Refractive-Index Measurements of LiF Ramp Compressed to 800 GPa
|
|
|
- Harry Nichols
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
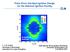
1 Refractive-Index Measurements of LiF Ramp Compressed to 8 GPa Pressure (GPa) Refractive index D. E. Fratanduono Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Weighted mean Wise Lalone Density (g/cc) 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Salt Lake City, UT November 11
2 Summary The refractive index of ramp-compressed LiF depends linearly on density up to 8 GPa Knowledge of LiF s compressed index of refraction is important for high-pressure equation-of-state (EOS) measurements The refractive index of shock-compressed LiF has previously been measured to 115 GPa* Ramp-compressed LiF is measured up to 8 GPa LiF is observed to remain transparent over this range A single-oscillator model suggests that the band gap will close at pressures above 4 GPa these are the highest ever refractive-index measurements of an insulator E19145b J. L. Wise and L. C. Chhabildas, Sandia National Laboratories, Report SAND-85-31C, NTIS (1985).
3 Outline I. Motivation II. Theory/technique III. Experiments A. Method of characteristics B. VISAR measurements C. Analysis IV. Results A. Refractive index B. Effective oscillator mode C. Metallization E387
4 Collaborators T. R. Boehly and D. D. Meyerhofer University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics M. A. Barrios, J. H. Eggert, D. G. Hicks, R. Smith, D. Braun, P. M. Celliers, and G. W. Collins Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
5 Motivation There is significant technical utility in ramp-compressed optical windows for material studies Optical velocimetry is a powerful tool that probes the response of materials under dynamic compression Drive Sample Velocimetry Transparent optical windows maintain compression within a sample enabling in-situ particle-velocity measurements for EOS studies Accurate optical velocimetry measurements require that the n(t) of the window is known Drive Sample Transparent window Velocimetry E388
6 Theory The refractive index of optical windows affects VISAR velocity measurements VISAR detects Doppler shifts from moving surfaces U true n = 1 VISAR Optical windows influence the Doppler shift Changes to the window alter the optical path length of the probe beam U app n 1 VISAR The refractive index is determined if the apparent velocity (U app ) and the true velocity (U true ) are known n shock n U app U shock VISAR E19483a
7 The transparency of shocks in LiF windows makes it possible for VISAR to probe the material interface U p LiF window U c LiF VISAR n c n Reflecting surface Single shocks up to 16 GPa are transparent in LiF* multishocks up to 5 GPa are transparent VISAR probes through the compressed material; this alters its sensitivity VISAR measures the rate of change of the optical path length corrections must be made for the compressed refractive index (n c ) E1846d *J. L. Wise and L. C. Chhabildas, Shock Waves in Condensed Matter 1985, DEAC4-DP789
8 Shock experiments are limited by Hugoniot melt and shock entropy Transparent insulators transform into conducting fluids pressure-induced reduction of the band gap and thermal promotion of electrons across that gap Entropy produced by high-pressure shock waves transforms materials into conductive matter highly reflective at the shock front Temperature (1 K) LiF* Boehler melt (1997) SESAME 771 SESAME 771 MD simulations 5 Melt line 1 Isentrope 15 Pressure (GPa) Hugoniot 5 3 E19149 *R. Boehler, M. Ross, and D. B Boercker, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 4589 (1997).
9 Technique A two-section target enables simultaneous measurements of the apparent and true particle velocity to be made Laser ablation Diamond LiF Drive beam U app U fs VISAR VISAR Compressed region Hayes* shows that for ramp compression duapp dn = n t dutrue d t Two measurable parameters are required to determine n(t) U true is determined using specially designed targets and the method of characteristics E1891e *D. Hayes, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 6484 (1).
10 Method of characteristics and impedance matching determines the true particle velocity Measure U fs (t) Pressure (GPa) Shot 57575: Applied pressure Time (ns) Drive beam = P(t)= Diamond U true U fs Compressed region Backward characteristic algorithm to drive surface Calculate P(t) Forward characteristic algorithm to diamond/lif interface Calculate U true (t) E389a Diamond ramp isentrope from D. K. Bradley et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 1, 7553 (9).
11 OMEGA Experiments LiF refractive-index experiments were performed using laser-drive ramp compression on OMEGA Laser ablation Diamond Drive beam U app U fs Compressed region VISAR LiF VISAR Image relay from target to interferometer Target Vacuum chamber Probe laser (53 nm) delivered through multimode fiber VISAR* beam splitter Self-emission from target SOP Streak camera Delay element Velocity interferometer Streak camera Experiments used laser energies between 7 to 77 J delivered in 3.7- or 7.-ns ramp profiles VISAR* has a time resolution of <3 ps E18346c *Velocity interferometer system for any reflector
12 The applied diamond-pressure scaling law is determined from VISAR and laser-power measurements* Pressure (GPa) Experiments Weighted mean Fit Intensity (TW/cm ) 1 P^GPah = 4^! 3h 8I_ TW cmib. 71^!. 1h E19616 *D. E. Fratanduono et al., J. Appl. Phys. 19, 1351 (11).
13 Diamond free-surface and apparent interface velocity are measured simultaneously with VISAR on OMEGA OMEGA Diamond LiF LiF Diamond Shot Shot Time (ns) Velocity (nm/ns) LiF Diamond Time (ns) E1956c
14 Applied pressure is determined from diamond freesurface velocity using the backward characteristics 7 6 Shot 57575: Free-surface characteristics Stress (GPa) Shot 57575: Applied pressure Time (ns) Pressure (GPa) Lagrangian depth (nm) Time (ns) E1957
15 The applied pressure is forward propagated through the LiF window to infer the true particle velocity Time (ns) Shot 57575: Interface characteristics Diamond Gap LiF Lagrangian depth (nm) Stress (GPa) Velocity (nm/ns) Shot 57575: Interface velocity Free-surface velocity Apparent velocity True velocity Time (ns) E19169
16 The Monte Carlo technique is used to estimate errors associated with the calculated true velocity Monte Carlo errors Experimental diamond isentrope standard deviations provided* LiF EOS (SESAME 771) assumed 1% error in pressure Gap thickness between diamond anvil and LiF window Timing errors (of the order of the etalon delay) were incorporated following the Monte Carlo routine Velocity (nm/ns) True velocity: Shot Time (ns) E19155 *D. K. Bradley et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 1, 7553 (9).
17 The apparent velocity depends linearly on the true particle velocitiy for 17 experiments Apparent velocity (nm/ns) Pressure (GPa) Vacuum gap (17 shots) True velocity (nm/ns) E19156d
18 LASNEX simulations were performed to validate the method of characteristics and address concerns regarding shock formation in the LiF window LASNEX simulations tested the effects of shock formation and gap thickness on the calculated interface velocity It was found that the gap thickness and shock formation do not significantly affect the interface velocity Excellent agreement was observed between LASNEX simulations and the method of characteristics Time (ns) Shot Peak compression Diamond Shock formation Gap LiF Lagrangian depth (nm) Stress (GPa) E19154
19 LASNEX simulations show that shock formation in the LiF window does not perturb interface measurements Velocity (nm/ns) Free-surface velocity Characteristics LASNEX Calculated diamond/lifinterface velocity Characteristics LASNEX 3 Shot Shot Time (ns) Time (ns) Agreement between LASNEX simulations and the method of characteristics validates this technique and uncertainties caused by the vacuum gap. E1961
20 A second-order, orthogonal-polynominal regression determines the relation of the apparent and true particle velocities Apparent velocity (nm/ns) Weighted mean Weighted data 16 Wise Wise data 14 Jensen 1.36 Lalone data Orthogonal fit Orthogonal fit Pressure (GPa) True velocity (nm/ns) Apparent/True Pressure (GPa) True particle velocity (nm/ns) E193
21 Results A linear dependence on refractive index is observed Refractive index is determined from the Hayes formula* du du app true = n For linear U app (U true )** n = a + bt dn t d t n = (±.8) +.44 (±.) t Refractive index Pressure (GPa) Weighted mean Wise Lalone Density (g/cc) E1916c * D. Hayes, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 6481 (1). ** D. E. Fratanduono et al., J. Appl. Phys. 19, 1351 (11).
22 The effective-oscillator model is used to interpret the linear dependence of the refractive index and density Only electronic excitations are considered ~ is assumed to lie above the vibrational modes Refractive index Vibrational modes Electronic modes Changes in the refractive index caused by increases in density are due to a shift in the electronic resonance to lower frequency E197 Extinction coefficient, k Frequency (Hz) Frequency of this study E. D. Palik, Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids (Academic Press, Orlando, 1985).
23 The single-oscillator model accurately describes the dispersion of the refractive index Over 1 solid and liquid insulators obey this model n 1 = E E d E & ~ E d is the dispersion energy E is the single-oscillator energy - for the alkali-halides, E is related to the excitonic energy (E T ) by E E T Previous studies on compressed H and H O to 1 s of GPa have shown that E d is insensitive to changes in density 1/(n 1) LiF Dispersion data Linear fit & ~ (ev ) E19484
24 An effective-oscillator model suggests LiF will remain transparent to pressures above 4 GPa E t (ev) = E (ev)/ Pressure (GPa) Weighted mean Exciton energy Hertzfeld closure Density (g/cc) E19485 Extrapolation of these results suggests metallization will occur at ~4 GPa.
25 The effective-oscillator model suggests LiF will remain transparent to pressures above the Goldhammer Herzfeld metallization E t (ev) = E (ev)/ Pressure (GPa) Weighted mean Exciton energy Hertzfeld closure Density (g/cc) P GH (GPa) P OA (GPa) P BSC (GPa) LiF 8 Rbl Kl Csl Xe He 11, Ne 158, GH: Goldhammer Hertzfeld criterion OA: Optical absorption BSC: Band structure calculation E19163a High metallization pressure of LiF suggests that it will be a valuable window for high-pressure ramp-compression experiments.
26 Summary/Conclusions The refractive index of ramp-compressed LiF depends linearly on density up to 8 GPa Knowledge of LiF s compressed index of refraction is important for high-pressure equation-of-state (EOS) measurements The refractive index of shock-compressed LiF has previously been measured to 115 GPa* Ramp-compressed LiF is measured up to 8 GPa LiF is observed to remain transparent over this range A single-oscillator model suggests that the band gap will close at pressures above 4 GPa these are the highest ever refractive-index measurements of an insulator E19145b J. L. Wise and L. C. Chhabildas, Sandia National Laboratories, Report SAND-85-31C, NTIS (1985).
Measurements of Strain-Induced Refractive-Index Changes in LiF Using Direct-Drive Ramp Compression
 Measurements of Strain-Induced Refractive-Index Changes in LiF Using Direct-Drive Ramp Compression Apparent particle velocity (nm/ns) 16 12 8 4 1 GPa 8 GPa 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 True particle velocity (nm/ns)
Measurements of Strain-Induced Refractive-Index Changes in LiF Using Direct-Drive Ramp Compression Apparent particle velocity (nm/ns) 16 12 8 4 1 GPa 8 GPa 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 True particle velocity (nm/ns)
High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry
 High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry Low intensity High intensity 4 nm CH 3 nm Mo 138 nm quartz VISAR SOP Simulated peak pressure (Mbar) 1 5 Laser backscatter 17.5 kev Mo K a Hard
High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry Low intensity High intensity 4 nm CH 3 nm Mo 138 nm quartz VISAR SOP Simulated peak pressure (Mbar) 1 5 Laser backscatter 17.5 kev Mo K a Hard
Adiabat Shaping of Direct-Drive OMEGA Capsules Using Ramped Pressure Profiles
 Adiabat Shaping of Direct-Drive OMEGA Capsules Using Ramped Pressure Profiles a r Lagrangian coordinate K. Anderson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 44th Annual Meeting of the American
Adiabat Shaping of Direct-Drive OMEGA Capsules Using Ramped Pressure Profiles a r Lagrangian coordinate K. Anderson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 44th Annual Meeting of the American
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA
 Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Nanosecond Broadband Spectroscopy For Laser-Driven Compression Experiments
 Nanosecond Broadband Spectroscopy For Laser-Driven Compression Experiments Dylan K. Spaulding, R. Jeanloz Department of Earth and Planetary Science, University of California, Berkeley307 McCone Hall, Berkeley,
Nanosecond Broadband Spectroscopy For Laser-Driven Compression Experiments Dylan K. Spaulding, R. Jeanloz Department of Earth and Planetary Science, University of California, Berkeley307 McCone Hall, Berkeley,
Shock compression of precompressed deuterium
 LLNL-PROC-491811 Shock compression of precompressed deuterium M. R. Armstrong, J. C. Crowhurst, J. M. Zaug, S. Bastea, A. F. Goncharov, B. Militzer August 3, 2011 Shock compression of precompressed deuterium
LLNL-PROC-491811 Shock compression of precompressed deuterium M. R. Armstrong, J. C. Crowhurst, J. M. Zaug, S. Bastea, A. F. Goncharov, B. Militzer August 3, 2011 Shock compression of precompressed deuterium
Shock-Wave Equation-of-State Measurements in Fused Silica up to 1600 GPa
 Shock-Wave Equation-of-State Measurements in Fused Silica up to 1600 GPa Introduction Silica is the single most-abundant compound in the earth s mantle and crust and an end member of the MgO-FeO-SiO2 system
Shock-Wave Equation-of-State Measurements in Fused Silica up to 1600 GPa Introduction Silica is the single most-abundant compound in the earth s mantle and crust and an end member of the MgO-FeO-SiO2 system
Measuring the Refractive Index of a Laser-Plasma System
 Measuring the Refractive Index of a Laser-Plasma System 1 dh ( 10 4 ) 0 1 J (dh) R (dh) 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 D. Turnbull University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Dm (Å) 58th Annual Meeting of the
Measuring the Refractive Index of a Laser-Plasma System 1 dh ( 10 4 ) 0 1 J (dh) R (dh) 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 D. Turnbull University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Dm (Å) 58th Annual Meeting of the
Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets
 Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets v rms of tr (mg/cm )..6 Si [4.%] Si [7.4%] Ge [.9%] DRACO simulations..4 Time (ns) S. X. Hu University
Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets v rms of tr (mg/cm )..6 Si [4.%] Si [7.4%] Ge [.9%] DRACO simulations..4 Time (ns) S. X. Hu University
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers
 Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
Strength effects in diamond under shock compression from 0.1 to 1 TPa
 Strength effects in diamond under shock compression from 0.1 to 1 TPa R. S. McWilliams, 1,2, * J. H. Eggert, 2 D. G. Hicks, 2 D. K. Bradley, 2 P. M. Celliers, 2 D. K. Spaulding, 1 T. R. Boehly, 3 G. W.
Strength effects in diamond under shock compression from 0.1 to 1 TPa R. S. McWilliams, 1,2, * J. H. Eggert, 2 D. G. Hicks, 2 D. K. Bradley, 2 P. M. Celliers, 2 D. K. Spaulding, 1 T. R. Boehly, 3 G. W.
COUPLING STATIC AND DYNAMIC COMPRESSIONS: FIRST MEASUREMENTS IN DENSE HYDROGEN
 High Pressure Research Vol. 24, No. 1, March 2004, pp. 25 31 COUPLING STATIC AND DYNAMIC COMPRESSIONS: FIRST MEASUREMENTS IN DENSE HYDROGEN P. LOUBEYRE a, *, P. M. CELLIERS b, D. G. HICKS b, E. HENRY f,
High Pressure Research Vol. 24, No. 1, March 2004, pp. 25 31 COUPLING STATIC AND DYNAMIC COMPRESSIONS: FIRST MEASUREMENTS IN DENSE HYDROGEN P. LOUBEYRE a, *, P. M. CELLIERS b, D. G. HICKS b, E. HENRY f,
Experiments on Dynamic Overpressure Stabilization of Ablative Richtmyer Meshkov Growth in ICF Targets on OMEGA
 Experiments on Dynamic Overpressure Stabilization of Ablative Richtmyer Meshkov Growth in ICF Targets on OMEGA Contributors: V. N. Goncharov P. A. Jaanimagi J. P. Knauer D. D. Meyerhofer O. V. Gotchev
Experiments on Dynamic Overpressure Stabilization of Ablative Richtmyer Meshkov Growth in ICF Targets on OMEGA Contributors: V. N. Goncharov P. A. Jaanimagi J. P. Knauer D. D. Meyerhofer O. V. Gotchev
Measurement of Long-Scale-Length Plasma Density Profiles for Two-Plasmon Decay Studies
 Measurement of Long-Scale-Length Plasma Density Profiles for Two-Plasmon Decay Studies Plasma density scale length at 10 21 cm 3 (nm) 350 300 250 200 150 100 0 Flat foil 2 4 6 8 10 100 Target diameter
Measurement of Long-Scale-Length Plasma Density Profiles for Two-Plasmon Decay Studies Plasma density scale length at 10 21 cm 3 (nm) 350 300 250 200 150 100 0 Flat foil 2 4 6 8 10 100 Target diameter
Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA
 Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA In-flight aspect ratio OMEGA cryogenic ignition hydro-equivalent design tr = 3 mg/cm 2, V imp = 3.7 7 cm/s 3 3 2 14 m = 48 ng
Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA In-flight aspect ratio OMEGA cryogenic ignition hydro-equivalent design tr = 3 mg/cm 2, V imp = 3.7 7 cm/s 3 3 2 14 m = 48 ng
Use of the Z Accelerator for Isentropic and Shock Compression Studies
 1 Use of the Z Accelerator for Isentropic and Shock Compression Studies Marcus D. Knudson 1.1 Introduction The high-pressure equation of state (EOS) of materials is usually determined by shock compression
1 Use of the Z Accelerator for Isentropic and Shock Compression Studies Marcus D. Knudson 1.1 Introduction The high-pressure equation of state (EOS) of materials is usually determined by shock compression
Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF
 Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF OMEGA polar-drive geometry 21.4 Backlit x-ray image OMEGA polar-drive implosion 21.4 58.2 77.8 42. 58.8 CR ~ 5 R = 77 nm 4 nm 4 nm P. B. Radha University of Rochester Laboratory
Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF OMEGA polar-drive geometry 21.4 Backlit x-ray image OMEGA polar-drive implosion 21.4 58.2 77.8 42. 58.8 CR ~ 5 R = 77 nm 4 nm 4 nm P. B. Radha University of Rochester Laboratory
Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale
 Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale Laser intensity ( 1 15 W/cm 2 ) 5 4 3 2 1 Laser spike is replaced with hot-electron spike 2 4 6 8 1 Gain 2 15 1 5 1. 1.2 1.4
Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale Laser intensity ( 1 15 W/cm 2 ) 5 4 3 2 1 Laser spike is replaced with hot-electron spike 2 4 6 8 1 Gain 2 15 1 5 1. 1.2 1.4
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
Monochromatic 8.05-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets
 Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents
 Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents 3.0 3~ beam 2.5 4~ TS beam 60 100 100-nm TS volume Thomsonscattered light 5 0 5 Wavelength shift (Å) 0.5 0.0 D. H. Froula University of Rochester
Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents 3.0 3~ beam 2.5 4~ TS beam 60 100 100-nm TS volume Thomsonscattered light 5 0 5 Wavelength shift (Å) 0.5 0.0 D. H. Froula University of Rochester
Framed X-Ray Imaging of Cryogenic Target Implosion Cores on OMEGA
 Framed X-Ray Imaging of Cryogenic Target Implosion Cores on OMEGA KBFRAMED optic assembly KBFRAMED core image OMEGA cryogenic DT target implosion shot 77064 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory
Framed X-Ray Imaging of Cryogenic Target Implosion Cores on OMEGA KBFRAMED optic assembly KBFRAMED core image OMEGA cryogenic DT target implosion shot 77064 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory
Thomson Scattering from Nonlinear Electron Plasma Waves
 Thomson Scattering from Nonlinear Electron Plasma Waves A. DAVIES, 1 J. KATZ, 1 S. BUCHT, 1 D. HABERBERGER, 1 J. BROMAGE, 1 J. D. ZUEGEL, 1 J. D. SADLER, 2 P. A. NORREYS, 3 R. BINGHAM, 4 R. TRINES, 5 L.O.
Thomson Scattering from Nonlinear Electron Plasma Waves A. DAVIES, 1 J. KATZ, 1 S. BUCHT, 1 D. HABERBERGER, 1 J. BROMAGE, 1 J. D. ZUEGEL, 1 J. D. SADLER, 2 P. A. NORREYS, 3 R. BINGHAM, 4 R. TRINES, 5 L.O.
Bulk Fluid Velocity Construction from NIF Neutron Spectral Diagnostics
 Bulk Fluid elocity Construction from NIF Neutron Spectral Diagnostics ntof-4.5 DT-Lo (64-309) ntof-3.9 DSF (64-275) ntof-4.5 BT (64-253) MRS ntof-4.5 DT-Hi (64-330) Spec E (90-174) Spec A (116-316) Spec
Bulk Fluid elocity Construction from NIF Neutron Spectral Diagnostics ntof-4.5 DT-Lo (64-309) ntof-3.9 DSF (64-275) ntof-4.5 BT (64-253) MRS ntof-4.5 DT-Hi (64-330) Spec E (90-174) Spec A (116-316) Spec
The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition
 The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition Normalized intensity 1..8.6.4.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Core self-emission. 3 2 1
The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition Normalized intensity 1..8.6.4.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Core self-emission. 3 2 1
Equation-of-State Measurements in Ta 2 O 5 Aerogel
 Equation-of-State Measurements in Ta 2 O 5 Aerogel Introduction In the last 15 years, there has been considerable interest in experiments that use laser-driven shock waves to measure high-energy-density
Equation-of-State Measurements in Ta 2 O 5 Aerogel Introduction In the last 15 years, there has been considerable interest in experiments that use laser-driven shock waves to measure high-energy-density
A Model of Laser Imprinting. V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V.
 A Model of Laser Imprinting V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V. Gotchev Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester The control of
A Model of Laser Imprinting V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V. Gotchev Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester The control of
Time resolved optical spectroscopy methods for organic photovoltaics. Enrico Da Como. Department of Physics, University of Bath
 Time resolved optical spectroscopy methods for organic photovoltaics Enrico Da Como Department of Physics, University of Bath Outline Introduction Why do we need time resolved spectroscopy in OPV? Short
Time resolved optical spectroscopy methods for organic photovoltaics Enrico Da Como Department of Physics, University of Bath Outline Introduction Why do we need time resolved spectroscopy in OPV? Short
High-Intensity Laser Interactions with Solid Targets and Implications for Fast-Ignition Experiments on OMEGA EP
 n n High-Intensity Laser Interactions with Solid Targets and Implications for Fast-Ignition Experiments on OMEGA EP a n n n n J. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual
n n High-Intensity Laser Interactions with Solid Targets and Implications for Fast-Ignition Experiments on OMEGA EP a n n n n J. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual
Equation of state of fluid helium at high temperatures and densities
 Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 005 Vol.48 No.6 695 705 695 Equation of state of fluid helium at high temperatures and densities CAI Lingcang, CHEN Qifeng, GU Yunjun, ZHANG Ying,
Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 005 Vol.48 No.6 695 705 695 Equation of state of fluid helium at high temperatures and densities CAI Lingcang, CHEN Qifeng, GU Yunjun, ZHANG Ying,
X-Ray Spectral Measurements of Cryogenic Capsules Imploded by OMEGA
 X-Ray Spectral Measurements of Cryogenic Capsules Imploded by OMEGA 1 15 1 14 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics kt =.65 kev 48386 (v ice = 1.5 nm) 2 48385 (v ice =
X-Ray Spectral Measurements of Cryogenic Capsules Imploded by OMEGA 1 15 1 14 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics kt =.65 kev 48386 (v ice = 1.5 nm) 2 48385 (v ice =
Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research
 Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research Ignition and Gain Total GtRH n (g/cm 2 ) 2 1.5.2.1 IAEA 21 DT, 22 kj IAEA 28 DT, 16 kj NIF.5 MJ NIF point design 1.5 MJ 1-D marginal ignition
Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research Ignition and Gain Total GtRH n (g/cm 2 ) 2 1.5.2.1 IAEA 21 DT, 22 kj IAEA 28 DT, 16 kj NIF.5 MJ NIF point design 1.5 MJ 1-D marginal ignition
High-Pressure Phase Transformations of Ramp-Compressed Aluminum and Sodium
 High-Pressure Phase Transformations of Ramp-Compressed Aluminum and Sodium by Danae Nicole Polsin Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy Supervised by
High-Pressure Phase Transformations of Ramp-Compressed Aluminum and Sodium by Danae Nicole Polsin Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy Supervised by
Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source
 3rd International EUVL Symposium NOVEMBER 1-4, 2004 Miyazaki, Japan Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source H. Tanaka, A. Matsumoto, K. Akinaga, A. Takahashi
3rd International EUVL Symposium NOVEMBER 1-4, 2004 Miyazaki, Japan Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source H. Tanaka, A. Matsumoto, K. Akinaga, A. Takahashi
Progress in the study of Warm Dense Matter
 Progress in the study of Warm Dense Matter Koenig, M., Benuzzi-Mounaix, A., Vinci, T., Ozaki, N., Lepape, S., Batani, D.,... Romagnani, L. (2005). Progress in the study of Warm Dense Matter. Plasma Physics
Progress in the study of Warm Dense Matter Koenig, M., Benuzzi-Mounaix, A., Vinci, T., Ozaki, N., Lepape, S., Batani, D.,... Romagnani, L. (2005). Progress in the study of Warm Dense Matter. Plasma Physics
Mechanical and optical response of [100] lithium fluoride to multi-megabar dynamic pressures
![Mechanical and optical response of [100] lithium fluoride to multi-megabar dynamic pressures Mechanical and optical response of [100] lithium fluoride to multi-megabar dynamic pressures](/thumbs/93/113437225.jpg) to multi-megabar dynamic pressures Jean-Paul Davis 1, Marcus D. Knudson 1,2, Luke Shulenburger 1, and Scott D. Crockett 3 1 Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, New Mexico 87185, USA 2 Institute
to multi-megabar dynamic pressures Jean-Paul Davis 1, Marcus D. Knudson 1,2, Luke Shulenburger 1, and Scott D. Crockett 3 1 Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, New Mexico 87185, USA 2 Institute
An Alternative Laser-Speckle-Smoothing Scheme for the NIF
 An Alternative Laser-Speckle-Smoothing Scheme for the NIF 1.5-MJ CH-foam target; end of acceleration 1-D SSD, 1.8 Å 1-D MultiFM, 8 Å 2-D SSD, 11 Å 1-D SSD 1-D, multiple-fm SSD 2-D SSD Density (g cm 3 )
An Alternative Laser-Speckle-Smoothing Scheme for the NIF 1.5-MJ CH-foam target; end of acceleration 1-D SSD, 1.8 Å 1-D MultiFM, 8 Å 2-D SSD, 11 Å 1-D SSD 1-D, multiple-fm SSD 2-D SSD Density (g cm 3 )
Cross-Beam Energy Transport in Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments
 Cross-Beam Energy Transport in Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments 35 3 Laser pulse Power (TW) 25 2 15 1 Modeled scattered light Measured 5 D. H. Edgell University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.5
Cross-Beam Energy Transport in Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments 35 3 Laser pulse Power (TW) 25 2 15 1 Modeled scattered light Measured 5 D. H. Edgell University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.5
High-Resolving-Power, Ultrafast Streaked X-Ray Spectroscopy on OMEGA EP
 High-Resolving-Power, Ultrafast Streaked X-Ray Spectroscopy on OMEGA EP Channel 1 Crystal chamber X-ray streak camera Chamber wall Re-entrant tube with collimators Normalized signal 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 Pulse
High-Resolving-Power, Ultrafast Streaked X-Ray Spectroscopy on OMEGA EP Channel 1 Crystal chamber X-ray streak camera Chamber wall Re-entrant tube with collimators Normalized signal 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 Pulse
Modeling the Effects Mix at the Hot Spot Surface in 1-D Simulations of Cryogenic All-DT Ignition Capsule Implosions
 Modeling the Effects Mix at the Hot Spot Surface in 1-D Simulations of Cryogenic All-DT Ignition Capsule Implosions 14 Time = 1.4 ns 25 Ion temperature (kev) 12 1 8 6 4 2 22.2 8.7 1.5 Gain =.45 2 15 1
Modeling the Effects Mix at the Hot Spot Surface in 1-D Simulations of Cryogenic All-DT Ignition Capsule Implosions 14 Time = 1.4 ns 25 Ion temperature (kev) 12 1 8 6 4 2 22.2 8.7 1.5 Gain =.45 2 15 1
First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA
 First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA MIT 1 mm 1 mm 100 µm C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division
First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA MIT 1 mm 1 mm 100 µm C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division
Stimulated Raman Scattering in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion
 Stimulated Raman Scattering in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion View ports 5 FABS Experiments carried out at the National Ignition Facility FABS power (arbitrary units) Plasma-producing beams (
Stimulated Raman Scattering in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion View ports 5 FABS Experiments carried out at the National Ignition Facility FABS power (arbitrary units) Plasma-producing beams (
Shock-wave equation-of-state measurements in fused silica up to 1600 GPa. Rochester, NY , USA. Rochester, NY 14620, USA
 Shock-wave equation-of-state measurements in fused silica up to 1600 GPa C. A. McCoy, 1,2 M. C. Gregor, 1,3 D. N. Polsin, 1,3 D. E. Fratanduono, 4 P. M. Celliers, 4 T. R. Boehly, 1 and D. D. Meyerhofer
Shock-wave equation-of-state measurements in fused silica up to 1600 GPa C. A. McCoy, 1,2 M. C. Gregor, 1,3 D. N. Polsin, 1,3 D. E. Fratanduono, 4 P. M. Celliers, 4 T. R. Boehly, 1 and D. D. Meyerhofer
Chamber Development Plan and Chamber Simulation Experiments
 Chamber Development Plan and Chamber Simulation Experiments Farrokh Najmabadi HAPL Meeting November 12-13, 2001 Livermore, CA Electronic copy: http://aries.ucsd.edu/najmabadi/talks UCSD IFE Web Site: http://aries.ucsd.edu/ife
Chamber Development Plan and Chamber Simulation Experiments Farrokh Najmabadi HAPL Meeting November 12-13, 2001 Livermore, CA Electronic copy: http://aries.ucsd.edu/najmabadi/talks UCSD IFE Web Site: http://aries.ucsd.edu/ife
Reaching the Extremes of Planet Formation Shockwave Experiments in the Giant Impact Regime
 Reaching the Extremes of Planet Formation Shockwave Experiments in the Giant Impact Regime Sarah T. Stewart Dept. Earth & Planetary Sciences, UC Davis Planet Formation Art by NASA Giant Impacts Art by
Reaching the Extremes of Planet Formation Shockwave Experiments in the Giant Impact Regime Sarah T. Stewart Dept. Earth & Planetary Sciences, UC Davis Planet Formation Art by NASA Giant Impacts Art by
OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics
 OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics Astronomical jets Experimental jets Instabilities 1.4 light years Ambient shocks Jet/ambient material interface 2.8 mm Collimated
OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics Astronomical jets Experimental jets Instabilities 1.4 light years Ambient shocks Jet/ambient material interface 2.8 mm Collimated
Relativistic Electron Beams, Forward Thomson Scattering, and Raman Scattering. A. Simon. Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U.
 Relativistic Electron Beams, Forward Thomson Scattering, and Raman Scattering A. Simon Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester Experiments at LLE (see abstract by D. Hicks at this meeting) show
Relativistic Electron Beams, Forward Thomson Scattering, and Raman Scattering A. Simon Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester Experiments at LLE (see abstract by D. Hicks at this meeting) show
Elastic and Inelastic Shock Compression of Diamond and Other Minerals. Ryan Stewart McWilliams. B.S. (University of Massachusetts, Amherst) 2001
 Elastic and Inelastic Shock Compression of Diamond and Other Minerals by Ryan Stewart McWilliams B.S. (University of Massachusetts, Amherst) A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements
Elastic and Inelastic Shock Compression of Diamond and Other Minerals by Ryan Stewart McWilliams B.S. (University of Massachusetts, Amherst) A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008
 Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets
 1 Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets Mayank Shukla 1), Yogesh Kashyap 1), P. S. Sarkar 1), A. Sinha 1), H. C. Pant 2), R.S.Rao 1), N.K.Gupta 1), B.K.Godwal 1)
1 Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets Mayank Shukla 1), Yogesh Kashyap 1), P. S. Sarkar 1), A. Sinha 1), H. C. Pant 2), R.S.Rao 1), N.K.Gupta 1), B.K.Godwal 1)
Collimation of a Positron Beam Using an Externally Applied Axially Symmetric Magnetic Field FSC
 Collimation of a Positron Beam Using an Externally Applied Axially Symmetric Magnetic Field Numbers (MeV/Sr) 1 12 1 11 1 1 1 9 Electrons Positrons Reference shot (no B fields) 1 15 Shot with B fields by
Collimation of a Positron Beam Using an Externally Applied Axially Symmetric Magnetic Field Numbers (MeV/Sr) 1 12 1 11 1 1 1 9 Electrons Positrons Reference shot (no B fields) 1 15 Shot with B fields by
Determination of the Flux Limiter in CH Targets from Experiments on the OMEGA Laser
 Determination of the Flux Limiter in CH Targets from Experiments on the OMEGA Laser f = 0.070 Neutron rate (1/s) Exp. f = 0.065 f = 0.060 J. A. Delettrez et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser
Determination of the Flux Limiter in CH Targets from Experiments on the OMEGA Laser f = 0.070 Neutron rate (1/s) Exp. f = 0.065 f = 0.060 J. A. Delettrez et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser
Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks. 26 June 2009
 PSFC/JA-8-8 Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks J. R. Rygg, J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Seguin, R. D. Petrasso, F.J. Marshalli, J. A. Delettrez, J.P. Knauer, D.D.
PSFC/JA-8-8 Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks J. R. Rygg, J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Seguin, R. D. Petrasso, F.J. Marshalli, J. A. Delettrez, J.P. Knauer, D.D.
Polar-Drive Hot-Spot Ignition Design for the National Ignition Facility
 Polar-Drive Hot-Spot Ignition Design for the National Ignition Facility At ignition, Gain=40 T. J. B. Collins University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics International Shock-Ignition Workshop
Polar-Drive Hot-Spot Ignition Design for the National Ignition Facility At ignition, Gain=40 T. J. B. Collins University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics International Shock-Ignition Workshop
Theory and simulations of hydrodynamic instabilities in inertial fusion
 Theory and simulations of hydrodynamic instabilities in inertial fusion R. Betti Fusion Science Center, Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester IPAM/UCLA Long Program PL2012 - March 12
Theory and simulations of hydrodynamic instabilities in inertial fusion R. Betti Fusion Science Center, Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester IPAM/UCLA Long Program PL2012 - March 12
Calculation of Half-Harmonic Emission Generated by the Two-Plasmon Decay Instability at exit boundary
 Calculation of Half-Harmonic Emission Generated by the wo-plasmon Decay Instability ^ h E D~ at exit boundary Arbitrary units 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.0 inear conversion Nonlinear conversion homson down-scattering
Calculation of Half-Harmonic Emission Generated by the wo-plasmon Decay Instability ^ h E D~ at exit boundary Arbitrary units 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.0 inear conversion Nonlinear conversion homson down-scattering
Presented at the Michigan Institute for Plasma Science and Engineering
 Presented at the Michigan Institute for Plasma Science and Engineering March 11, 2015 LLNL-PRES-XXXXXX This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-07NA27344.
Presented at the Michigan Institute for Plasma Science and Engineering March 11, 2015 LLNL-PRES-XXXXXX This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-07NA27344.
Hiromitsu TOMIZAWA XFEL Division /SPring-8
 TUPLB10 (Poster: TUPB080) Non-destructive Real-time Monitor to measure 3D- Bunch Charge Distribution with Arrival Timing to maximize 3D-overlapping for HHG-seeded EUV-FEL Hiromitsu TOMIZAWA XFEL Division
TUPLB10 (Poster: TUPB080) Non-destructive Real-time Monitor to measure 3D- Bunch Charge Distribution with Arrival Timing to maximize 3D-overlapping for HHG-seeded EUV-FEL Hiromitsu TOMIZAWA XFEL Division
Shock wave propagation in soda lime glass using optical shadowgraphy
 Pramana J. Phys. (2016) 87: 9 DOI 10.1007/s12043-016-1212-z c Indian Academy of Sciences Shock wave propagation in soda lime glass using optical shadowgraphy Y B S R PRASAD 1,2,, SBARNWAL 1,2,PANAIK 1,2,
Pramana J. Phys. (2016) 87: 9 DOI 10.1007/s12043-016-1212-z c Indian Academy of Sciences Shock wave propagation in soda lime glass using optical shadowgraphy Y B S R PRASAD 1,2,, SBARNWAL 1,2,PANAIK 1,2,
Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility
 Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility R (mm) 1 8 6 4 End of acceleration phase r(g/cc) 7.5 3.5.5 Gain 4 3 2 1 1 2 2 s (mm) 5 25 25 5 Z (mm) P. W. McKenty
Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility R (mm) 1 8 6 4 End of acceleration phase r(g/cc) 7.5 3.5.5 Gain 4 3 2 1 1 2 2 s (mm) 5 25 25 5 Z (mm) P. W. McKenty
ISENTROPIC COMPRESSION OF HIGH EXPLOSIVES WITH THE Z ACCELERATOR
 ISENTROPIC COMPRESSION OF HIGH EXPLOSIVES WITH THE Z ACCELERATOR David B. Reisman, Jerry W. Forbes, Craig M. Tarver, and Frank Garcia Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, CA 94551 Dennis B.
ISENTROPIC COMPRESSION OF HIGH EXPLOSIVES WITH THE Z ACCELERATOR David B. Reisman, Jerry W. Forbes, Craig M. Tarver, and Frank Garcia Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, CA 94551 Dennis B.
Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil
 Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil Matthew Allen Department of Nuclear Engineering UC Berkeley mallen@nuc.berkeley.edu March 15, 2004 8th Nuclear Energy
Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil Matthew Allen Department of Nuclear Engineering UC Berkeley mallen@nuc.berkeley.edu March 15, 2004 8th Nuclear Energy
T T Fusion Neutron Spectrum Measured in Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiment
 T T Fusion Neutron Spectrum Measured in Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiment V. Yu. Glebov University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
T T Fusion Neutron Spectrum Measured in Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiment V. Yu. Glebov University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
Two-Plasmon-Decay Hot Electron Generation and Reheating in OMEGA Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments
 Two-Plasmon-Decay Hot Electron Generation and Reheating in OMEGA Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments r 1/4 ~500 nm Ne To sheath e Laser r e To core 20 nm J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for
Two-Plasmon-Decay Hot Electron Generation and Reheating in OMEGA Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments r 1/4 ~500 nm Ne To sheath e Laser r e To core 20 nm J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for
Supplemental material for Bound electron nonlinearity beyond the ionization threshold
 Supplemental material for Bound electron nonlinearity beyond the ionization threshold 1. Experimental setup The laser used in the experiments is a λ=800 nm Ti:Sapphire amplifier producing 42 fs, 10 mj
Supplemental material for Bound electron nonlinearity beyond the ionization threshold 1. Experimental setup The laser used in the experiments is a λ=800 nm Ti:Sapphire amplifier producing 42 fs, 10 mj
Shock Wave Experiments Using PDV: Window Characterization at 1550 nm
 Shock Wave Experiments Using PDV: Window Characterization at 1550 nm B. J. Jensen (DE-9), D. Holtkamp (P-22), D. H. Dolan (Sandia) Los Alamos National Laboratory Acknowlegements: Tim Pierce (DE-9), Mark
Shock Wave Experiments Using PDV: Window Characterization at 1550 nm B. J. Jensen (DE-9), D. Holtkamp (P-22), D. H. Dolan (Sandia) Los Alamos National Laboratory Acknowlegements: Tim Pierce (DE-9), Mark
Using a Relativistic Electron Beam to Generate Warm Dense Matter for Equation of State Studies
 Using a Relativistic Electron Beam to Generate Warm Dense Matter for Equation of State Studies DOE/NV/25946--1257 M. J. Berninger National Security Technologies, LLC, Los Alamos, NM 87544 T. J. T. Kwan,
Using a Relativistic Electron Beam to Generate Warm Dense Matter for Equation of State Studies DOE/NV/25946--1257 M. J. Berninger National Security Technologies, LLC, Los Alamos, NM 87544 T. J. T. Kwan,
Introduction to intense laser-matter interaction
 Pohang, 22 Aug. 2013 Introduction to intense laser-matter interaction Chul Min Kim Advanced Photonics Research Institute (APRI), Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) & Center for Relativistic
Pohang, 22 Aug. 2013 Introduction to intense laser-matter interaction Chul Min Kim Advanced Photonics Research Institute (APRI), Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) & Center for Relativistic
Lecture 3: Optical Properties of Insulators, Semiconductors, and Metals. 5 nm
 Metals Lecture 3: Optical Properties of Insulators, Semiconductors, and Metals 5 nm Course Info Next Week (Sept. 5 and 7) no classes First H/W is due Sept. 1 The Previous Lecture Origin frequency dependence
Metals Lecture 3: Optical Properties of Insulators, Semiconductors, and Metals 5 nm Course Info Next Week (Sept. 5 and 7) no classes First H/W is due Sept. 1 The Previous Lecture Origin frequency dependence
Simple strategy for enhancing terahertz emission from coherent longitudinal optical phonons using undoped GaAs/n-type GaAs epitaxial layer structures
 Presented at ISCS21 June 4, 21 Session # FrP3 Simple strategy for enhancing terahertz emission from coherent longitudinal optical phonons using undoped GaAs/n-type GaAs epitaxial layer structures Hideo
Presented at ISCS21 June 4, 21 Session # FrP3 Simple strategy for enhancing terahertz emission from coherent longitudinal optical phonons using undoped GaAs/n-type GaAs epitaxial layer structures Hideo
Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors
 Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors Frank Ceballos 1, Ming-Gang Ju 2 Samuel D. Lane 1, Xiao Cheng Zeng 2 & Hui Zhao 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors Frank Ceballos 1, Ming-Gang Ju 2 Samuel D. Lane 1, Xiao Cheng Zeng 2 & Hui Zhao 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
X-ray driven implosions at ignition relevant velocities on the National Ignition Facilitya) Phys. Plasmas 20, (2013); /1.
 A Particle X-ray Temporal Diagnostic (PXTD) for studies of kinetic, multi-ion effects, and ion-electron equilibration rates in Inertial Confinement Fusion plasmas at OMEGA (invited) H. Sio, J. A. Frenje,
A Particle X-ray Temporal Diagnostic (PXTD) for studies of kinetic, multi-ion effects, and ion-electron equilibration rates in Inertial Confinement Fusion plasmas at OMEGA (invited) H. Sio, J. A. Frenje,
Journal of Applied and Theoretical Physics Research
 Journal of Applied and Theoretical Physics Research Diagnostics and Production of Warm Dense Matter with Multishock Reverberation Compression Technique Qifeng Chen *, Zhiguo Li, YunjunGu, Jun Zheng, Chengjun
Journal of Applied and Theoretical Physics Research Diagnostics and Production of Warm Dense Matter with Multishock Reverberation Compression Technique Qifeng Chen *, Zhiguo Li, YunjunGu, Jun Zheng, Chengjun
Progress Report on Chamber Dynamics and Clearing
 Progress Report on Chamber Dynamics and Clearing Farrokh Najmabadi, Rene Raffray, Mark S. Tillack, John Pulsifer, Zoran Dragovlovic (UCSD) Ahmed Hassanein (ANL) Laser-IFE Program Workshop May31-June 1,
Progress Report on Chamber Dynamics and Clearing Farrokh Najmabadi, Rene Raffray, Mark S. Tillack, John Pulsifer, Zoran Dragovlovic (UCSD) Ahmed Hassanein (ANL) Laser-IFE Program Workshop May31-June 1,
Laser matter interaction
 Laser matter interaction PH413 Lasers & Photonics Lecture 26 Why study laser matter interaction? Fundamental physics Chemical analysis Material processing Biomedical applications Deposition of novel structures
Laser matter interaction PH413 Lasers & Photonics Lecture 26 Why study laser matter interaction? Fundamental physics Chemical analysis Material processing Biomedical applications Deposition of novel structures
Performance Limits of Delay Lines Based on "Slow" Light. Robert W. Boyd
 Performance Limits of Delay Lines Based on "Slow" Light Robert W. Boyd Institute of Optics and Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Representing the DARPA Slow-Light-in-Fibers Team:
Performance Limits of Delay Lines Based on "Slow" Light Robert W. Boyd Institute of Optics and Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Representing the DARPA Slow-Light-in-Fibers Team:
Elements of Quantum Optics
 Pierre Meystre Murray Sargent III Elements of Quantum Optics Fourth Edition With 124 Figures fya Springer Contents 1 Classical Electromagnetic Fields 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations in a Vacuum 2 1.2 Maxwell's
Pierre Meystre Murray Sargent III Elements of Quantum Optics Fourth Edition With 124 Figures fya Springer Contents 1 Classical Electromagnetic Fields 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations in a Vacuum 2 1.2 Maxwell's
HIGH ACCURACY ISENTROPIC COMPRESSION STUDIES WITH HIGH EXPLOSIVE PULSED POWER
 HIGH ACCURACY ISENTROPIC COMPRESSION STUDIES WITH HIGH EPLOSIVE PULSED POWER D.G. Tasker ξ, J.H. Goforth, H. Oona Los Alamos National Laboratory, DE-6, MS J566 Los Alamos, NM 87545, USA Abstract An study
HIGH ACCURACY ISENTROPIC COMPRESSION STUDIES WITH HIGH EPLOSIVE PULSED POWER D.G. Tasker ξ, J.H. Goforth, H. Oona Los Alamos National Laboratory, DE-6, MS J566 Los Alamos, NM 87545, USA Abstract An study
Measurement of wakefields in hollow plasma channels Carl A. Lindstrøm (University of Oslo)
 Measurement of wakefields in hollow plasma channels Carl A. Lindstrøm (University of Oslo) in collaboration with Spencer Gessner (CERN) presented by Erik Adli (University of Oslo) FACET-II Science Workshop
Measurement of wakefields in hollow plasma channels Carl A. Lindstrøm (University of Oslo) in collaboration with Spencer Gessner (CERN) presented by Erik Adli (University of Oslo) FACET-II Science Workshop
Picket Pulses with 1-D MultiFM Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) for the NIF
 Picket Pulses with 1-D MultiFM Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) for the NIF 500 MultiFM DesignSpace = [21.2,22.8,31.9] University of Roch Using: analyzelmf 500 MultiFM DesignSpace = [21.2,22.8,31.9]
Picket Pulses with 1-D MultiFM Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) for the NIF 500 MultiFM DesignSpace = [21.2,22.8,31.9] University of Roch Using: analyzelmf 500 MultiFM DesignSpace = [21.2,22.8,31.9]
Density Functional Theory Methods for Transport and Optical Properties: Application to Warm Dense Silicon
 Density Functional Theory Methods for Transport and Optical Properties: Application to Warm Dense Silicon 2200 Si, T = 62.5 kk K-edge position (ev) 2100 2000 1900 DFT (shifted by 50 ev) AOT Significant
Density Functional Theory Methods for Transport and Optical Properties: Application to Warm Dense Silicon 2200 Si, T = 62.5 kk K-edge position (ev) 2100 2000 1900 DFT (shifted by 50 ev) AOT Significant
16. More About Polarization
 16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
SIMULATION OF DOUBLE-PULSE LASER ABLATION OF METALS
 SIMULATION OF DOUBLE-PULSE LASER ABLATION OF METALS M. Povarnitsyn, K. Khishchenko, P. Levashov Joint Institute for High Temperatures, RAS, Moscow, Russia povar@ihed.ras.ru T. Itina Laboratoire Hubert
SIMULATION OF DOUBLE-PULSE LASER ABLATION OF METALS M. Povarnitsyn, K. Khishchenko, P. Levashov Joint Institute for High Temperatures, RAS, Moscow, Russia povar@ihed.ras.ru T. Itina Laboratoire Hubert
Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled, cone-in-shell, fast-ignitor targets on the OMEGA Laser
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (25) B859 B867 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:1.188/741-3335/47/12b/s68 Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled,
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (25) B859 B867 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:1.188/741-3335/47/12b/s68 Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled,
Magnetic fields applied to laser-generated plasma to enhance the ion yield acceleration
 Magnetic fields applied to laser-generated plasma to enhance the ion yield acceleration L. Torrisi, G. Costa, and G. Ceccio Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche MIFT, Università di Messina, V.le F.S. D Alcontres
Magnetic fields applied to laser-generated plasma to enhance the ion yield acceleration L. Torrisi, G. Costa, and G. Ceccio Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche MIFT, Università di Messina, V.le F.S. D Alcontres
Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width
 Introduction Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width A. B. Zylstra, M. Rosenberg, N. Sinenian, C. Li, F. Seguin, J. Frenje, R. Petrasso (MIT) R. Rygg, D. Hicks, S. Friedrich,
Introduction Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width A. B. Zylstra, M. Rosenberg, N. Sinenian, C. Li, F. Seguin, J. Frenje, R. Petrasso (MIT) R. Rygg, D. Hicks, S. Friedrich,
The Sound Velocity and Grüneisen Parameter of Fused Silica, Periclase, and Polystyrene shocked to TPa pressures
 The Sound Velocity and Grüneisen Parameter of Fused Silica, Periclase, and Polystyrene shocked to TPa pressures Chad August McCoy Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor
The Sound Velocity and Grüneisen Parameter of Fused Silica, Periclase, and Polystyrene shocked to TPa pressures Chad August McCoy Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor
Determination of Hot-Electron Conversion Efficiencies and Isochoric Heating of Low-Mass Targets Irradiated by the Multi-Terawatt Laser
 Determination of Hot-Electron Conversion Efficiencies and Isochoric Heating of Low-Mass Targets Irradiated by the Multi-Terawatt Laser 1.2 Total energy K a /laser energy 1 3 1 4 Refluxing No refluxing
Determination of Hot-Electron Conversion Efficiencies and Isochoric Heating of Low-Mass Targets Irradiated by the Multi-Terawatt Laser 1.2 Total energy K a /laser energy 1 3 1 4 Refluxing No refluxing
Computer Simulation of Shock Waves in Condensed Matter. Matthew R. Farrow 2 November 2007
 Computer Simulation of Shock Waves in Condensed Matter Matthew R. Farrow 2 November 2007 Outline of talk Shock wave theory Results Conclusion Computer simulation of shock waves Shock Wave Theory Shock
Computer Simulation of Shock Waves in Condensed Matter Matthew R. Farrow 2 November 2007 Outline of talk Shock wave theory Results Conclusion Computer simulation of shock waves Shock Wave Theory Shock
Where are we with laser fusion?
 Where are we with laser fusion? R. Betti Laboratory for Laser Energetics Fusion Science Center Dept. Mechanical Engineering and Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester HEDSA HEDP Summer School August
Where are we with laser fusion? R. Betti Laboratory for Laser Energetics Fusion Science Center Dept. Mechanical Engineering and Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester HEDSA HEDP Summer School August
Supplementary Information: Linear dependence of surface expansion speed on initial plasma temperature in warm dense matter
 Supplementary Information: Linear dependence of surface expansion speed on initial plasma temperature in warm dense matter W. Bang, 1 B. J. Albright, 1 P. A. Bradley, 1 E. L. Vold, 1 J. C. Boettger, 1
Supplementary Information: Linear dependence of surface expansion speed on initial plasma temperature in warm dense matter W. Bang, 1 B. J. Albright, 1 P. A. Bradley, 1 E. L. Vold, 1 J. C. Boettger, 1
Two-Plasmon Decay Driven by Multiple Incoherent Laser Beams
 Two-Plasmon Decay Driven by Multiple Incoherent Laser Beams 2 # # E^xyt,, h dy dy^arbitrary h n Two coherent e /n c plane waves Dm = 8.8 Å Dm = 17.6 Å.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27 2 Arbitrary
Two-Plasmon Decay Driven by Multiple Incoherent Laser Beams 2 # # E^xyt,, h dy dy^arbitrary h n Two coherent e /n c plane waves Dm = 8.8 Å Dm = 17.6 Å.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27 2 Arbitrary
Laser Ablation Studies at UCSD and Plans for Time and Space Resolved Ejecta Measurements
 Laser Ablation Studies at UCSD and Plans for Time and Space Resolved Ejecta Measurements M. S. Tillack, Y. Tao, Y. Ueno*, R. Burdt, S. Yuspeh, A. Farkas, 2 nd TITAN workshop on MFE/IFE common research
Laser Ablation Studies at UCSD and Plans for Time and Space Resolved Ejecta Measurements M. S. Tillack, Y. Tao, Y. Ueno*, R. Burdt, S. Yuspeh, A. Farkas, 2 nd TITAN workshop on MFE/IFE common research
Limits on the Time Delay Induced by Slow-Light Propagation
 Limits on the Time Delay Induced by Slow-Light Propagation Robert W. Boyd Institute of Optics, University of Rochester Daniel J. Gauthier Department of Physics, Duke University Alexander L. Gaeta Applied
Limits on the Time Delay Induced by Slow-Light Propagation Robert W. Boyd Institute of Optics, University of Rochester Daniel J. Gauthier Department of Physics, Duke University Alexander L. Gaeta Applied
9 Atomic Coherence in Three-Level Atoms
 9 Atomic Coherence in Three-Level Atoms 9.1 Coherent trapping - dark states In multi-level systems coherent superpositions between different states (atomic coherence) may lead to dramatic changes of light
9 Atomic Coherence in Three-Level Atoms 9.1 Coherent trapping - dark states In multi-level systems coherent superpositions between different states (atomic coherence) may lead to dramatic changes of light
Temperature time-history measurements in a shock tube using diode laser absorption of CO 2 near 2.7 µm
 23 rd ICDERS July 24-29, 2011 Irvine, USA Temperature time-history measurements in a shock tube using diode laser absorption of CO 2 near 2.7 µm Wei Ren, Sijie Li, David F Davidson, and Ronald K Hanson
23 rd ICDERS July 24-29, 2011 Irvine, USA Temperature time-history measurements in a shock tube using diode laser absorption of CO 2 near 2.7 µm Wei Ren, Sijie Li, David F Davidson, and Ronald K Hanson
Optimization of EUV Lithography Plasma Radiation Source Characteristics Using HELIOS-CR
 Optimization of EUV Lithography Plasma Radiation Source Characteristics Using HELIOS-CR J. J. MacFarlane, P. Wang, I. E. Golovkin, P. R. Woodruff Prism Computational Sciences, Inc. Madison, WI (USA) http://www.prism-cs.com
Optimization of EUV Lithography Plasma Radiation Source Characteristics Using HELIOS-CR J. J. MacFarlane, P. Wang, I. E. Golovkin, P. R. Woodruff Prism Computational Sciences, Inc. Madison, WI (USA) http://www.prism-cs.com
Improved target stability using picket pulses to increase and shape the ablator adiabat a
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS 12, 056306 2005 Improved target stability using picket pulses to increase and shape the ablator adiabat a J. P. Knauer, b K. Anderson, R. Betti, T. J. B. Collins, V. N. Goncharov, P.
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS 12, 056306 2005 Improved target stability using picket pulses to increase and shape the ablator adiabat a J. P. Knauer, b K. Anderson, R. Betti, T. J. B. Collins, V. N. Goncharov, P.
The Magnetic Recoil Spectrometer (MRSt) for time-resolved measurements of the neutron spectrum at the National Ignition Facility (NIF)
 PSFC/JA-16-32 The Magnetic Recoil Spectrometer (MRSt) for time-resolved measurements of the neutron spectrum at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) J.A. Frenje 1 T.J. Hilsabeck 2, C. Wink1, P. Bell 3,
PSFC/JA-16-32 The Magnetic Recoil Spectrometer (MRSt) for time-resolved measurements of the neutron spectrum at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) J.A. Frenje 1 T.J. Hilsabeck 2, C. Wink1, P. Bell 3,
