GQ and Schnorr Identification Schemes: Proofs of Security against Impersonation under Active and Concurrent Attacks
|
|
|
- Juliet O’Connor’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GQ and Schnorr Identification Schemes: Proofs of Security against Impersonation under Active and Concurrent Attacks [Mihir Bellare, Adriana Palacio] Iliopoulos Fotis School of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Technical University of Athens January 28, 2013 F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
2 Introduction What is an Identfication Scheme? Prover - holds Secret Key Verifer - verifies the identity of the prover Zero Knowledge Fiat-Shamir Identification Scheme F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
3 Security under different kinds of attacks Passive Attack - The adversary obtains transcript of interractions between the prover and verifier. Active Attack - The adversary as a cheating verifier - interacts with the prover before impersonation attempt Concurrent Attack - The adversary as cheating verifierinteracts with many differnt prover-clones concurrently F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
4 Impersonation under Concurrent Attack A game with two phases 1 Impersonator acts as a cheating verifier, interracts with multiple prover clones (all the same pk) 2 Impersonator acts as a cheating prover interactig with the verifier While concurrent attacks, phase 1 is completed before phase 2 stars Model for ATMs, smart cards - not for Internet! F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
5 GQ Identification Scheme - Initialisation AlgorithmK(k) (N, e, d) K rsa (k) x R Z N X x e mod N pk N, e, X sk (N, x) Return(pk, sk) F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
6 GQ Identification Scheme - Interaction Prover P Verifier V y R Z N Y y e mod N z yx c mod N Y c z c R {0, 1} l(k) If z e YX c mod N then d 1 else d 0 F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
7 Schnorr - Initialisation AlgorithmK(k) (q, g) K dl (k) x R Z q X g x pk (q, g, X ) sk (q, x) Return(pk, sk) F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
8 Schnorr Identification Scheme - Interaction Prover P Verifier V y R Z q Y g y z y + cx mod q Y c z c R {0, 1} l(k) If g z YX c then d 1 else d 0 F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
9 Main Results GQ ID is secure against impersonation under concurrent attacks if RSA is secure under one or more inversions Schnorr ID is secure against impersonation under concurrent attacks if DL is secure under one or more inversions in the underlying group First proofs for security of this kind Turns the problem of security into a number theoretic problem F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
10 RSA security under one or more inversions assumption An rsa-omi adversary is a randomized polynomial-time algorithm I, inputs N,e and access to two oracles RSA-inversion Oracle: given Y Z N returns Y d mod N Challenge Oracle: Returns a random challenge point W Z N Adversary wins if outputs the RSA inverse of every chalenge -output of Challenge Oracle - and also the number of queries to RSA-inversion oracle is stricly less than to Challenge oracle F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
11 Main Theorem Theorem Let ID = (K, P, V) be the GQ identification scheme associated to prime-exponent RSA key generator K RSA and challenge length l. Let A = ( ˆV, ˆP) be an imp-ca adversary of time complexity t( ) attacking ID. Then there exists an rsa-omi adversary I attacking K rsa such that for every k Adv imp ca ID,A (k) 2 l(k) + Adv rsa omi K rsa,i (k) (1) Furthermore, the time complexity of I is 2t(k) + O(k 4 + (n(k) + 1) l(k) k 2 ), where n(k) is the number of prover clones with which ˆV interacts. F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
12 Proof Sketch 1 Reset lemma: Upper bounds the probability that a cheating prover can convince the verifier to accept as a function of the probability that a certain experiment based on resetting the prover yields two accepting conversation transcripts. 2 I can simulate the envivorment of adversary A (via oracles) 3 The probability that I wins is equal to the probability that the cheating prover manages two accepting conversation transcripts given that the verifier s challanges are different. F. Iliopoulos (NTUA) Crypto Project January 28, / 12
An Identification Scheme Based on KEA1 Assumption
 All rights are reserved and copyright of this manuscript belongs to the authors. This manuscript has been published without reviewing and editing as received from the authors: posting the manuscript to
All rights are reserved and copyright of this manuscript belongs to the authors. This manuscript has been published without reviewing and editing as received from the authors: posting the manuscript to
PAPER An Identification Scheme with Tight Reduction
 IEICE TRANS. FUNDAMENTALS, VOL.Exx A, NO.xx XXXX 200x PAPER An Identification Scheme with Tight Reduction Seiko ARITA, Member and Natsumi KAWASHIMA, Nonmember SUMMARY There are three well-known identification
IEICE TRANS. FUNDAMENTALS, VOL.Exx A, NO.xx XXXX 200x PAPER An Identification Scheme with Tight Reduction Seiko ARITA, Member and Natsumi KAWASHIMA, Nonmember SUMMARY There are three well-known identification
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography
 Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Identity-Based Identification Schemes
 Identity-Based Identification Schemes Guomin Yang Centre for Computer and Information Security Research School of Computing and Information Technology University of Wollongong G. Yang (CCISR, SCIT, UOW)
Identity-Based Identification Schemes Guomin Yang Centre for Computer and Information Security Research School of Computing and Information Technology University of Wollongong G. Yang (CCISR, SCIT, UOW)
Schnorr Signature. Schnorr Signature. October 31, 2012
 . October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
. October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
Introduction to cryptology (GBIN8U16) More on discrete-logarithm based schemes
 Introduction to cryptology (GBIN8U16) More on discrete-logarithm based schemes Pierre Karpman pierre.karpman@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr https://www-ljk.imag.fr/membres/pierre.karpman/tea.html 2018 03 13 More
Introduction to cryptology (GBIN8U16) More on discrete-logarithm based schemes Pierre Karpman pierre.karpman@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr https://www-ljk.imag.fr/membres/pierre.karpman/tea.html 2018 03 13 More
PAIRING-BASED IDENTIFICATION SCHEMES
 PAIRING-BASED IDENTIFICATION SCHEMES DAVID FREEMAN Abstract. We propose four different identification schemes that make use of bilinear pairings, and prove their security under certain computational assumptions.
PAIRING-BASED IDENTIFICATION SCHEMES DAVID FREEMAN Abstract. We propose four different identification schemes that make use of bilinear pairings, and prove their security under certain computational assumptions.
Practical Key Recovery for Discrete-Logarithm Based Authentication Schemes from Random Nonce Bits
 Practical Key Recovery for Discrete-Logarithm Based Authentication Schemes from Random Nonce Bits Damien Vergnaud École normale supérieure CHES September, 15th 2015 (with Aurélie Bauer) Damien Vergnaud
Practical Key Recovery for Discrete-Logarithm Based Authentication Schemes from Random Nonce Bits Damien Vergnaud École normale supérieure CHES September, 15th 2015 (with Aurélie Bauer) Damien Vergnaud
Identification Schemes of Proofs of Ability Secure against Concurrent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
 Identification Schemes of Proofs of Ability Secure against Concurrent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Hiroaki Anada and Seiko Arita Institute of Information Security, Yokohama, Japan hiroaki.anada@gmail.com,
Identification Schemes of Proofs of Ability Secure against Concurrent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Hiroaki Anada and Seiko Arita Institute of Information Security, Yokohama, Japan hiroaki.anada@gmail.com,
Entity Authentication
 Entity Authentication Sven Laur swen@math.ut.ee University of Tartu Formal Syntax Entity authentication pk (sk, pk) Gen α 1 β 1 β i V pk (α 1,...,α i 1 ) α i P sk (β 1,...,β i 1 ) Is it Charlie? α k The
Entity Authentication Sven Laur swen@math.ut.ee University of Tartu Formal Syntax Entity authentication pk (sk, pk) Gen α 1 β 1 β i V pk (α 1,...,α i 1 ) α i P sk (β 1,...,β i 1 ) Is it Charlie? α k The
A Note on the Cramer-Damgård Identification Scheme
 A Note on the Cramer-Damgård Identification Scheme Yunlei Zhao 1, Shirley H.C. Cheung 2,BinyuZang 1,andBinZhu 3 1 Software School, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, P.R. China {990314, byzang}@fudan.edu.cn
A Note on the Cramer-Damgård Identification Scheme Yunlei Zhao 1, Shirley H.C. Cheung 2,BinyuZang 1,andBinZhu 3 1 Software School, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, P.R. China {990314, byzang}@fudan.edu.cn
The Double-Hash Transform: From Identification to (Double-Authentication-Preventing) Signatures, Tightly
 The Double-Hash Transform: From Identification to (Double-Authentication-Preventing) Signatures, Tightly Mihir Bellare 1 Douglas Stebila 2 December 2015 Abstract We give a new method to turn identification
The Double-Hash Transform: From Identification to (Double-Authentication-Preventing) Signatures, Tightly Mihir Bellare 1 Douglas Stebila 2 December 2015 Abstract We give a new method to turn identification
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants. COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from
 Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Pairing-Based Identification Schemes
 Pairing-Based Identification Schemes David Freeman Information Theory Research HP Laboratories Palo Alto HPL-2005-154 August 24, 2005* public-key cryptography, identification, zero-knowledge, pairings
Pairing-Based Identification Schemes David Freeman Information Theory Research HP Laboratories Palo Alto HPL-2005-154 August 24, 2005* public-key cryptography, identification, zero-knowledge, pairings
VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic
 VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic - as already seen signatures can be used and are used in practice to design identification protocols - next we show how we can obtain signatures schemes from - protocols using
VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic - as already seen signatures can be used and are used in practice to design identification protocols - next we show how we can obtain signatures schemes from - protocols using
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography. Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2018
 COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2018 Identification Identification Non- Repudiation Consider signature- based C- R sk ch=r res = Sig(vk,ch) Bob can prove to police
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2018 Identification Identification Non- Repudiation Consider signature- based C- R sk ch=r res = Sig(vk,ch) Bob can prove to police
March 19: Zero-Knowledge (cont.) and Signatures
 March 19: Zero-Knowledge (cont.) and Signatures March 26, 2013 1 Zero-Knowledge (review) 1.1 Review Alice has y, g, p and claims to know x such that y = g x mod p. Alice proves knowledge of x to Bob w/o
March 19: Zero-Knowledge (cont.) and Signatures March 26, 2013 1 Zero-Knowledge (review) 1.1 Review Alice has y, g, p and claims to know x such that y = g x mod p. Alice proves knowledge of x to Bob w/o
Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge
 Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge - interactive protocols formalize what can be recognized by polynomial time restricted verifiers in arbitrary protocols - generalizes NP - zero-knowledge formalizes
Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge - interactive protocols formalize what can be recognized by polynomial time restricted verifiers in arbitrary protocols - generalizes NP - zero-knowledge formalizes
Attribute-Based Signatures without Pairings via the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm
 Attribute-Based Signatures without Pairings via the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Hiroaki Anada Institute of Systems, Information Technologies and Nanotechnologies (ISIT) Fukuoka SRP Center Bldg. 7F Momochihama
Attribute-Based Signatures without Pairings via the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Hiroaki Anada Institute of Systems, Information Technologies and Nanotechnologies (ISIT) Fukuoka SRP Center Bldg. 7F Momochihama
Provable security. Michel Abdalla
 Lecture 1: Provable security Michel Abdalla École normale supérieure & CNRS Cryptography Main goal: Enable secure communication in the presence of adversaries Adversary Sender 10110 10110 Receiver Only
Lecture 1: Provable security Michel Abdalla École normale supérieure & CNRS Cryptography Main goal: Enable secure communication in the presence of adversaries Adversary Sender 10110 10110 Receiver Only
Tightly-Secure Signatures From Lossy Identification Schemes
 Tightly-Secure Signatures From Lossy Identification Schemes Michel Abdalla, Pierre-Alain Fouque, Vadim Lyubashevsky, and Mehdi Tibouchi 2 École normale supérieure {michel.abdalla,pierre-alain.fouque,vadim.lyubashevsky}@ens.fr
Tightly-Secure Signatures From Lossy Identification Schemes Michel Abdalla, Pierre-Alain Fouque, Vadim Lyubashevsky, and Mehdi Tibouchi 2 École normale supérieure {michel.abdalla,pierre-alain.fouque,vadim.lyubashevsky}@ens.fr
Cryptography CS 555. Topic 23: Zero-Knowledge Proof and Cryptographic Commitment. CS555 Topic 23 1
 Cryptography CS 555 Topic 23: Zero-Knowledge Proof and Cryptographic Commitment CS555 Topic 23 1 Outline and Readings Outline Zero-knowledge proof Fiat-Shamir protocol Schnorr protocol Commitment schemes
Cryptography CS 555 Topic 23: Zero-Knowledge Proof and Cryptographic Commitment CS555 Topic 23 1 Outline and Readings Outline Zero-knowledge proof Fiat-Shamir protocol Schnorr protocol Commitment schemes
Lecture 10: Zero-Knowledge Proofs
 Lecture 10: Zero-Knowledge Proofs Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Applebaum Tel-Aviv University Fall Semester, 2011 12 Some of these slides are based on note by Boaz Barak. Quo vadis? Eo Romam
Lecture 10: Zero-Knowledge Proofs Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Applebaum Tel-Aviv University Fall Semester, 2011 12 Some of these slides are based on note by Boaz Barak. Quo vadis? Eo Romam
George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK
 George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
III. Authentication - identification protocols
 III. Authentication - identification protocols Definition 3.1 A cryptographic protocol is a distributed algorithm describing precisely the interaction between two or more parties, achieving certain security
III. Authentication - identification protocols Definition 3.1 A cryptographic protocol is a distributed algorithm describing precisely the interaction between two or more parties, achieving certain security
From Identification to Signatures, Tightly: A Framework and Generic Transforms
 From Identification to Signatures, Tightly: A Framework and Generic Transforms Mihir Bellare 1 Bertram Poettering 2 Douglas Stebila 3 February 2016 Abstract This paper provides a framework to treat the
From Identification to Signatures, Tightly: A Framework and Generic Transforms Mihir Bellare 1 Bertram Poettering 2 Douglas Stebila 3 February 2016 Abstract This paper provides a framework to treat the
Security Proofs for Identity-Based Identification and Signature Schemes
 A preliminary version of this paper appears in Advances in Cryptology EUROCRYPT 2004, volume 3027 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, C. Cachin and J. Camenisch ed., Springer-Verlag, 2004. This is the
A preliminary version of this paper appears in Advances in Cryptology EUROCRYPT 2004, volume 3027 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, C. Cachin and J. Camenisch ed., Springer-Verlag, 2004. This is the
Homework 3 Solutions
 5233/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, Fall 205 Instructor Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 3 Solutions 7-Dec-205 Scribe Amir Rezapour. Consider an unfair coin with head probability 0.5. Assume that the coin
5233/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, Fall 205 Instructor Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 3 Solutions 7-Dec-205 Scribe Amir Rezapour. Consider an unfair coin with head probability 0.5. Assume that the coin
Outline. Provable Security in the Computational Model. III Signatures. Public-Key Encryption. Outline. David Pointcheval.
 Provable Security in the Computational Model III Signatures David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRI Public-Key Encryption Signatures 2 dvanced Security for Signature dvanced Security Notions
Provable Security in the Computational Model III Signatures David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRI Public-Key Encryption Signatures 2 dvanced Security for Signature dvanced Security Notions
Universal Designated Verifier Signature Proof (or How to Efficiently Prove Knowledge of a Signature)
 Universal Designated Verifier Signature Proof (or How to Efficiently Prove Knowledge of a Signature) Joonsang Baek, Reihaneh Safavi-Naini, and Willy Susilo Centre for Information Security, School of Information
Universal Designated Verifier Signature Proof (or How to Efficiently Prove Knowledge of a Signature) Joonsang Baek, Reihaneh Safavi-Naini, and Willy Susilo Centre for Information Security, School of Information
ON DEFINING PROOFS OF KNOWLEDGE IN THE BARE PUBLIC-KEY MODEL
 1 ON DEFINING PROOFS OF KNOWLEDGE IN THE BARE PUBLIC-KEY MODEL GIOVANNI DI CRESCENZO Telcordia Technologies, Piscataway, NJ, USA. E-mail: giovanni@research.telcordia.com IVAN VISCONTI Dipartimento di Informatica
1 ON DEFINING PROOFS OF KNOWLEDGE IN THE BARE PUBLIC-KEY MODEL GIOVANNI DI CRESCENZO Telcordia Technologies, Piscataway, NJ, USA. E-mail: giovanni@research.telcordia.com IVAN VISCONTI Dipartimento di Informatica
Lecture 10. Public Key Cryptography: Encryption + Signatures. Identification
 Lecture 10 Public Key Cryptography: Encryption + Signatures 1 Identification Public key cryptography can be also used for IDENTIFICATION Identification is an interactive protocol whereby one party: prover
Lecture 10 Public Key Cryptography: Encryption + Signatures 1 Identification Public key cryptography can be also used for IDENTIFICATION Identification is an interactive protocol whereby one party: prover
TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITEIT EINDHOVEN Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Friday 25 January 2019
 Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Friday 25 January 2019 Name : TU/e student number : Exercise 1 2 3 4 5 total points Notes: Please hand in all sheets at the end of the exam.
Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Friday 25 January 2019 Name : TU/e student number : Exercise 1 2 3 4 5 total points Notes: Please hand in all sheets at the end of the exam.
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited
 From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
On the Security of Classic Protocols for Unique Witness Relations
 On the Security of Classic Protocols for Unique Witness Relations Yi Deng 1,2, Xuyang Song 1,2, Jingyue Yu 1,2, and Yu Chen 1,2 1 State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Information
On the Security of Classic Protocols for Unique Witness Relations Yi Deng 1,2, Xuyang Song 1,2, Jingyue Yu 1,2, and Yu Chen 1,2 1 State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Information
3-Move Undeniable Signature Scheme
 3-Move Undeniable Signature Scheme Kaoru Kurosawa 1 and Swee-Huay Heng 2 1 Ibaraki University, 4-12-1 Nakanarusawa, Hitachi, Ibaraki 316-8511, Japan kurosawa@cis.ibaraki.ac.jp 2 Multimedia University,
3-Move Undeniable Signature Scheme Kaoru Kurosawa 1 and Swee-Huay Heng 2 1 Ibaraki University, 4-12-1 Nakanarusawa, Hitachi, Ibaraki 316-8511, Japan kurosawa@cis.ibaraki.ac.jp 2 Multimedia University,
Dr George Danezis University College London, UK
 Dr George Danezis University College London, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
Dr George Danezis University College London, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
Digital Signatures. Adam O Neill based on
 Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes
 Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge
 Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge - interactive protocols formalize what can be recognized by polynomial time restricted verifiers in arbitrary protocols - generalizes NP - zero-knowledge formalizes
Interactive protocols & zero-knowledge - interactive protocols formalize what can be recognized by polynomial time restricted verifiers in arbitrary protocols - generalizes NP - zero-knowledge formalizes
Digital Signatures from Challenge-Divided Σ-Protocols
 Digital Signatures from Challenge-Divided Σ-Protocols Andrew C. Yao Yunlei Zhao Abstract Digital signature is one of the basic primitives in cryptography. A common paradigm of obtaining signatures, known
Digital Signatures from Challenge-Divided Σ-Protocols Andrew C. Yao Yunlei Zhao Abstract Digital signature is one of the basic primitives in cryptography. A common paradigm of obtaining signatures, known
Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures
 CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography October 30, 2017 Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Willy Quach & Giorgos Zirdelis 1 Topic Covered. Trapdoor Permutations.
CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography October 30, 2017 Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Willy Quach & Giorgos Zirdelis 1 Topic Covered. Trapdoor Permutations.
Research Article Efficient and Provable Secure Pairing-Free Security-Mediated Identity-Based Identification Schemes
 e Scientific World Journal Article ID 170906 14 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/170906 Research Article Efficient and Provable Secure Pairing-Free Security-Mediated Identity-Based Identification Schemes
e Scientific World Journal Article ID 170906 14 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/170906 Research Article Efficient and Provable Secure Pairing-Free Security-Mediated Identity-Based Identification Schemes
Tighter Reductions for Forward-Secure Signature Schemes
 This is the Full Version of the Extended Abstract that appears in the Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Practice and Theory in Public-Key Cryptography (PKC 13) (26 February 1 March 2013,
This is the Full Version of the Extended Abstract that appears in the Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Practice and Theory in Public-Key Cryptography (PKC 13) (26 February 1 March 2013,
Resettable Zero-Knowledge in the Weak Public-Key Model
 Resettable Zero-Knowledge in the Weak Public-Key Model Yunlei Zhao 1,3, Xiaotie Deng 2, C.H. Lee 2, and Hong Zhu 3 1 Software School Fudan University, Shanghai, China csylzhao@cityu.edu.hk 2 Department
Resettable Zero-Knowledge in the Weak Public-Key Model Yunlei Zhao 1,3, Xiaotie Deng 2, C.H. Lee 2, and Hong Zhu 3 1 Software School Fudan University, Shanghai, China csylzhao@cityu.edu.hk 2 Department
Constant-Round Concurrently-Secure rzk in the (Real) Bare Public-Key Model
 Electronic Colloquium on Computational Complexity, Revision 1 of Report No. 48 (2005) Constant-Round Concurrently-Secure rzk in the (Real) Bare Public-Key Model Moti Yung Yunlei Zhao Abstract We present
Electronic Colloquium on Computational Complexity, Revision 1 of Report No. 48 (2005) Constant-Round Concurrently-Secure rzk in the (Real) Bare Public-Key Model Moti Yung Yunlei Zhao Abstract We present
Outline. The Game-based Methodology for Computational Security Proofs. Public-Key Cryptography. Outline. Introduction Provable Security
 The Game-based Methodology for Computational s David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA Computational and Symbolic Proofs of Security Atagawa Heights Japan April 6th, 2009 1/39 2/39 Public-Key
The Game-based Methodology for Computational s David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA Computational and Symbolic Proofs of Security Atagawa Heights Japan April 6th, 2009 1/39 2/39 Public-Key
Cryptanalysis of a Zero-Knowledge Identification Protocol of Eurocrypt 95
 Cryptanalysis of a Zero-Knowledge Identification Protocol of Eurocrypt 95 Jean-Sébastien Coron and David Naccache Gemplus Card International 34 rue Guynemer, 92447 Issy-les-Moulineaux, France {jean-sebastien.coron,
Cryptanalysis of a Zero-Knowledge Identification Protocol of Eurocrypt 95 Jean-Sébastien Coron and David Naccache Gemplus Card International 34 rue Guynemer, 92447 Issy-les-Moulineaux, France {jean-sebastien.coron,
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 10/3/16. Lecture 9 RSA Encryption and Diffie-Helmann Key Exchange
 ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 10/3/16 Lecture 9 RSA Encryption and Diffie-Helmann Key Exchange Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 10/3/16 Lecture 9 RSA Encryption and Diffie-Helmann Key Exchange Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
Discrete-Log-Based Signatures May Not Be Equivalent to Discrete Log
 Discrete-Log-Based Signatures May Not Be Equivalent to Discrete Log Pascal Paillier, Damien Vergnaud To cite this version: Pascal Paillier, Damien Vergnaud. Discrete-Log-Based Signatures May Not Be Equivalent
Discrete-Log-Based Signatures May Not Be Equivalent to Discrete Log Pascal Paillier, Damien Vergnaud To cite this version: Pascal Paillier, Damien Vergnaud. Discrete-Log-Based Signatures May Not Be Equivalent
Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures
 Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures Zhou Sujing Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, zhousujing@pmail.ntu.edu.sg Abstract. Transitive signature, motivated by signing
Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures Zhou Sujing Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, zhousujing@pmail.ntu.edu.sg Abstract. Transitive signature, motivated by signing
Applied cryptography
 Applied cryptography Identity-based Cryptography Andreas Hülsing 19 November 2015 1 / 37 The public key problem How to obtain the correct public key of a user? How to check its authenticity? General answer:
Applied cryptography Identity-based Cryptography Andreas Hülsing 19 November 2015 1 / 37 The public key problem How to obtain the correct public key of a user? How to check its authenticity? General answer:
A Fair and Efficient Solution to the Socialist Millionaires Problem
 In Discrete Applied Mathematics, 111 (2001) 23 36. (Special issue on coding and cryptology) A Fair and Efficient Solution to the Socialist Millionaires Problem Fabrice Boudot a Berry Schoenmakers b Jacques
In Discrete Applied Mathematics, 111 (2001) 23 36. (Special issue on coding and cryptology) A Fair and Efficient Solution to the Socialist Millionaires Problem Fabrice Boudot a Berry Schoenmakers b Jacques
Interactive Zero-Knowledge with Restricted Random Oracles
 Interactive Zero-Knowledge with Restricted Random Oracles Moti Yung 1 and Yunlei Zhao 2 1 RSA Laboratories and Department of Computer Science, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA. moti@cs.columbia.edu
Interactive Zero-Knowledge with Restricted Random Oracles Moti Yung 1 and Yunlei Zhao 2 1 RSA Laboratories and Department of Computer Science, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA. moti@cs.columbia.edu
Cryptographic e-cash. Jan Camenisch. IBM Research ibm.biz/jancamenisch. IACR Summerschool Blockchain Technologies
 IACR Summerschool Blockchain Technologies Cryptographic e-cash Jan Camenisch IBM Research Zurich @JanCamenisch ibm.biz/jancamenisch ecash scenario & requirements Bank Withdrawal User Spend Deposit Merchant
IACR Summerschool Blockchain Technologies Cryptographic e-cash Jan Camenisch IBM Research Zurich @JanCamenisch ibm.biz/jancamenisch ecash scenario & requirements Bank Withdrawal User Spend Deposit Merchant
The Random Oracle Paradigm. Mike Reiter. Random oracle is a formalism to model such uses of hash functions that abound in practical cryptography
 1 The Random Oracle Paradigm Mike Reiter Based on Random Oracles are Practical: A Paradigm for Designing Efficient Protocols by M. Bellare and P. Rogaway Random Oracles 2 Random oracle is a formalism to
1 The Random Oracle Paradigm Mike Reiter Based on Random Oracles are Practical: A Paradigm for Designing Efficient Protocols by M. Bellare and P. Rogaway Random Oracles 2 Random oracle is a formalism to
Lecture 13: Seed-Dependent Key Derivation
 Randomness in Cryptography April 11, 2013 Lecture 13: Seed-Dependent Key Derivation Lecturer: Yevgeniy Dodis Scribe: Eric Miles In today s lecture, we study seeded key-derivation functions (KDFs) in the
Randomness in Cryptography April 11, 2013 Lecture 13: Seed-Dependent Key Derivation Lecturer: Yevgeniy Dodis Scribe: Eric Miles In today s lecture, we study seeded key-derivation functions (KDFs) in the
Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme
 Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme Kwangsu Lee Dong Hoon Lee Abstract Identity-based signature (IBS) is a specific type of public-key signature (PKS) where any
Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme Kwangsu Lee Dong Hoon Lee Abstract Identity-based signature (IBS) is a specific type of public-key signature (PKS) where any
Limitations of the Meta-Reduction Technique: The Case of Schnorr Signatures
 An extended abstract of this paper appears at Eurocrypt 2013. Limitations of the Meta-Reduction Technique: The Case of Schnorr Signatures Marc Fischlin 1 Nils Fleischhacker 2 1 Technische Universität Darmstadt
An extended abstract of this paper appears at Eurocrypt 2013. Limitations of the Meta-Reduction Technique: The Case of Schnorr Signatures Marc Fischlin 1 Nils Fleischhacker 2 1 Technische Universität Darmstadt
The Representation Problem Based on Factoring
 The Representation Problem Based on Factoring Marc Fischlin and Roger Fischlin Fachbereich Mathematik (AG 7.2) Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main Postfach 111932 60054 Frankfurt/Main,
The Representation Problem Based on Factoring Marc Fischlin and Roger Fischlin Fachbereich Mathematik (AG 7.2) Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main Postfach 111932 60054 Frankfurt/Main,
On the (In)security of the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm
 On the (In)security of the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Shafi Goldwasser Yael Tauman February 2, 2004 Abstract In 1986, Fiat and Shamir proposed a general method for transforming secure 3-round public-coin identification
On the (In)security of the Fiat-Shamir Paradigm Shafi Goldwasser Yael Tauman February 2, 2004 Abstract In 1986, Fiat and Shamir proposed a general method for transforming secure 3-round public-coin identification
Communication-Efficient Non-Interactive Proofs of Knowledge with Online Extractors
 Communication-Efficient Non-Interactive Proofs of Knowledge with Online Extractors Marc Fischlin Institute for Theoretical Computer Science, ETH Zürich, Switzerland marc.fischlin @ inf.ethz.ch http://www.fischlin.de/
Communication-Efficient Non-Interactive Proofs of Knowledge with Online Extractors Marc Fischlin Institute for Theoretical Computer Science, ETH Zürich, Switzerland marc.fischlin @ inf.ethz.ch http://www.fischlin.de/
Proofs of Storage from Homomorphic Identification Protocols
 Proofs of Storage from Homomorphic Identification Protocols Giuseppe Ateniese The Johns Hopkins University ateniese@cs.jhu.edu Seny Kamara Microsoft Research senyk@microsoft.com Jonathan Katz University
Proofs of Storage from Homomorphic Identification Protocols Giuseppe Ateniese The Johns Hopkins University ateniese@cs.jhu.edu Seny Kamara Microsoft Research senyk@microsoft.com Jonathan Katz University
On The Security of The ElGamal Encryption Scheme and Damgård s Variant
 On The Security of The ElGamal Encryption Scheme and Damgård s Variant J. Wu and D.R. Stinson David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON, Canada {j32wu,dstinson}@uwaterloo.ca
On The Security of The ElGamal Encryption Scheme and Damgård s Variant J. Wu and D.R. Stinson David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON, Canada {j32wu,dstinson}@uwaterloo.ca
Some Security Comparisons of GOST R and ECDSA Signature Schemes
 Some Security Comparisons of GOST R 34.10-2012 and ECDSA Signature Schemes Trieu Quang Phong Nguyen Quoc Toan Institute of Cryptography Science and Technology Gover. Info. Security Committee, Viet Nam
Some Security Comparisons of GOST R 34.10-2012 and ECDSA Signature Schemes Trieu Quang Phong Nguyen Quoc Toan Institute of Cryptography Science and Technology Gover. Info. Security Committee, Viet Nam
II. Digital signatures
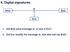 II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
Anonymous Credentials Light
 Anonymous Credentials Light Foteini Baldimtsi, Anna Lysyanskaya foteini,anna@cs.brown.edu Computer Science Department, Brown University Abstract. We define and propose an efficient and provably secure
Anonymous Credentials Light Foteini Baldimtsi, Anna Lysyanskaya foteini,anna@cs.brown.edu Computer Science Department, Brown University Abstract. We define and propose an efficient and provably secure
Certificateless Signcryption without Pairing
 Certificateless Signcryption without Pairing Wenjian Xie Zhang Zhang College of Mathematics and Computer Science Guangxi University for Nationalities, Nanning 530006, China Abstract. Certificateless public
Certificateless Signcryption without Pairing Wenjian Xie Zhang Zhang College of Mathematics and Computer Science Guangxi University for Nationalities, Nanning 530006, China Abstract. Certificateless public
ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION
 ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION 1 / 1 Recommended Book Steven Levy. Crypto. Penguin books. 2001. A non-technical account of the history of public-key cryptography and the colorful characters involved. 2 / 1 Recall
ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION 1 / 1 Recommended Book Steven Levy. Crypto. Penguin books. 2001. A non-technical account of the history of public-key cryptography and the colorful characters involved. 2 / 1 Recall
Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Applications
 Tecniche di Sicurezza Informatica dei Dati e delle Reti May 21, 2015 Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Applications Guest Lecturer: Daniele Venturi Lecturer: Antonio Villani Abstract The material below covers
Tecniche di Sicurezza Informatica dei Dati e delle Reti May 21, 2015 Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Applications Guest Lecturer: Daniele Venturi Lecturer: Antonio Villani Abstract The material below covers
Cryptanalysis and improvement of an ID-based ad-hoc anonymous identification scheme at CT-RSA 05
 Cryptanalysis and improvement of an ID-based ad-hoc anonymous identification scheme at CT-RSA 05 Fangguo Zhang 1 and Xiaofeng Chen 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Sun Yat-sen
Cryptanalysis and improvement of an ID-based ad-hoc anonymous identification scheme at CT-RSA 05 Fangguo Zhang 1 and Xiaofeng Chen 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Sun Yat-sen
Constant-Round Concurrently-Secure rzk in the (Real) Bare Public-Key Model
 Electronic Colloquium on Computational Complexity, Report No. 48 (2005) Constant-Round Concurrently-Secure rzk in the (Real) Bare Public-Key Model Moti Yung Yunlei Zhao Abstract We present constant-round
Electronic Colloquium on Computational Complexity, Report No. 48 (2005) Constant-Round Concurrently-Secure rzk in the (Real) Bare Public-Key Model Moti Yung Yunlei Zhao Abstract We present constant-round
Deterring Certificate Subversion: Efficient Double-Authentication-Preventing Signatures
 Deterring Certificate Subversion: Efficient Double-Authentication-Preventing Signatures Mihir Bellare 1 Bertram Poettering 2 Douglas Stebila 3 October 2016 Abstract This paper presents highly efficient
Deterring Certificate Subversion: Efficient Double-Authentication-Preventing Signatures Mihir Bellare 1 Bertram Poettering 2 Douglas Stebila 3 October 2016 Abstract This paper presents highly efficient
Security Proofs for Signature Schemes. Ecole Normale Superieure. 45, rue d'ulm Paris Cedex 05
 Security Proofs for Signature Schemes David Pointcheval David.Pointcheval@ens.fr Jacques Stern Jacques.Stern@ens.fr Ecole Normale Superieure Laboratoire d'informatique 45, rue d'ulm 75230 Paris Cedex 05
Security Proofs for Signature Schemes David Pointcheval David.Pointcheval@ens.fr Jacques Stern Jacques.Stern@ens.fr Ecole Normale Superieure Laboratoire d'informatique 45, rue d'ulm 75230 Paris Cedex 05
5.4 ElGamal - definition
 5.4 ElGamal - definition In this section we define the ElGamal encryption scheme. Next to RSA it is the most important asymmetric encryption scheme. Recall that for a cyclic group G, an element g G is
5.4 ElGamal - definition In this section we define the ElGamal encryption scheme. Next to RSA it is the most important asymmetric encryption scheme. Recall that for a cyclic group G, an element g G is
Simple SK-ID-KEM 1. 1 Introduction
 1 Simple SK-ID-KEM 1 Zhaohui Cheng School of Computing Science, Middlesex University The Burroughs, Hendon, London, NW4 4BT, United Kingdom. m.z.cheng@mdx.ac.uk Abstract. In 2001, Boneh and Franklin presented
1 Simple SK-ID-KEM 1 Zhaohui Cheng School of Computing Science, Middlesex University The Burroughs, Hendon, London, NW4 4BT, United Kingdom. m.z.cheng@mdx.ac.uk Abstract. In 2001, Boneh and Franklin presented
Some Comments on the Security of RSA. Debdeep Mukhopadhyay
 Some Comments on the Security of RSA Debdeep Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur INDIA -721302 Objectives Computing
Some Comments on the Security of RSA Debdeep Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur INDIA -721302 Objectives Computing
18734: Foundations of Privacy. Anonymous Cash. Anupam Datta. CMU Fall 2018
 18734: Foundations of Privacy Anonymous Cash Anupam Datta CMU Fall 2018 Today: Electronic Cash Goals Alice can ask for Bank to issue coins from her account. Alice can spend coins. Bank cannot track what
18734: Foundations of Privacy Anonymous Cash Anupam Datta CMU Fall 2018 Today: Electronic Cash Goals Alice can ask for Bank to issue coins from her account. Alice can spend coins. Bank cannot track what
5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall
 5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall Homework 2 Reference Solution 1. This is about the RSA common modulus problem. Consider that two users A and B use the same modulus n = 146171 for the RSA encryption.
5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall Homework 2 Reference Solution 1. This is about the RSA common modulus problem. Consider that two users A and B use the same modulus n = 146171 for the RSA encryption.
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes
 From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Uninstantiability of Full-Domain Hash
 Uninstantiability of based on On the Generic Insecurity of, Crypto 05, joint work with Y.Dodis and R.Oliveira Krzysztof Pietrzak CWI Amsterdam June 3, 2008 Why talk about this old stuff? Why talk about
Uninstantiability of based on On the Generic Insecurity of, Crypto 05, joint work with Y.Dodis and R.Oliveira Krzysztof Pietrzak CWI Amsterdam June 3, 2008 Why talk about this old stuff? Why talk about
From 5-pass MQ-based identification to MQ-based signatures
 From 5-pass MQ-based identification to MQ-based signatures Andreas Hülsing, Joost Rijneveld, Simona Samardjiska, and Peter Schwabe 30 June 2016 1 / 31 Our take on PQ-Crypto Prepare for actual use Reliable
From 5-pass MQ-based identification to MQ-based signatures Andreas Hülsing, Joost Rijneveld, Simona Samardjiska, and Peter Schwabe 30 June 2016 1 / 31 Our take on PQ-Crypto Prepare for actual use Reliable
Notes on Zero Knowledge
 U.C. Berkeley CS172: Automata, Computability and Complexity Handout 9 Professor Luca Trevisan 4/21/2015 Notes on Zero Knowledge These notes on zero knowledge protocols for quadratic residuosity are based
U.C. Berkeley CS172: Automata, Computability and Complexity Handout 9 Professor Luca Trevisan 4/21/2015 Notes on Zero Knowledge These notes on zero knowledge protocols for quadratic residuosity are based
Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model
 Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt (CASED) - TU Darmstadt, Germany June, 21st, 2012 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt (CASED) - TU Darmstadt, Germany June, 21st, 2012 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Lecture 16 Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko. 1 Digital Signature Schemes. CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004
 CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
Advanced Cryptography 1st Semester Public Encryption
 Advanced Cryptography 1st Semester 2007-2008 Pascal Lafourcade Université Joseph Fourrier, Verimag Master: October 1st 2007 1 / 64 Last Time (I) Indistinguishability Negligible function Probabilities Indistinguishability
Advanced Cryptography 1st Semester 2007-2008 Pascal Lafourcade Université Joseph Fourrier, Verimag Master: October 1st 2007 1 / 64 Last Time (I) Indistinguishability Negligible function Probabilities Indistinguishability
Digital Signatures. p1.
 Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
A Novel Strong Designated Verifier Signature Scheme without Random Oracles
 1 A Novel Strong Designated Verifier Signature Scheme without Random Oracles Maryam Rajabzadeh Asaar 1, Mahmoud Salmasizadeh 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, 2 Electronics Research Institute (Center),
1 A Novel Strong Designated Verifier Signature Scheme without Random Oracles Maryam Rajabzadeh Asaar 1, Mahmoud Salmasizadeh 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, 2 Electronics Research Institute (Center),
On the CCA1-Security of Elgamal and Damgård s Elgamal
 On the CCA1-Security of Elgamal and Damgård s Elgamal Cybernetica AS, Estonia Tallinn University, Estonia October 21, 2010 Outline I Motivation 1 Motivation 2 3 Motivation Three well-known security requirements
On the CCA1-Security of Elgamal and Damgård s Elgamal Cybernetica AS, Estonia Tallinn University, Estonia October 21, 2010 Outline I Motivation 1 Motivation 2 3 Motivation Three well-known security requirements
A New Identification Scheme Based on the Perceptrons Problem
 Advances in Cryptology Proceedings of EUROCRYPT 95 (may 21 25, 1995, Saint-Malo, France) L.C. Guillou and J.-J. Quisquater, Eds. Springer-Verlag, LNCS 921, pages 319 328. A New Identification Scheme Based
Advances in Cryptology Proceedings of EUROCRYPT 95 (may 21 25, 1995, Saint-Malo, France) L.C. Guillou and J.-J. Quisquater, Eds. Springer-Verlag, LNCS 921, pages 319 328. A New Identification Scheme Based
Comparing With RSA. 1 ucl Crypto Group
 Comparing With RSA Julien Cathalo 1, David Naccache 2, and Jean-Jacques Quisquater 1 1 ucl Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, b-1348, Belgium julien.cathalo@uclouvain.be, jean-jacques.quisquater@uclouvain.be
Comparing With RSA Julien Cathalo 1, David Naccache 2, and Jean-Jacques Quisquater 1 1 ucl Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, b-1348, Belgium julien.cathalo@uclouvain.be, jean-jacques.quisquater@uclouvain.be
1 Number Theory Basics
 ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
Zero-knowledge proofs of knowledge for group homomorphisms
 Des. Codes Cryptogr. (2015) 77:663 676 DOI 10.1007/s10623-015-0103-5 Zero-knowledge proofs of knowledge for group homomorphisms Ueli Maurer 1 Received: 13 October 2014 / Revised: 23 May 2015 / Accepted:
Des. Codes Cryptogr. (2015) 77:663 676 DOI 10.1007/s10623-015-0103-5 Zero-knowledge proofs of knowledge for group homomorphisms Ueli Maurer 1 Received: 13 October 2014 / Revised: 23 May 2015 / Accepted:
Statistically Secure Sigma Protocols with Abort
 AARHUS UNIVERSITY COMPUTER SCIENCE MASTER S THESIS Statistically Secure Sigma Protocols with Abort Author: Anders Fog BUNZEL (20112293) Supervisor: Ivan Bjerre DAMGÅRD September 2016 AARHUS AU UNIVERSITY
AARHUS UNIVERSITY COMPUTER SCIENCE MASTER S THESIS Statistically Secure Sigma Protocols with Abort Author: Anders Fog BUNZEL (20112293) Supervisor: Ivan Bjerre DAMGÅRD September 2016 AARHUS AU UNIVERSITY
Q B (pk, sk) Gen x u M pk y Map pk (x) return [B(pk, y)? = x]. (m, s) A O h
![Q B (pk, sk) Gen x u M pk y Map pk (x) return [B(pk, y)? = x]. (m, s) A O h Q B (pk, sk) Gen x u M pk y Map pk (x) return [B(pk, y)? = x]. (m, s) A O h](/thumbs/89/100584859.jpg) MTAT.07.003 Cryptology II Spring 2012 / Exercise session?? / Example Solution Exercise (FRH in RO model). Show that the full domain hash signature is secure against existential forgeries in the random
MTAT.07.003 Cryptology II Spring 2012 / Exercise session?? / Example Solution Exercise (FRH in RO model). Show that the full domain hash signature is secure against existential forgeries in the random
Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles
 Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Weiwei Liu School of Computer Science and Software Engineering 1/32 Weiwei Liu Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random
Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Weiwei Liu School of Computer Science and Software Engineering 1/32 Weiwei Liu Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random
EXAM IN. TDA352 (Chalmers) - DIT250 (GU) 18 January 2019, 08:
 CHALMERS GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM IN CRYPTOGRAPHY TDA352 (Chalmers) - DIT250 (GU) 18 January 2019, 08:30 12.30 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Typgodkänd räknare. Annan minnestömd räknare får användas efter godkännande
CHALMERS GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM IN CRYPTOGRAPHY TDA352 (Chalmers) - DIT250 (GU) 18 January 2019, 08:30 12.30 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Typgodkänd räknare. Annan minnestömd räknare får användas efter godkännande
A New NP-Complete Problem and Public-Key Identification
 C Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 28, 5 31, 2003 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. A New NP-Complete Problem and Public-Key Identification DAVID POINTCHEVAL Département
C Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 28, 5 31, 2003 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. A New NP-Complete Problem and Public-Key Identification DAVID POINTCHEVAL Département
Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman
 Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman Dan Boneh 1, Emily Shen 1, and Brent Waters 2 1 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA {dabo,emily}@cs.stanford.edu
Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman Dan Boneh 1, Emily Shen 1, and Brent Waters 2 1 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA {dabo,emily}@cs.stanford.edu
(Convertible) Undeniable Signatures without Random Oracles
 Convertible) Undeniable Signatures without Random Oracles Tsz Hon Yuen 1, Man Ho Au 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, and Willy Susilo 1 1 Centre for Computer and Information Security Research School of Computer Science
Convertible) Undeniable Signatures without Random Oracles Tsz Hon Yuen 1, Man Ho Au 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, and Willy Susilo 1 1 Centre for Computer and Information Security Research School of Computer Science
