Multi-key Hierarchical Identity-Based Signatures
|
|
|
- Gyles Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Multi-key Hierarchical Identity-Based Signatures Hoon Wei Lim Nanyang Technological University 9 June 2010
2 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Preliminaries 3 Multi-key HIBS 4 Security Analysis 5 Discussion 6 Open Problems 2/ 30
3 Introduction Motivating examples Role-based access control: Role signatures based on hierarchical identity-based signatures (HIBS): using signing keys associated with role identifiers; hierarchical namespace. Let Alice have roles r 1 =lecturer, r 2 = professor and r 3 = IEEE member. If Alice wants to access some restricted documents using roles r 1 and r 3 : principle of least privilege; then she signs a request using the corresponding private keys. 3/ 30
4 Introduction Motivating examples Level 0 Level 1 Level 2 TA Uni 1 Uni2 r 2 r 3 r 2 r 4 r 1 4/ 30
5 Introduction Motivating examples Mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs): Use of identity-based cryptography is attractive: avoids certificate management; meets low bandwidth requirement. Nodes may be compromised or unavailable: so it is desirable to distribute the function of a trusted authority (TA) across multiple nodes. Nodes can obtain multiple private keys from multiple TAs: private keys are then aggregated when used for signing. 5/ 30
6 Introduction Motivating examples Level 0 Level 1 Level 2 Root TA TA 1 TA 2 TA3 6/ 30
7 Introduction Multi-key HIBS Question to be answered: How do we efficiently and securely aggregate a set of private keys when signing a message? The essence of our new primitive, i.e. multi-key signatures: based on hierarchical identity-based cryptography; user owns multiple identifiers and thus possesses a set of corresponding private keys; a single signature is produced using a combination of multiple private keys on a selected message; identifiers may be located at arbitrary positions in the hierarchy. 7/ 30
8 Introduction Related concepts Identity-based multi-signatures [Gentry-Ramzan 06, Bellare-Neven 07]: a set of users all sign the same message; non-interactive and interactive. Identity-based aggregate signatures [Gentry-Ramzan 06]: a set of users each signs a different message; non-interactive (but requires coordination of state). Identity-based threshold signatures [Baek-Zheng 04]: t (threshold) out of n parties first compute individual shares, which are then combined into a single signature; interactive. Differences from multi-key HIBS: efficiency, security, flexibility. 8/ 30
9 Introduction Related concepts 9/ 30
10 Preliminaries Pairings Let G and G T be two cyclic groups where G = G T = q, a large prime, then an admissible pairing e : G G G T has properties: Bilinear: Given P, Q, R G 1, we have ê(p, Q + R) = ê(p, Q) ê(p, R) and ê(p + Q, R) = ê(p, R) ê(q, R). Hence, for any a, b Z q, we have ê(ap, bq) = ê(abp, Q) = ê(p, abq) = ê(ap, Q) b = ê(p, Q) ab. non-degeneracy: e(p, P) 1 for some P G. computability: e(p, Q) can be efficiently computed. 10/ 30
11 Preliminaries Assumption Computational Diffie-Hellman (CDH) problem in G: Given P, ap, bp G for some random P G and randomly chosen a,b Z q, compute abp G. 11/ 30
12 Multi-key HIBS Definition Root Setup: It generates the system parameters and a master secret on input a security parameter λ. Lower-level Setup: It picks a secret value to be used to issue private keys to lower-level children. Extract: An entity with identifier ID t = id 1,...,id t computes a private key S t+1 for any of its children with identifier ID t+1 = id 1,...,id t,id t+1. 12/ 30
13 Multi-key HIBS Definition Sign: Given a set SK = {S j t j : 1 j n} of private keys, a message M, and the system parameters, this algorithm outputs a signature σ. Verify: Given a signature σ S, a set ID = {ID j t j : 1 j n} of identifiers, a message M, and the system parameters, this algorithm outputs valid or invalid. Consistency: Verify(Sign(SK, M), ID, M) = valid. 13/ 30
14 Multi-key HIBS Security model Extend the normal HIBS security game [Gentry-Silverberg 02]: Challenger runs Root Setup and adversary A is given the system parameters. A is given access to extract and sign oracles. A outputs a forgery σ, a set of target identifiers ID, and a message M. A wins the game if the following are all true: Verify(σ, ID, M ) = valid; The adversary has not made a sign query on input ID, M ; There exists an identifier ID ID for which the adversary has not made an extract query on ID or any of its ancestors. 14/ 30
15 Multi-key HIBS Security model 15/ 30
16 Multi-key HIBS Construction Main idea: Adaptation of the Gentry-Silverberg HIBS scheme: re-use of the Root Setup, Lower-level Setup and Extract algorithms. When signing: arrange identifiers in lexicographic order; private key components are summed before generating a normal HIBS. For verification: extend the Verify algorithm of the Gentry-Silverberg scheme. 16/ 30
17 Multi-key HIBS Construction Root Setup: The root Private Key Generator (PKG) generates G and G T of prime order q and an admissible pairing e : G G G T on input λ; chooses a generator P 0 G; picks a random value s 0 Z q and sets Q 0 = s 0 P 0 ; selects cryptographic hash functions H 1 : {0, 1} G and H 2 : {0, 1} G; sets the master secret to be s 0 and the system parameters G, G T, e, q, P 0, Q 0, H 1, H 2. Lower-level Setup: A lower-level entity (lower-level PKG or user) at level t 1 picks a random secret s t Z q. 17/ 30
18 Multi-key HIBS Construction Extract: For an entity with identifier ID t = id 1,...,id t, the entity s parent: computes P t = H 1 (ID t ) G; sets S t = t i=1 s i 1P i = S t 1 + s t 1 P t ; defines Q i = s i P 0 for 1 i t 1; private key S t, Q 1,..., Q t 1 is given to the entity by its parent. Note that up to this point, our scheme is identical to the Gentry-Silverberg HIBS scheme. 18/ 30
19 Multi-key HIBS Construction Sign: Given any n 1 and a set SK = { St j j,q j 1,...,Qj t j 1 : 1 j n} of n private keys associated with a set ID = {ID j t j : 1 j n} of identifiers, and a message M, the signer: chooses a secret value s ϕ Z q ; computes P M = H 2 (ID 1 t 1,..., ID n t n, M); calculates n ϕ = St j j + s ϕ P M and Q ϕ = s ϕ P 0 ; j=1 outputs the signature σ = ϕ, Q, Q ϕ, where Q = {Q j i : 1 i t j 1, 1 j n}. 19/ 30
20 Multi-key HIBS Construction Verify: Given σ = ϕ,q,q ϕ, a set of identifiers ID = {ID 1 t 1,...,ID n t n } and a message M, the verifier: computes P j i = H 1 (ID j i ) for 1 i t j and 1 j n; computes P M = H 2 (ID 1 t 1,..., ID n t n, M); checks if e(p 0, ϕ) is equal to t n j e(q j i 1, Pj i ) e(q ϕ, P M ), j=1 i=1 outputting valid if this equation holds, and invalid otherwise. 20/ 30
21 Security Analysis We first look at the security of our multi-key IBS (1-level multi-key HIBS) scheme. Our security proof is in the Random Oracle Model. We extend proof techniques used for the Boneh-Franklin IBE scheme. 21/ 30
22 Security Analysis Theorem Suppose that A is a forger against our multi-key IBS scheme that has success probability ǫ. Then there is an algorithm B which solves the CDH problem in groups G equipped with a pairing, with advantage at least ǫ/(e q H1 q H2 ). 22/ 30
23 Security Analysis Proof techniques: Based on interactions between algorithms A (forger) and B (simulator); B generates the system parameters and embeds an instance of the CDH problem; A submits queries to B; B injects an instance of the CDH problem in one randomly chosen response to a H 1 query: so that A s forgery may help B solve the CDH problem; B controls the relevant oracles and must either respond correctly or abort. 23/ 30
24 Security Analysis Proof techniques for the more complicated multi-key HIBS scheme: Borrow Gentry-Silverberg s simulation techniques for handling H 1 and extract queries in the hierarchical setting: B randomly injects an instance of the CDH problem into responses to H 1 queries. Combine the above techniques with our approach to handling sign queries, and obtain a security reduction. However, so far we have only obtained a security proof for some special cases: constructing a proof for the general case remains an open problem. 24/ 30
25 Discussion Efficiency comparison ADD emul PAI HASH mmul EXP Bellare-Neven IBMS signing n(n + 1) n 2 + n 1 2n verification n 1 n 2 Gentry-Ramzan IBMS signing 3n 2 2n 0 n - - verification n n Multi-key IBS signing n verification n n Main saving signing cost! 25/ 30
26 Discussion Reducing verification cost Our verification algorithm can be optimised in special cases, when identifiers are: at the same level, and have a common parent; at the same level, but have different parents; at different levels, but have a common ancestor; Having common ancestors indicate common Q-values and public keys, thus certain pairing computations can be eliminated. t n j e(p 0,ϕ) = e(q j i 1,Pj i ) e(q ϕ,p M ) j=1 i=1 26/ 30
27 Discussion Extension From hierarchical to workflow signatures: reflecting workflow logical relationships, such as AND-join and AND-split. providing proofs of workflow compliance, reflecting the sequence of task execution and the relevant logical relationships. Modification to the multi-key HIBS scheme: the Extract algorithm may now take as input multiple private keys. 27/ 30
28 Discussion Extension 28/ 30
29 Open Problems Constant size signatures potentially more efficient verification. Instantiation in the standard model. Generalisation of multi-key HIBS to the threshold setting: demonstrate knowledge of a subset of size t of a set of private keys of size n. Construction in the normal (non-identity-based) public key setting: perhaps by adapting the BGLS aggregate signature scheme. 29/ 30
30 Acknowledgement Joint work with Professor Kenny Paterson, Royal Holloway, University of London. Research was funded by the UK EPSRC under grant EP/D051878/1. 30/ 30
Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme
 Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme Kwangsu Lee Dong Hoon Lee Abstract Identity-based signature (IBS) is a specific type of public-key signature (PKS) where any
Security Analysis of an Identity-Based Strongly Unforgeable Signature Scheme Kwangsu Lee Dong Hoon Lee Abstract Identity-based signature (IBS) is a specific type of public-key signature (PKS) where any
ID-based Encryption Scheme Secure against Chosen Ciphertext Attacks
 ID-based Encryption Scheme Secure against Chosen Ciphertext Attacks ongxing Lu and Zhenfu Cao Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200030, P.. China {cao-zf,
ID-based Encryption Scheme Secure against Chosen Ciphertext Attacks ongxing Lu and Zhenfu Cao Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200030, P.. China {cao-zf,
Pairing-Based Cryptography An Introduction
 ECRYPT Summer School Samos 1 Pairing-Based Cryptography An Introduction Kenny Paterson kenny.paterson@rhul.ac.uk May 4th 2007 ECRYPT Summer School Samos 2 The Pairings Explosion Pairings originally used
ECRYPT Summer School Samos 1 Pairing-Based Cryptography An Introduction Kenny Paterson kenny.paterson@rhul.ac.uk May 4th 2007 ECRYPT Summer School Samos 2 The Pairings Explosion Pairings originally used
Efficient Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles
 Efficient Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Abstract We present the first efficient Identity-Based Encryption (IBE) scheme that is fully secure without random oracles. We first
Efficient Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Abstract We present the first efficient Identity-Based Encryption (IBE) scheme that is fully secure without random oracles. We first
Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles
 Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Weiwei Liu School of Computer Science and Software Engineering 1/32 Weiwei Liu Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random
Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random Oracles Brent Waters Weiwei Liu School of Computer Science and Software Engineering 1/32 Weiwei Liu Efficient Identity-based Encryption Without Random
A Strong Identity Based Key-Insulated Cryptosystem
 A Strong Identity Based Key-Insulated Cryptosystem Jin Li 1, Fangguo Zhang 2,3, and Yanming Wang 1,4 1 School of Mathematics and Computational Science, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510275, P.R.China
A Strong Identity Based Key-Insulated Cryptosystem Jin Li 1, Fangguo Zhang 2,3, and Yanming Wang 1,4 1 School of Mathematics and Computational Science, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510275, P.R.China
Short Signatures Without Random Oracles
 Short Signatures Without Random Oracles Dan Boneh and Xavier Boyen (presented by Aleksandr Yampolskiy) Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion Why signatures without
Short Signatures Without Random Oracles Dan Boneh and Xavier Boyen (presented by Aleksandr Yampolskiy) Outline Motivation Preliminaries Secure short signature Extensions Conclusion Why signatures without
Cryptography from Pairings
 DIAMANT/EIDMA Symposium, May 31st/June 1st 2007 1 Cryptography from Pairings Kenny Paterson kenny.paterson@rhul.ac.uk May 31st 2007 DIAMANT/EIDMA Symposium, May 31st/June 1st 2007 2 The Pairings Explosion
DIAMANT/EIDMA Symposium, May 31st/June 1st 2007 1 Cryptography from Pairings Kenny Paterson kenny.paterson@rhul.ac.uk May 31st 2007 DIAMANT/EIDMA Symposium, May 31st/June 1st 2007 2 The Pairings Explosion
Verifiable Security of Boneh-Franklin Identity-Based Encryption. Federico Olmedo Gilles Barthe Santiago Zanella Béguelin
 Verifiable Security of Boneh-Franklin Identity-Based Encryption Federico Olmedo Gilles Barthe Santiago Zanella Béguelin IMDEA Software Institute, Madrid, Spain 5 th International Conference on Provable
Verifiable Security of Boneh-Franklin Identity-Based Encryption Federico Olmedo Gilles Barthe Santiago Zanella Béguelin IMDEA Software Institute, Madrid, Spain 5 th International Conference on Provable
Remove Key Escrow from The Identity-Based Encryption System
 Remove Key Escrow from The Identity-Based Encryption System Zhaohui Cheng, Richard Comley and Luminita Vasiu School of Computing Science, Middlesex University, White Hart Lane, London N17 8HR, UK. {m.z.cheng,r.comley,l.vasiu}@mdx.ac.uk
Remove Key Escrow from The Identity-Based Encryption System Zhaohui Cheng, Richard Comley and Luminita Vasiu School of Computing Science, Middlesex University, White Hart Lane, London N17 8HR, UK. {m.z.cheng,r.comley,l.vasiu}@mdx.ac.uk
Security Analysis of Some Batch Verifying Signatures from Pairings
 International Journal of Network Security, Vol.3, No.2, PP.138 143, Sept. 2006 (http://ijns.nchu.edu.tw/) 138 Security Analysis of Some Batch Verifying Signatures from Pairings Tianjie Cao 1,2,3, Dongdai
International Journal of Network Security, Vol.3, No.2, PP.138 143, Sept. 2006 (http://ijns.nchu.edu.tw/) 138 Security Analysis of Some Batch Verifying Signatures from Pairings Tianjie Cao 1,2,3, Dongdai
Lecture 7: Boneh-Boyen Proof & Waters IBE System
 CS395T Advanced Cryptography 2/0/2009 Lecture 7: Boneh-Boyen Proof & Waters IBE System Instructor: Brent Waters Scribe: Ioannis Rouselakis Review Last lecture we discussed about the Boneh-Boyen IBE system,
CS395T Advanced Cryptography 2/0/2009 Lecture 7: Boneh-Boyen Proof & Waters IBE System Instructor: Brent Waters Scribe: Ioannis Rouselakis Review Last lecture we discussed about the Boneh-Boyen IBE system,
A Security Proof of KCDSA using an extended Random Oracle Model
 A Security Proof of KCDSA using an extended Random Oracle Model Vikram Singh Abstract We describe a tight security reduction to the discrete logarithm problem for KCDSA under an extended Random Oracle
A Security Proof of KCDSA using an extended Random Oracle Model Vikram Singh Abstract We describe a tight security reduction to the discrete logarithm problem for KCDSA under an extended Random Oracle
Recent Advances in Identity-based Encryption Pairing-based Constructions
 Fields Institute Workshop on New Directions in Cryptography 1 Recent Advances in Identity-based Encryption Pairing-based Constructions Kenny Paterson kenny.paterson@rhul.ac.uk June 25th 2008 Fields Institute
Fields Institute Workshop on New Directions in Cryptography 1 Recent Advances in Identity-based Encryption Pairing-based Constructions Kenny Paterson kenny.paterson@rhul.ac.uk June 25th 2008 Fields Institute
An Efficient ID-based Digital Signature with Message Recovery Based on Pairing
 An Efficient ID-based Digital Signature with Message Recovery Based on Pairing Raylin Tso, Chunxiang Gu, Takeshi Okamoto, and Eiji Okamoto Department of Risk Engineering Graduate School of Systems and
An Efficient ID-based Digital Signature with Message Recovery Based on Pairing Raylin Tso, Chunxiang Gu, Takeshi Okamoto, and Eiji Okamoto Department of Risk Engineering Graduate School of Systems and
Outline. The Game-based Methodology for Computational Security Proofs. Public-Key Cryptography. Outline. Introduction Provable Security
 The Game-based Methodology for Computational s David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA Computational and Symbolic Proofs of Security Atagawa Heights Japan April 6th, 2009 1/39 2/39 Public-Key
The Game-based Methodology for Computational s David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA Computational and Symbolic Proofs of Security Atagawa Heights Japan April 6th, 2009 1/39 2/39 Public-Key
An Introduction to Pairings in Cryptography
 An Introduction to Pairings in Cryptography Craig Costello Information Security Institute Queensland University of Technology INN652 - Advanced Cryptology, October 2009 Outline 1 Introduction to Pairings
An Introduction to Pairings in Cryptography Craig Costello Information Security Institute Queensland University of Technology INN652 - Advanced Cryptology, October 2009 Outline 1 Introduction to Pairings
One-Round ID-Based Blind Signature Scheme without ROS Assumption
 One-Round ID-Based Blind Signature Scheme without ROS Assumption Wei Gao 1, Xueli Wang 2, Guilin Wang 3, and Fei Li 4 1 College of Mathematics and Econometrics, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
One-Round ID-Based Blind Signature Scheme without ROS Assumption Wei Gao 1, Xueli Wang 2, Guilin Wang 3, and Fei Li 4 1 College of Mathematics and Econometrics, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
Secure Certificateless Public Key Encryption without Redundancy
 Secure Certificateless Public Key Encryption without Redundancy Yinxia Sun and Futai Zhang School of Mathematics and Computer Science Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210097, P.R.China Abstract. Certificateless
Secure Certificateless Public Key Encryption without Redundancy Yinxia Sun and Futai Zhang School of Mathematics and Computer Science Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210097, P.R.China Abstract. Certificateless
Cryptanalysis and improvement of an ID-based ad-hoc anonymous identification scheme at CT-RSA 05
 Cryptanalysis and improvement of an ID-based ad-hoc anonymous identification scheme at CT-RSA 05 Fangguo Zhang 1 and Xiaofeng Chen 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Sun Yat-sen
Cryptanalysis and improvement of an ID-based ad-hoc anonymous identification scheme at CT-RSA 05 Fangguo Zhang 1 and Xiaofeng Chen 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Sun Yat-sen
Identity-Based Aggregate Signatures
 Identity-Based Aggregate Signatures Craig Gentry 1, and Zulfikar Ramzan 2 1 Stanford University cgentry@cs.stanford.edu 2 DoCoMo Communications Laboratories USA, Inc. ramzan@docomolabs-usa.com Abstract.
Identity-Based Aggregate Signatures Craig Gentry 1, and Zulfikar Ramzan 2 1 Stanford University cgentry@cs.stanford.edu 2 DoCoMo Communications Laboratories USA, Inc. ramzan@docomolabs-usa.com Abstract.
REMARKS ON IBE SCHEME OF WANG AND CAO
 REMARKS ON IBE SCEME OF WANG AND CAO Sunder Lal and Priyam Sharma Derpartment of Mathematics, Dr. B.R.A.(Agra), University, Agra-800(UP), India. E-mail- sunder_lal@rediffmail.com, priyam_sharma.ibs@rediffmail.com
REMARKS ON IBE SCEME OF WANG AND CAO Sunder Lal and Priyam Sharma Derpartment of Mathematics, Dr. B.R.A.(Agra), University, Agra-800(UP), India. E-mail- sunder_lal@rediffmail.com, priyam_sharma.ibs@rediffmail.com
Identity Based Deterministic Signature Scheme Without Forking-Lemma
 Identity Based Deterministic ignature cheme Without Forking-Lemma. harmila Deva elvi,. ree Vivek, C. Pandu Rangan Theoretical Computer cience Laboratory, Department of Computer cience and Engineering,
Identity Based Deterministic ignature cheme Without Forking-Lemma. harmila Deva elvi,. ree Vivek, C. Pandu Rangan Theoretical Computer cience Laboratory, Department of Computer cience and Engineering,
Pairing-Based Cryptographic Protocols : A Survey
 Pairing-Based Cryptographic Protocols : A Survey Ratna Dutta, Rana Barua and Palash Sarkar Cryptology Research Group Stat-Math and Applied Statistics Unit 203, B. T. Road, Kolkata India 700108 e-mail :{ratna
Pairing-Based Cryptographic Protocols : A Survey Ratna Dutta, Rana Barua and Palash Sarkar Cryptology Research Group Stat-Math and Applied Statistics Unit 203, B. T. Road, Kolkata India 700108 e-mail :{ratna
Applied cryptography
 Applied cryptography Identity-based Cryptography Andreas Hülsing 19 November 2015 1 / 37 The public key problem How to obtain the correct public key of a user? How to check its authenticity? General answer:
Applied cryptography Identity-based Cryptography Andreas Hülsing 19 November 2015 1 / 37 The public key problem How to obtain the correct public key of a user? How to check its authenticity? General answer:
Identity-based encryption
 Identity-based encryption Michel Abdalla ENS & CNRS MPRI - Course 2-12-1 Michel Abdalla (ENS & CNRS) Identity-based encryption 1 / 43 Identity-based encryption (IBE) Goal: Allow senders to encrypt messages
Identity-based encryption Michel Abdalla ENS & CNRS MPRI - Course 2-12-1 Michel Abdalla (ENS & CNRS) Identity-based encryption 1 / 43 Identity-based encryption (IBE) Goal: Allow senders to encrypt messages
CSC 774 Advanced Network Security
 CSC 774 Advanced Network Security Topic 2.6 ID Based Cryptography #2 Slides by An Liu Outline Applications Elliptic Curve Group over real number and F p Weil Pairing BasicIdent FullIdent Extensions Escrow
CSC 774 Advanced Network Security Topic 2.6 ID Based Cryptography #2 Slides by An Liu Outline Applications Elliptic Curve Group over real number and F p Weil Pairing BasicIdent FullIdent Extensions Escrow
CSC 774 Advanced Network Security
 CSC 774 Advanced Network Security Topic 2.6 ID Based Cryptography #2 Slides by An Liu Outline Applications Elliptic Curve Group over real number and F p Weil Pairing BasicIdent FullIdent Extensions Escrow
CSC 774 Advanced Network Security Topic 2.6 ID Based Cryptography #2 Slides by An Liu Outline Applications Elliptic Curve Group over real number and F p Weil Pairing BasicIdent FullIdent Extensions Escrow
Generic construction of (identity-based) perfect concurrent signatures
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Informatics - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2005 Generic construction of (identity-based) perfect concurrent signatures
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Informatics - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2005 Generic construction of (identity-based) perfect concurrent signatures
Practical Hierarchical Identity Based Encryption and Signature schemes Without Random Oracles
 Practical Hierarchical Identity Based Encryption and Signature schemes Without Random Oracles Man Ho Au 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, Tsz Hon Yuen 3, and Duncan S. Wong 4 1 Centre for Information Security Research
Practical Hierarchical Identity Based Encryption and Signature schemes Without Random Oracles Man Ho Au 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, Tsz Hon Yuen 3, and Duncan S. Wong 4 1 Centre for Information Security Research
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes
 Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
Constructing Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signature Schemes Chethan Kamath Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 23, 2013 Overview Table of contents Background Formal Definitions Schnorr Signature
Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman
 Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman Dan Boneh 1, Emily Shen 1, and Brent Waters 2 1 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA {dabo,emily}@cs.stanford.edu
Strongly Unforgeable Signatures Based on Computational Diffie-Hellman Dan Boneh 1, Emily Shen 1, and Brent Waters 2 1 Computer Science Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA {dabo,emily}@cs.stanford.edu
Identity-Based Online/Offline Encryption
 Fuchun Guo 2 Yi Mu 1 Zhide Chen 2 1 University of Wollongong, Australia ymu@uow.edu.au 2 Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China fuchunguo1982@gmail.com Outline 1 2 3 4 Identity-based Encryption Review
Fuchun Guo 2 Yi Mu 1 Zhide Chen 2 1 University of Wollongong, Australia ymu@uow.edu.au 2 Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China fuchunguo1982@gmail.com Outline 1 2 3 4 Identity-based Encryption Review
An ID-based Server-aided Verification Short Signature Scheme Avoid Key Escrow
 An ID-based Server-aided Verification Short Signature Scheme Avoid Key Escrow Jianhong Zhang 1,2 and Zhibin Sun 1 1 College of Science, North China University of Technology,, Beijing 100144, P.R.China,
An ID-based Server-aided Verification Short Signature Scheme Avoid Key Escrow Jianhong Zhang 1,2 and Zhibin Sun 1 1 College of Science, North China University of Technology,, Beijing 100144, P.R.China,
G Advanced Cryptography April 10th, Lecture 11
 G.30-001 Advanced Cryptography April 10th, 007 Lecturer: Victor Shoup Lecture 11 Scribe: Kristiyan Haralambiev We continue the discussion of public key encryption. Last time, we studied Hash Proof Systems
G.30-001 Advanced Cryptography April 10th, 007 Lecturer: Victor Shoup Lecture 11 Scribe: Kristiyan Haralambiev We continue the discussion of public key encryption. Last time, we studied Hash Proof Systems
Boneh-Franklin Identity Based Encryption Revisited
 Boneh-Franklin Identity Based Encryption Revisited David Galindo Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Radboud University Nijmegen P.O.Box 9010 6500 GL, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. d.galindo@cs.ru.nl
Boneh-Franklin Identity Based Encryption Revisited David Galindo Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Radboud University Nijmegen P.O.Box 9010 6500 GL, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. d.galindo@cs.ru.nl
Improved ID-based Authenticated Group Key Agreement Secure Against Impersonation Attack by Insider
 All rights are reserved and copyright of this manuscript belongs to the authors. This manuscript has been published without reviewing and editing as received from the authors: posting the manuscript to
All rights are reserved and copyright of this manuscript belongs to the authors. This manuscript has been published without reviewing and editing as received from the authors: posting the manuscript to
Gentry IBE Paper Reading
 Gentry IBE Paper Reading Y. Jiang 1 1 University of Wollongong September 5, 2014 Literature Craig Gentry. Practical Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles. Advances in Cryptology - EUROCRYPT
Gentry IBE Paper Reading Y. Jiang 1 1 University of Wollongong September 5, 2014 Literature Craig Gentry. Practical Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles. Advances in Cryptology - EUROCRYPT
Threshold RSA for Dynamic and Ad-Hoc Groups
 Threshold RSA for Dynamic and Ad-Hoc Groups Rosario Gennaro, Shai Halevi, Hugo Krawczyk, Tal Rabin IBM T.J.Watson Research Center Hawthorne, NY USA Abstract. We consider the use of threshold signatures
Threshold RSA for Dynamic and Ad-Hoc Groups Rosario Gennaro, Shai Halevi, Hugo Krawczyk, Tal Rabin IBM T.J.Watson Research Center Hawthorne, NY USA Abstract. We consider the use of threshold signatures
Identity Based Undeniable Signatures
 Identity Based Undeniable Signatures Benoît Libert Jean-Jacques Quisquater UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant, 3. B-1348 Louvain-La-Neuve. Belgium {libert,jjq}@dice.ucl.ac.be http://www.uclcrypto.org/ Abstract.
Identity Based Undeniable Signatures Benoît Libert Jean-Jacques Quisquater UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant, 3. B-1348 Louvain-La-Neuve. Belgium {libert,jjq}@dice.ucl.ac.be http://www.uclcrypto.org/ Abstract.
Introduction to Elliptic Curve Cryptography. Anupam Datta
 Introduction to Elliptic Curve Cryptography Anupam Datta 18-733 Elliptic Curve Cryptography Public Key Cryptosystem Duality between Elliptic Curve Cryptography and Discrete Log Based Cryptography Groups
Introduction to Elliptic Curve Cryptography Anupam Datta 18-733 Elliptic Curve Cryptography Public Key Cryptosystem Duality between Elliptic Curve Cryptography and Discrete Log Based Cryptography Groups
Simple SK-ID-KEM 1. 1 Introduction
 1 Simple SK-ID-KEM 1 Zhaohui Cheng School of Computing Science, Middlesex University The Burroughs, Hendon, London, NW4 4BT, United Kingdom. m.z.cheng@mdx.ac.uk Abstract. In 2001, Boneh and Franklin presented
1 Simple SK-ID-KEM 1 Zhaohui Cheng School of Computing Science, Middlesex University The Burroughs, Hendon, London, NW4 4BT, United Kingdom. m.z.cheng@mdx.ac.uk Abstract. In 2001, Boneh and Franklin presented
Available online at J. Math. Comput. Sci. 6 (2016), No. 3, ISSN:
 Available online at http://scik.org J. Math. Comput. Sci. 6 (2016), No. 3, 281-289 ISSN: 1927-5307 AN ID-BASED KEY-EXPOSURE FREE CHAMELEON HASHING UNDER SCHNORR SIGNATURE TEJESHWARI THAKUR, BIRENDRA KUMAR
Available online at http://scik.org J. Math. Comput. Sci. 6 (2016), No. 3, 281-289 ISSN: 1927-5307 AN ID-BASED KEY-EXPOSURE FREE CHAMELEON HASHING UNDER SCHNORR SIGNATURE TEJESHWARI THAKUR, BIRENDRA KUMAR
A NEW ID-BASED SIGNATURE WITH BATCH VERIFICATION
 Trends in Mathematics Information Center for Mathematical Sciences Volume 8, Number 1, June, 2005, Pages 119 131 A NEW ID-BASED SIGNATURE WITH BATCH VERIFICATION JUNG HEE CHEON 1, YONGDAE KIM 2 AND HYO
Trends in Mathematics Information Center for Mathematical Sciences Volume 8, Number 1, June, 2005, Pages 119 131 A NEW ID-BASED SIGNATURE WITH BATCH VERIFICATION JUNG HEE CHEON 1, YONGDAE KIM 2 AND HYO
Short Signature Scheme From Bilinear Pairings
 Sedat Akleylek, Barış Bülent Kırlar, Ömer Sever, and Zaliha Yüce Institute of Applied Mathematics, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey {akleylek,kirlar}@metu.edu.tr,severomer@yahoo.com,zyuce@stm.com.tr
Sedat Akleylek, Barış Bülent Kırlar, Ömer Sever, and Zaliha Yüce Institute of Applied Mathematics, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey {akleylek,kirlar}@metu.edu.tr,severomer@yahoo.com,zyuce@stm.com.tr
Secure and Practical Identity-Based Encryption
 Secure and Practical Identity-Based Encryption David Naccache Groupe de Cyptographie, Deṕartement d Informatique École Normale Supérieure 45 rue d Ulm, 75005 Paris, France david.nacache@ens.fr Abstract.
Secure and Practical Identity-Based Encryption David Naccache Groupe de Cyptographie, Deṕartement d Informatique École Normale Supérieure 45 rue d Ulm, 75005 Paris, France david.nacache@ens.fr Abstract.
Public-Key Cryptography. Public-Key Certificates. Public-Key Certificates: Use
 Public-Key Cryptography Tutorial on Dr. Associate Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur http://cse.iitkgp.ac.in/ abhij/ January 30, 2017 Short
Public-Key Cryptography Tutorial on Dr. Associate Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur http://cse.iitkgp.ac.in/ abhij/ January 30, 2017 Short
Toward Hierarchical Identity-Based Encryption
 Toward Hierarchical Identity-Based Encryption Jeremy Horwitz and Ben Lynn Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA, {horwitz blynn}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract. We introduce the concept of hierarchical
Toward Hierarchical Identity-Based Encryption Jeremy Horwitz and Ben Lynn Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA, {horwitz blynn}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract. We introduce the concept of hierarchical
Lecture 1: Introduction to Public key cryptography
 Lecture 1: Introduction to Public key cryptography Thomas Johansson T. Johansson (Lund University) 1 / 44 Key distribution Symmetric key cryptography: Alice and Bob share a common secret key. Some means
Lecture 1: Introduction to Public key cryptography Thomas Johansson T. Johansson (Lund University) 1 / 44 Key distribution Symmetric key cryptography: Alice and Bob share a common secret key. Some means
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signa
 Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography
 Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Short Signatures from the Weil Pairing
 Short Signatures from the Weil Pairing Dan Boneh dabo@cs.stanford.edu Ben Lynn blynn@cs.stanford.edu Hovav Shacham hovav@cs.stanford.edu Abstract We introduce a short signature scheme based on the Computational
Short Signatures from the Weil Pairing Dan Boneh dabo@cs.stanford.edu Ben Lynn blynn@cs.stanford.edu Hovav Shacham hovav@cs.stanford.edu Abstract We introduce a short signature scheme based on the Computational
Certificate-Based Signature Schemes without Pairings or Random Oracles
 Certificate-Based Signature Schemes without Pairings or Random Oracles Joseph K. Liu 1, Joonsang Baek 1, Willy Susilo 2, and Jianying Zhou 1 1 Cryptography and Security Department Institute for Infocomm
Certificate-Based Signature Schemes without Pairings or Random Oracles Joseph K. Liu 1, Joonsang Baek 1, Willy Susilo 2, and Jianying Zhou 1 1 Cryptography and Security Department Institute for Infocomm
On the relations between non-interactive key distribution, identity-based encryption and trapdoor discrete log groups
 Des. Codes Cryptogr. (2009) 52:219 241 DOI 10.1007/s10623-009-9278-y On the relations between non-interactive key distribution, identity-based encryption and trapdoor discrete log groups Kenneth G. Paterson
Des. Codes Cryptogr. (2009) 52:219 241 DOI 10.1007/s10623-009-9278-y On the relations between non-interactive key distribution, identity-based encryption and trapdoor discrete log groups Kenneth G. Paterson
An Efficient Signature Scheme from Bilinear Pairings and Its Applications
 An Efficient Signature Scheme from Bilinear Pairings and Its Applications Fangguo Zhang, Reihaneh Safavi-Naini and Willy Susilo School of Information Technology and Computer Science University of Wollongong,
An Efficient Signature Scheme from Bilinear Pairings and Its Applications Fangguo Zhang, Reihaneh Safavi-Naini and Willy Susilo School of Information Technology and Computer Science University of Wollongong,
An efficient variant of Boneh-Gentry-Hamburg's identity-based encryption without pairing
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2015 An efficient variant of Boneh-Gentry-Hamburg's
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2015 An efficient variant of Boneh-Gentry-Hamburg's
An Efficient Signature Scheme from Bilinear Pairings and Its Applications
 An Efficient Signature Scheme from Bilinear Pairings and Its Applications Fangguo Zhang, Reihaneh Safavi-Naini and Willy Susilo School of Information Technology and Computer Science University of Wollongong,
An Efficient Signature Scheme from Bilinear Pairings and Its Applications Fangguo Zhang, Reihaneh Safavi-Naini and Willy Susilo School of Information Technology and Computer Science University of Wollongong,
Pairing-Based Identification Schemes
 Pairing-Based Identification Schemes David Freeman Information Theory Research HP Laboratories Palo Alto HPL-2005-154 August 24, 2005* public-key cryptography, identification, zero-knowledge, pairings
Pairing-Based Identification Schemes David Freeman Information Theory Research HP Laboratories Palo Alto HPL-2005-154 August 24, 2005* public-key cryptography, identification, zero-knowledge, pairings
Ring Group Signatures
 Ring Group Signatures Liqun Chen Hewlett-Packard Laboratories, Long Down Avenue, Stoke Gifford, Bristol, BS34 8QZ, United Kingdom. liqun.chen@hp.com Abstract. In many applications of group signatures,
Ring Group Signatures Liqun Chen Hewlett-Packard Laboratories, Long Down Avenue, Stoke Gifford, Bristol, BS34 8QZ, United Kingdom. liqun.chen@hp.com Abstract. In many applications of group signatures,
Authentication. Chapter Message Authentication
 Chapter 5 Authentication 5.1 Message Authentication Suppose Bob receives a message addressed from Alice. How does Bob ensure that the message received is the same as the message sent by Alice? For example,
Chapter 5 Authentication 5.1 Message Authentication Suppose Bob receives a message addressed from Alice. How does Bob ensure that the message received is the same as the message sent by Alice? For example,
The odd couple: MQV and HMQV
 The odd couple: MQV and HMQV Jean-Philippe Aumasson 1 / 49 Summary MQV = EC-DH-based key agreement protocol, proposed by Menezes, Qu and Vanstone (1995), improved with Law and Solinas (1998), widely standardized
The odd couple: MQV and HMQV Jean-Philippe Aumasson 1 / 49 Summary MQV = EC-DH-based key agreement protocol, proposed by Menezes, Qu and Vanstone (1995), improved with Law and Solinas (1998), widely standardized
Schnorr Signature. Schnorr Signature. October 31, 2012
 . October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
. October 31, 2012 Table of contents Salient Features Preliminaries Security Proofs Random Oracle Heuristic PKS and its Security Models Hardness Assumption The Construction Oracle Replay Attack Security
ID-based tripartite key agreement with signatures
 -based tripartite key agreement with signatures 1 Divya Nalla ILab, Dept of omputer/info Sciences, University of Hyderabad, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, 500046, India divyanalla@yahoocom bstract : This paper
-based tripartite key agreement with signatures 1 Divya Nalla ILab, Dept of omputer/info Sciences, University of Hyderabad, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, 500046, India divyanalla@yahoocom bstract : This paper
[6] was based on the quadratic residuosity problem, whilst the second given by Boneh and Franklin [3] was based on the Weil pairing. Originally the ex
![[6] was based on the quadratic residuosity problem, whilst the second given by Boneh and Franklin [3] was based on the Weil pairing. Originally the ex [6] was based on the quadratic residuosity problem, whilst the second given by Boneh and Franklin [3] was based on the Weil pairing. Originally the ex](/thumbs/92/110217767.jpg) Exponent Group Signature Schemes and Ecient Identity Based Signature Schemes Based on Pairings F. Hess Dept. Computer Science, University of Bristol, Merchant Venturers Building, Woodland Road, Bristol,
Exponent Group Signature Schemes and Ecient Identity Based Signature Schemes Based on Pairings F. Hess Dept. Computer Science, University of Bristol, Merchant Venturers Building, Woodland Road, Bristol,
Delegation in Predicate Encryption Supporting Disjunctive Queries
 Author manuscript, published in "Security and Privacy - Silver Linings in the Cloud Springer Ed. 2012 229-240" DOI : 10.1007/978-3-642-15257-3_21 Delegation in Predicate Encryption Supporting Disjunctive
Author manuscript, published in "Security and Privacy - Silver Linings in the Cloud Springer Ed. 2012 229-240" DOI : 10.1007/978-3-642-15257-3_21 Delegation in Predicate Encryption Supporting Disjunctive
Computer Networks. Efficient many-to-one authentication with certificateless aggregate signatures
 Computer Networks 4 (21) 2482 2491 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Computer Networks journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/comnet Efficient many-to-one authentication with certificateless
Computer Networks 4 (21) 2482 2491 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Computer Networks journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/comnet Efficient many-to-one authentication with certificateless
1 Number Theory Basics
 ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
Recent Advances in Identity-based Encryption Pairing-free Constructions
 Fields Institute Workshop on New Directions in Cryptography 1 Recent Advances in Identity-based Encryption Pairing-free Constructions Kenny Paterson kenny.paterson@rhul.ac.uk June 25th 2008 Fields Institute
Fields Institute Workshop on New Directions in Cryptography 1 Recent Advances in Identity-based Encryption Pairing-free Constructions Kenny Paterson kenny.paterson@rhul.ac.uk June 25th 2008 Fields Institute
Efficient Selective Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles
 Efficient Selective Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles Dan Boneh Xavier Boyen March 21, 2011 Abstract We construct two efficient Identity-Based Encryption (IBE) systems that admit selectiveidentity
Efficient Selective Identity-Based Encryption Without Random Oracles Dan Boneh Xavier Boyen March 21, 2011 Abstract We construct two efficient Identity-Based Encryption (IBE) systems that admit selectiveidentity
Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample
 Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample Fuchun Guo 1, Rongmao Chen 2, Willy Susilo 1, Jianchang Lai 1, Guomin Yang 1, and Yi Mu 1 1 Institute
Optimal Security Reductions for Unique Signatures: Bypassing Impossibilities with A Counterexample Fuchun Guo 1, Rongmao Chen 2, Willy Susilo 1, Jianchang Lai 1, Guomin Yang 1, and Yi Mu 1 1 Institute
An Enhanced ID-based Deniable Authentication Protocol on Pairings
 An Enhanced ID-based Deniable Authentication Protocol on Pairings Meng-Hui Lim*, Sanggon Lee**, Youngho Park***, Hoonjae Lee** *Department of Ubiquitous IT, Graduate school of Design & IT, Dongseo University,
An Enhanced ID-based Deniable Authentication Protocol on Pairings Meng-Hui Lim*, Sanggon Lee**, Youngho Park***, Hoonjae Lee** *Department of Ubiquitous IT, Graduate school of Design & IT, Dongseo University,
Identity-Based Authenticated Asymmetric Group Key Agreement Protocol
 Identity-Based Authenticated Asymmetric Group Key Agreement Protocol Lei Zhang, Qianhong Wu,2, Bo Qin,3, Josep Domingo-Ferrer Universitat Rovira i Virgili, Dept of Comp Eng and Maths UNESCO Chair in Data
Identity-Based Authenticated Asymmetric Group Key Agreement Protocol Lei Zhang, Qianhong Wu,2, Bo Qin,3, Josep Domingo-Ferrer Universitat Rovira i Virgili, Dept of Comp Eng and Maths UNESCO Chair in Data
ID-Based Blind Signature and Ring Signature from Pairings
 ID-Based Blind Signature and Ring Signature from Pairings Fangguo Zhang and Kwangjo Kim International Research center for Information Security (IRIS) Information and Communications University(ICU), 58-4
ID-Based Blind Signature and Ring Signature from Pairings Fangguo Zhang and Kwangjo Kim International Research center for Information Security (IRIS) Information and Communications University(ICU), 58-4
On (Hierarchical) Identity Based Encryption Protocols with Short Public Parameters (With an Exposition of Waters Artificial Abort Technique)
 On (Hierarchical) Identity Based Encryption Protocols with Short Public Parameters (With an Exposition of Waters Artificial Abort Technique) Sanjit Chatterjee and Palash Sarkar Applied Statistics Unit
On (Hierarchical) Identity Based Encryption Protocols with Short Public Parameters (With an Exposition of Waters Artificial Abort Technique) Sanjit Chatterjee and Palash Sarkar Applied Statistics Unit
On the security of Jhanwar-Barua Identity-Based Encryption Scheme
 On the security of Jhanwar-Barua Identity-Based Encryption Scheme Adrian G. Schipor aschipor@info.uaic.ro 1 Department of Computer Science Al. I. Cuza University of Iași Iași 700506, Romania Abstract In
On the security of Jhanwar-Barua Identity-Based Encryption Scheme Adrian G. Schipor aschipor@info.uaic.ro 1 Department of Computer Science Al. I. Cuza University of Iași Iași 700506, Romania Abstract In
Attribute-Based Ring Signatures
 Attribute-Based Ring Signatures Jin Li and Kwangjo Kim International Research center for Information Security (IRIS) Information and Communications University(ICU) 103-6 Munji-Dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon,
Attribute-Based Ring Signatures Jin Li and Kwangjo Kim International Research center for Information Security (IRIS) Information and Communications University(ICU) 103-6 Munji-Dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon,
II. Digital signatures
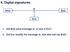 II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
Identity Based Proxy Signature from RSA without Pairings
 International Journal of Network Security, Vol.19, No.2, PP.229-235, Mar. 2017 (DOI: 10.6633/IJNS.201703.19(2).07) 229 Identity Based Proxy Signature from RSA without Pairings Lunzhi Deng, Huawei Huang,
International Journal of Network Security, Vol.19, No.2, PP.229-235, Mar. 2017 (DOI: 10.6633/IJNS.201703.19(2).07) 229 Identity Based Proxy Signature from RSA without Pairings Lunzhi Deng, Huawei Huang,
A Pairing-Based DAA Scheme Further Reducing TPM Resources
 A Pairing-Based DAA Scheme Further Reducing TPM Resources Ernie Brickell Intel Corporation ernie.brickell@intel.com Jiangtao Li Intel Labs jiangtao.li@intel.com Abstract Direct Anonymous Attestation (DAA)
A Pairing-Based DAA Scheme Further Reducing TPM Resources Ernie Brickell Intel Corporation ernie.brickell@intel.com Jiangtao Li Intel Labs jiangtao.li@intel.com Abstract Direct Anonymous Attestation (DAA)
New Identity-based Key-exposure Free Chameleon Hash from Bilinear Pairings
 1756 JOURNAL OF NETWORKS, VOL. 9, NO. 7, JULY 2014 New Identity-based Key-exposure Free Chameleon Hash from Bilinear Pairings Chunhui Wu a, Qin Li b, Chuan Lin a a Department of Computer Science, Guangdong
1756 JOURNAL OF NETWORKS, VOL. 9, NO. 7, JULY 2014 New Identity-based Key-exposure Free Chameleon Hash from Bilinear Pairings Chunhui Wu a, Qin Li b, Chuan Lin a a Department of Computer Science, Guangdong
Digital Signatures. Adam O Neill based on
 Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
A New Approach to Threshold Attribute Based Signatures
 A New Approach to Threshold Attribute Based Signatures S Sharmila Deva Selvi, Subhashini Venugopalan, C. Pandu Rangan Theoretical Computer Science Laboratory Department of Computer Science and Engineering
A New Approach to Threshold Attribute Based Signatures S Sharmila Deva Selvi, Subhashini Venugopalan, C. Pandu Rangan Theoretical Computer Science Laboratory Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Certificateless Signcryption without Pairing
 Certificateless Signcryption without Pairing Wenjian Xie Zhang Zhang College of Mathematics and Computer Science Guangxi University for Nationalities, Nanning 530006, China Abstract. Certificateless public
Certificateless Signcryption without Pairing Wenjian Xie Zhang Zhang College of Mathematics and Computer Science Guangxi University for Nationalities, Nanning 530006, China Abstract. Certificateless public
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited
 From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
From Fixed-Length to Arbitrary-Length RSA Encoding Schemes Revisited Julien Cathalo 1, Jean-Sébastien Coron 2, and David Naccache 2,3 1 UCL Crypto Group Place du Levant 3, Louvain-la-Neuve, B-1348, Belgium
A New Certificateless Blind Signature Scheme
 Sangeetha Jose, Akash Gautam, and C Pandu Rangan Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras, Chennai-36, Tamilnadu, India {sangeethajosem, akash.gautam24, prangan55}@gmail.com Abstract Blind signatures
Sangeetha Jose, Akash Gautam, and C Pandu Rangan Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras, Chennai-36, Tamilnadu, India {sangeethajosem, akash.gautam24, prangan55}@gmail.com Abstract Blind signatures
Identity-Based Chameleon Hash Scheme Without Key Exposure
 Identity-Based Chameleon Hash Scheme Without Key Exposure Xiaofeng Chen, Fangguo Zhang, Haibo Tian, and Kwangjo Kim 1 Key Laboratory of Computer Networks and Information Security, Ministry of Education,
Identity-Based Chameleon Hash Scheme Without Key Exposure Xiaofeng Chen, Fangguo Zhang, Haibo Tian, and Kwangjo Kim 1 Key Laboratory of Computer Networks and Information Security, Ministry of Education,
On Two Round Rerunnable MPC Protocols
 On Two Round Rerunnable MPC Protocols Paul Laird Dublin Institute of Technology, Dublin, Ireland email: {paul.laird}@dit.ie Abstract. Two-rounds are minimal for all MPC protocols in the absence of a trusted
On Two Round Rerunnable MPC Protocols Paul Laird Dublin Institute of Technology, Dublin, Ireland email: {paul.laird}@dit.ie Abstract. Two-rounds are minimal for all MPC protocols in the absence of a trusted
Provable Security Proofs and their Interpretation in the Real World
 Provable Security Proofs and their Interpretation in the Real World Vikram Singh Abstract This paper analyses provable security proofs, using the EDL signature scheme as its case study, and interprets
Provable Security Proofs and their Interpretation in the Real World Vikram Singh Abstract This paper analyses provable security proofs, using the EDL signature scheme as its case study, and interprets
New Techniques for Dual System Encryption and Fully Secure HIBE with Short Ciphertexts
 New Techniques for Dual System Encryption and Fully Secure HIBE with Short Ciphertexts Allison Lewko University of Texas at Austin alewko@cs.utexas.edu Brent Waters University of Texas at Austin bwaters@cs.utexas.edu
New Techniques for Dual System Encryption and Fully Secure HIBE with Short Ciphertexts Allison Lewko University of Texas at Austin alewko@cs.utexas.edu Brent Waters University of Texas at Austin bwaters@cs.utexas.edu
An Improved Online/Offline Identity-based Signature Scheme for WSNs
 International Journal of Network Security, Vol.18, No.6, PP.1143-1151, Nov. 2016 1143 An Improved Online/Offline Identity-based Signature Scheme for WSNs Ya Gao 1, Peng Zeng 1, Kim-Kwang Raymond Choo 2,
International Journal of Network Security, Vol.18, No.6, PP.1143-1151, Nov. 2016 1143 An Improved Online/Offline Identity-based Signature Scheme for WSNs Ya Gao 1, Peng Zeng 1, Kim-Kwang Raymond Choo 2,
Round-Optimal ID-Based Blind Signature Schemes without ROS Assumption
 JOURNAL OF COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 7, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2012 909 Round-Optimal ID-Based Blind Signature Schemes without ROS Assumption Wei Gao Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao
JOURNAL OF COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 7, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2012 909 Round-Optimal ID-Based Blind Signature Schemes without ROS Assumption Wei Gao Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao
Synchronized Aggregate Signatures from the RSA Assumption
 Synchronized Aggregate Signatures from the RSA Assumption Susan Hohenberger Johns Hopkins University susan@cs.jhu.edu Brent Waters UT Austin bwaters@cs.utexas.edu January 18, 2018 Abstract In this work
Synchronized Aggregate Signatures from the RSA Assumption Susan Hohenberger Johns Hopkins University susan@cs.jhu.edu Brent Waters UT Austin bwaters@cs.utexas.edu January 18, 2018 Abstract In this work
A DAA Scheme Requiring Less TPM Resources
 A DAA Scheme Requiring Less TPM Resources Liqun Chen Hewlett-Packard Laboratories liqun.chen@hp.com Abstract. Direct anonymous attestation (DAA) is a special digital signature primitive, which provides
A DAA Scheme Requiring Less TPM Resources Liqun Chen Hewlett-Packard Laboratories liqun.chen@hp.com Abstract. Direct anonymous attestation (DAA) is a special digital signature primitive, which provides
Post-quantum security models for authenticated encryption
 Post-quantum security models for authenticated encryption Vladimir Soukharev David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science February 24, 2016 Introduction Bellare and Namprempre in 2008, have shown that
Post-quantum security models for authenticated encryption Vladimir Soukharev David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science February 24, 2016 Introduction Bellare and Namprempre in 2008, have shown that
Efficient Ring Signatures without Random Oracles
 Efficient Ring Signatures without Random Oracles Hovav Shacham Weizmann Institute of Science hovav.shacham@weizmann.ac.il Brent Waters SRI International bwaters@csl.sri.com August 24, 2006 Abstract We
Efficient Ring Signatures without Random Oracles Hovav Shacham Weizmann Institute of Science hovav.shacham@weizmann.ac.il Brent Waters SRI International bwaters@csl.sri.com August 24, 2006 Abstract We
Attribute-Based Signatures
 Attribute-Based Signatures Hemanta K. Maji Manoj Prabhakaran Mike Rosulek Abstract We introduce Attribute-Based Signatures (ABS), a versatile primitive that allows a party to sign a message with fine-grained
Attribute-Based Signatures Hemanta K. Maji Manoj Prabhakaran Mike Rosulek Abstract We introduce Attribute-Based Signatures (ABS), a versatile primitive that allows a party to sign a message with fine-grained
Constrained Pseudorandom Functions and Their Applications
 Constrained Pseudorandom Functions and Their Applications Dan Boneh dabo@cs.stanford.edu Brent Waters bwaters@cs.utexas.edu September 9, 2013 Abstract We put forward a new notion of pseudorandom functions
Constrained Pseudorandom Functions and Their Applications Dan Boneh dabo@cs.stanford.edu Brent Waters bwaters@cs.utexas.edu September 9, 2013 Abstract We put forward a new notion of pseudorandom functions
CS-E4320 Cryptography and Data Security Lecture 11: Key Management, Secret Sharing
 Lecture 11: Key Management, Secret Sharing Céline Blondeau Email: celine.blondeau@aalto.fi Department of Computer Science Aalto University, School of Science Key Management Secret Sharing Shamir s Threshold
Lecture 11: Key Management, Secret Sharing Céline Blondeau Email: celine.blondeau@aalto.fi Department of Computer Science Aalto University, School of Science Key Management Secret Sharing Shamir s Threshold
A Novel Strong Designated Verifier Signature Scheme without Random Oracles
 1 A Novel Strong Designated Verifier Signature Scheme without Random Oracles Maryam Rajabzadeh Asaar 1, Mahmoud Salmasizadeh 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, 2 Electronics Research Institute (Center),
1 A Novel Strong Designated Verifier Signature Scheme without Random Oracles Maryam Rajabzadeh Asaar 1, Mahmoud Salmasizadeh 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, 2 Electronics Research Institute (Center),
Ring Signatures without Random Oracles
 Ring Signatures without Random Oracles Sherman S. M. Chow 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, Victor K. Wei 3 and Tsz Hon Yuen 3 1 Department of Computer Science Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University,
Ring Signatures without Random Oracles Sherman S. M. Chow 1, Joseph K. Liu 2, Victor K. Wei 3 and Tsz Hon Yuen 3 1 Department of Computer Science Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University,
