THIRD SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION (2013 Scheme) ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-II (ABCEFHMNPRSTU) MODEL QUESTION PAPER
|
|
|
- Madeleine Roberts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THIRD SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION (2013 Scheme) ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-II (ABCEFHMNPRSTU) MODEL QUESTION PAPER Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 100 PART-A Answer all questions. Each question carries 4 marks 1. A particle moves so that its position vector is given by, show that the velocity of the particle is perpendicular to. 2. If Show that 3. Find the cosine transform of in. 4. Solve the partial differential equation if. 5. State the assumptions involved in the derivation of one dimensional Heat equation. PART-B Answer one full question from each module. Each question carries 20 marks. MODULE-I 6. a) Find the constants and so that the surfaces and may cut orthogonally at the point. b) If is a scalar point function, use Stoke s theorem to prove that. c) Evaluate by Green s theorem in the plane for where is the boundary of the triangle whose vertices are 7. a) If prove that where. b) Show that is irrotational and find its scalar potential. c) Using divergence theorem, evaluate where and is the surface bounding and
2 MODULE-II 8. a) Obtain the Fourier series of the function in b) Find the Fourier transform of Hence evaluate 9. a) Find the Fourier series of b) Find the Fourier cosine transform of and hence show that MODULE-III 10. a) Solve the pde. b) Solve the pde ( 11. a) Solve the partial differential equation b) Solve the pde ( MODULE-IV 12. a) Using the method of separation of variables, solve given that when. b) A string of length is fixed at both the ends. The midpoint of the string is taken to a height and then released from rest in that position. Find the displacement of the string. 13. a) Solve subject to the condition, and = in (0, ) b) A rod of length has its ends A and B kept at and respectively until steady conditions prevail. The temperature at A is suddenly raised to and at the same time that B is lowered to and the end temperatures are thereafter maintained. Find the temperature function
3 THIRD SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION (2013Scheme) HUMANITIES (BEFMRSU) MODEL QUESTION PAPER Time: 3Hours Max. Marks: 100 Instructions: Answer Part-I and Part-II in separate Answer Books. PART-I (Economics) Time: 2 hrs Max. Marks: 70 PART-A Answer all questions. Each question carries 2 marks. 1. Distinguish between Producer good and consumer good. 2. Define production function. 3. Give an example of diminishing returns to scale. 4. Who is an entrepreneur? 5. Define the concept of Marginal Product. 6. What is meant by reserve requirement by banks? 7. Name the methods of measuring National Income. 8. What is stagflation? 9. List out two reasons for Privatisation. 10. Define the concept of Poverty. (2 x10= 20 marks) PART-B Answer any one full question from each Module. Each full question carries 25 Marks MODULE - I 11. What are the Central problems of an economy? Why do they arise? Do all economies have identical Central Problems? 12. Explain the Law of variable proportion and Law of Returns to Scale. MODULE - II 13. Explain the different concepts related to National Income calculation. Explain the sectoral distribution of National Income in India and what are the issues associated to it.
4 14. a) Discuss the impact of multinational companies in Indian Economy. b) Discuss the impact of globalization on Telecom and Financial sector. PART-II (Accountancy) Time: 1 hr Max. Marks: 30 Answer any two questions. Each question carries 15 marks. 1. Explain the concepts and conventions of accountancy. 2. (a) What are journal accounts? Explain the rules for journalizing. (b) Briefly explain the accounting package. 3. Based on the following trial balance prepare a profit and loss account and a balance sheet. The following is the trial balance of Mr. Alex as on 31 st December, Dr (Rs) Cr (Rs) Plant and machinery 45,000 Freehold premises 55,000 Stock 1 st January ,500 Salaries 7,600 Purchases 65,000 Sales 1,21,000 Furniture and fitting 6,000 Carriage inwards 1,675 Carriage outwards 1,315 Sales returns 2,400 Purchases returns 1,365 Discount received 635 Discount allowed 430 Wages 16,100 Sundry debtors 41,000 Sundry creditors 28,800 Alex s capital 1,10,000 Rent, rates and taxes 1,430 Advertisement 2,400 Cash in hand 450 Cash at bank 2,500 Drawings 3,000 Loan from Rajesh 26,000 Total 2,87,800 2,87,800
5 THIRD SEMESTER BTECH DEGREE EXAMINATION 2014 (SCHEME: 2013) Branch: Electrical and Electronics Engineering NETWKS AND SYSTEMS (E) MODEL QUESTION PAPER Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 100 PART-A Answer all questions. Each question carries 2 marks 1. Explain dot rule for coupled circuits. 2. Explain neutral displacement in 3, 3 wire system. 3. What are the drawbacks of K-derived filter. 4. Differentiate between low pass, high pass and band pass filter. 5. What is meant by poles and zeros of a network function. 6. Explain the design procedures of m-derived filter. 7. Explain how the knowledge of wave symmetry helps in simplifying the Fourier analysis. 8. Explain the properties of LC admittance function. 9. With the help of phasor diagram, obtain the relationship between phase and line voltages of a 3 star connected load. 10. Define Image Impedance. ( 10 x 2 Marks = 20 Marks) PART-B Answer one full question from each module. Each question carries 20 marks. MODULE - I 11. (a) For the circuit in Fig.(1), find the current through 5 using Nodal method. Fig. (1) (8 Marks)
6 (b) A 3 phase, 400V,RYB system supplies an unbalanced 3 wire, star connected load of Z R = (4+i8), Z Y = (3+j4), Z B = (15+i20). Find the line currents and neutral shift voltage. (12 Marks) 12.(a) Find the voltage across the 5 resistor in Fig.(2). Fig.(2) (6 Marks) (b) Find the Fourier series for the wave form in Fig.(3). v V -π 0 π 2π 3π 4π 5π wt Fig. (3) (14 Marks) MODULE - II 13. (a) Sketch the Pole Zero plots of Z 11 and Z 21 of the network shown in Fig. (4). 4Ω 1H DC V 1 (s) 1/3Ω 1F Fig. (4) (8 Marks)
7 (b) The inductor L 1 has an initial current of 1A and inductor L 2 has an initial current of 1A in the direction in Fig. (5). Determine the total response of V 0 (t) if V s (t) = 2u(t) V. Fig. (5) (12 Marks) 14. (a) Draw the linear oriented graph of the network shown in Fig. (6), and write the incidence matrix. R 7 E 2 R 6 R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 5 E 4 E 1 E 3 Fig. (6) (14 Marks) (b) For the graph and the corresponding tree of the graph shown in Fig 7, find the f-cut set matrix. Fig. 7 (a) Fig. 7(b) (6Marks) MODEULE - III 15. (a) Find Y parameters in terms of (i) ABCD parameters, (ii) h parameters. (8Marks) (b) Find the admittance parameters of the given two port network in Fig. (8).
8 I 1 3V Ω V 1 2Ω 2Ω V 2 I 2 - Fig. (8) (12 Marks) 16. (a) Design an m derived low pass filter having design resistance R = 500, cut off frequency = 1500Hz and infinite attenuation frequency 2000Hz. (10 Marks) (b) Design a constant k type high pass filter with T section, to be terminated in 600 resistance and cut off frequency 10Hz. Find the characteristic impedance and phase constant at 25kHz. (10 Marks) MODULE - IV 17. (a) Synthesize the network function Z(s) = as Foster I and Foster II forms. (14 Marks) (b) Determine whether the following functions represent driving point impedance of an RC network. Z 1 (s) = Z 2 (s) = (6 Marks) 18. (a)find whether the following systems are linear or non linear. (i) y(t)=2 d[x(t)]/dt (ii) y(t) = log[x(t)] (10 Marks) (b) Define LTI system and (i) verify whether the given system is linear and time invariant 3 dy(t)/dt + 5y(t) = x(t) (ii) Find whether the following systems are casual or non casual. (a) y(t) = x(t) + x(t-1), (b) y(t) = x(t 2 ) (10 Marks)
9 THIRD SEMESTER BTECH DEGREE EXAMINATION 2014 (SCHEME: 2013) Branch: Electrical and Electronics Engineering ANALOG ELECTRONICS (E) MODEL QUESTION PAPER Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 100 PART-A Answer all questions. Each question carries 2 marks 1. Explain the term dc load line. Show how to locate it on the characteristics of a PNP transistor. 2. What are the factors that cause bias instability of a transistor amplifier? 3. Draw the h-parameter equivalent model of a transistor in CE configuration. 4. Define the following terms (i) I DSS (ii) Pinch off voltage. 5. State Barkhausen criterion for sustained oscillation. 6. Explain cross over distortion in a class B amplifiers. 7. Explain the frequency response curve of RC coupled amplifier. 8. What is meant by CMRR? 9. Explain the frequency compensation of OP-AMP. 10. An OP-AMP has a slew rate of 1V/µ sec. Find the maximum frequency at which an undistorted sinusoidal output of 10V peak can be obtained. ( 10 x 2 Marks = 20 Marks) PART-B Answer one full question from each module. Each question carries 20 marks. MODULE - I 11. (a) In a silicon transistor design the different resistance values in a potential divider circuit with β=50, V BE =0.6V, V CC =22.5V & R C =5.6kΩ. It is desired to establish the Q-point at V CE =12V, I C =1.5mA & stability factor S 3. Also draw the designed circuit. (12 marks) (b) Explain the thermistor compensation in a transistor with a neat circuit. (8 marks)
10 12. (a)for a transistor connected in common emitter amplifier the h parameters are hie=1kω, hfe=50, hre=2.5µmho. If Rs=1kΩ & R L =5kΩ. Calculate the current gain, voltage gain, input impedance & output impedance. (10 marks) (b) Explain the graphical determination of h parameters of a common emitter amplifier. (10 marks) MODULE - II 13. (a)draw and explain a common source FET amplifier with voltage divider self bias circuit using a small signal low frequency equivalent circuit. Derive the expression for voltage gain of the FET amplifier. (15marks) (b) Define FET parameters. (5marks) 14. (a) Draw and explain the construction, principle of working and characteristics of p- channel enhancement MOSFET. (10marks) (b) Explain the working principle and characteristics of UJT. (10marks ) MODULE - III 15. (a)explain the operation of class B amplifier. Obtain the expression for overall efficiency. Show that maximum overall efficiency of a class B amplifier is 78.5%. (12marks) (b) Explain with a neat circuit diagram the working of series transistor voltage regulator. (8marks) 16. (a)with a neat circuit diagram explain the working of a Wien bridge oscillator. Derive the expression for frequency of oscillation and condition for oscillation. (12marks) (b) Explain the effect of negative feedback on amplifier gain, bandwidth, nonlinear distortion and noise. (8marks) MODULE - IV 17. (a) What are the characteristics of an ideal op-amp? With necessary diagrams, derive an expression for a practical inverting op-amp. (10marks) (b) Draw the circuit of an emitter- coupled differential amplifier. Derive the expression for Ac, Ad and CMRR. (10marks) 18. (a)an op-amp is configured as non inverting summing amplifier. The input voltages are V 1 =3V, V 2 =1V & V 3 =2V. The resistances on input side are R 1 =R 2 =R 3 =1kΩ and the feedback resistance Rf=2kΩ. Determine the output voltage V 0. Assume that the opamp is initially nulled. (10marks) (b) Explain the following using op-amp with relevant waveforms (i) triangular waveform generation (ii) schmitt trigger (10marks)
11 THIRD SEMESTER BTECH DEGREE EXAMINATION 2014 (SCHEME: 2013) Branch: Electrical and Electronics Engineering DC MACHINES & TRANSFMERS (E) MODEL QUESTION PAPER Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 100 PART-A Answer all questions. Each question carries 2 marks 1. What are main parts of DC machine? Explain briefly their functions? 2. Distinguish between pole pitch and commutator pitch. 3. Explain briefly one method of improving commutation. 4. Deduce the expression for torque developed by a DC motor. 5. Explain briefly the Retardation test on DC motor. 6. Draw and explain the noload phasor diagram for a single phase transformer. 7. Outline the procedure for performing the polarity test on a single phase transformer. 8. In what way All Day efficiency of a transformer different from conventional efficiency. 9. What is the principle of autotransformer? Show the distribution of currents in the winding sections of a step up auto transformer. 10. Explain the working of ON load tapchanging trasformer with help of neat diagram. ( 10 x 2 Marks = 20 Marks) PART-B Answer one full question from each module. Each question carries 20 marks. MODULE - I 11. (a) Derive the emf equation of a DC generator. (5 marks) (b) What is the fuction of interpoles. (5 marks) (c) Draw the load characteristics of DC shunt and series generators and explain the shape mentioning their applications. (10 marks) 12. (a) What is armature reaction in DC machines? What are its effects? Explain with relevant diagrams. (10 Marks)
12 (b) Two DC shunt generators operating in parallel supply a total load current of 200 A. The terminal voltage of one generator falls uniformly from 240 V to 225 V, when delivering 120 A. The terminal voltage of second generator falls uniformly from 230 V to 215 V delivering 100 A. Find the load current shared by each generator and bus bar voltage. (10 Marks) MODULE - II 13. (a) How can the efficiency of a DC shunt motor be predetermined? Explain with circuit diagram and relevant calculations. Discuss the merits and demerits of this test. (10 Marks) (b) The maximum current during starting for a 500 V DC shunt motor is to be limited to 125 A. The resistance of the armature is 0.25 ohm. Find the resistant elements for a 12 element starter. (10 marks) 14. (a) Explain any three methods for speed control of DC motors. (10 Marks) (b) Why DC series motors are preferred for Electric Traction? Explain with help of different characteristic curves. (5 Marks) (c) How does a DC motor automatically adjust its input to match the mechanical load on the motor. (5 Marks) MODULE - III 15. (a) Describe the open circuit and short circuit tests on single phase transformer. Explain how the equivalent circuit of such transformer can be obtained from test data. (10 Marks) (b) The maximum efficiency of a 500 kva, 3300/500V, 50Hz, single phase transformer is 97% and occurs at full load unity power factor. Find the efficiency of this transformer when its supplies 3/4 th full load at 0.8 p.f. (10 Marks) 16. (a) Explain why parallel operation of transformers is necessary. (5 Marks) (b) Explain why transformer rating is expressed in kva. (5 Marks) (c) Derive the condition for maximum efficiency of a single phase transformer. (5 Marks) (d) Draw the phasor diagram of the transformer supplying leading p.f. load. (5 Marks)
13 MODULE - IV 17. (a) Describe the standard connections for three phase transformers. (10 Marks) (b) Find the expressions for saving in copper in an auto transformer. (5 Marks) (c) What are the necessary conditions for parallel operation of three phase transformers? (5 Marks) 18. Write short notes on (a) Three winding transformer. (7 Marks) (b) Harmonics in transformers. (7 marks) (c) Dry type transformers. (6 marks)
14 THIRD SEMESTER BTECH DEGREE EXAMINATION 2014 (SCHEME: 2013) Branch: Electrical and Electronics Engineering HYDRAULIC MACHINES AND HEAT ENGINES (E) MODEL QUESTION PAPER Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 100 PART-A Answer all questions. Each question carries 2 marks 1. Define the terms: Density, Specific weight, Specific volume and Specific gravity 2. Distinguish between Gauge, Absolute and Vacuum pressures. 3. Explain the significance of Reynolds number. 4. How hydraulic turbines are classified? 5. What is the significance of draft tube in a reaction turbine? 6. Explain the phenomenon of Cavitation. 7. What is the use of Air-vessel in reciprocating pumps? 8. Define the terms related to Internal Combustion engines Brake power, Indicated power, Thermal efficiency and Volumetric efficiency 9. Differentiate between SI and CI engines. 10. Explain Open cycle gas turbine and Closed cycle gas turbine with neat sketches. ( 10 x 2 Marks = 20 Marks) PART-B Answer one full question from each module. Each question carries 20 marks. MODULE - I 11. (a) State and prove Pascal s law (8 Marks) (b) A U-tube manometer has been employed to measure the pressure of water in a pipe line which is in excess of at atmospheric pressure. The right limb of the manometer contains mercury and is open to atmosphere. The contact between the water and mercury is in the left limb. Determine the pressure of water in the pipe if the difference in level of mercury in the limbs of the U tube is 10cm and the free surface of mercury is in level with the centre of pipe. If the pressure of water in the pipe line reduces to 10kN/m 2,
15 calculate the new difference in the level of mercury. Take specific weight of water as 10kN/m 3. (12Marks) 12. (a) Derive Bernoulli s equation. State the assumptions (8Marks) (b) A horizontal venturimeter with inlet and throat diameters 300mm and 100mm respectively is used to measure the flow of water. The pressure at inlet is 120kN/m 2 while the vacuum pressure head at the throat is 350mm of mercury. Assuming that 3% of differential head is lost in between the inlet and throat, find (i) Rate of flow and (ii) Coefficient of discharge for the venturimeter. (12Marks) MODULE - II 13. (a) Explain Governing of a turbine. With a neat sketch explain the working of a centrifugal governor. (8 Marks) (b) A single jet of Pelton wheel run at 350 rpm under a head of 510m. The jet diameter is 200mm. Its deflection inside the bucket is and its relative velocity is reduced by 15% due to friction. Find (i) water power (ii) resultant force on the bucket (iii) brake power if mechanical losses are 3% of power supplied and (iv) overall efficiency. Assume suitable values for the velocity coefficient and speed ratio. (12 Marks) 14. (a) Sketch the plant layout for a Hydraulic power plant and explain the significance of Surge tank. (8 Marks) (b) The inner and outer diameter of an inward flow reaction turbine are 100cm and 80cm respectively and its breadth at inlet is 20cm. 10% of the flow area is blocked by the blade thickness. The flow velocity at inlet is 2.5m/s and runner speed is 300rpm. The guide vanes at the inlet make an angle of 12 0 to the wheel tangent. Assuming the discharge is radial and inlet and outlet flow velocity is same. Find out the following (a) Flow through the runner (b) Blade angles at inlet and outlet (c) Absolute and relative velocities of water entering the runner blade. (12 Marks) MODULE - III 15. (a) Derive an expression for specific speed of a centrifugal pump. (8 Marks) b) The inlet and outlet blade angles of the impeller of a centrifugal pump are 60 0 and 40 0 respectively. The width of the impeller is 30mm. The inlet and outlet diameters of the
16 impeller are 180mm and 600mm respectively. Find the speed of the pump to deliver 0.15 m 3 /s of water. Flow at inlet is entirely radical. Find also the head generated by the impeller and the manometric head and the impeller power. The manometric efficiency or hydraulic efficiency of the pump is 85%. (12 Marks) 16. (a) Explain with neat sketch working of a double acting reciprocating pump. (8 Marks) (b) A single acting reciprocating pump has a bore of 75mm diameter and a stroke of 150mm. It draws water from sump whose water level is 3m below the pump axis, through a pipe 30mm in diameter and 4.25m in length. The pump delivers water to a tank through a 15m long pipe, 25mm in diameter to a height of 12m above the pump axis. If separation occurs at 2.5m (absolute), find the maximum speed of the pump. Take atmospheric pressure head 760mm of mercury. (12 Marks) MODULE - IV 17. (a) Explain Morse test for IC engines. (8 Marks) (b) A four cylinder, four stroke diesel engine, has a bore of 200mm and stroke of 300mm. At full load, at 720rpm, the BMEP is 5.93 bar and the specific fuel consumption is kg/kwh. The air-fuel ratio as determined by exhaust gas analysis is 25:1. Calculate the brake thermal efficiency and volumetric efficiency of the engine. Atmospheric conditions are 1.01bar and 15 0 C and calorific value of the fuel may be taken as kj/kg. (12 Marks) 18. (a) Discuss the effect of inter cooling on the performance of gas turbines. (8 Marks) (b) In an open cycle constant pressure gas turbine air enters the compressor at 1.03bar and The pressure of air after the compression is 4bar. The isentropic efficiencies of compressor and turbine are 80% and 85% respectively. The air fuel ratio use is 80:1. Find the thermal efficiency of the cycle, if the flow rate is 2.5kg/s. Take Cp = 1kJ/kgK and γ=1.4 for air and gases. Calorific value of fuel used = 42000kJ/kg. (12 Marks) *********
17
SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
3. (a) Figure 3(a) shows a Bridge T network used in control systems. The element values are clearly marked in the figure.
 I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -11. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before. attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03
![Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03](/thumbs/94/118747664.jpg) EE 4 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 016 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS NETWORK ANALYSIS Time: Three Hours Answer Question
EE 4 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 016 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS NETWORK ANALYSIS Time: Three Hours Answer Question
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
Conventional Paper I-2010
 Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND STATICS
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Fluid Mechanics (16CE106) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch:
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Fluid Mechanics (16CE106) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch:
Please welcome for any correction or misprint in the entire manuscript and your valuable suggestions kindly mail us
 Problems of Practices Of Fluid Mechanics Compressible Fluid Flow Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi Bhooshan
Problems of Practices Of Fluid Mechanics Compressible Fluid Flow Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi Bhooshan
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous)
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Computer Methods in Power Systems Course Code : A60222
CHAPTER 14 SIGNAL GENERATORS AND WAVEFORM SHAPING CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 4 SIGNA GENERATORS AND WAEFORM SHAPING CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 4. Basic Principles of Sinusoidal Oscillators 4. Op Amp RC Oscillators 4.3 C and Crystal Oscillators 4.4 Bistable Multivibrators
CHAPTER 4 SIGNA GENERATORS AND WAEFORM SHAPING CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 4. Basic Principles of Sinusoidal Oscillators 4. Op Amp RC Oscillators 4.3 C and Crystal Oscillators 4.4 Bistable Multivibrators
ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS. CHAPTER 1 Properties of Fluids
 CHAPTER 1 Properties of Fluids ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Development of Fluid Mechanics 1.3 Units of Measurement (SI units) 1.4 Mass, Density, Specific Weight, Specific Volume, Specific
CHAPTER 1 Properties of Fluids ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Development of Fluid Mechanics 1.3 Units of Measurement (SI units) 1.4 Mass, Density, Specific Weight, Specific Volume, Specific
+ ( )= with initial condition
 Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
EC T32 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 EC T32 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-I - TRANSFORMER 1. What is a transformer? 2. Briefly explain the principle of operation of transformers. 3. What are the parts of a transformer? 4. What are the types
EC T32 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-I - TRANSFORMER 1. What is a transformer? 2. Briefly explain the principle of operation of transformers. 3. What are the parts of a transformer? 4. What are the types
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering. EE 1352 Power System Analysis
 B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
Homework Assignment 08
 Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
An Introduction to Electrical Machines. P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy
 An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
mywbut.com Hydraulic Turbines
 Hydraulic Turbines Hydro-electric power accounts for up to 0% of the world s electrical generation. Hydraulic turbines come in a variety of shapes determined by the available head and a number of sizes
Hydraulic Turbines Hydro-electric power accounts for up to 0% of the world s electrical generation. Hydraulic turbines come in a variety of shapes determined by the available head and a number of sizes
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Dr. S. Ramachandran Prof. R. Devaraj. Mr. YVS. Karthick AIR WALK PUBLICATIONS
 Fluid Machinery As per Revised Syllabus of Leading Universities including APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Dr. S. Ramachandran Prof. R. Devaraj Professors School of Mechanical Engineering Sathyabama
Fluid Machinery As per Revised Syllabus of Leading Universities including APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Dr. S. Ramachandran Prof. R. Devaraj Professors School of Mechanical Engineering Sathyabama
EXPERIMENT No.1 FLOW MEASUREMENT BY ORIFICEMETER
 EXPERIMENT No.1 FLOW MEASUREMENT BY ORIFICEMETER 1.1 AIM: To determine the co-efficient of discharge of the orifice meter 1.2 EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: Orifice meter test rig, Stopwatch 1.3 PREPARATION 1.3.1
EXPERIMENT No.1 FLOW MEASUREMENT BY ORIFICEMETER 1.1 AIM: To determine the co-efficient of discharge of the orifice meter 1.2 EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: Orifice meter test rig, Stopwatch 1.3 PREPARATION 1.3.1
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
55:041 Electronic Circuits The University of Iowa Fall Final Exam
 Final Exam Name: Score Max: 135 Question 1 (1 point unless otherwise noted) a. What is the maximum theoretical efficiency for a class-b amplifier? Answer: 78% b. The abbreviation/term ESR is often encountered
Final Exam Name: Score Max: 135 Question 1 (1 point unless otherwise noted) a. What is the maximum theoretical efficiency for a class-b amplifier? Answer: 78% b. The abbreviation/term ESR is often encountered
 CE 6303 MECHANICS OF FLUIDS L T P C QUESTION BANK 3 0 0 3 UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND FLUID STATICS PART - A 1. Define fluid and fluid mechanics. 2. Define real and ideal fluids. 3. Define mass density
CE 6303 MECHANICS OF FLUIDS L T P C QUESTION BANK 3 0 0 3 UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND FLUID STATICS PART - A 1. Define fluid and fluid mechanics. 2. Define real and ideal fluids. 3. Define mass density
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
R13 SET Derive the expression for the maximum bending stress developed in the leaf spring and also the central deflection of a leaf spring.
 Code No: RT22013 R13 SET - 41 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS - II (Civil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer ALL the question in
Code No: RT22013 R13 SET - 41 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS - II (Civil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer ALL the question in
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 1 Introduction to Fluid Machines Well, good
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 1 Introduction to Fluid Machines Well, good
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers A Linear IC circuit Operational Amplifier (op-amp) An op-amp is a high-gain amplifier that has high input impedance and low output impedance. An ideal op-amp has infinite gain and
Operational Amplifiers A Linear IC circuit Operational Amplifier (op-amp) An op-amp is a high-gain amplifier that has high input impedance and low output impedance. An ideal op-amp has infinite gain and
Introduction to Fluid Machines (Lectures 49 to 53)
 Introduction to Fluid Machines (Lectures 49 to 5) Q. Choose the crect answer (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) A hydraulic turbine rotates at N rpm operating under a net head H and having a discharge Q while developing
Introduction to Fluid Machines (Lectures 49 to 5) Q. Choose the crect answer (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) A hydraulic turbine rotates at N rpm operating under a net head H and having a discharge Q while developing
SILVER OAK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
 BE - SEMESTER VI MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION SUMMER 2015 SUBJECT: DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (161901) DATE: 09-03-2015 TIME: 02:00 pm to 03:13 pm TOTAL MARKS: 30 Q.1 (a) Define the following terms in short: (i)
BE - SEMESTER VI MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION SUMMER 2015 SUBJECT: DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (161901) DATE: 09-03-2015 TIME: 02:00 pm to 03:13 pm TOTAL MARKS: 30 Q.1 (a) Define the following terms in short: (i)
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Electric Machines
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATIONS 2012/2013 XE121. ENGINEERING CONCEPTS (Test)
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 202/203 XE2 ENGINEERING CONCEPTS (Test) Time allowed: TWO hours Answer: Attempt FOUR questions only, a maximum of TWO questions
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 202/203 XE2 ENGINEERING CONCEPTS (Test) Time allowed: TWO hours Answer: Attempt FOUR questions only, a maximum of TWO questions
B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER (Examination at the end of Second Year First Semester) (Electricals and Electronics)
 (DEE 11) B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 008. (Examination at the end of Second Year First Semester) (Electricals and Electronics) Paper I MATHEMATICS III Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 marks Answer
(DEE 11) B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 008. (Examination at the end of Second Year First Semester) (Electricals and Electronics) Paper I MATHEMATICS III Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 marks Answer
Fluid Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions
 019 MPROVEMENT Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions 1 Fluid Properties 1. (c). (b) 3. (c) 4. (576) 5. (3.61)(3.50 to 3.75) 6. (0.058)(0.05 to 0.06) 7.
019 MPROVEMENT Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions 1 Fluid Properties 1. (c). (b) 3. (c) 4. (576) 5. (3.61)(3.50 to 3.75) 6. (0.058)(0.05 to 0.06) 7.
Introduction to Fluid Machines, and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Fluid Machines, and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Introduction to Reaction Type of Hydraulic
Introduction to Fluid Machines, and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Introduction to Reaction Type of Hydraulic
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
Experiment- To determine the coefficient of impact for vanes. Experiment To determine the coefficient of discharge of an orifice meter.
 SUBJECT: FLUID MECHANICS VIVA QUESTIONS (M.E 4 th SEM) Experiment- To determine the coefficient of impact for vanes. Q1. Explain impulse momentum principal. Ans1. Momentum equation is based on Newton s
SUBJECT: FLUID MECHANICS VIVA QUESTIONS (M.E 4 th SEM) Experiment- To determine the coefficient of impact for vanes. Q1. Explain impulse momentum principal. Ans1. Momentum equation is based on Newton s
Lecture 7: Transistors and Amplifiers
 Lecture 7: Transistors and Amplifiers Hybrid Transistor Model for small AC : The previous model for a transistor used one parameter (β, the current gain) to describe the transistor. doesn't explain many
Lecture 7: Transistors and Amplifiers Hybrid Transistor Model for small AC : The previous model for a transistor used one parameter (β, the current gain) to describe the transistor. doesn't explain many
EDEXCEL NATIONALS UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES. ASSIGNMENT No. 3 - ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
 EDEXCEL NATIONALS UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES ASSIGNMENT No. 3 - ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION NAME: I agree to the assessment as contained in this assignment. I confirm that the work submitted
EDEXCEL NATIONALS UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES ASSIGNMENT No. 3 - ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION NAME: I agree to the assessment as contained in this assignment. I confirm that the work submitted
nozzle which is fitted to a pipe through which the liquid is flowing under pressure.
 Impact of Jets 1. The liquid comes out in the form of a jet from the outlet of a nozzle which is fitted to a pipe through which the liquid is flowing under pressure. The following cases of the impact of
Impact of Jets 1. The liquid comes out in the form of a jet from the outlet of a nozzle which is fitted to a pipe through which the liquid is flowing under pressure. The following cases of the impact of
 TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
OR Explain thermal breakdown in solid dielectrics. How this mechanism is
 Subject : High Voltage Engineering (2090) ITM Universe, Vadodara Electrical Engineering Department Class : Electrical Sem : th Long Questions Sr. No Question Unit No : 0 Explain Charge Simulation method
Subject : High Voltage Engineering (2090) ITM Universe, Vadodara Electrical Engineering Department Class : Electrical Sem : th Long Questions Sr. No Question Unit No : 0 Explain Charge Simulation method
1) Specific Gravity It is the ratio of specific weight of fluid to the specific weight of water.
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
R a) Compare open loop and closed loop control systems. b) Clearly bring out, from basics, Force-current and Force-Voltage analogies.
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 01 1. a) Compare open loop and closed loop control systems. b) Clearly bring out, from basics, Force-current and Force-Voltage analogies..
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 01 1. a) Compare open loop and closed loop control systems. b) Clearly bring out, from basics, Force-current and Force-Voltage analogies..
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 QUESTION PAPER INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : /10/2016 Marks: 0 Subject & Code: BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING -15ELE15 Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty : Dhanashree Bhate, Hema B, Prashanth V Time :
QUESTION PAPER INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : /10/2016 Marks: 0 Subject & Code: BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING -15ELE15 Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty : Dhanashree Bhate, Hema B, Prashanth V Time :
EEE3405 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 2 - TEST
 ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING
 INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
FIRST TERM EXAMINATION (07 SEPT 2015) Paper - PHYSICS Class XII (SET B) Time: 3hrs. MM: 70
 FIRST TERM EXAMINATION (07 SEPT 205) Paper - PHYSICS Class XII (SET B) Time: 3hrs. MM: 70 Instructions:. All questions are compulsory. 2. Q.no. to 5 carry mark each. 3. Q.no. 6 to 0 carry 2 marks each.
FIRST TERM EXAMINATION (07 SEPT 205) Paper - PHYSICS Class XII (SET B) Time: 3hrs. MM: 70 Instructions:. All questions are compulsory. 2. Q.no. to 5 carry mark each. 3. Q.no. 6 to 0 carry 2 marks each.
Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control. The General Control System
 WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
B.TECH ENGINEERING MODEL PRACTICAL QUESTION PAPER
 B.TECH ENGINEERING MODEL PRACTICAL QUESTION PAPER B.TECH IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SECOND YEAR THIRD SEMESTER FLUID MECHANICS LAB 1. Determination of coefficient of discharge of a Venturimeter (or) Orifice
B.TECH ENGINEERING MODEL PRACTICAL QUESTION PAPER B.TECH IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SECOND YEAR THIRD SEMESTER FLUID MECHANICS LAB 1. Determination of coefficient of discharge of a Venturimeter (or) Orifice
POWER SEMICONDUCTOR BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES
 POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34) NOTE: FOR NUMERICAL PROBLEMS FOR ALL UNITS EXCEPT UNIT 5 REFER THE E-BOOK ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS, 7 th EDITION HAYT AND KIMMERLY. PAGE NUMBERS OF
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34) NOTE: FOR NUMERICAL PROBLEMS FOR ALL UNITS EXCEPT UNIT 5 REFER THE E-BOOK ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS, 7 th EDITION HAYT AND KIMMERLY. PAGE NUMBERS OF
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8.
 Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
9. Pumps (compressors & turbines) Partly based on Chapter 10 of the De Nevers textbook.
 Lecture Notes CHE 31 Fluid Mechanics (Fall 010) 9. Pumps (compressors & turbines) Partly based on Chapter 10 of the De Nevers textbook. Basics (pressure head, efficiency, working point, stability) Pumps
Lecture Notes CHE 31 Fluid Mechanics (Fall 010) 9. Pumps (compressors & turbines) Partly based on Chapter 10 of the De Nevers textbook. Basics (pressure head, efficiency, working point, stability) Pumps
Frequency Dependent Aspects of Op-amps
 Frequency Dependent Aspects of Op-amps Frequency dependent feedback circuits The arguments that lead to expressions describing the circuit gain of inverting and non-inverting amplifier circuits with resistive
Frequency Dependent Aspects of Op-amps Frequency dependent feedback circuits The arguments that lead to expressions describing the circuit gain of inverting and non-inverting amplifier circuits with resistive
3 Energy Exchange in Turbomachines
 3 Energy Exchange in Turbomachines Problem 1 The solved and unsolved examples of this chapter are meant to illustrate the various forms of velocity triangles and the variety of the turbomachines. In addition,
3 Energy Exchange in Turbomachines Problem 1 The solved and unsolved examples of this chapter are meant to illustrate the various forms of velocity triangles and the variety of the turbomachines. In addition,
Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines
 Contents 1- Introduction. - Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Contents 1- Introduction. - Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Bridge Measurement 2.1 INTRODUCTION Advantages of Bridge Circuit
 2 Bridge Measurement 2.1 INTRODUCTION Bridges are often used for the precision measurement of component values, like resistance, inductance, capacitance, etc. The simplest form of a bridge circuit consists
2 Bridge Measurement 2.1 INTRODUCTION Bridges are often used for the precision measurement of component values, like resistance, inductance, capacitance, etc. The simplest form of a bridge circuit consists
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 24 Axial Flow Compressor Part I Good morning
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 24 Axial Flow Compressor Part I Good morning
B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER (Examination at the end of Second Year) Electricals and Electronics. Paper I MATHEMATICS III
 (DEE 11) B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 009. (Examination at the end of Second Year) Electricals and Electronics Paper I MATHEMATICS III Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 marks Answer Question No.
(DEE 11) B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 009. (Examination at the end of Second Year) Electricals and Electronics Paper I MATHEMATICS III Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 marks Answer Question No.
SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -1. Please read the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK : AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING.
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A- Two marks questions
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. Define specific magnetic
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. Define specific magnetic
1.1 An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system.
 . An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system x(t) (b) stable system (c) causal system (d) unstable system t=t t. In a series
. An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system x(t) (b) stable system (c) causal system (d) unstable system t=t t. In a series
= A x (t) + B utt), by d{ _-=-=-
 M.Tech. [ 24 103 ] Degree Examination ndustrial Process nstrumentation First Semester COMPUTER CONTROL OF PROCESSES (Effective from the Admitted Batch of2003-2004) Time: 3 Hours Maximum marks: 100 Answer
M.Tech. [ 24 103 ] Degree Examination ndustrial Process nstrumentation First Semester COMPUTER CONTROL OF PROCESSES (Effective from the Admitted Batch of2003-2004) Time: 3 Hours Maximum marks: 100 Answer
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Hydraulic modeling assessment Copyright 2010, Optimized Technical Solutions, LLC
 Hydraulic modeling assessment Copyright 2010, Optimized Technical Solutions, LLC Name: Date: Please answer the following questions with the complete piping configuration shown in Figure 1 below. Assume
Hydraulic modeling assessment Copyright 2010, Optimized Technical Solutions, LLC Name: Date: Please answer the following questions with the complete piping configuration shown in Figure 1 below. Assume
R13 SET - 1 '' ' '' ''' '' Code No: RT21023
 Code No: RT103 R13 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 015 BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DEVICES 1. a) Define Mobility b) Explain the operation of Light Emitting Diode. c) Define Load and
Code No: RT103 R13 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 015 BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DEVICES 1. a) Define Mobility b) Explain the operation of Light Emitting Diode. c) Define Load and
CBSE Physics Set I Outer Delhi Board 2012
 Q28. a) In Young s double slit experiment, derive the condition for (I) constructive interference and (II) destructive interference at a point on the screen. b) A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths,
Q28. a) In Young s double slit experiment, derive the condition for (I) constructive interference and (II) destructive interference at a point on the screen. b) A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths,
THIRD SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION (2013 Scheme) ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-II (ABCEFHMNPRSTU) MODEL QUESTION PAPER
 THIRD SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION (2013 Scheme) 13.301 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-II (ABCEFHMNPRSTU) MODEL QUESTION PAPER Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 100 PART-A Answer all questions. Each question
THIRD SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION (2013 Scheme) 13.301 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-II (ABCEFHMNPRSTU) MODEL QUESTION PAPER Time: 3 hours Maximum marks: 100 PART-A Answer all questions. Each question
R10 JNTUWORLD B 1 M 1 K 2 M 2. f(t) Figure 1
 Code No: R06 R0 SET - II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations April/May 03 CONTROL SYSTEMS (Com. to EEE, ECE, EIE, ECC, AE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry
Code No: R06 R0 SET - II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations April/May 03 CONTROL SYSTEMS (Com. to EEE, ECE, EIE, ECC, AE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS 2.1 The Ideal Op Amp (Chapter 2.1) Amplifier Applications 2.2 The Inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.2) 2.3 The Non-inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.3) 2.4 Difference
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS 2.1 The Ideal Op Amp (Chapter 2.1) Amplifier Applications 2.2 The Inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.2) 2.3 The Non-inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.3) 2.4 Difference
Answers to questions in each section should be tied together and handed in separately.
 EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
Set 2 (d) 150 C (a) 0.45 (d) can be positive, negative or zero (C) 8.5 J/K (a) 0.1
 Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
R09. d water surface. Prove that the depth of pressure is equal to p +.
 Code No:A109210105 R09 SET-1 B.Tech II Year - I Semester Examinations, December 2011 FLUID MECHANICS (CIVIL ENGINEERING) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any five questions All questions carry equal
Code No:A109210105 R09 SET-1 B.Tech II Year - I Semester Examinations, December 2011 FLUID MECHANICS (CIVIL ENGINEERING) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any five questions All questions carry equal
UNIVERSITY OF KERALA
 UNIVERSITY OF KERALA B. TECH. DEGREE COURSE (2013 SCHEME) SYLLABUS FOR III SEMESTER ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SCHEME -2013 III SEMESTER ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ( E ) Course
UNIVERSITY OF KERALA B. TECH. DEGREE COURSE (2013 SCHEME) SYLLABUS FOR III SEMESTER ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING SCHEME -2013 III SEMESTER ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ( E ) Course
Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook. THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 Fluid Flow
 Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 REFERENCES REFERENCES Streeter, Victor L., Fluid Mechanics, 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, ISBN 07-062191-9.
Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 REFERENCES REFERENCES Streeter, Victor L., Fluid Mechanics, 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, ISBN 07-062191-9.
2002 Prentice Hall, Inc. Gene F. Franklin, J. David Powell, Abbas Emami-Naeini Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems, 4e
 u Figure 2.1 Cruise-control model x Friction force bx m x u Figure 2.2 Free-body diagram for cruise control S P 278 Figure 2.3 Automobile suspension y m 2 k s b v car x m 1 k w Road surface r Inertial
u Figure 2.1 Cruise-control model x Friction force bx m x u Figure 2.2 Free-body diagram for cruise control S P 278 Figure 2.3 Automobile suspension y m 2 k s b v car x m 1 k w Road surface r Inertial
Electronic Circuits Summary
 Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering
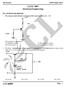 Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
B. Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY (Examination at the end of Second Year) ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATIONS. Paper - I : Mathematics - III
 (DEC 11) B. Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY - 015 (Examination at the end of Second Year) ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATIONS Paper - I : Mathematics - III Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 75 Answer question No.1
(DEC 11) B. Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY - 015 (Examination at the end of Second Year) ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATIONS Paper - I : Mathematics - III Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 75 Answer question No.1
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Electronic Circuits and Design I
![S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Electronic Circuits and Design I S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Electronic Circuits and Design I](/thumbs/95/124107626.jpg) S.E. Sem. [ETRX] Electronic ircuits and Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) What happens when diode is operated at high frequency? [5] Ans.: Diode High Frequency Model : This
S.E. Sem. [ETRX] Electronic ircuits and Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) What happens when diode is operated at high frequency? [5] Ans.: Diode High Frequency Model : This
Final Exam. 55:041 Electronic Circuits. The University of Iowa. Fall 2013.
 Final Exam Name: Max: 130 Points Question 1 In the circuit shown, the op-amp is ideal, except for an input bias current I b = 1 na. Further, R F = 10K, R 1 = 100 Ω and C = 1 μf. The switch is opened at
Final Exam Name: Max: 130 Points Question 1 In the circuit shown, the op-amp is ideal, except for an input bias current I b = 1 na. Further, R F = 10K, R 1 = 100 Ω and C = 1 μf. The switch is opened at
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *0123456789* PHYSICS 9702/04 Paper 4 A Level Structured Questions For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *0123456789* PHYSICS 9702/04 Paper 4 A Level Structured Questions For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1
 Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 Electricity May 02 1. The graphs show the variation with potential difference V of the current I for three circuit elements. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com When the four lamps are connected as shown in diagram
Electricity May 02 1. The graphs show the variation with potential difference V of the current I for three circuit elements. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com When the four lamps are connected as shown in diagram
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE & NAME: EE 2303 - TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION YEAR / SEM: III/V UNIT-I TRANSMISSION SYSTEM INTRODUCTION PART-A 1. What is
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE & NAME: EE 2303 - TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION YEAR / SEM: III/V UNIT-I TRANSMISSION SYSTEM INTRODUCTION PART-A 1. What is
R16. Explain the effects of negative feedback on amplifier characteristics?
 Code No: 21023 SET - 1 BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DEVICES (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) 3. Answer any FOUR Questions from Part-B 1. a) State the continuity equation (2M) b) List the applications
Code No: 21023 SET - 1 BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DEVICES (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) 3. Answer any FOUR Questions from Part-B 1. a) State the continuity equation (2M) b) List the applications
Basic. Theory. ircuit. Charles A. Desoer. Ernest S. Kuh. and. McGraw-Hill Book Company
 Basic C m ш ircuit Theory Charles A. Desoer and Ernest S. Kuh Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley McGraw-Hill Book Company New York St. Louis San
Basic C m ш ircuit Theory Charles A. Desoer and Ernest S. Kuh Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley McGraw-Hill Book Company New York St. Louis San
Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines
 Contents 1- Introduction. 2- Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Contents 1- Introduction. 2- Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
