by Dominic Unruh
 Analysis - "Post-Quantum Security of Fiat-Shamir" by Dominic Unruh Bruno Produit Institute of Computer Science University of Tartu produit@ut.ee December 19, 2017 Abstract This document is an analysis
Analysis - "Post-Quantum Security of Fiat-Shamir" by Dominic Unruh Bruno Produit Institute of Computer Science University of Tartu produit@ut.ee December 19, 2017 Abstract This document is an analysis
On The (In)security Of Fischlin s Paradigm
 On The (In)security Of Fischlin s Paradigm PRABHANJAN ANANTH Microsoft Research India prabhanjan.va@gmail.com RAGHAV BHASKAR Microsoft Research India rbhaskar@microsoft.com VIPUL GOYAL Microsoft Research
On The (In)security Of Fischlin s Paradigm PRABHANJAN ANANTH Microsoft Research India prabhanjan.va@gmail.com RAGHAV BHASKAR Microsoft Research India rbhaskar@microsoft.com VIPUL GOYAL Microsoft Research
Entity Authentication
 Entity Authentication Sven Laur swen@math.ut.ee University of Tartu Formal Syntax Entity authentication pk (sk, pk) Gen α 1 β 1 β i V pk (α 1,...,α i 1 ) α i P sk (β 1,...,β i 1 ) Is it Charlie? α k The
Entity Authentication Sven Laur swen@math.ut.ee University of Tartu Formal Syntax Entity authentication pk (sk, pk) Gen α 1 β 1 β i V pk (α 1,...,α i 1 ) α i P sk (β 1,...,β i 1 ) Is it Charlie? α k The
Lecture 6. Winter 2018 CS 485/585 Introduction to Cryptography. Constructing CPA-secure ciphers
 1 Winter 2018 CS 485/585 Introduction to Cryptography Lecture 6 Portland State University Jan. 25, 2018 Lecturer: Fang Song Draft note. Version: February 4, 2018. Email fang.song@pdx.edu for comments and
1 Winter 2018 CS 485/585 Introduction to Cryptography Lecture 6 Portland State University Jan. 25, 2018 Lecturer: Fang Song Draft note. Version: February 4, 2018. Email fang.song@pdx.edu for comments and
PAPER An Identification Scheme with Tight Reduction
 IEICE TRANS. FUNDAMENTALS, VOL.Exx A, NO.xx XXXX 200x PAPER An Identification Scheme with Tight Reduction Seiko ARITA, Member and Natsumi KAWASHIMA, Nonmember SUMMARY There are three well-known identification
IEICE TRANS. FUNDAMENTALS, VOL.Exx A, NO.xx XXXX 200x PAPER An Identification Scheme with Tight Reduction Seiko ARITA, Member and Natsumi KAWASHIMA, Nonmember SUMMARY There are three well-known identification
1 Number Theory Basics
 ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
Interactive Zero-Knowledge with Restricted Random Oracles
 Interactive Zero-Knowledge with Restricted Random Oracles Moti Yung 1 and Yunlei Zhao 2 1 RSA Laboratories and Department of Computer Science, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA. moti@cs.columbia.edu
Interactive Zero-Knowledge with Restricted Random Oracles Moti Yung 1 and Yunlei Zhao 2 1 RSA Laboratories and Department of Computer Science, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA. moti@cs.columbia.edu
Attribute-Based Signatures without Pairings via the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm
 Attribute-Based Signatures without Pairings via the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Hiroaki Anada Institute of Systems, Information Technologies and Nanotechnologies (ISIT) Fukuoka SRP Center Bldg. 7F Momochihama
Attribute-Based Signatures without Pairings via the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Hiroaki Anada Institute of Systems, Information Technologies and Nanotechnologies (ISIT) Fukuoka SRP Center Bldg. 7F Momochihama
Lecture 13: Seed-Dependent Key Derivation
 Randomness in Cryptography April 11, 2013 Lecture 13: Seed-Dependent Key Derivation Lecturer: Yevgeniy Dodis Scribe: Eric Miles In today s lecture, we study seeded key-derivation functions (KDFs) in the
Randomness in Cryptography April 11, 2013 Lecture 13: Seed-Dependent Key Derivation Lecturer: Yevgeniy Dodis Scribe: Eric Miles In today s lecture, we study seeded key-derivation functions (KDFs) in the
Multi-Key Homomorphic Signatures Unforgeable under Insider Corruption
 Multi-Key Homomorphic Signatures Unforgeable under Insider Corruption Russell W. F. Lai 1,2, Raymond K. H. Tai 1, Harry W. H. Wong 1, and Sherman S. M. Chow 1 1 Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Multi-Key Homomorphic Signatures Unforgeable under Insider Corruption Russell W. F. Lai 1,2, Raymond K. H. Tai 1, Harry W. H. Wong 1, and Sherman S. M. Chow 1 1 Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signa
 Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
Uninstantiability of Full-Domain Hash
 Uninstantiability of based on On the Generic Insecurity of, Crypto 05, joint work with Y.Dodis and R.Oliveira Krzysztof Pietrzak CWI Amsterdam June 3, 2008 Why talk about this old stuff? Why talk about
Uninstantiability of based on On the Generic Insecurity of, Crypto 05, joint work with Y.Dodis and R.Oliveira Krzysztof Pietrzak CWI Amsterdam June 3, 2008 Why talk about this old stuff? Why talk about
Authentication. Chapter Message Authentication
 Chapter 5 Authentication 5.1 Message Authentication Suppose Bob receives a message addressed from Alice. How does Bob ensure that the message received is the same as the message sent by Alice? For example,
Chapter 5 Authentication 5.1 Message Authentication Suppose Bob receives a message addressed from Alice. How does Bob ensure that the message received is the same as the message sent by Alice? For example,
On the Non-malleability of the Fiat-Shamir Transform
 An extended abstract of this paper is published in the proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Cryptology in India [21] Indocrypt 2012. This is the full version. On the Non-malleability of
An extended abstract of this paper is published in the proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Cryptology in India [21] Indocrypt 2012. This is the full version. On the Non-malleability of
Anonymous Credentials Light
 Anonymous Credentials Light Foteini Baldimtsi, Anna Lysyanskaya foteini,anna@cs.brown.edu Computer Science Department, Brown University Abstract. We define and propose an efficient and provably secure
Anonymous Credentials Light Foteini Baldimtsi, Anna Lysyanskaya foteini,anna@cs.brown.edu Computer Science Department, Brown University Abstract. We define and propose an efficient and provably secure
Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles
 Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Weiwei Liu School of Computer Science and Software Engineering 1/32 Weiwei Liu Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random
Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Weiwei Liu School of Computer Science and Software Engineering 1/32 Weiwei Liu Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random
Introduction to Cryptography
 B504 / I538: Introduction to Cryptography Spring 2017 Lecture 12 Recall: MAC existential forgery game 1 n Challenger (C) k Gen(1 n ) Forger (A) 1 n m 1 m 1 M {m} t 1 MAC k (m 1 ) t 1 m 2 m 2 M {m} t 2
B504 / I538: Introduction to Cryptography Spring 2017 Lecture 12 Recall: MAC existential forgery game 1 n Challenger (C) k Gen(1 n ) Forger (A) 1 n m 1 m 1 M {m} t 1 MAC k (m 1 ) t 1 m 2 m 2 M {m} t 2
Provably Secure Partially Blind Signatures
 Provably Secure Partially Blind Signatures Masayuki ABE and Tatsuaki OKAMOTO NTT Laboratories Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation 1-1 Hikari-no-oka Yokosuka-shi Kanagawa-ken, 239-0847 Japan E-mail:
Provably Secure Partially Blind Signatures Masayuki ABE and Tatsuaki OKAMOTO NTT Laboratories Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation 1-1 Hikari-no-oka Yokosuka-shi Kanagawa-ken, 239-0847 Japan E-mail:
Lecture 6. 2 Adaptively-Secure Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge
 CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography February 12, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 6 Scribe(s): Omer Horvitz John Trafton Zhongchao Yu Akhil Gupta 1 Introduction In this lecture, we show how to
CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography February 12, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 6 Scribe(s): Omer Horvitz John Trafton Zhongchao Yu Akhil Gupta 1 Introduction In this lecture, we show how to
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes
 From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Revisiting Post-Quantum Fiat-Shamir
 Revisiting Post-Quantum Fiat-Shamir Qipeng Liu, Mark Zhandry Princeton University, Princeton NJ 08544, USA Abstract. The Fiat-Shamir transformation is a useful approach to building non-interactive arguments
Revisiting Post-Quantum Fiat-Shamir Qipeng Liu, Mark Zhandry Princeton University, Princeton NJ 08544, USA Abstract. The Fiat-Shamir transformation is a useful approach to building non-interactive arguments
On The (In)security Of Fischlin s Paradigm
 On The (In)security Of Fischlin s Paradigm Prabhanjan Ananth 1, Raghav Bhaskar 1, Vipul Goyal 1, and Vanishree Rao 2 1 Microsoft Research India prabhanjan.va@gmail.com,{rbhaskar,vipul}@microsoft.com 2
On The (In)security Of Fischlin s Paradigm Prabhanjan Ananth 1, Raghav Bhaskar 1, Vipul Goyal 1, and Vanishree Rao 2 1 Microsoft Research India prabhanjan.va@gmail.com,{rbhaskar,vipul}@microsoft.com 2
CLASSICAL CRYPTOSYSTEMS IN A QUANTUM WORLD
 CLASSICAL CRYPTOSYSTEMS IN A QUANTUM WORLD Mark Zhandry Stanford University * Joint work with Dan Boneh But First: My Current Work Indistinguishability Obfuscation (and variants) Multiparty NIKE without
CLASSICAL CRYPTOSYSTEMS IN A QUANTUM WORLD Mark Zhandry Stanford University * Joint work with Dan Boneh But First: My Current Work Indistinguishability Obfuscation (and variants) Multiparty NIKE without
A survey on quantum-secure cryptographic systems
 A survey on quantum-secure cryptographic systems Tomoka Kan May 24, 2018 1 Abstract Post-quantum cryptography refers to the search for classical cryptosystems which remain secure in the presence of a quantum
A survey on quantum-secure cryptographic systems Tomoka Kan May 24, 2018 1 Abstract Post-quantum cryptography refers to the search for classical cryptosystems which remain secure in the presence of a quantum
Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures
 CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography October 30, 2017 Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Willy Quach & Giorgos Zirdelis 1 Topic Covered. Trapdoor Permutations.
CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography October 30, 2017 Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Willy Quach & Giorgos Zirdelis 1 Topic Covered. Trapdoor Permutations.
Non-Interactive ZK:The Feige-Lapidot-Shamir protocol
 Non-Interactive ZK: The Feige-Lapidot-Shamir protocol April 20, 2009 Remainders FLS protocol Definition (Interactive proof system) A pair of interactive machines (P, V ) is called an interactive proof
Non-Interactive ZK: The Feige-Lapidot-Shamir protocol April 20, 2009 Remainders FLS protocol Definition (Interactive proof system) A pair of interactive machines (P, V ) is called an interactive proof
G Advanced Cryptography April 10th, Lecture 11
 G.30-001 Advanced Cryptography April 10th, 007 Lecturer: Victor Shoup Lecture 11 Scribe: Kristiyan Haralambiev We continue the discussion of public key encryption. Last time, we studied Hash Proof Systems
G.30-001 Advanced Cryptography April 10th, 007 Lecturer: Victor Shoup Lecture 11 Scribe: Kristiyan Haralambiev We continue the discussion of public key encryption. Last time, we studied Hash Proof Systems
Round Optimal Blind Signatures
 Round Optimal Blind Signatures Dominique Schröder University of Maryland Dominique Unruh Saarland University May 25, 2011 Abstract. All known round optimal (i.e., two-move) blind signature schemes either
Round Optimal Blind Signatures Dominique Schröder University of Maryland Dominique Unruh Saarland University May 25, 2011 Abstract. All known round optimal (i.e., two-move) blind signature schemes either
Anonymous Signatures Made Easy
 Anonymous Signatures Made Easy Marc Fischlin Darmstadt University of Technology, Germany marc.fischlin @ gmail.com www.fischlin.de Abstract. At PKC 2006, Yang, Wong, Deng and Wang proposed the notion of
Anonymous Signatures Made Easy Marc Fischlin Darmstadt University of Technology, Germany marc.fischlin @ gmail.com www.fischlin.de Abstract. At PKC 2006, Yang, Wong, Deng and Wang proposed the notion of
The Fiat Shamir Transformation in a Quantum World
 The Fiat Shamir Transformation in a Quantum World Özgür Dagdelen Marc Fischlin Tommaso Gagliardoni Technische Universität Darmstadt, Germany www.cryptoplexity.de oezguer.dagdelen @ cased.de marc.fischlin
The Fiat Shamir Transformation in a Quantum World Özgür Dagdelen Marc Fischlin Tommaso Gagliardoni Technische Universität Darmstadt, Germany www.cryptoplexity.de oezguer.dagdelen @ cased.de marc.fischlin
Digital signature schemes
 Digital signature schemes Martin Stanek Department of Computer Science Comenius University stanek@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Cryptology 1 (2017/18) Content Introduction digital signature scheme security of digital
Digital signature schemes Martin Stanek Department of Computer Science Comenius University stanek@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Cryptology 1 (2017/18) Content Introduction digital signature scheme security of digital
The Random Oracle Paradigm. Mike Reiter. Random oracle is a formalism to model such uses of hash functions that abound in practical cryptography
 1 The Random Oracle Paradigm Mike Reiter Based on Random Oracles are Practical: A Paradigm for Designing Efficient Protocols by M. Bellare and P. Rogaway Random Oracles 2 Random oracle is a formalism to
1 The Random Oracle Paradigm Mike Reiter Based on Random Oracles are Practical: A Paradigm for Designing Efficient Protocols by M. Bellare and P. Rogaway Random Oracles 2 Random oracle is a formalism to
SIS-based Signatures
 Lattices and Homomorphic Encryption, Spring 2013 Instructors: Shai Halevi, Tal Malkin February 26, 2013 Basics We will use the following parameters: n, the security parameter. =poly(n). m 2n log s 2 n
Lattices and Homomorphic Encryption, Spring 2013 Instructors: Shai Halevi, Tal Malkin February 26, 2013 Basics We will use the following parameters: n, the security parameter. =poly(n). m 2n log s 2 n
From 5-pass MQ-based identification to MQ-based signatures
 From 5-pass MQ-based identification to MQ-based signatures Andreas Hülsing, Joost Rijneveld, Simona Samardjiska, and Peter Schwabe 30 June 2016 1 / 31 Our take on PQ-Crypto Prepare for actual use Reliable
From 5-pass MQ-based identification to MQ-based signatures Andreas Hülsing, Joost Rijneveld, Simona Samardjiska, and Peter Schwabe 30 June 2016 1 / 31 Our take on PQ-Crypto Prepare for actual use Reliable
Communication-Efficient Non-Interactive Proofs of Knowledge with Online Extractors
 Communication-Efficient Non-Interactive Proofs of Knowledge with Online Extractors Marc Fischlin Institute for Theoretical Computer Science, ETH Zürich, Switzerland marc.fischlin @ inf.ethz.ch http://www.fischlin.de/
Communication-Efficient Non-Interactive Proofs of Knowledge with Online Extractors Marc Fischlin Institute for Theoretical Computer Science, ETH Zürich, Switzerland marc.fischlin @ inf.ethz.ch http://www.fischlin.de/
Session 4: Efficient Zero Knowledge. Yehuda Lindell Bar-Ilan University
 Session 4: Efficient Zero Knowledge Yehuda Lindell Bar-Ilan University 1 Proof Systems Completeness: can convince of a true statement Soundness: cannot convince for a false statement Classic proofs: Written
Session 4: Efficient Zero Knowledge Yehuda Lindell Bar-Ilan University 1 Proof Systems Completeness: can convince of a true statement Soundness: cannot convince for a false statement Classic proofs: Written
On the Security of Classic Protocols for Unique Witness Relations
 On the Security of Classic Protocols for Unique Witness Relations Yi Deng 1,2, Xuyang Song 1,2, Jingyue Yu 1,2, and Yu Chen 1,2 1 State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Information
On the Security of Classic Protocols for Unique Witness Relations Yi Deng 1,2, Xuyang Song 1,2, Jingyue Yu 1,2, and Yu Chen 1,2 1 State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Information
Post-Quantum Zero-Knowledge Proofs for Accumulators with Applications to Ring Signatures from Symmetric-Key Primitives
 Post-Quantum Zero-Knowledge Proofs for Accumulators with Applications to Ring Signatures from Symmetric-Key Primitives David Derler 1, Sebastian Ramacher 1, and Daniel Slamanig 2 1 IAIK, Graz University
Post-Quantum Zero-Knowledge Proofs for Accumulators with Applications to Ring Signatures from Symmetric-Key Primitives David Derler 1, Sebastian Ramacher 1, and Daniel Slamanig 2 1 IAIK, Graz University
On the (In)security of SNARKs in the Presence of Oracles
 On the (In)security of SNARKs in the Presence of Oracles Dario Fiore 1 and Anca Nitulescu 2 1 IMDEA Software Institute, Madrid, Spain dario.fiore@imdea.org 2 CNRS, ENS, INRIA, and PSL, Paris, France anca.nitulescu@ens.fr
On the (In)security of SNARKs in the Presence of Oracles Dario Fiore 1 and Anca Nitulescu 2 1 IMDEA Software Institute, Madrid, Spain dario.fiore@imdea.org 2 CNRS, ENS, INRIA, and PSL, Paris, France anca.nitulescu@ens.fr
Anonymous Proxy Signature with Restricted Traceability
 Anonymous Proxy Signature with Restricted Traceability Jiannan Wei Joined work with Guomin Yang and Yi Mu University of Wollongong Outline Introduction Motivation and Potential Solutions Anonymous Proxy
Anonymous Proxy Signature with Restricted Traceability Jiannan Wei Joined work with Guomin Yang and Yi Mu University of Wollongong Outline Introduction Motivation and Potential Solutions Anonymous Proxy
CMSC 858K Introduction to Secure Computation October 18, Lecture 19
 CMSC 858K Introduction to Secure Computation October 18, 2013 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 19 Scribe(s): Alex J. Malozemoff 1 Zero Knowledge Variants and Results Recall that a proof-of-knowledge (PoK)
CMSC 858K Introduction to Secure Computation October 18, 2013 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 19 Scribe(s): Alex J. Malozemoff 1 Zero Knowledge Variants and Results Recall that a proof-of-knowledge (PoK)
Identification Schemes of Proofs of Ability Secure against Concurrent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
 Identification Schemes of Proofs of Ability Secure against Concurrent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Hiroaki Anada and Seiko Arita Institute of Information Security, Yokohama, Japan hiroaki.anada@gmail.com,
Identification Schemes of Proofs of Ability Secure against Concurrent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Hiroaki Anada and Seiko Arita Institute of Information Security, Yokohama, Japan hiroaki.anada@gmail.com,
Q B (pk, sk) Gen x u M pk y Map pk (x) return [B(pk, y)? = x]. (m, s) A O h
![Q B (pk, sk) Gen x u M pk y Map pk (x) return [B(pk, y)? = x]. (m, s) A O h Q B (pk, sk) Gen x u M pk y Map pk (x) return [B(pk, y)? = x]. (m, s) A O h](/thumbs/89/100584859.jpg) MTAT.07.003 Cryptology II Spring 2012 / Exercise session?? / Example Solution Exercise (FRH in RO model). Show that the full domain hash signature is secure against existential forgeries in the random
MTAT.07.003 Cryptology II Spring 2012 / Exercise session?? / Example Solution Exercise (FRH in RO model). Show that the full domain hash signature is secure against existential forgeries in the random
Secure Signatures and Chosen Ciphertext Security in a Quantum Computing World. Dan Boneh and Mark Zhandry Stanford University
 Secure Signatures and Chosen Ciphertext Security in a Quantu Coputing World Dan Boneh and Mark Zhandry Stanford University Classical Chosen Message Attack (CMA) σ = S(sk, ) signing key sk Classical CMA
Secure Signatures and Chosen Ciphertext Security in a Quantu Coputing World Dan Boneh and Mark Zhandry Stanford University Classical Chosen Message Attack (CMA) σ = S(sk, ) signing key sk Classical CMA
Evaluation Report on the ECDSA signature scheme
 Evaluation Report on the ECDSA signature scheme Jacques Stern 1 Introduction This document is an evaluation of the ECDSA signature scheme. Our work is based on the analysis of various documents [1, 32,
Evaluation Report on the ECDSA signature scheme Jacques Stern 1 Introduction This document is an evaluation of the ECDSA signature scheme. Our work is based on the analysis of various documents [1, 32,
Identity-Based Identification Schemes
 Identity-Based Identification Schemes Guomin Yang Centre for Computer and Information Security Research School of Computing and Information Technology University of Wollongong G. Yang (CCISR, SCIT, UOW)
Identity-Based Identification Schemes Guomin Yang Centre for Computer and Information Security Research School of Computing and Information Technology University of Wollongong G. Yang (CCISR, SCIT, UOW)
Security of Blind Signatures Revisited
 Security of Blind Signatures Revisited Dominique Schröder 1 and Dominique Unruh 2 1 University of Maryland, USA 2 University of Tartu, Estonia Abstract. We revisit the definition of unforgeability of blind
Security of Blind Signatures Revisited Dominique Schröder 1 and Dominique Unruh 2 1 University of Maryland, USA 2 University of Tartu, Estonia Abstract. We revisit the definition of unforgeability of blind
Limitations of the Meta-Reduction Technique: The Case of Schnorr Signatures
 An extended abstract of this paper appears at Eurocrypt 2013. Limitations of the Meta-Reduction Technique: The Case of Schnorr Signatures Marc Fischlin 1 Nils Fleischhacker 2 1 Technische Universität Darmstadt
An extended abstract of this paper appears at Eurocrypt 2013. Limitations of the Meta-Reduction Technique: The Case of Schnorr Signatures Marc Fischlin 1 Nils Fleischhacker 2 1 Technische Universität Darmstadt
Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample
 Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample Fuchun Guo 1, Rongmao Chen 2, Willy Susilo 1, Jianchang Lai 1, Guomin Yang 1, and Yi Mu 1 1 Institute
Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample Fuchun Guo 1, Rongmao Chen 2, Willy Susilo 1, Jianchang Lai 1, Guomin Yang 1, and Yi Mu 1 1 Institute
Cryptography CS 555. Topic 23: Zero-Knowledge Proof and Cryptographic Commitment. CS555 Topic 23 1
 Cryptography CS 555 Topic 23: Zero-Knowledge Proof and Cryptographic Commitment CS555 Topic 23 1 Outline and Readings Outline Zero-knowledge proof Fiat-Shamir protocol Schnorr protocol Commitment schemes
Cryptography CS 555 Topic 23: Zero-Knowledge Proof and Cryptographic Commitment CS555 Topic 23 1 Outline and Readings Outline Zero-knowledge proof Fiat-Shamir protocol Schnorr protocol Commitment schemes
A Second Look at s Transforma3on
 A Second Look at s Transforma3on - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Özgür Dagdelen Technische Universität Darmstadt Daniele Venturi Sapienza University
A Second Look at s Transforma3on - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Özgür Dagdelen Technische Universität Darmstadt Daniele Venturi Sapienza University
Relaxed Lattice-Based Signatures with Short Zero-Knowledge Proofs
 Relaxed Lattice-Based Signatures with Short Zero-Knowledge Proofs Cecilia Boschini, Jan Camenisch, and Gregory Neven IBM Research Zurich {bos, jca, nev}@zurich.ibm.com Abstract. Higher-level cryptographic
Relaxed Lattice-Based Signatures with Short Zero-Knowledge Proofs Cecilia Boschini, Jan Camenisch, and Gregory Neven IBM Research Zurich {bos, jca, nev}@zurich.ibm.com Abstract. Higher-level cryptographic
George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK
 George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
Lecture 9 Julie Staub Avi Dalal Abheek Anand Gelareh Taban. 1 Introduction. 2 Background. CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography February 24, 2004
 CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography February 24, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 9 Scribe(s): Julie Staub Avi Dalal Abheek Anand Gelareh Taban 1 Introduction In previous lectures, we constructed
CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography February 24, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 9 Scribe(s): Julie Staub Avi Dalal Abheek Anand Gelareh Taban 1 Introduction In previous lectures, we constructed
Augmented Black-Box Simulation and Zero Knowledge Argument for NP
 Augmented Black-Box Simulation and Zero Knowledge Argument for N Li Hongda, an Dongxue, Ni eifang The Data Assurance and Communication Security Research Center, School of Cyber Security, University of
Augmented Black-Box Simulation and Zero Knowledge Argument for N Li Hongda, an Dongxue, Ni eifang The Data Assurance and Communication Security Research Center, School of Cyber Security, University of
Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme
 Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme Kwangsu Lee Dong Hoon Lee Abstract Identity-based signature (IBS) is a specific type of public-key signature (PKS) where any
Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme Kwangsu Lee Dong Hoon Lee Abstract Identity-based signature (IBS) is a specific type of public-key signature (PKS) where any
Practice Final Exam Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017
 Practice Final Exam Name: Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total
Practice Final Exam Name: Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total
Notes on Zero Knowledge
 U.C. Berkeley CS172: Automata, Computability and Complexity Handout 9 Professor Luca Trevisan 4/21/2015 Notes on Zero Knowledge These notes on zero knowledge protocols for quadratic residuosity are based
U.C. Berkeley CS172: Automata, Computability and Complexity Handout 9 Professor Luca Trevisan 4/21/2015 Notes on Zero Knowledge These notes on zero knowledge protocols for quadratic residuosity are based
Homework 3 Solutions
 5233/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, Fall 205 Instructor Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 3 Solutions 7-Dec-205 Scribe Amir Rezapour. Consider an unfair coin with head probability 0.5. Assume that the coin
5233/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, Fall 205 Instructor Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 3 Solutions 7-Dec-205 Scribe Amir Rezapour. Consider an unfair coin with head probability 0.5. Assume that the coin
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography. Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017
 COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Previously Digital Signatures Algorithms: Gen() à (sk,pk) Sign(sk,m) à σ Ver(pk,m,σ) à 0/1 Correctness: Pr[Ver(pk,m,Sign(sk,m))=1:
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Previously Digital Signatures Algorithms: Gen() à (sk,pk) Sign(sk,m) à σ Ver(pk,m,σ) à 0/1 Correctness: Pr[Ver(pk,m,Sign(sk,m))=1:
Non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs in the quantum random oracle model
 Non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs in the quantum random oracle model Dominique Unruh University of Tartu Abstract. We present a construction for non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs of knowledge in
Non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs in the quantum random oracle model Dominique Unruh University of Tartu Abstract. We present a construction for non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs of knowledge in
Cryptographic Protocols Notes 2
 ETH Zurich, Department of Computer Science SS 2018 Prof. Ueli Maurer Dr. Martin Hirt Chen-Da Liu Zhang Cryptographic Protocols Notes 2 Scribe: Sandro Coretti (modified by Chen-Da Liu Zhang) About the notes:
ETH Zurich, Department of Computer Science SS 2018 Prof. Ueli Maurer Dr. Martin Hirt Chen-Da Liu Zhang Cryptographic Protocols Notes 2 Scribe: Sandro Coretti (modified by Chen-Da Liu Zhang) About the notes:
Memory Lower Bounds of Reductions Revisited
 Memory Lower Bounds of Reductions Revisited Yuyu Wang 1,2,3, Takahiro Matsuda 2, Goichiro Hanaoka 2, and Keisuke Tanaka 1 1 Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan wang.y.ar@m.titech.ac.jp, keisuke@is.titech.ac.jp
Memory Lower Bounds of Reductions Revisited Yuyu Wang 1,2,3, Takahiro Matsuda 2, Goichiro Hanaoka 2, and Keisuke Tanaka 1 1 Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan wang.y.ar@m.titech.ac.jp, keisuke@is.titech.ac.jp
Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Applications
 Tecniche di Sicurezza Informatica dei Dati e delle Reti May 21, 2015 Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Applications Guest Lecturer: Daniele Venturi Lecturer: Antonio Villani Abstract The material below covers
Tecniche di Sicurezza Informatica dei Dati e delle Reti May 21, 2015 Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Applications Guest Lecturer: Daniele Venturi Lecturer: Antonio Villani Abstract The material below covers
PAIRING-BASED IDENTIFICATION SCHEMES
 PAIRING-BASED IDENTIFICATION SCHEMES DAVID FREEMAN Abstract. We propose four different identification schemes that make use of bilinear pairings, and prove their security under certain computational assumptions.
PAIRING-BASED IDENTIFICATION SCHEMES DAVID FREEMAN Abstract. We propose four different identification schemes that make use of bilinear pairings, and prove their security under certain computational assumptions.
Lecture 10 - MAC s continued, hash & MAC
 Lecture 10 - MAC s continued, hash & MAC Boaz Barak March 3, 2010 Reading: Boneh-Shoup chapters 7,8 The field GF(2 n ). A field F is a set with a multiplication ( ) and addition operations that satisfy
Lecture 10 - MAC s continued, hash & MAC Boaz Barak March 3, 2010 Reading: Boneh-Shoup chapters 7,8 The field GF(2 n ). A field F is a set with a multiplication ( ) and addition operations that satisfy
Pairing-Based Identification Schemes
 Pairing-Based Identification Schemes David Freeman Information Theory Research HP Laboratories Palo Alto HPL-2005-154 August 24, 2005* public-key cryptography, identification, zero-knowledge, pairings
Pairing-Based Identification Schemes David Freeman Information Theory Research HP Laboratories Palo Alto HPL-2005-154 August 24, 2005* public-key cryptography, identification, zero-knowledge, pairings
1 Basic Number Theory
 ECS 228 (Franklin), Winter 2013, Crypto Review 1 Basic Number Theory This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
ECS 228 (Franklin), Winter 2013, Crypto Review 1 Basic Number Theory This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
Statistical WI (and more) in Two Messages
 Statistical WI (and more) in Two Messages Yael Tauman Kalai MSR Cambridge, USA. yael@microsoft.com Dakshita Khurana UCLA, USA. dakshita@cs.ucla.edu Amit Sahai UCLA, USA. sahai@cs.ucla.edu Abstract Two-message
Statistical WI (and more) in Two Messages Yael Tauman Kalai MSR Cambridge, USA. yael@microsoft.com Dakshita Khurana UCLA, USA. dakshita@cs.ucla.edu Amit Sahai UCLA, USA. sahai@cs.ucla.edu Abstract Two-message
PSS Is Secure against Random Fault Attacks
 PSS Is Secure against Random Fault Attacks Jean-Sébastien Coron and Avradip Mandal University of Luxembourg Abstract. A fault attack consists in inducing hardware malfunctions in order to recover secrets
PSS Is Secure against Random Fault Attacks Jean-Sébastien Coron and Avradip Mandal University of Luxembourg Abstract. A fault attack consists in inducing hardware malfunctions in order to recover secrets
G /G Advanced Cryptography November 11, Lecture 10. defined Adaptive Soundness and Adaptive Zero Knowledge
 G22.3220-001/G63.2180 Advanced Cryptography November 11, 2009 Lecture 10 Lecturer: Yevgeniy Dodis Scribe: Adriana Lopez Last time we: defined Adaptive Soundness and Adaptive Zero Knowledge defined Unbounded
G22.3220-001/G63.2180 Advanced Cryptography November 11, 2009 Lecture 10 Lecturer: Yevgeniy Dodis Scribe: Adriana Lopez Last time we: defined Adaptive Soundness and Adaptive Zero Knowledge defined Unbounded
BEYOND POST QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY
 BEYOND POST QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY Mark Zhandry Stanford University Joint work with Dan Boneh Classical Cryptography Post-Quantum Cryptography All communication stays classical Beyond Post-Quantum Cryptography
BEYOND POST QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY Mark Zhandry Stanford University Joint work with Dan Boneh Classical Cryptography Post-Quantum Cryptography All communication stays classical Beyond Post-Quantum Cryptography
5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall
 5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall Homework 2 Reference Solution 1. This is about the RSA common modulus problem. Consider that two users A and B use the same modulus n = 146171 for the RSA encryption.
5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall Homework 2 Reference Solution 1. This is about the RSA common modulus problem. Consider that two users A and B use the same modulus n = 146171 for the RSA encryption.
