A Model of Laser Imprinting. V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V.
|
|
|
- Janice Carson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Model of Laser Imprinting V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V. Gotchev Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester The control of laser imprint is of crucial importance for the successful implosion of direct-drive inertial confinement fusion targets. Irradiation nonuniformities generate, or imprint, modulations in the ablation pressure that seed the Rayleigh Taylor (RT) and Bell Plesset (BP) instabilities, which in turn degrade the symmetry of the implosion and reduce the target performance. To gain physical insight, an analytical model of imprint has been developed. The model takes into account the dynamics of the conduction zone, mass ablation, and the SSD smoothing scheme. The important parameters that characterize laser imprint are found to be the time scale for plasma atmosphere formation, the ablation velocity, and the density-gradient scale length. The first determines the smoothing rate due to thermal transport in the conduction zone, and the last two characterize the dynamic overpressure stabilization described in Ref. [1]. The model has been validated by comparisons to detailed multidimensional hydrocode simulations using a range of ablator materials, perturbation wavelengths, and pulse shapes. The model has been found to be in good agreement with a series of planar-foil imprint experiments performed on the OMEGA laser system at the University of Rochester s Laboratory for Laser Energetics. Imprint s effect on NIF and NIF-scaled OMEGA cryogenic targets has been studied. It is has been shown that such targets will remain intact during the implosion when the laser is smoothed with 1 THz 2-D SSD. This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inertial Confinement Fusion under Cooperative Agreement No. DE-FC03-92SF19460, the University of Rochester, and the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority. [1] V. N. Goncharov, Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 2091 (1999).
2 A Model of Laser Imprinting V. N. Goncharov University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 41st Annual Meeting of the Americal Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Seattle, WA November 1999
3 Collaborators S. Skupsky, P. W. McKenty, R. P. J. Town, T. R. Boehly, D. D. Meyerhofer, and O. V. Gotchev University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics
4 Summary An analytical model is developed to gain physical insight of the laser imprint Laser nonuniformities imprint surface modulations that degrade the symmetry of implosion. An analytical model has been developed to determine the physical processes contributing to imprint. Hydrodynamic flow is the main imprinting mechanism. Thermal smooting and the dynamic overpressure are the main processes reducing the imprint. Laser imprint, with 1-THz SSD beam smoothing, will not significantly degrade cryogenic-target performance. TC5213
5 Outline Laser imprint in direct-drive ICF Processes contributing to laser imprint Processes reducing laser imprint Analytic imprint model comparison with 2-D numerical simulation comparison with imprint experiments Effect of imprint upon NIF ignition targets polymer overcoat SSD beam smoothing target gain TC5227
6 In direct-drive target designs developed at LLE, the fuel isentrope is controlled by the shock preheat Direct-drive, α = 3, NIF ignition target design CH Power (TW) 100 Foot Main drive DT DT gas 1.69 mm mm Time (ns) TC5216
7 Laser imprint degrades target performance Laser t = Surface finish: σ inner = 1.00 µm σ outer = 0.08 µm Gain D gain Maximum compression rms imprint (µm) t At the beginning of the main drive TC5217
8 Processes contributing to imprint Velocity pertubation due to nonuniform shock propagation Acceleration perturbation from the lateral flow in the compressed region TC5218
9 Hydrodynamic flow is the main imprint mechanism: velocity perturbation Shock speed depends of the ablation pressure U s ~ p a U s δu s p a 0 δ pa Shock Laser ṽ ~ δu s ~ 1 2 U s δp a p a 0 U s + δu s p a 0 + δpa Shock front Ablation front p 0 ρ 0 c 0 Pressure Density Sound speed p a ρ c s η dη dt = ṽ ~ U s δp a p a η vel = ṽt ~ δp a p a c s t TC5215
10 Hydrodynamic flow is the main imprint mechanism: acceleration perturbation Rippled shock creates lateral mass flow. p a + p p a y ~ v y Perturbed acceleration ~ a d 2 η dt 2 = ã k δp a ρ η ac k δp a p a c s 2 t 2 Shock front η = η vel + η ac η t t 2 TC kc s t
11 Physical mechanisms reducing imprint Thermal smoothing Dynamic overpressure (rocket effect) ablation-surface oscillation Fire polishing, vorticity convection TC5273
12 Thermal smoothing 1 suppresses acceleration perturbation Ablation front Absorption region δp a p a δp e kx δi I e kd c kd c δp a /p a D c V c t Time (ns) t D η vel >> η ac Laser perturbations decouple from the ablation front when kd c ~1 Decoupling time t D (kv c ) 1 TC K. A. Brueckner and S. Jorna, Rev. Mod. Phys. 46, 325 (1974).
13 Imprint growth is reduced by thermal smoothing After decoupling time t > t D, a ~ = 0. ~ v = v ~ D η ṽ D δi I c s 2 V c Without thermal smoothing With thermal smoothing 1 Ablation front η at ~ 2 t D ~ η v D t kcst TC A. Velikovich et al., Phys. Plasmas 5, 1491 (1998).
14 Late-time imprint growth is stabilized by dynamic overpressure Rate of change of mass Thrust force = MV bl V bl Exhaust velocity V bl + V bl Absorption region η V bl V bl Ablation front Velocity of blowoff plasma Mass ablation rate TC5276 Dynamic overpressure = m V bl mv bl kη
15 Late-time imprint growth is stabilized by the dynamic overpressure F Ablation front ~ v D p d = mv bl kη F = ( p d ) = k 2 mv bl η F = k bl η Effective spring constant k bl Mass-spring system M ~ v D F = Kη Oscillations η TC5277 Spring Ablation front ω = Œ K/M ω = Œ k bl /ρ = kœ V a V bl
16 Imprint amplitude is determined by the decoupling velocity and oscillation frequency Kinetic energy εk Potential energy εp ε k = ρṽ D 2 2 ε p = k bl η 2 2 = ρω 2 η 2 2 Front amplitude η max = 2ε k = ṽd k bl ω Time TC5278 η max δi I c s 2 V c k V a V bl
17 The most damaging modes oscillate during the shock propagation 4 3 Single-mode imprint ORCHID simulations NIF α = 3 target design l = 50 Amplitude (nm) Time (ns) Shock breakout TC5270
18 Imprint model Description of the model Results ablation-surface oscillations imprint amplitude Comparison with simulations Comparison with imprint experiments TC5279
19 The analytic model is based on solution of the sharp boundary model Undriven target ρ 0 Hugoniot relations Shock front ρ 1 Compressed target [ 2 t cs 2 x 2 k 2 ( )] p = 0 Ablation front Blowoff plasma ρ bl Isotherm y x Assumptions ṽ bl y ṽy h = k ηa ( V bl V a ) V a C s << 1 V b1 Cs ~ 1 D c = V c t Model is solved by multiple-scale technique. τ = k c s t T = k V a V bl t ξ = k V a t η a e 2ξ Oscillations are damped by fire polishing and vorticity convection. sint t TC5214
20 The imprint amplitude is determined by the decoupling velocity and oscillation frequency (η max = ~ v D /ω) Comparison of CH and cryo DT ablators, I = W/cm 2 Decoupling velocity ṽ D ~ c s 2 Vc Oscillation frequency ω = k V a V bl 20 V a CH = 1.0 µm ns Va DT = 2.5 µm ns D c (µm) CH DT η DT CH Time (ns) Time (ns) ṽ D DT ṽ D CH 2.5 ηdt max ηmax CH ω DT 2.5 ωch TC5222
21 ORCHID simulations confirm the predictions of the model Front amplitude (µm)/(δi/i) Perturbation wavelength λ = 40 µm DT CH Time (ns) TC5280 ηdt max ηmax CH
22 The imprint amplitude and oscillation period are reduced by increasing laser intensity Scaling η η max sin ωt ~ δi I V c ~ V a V bl c2 s V a V bl V a ~ I c s ~ I 1/3 V a ~ V bl ~ I 1/3 h max ~ I 2/3 T osc ~ I 1/3 Detailed model results cryo DT planar foil thickness = 345 µm flat-top laser pulse η(µm)/(δi/i) I = W/cm 2 I = W/cm 2 I = W/cm TC5223 Time (ns)
23 Simulations confirm that the imprint amplitude and laser oscillation period are reduced by increasing laser intensity I = W/cm 2 η(µm)/(δi/i) W/cm W/cm 2 Cryo DT planar foil Thickness = 345 µm Flat-top laser pulse Time (ns) TC5281 ç max ~ I 1.0 T osc ~ I 0.4
24 Shorter-wavelength nonuniformities have lower imprint amplitudes and shorter oscillation periods Model: η max ~ λ; T osc ~ λ ORCHID simulation: DD, NIF, α = 3, all-dt target design I = W/cm 2 thickness = 345 µm µm η m ~ λ 1.6 ; T osc ~ λ 1.1 η(µm)/(δi/i) µm 20 µm TC Time (ns)
25 The model has been tested against planar-foil imprint experiments performed on the OMEGA laser system* 20-µm-thick CH Two laser pulse shapes; two perturbation wavelengths Nonuniformities were measured using through-foil x-ray radiography. Intensity (10 14 W/cm 2 ) Foot ramp 3 ns, flat Preimposed mode A pre Imprint A imp Time (ns) Imprint is quantified by the mass equivalence. TC5226 A EQ = A imprint A pre A pre t = 0 ( ) * T. R. Boehly et al., CO2.01, this conference.
26 The results of the experiments agree with imprint simulations and predictions of models Mass equivalence (µm)/(δi/i) Foot ramp 3-ns square η60 ramp η60 square η60 square η30 square Experiments 1.7± ±0.6 Simulations Wavelength (µm) TC5271 Higher intensities and shorter perturbation wavelengths imprint less for modes with t D < shock breakout time
27 Application of the model: effect of imprint on direct-drive NIF ignition design Effect of polymer overcoat Effect of SSD Target gain TC5282
28 The thin polymer layer required for target fabrication results in enhanced imprint Rayleigh Taylor instability Pressure DT CH Ablation front Transmitted shock g Rarefaction wave Shock t = t rw Velocity perturbation Ablation front Rarefaction wave g = 0 g > 0 TC5228 Shock
29 Simulations show increased imprint for polymer overcoated targets ORCHID simulation; pertubation wavelength λ = 40 µm g (µm/ns 2 ) p p g peak ~ CH DT ρ CH d CH t ac ~ d CH c s CH t rw Time (ns) Amplitude (µm)/(δi/i) DT + 4 µm CH CH 0.5 DT Time (ns) TC5283 RT growth factor ~ exp( kgät2 ac )~ exp kd CH ( )
30 Without SSD, thermal smoothing and dynamic overpressure do not reduce imprint to the levels required for high-gain implosions NIF direct-drive, α = 3 target design mode spectrum from DPP s and DPR s; no SSD 40 overlapping beams rms imprint (nm) Beginning of main drive pulse Distance (µm) ORCHID simulation and RT modeling with 3-D saturation Mix (imprint only) Shell thickness TC Mode number Time (ns) Temporal beam smoothing is required.
31 SSD reduces time-averaged laser nonuniformity Target plane Phase plate Focus lens TC5220 σ rms ~ t c t σ0 rms rms nonuniformity (%) *S. Skupsky, Phys. Plasmas 6, 2157 (1999) [ ] 1 t * c = νsin( kδ 2) ν: bandwidth δ: speckle size <t>
32 Imprint amplitude can be reduced by applying SSD smoothing technique (continued) ORCHID simulations For constant-intensity foot pulse δi = δi 0 t c t. Example: CH foil, I = W/cm 2 laser pulse, t c = 8 ps δp a /P a No SSD 0.4 SSD, t 0.2 c = 8 ps t 0.0 D Amplitude (µm) No SSD SSD Time (ps) Time (ns) TC5188 η SSD ηno SSD ~ t c t D ( νkδ) 1 ( ) 1 = V c kv c νδ
33 2-D SSD with the bandwidth ~1 THz gives sufficient nonuniformity reduction Mode spectrum at the beginning of main drive ORCHID simulations and RT analytic modeling with 3-D saturation rms imprint (nm) No SSD 1-THz SSD Gain σ inner = 1.00 µm σ outer = 0.08 µm Mode number Bandwidth (THz) TC5285
34 Summary/Conclusions An analytical model is developed to gain physical insight of the laser imprint Laser nonuniformities imprint surface modulations that degrade the symmetry of implosion. An analytical model has been developed to determine the physical processes contributing to imprint. Hydrodynamic flow is the main imprinting mechanism. Thermal smoothing and the dynamic overpressure are the main processes reducing the imprint. Laser imprint, with 1-THz SSD beam smoothing, will not significantly degrade cryogenic target performance. TC5213a
Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility
 Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility R (mm) 1 8 6 4 End of acceleration phase r(g/cc) 7.5 3.5.5 Gain 4 3 2 1 1 2 2 s (mm) 5 25 25 5 Z (mm) P. W. McKenty
Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility R (mm) 1 8 6 4 End of acceleration phase r(g/cc) 7.5 3.5.5 Gain 4 3 2 1 1 2 2 s (mm) 5 25 25 5 Z (mm) P. W. McKenty
Experiments on Dynamic Overpressure Stabilization of Ablative Richtmyer Meshkov Growth in ICF Targets on OMEGA
 Experiments on Dynamic Overpressure Stabilization of Ablative Richtmyer Meshkov Growth in ICF Targets on OMEGA Contributors: V. N. Goncharov P. A. Jaanimagi J. P. Knauer D. D. Meyerhofer O. V. Gotchev
Experiments on Dynamic Overpressure Stabilization of Ablative Richtmyer Meshkov Growth in ICF Targets on OMEGA Contributors: V. N. Goncharov P. A. Jaanimagi J. P. Knauer D. D. Meyerhofer O. V. Gotchev
Direct-Drive, High-Convergence-Ratio Implosion Studies on the OMEGA Laser System
 Direct-Drive, High-Convergence-Ratio Implosion Studies on the OMEGA Laser System F. J. Marshall, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, V. Yu. Glebov, D. D. Meyerhofer, R. D. Petrasso,P.B.Radha,V.A.Smalyuk,J.M.Soures,C.Stoekl,R.P.J.Town,
Direct-Drive, High-Convergence-Ratio Implosion Studies on the OMEGA Laser System F. J. Marshall, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, V. Yu. Glebov, D. D. Meyerhofer, R. D. Petrasso,P.B.Radha,V.A.Smalyuk,J.M.Soures,C.Stoekl,R.P.J.Town,
Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets
 Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets v rms of tr (mg/cm )..6 Si [4.%] Si [7.4%] Ge [.9%] DRACO simulations..4 Time (ns) S. X. Hu University
Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets v rms of tr (mg/cm )..6 Si [4.%] Si [7.4%] Ge [.9%] DRACO simulations..4 Time (ns) S. X. Hu University
First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA
 First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA MIT 1 mm 1 mm 100 µm C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division
First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA MIT 1 mm 1 mm 100 µm C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division
Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF
 Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF OMEGA polar-drive geometry 21.4 Backlit x-ray image OMEGA polar-drive implosion 21.4 58.2 77.8 42. 58.8 CR ~ 5 R = 77 nm 4 nm 4 nm P. B. Radha University of Rochester Laboratory
Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF OMEGA polar-drive geometry 21.4 Backlit x-ray image OMEGA polar-drive implosion 21.4 58.2 77.8 42. 58.8 CR ~ 5 R = 77 nm 4 nm 4 nm P. B. Radha University of Rochester Laboratory
Adiabat Shaping of Direct-Drive OMEGA Capsules Using Ramped Pressure Profiles
 Adiabat Shaping of Direct-Drive OMEGA Capsules Using Ramped Pressure Profiles a r Lagrangian coordinate K. Anderson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 44th Annual Meeting of the American
Adiabat Shaping of Direct-Drive OMEGA Capsules Using Ramped Pressure Profiles a r Lagrangian coordinate K. Anderson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 44th Annual Meeting of the American
Improved target stability using picket pulses to increase and shape the ablator adiabat a
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS 12, 056306 2005 Improved target stability using picket pulses to increase and shape the ablator adiabat a J. P. Knauer, b K. Anderson, R. Betti, T. J. B. Collins, V. N. Goncharov, P.
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS 12, 056306 2005 Improved target stability using picket pulses to increase and shape the ablator adiabat a J. P. Knauer, b K. Anderson, R. Betti, T. J. B. Collins, V. N. Goncharov, P.
Modeling the Effects Mix at the Hot Spot Surface in 1-D Simulations of Cryogenic All-DT Ignition Capsule Implosions
 Modeling the Effects Mix at the Hot Spot Surface in 1-D Simulations of Cryogenic All-DT Ignition Capsule Implosions 14 Time = 1.4 ns 25 Ion temperature (kev) 12 1 8 6 4 2 22.2 8.7 1.5 Gain =.45 2 15 1
Modeling the Effects Mix at the Hot Spot Surface in 1-D Simulations of Cryogenic All-DT Ignition Capsule Implosions 14 Time = 1.4 ns 25 Ion temperature (kev) 12 1 8 6 4 2 22.2 8.7 1.5 Gain =.45 2 15 1
Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA
 Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA In-flight aspect ratio OMEGA cryogenic ignition hydro-equivalent design tr = 3 mg/cm 2, V imp = 3.7 7 cm/s 3 3 2 14 m = 48 ng
Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA In-flight aspect ratio OMEGA cryogenic ignition hydro-equivalent design tr = 3 mg/cm 2, V imp = 3.7 7 cm/s 3 3 2 14 m = 48 ng
Polar-Drive Hot-Spot Ignition Design for the National Ignition Facility
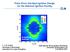 Polar-Drive Hot-Spot Ignition Design for the National Ignition Facility At ignition, Gain=40 T. J. B. Collins University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics International Shock-Ignition Workshop
Polar-Drive Hot-Spot Ignition Design for the National Ignition Facility At ignition, Gain=40 T. J. B. Collins University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics International Shock-Ignition Workshop
Optical and Plasma Smoothing of Laser Imprinting in Targets Driven by Lasers with SSD Bandwidths up to 1 THz
 Optical and Plasma Smoothing of Laser Imprinting in Targets Driven by Lasers with SSD Bandwidths up to 1 THz Introduction A key issue for inertial confinement fusion (ICF) 1 3 is the Rayleigh Taylor (RT)
Optical and Plasma Smoothing of Laser Imprinting in Targets Driven by Lasers with SSD Bandwidths up to 1 THz Introduction A key issue for inertial confinement fusion (ICF) 1 3 is the Rayleigh Taylor (RT)
Charged-Particle Spectra Using Particle Tracking on a Two-Dimensional Grid. P. B. Radha, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, S. Skupsky, and J. M.
 Charged-Particle Spectra Using Particle Tracking on a Two-Dimensional Grid P. B. Radha, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, S. Skupsky, and J. M. Soures Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester S. Cremer
Charged-Particle Spectra Using Particle Tracking on a Two-Dimensional Grid P. B. Radha, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, S. Skupsky, and J. M. Soures Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester S. Cremer
Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks. 26 June 2009
 PSFC/JA-8-8 Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks J. R. Rygg, J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Seguin, R. D. Petrasso, F.J. Marshalli, J. A. Delettrez, J.P. Knauer, D.D.
PSFC/JA-8-8 Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks J. R. Rygg, J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Seguin, R. D. Petrasso, F.J. Marshalli, J. A. Delettrez, J.P. Knauer, D.D.
Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale
 Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale Laser intensity ( 1 15 W/cm 2 ) 5 4 3 2 1 Laser spike is replaced with hot-electron spike 2 4 6 8 1 Gain 2 15 1 5 1. 1.2 1.4
Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale Laser intensity ( 1 15 W/cm 2 ) 5 4 3 2 1 Laser spike is replaced with hot-electron spike 2 4 6 8 1 Gain 2 15 1 5 1. 1.2 1.4
Capsule-areal-density asymmetries inferred from 14.7-MeV deuterium helium protons in direct-drive OMEGA implosions a
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 10, NUMBER 5 MAY 2003 Capsule-areal-density asymmetries inferred from 14.7-MeV deuterium helium protons in direct-drive OMEGA implosions a C. K. Li, b) F. H. Séguin, J. A. Frenje,
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 10, NUMBER 5 MAY 2003 Capsule-areal-density asymmetries inferred from 14.7-MeV deuterium helium protons in direct-drive OMEGA implosions a C. K. Li, b) F. H. Séguin, J. A. Frenje,
The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition
 The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition Normalized intensity 1..8.6.4.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Core self-emission. 3 2 1
The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition Normalized intensity 1..8.6.4.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Core self-emission. 3 2 1
Determination of the Flux Limiter in CH Targets from Experiments on the OMEGA Laser
 Determination of the Flux Limiter in CH Targets from Experiments on the OMEGA Laser f = 0.070 Neutron rate (1/s) Exp. f = 0.065 f = 0.060 J. A. Delettrez et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser
Determination of the Flux Limiter in CH Targets from Experiments on the OMEGA Laser f = 0.070 Neutron rate (1/s) Exp. f = 0.065 f = 0.060 J. A. Delettrez et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser
An Alternative Laser-Speckle-Smoothing Scheme for the NIF
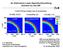 An Alternative Laser-Speckle-Smoothing Scheme for the NIF 1.5-MJ CH-foam target; end of acceleration 1-D SSD, 1.8 Å 1-D MultiFM, 8 Å 2-D SSD, 11 Å 1-D SSD 1-D, multiple-fm SSD 2-D SSD Density (g cm 3 )
An Alternative Laser-Speckle-Smoothing Scheme for the NIF 1.5-MJ CH-foam target; end of acceleration 1-D SSD, 1.8 Å 1-D MultiFM, 8 Å 2-D SSD, 11 Å 1-D SSD 1-D, multiple-fm SSD 2-D SSD Density (g cm 3 )
Volume 71 April-June 1997 DOE/SF/ : UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER ./ 4 LABORATORY FOR LASER ENERGETICS. LLE Review. -$ Quarterly Report
 ' 4: UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER./ 4 LABORATORY FOR LASER ENERGETICS Volume 71 April-June 1997 DOE/SF/19460-186 LLE Review -$ Quarterly Report 7 About the Cover: Photograph of planar-foil target used for Rayleigh
' 4: UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER./ 4 LABORATORY FOR LASER ENERGETICS Volume 71 April-June 1997 DOE/SF/19460-186 LLE Review -$ Quarterly Report 7 About the Cover: Photograph of planar-foil target used for Rayleigh
High-Performance Inertial Confinement Fusion Target Implosions on OMEGA
 High-Performance Inertial Confinement Fusion Target Implosions on OMEGA D.D. Meyerhofer 1), R.L. McCrory 1), R. Betti 1), T.R. Boehly 1), D.T. Casey, 2), T.J.B. Collins 1), R.S. Craxton 1), J.A. Delettrez
High-Performance Inertial Confinement Fusion Target Implosions on OMEGA D.D. Meyerhofer 1), R.L. McCrory 1), R. Betti 1), T.R. Boehly 1), D.T. Casey, 2), T.J.B. Collins 1), R.S. Craxton 1), J.A. Delettrez
Relativistic Electron Beams, Forward Thomson Scattering, and Raman Scattering. A. Simon. Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U.
 Relativistic Electron Beams, Forward Thomson Scattering, and Raman Scattering A. Simon Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester Experiments at LLE (see abstract by D. Hicks at this meeting) show
Relativistic Electron Beams, Forward Thomson Scattering, and Raman Scattering A. Simon Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester Experiments at LLE (see abstract by D. Hicks at this meeting) show
Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research
 Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research Ignition and Gain Total GtRH n (g/cm 2 ) 2 1.5.2.1 IAEA 21 DT, 22 kj IAEA 28 DT, 16 kj NIF.5 MJ NIF point design 1.5 MJ 1-D marginal ignition
Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research Ignition and Gain Total GtRH n (g/cm 2 ) 2 1.5.2.1 IAEA 21 DT, 22 kj IAEA 28 DT, 16 kj NIF.5 MJ NIF point design 1.5 MJ 1-D marginal ignition
Rayleigh Taylor Growth Measurements of 3-D Modulations
 Rayleigh Taylor Growth Measurements of -D Modulations in a Nonlinear Regime Introduction Rayleigh Taylor (RT), instability is of critical importance in inertial confinement fusion (ICF) and astrophysics.
Rayleigh Taylor Growth Measurements of -D Modulations in a Nonlinear Regime Introduction Rayleigh Taylor (RT), instability is of critical importance in inertial confinement fusion (ICF) and astrophysics.
The 1-D Cryogenic Implosion Campaign on OMEGA
 The 1-D Cryogenic Implosion Campaign on OMEGA Yield Exp (#1 14 ) 1.4 1.2 1..8.6.4 1-D campaign neutron yields.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.2.4.6.8 1. 1.2 LILAC 4 8.
The 1-D Cryogenic Implosion Campaign on OMEGA Yield Exp (#1 14 ) 1.4 1.2 1..8.6.4 1-D campaign neutron yields.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.2.4.6.8 1. 1.2 LILAC 4 8.
Theory and simulations of hydrodynamic instabilities in inertial fusion
 Theory and simulations of hydrodynamic instabilities in inertial fusion R. Betti Fusion Science Center, Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester IPAM/UCLA Long Program PL2012 - March 12
Theory and simulations of hydrodynamic instabilities in inertial fusion R. Betti Fusion Science Center, Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester IPAM/UCLA Long Program PL2012 - March 12
Cross-Beam Energy Transport in Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments
 Cross-Beam Energy Transport in Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments 35 3 Laser pulse Power (TW) 25 2 15 1 Modeled scattered light Measured 5 D. H. Edgell University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.5
Cross-Beam Energy Transport in Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments 35 3 Laser pulse Power (TW) 25 2 15 1 Modeled scattered light Measured 5 D. H. Edgell University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.5
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/319/5867/1223/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Proton Radiography of Inertial Fusion Implosions J. R. Rygg, F. H. Séguin, C. K. Li, J. A. Frenje, M. J.-E. Manuel,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/319/5867/1223/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Proton Radiography of Inertial Fusion Implosions J. R. Rygg, F. H. Séguin, C. K. Li, J. A. Frenje, M. J.-E. Manuel,
Hydrodynamic instability measurements in DTlayered ICF capsules using the layered-hgr platform
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic instability measurements in DTlayered ICF capsules using the layered-hgr platform Related content - Mix and hydrodynamic instabilities
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic instability measurements in DTlayered ICF capsules using the layered-hgr platform Related content - Mix and hydrodynamic instabilities
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics
 1 Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics R.L. McCrory 1), D.D. Meyerhofer 1), S.J. Loucks 1), S. Skupsky 1) R.E. Bahr 1), R. Betti 1), T.R.
1 Progress in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion Research at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics R.L. McCrory 1), D.D. Meyerhofer 1), S.J. Loucks 1), S. Skupsky 1) R.E. Bahr 1), R. Betti 1), T.R.
Critical Path to Impact Fast Ignition Suppression of the Rayleigh-Taylor Instability
 Critical Path to Impact Fast Ignition Suppression of the Rayleigh-Taylor Instability H. Azechi Vice Director Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University Jpn-US WS on HIF and HEDP September 28, 2005
Critical Path to Impact Fast Ignition Suppression of the Rayleigh-Taylor Instability H. Azechi Vice Director Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University Jpn-US WS on HIF and HEDP September 28, 2005
High Gain Direct Drive Target Designs and Supporting Experiments with KrF )
 High Gain Direct Drive Target Designs and Supporting Experiments with KrF ) Max KARASIK, Yefim AGLITSKIY 1), Jason W. BATES, Denis G. COLOMBANT 4), David M. KEHNE, Wallace M. MANHEIMER 2), Nathan METZLER
High Gain Direct Drive Target Designs and Supporting Experiments with KrF ) Max KARASIK, Yefim AGLITSKIY 1), Jason W. BATES, Denis G. COLOMBANT 4), David M. KEHNE, Wallace M. MANHEIMER 2), Nathan METZLER
High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry
 High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry Low intensity High intensity 4 nm CH 3 nm Mo 138 nm quartz VISAR SOP Simulated peak pressure (Mbar) 1 5 Laser backscatter 17.5 kev Mo K a Hard
High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry Low intensity High intensity 4 nm CH 3 nm Mo 138 nm quartz VISAR SOP Simulated peak pressure (Mbar) 1 5 Laser backscatter 17.5 kev Mo K a Hard
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents
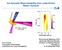 Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents 3.0 3~ beam 2.5 4~ TS beam 60 100 100-nm TS volume Thomsonscattered light 5 0 5 Wavelength shift (Å) 0.5 0.0 D. H. Froula University of Rochester
Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents 3.0 3~ beam 2.5 4~ TS beam 60 100 100-nm TS volume Thomsonscattered light 5 0 5 Wavelength shift (Å) 0.5 0.0 D. H. Froula University of Rochester
Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions
 Modelisation and Numerical Methods for Hot Plasmas Talence, October 14, 2015 Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions V. T. Tikhonchuk, A. Colaïtis, A. Vallet, E. Llor
Modelisation and Numerical Methods for Hot Plasmas Talence, October 14, 2015 Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions V. T. Tikhonchuk, A. Colaïtis, A. Vallet, E. Llor
Inertial Confinement Fusion
 Inertial Confinement Fusion Prof. Dr. Mathias Groth Aalto University School of Science, Department of Applied Physics Outline Principles of inertial confinement fusion Implosion/compression physics Direct
Inertial Confinement Fusion Prof. Dr. Mathias Groth Aalto University School of Science, Department of Applied Physics Outline Principles of inertial confinement fusion Implosion/compression physics Direct
Hydrodynamic growth experiments with the 3-D, native-roughness modulations on NIF
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic growth experiments with the 3-D, native-roughness modulations on NIF To cite this article: V A Smalyuk et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic growth experiments with the 3-D, native-roughness modulations on NIF To cite this article: V A Smalyuk et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Dual Nuclear Shock Burn:
 Dual Nuclear Shock Burn: Experiment, Simulation, and the Guderley Model J.R. Rygg, J.A. Frenje, C.K. Li, F.H. Séguin, and R.D. Petrasso MIT PSFC J.A. Delettrez, V.Yu Glebov, D.D. Meyerhofer, and T.C. Sangster
Dual Nuclear Shock Burn: Experiment, Simulation, and the Guderley Model J.R. Rygg, J.A. Frenje, C.K. Li, F.H. Séguin, and R.D. Petrasso MIT PSFC J.A. Delettrez, V.Yu Glebov, D.D. Meyerhofer, and T.C. Sangster
Where are we with laser fusion?
 Where are we with laser fusion? R. Betti Laboratory for Laser Energetics Fusion Science Center Dept. Mechanical Engineering and Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester HEDSA HEDP Summer School August
Where are we with laser fusion? R. Betti Laboratory for Laser Energetics Fusion Science Center Dept. Mechanical Engineering and Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester HEDSA HEDP Summer School August
An Investigation of Two-Plasmon Decay Localization in Spherical Implosion Experiments on OMEGA
 An Investigation of Two-lasmon Decay Localization in Spherical Implosion Experiments on OMEGA 1 12 50 23 14 27 18 32 J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 24 56th Annual Meeting
An Investigation of Two-lasmon Decay Localization in Spherical Implosion Experiments on OMEGA 1 12 50 23 14 27 18 32 J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 24 56th Annual Meeting
Multibeam Stimulated Brillouin Scattering from Hot Solid-Target Plasmas
 Multibeam Stimulated Brillouin Scattering from Hot Solid-Target Plasmas Introduction We report on the first multibeam laser plasma interaction experiments with a critical density surface present at all
Multibeam Stimulated Brillouin Scattering from Hot Solid-Target Plasmas Introduction We report on the first multibeam laser plasma interaction experiments with a critical density surface present at all
Three-Dimensional Studies of the Effect of Residual Kinetic Energy on Yield Degradation
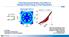 Threeimensional Studies of the Effect of Residual Kinetic Energy on Yield Degradation Kinetic energy density for single-mode, = 1, m = 6 1. YOC model = (1 RKE) 4.4 1 3 to ( Jm / ) 5.797 1 15 1.44 1 1 z
Threeimensional Studies of the Effect of Residual Kinetic Energy on Yield Degradation Kinetic energy density for single-mode, = 1, m = 6 1. YOC model = (1 RKE) 4.4 1 3 to ( Jm / ) 5.797 1 15 1.44 1 1 z
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA
 Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Two-Plasmon Decay Driven by Multiple Incoherent Laser Beams
 Two-Plasmon Decay Driven by Multiple Incoherent Laser Beams 2 # # E^xyt,, h dy dy^arbitrary h n Two coherent e /n c plane waves Dm = 8.8 Å Dm = 17.6 Å.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27 2 Arbitrary
Two-Plasmon Decay Driven by Multiple Incoherent Laser Beams 2 # # E^xyt,, h dy dy^arbitrary h n Two coherent e /n c plane waves Dm = 8.8 Å Dm = 17.6 Å.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27 2 Arbitrary
Monochromatic 8.05-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets
 Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
The Effect of Laser Spot Shapes on Polar-Direct-Drive Implosions on the National. Ignition Facility. 250 East River Road, Rochester, NY 14623
 The Effect of Laser Spot Shapes on Polar-Direct-Drive Implosions on the National Ignition Facility F. Weilacher, 1,2 P. B. Radha, 1,* T. J. B. Collins, 1 and J. A. Marozas 1 1 Laboratory for Laser Energetics,
The Effect of Laser Spot Shapes on Polar-Direct-Drive Implosions on the National Ignition Facility F. Weilacher, 1,2 P. B. Radha, 1,* T. J. B. Collins, 1 and J. A. Marozas 1 1 Laboratory for Laser Energetics,
Two-Plasmon-Decay Hot Electron Generation and Reheating in OMEGA Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments
 Two-Plasmon-Decay Hot Electron Generation and Reheating in OMEGA Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments r 1/4 ~500 nm Ne To sheath e Laser r e To core 20 nm J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for
Two-Plasmon-Decay Hot Electron Generation and Reheating in OMEGA Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments r 1/4 ~500 nm Ne To sheath e Laser r e To core 20 nm J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for
Exploration of the Feasibility of Polar Drive on the LMJ. Lindsay M. Mitchel. Spencerport High School. Spencerport, New York
 Exploration of the Feasibility of Polar Drive on the LMJ Lindsay M. Mitchel Spencerport High School Spencerport, New York Advisor: Dr. R. S. Craxton Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester
Exploration of the Feasibility of Polar Drive on the LMJ Lindsay M. Mitchel Spencerport High School Spencerport, New York Advisor: Dr. R. S. Craxton Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester
Stimulated Raman Scattering in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion
 Stimulated Raman Scattering in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion View ports 5 FABS Experiments carried out at the National Ignition Facility FABS power (arbitrary units) Plasma-producing beams (
Stimulated Raman Scattering in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion View ports 5 FABS Experiments carried out at the National Ignition Facility FABS power (arbitrary units) Plasma-producing beams (
Multiple-FM Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion An Augmented Laser Speckle Smoothing Scheme
 Multiple-FM Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion An Augmented Laser Speckle Smoothing Scheme Introduction Polar-drive (PD) 1 4 implosions on the National Ignition Facility (NIF) require smoothing of the laser-imposed
Multiple-FM Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion An Augmented Laser Speckle Smoothing Scheme Introduction Polar-drive (PD) 1 4 implosions on the National Ignition Facility (NIF) require smoothing of the laser-imposed
Inertial Confinement Fusion DR KATE LANCASTER YORK PLASMA INSTITUTE
 Inertial Confinement Fusion DR KATE LANCASTER YORK PLASMA INSTITUTE In the beginning In the late fifties, alternative applications of nuclear explosions were being considered the number one suggestion
Inertial Confinement Fusion DR KATE LANCASTER YORK PLASMA INSTITUTE In the beginning In the late fifties, alternative applications of nuclear explosions were being considered the number one suggestion
ICF ignition and the Lawson criterion
 ICF ignition and the Lawson criterion Riccardo Betti Fusion Science Center Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester Seminar Massachusetts Institute of Technology, January 0, 010, Cambridge
ICF ignition and the Lawson criterion Riccardo Betti Fusion Science Center Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester Seminar Massachusetts Institute of Technology, January 0, 010, Cambridge
D- 3 He Protons as a Diagnostic for Target ρr
 D- 3 He Protons as a Diagnostic for Target ρr Areal density (ρr) is an important parameter for measuring compression in ICF experiments. Several diagnostics employing nuclear particles have been considered
D- 3 He Protons as a Diagnostic for Target ρr Areal density (ρr) is an important parameter for measuring compression in ICF experiments. Several diagnostics employing nuclear particles have been considered
Polar-Drive Implosions on OMEGA and the National Ignition Facility
 Polar-Drive Implosions on OMEGA and the National Ignition Facility Introduction Polar drive (PD) 1 provides the capability to perform directdrive ignition experiments on laser facilities like the National
Polar-Drive Implosions on OMEGA and the National Ignition Facility Introduction Polar drive (PD) 1 provides the capability to perform directdrive ignition experiments on laser facilities like the National
Modeling Nonlinear Optics Of Plasmas (Relevant To IFE)
 Modeling Nonlinear Optics Of Plasmas (Relevant To IFE) F.S.Tsung and the UCLA Simulation Group University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) 1 F. S. Tsung/OSIRIS Workshop 2017 Summary/Conclusion Introduction
Modeling Nonlinear Optics Of Plasmas (Relevant To IFE) F.S.Tsung and the UCLA Simulation Group University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) 1 F. S. Tsung/OSIRIS Workshop 2017 Summary/Conclusion Introduction
Growth rates of the ablative Rayleigh Taylor instability in inertial confinement fusion
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 5, NUMBER 5 MAY 998 Growth rates of the ablative Rayleigh Taylor instability in inertial confinement fusion R. Betti, V. N. Goncharov, R. L. McCrory, and C. P. Verdon Laboratory
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 5, NUMBER 5 MAY 998 Growth rates of the ablative Rayleigh Taylor instability in inertial confinement fusion R. Betti, V. N. Goncharov, R. L. McCrory, and C. P. Verdon Laboratory
Measurements of fuel and shell areal densities of OMEGA capsule implosions using elastically scattered protons
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 9, NUMBER 11 NOVEMBER 2002 Measurements of fuel and shell areal densities of OMEGA capsule implosions using elastically scattered protons J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Séguin,
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 9, NUMBER 11 NOVEMBER 2002 Measurements of fuel and shell areal densities of OMEGA capsule implosions using elastically scattered protons J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Séguin,
Classical and ablative Richtmyer-Meshkov instability and other ICF-relevant plasma flows diagnosed with monochromatic x-ray imaging
 Classical and ablative Richtmyer-Meshkov instability and other ICF-relevant plasma flows diagnosed with monochromatic x-ray imaging Y Aglitskiy 1,2, M Karasik 2, A L Velikovich 2, N Metzler 1, S Zalesak
Classical and ablative Richtmyer-Meshkov instability and other ICF-relevant plasma flows diagnosed with monochromatic x-ray imaging Y Aglitskiy 1,2, M Karasik 2, A L Velikovich 2, N Metzler 1, S Zalesak
What is. Inertial Confinement Fusion?
 What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
Direct-Drive Ignition Designs with Mid-Z Ablators
 Direct-Drive Ignition Designs with Mid-Z Ablators Introduction In laser-driven inertial confinement fusion (ICF), 1, a spherical capsule filled with deuterium tritium (DT) is irradiated by direct laser
Direct-Drive Ignition Designs with Mid-Z Ablators Introduction In laser-driven inertial confinement fusion (ICF), 1, a spherical capsule filled with deuterium tritium (DT) is irradiated by direct laser
Integrated Modeling of Fast Ignition Experiments
 Integrated Modeling of Fast Ignition Experiments Presented to: 9th International Fast Ignition Workshop Cambridge, MA November 3-5, 2006 R. P. J. Town AX-Division Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Integrated Modeling of Fast Ignition Experiments Presented to: 9th International Fast Ignition Workshop Cambridge, MA November 3-5, 2006 R. P. J. Town AX-Division Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Update on MJ Laser Target Physics
 Update on MJ Laser Target Physics P.A.Holstein, J.Giorla, M.Casanova, F.Chaland, C.Cherfils, E. Dattolo, D.Galmiche, S.Laffite, E.Lefebvre, P.Loiseau, M.C. Monteil, F.Poggi, G.Riazuelo, Y.Saillard CEA
Update on MJ Laser Target Physics P.A.Holstein, J.Giorla, M.Casanova, F.Chaland, C.Cherfils, E. Dattolo, D.Galmiche, S.Laffite, E.Lefebvre, P.Loiseau, M.C. Monteil, F.Poggi, G.Riazuelo, Y.Saillard CEA
Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor. Katherine Manfred
 Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor Katherine Manfred Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor Katherine M. Manfred Fairport High
Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor Katherine Manfred Polar Direct-Drive Simulations for a Laser-Driven HYLIFE-II Fusion Reactor Katherine M. Manfred Fairport High
Laser Inertial Fusion Energy
 Laser Inertial Fusion Energy presentation before the HEDLP committee at the WORKSHOP ON SCIENTIFIC OPPORTUNITIES IN HIGH ENERGY DENSITY PLASMA PHYSICS 25 August 2006 Washington DC presented by A. J. Schmitt,
Laser Inertial Fusion Energy presentation before the HEDLP committee at the WORKSHOP ON SCIENTIFIC OPPORTUNITIES IN HIGH ENERGY DENSITY PLASMA PHYSICS 25 August 2006 Washington DC presented by A. J. Schmitt,
Picket Pulses with 1-D MultiFM Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) for the NIF
 Picket Pulses with 1-D MultiFM Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) for the NIF 500 MultiFM DesignSpace = [21.2,22.8,31.9] University of Roch Using: analyzelmf 500 MultiFM DesignSpace = [21.2,22.8,31.9]
Picket Pulses with 1-D MultiFM Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) for the NIF 500 MultiFM DesignSpace = [21.2,22.8,31.9] University of Roch Using: analyzelmf 500 MultiFM DesignSpace = [21.2,22.8,31.9]
Measuring the Refractive Index of a Laser-Plasma System
 Measuring the Refractive Index of a Laser-Plasma System 1 dh ( 10 4 ) 0 1 J (dh) R (dh) 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 D. Turnbull University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Dm (Å) 58th Annual Meeting of the
Measuring the Refractive Index of a Laser-Plasma System 1 dh ( 10 4 ) 0 1 J (dh) R (dh) 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 D. Turnbull University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Dm (Å) 58th Annual Meeting of the
Rayleigh-Taylor Growth Rates for Arbitrary Density Profiles Calculated with a Variational Method. Jue Liao
 Rayleigh-Taylor Growth Rates for Arbitrary Density Profiles Calculated with a Variational Method Jue Liao Rayleigh-Taylor growth rates for arbitrary density profiles calculated with a variational method
Rayleigh-Taylor Growth Rates for Arbitrary Density Profiles Calculated with a Variational Method Jue Liao Rayleigh-Taylor growth rates for arbitrary density profiles calculated with a variational method
High-density implosion via suppression of Rayleigh Taylor instability
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS High-density implosion via suppression of Rayleigh Taylor instability Recent citations - Experimental study of shock-accelerated inclined heavy gas
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS High-density implosion via suppression of Rayleigh Taylor instability Recent citations - Experimental study of shock-accelerated inclined heavy gas
Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Stability of Low-Entropy Laser-Driven Acceleration of Thin Foil.
 Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Stability of Low-Entropy Laser-Driven Acceleration of Thin Foil. Sergey Gus kov and Masakatsu Murakami INTRODUCTION The importance to understand of effectiveness limits of
Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Stability of Low-Entropy Laser-Driven Acceleration of Thin Foil. Sergey Gus kov and Masakatsu Murakami INTRODUCTION The importance to understand of effectiveness limits of
Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled, cone-in-shell, fast-ignitor targets on the OMEGA Laser
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (25) B859 B867 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:1.188/741-3335/47/12b/s68 Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled,
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (25) B859 B867 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:1.188/741-3335/47/12b/s68 Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled,
Areal-Density-Growth Measurements with Proton Spectroscopy on OMEGA
 Areal-Density-Growth Measurements with Proton Spectroscopy on OMEGA Areal density (mg/cm ) 5 15 1 5 4 atm D 3 He 1.6 1... 1 1 1 1 19 1 1 Neutron rate (s 1 ) V. A. Smalyuk Laboratory for Laser Energetics
Areal-Density-Growth Measurements with Proton Spectroscopy on OMEGA Areal density (mg/cm ) 5 15 1 5 4 atm D 3 He 1.6 1... 1 1 1 1 19 1 1 Neutron rate (s 1 ) V. A. Smalyuk Laboratory for Laser Energetics
The Ignition Physics Campaign on NIF: Status and Progress
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Ignition Physics Campaign on NIF: Status and Progress To cite this article: M. J. Edwards and Ignition Team 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 688 1217
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Ignition Physics Campaign on NIF: Status and Progress To cite this article: M. J. Edwards and Ignition Team 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 688 1217
Polar-Direct-Drive Experiments on the National Ignition Facility
 Polar-Direct-Drive Experiments on the National Ignition Facility M. Hohenberger, 1 P. B. Radha, 1 J. F. Myatt, 1 S. LePape, 2 J. A. Marozas, 1 F. J. Marshall, 1 D. T. Michel, 1 S. P. Regan, 1 W. Seka,
Polar-Direct-Drive Experiments on the National Ignition Facility M. Hohenberger, 1 P. B. Radha, 1 J. F. Myatt, 1 S. LePape, 2 J. A. Marozas, 1 F. J. Marshall, 1 D. T. Michel, 1 S. P. Regan, 1 W. Seka,
X-Ray Spectral Measurements of Cryogenic Capsules Imploded by OMEGA
 X-Ray Spectral Measurements of Cryogenic Capsules Imploded by OMEGA 1 15 1 14 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics kt =.65 kev 48386 (v ice = 1.5 nm) 2 48385 (v ice =
X-Ray Spectral Measurements of Cryogenic Capsules Imploded by OMEGA 1 15 1 14 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics kt =.65 kev 48386 (v ice = 1.5 nm) 2 48385 (v ice =
Polar-drive implosions on OMEGA and the National Ignition Facility
 Polar-drive implosions on OMEGA and the National Ignition Facility P. B. Radha, F. J. Marshall, J. A. Marozas, A. Shvydky, I. Gabalski et al. Citation: Phys. Plasmas 20, 056306 (2013); doi: 10.1063/1.4803083
Polar-drive implosions on OMEGA and the National Ignition Facility P. B. Radha, F. J. Marshall, J. A. Marozas, A. Shvydky, I. Gabalski et al. Citation: Phys. Plasmas 20, 056306 (2013); doi: 10.1063/1.4803083
Progress in detailed modelling of low foot and high foot implosion experiments on the National Ignition Facility
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Progress in detailed modelling of low foot and high foot implosion experiments on the National Ignition Facility Related content - Capsule modeling
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Progress in detailed modelling of low foot and high foot implosion experiments on the National Ignition Facility Related content - Capsule modeling
A Single-Beam, Ponderomotive-Optical Trap for Energetic Free Electrons
 A Single-Beam, Ponderomotive-Optical Trap for Energetic Free Electrons Traditionally, there have been many advantages to using laser beams with Gaussian spatial profiles in the study of high-field atomic
A Single-Beam, Ponderomotive-Optical Trap for Energetic Free Electrons Traditionally, there have been many advantages to using laser beams with Gaussian spatial profiles in the study of high-field atomic
Crossed-Beam Energy Transfer in Inertial Confinement Fusion Implosions on OMEGA
 Crossed-Beam Energy Transfer in Inertial Confinement Fusion Implosions on OMEGA Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) uses the energy of multiple laser beams to implode a millimeter-scale capsule containing
Crossed-Beam Energy Transfer in Inertial Confinement Fusion Implosions on OMEGA Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) uses the energy of multiple laser beams to implode a millimeter-scale capsule containing
Effects of Atomic Mixing in Inertial Confinement Fusion by Multifluid Interpenetration Mix Model
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 52 (2009) pp. 1102 1106 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 52, No. 6, December 15, 2009 Effects of Atomic Mixing in Inertial Confinement Fusion
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 52 (2009) pp. 1102 1106 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 52, No. 6, December 15, 2009 Effects of Atomic Mixing in Inertial Confinement Fusion
Measurement of Long-Scale-Length Plasma Density Profiles for Two-Plasmon Decay Studies
 Measurement of Long-Scale-Length Plasma Density Profiles for Two-Plasmon Decay Studies Plasma density scale length at 10 21 cm 3 (nm) 350 300 250 200 150 100 0 Flat foil 2 4 6 8 10 100 Target diameter
Measurement of Long-Scale-Length Plasma Density Profiles for Two-Plasmon Decay Studies Plasma density scale length at 10 21 cm 3 (nm) 350 300 250 200 150 100 0 Flat foil 2 4 6 8 10 100 Target diameter
T T Fusion Neutron Spectrum Measured in Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiment
 T T Fusion Neutron Spectrum Measured in Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiment V. Yu. Glebov University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
T T Fusion Neutron Spectrum Measured in Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiment V. Yu. Glebov University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets
 1 Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets Mayank Shukla 1), Yogesh Kashyap 1), P. S. Sarkar 1), A. Sinha 1), H. C. Pant 2), R.S.Rao 1), N.K.Gupta 1), B.K.Godwal 1)
1 Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets Mayank Shukla 1), Yogesh Kashyap 1), P. S. Sarkar 1), A. Sinha 1), H. C. Pant 2), R.S.Rao 1), N.K.Gupta 1), B.K.Godwal 1)
Measurements of Strain-Induced Refractive-Index Changes in LiF Using Direct-Drive Ramp Compression
 Measurements of Strain-Induced Refractive-Index Changes in LiF Using Direct-Drive Ramp Compression Apparent particle velocity (nm/ns) 16 12 8 4 1 GPa 8 GPa 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 True particle velocity (nm/ns)
Measurements of Strain-Induced Refractive-Index Changes in LiF Using Direct-Drive Ramp Compression Apparent particle velocity (nm/ns) 16 12 8 4 1 GPa 8 GPa 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 True particle velocity (nm/ns)
FPEOS: A First-Principles Equation of State Table of Deuterium for Inertial Confinement Fusion Applications
 FPEOS: A First-Principles Equation of State Table of Deuterium for Inertial Confinement Fusion Applications S. X. Hu 1,, B. Militzer 2, V. N. Goncharov 1, S. Skupsky 1 1. Laboratory for Laser Energetics,
FPEOS: A First-Principles Equation of State Table of Deuterium for Inertial Confinement Fusion Applications S. X. Hu 1,, B. Militzer 2, V. N. Goncharov 1, S. Skupsky 1 1. Laboratory for Laser Energetics,
Proton Temporal Diagnostic for ICF Experiments on OMEGA
 Proton Temporal Diagnostic for ICF Experiments on OMEGA Introduction In an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) 1 experiment, a capsule filled with deuterium (D 2 ) or a deuterium tritium (DT) fuel is heated
Proton Temporal Diagnostic for ICF Experiments on OMEGA Introduction In an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) 1 experiment, a capsule filled with deuterium (D 2 ) or a deuterium tritium (DT) fuel is heated
Measurement by X U V Laser Radiography of Hydrodp,amic Perturbations in Laser Accelerated Thin Foil Targets
 'I UCRL-JC-121586 PREPRINT Measurement by X U V Laser Radiography of Hydrodp,amic Perturbations in Laser Accelerated Thin Foil Targets M. H. Key, D. H. Kalantar, T. W. Barbee, L. B. Da Silva, S. G. Glendinning,
'I UCRL-JC-121586 PREPRINT Measurement by X U V Laser Radiography of Hydrodp,amic Perturbations in Laser Accelerated Thin Foil Targets M. H. Key, D. H. Kalantar, T. W. Barbee, L. B. Da Silva, S. G. Glendinning,
Anomalous Stimulated Raman Scattering and Electron Acoustic Waves in Laser-Produced Plasmas: A Linear Model
 Anomalous Stimulated Raman Scattering and Electron Acoustic Waves in Laser-Produced Plasmas: A Linear Model Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS, an instability in which light is scattered by and amplifies
Anomalous Stimulated Raman Scattering and Electron Acoustic Waves in Laser-Produced Plasmas: A Linear Model Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS, an instability in which light is scattered by and amplifies
Polymath Research Inc.
 Can We Really Control Stimulated Raman and Brillouin Backscattering by Surposing Large Amplitude Waves onto the Plasma an Making it an Inhospitable Environment for Their Growth? Bedros Afeyan & M.Mardirian
Can We Really Control Stimulated Raman and Brillouin Backscattering by Surposing Large Amplitude Waves onto the Plasma an Making it an Inhospitable Environment for Their Growth? Bedros Afeyan & M.Mardirian
D 3 He proton spectra for diagnosing shell R and fuel T i of imploded capsules at OMEGA
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 7, NUMBER 6 JUNE 2000 D 3 He proton spectra for diagnosing shell R and fuel T i of imploded capsules at OMEGA C. K. Li, D. G. Hicks, F. H. Séguin, J. A. Frenje, and R. D. Petrasso
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 7, NUMBER 6 JUNE 2000 D 3 He proton spectra for diagnosing shell R and fuel T i of imploded capsules at OMEGA C. K. Li, D. G. Hicks, F. H. Séguin, J. A. Frenje, and R. D. Petrasso
PROGRESS OF DIRECT DRIVE LASER FUSION RESEARCH AT ILE, OSAKA
 PROGRESS OF DIRECT DRIVE LASER FUSION RESEARCH AT ILE, OSAKA K.MIMA, H.AZECHI, H.FUJITA, N.IZUMI, T.JITSUNO, Y.KATO, T.KANABE, Y.KITAGAWA, R.KODAMA, N.MIYANAGA, M.NAKAI, M.NAKATSUKA, S.NAKAI, H.NAGATOMO,
PROGRESS OF DIRECT DRIVE LASER FUSION RESEARCH AT ILE, OSAKA K.MIMA, H.AZECHI, H.FUJITA, N.IZUMI, T.JITSUNO, Y.KATO, T.KANABE, Y.KITAGAWA, R.KODAMA, N.MIYANAGA, M.NAKAI, M.NAKATSUKA, S.NAKAI, H.NAGATOMO,
Longitudinal Waves. waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation
 Longitudinal Waves waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation Longitudinal waves propagate as sound waves in all phases of matter, plasmas, gases,
Longitudinal Waves waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation Longitudinal waves propagate as sound waves in all phases of matter, plasmas, gases,
Magnetic Field Penetration Into a Conducting Hohlraum
 Kirkley, Alec 1 Magnetic Field Penetration Into a Conducting Hohlraum Alec Kirkley Pittsford Sutherland High School Pittsford, NY Advisor: Dr. Gennady Fiksel Laboratory for Laser Energetics University
Kirkley, Alec 1 Magnetic Field Penetration Into a Conducting Hohlraum Alec Kirkley Pittsford Sutherland High School Pittsford, NY Advisor: Dr. Gennady Fiksel Laboratory for Laser Energetics University
Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil
 Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil Matthew Allen Department of Nuclear Engineering UC Berkeley mallen@nuc.berkeley.edu March 15, 2004 8th Nuclear Energy
Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil Matthew Allen Department of Nuclear Engineering UC Berkeley mallen@nuc.berkeley.edu March 15, 2004 8th Nuclear Energy
Downloaded 11 Oct 2012 to Redistribution subject to AIP license or copyright; see
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 2004 REVIEW ARTICLE The physics basis for ignition using indirect-drive targets on the National Ignition Facility John D. Lindl, Peter Amendt, Richard L.
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 2004 REVIEW ARTICLE The physics basis for ignition using indirect-drive targets on the National Ignition Facility John D. Lindl, Peter Amendt, Richard L.
Modeling Laser-Plasma Interactions in MagLIF Experiment on NIF
 Modeling Laser-Plasma Interactions in MagLIF Experiment on NIF Anomalous Absorption Meeting 5 May 2016 D. J. Strozzi, R. L. Berger, A. B. Sefkow, S. H. Langer, T. Chapman, B. Pollock, C. Goyon, J. Moody
Modeling Laser-Plasma Interactions in MagLIF Experiment on NIF Anomalous Absorption Meeting 5 May 2016 D. J. Strozzi, R. L. Berger, A. B. Sefkow, S. H. Langer, T. Chapman, B. Pollock, C. Goyon, J. Moody
DIRECT DRIVE FUSION ENERGY SHOCK IGNITION DESIGNS FOR SUB-MJ LASERS
 DIRECT DRIVE FUSION ENERGY SHOCK IGNITION DESIGNS FOR SUB-MJ LASERS Andrew J. Schmitt, J. W. Bates, S. P. Obenschain, and S. T. Zalesak Plasma Physics Division, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington DC
DIRECT DRIVE FUSION ENERGY SHOCK IGNITION DESIGNS FOR SUB-MJ LASERS Andrew J. Schmitt, J. W. Bates, S. P. Obenschain, and S. T. Zalesak Plasma Physics Division, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington DC
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS. To cite this article: T J Murphy et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Progress in the development of the MARBLE platform for studying thermonuclear burn in the presence of heterogeneous mix on OMEGA and the National
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Progress in the development of the MARBLE platform for studying thermonuclear burn in the presence of heterogeneous mix on OMEGA and the National
Direct-drive laser target designs for sub-megajoule energies
 Direct-drive laser target designs for sub-megajoule energies D.G. Colombant, A.J. Schmitt, S.P. Obenschain, S.T. Zalesak, A.L. Velikovich, and J.W. Bates Plasma Physics Division, Naval Research Laboratory,
Direct-drive laser target designs for sub-megajoule energies D.G. Colombant, A.J. Schmitt, S.P. Obenschain, S.T. Zalesak, A.L. Velikovich, and J.W. Bates Plasma Physics Division, Naval Research Laboratory,
