Short Signatures Without Random Oracles
|
|
|
- Jasmine Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Short Signatures Without Random Oracles Dan Boneh and Xavier Boyen (presented by Aleksandr Yampolskiy)
2 Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion
3 Why signatures without random oracles? random oracle model H( ) ¼ perfectly random function [FS87] useful yet often unrealistic [CGH98] most signatures without random oracles [GHR99, CS00] based on strong RSA assumption
4 Why this paper? strong RSA problem Given N=pq, g2 Z n*, find (c, g 1/c ), c2 Z. Difficult because group order φ(n) is hidden. Useful property: From (N, g), we can construct (N, h) with q known solutions (c i, h 1/c i). Any new solution (c *, h 1/c* ) gives solution to original scheme. Can we have a similar property in a group with known order p?
5 Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion
6 Secure Signatures signature scheme = (KeyGen, Sign, Verify) strong existential unforgeability (suf-cma) [ADR02] setup (PK, SK) Ã KeyGen PK challenger adversary
7 Secure Signatures (cont.) signature scheme = (KeyGen, Sign, Verify) strong existential unforgeability (suf-cma) [ADR02] setup queries (M 1, σ 1 ),, (M qs, σ qs ) (PK, SK) M i PK σ i = Sign(SK i, M i ) challenger adversary
8 Secure Signatures (cont.) signature scheme = (KeyGen, Sign, Verify) strong existential unforgeability (suf-cma) [ADR02] setup queries (M 1, σ 1 ),, (M qs, σ qs ) outputs new (M *, σ * )? (M i, σ i ); wins if valid (PK, SK) (Μ, σ ) PK challenger adversary
9 Secure Signatures (cont.) signature weak scheme = (KeyGen, Sign, Verify) strong existential unforgeability (wuf-cma) setup non-adaptive queries (M 1, σ 1 ),, (M qs, σ qs ) 8i M *? M i outputs new (M *, σ * )? (M i, σ i ); wins if valid (PK, SK) (Μ, σ ) PK challenger adversary
10 Bilinear Groups G 1, G 2 : cyclic groups of prime order p; G T : group of order p bilinear map e: G 1 G 2 a G T bilinear: 8u2 G 1, v2 G 2 ; 8a,b 2 Z e(u a, v b ) = e(u, v) ab non-degenerate: e(g 1, g 2 )? 1 efficiently computable: 9Ψ: G 2 a G 1 can construct bilinear maps from Weil pairing [JN01]
11 Strong Diffie-Hellman Assumption q-sdh problem: given (g 1, g 2, g 2x,, g 2 (x q ) ), output (c, g 1 1/(x+c) ), where c 2 Z p * ( hard Checking that (c, s) is a valid pair ( easy Simply test if e(s, g 2c g 2x ) = e(g 1, g 2 )? Prior works [BB04, MSK02] used weaker q-dhi problem: given (g 1, g 2, g 2x,, g 2 (x q ) ; c ), output g 1 1/(x+c).
12 Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion
13 Short Signature Scheme S Key generation: Pick x,y 2 r Z p*. Let u=g 1x, v=g 2y. Public key is PK = (g 1, g 2, u, v). Secret key is SK = (x, y). Signing: To sign m2 Z p*, pick r2 r Z p*. Compute σ = g 1 1/(x+m+yr). Signature is (σ, r). Verification: Given m and σ, output valid if e(σ, u g 2m v r ) = e(g 1, g 2 ). 2log 2 (p) bits ¼ 40 bytes
14 Main Theorem Thm: Suppose (q, t', ε')-sdh assumption holds. Then signature scheme S is (q s, t, ε)-secure against existential forgeries under (strong) CMA, where t' ¼ t, q s < q, and ε' ¼ ε/2.
15 Proof Idea : big picture 1. Simplified signature scheme S' 2. q-sdh is hard ) S' is wuf-cma 3. S' is wuf-cma ) S is suf-cma Hence, q-sdh is hard ) S is suf-cma
16 Proof Idea : 1/3 Simplified signature S Key Generation: PK = (g 1, g 2, g 2x ), SK = x Signing: To sign m, compute σ = g 1 1/(x+m) Verification: On input (m, σ), return valid if e(σ, g 2x g 2m ) = e(g 1, g 2 )
17 Proof Idea : 2/3 Lemma: q-sdh is hard ) S' is wuf-cma Idea: property of q-sdh ¼ property of strong RSA Given g 2, g 2x,, g 2 x q Can construct new instance h, h x,, h xq with q -1 known solutions (c i, h 1/(x+c i ) ) for specially chosen c i so that any new solution (c *, h 1/(x+c*) ) produced by forger yields a solution (c, g 2 1/(x+c) ).
18 Proof Idea : 3/3 Lemma: S' is wuf-cma ) S is suf-cma Idea: σ 1,,σ q B weak A strong challenger w 1,, w q PK=(g 1, g 2, u) A sends m 1,, m q to B. Gets back (s i, r i ), i=1..q s. Then A outputs forgery (m *, s *, r * ). Let w i = m i + yr i for i=1.. q s and w * = m * + yr *. Type-1 forger: w *? w 1,, w qs Type-2 forger: w * is one of w 1,, w qs
19 Proof Idea : 3/3 (cont.) Upon startup, B guesses what type of forger A is If B chose Type-1: it picks y2 Z p*, PK = (g 1, g 2, u, g 2y ) on l-th Sign(m) request from A, set r l = (w l m) / y and return (σ l, r l ) given forgery (m *, s *, r * ) by A, return (w *, s * ) If B chose Type-2: it picks x2 Z p*, PK = (g 1, g 2, g 2x, u) on l-th Sign(m) request from A, set r l = (x + m) / w l and return (σ l 1/r l, r l ) given forgery (m *, s *, r * ) by A, return ((x+m * )/r *, s * ).
20 Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion
21 Extensions To sign arbitrary messages, simply hash them in advance: h: {0,1} * a Z p * We can use Pollard s Λ method for limited message recovery. If we use random oracles, we can achieve even shorter signatures: σ Ã g 1 1/(x+H(m))
22 Conclusion Short signature based on a novel q-sdh assumption. Proved secure without random oracles! Final thoughts: Is there anything left to extend? Can q-sdh be utilized for something else? (BBS04)
Pairing-Based Identification Schemes
 Pairing-Based Identification Schemes David Freeman Information Theory Research HP Laboratories Palo Alto HPL-2005-154 August 24, 2005* public-key cryptography, identification, zero-knowledge, pairings
Pairing-Based Identification Schemes David Freeman Information Theory Research HP Laboratories Palo Alto HPL-2005-154 August 24, 2005* public-key cryptography, identification, zero-knowledge, pairings
Schnorr Signature. Schnorr Signature. October 31, 2012
 . October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
. October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
Short Signatures Without Random Oracles and the SDH Assumption in Bilinear Groups*
 J. Cryptol. (2008) 2: 49 77 DOI: 0.007/s0045-007-9005-7 Short Signatures Without Random Oracles and the SDH Assumption in Bilinear Groups* Dan Boneh Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA dabo@cs.stanford.edu
J. Cryptol. (2008) 2: 49 77 DOI: 0.007/s0045-007-9005-7 Short Signatures Without Random Oracles and the SDH Assumption in Bilinear Groups* Dan Boneh Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA dabo@cs.stanford.edu
Digital Signatures. Adam O Neill based on
 Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman
 Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman Dan Boneh 1, Emily Shen 1, and Brent Waters 2 1 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA {dabo,emily}@cs.stanford.edu
Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman Dan Boneh 1, Emily Shen 1, and Brent Waters 2 1 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA {dabo,emily}@cs.stanford.edu
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model. A. Hülsing
 Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
PAIRING-BASED IDENTIFICATION SCHEMES
 PAIRING-BASED IDENTIFICATION SCHEMES DAVID FREEMAN Abstract. We propose four different identification schemes that make use of bilinear pairings, and prove their security under certain computational assumptions.
PAIRING-BASED IDENTIFICATION SCHEMES DAVID FREEMAN Abstract. We propose four different identification schemes that make use of bilinear pairings, and prove their security under certain computational assumptions.
Identity-based encryption
 Identity-based encryption Michel Abdalla ENS & CNRS MPRI - Course 2-12-1 Michel Abdalla (ENS & CNRS) Identity-based encryption 1 / 43 Identity-based encryption (IBE) Goal: Allow senders to encrypt messages
Identity-based encryption Michel Abdalla ENS & CNRS MPRI - Course 2-12-1 Michel Abdalla (ENS & CNRS) Identity-based encryption 1 / 43 Identity-based encryption (IBE) Goal: Allow senders to encrypt messages
Lecture 7: Boneh-Boyen Proof & Waters IBE System
 CS395T Advanced Cryptography 2/0/2009 Lecture 7: Boneh-Boyen Proof & Waters IBE System Instructor: Brent Waters Scribe: Ioannis Rouselakis Review Last lecture we discussed about the Boneh-Boyen IBE system,
CS395T Advanced Cryptography 2/0/2009 Lecture 7: Boneh-Boyen Proof & Waters IBE System Instructor: Brent Waters Scribe: Ioannis Rouselakis Review Last lecture we discussed about the Boneh-Boyen IBE system,
Applied cryptography
 Applied cryptography Identity-based Cryptography Andreas Hülsing 19 November 2015 1 / 37 The public key problem How to obtain the correct public key of a user? How to check its authenticity? General answer:
Applied cryptography Identity-based Cryptography Andreas Hülsing 19 November 2015 1 / 37 The public key problem How to obtain the correct public key of a user? How to check its authenticity? General answer:
A Security Proof of KCDSA using an extended Random Oracle Model
 A Security Proof of KCDSA using an extended Random Oracle Model Vikram Singh Abstract We describe a tight security reduction to the discrete logarithm problem for KCDSA under an extended Random Oracle
A Security Proof of KCDSA using an extended Random Oracle Model Vikram Singh Abstract We describe a tight security reduction to the discrete logarithm problem for KCDSA under an extended Random Oracle
Outline. The Game-based Methodology for Computational Security Proofs. Public-Key Cryptography. Outline. Introduction Provable Security
 The Game-based Methodology for Computational s David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA Computational and Symbolic Proofs of Security Atagawa Heights Japan April 6th, 2009 1/39 2/39 Public-Key
The Game-based Methodology for Computational s David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA Computational and Symbolic Proofs of Security Atagawa Heights Japan April 6th, 2009 1/39 2/39 Public-Key
Practical Hierarchical Identity Based Encryption and Signature schemes Without Random Oracles
 Practical Hierarchical Identity Based Encryption and Signature schemes Without Random Oracles Man Ho Au 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, Tsz Hon Yuen 3, and Duncan S. Wong 4 1 Centre for Information Security Research
Practical Hierarchical Identity Based Encryption and Signature schemes Without Random Oracles Man Ho Au 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, Tsz Hon Yuen 3, and Duncan S. Wong 4 1 Centre for Information Security Research
Multi-key Hierarchical Identity-Based Signatures
 Multi-key Hierarchical Identity-Based Signatures Hoon Wei Lim Nanyang Technological University 9 June 2010 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Preliminaries 3 Multi-key HIBS 4 Security Analysis 5 Discussion 6 Open
Multi-key Hierarchical Identity-Based Signatures Hoon Wei Lim Nanyang Technological University 9 June 2010 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Preliminaries 3 Multi-key HIBS 4 Security Analysis 5 Discussion 6 Open
Short Signatures from the Weil Pairing
 Short Signatures from the Weil Pairing Dan Boneh dabo@cs.stanford.edu Ben Lynn blynn@cs.stanford.edu Hovav Shacham hovav@cs.stanford.edu Abstract We introduce a short signature scheme based on the Computational
Short Signatures from the Weil Pairing Dan Boneh dabo@cs.stanford.edu Ben Lynn blynn@cs.stanford.edu Hovav Shacham hovav@cs.stanford.edu Abstract We introduce a short signature scheme based on the Computational
Short Signatures From Diffie-Hellman: Realizing Short Public Key
 Short Signatures From Diffie-Hellman: Realizing Short Public Key Jae Hong Seo Department of Mathematics, Myongji University Yongin, Republic of Korea jaehongseo@mju.ac.kr Abstract. Efficient signature
Short Signatures From Diffie-Hellman: Realizing Short Public Key Jae Hong Seo Department of Mathematics, Myongji University Yongin, Republic of Korea jaehongseo@mju.ac.kr Abstract. Efficient signature
Efficient Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles
 Efficient Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Abstract We present the first efficient Identity-Based Encryption (IBE) scheme that is fully secure without random oracles. We first
Efficient Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Abstract We present the first efficient Identity-Based Encryption (IBE) scheme that is fully secure without random oracles. We first
Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme
 Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme Kwangsu Lee Dong Hoon Lee Abstract Identity-based signature (IBS) is a specific type of public-key signature (PKS) where any
Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme Kwangsu Lee Dong Hoon Lee Abstract Identity-based signature (IBS) is a specific type of public-key signature (PKS) where any
Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles
 Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Weiwei Liu School of Computer Science and Software Engineering 1/32 Weiwei Liu Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random
Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Weiwei Liu School of Computer Science and Software Engineering 1/32 Weiwei Liu Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random
Improved Security for Linearly Homomorphic Signatures: A Generic Framework
 An extended abstract of this work will appear in Public Key Cryptography PKC 2012. This is the full version. Improved Security for Linearly Homomorphic Signatures: A Generic Framework DAVID MANDELL FREEMAN
An extended abstract of this work will appear in Public Key Cryptography PKC 2012. This is the full version. Improved Security for Linearly Homomorphic Signatures: A Generic Framework DAVID MANDELL FREEMAN
Digital Signatures from Strong RSA without Prime Genera7on. David Cash Rafael Dowsley Eike Kiltz
 Digital Signatures from Strong RSA without Prime Genera7on David Cash Rafael Dowsley Eike Kiltz Digital Signatures Digital signatures are one of mostly deployed cryptographic primi7ves. Digital Signatures
Digital Signatures from Strong RSA without Prime Genera7on David Cash Rafael Dowsley Eike Kiltz Digital Signatures Digital signatures are one of mostly deployed cryptographic primi7ves. Digital Signatures
Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures
 CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography October 30, 2017 Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Willy Quach & Giorgos Zirdelis 1 Topic Covered. Trapdoor Permutations.
CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography October 30, 2017 Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Willy Quach & Giorgos Zirdelis 1 Topic Covered. Trapdoor Permutations.
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes
 Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
Essam Ghadafi CT-RSA 2016
 SHORT STRUCTURE-PRESERVING SIGNATURES Essam Ghadafi e.ghadafi@ucl.ac.uk Department of Computer Science, University College London CT-RSA 2016 SHORT STRUCTURE-PRESERVING SIGNATURES OUTLINE 1 BACKGROUND
SHORT STRUCTURE-PRESERVING SIGNATURES Essam Ghadafi e.ghadafi@ucl.ac.uk Department of Computer Science, University College London CT-RSA 2016 SHORT STRUCTURE-PRESERVING SIGNATURES OUTLINE 1 BACKGROUND
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography
 Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample
 Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample Fuchun Guo 1, Rongmao Chen 2, Willy Susilo 1, Jianchang Lai 1, Guomin Yang 1, and Yi Mu 1 1 Institute
Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample Fuchun Guo 1, Rongmao Chen 2, Willy Susilo 1, Jianchang Lai 1, Guomin Yang 1, and Yi Mu 1 1 Institute
Lecture 16 Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko. 1 Digital Signature Schemes. CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004
 CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signa
 Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
Post-quantum security models for authenticated encryption
 Post-quantum security models for authenticated encryption Vladimir Soukharev David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science February 24, 2016 Introduction Bellare and Namprempre in 2008, have shown that
Post-quantum security models for authenticated encryption Vladimir Soukharev David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science February 24, 2016 Introduction Bellare and Namprempre in 2008, have shown that
A new signature scheme without random oracles from bilinear pairings
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Informatics - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2006 A new signature scheme without random oracles from bilinear pairings
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Informatics - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2006 A new signature scheme without random oracles from bilinear pairings
Introduction to Elliptic Curve Cryptography
 Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata May 19, 2017 ElGamal Public Key Cryptosystem, 1984 Key Generation: 1 Choose a suitable large prime p 2 Choose a generator g of the cyclic group IZ p 3 Choose a cyclic
Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata May 19, 2017 ElGamal Public Key Cryptosystem, 1984 Key Generation: 1 Choose a suitable large prime p 2 Choose a generator g of the cyclic group IZ p 3 Choose a cyclic
Unique Signature with Short Output from CDH Assumption
 Unique Signature with Short Output from CDH Assumption Shiuan-Tzuo Shen, Amir Rezapour, and Wen-Guey Tzeng Department of Computer Science, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan {vink,rezapour,wgtzeng}@cs.nctu.edu.tw
Unique Signature with Short Output from CDH Assumption Shiuan-Tzuo Shen, Amir Rezapour, and Wen-Guey Tzeng Department of Computer Science, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan {vink,rezapour,wgtzeng}@cs.nctu.edu.tw
1 Number Theory Basics
 ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
Towards Tightly Secure Lattice Short Signature and Id-Based Encryption
 Towards Tightly Secure Lattice Short Signature and Id-Based Encryption Xavier Boyen Qinyi Li QUT Asiacrypt 16 2016-12-06 1 / 19 Motivations 1. Short lattice signature with tight security reduction w/o
Towards Tightly Secure Lattice Short Signature and Id-Based Encryption Xavier Boyen Qinyi Li QUT Asiacrypt 16 2016-12-06 1 / 19 Motivations 1. Short lattice signature with tight security reduction w/o
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants. COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from
 Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Lecture 14 More on Digital Signatures and Variants COSC-260 Codes and Ciphers Adam O Neill Adapted from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse107/ Setting the Stage We will cover in more depth some issues for
Short Unique Signatures from RSA with a Tight Security Reduction (in the Random Oracle Model)
 Short Unique Signatures from RSA with a Tight Security Reduction (in the Random Oracle Model) Hovav Shacham UC San Diego and UT Austin Abstract. A signature scheme is unique if for every public key and
Short Unique Signatures from RSA with a Tight Security Reduction (in the Random Oracle Model) Hovav Shacham UC San Diego and UT Austin Abstract. A signature scheme is unique if for every public key and
Improved Security for Linearly Homomorphic Signatures: A Generic Framework
 Improved Security for Linearly Homomorphic Signatures: A Generic Framework Stanford University, USA PKC 2012 Darmstadt, Germany 23 May 2012 Problem: Computing on Authenticated Data Q: How do we delegate
Improved Security for Linearly Homomorphic Signatures: A Generic Framework Stanford University, USA PKC 2012 Darmstadt, Germany 23 May 2012 Problem: Computing on Authenticated Data Q: How do we delegate
ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011
 ECS 127: Cryptography Handout F UC Davis Phillip Rogaway June 9, 2011 ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011 Hints for success: Good luck on the exam. I don t think it s all that hard (I do believe I
ECS 127: Cryptography Handout F UC Davis Phillip Rogaway June 9, 2011 ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011 Hints for success: Good luck on the exam. I don t think it s all that hard (I do believe I
Hash-based signatures & Hash-and-sign without collision-resistance
 Hash-based signatures & Hash-and-sign without collision-resistance Andreas Hülsing 22.12.2016 Hash-based Signature Schemes [Mer89] Post quantum Only secure hash function Security well understood Fast 22-12-2016
Hash-based signatures & Hash-and-sign without collision-resistance Andreas Hülsing 22.12.2016 Hash-based Signature Schemes [Mer89] Post quantum Only secure hash function Security well understood Fast 22-12-2016
Proofs on Encrypted Values in Bilinear Groups and an Application to Anonymity of Signatures
 Proofs on Encrypted Values in Bilinear Groups and an Application to Anonymity of Signatures G. Fuchsbauer D. Pointcheval École normale supérieure Pairing'09, 13.08.2009 Fuchsbauer, Pointcheval (ENS) Proofs
Proofs on Encrypted Values in Bilinear Groups and an Application to Anonymity of Signatures G. Fuchsbauer D. Pointcheval École normale supérieure Pairing'09, 13.08.2009 Fuchsbauer, Pointcheval (ENS) Proofs
John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes. Table of contents
 John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time: Good news and bad There
John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time: Good news and bad There
Attribute-Based Ring Signatures
 Attribute-Based Ring Signatures Jin Li and Kwangjo Kim International Research center for Information Security (IRIS) Information and Communications University(ICU) 103-6 Munji-Dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon,
Attribute-Based Ring Signatures Jin Li and Kwangjo Kim International Research center for Information Security (IRIS) Information and Communications University(ICU) 103-6 Munji-Dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon,
Short and Stateless Signatures from the RSA Assumption
 Short and Stateless Signatures from the RSA Assumption Susan Hohenberger 1, and Brent Waters 2, 1 Johns Hopkins University, susan@cs.jhu.edu 2 University of Texas at Austin, bwaters@cs.utexas.edu Abstract.
Short and Stateless Signatures from the RSA Assumption Susan Hohenberger 1, and Brent Waters 2, 1 Johns Hopkins University, susan@cs.jhu.edu 2 University of Texas at Austin, bwaters@cs.utexas.edu Abstract.
CSC 774 Advanced Network Security
 CSC 774 Advanced Network Security Topic 2.6 ID Based Cryptography #2 Slides by An Liu Outline Applications Elliptic Curve Group over real number and F p Weil Pairing BasicIdent FullIdent Extensions Escrow
CSC 774 Advanced Network Security Topic 2.6 ID Based Cryptography #2 Slides by An Liu Outline Applications Elliptic Curve Group over real number and F p Weil Pairing BasicIdent FullIdent Extensions Escrow
CSC 774 Advanced Network Security
 CSC 774 Advanced Network Security Topic 2.6 ID Based Cryptography #2 Slides by An Liu Outline Applications Elliptic Curve Group over real number and F p Weil Pairing BasicIdent FullIdent Extensions Escrow
CSC 774 Advanced Network Security Topic 2.6 ID Based Cryptography #2 Slides by An Liu Outline Applications Elliptic Curve Group over real number and F p Weil Pairing BasicIdent FullIdent Extensions Escrow
TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITEIT EINDHOVEN Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Friday 25 January 2019
 Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Friday 25 January 2019 Name : TU/e student number : Exercise 1 2 3 4 5 total points Notes: Please hand in all sheets at the end of the exam.
Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Friday 25 January 2019 Name : TU/e student number : Exercise 1 2 3 4 5 total points Notes: Please hand in all sheets at the end of the exam.
Tightly-Secure Signatures From Lossy Identification Schemes
 Tightly-Secure Signatures From Lossy Identification Schemes Michel Abdalla, Pierre-Alain Fouque, Vadim Lyubashevsky, and Mehdi Tibouchi 2 École normale supérieure {michel.abdalla,pierre-alain.fouque,vadim.lyubashevsky}@ens.fr
Tightly-Secure Signatures From Lossy Identification Schemes Michel Abdalla, Pierre-Alain Fouque, Vadim Lyubashevsky, and Mehdi Tibouchi 2 École normale supérieure {michel.abdalla,pierre-alain.fouque,vadim.lyubashevsky}@ens.fr
Practice Final Exam Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017
 Practice Final Exam Name: Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total
Practice Final Exam Name: Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total
AN OBSERVATION ABOUT VARIATIONS OF THE DIFFIE-HELLMAN ASSUMPTION
 AN OBSERVATION ABOUT VARIATIONS OF THE DIFFIE-HELLMAN ASSUMPTION R. BHASKAR, K. CHANDRASEKARAN, S. LOKAM, P.L. MONTGOMERY, R. VENKATESAN, AND Y. YACOBI Abstract. We generalize the Strong Boneh-Boyen (SBB)
AN OBSERVATION ABOUT VARIATIONS OF THE DIFFIE-HELLMAN ASSUMPTION R. BHASKAR, K. CHANDRASEKARAN, S. LOKAM, P.L. MONTGOMERY, R. VENKATESAN, AND Y. YACOBI Abstract. We generalize the Strong Boneh-Boyen (SBB)
Anonymous Proxy Signature with Restricted Traceability
 Anonymous Proxy Signature with Restricted Traceability Jiannan Wei Joined work with Guomin Yang and Yi Mu University of Wollongong Outline Introduction Motivation and Potential Solutions Anonymous Proxy
Anonymous Proxy Signature with Restricted Traceability Jiannan Wei Joined work with Guomin Yang and Yi Mu University of Wollongong Outline Introduction Motivation and Potential Solutions Anonymous Proxy
ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION
 ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION 1 / 1 Recommended Book Steven Levy. Crypto. Penguin books. 2001. A non-technical account of the history of public-key cryptography and the colorful characters involved. 2 / 1 Recall
ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION 1 / 1 Recommended Book Steven Levy. Crypto. Penguin books. 2001. A non-technical account of the history of public-key cryptography and the colorful characters involved. 2 / 1 Recall
Digital Signatures. p1.
 Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
Searchable encryption & Anonymous encryption
 Searchable encryption & Anonymous encryption Michel Abdalla ENS & CNS February 17, 2014 MPI - Course 2-12-1 Michel Abdalla (ENS & CNS) Searchable encryption & Anonymous encryption February 17, 2014 1 /
Searchable encryption & Anonymous encryption Michel Abdalla ENS & CNS February 17, 2014 MPI - Course 2-12-1 Michel Abdalla (ENS & CNS) Searchable encryption & Anonymous encryption February 17, 2014 1 /
A Verifiable Random Function With Short Proofs and Keys
 A Verifiable Random Function With Short Proofs and Keys Yevgeniy Dodis and Aleksandr Yampolskiy Abstract. We give a simple and efficient construction of a verifiable random function (VRF) on bilinear groups.
A Verifiable Random Function With Short Proofs and Keys Yevgeniy Dodis and Aleksandr Yampolskiy Abstract. We give a simple and efficient construction of a verifiable random function (VRF) on bilinear groups.
An Efficient ID-based Digital Signature with Message Recovery Based on Pairing
 An Efficient ID-based Digital Signature with Message Recovery Based on Pairing Raylin Tso, Chunxiang Gu, Takeshi Okamoto, and Eiji Okamoto Department of Risk Engineering Graduate School of Systems and
An Efficient ID-based Digital Signature with Message Recovery Based on Pairing Raylin Tso, Chunxiang Gu, Takeshi Okamoto, and Eiji Okamoto Department of Risk Engineering Graduate School of Systems and
II. Digital signatures
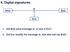 II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
Public-Key Cryptography. Lecture 9 Public-Key Encryption Diffie-Hellman Key-Exchange
 Public-Key Cryptography Lecture 9 Public-Key Encryption Diffie-Hellman Key-Exchange Shared/Symmetric-Key Encryption (a.k.a. private-key encryption) SKE: Syntax KeyGen outputs K K E scheme E Syntax a.k.a.
Public-Key Cryptography Lecture 9 Public-Key Encryption Diffie-Hellman Key-Exchange Shared/Symmetric-Key Encryption (a.k.a. private-key encryption) SKE: Syntax KeyGen outputs K K E scheme E Syntax a.k.a.
Tight Proofs for Signature Schemes without Random Oracles
 Tight Proofs for Signature Schemes without Random Oracles Sven Schäge Horst Görtz Institute for IT-Security Ruhr-University of Bochum sven.schaege@rub.de Abstract. We present the first tight security proofs
Tight Proofs for Signature Schemes without Random Oracles Sven Schäge Horst Görtz Institute for IT-Security Ruhr-University of Bochum sven.schaege@rub.de Abstract. We present the first tight security proofs
Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures
 Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures Zhou Sujing Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, zhousujing@pmail.ntu.edu.sg Abstract. Transitive signature, motivated by signing
Transitive Signatures Based on Non-adaptive Standard Signatures Zhou Sujing Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, zhousujing@pmail.ntu.edu.sg Abstract. Transitive signature, motivated by signing
VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic
 VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic - as already seen signatures can be used and are used in practice to design identification protocols - next we show how we can obtain signatures schemes from - protocols using
VI. The Fiat-Shamir Heuristic - as already seen signatures can be used and are used in practice to design identification protocols - next we show how we can obtain signatures schemes from - protocols using
Short Group Signatures with Efficient Flexible Join
 All rights are reserved and copyright of this manuscript belongs to the authors. This manuscript has been published without reviewing and editing as received from the authors: posting the manuscript to
All rights are reserved and copyright of this manuscript belongs to the authors. This manuscript has been published without reviewing and editing as received from the authors: posting the manuscript to
CONSTRUCTIONS SECURE AGAINST RECEIVER SELECTIVE OPENING AND CHOSEN CIPHERTEXT ATTACKS
 CONSRUCIONS SECURE AGAINS RECEIVER SELECIVE OPENING AND CHOSEN CIPHEREX AACKS Dingding Jia, Xianhui Lu, Bao Li jiadingding@iie.ac.cn C-RSA 2017 02-17 Outline Background Motivation Our contribution Existence:
CONSRUCIONS SECURE AGAINS RECEIVER SELECIVE OPENING AND CHOSEN CIPHEREX AACKS Dingding Jia, Xianhui Lu, Bao Li jiadingding@iie.ac.cn C-RSA 2017 02-17 Outline Background Motivation Our contribution Existence:
ID-based Encryption Scheme Secure against Chosen Ciphertext Attacks
 ID-based Encryption Scheme Secure against Chosen Ciphertext Attacks ongxing Lu and Zhenfu Cao Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200030, P.. China {cao-zf,
ID-based Encryption Scheme Secure against Chosen Ciphertext Attacks ongxing Lu and Zhenfu Cao Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200030, P.. China {cao-zf,
SIS-based Signatures
 Lattices and Homomorphic Encryption, Spring 2013 Instructors: Shai Halevi, Tal Malkin February 26, 2013 Basics We will use the following parameters: n, the security parameter. =poly(n). m 2n log s 2 n
Lattices and Homomorphic Encryption, Spring 2013 Instructors: Shai Halevi, Tal Malkin February 26, 2013 Basics We will use the following parameters: n, the security parameter. =poly(n). m 2n log s 2 n
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited
 From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
Secure and Practical Identity-Based Encryption
 Secure and Practical Identity-Based Encryption David Naccache Groupe de Cyptographie, Deṕartement d Informatique École Normale Supérieure 45 rue d Ulm, 75005 Paris, France david.nacache@ens.fr Abstract.
Secure and Practical Identity-Based Encryption David Naccache Groupe de Cyptographie, Deṕartement d Informatique École Normale Supérieure 45 rue d Ulm, 75005 Paris, France david.nacache@ens.fr Abstract.
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 10/3/16. Lecture 9 RSA Encryption and Diffie-Helmann Key Exchange
 ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 10/3/16 Lecture 9 RSA Encryption and Diffie-Helmann Key Exchange Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 10/3/16 Lecture 9 RSA Encryption and Diffie-Helmann Key Exchange Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
Cryptography IV: Asymmetric Ciphers
 Cryptography IV: Asymmetric Ciphers Computer Security Lecture 7 David Aspinall School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 31st January 2011 Outline Background RSA Diffie-Hellman ElGamal Summary Outline
Cryptography IV: Asymmetric Ciphers Computer Security Lecture 7 David Aspinall School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 31st January 2011 Outline Background RSA Diffie-Hellman ElGamal Summary Outline
Week : Public Key Cryptosystem and Digital Signatures
 Week 10-11 : Public Key Cryptosystem and Digital Signatures 1. Public Key Encryptions RSA, ElGamal, 2 RSA- PKC(1/3) 1st public key cryptosystem R.L.Rivest, A.Shamir, L.Adleman, A Method for Obtaining Digital
Week 10-11 : Public Key Cryptosystem and Digital Signatures 1. Public Key Encryptions RSA, ElGamal, 2 RSA- PKC(1/3) 1st public key cryptosystem R.L.Rivest, A.Shamir, L.Adleman, A Method for Obtaining Digital
Realizing Hash-and-Sign Signatures under Standard Assumptions
 Realizing Hash-and-Sign Signatures under Standard Assumptions Susan Hohenberger 1, and Brent Waters 2, 1 Johns Hopkins University, susan@cs.jhu.edu 2 University of Texas at Austin, bwaters@cs.utexas.edu
Realizing Hash-and-Sign Signatures under Standard Assumptions Susan Hohenberger 1, and Brent Waters 2, 1 Johns Hopkins University, susan@cs.jhu.edu 2 University of Texas at Austin, bwaters@cs.utexas.edu
Digital Signatures from Challenge-Divided Σ-Protocols
 Digital Signatures from Challenge-Divided Σ-Protocols Andrew C. Yao Yunlei Zhao Abstract Digital signature is one of the basic primitives in cryptography. A common paradigm of obtaining signatures, known
Digital Signatures from Challenge-Divided Σ-Protocols Andrew C. Yao Yunlei Zhao Abstract Digital signature is one of the basic primitives in cryptography. A common paradigm of obtaining signatures, known
A Second Look at s Transforma3on
 A Second Look at s Transforma3on - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Özgür Dagdelen Technische Universität Darmstadt Daniele Venturi Sapienza University
A Second Look at s Transforma3on - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Özgür Dagdelen Technische Universität Darmstadt Daniele Venturi Sapienza University
A Strong Identity Based Key-Insulated Cryptosystem
 A Strong Identity Based Key-Insulated Cryptosystem Jin Li 1, Fangguo Zhang 2,3, and Yanming Wang 1,4 1 School of Mathematics and Computational Science, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510275, P.R.China
A Strong Identity Based Key-Insulated Cryptosystem Jin Li 1, Fangguo Zhang 2,3, and Yanming Wang 1,4 1 School of Mathematics and Computational Science, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510275, P.R.China
CS 4770: Cryptography. CS 6750: Cryptography and Communication Security. Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University
 CS 4770: Cryptography CS 6750: Cryptography and Communication Security Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University March 26 2017 Outline RSA encryption in practice Transform RSA trapdoor
CS 4770: Cryptography CS 6750: Cryptography and Communication Security Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University March 26 2017 Outline RSA encryption in practice Transform RSA trapdoor
Bilinear maps in Verifiable Random Functions
 Bilinear maps in Verifiable Random Functions Ananth Raghunathan ananthr@stanford.edu Stanford University Abstract One of the biggest reasons for the popularity and versatility of elliptic curves in cryptography,
Bilinear maps in Verifiable Random Functions Ananth Raghunathan ananthr@stanford.edu Stanford University Abstract One of the biggest reasons for the popularity and versatility of elliptic curves in cryptography,
A Novel Strong Designated Verifier Signature Scheme without Random Oracles
 1 A Novel Strong Designated Verifier Signature Scheme without Random Oracles Maryam Rajabzadeh Asaar 1, Mahmoud Salmasizadeh 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, 2 Electronics Research Institute (Center),
1 A Novel Strong Designated Verifier Signature Scheme without Random Oracles Maryam Rajabzadeh Asaar 1, Mahmoud Salmasizadeh 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, 2 Electronics Research Institute (Center),
Short Signature Scheme From Bilinear Pairings
 Sedat Akleylek, Barış Bülent Kırlar, Ömer Sever, and Zaliha Yüce Institute of Applied Mathematics, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey {akleylek,kirlar}@metu.edu.tr,severomer@yahoo.com,zyuce@stm.com.tr
Sedat Akleylek, Barış Bülent Kırlar, Ömer Sever, and Zaliha Yüce Institute of Applied Mathematics, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey {akleylek,kirlar}@metu.edu.tr,severomer@yahoo.com,zyuce@stm.com.tr
RSA-OAEP and Cramer-Shoup
 RSA-OAEP and Cramer-Shoup Olli Ahonen Laboratory of Physics, TKK 11th Dec 2007 T-79.5502 Advanced Cryptology Part I: Outline RSA, OAEP and RSA-OAEP Preliminaries for the proof Proof of IND-CCA2 security
RSA-OAEP and Cramer-Shoup Olli Ahonen Laboratory of Physics, TKK 11th Dec 2007 T-79.5502 Advanced Cryptology Part I: Outline RSA, OAEP and RSA-OAEP Preliminaries for the proof Proof of IND-CCA2 security
Realizing Hash-and-Sign Signatures under Standard Assumptions
 Realizing Hash-and-Sign Signatures under Standard Assumptions Susan Hohenberger Johns Hopkins University Brent Waters University of Texas at Austin June 14, 2009 Abstract Currently, there are relatively
Realizing Hash-and-Sign Signatures under Standard Assumptions Susan Hohenberger Johns Hopkins University Brent Waters University of Texas at Austin June 14, 2009 Abstract Currently, there are relatively
EXAM IN. TDA352 (Chalmers) - DIT250 (GU) 12 January 2018, 08:
 CHALMERS GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM IN CRYPTOGRAPHY TDA352 (Chalmers) - DIT250 (GU) 12 January 2018, 08:30 12.30 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Typgodkänd räknare. Annan minnestömd räknare får användas efter godkännande
CHALMERS GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM IN CRYPTOGRAPHY TDA352 (Chalmers) - DIT250 (GU) 12 January 2018, 08:30 12.30 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Typgodkänd räknare. Annan minnestömd räknare får användas efter godkännande
Hash-based Signatures. Andreas Hülsing
 Hash-based Signatures Andreas Hülsing Post-Quantum Signatures Lattice, MQ, Coding Signature and/or key sizes Runtimes Secure parameters 23-2-2016 PAGE 2... 1 3 1 4 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 1 y x x x x
Hash-based Signatures Andreas Hülsing Post-Quantum Signatures Lattice, MQ, Coding Signature and/or key sizes Runtimes Secure parameters 23-2-2016 PAGE 2... 1 3 1 4 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 1 y x x x x
Q B (pk, sk) Gen x u M pk y Map pk (x) return [B(pk, y)? = x]. (m, s) A O h
![Q B (pk, sk) Gen x u M pk y Map pk (x) return [B(pk, y)? = x]. (m, s) A O h Q B (pk, sk) Gen x u M pk y Map pk (x) return [B(pk, y)? = x]. (m, s) A O h](/thumbs/89/100584859.jpg) MTAT.07.003 Cryptology II Spring 2012 / Exercise session?? / Example Solution Exercise (FRH in RO model). Show that the full domain hash signature is secure against existential forgeries in the random
MTAT.07.003 Cryptology II Spring 2012 / Exercise session?? / Example Solution Exercise (FRH in RO model). Show that the full domain hash signature is secure against existential forgeries in the random
Short Signatures from Diffie-Hellman, Revisited: Sublinear Public Key, CMA Security, and Tighter Reduction
 Short Signatures from Diffie-Hellman, Revisited: Sublinear Public Key, CMA Security, and Tighter Reduction Jae Hong Seo Myongji University jaehongseo@mju.ac.kr Abstract. Designing efficient signature scheme
Short Signatures from Diffie-Hellman, Revisited: Sublinear Public Key, CMA Security, and Tighter Reduction Jae Hong Seo Myongji University jaehongseo@mju.ac.kr Abstract. Designing efficient signature scheme
G Advanced Cryptography April 10th, Lecture 11
 G.30-001 Advanced Cryptography April 10th, 007 Lecturer: Victor Shoup Lecture 11 Scribe: Kristiyan Haralambiev We continue the discussion of public key encryption. Last time, we studied Hash Proof Systems
G.30-001 Advanced Cryptography April 10th, 007 Lecturer: Victor Shoup Lecture 11 Scribe: Kristiyan Haralambiev We continue the discussion of public key encryption. Last time, we studied Hash Proof Systems
Fully Anonymous Group Signatures without Random Oracles
 Fully Anonymous Group Signatures without Random Oracles Jens Groth University College London j.groth@ucl.ac.uk March 25, 2013 Abstract We construct a new group signature scheme using bilinear groups. The
Fully Anonymous Group Signatures without Random Oracles Jens Groth University College London j.groth@ucl.ac.uk March 25, 2013 Abstract We construct a new group signature scheme using bilinear groups. The
Fully Anonymous Group Signatures without Random Oracles
 Fully Anonymous Group Signatures without Random Oracles Jens Groth University College London E-mail: j.groth@ucl.ac.uk September 7, 2007 Abstract We construct a new group signature scheme using bilinear
Fully Anonymous Group Signatures without Random Oracles Jens Groth University College London E-mail: j.groth@ucl.ac.uk September 7, 2007 Abstract We construct a new group signature scheme using bilinear
TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITEIT EINDHOVEN Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Tuesday 30 October 2018
 Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Tuesday 30 October 2018 Name : TU/e student number : Exercise 1 2 3 4 5 total points Notes: Please hand in all sheets at the end of the exam.
Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science Exam Cryptology, Tuesday 30 October 2018 Name : TU/e student number : Exercise 1 2 3 4 5 total points Notes: Please hand in all sheets at the end of the exam.
A Pairing-Based DAA Scheme Further Reducing TPM Resources
 A Pairing-Based DAA Scheme Further Reducing TPM Resources Ernie Brickell Intel Corporation ernie.brickell@intel.com Jiangtao Li Intel Labs jiangtao.li@intel.com Abstract Direct Anonymous Attestation (DAA)
A Pairing-Based DAA Scheme Further Reducing TPM Resources Ernie Brickell Intel Corporation ernie.brickell@intel.com Jiangtao Li Intel Labs jiangtao.li@intel.com Abstract Direct Anonymous Attestation (DAA)
Foundations of Cryptography
 - 111 - Foundations of Cryptography Notes of lecture No. 10B & 11 (given on June 11 & 18, 1989) taken by Sergio Rajsbaum Summary In this lecture we define unforgeable digital signatures and present such
- 111 - Foundations of Cryptography Notes of lecture No. 10B & 11 (given on June 11 & 18, 1989) taken by Sergio Rajsbaum Summary In this lecture we define unforgeable digital signatures and present such
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes
 From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Provable security. Michel Abdalla
 Lecture 1: Provable security Michel Abdalla École normale supérieure & CNRS Cryptography Main goal: Enable secure communication in the presence of adversaries Adversary Sender 10110 10110 Receiver Only
Lecture 1: Provable security Michel Abdalla École normale supérieure & CNRS Cryptography Main goal: Enable secure communication in the presence of adversaries Adversary Sender 10110 10110 Receiver Only
Policy-based Signatures for Predicates
 International Journal of Network Security, Vol.19, No.5, PP.811-822, Sept. 2017 (DOI: 10.6633/IJNS.201709.19(5).19) 811 Policy-based Signatures for Predicates Fei Tang, Yousheng Zhou (Corresponding authors:
International Journal of Network Security, Vol.19, No.5, PP.811-822, Sept. 2017 (DOI: 10.6633/IJNS.201709.19(5).19) 811 Policy-based Signatures for Predicates Fei Tang, Yousheng Zhou (Corresponding authors:
How to Use Linear Homomorphic Signature in Network Coding
 How to Use Linear Homomorphic Signature in Network Coding Li Chen lichen.xd at gmail.com Xidian University September 28, 2013 How to Use Linear Homomorphic Signature in Network Coding Outline 1 Linear
How to Use Linear Homomorphic Signature in Network Coding Li Chen lichen.xd at gmail.com Xidian University September 28, 2013 How to Use Linear Homomorphic Signature in Network Coding Outline 1 Linear
Foundations. P =! NP oneway function signature schemes Trapdoor oneway function PKC, IBS IBE
 Foundations P =! NP oneway function signature schemes Trapdoor oneway function PKC, IBS IBE NP problems: IF, DL, Knapsack Hardness of these problems implies the security of cryptosytems? 2 Relations of
Foundations P =! NP oneway function signature schemes Trapdoor oneway function PKC, IBS IBE NP problems: IF, DL, Knapsack Hardness of these problems implies the security of cryptosytems? 2 Relations of
Identification Schemes of Proofs of Ability Secure against Concurrent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
 Identification Schemes of Proofs of Ability Secure against Concurrent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Hiroaki Anada and Seiko Arita Institute of Information Security, Yokohama, Japan hiroaki.anada@gmail.com,
Identification Schemes of Proofs of Ability Secure against Concurrent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Hiroaki Anada and Seiko Arita Institute of Information Security, Yokohama, Japan hiroaki.anada@gmail.com,
Privacy-enhanced Designated Confirmer Signature without Random Oracles
 International Journal of Network Security, Vol.16, No.4, PP.261-269, July 2014 261 Privacy-enhanced Designated Confirmer Signature without Random Oracles Shengke Zeng 1,2 and Hu Xiong 1 (Corresponding
International Journal of Network Security, Vol.16, No.4, PP.261-269, July 2014 261 Privacy-enhanced Designated Confirmer Signature without Random Oracles Shengke Zeng 1,2 and Hu Xiong 1 (Corresponding
Digital signature schemes
 Digital signature schemes Martin Stanek Department of Computer Science Comenius University stanek@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Cryptology 1 (2017/18) Content Introduction digital signature scheme security of digital
Digital signature schemes Martin Stanek Department of Computer Science Comenius University stanek@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Cryptology 1 (2017/18) Content Introduction digital signature scheme security of digital
Public-Key Cryptography. Lecture 10 DDH Assumption El Gamal Encryption Public-Key Encryption from Trapdoor OWP
 Public-Key Cryptography Lecture 10 DDH Assumption El Gamal Encryption Public-Key Encryption from Trapdoor OWP Diffie-Hellman Key-exchange Secure under DDH: (g x,g x,g xy ) (g x,g x,g r ) Random x {0,..,
Public-Key Cryptography Lecture 10 DDH Assumption El Gamal Encryption Public-Key Encryption from Trapdoor OWP Diffie-Hellman Key-exchange Secure under DDH: (g x,g x,g xy ) (g x,g x,g r ) Random x {0,..,
REMARKS ON IBE SCHEME OF WANG AND CAO
 REMARKS ON IBE SCEME OF WANG AND CAO Sunder Lal and Priyam Sharma Derpartment of Mathematics, Dr. B.R.A.(Agra), University, Agra-800(UP), India. E-mail- sunder_lal@rediffmail.com, priyam_sharma.ibs@rediffmail.com
REMARKS ON IBE SCEME OF WANG AND CAO Sunder Lal and Priyam Sharma Derpartment of Mathematics, Dr. B.R.A.(Agra), University, Agra-800(UP), India. E-mail- sunder_lal@rediffmail.com, priyam_sharma.ibs@rediffmail.com
Short signatures from the Weil pairing
 Short signatures from the Weil pairing Dan Boneh, Ben Lynn, and Hovav Shacham Computer Science Department, Stanford University {dabo,blynn,hovav}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract. We introduce a short signature
Short signatures from the Weil pairing Dan Boneh, Ben Lynn, and Hovav Shacham Computer Science Department, Stanford University {dabo,blynn,hovav}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract. We introduce a short signature
