Relativistic Electron Beams, Forward Thomson Scattering, and Raman Scattering. A. Simon. Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U.
|
|
|
- Jemimah Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Relativistic Electron Beams, Forward Thomson Scattering, and Raman Scattering A. Simon Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester Experiments at LLE (see abstract by D. Hicks at this meeting) show that surprisingly high potentials (+0.5 to 2.0 MV) develop in plasmas irradiated by high-energy lasers. The highly conducting plasma will be a near equipotential and should attract return-current electrons in a radial beam-like distribution, especially in the outer low-density regions. This will initiate the BOT instability, creating large plasma waves with phase velocities close to c. Coherent Thomson scattering of the interaction beam from these waves must occur primarily in the forward direction. This will appear to be backward SRS upon reflection from a critical surface. We will show that the resulting spectrum is fairly broad and at short wavelengths. Collisional absorption of the scattered EM wave limits the reflectivity to low values (depending on the density scale length). Thus, a distinct difference exists between the spectrum for thick targets (n c surface present) and thin targets (gasbags, etc., from which primarily a narrow absolute-srs backward emission occurs, at the peak density). The thick-target, reflected-wave angular distribution will be concentrated in the backward direction. The corresponding plasma-wave k-vector will be a fraction of k 0. The variation of the spectrum with potential and angle will be discussed. Comparison will be made with recent results at LLE and LLNL. This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inertial Confinement Fusion under Cooperative Agreement No. DE-FC03-92SF19460, UR, and NYSERDA.
2 Relativistic Electron Beams, Forward Thomson Scattering, and Raman Scattering A. Simon University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 41st Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Seattle, WA November 1999
3 Summary Relativistic electron beams, forward Thompson scattering, and Raman scattering Raman scattering continues to elude explanation on the basis of linear SRS theory. Experiments have shown the existence of very large and robust positive potentials on targets irradiated by high-energy laser beams. This suggests a new model for the source of directed electron beams, and for reconciling theory and experiment via enhanced Thomson scattering. Relativistic analysis becomes necessary for the more recent experiments there are some interesting new effects. Future experiments should study correlation between the potential and the Raman spectrum. P2046
4 Can the SRS linear theory and observations of Raman scattering be reconciled? The answer still seems to be no! Even though we now have much smoother laser beams and improved diagnostics, the following problems remain: The famous gap! The threshold should decrease linearly with increasing density and become absolute at n c /4. We often see emission at densities so low that Landau damping should dominate. Qualitative differences between thick-target spectra and those from underdense targets. The angular variation of the intensity and spectrum does not follow linear SRS prediction. Unexplained scintillation in time Spiky structure in λ s and time White noise flashes P2047
5 Enhanced Thomson scattering (ETS), owing to electron beams in the plasma, was proposed in 1984 The proposal was based in part on Perkins and Salpeter s explanation of the enhanced plasma line in ionospheric scattering (1965). When available, the theory used hot x-ray temperature to select the beam velocity, and this readily reproduced the observed spectrum; however, the source of electron beams remained a problem. The original postulate, that the beam source was at n c /4 or at n c and involved the two-plasmon or critical surface instabilities, had three difficulties: The beam started out in the wrong direction. No predictive capability existed for the beam velocity or density. Raman was often seen in the absence of n c or n c /4 surfaces. P2048
6 Recent measurements of high plasma potentials have changed the picture There is strong evidence that robust plasma potentials persist while the laser beam is on target. The highly conducting positive plasma should produce a radial electrostatic field that induces a directed electron return current (drawn from the outer circulating cloud). This return current might be expected to be beam-like in the outer regions of the plasma. ETS from these beam-induced waves now becomes a candidate for reconciliation of theory and experiment. P2049
7 What is different about this picture? The electron beams start off in the right direction. The potential, and its variation in time, becomes critical to the beam s existence. There is now the possibility of observing a correlation between the plasma potential and the Raman spectrum. High-energy irradiations have shown evidence of very high potentials that should produce relativistic beams. ETS theory has been extended to encompass such cases. The relativistic results show some interesting features. P2050
8 Here are some characteristics of ETS from a plasma with a relativistic beam Relativistic-beam ETS will occur primarily in forward directions (typically up to 20 from forward) for plasma potentials above 115 kv; hence, reflection is necessary to produce backward scatter. Enhanced plasma waves will be in the k 0 /3 to k 0 /5 range. Thomson probe experiments have not looked at this region. The ETS matching conditions (v φ c) are satisfied only below the 0.1-n c range. The resonant k p and ω p both decrease as beam velocity increases (for forward scatter). Of course, the theory, as before, can only identify wavelength bands within which ETS can occur. It cannot predict the scattered intensity or even its variation within the band. P2051
9 Can ETS explain more recent experiments with greater laser energy, scale lengths, and with smoothing? Thick targets (e.g., hohlraums, OMEGA pellet compression, etc.) allow reflection of ETS from critical surfaces; however, absorption will limit reflectivity to low values (typically, a few percent). A fairly broad wavelength band will occur and correspond to quite low densities (0.1 n c or less). Underdense targets (e.g., gasbags) will not reflect forward ETS; however, true absolute SRS should occur at the density profile peak and produce a narrow backscatter line. P2052
10 As an example we have applied this picture to the LSP plasma experiments at LLE 1 UV light at up to 20 kj irradiated thick CH foils and solid targets (DPP smoothing used). Direct backscattering was observed with reflectivities less than 5%. The scattered light is in the 450- to 550-nm range. For such λ s and plasma temperature ( 4 kev) very strong Landau damping would occur in a Maxwellian plasma. A plasma potential of 1.5 MV would create ETS that reproduces the observed spectrum (see next viewgraph). Unfortunately, no potential measurement was made, but this value is consistent with the range of potentials observed in OMEGA compressions (see KO2.09, this meeting). 1 S. P. Regan et al., Phys. Plasmas 6, 2072 (1999). P2053
11 Forward ETS wavelength zones versus beam number fraction 10 4 V = 1.5 MV, T c = 4.0 kev, λ 0 = 0.35 µm, E B = 80 kev 10 5 f B P Scattered wavelength (µm)
12 Angular variation of ETS scattering 30 f B = 10 6, V = 1.5 MV, T c = 4.0 kev, λ 0 = 0.35 µm, E B = 80 kev 20 Angle ( ) Scattered wavelength (µm) P2055
13 Summary/Conclusions Relativistic electron beams, forward Thompson scattering, and Raman scattering Raman scattering continues to elude explanation on the basis of linear SRS theory. Experiments have shown the existence of very large and robust positive potentials on targets irradiated by high-energy laser beams. This suggests a new model for the source of directed electron beams, and for reconciling theory and experiment via enhanced Thomson scattering. Relativistic analysis becomes necessary for the more recent experiments there are some interesting new effects. Future experiments should study correlation between the potential and the Raman spectrum. P2046
Stimulated Raman Scattering in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion
 Stimulated Raman Scattering in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion View ports 5 FABS Experiments carried out at the National Ignition Facility FABS power (arbitrary units) Plasma-producing beams (
Stimulated Raman Scattering in Direct-Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion View ports 5 FABS Experiments carried out at the National Ignition Facility FABS power (arbitrary units) Plasma-producing beams (
Direct-Drive, High-Convergence-Ratio Implosion Studies on the OMEGA Laser System
 Direct-Drive, High-Convergence-Ratio Implosion Studies on the OMEGA Laser System F. J. Marshall, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, V. Yu. Glebov, D. D. Meyerhofer, R. D. Petrasso,P.B.Radha,V.A.Smalyuk,J.M.Soures,C.Stoekl,R.P.J.Town,
Direct-Drive, High-Convergence-Ratio Implosion Studies on the OMEGA Laser System F. J. Marshall, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, V. Yu. Glebov, D. D. Meyerhofer, R. D. Petrasso,P.B.Radha,V.A.Smalyuk,J.M.Soures,C.Stoekl,R.P.J.Town,
Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents
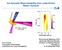 Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents 3.0 3~ beam 2.5 4~ TS beam 60 100 100-nm TS volume Thomsonscattered light 5 0 5 Wavelength shift (Å) 0.5 0.0 D. H. Froula University of Rochester
Ion-Acoustic-Wave Instability from Laser-Driven Return Currents 3.0 3~ beam 2.5 4~ TS beam 60 100 100-nm TS volume Thomsonscattered light 5 0 5 Wavelength shift (Å) 0.5 0.0 D. H. Froula University of Rochester
Charged-Particle Spectra Using Particle Tracking on a Two-Dimensional Grid. P. B. Radha, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, S. Skupsky, and J. M.
 Charged-Particle Spectra Using Particle Tracking on a Two-Dimensional Grid P. B. Radha, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, S. Skupsky, and J. M. Soures Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester S. Cremer
Charged-Particle Spectra Using Particle Tracking on a Two-Dimensional Grid P. B. Radha, J. A. Delettrez, R. Epstein, S. Skupsky, and J. M. Soures Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester S. Cremer
Modeling Nonlinear Optics Of Plasmas (Relevant To IFE)
 Modeling Nonlinear Optics Of Plasmas (Relevant To IFE) F.S.Tsung and the UCLA Simulation Group University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) 1 F. S. Tsung/OSIRIS Workshop 2017 Summary/Conclusion Introduction
Modeling Nonlinear Optics Of Plasmas (Relevant To IFE) F.S.Tsung and the UCLA Simulation Group University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) 1 F. S. Tsung/OSIRIS Workshop 2017 Summary/Conclusion Introduction
Particle-in-Cell Simulations of Particle Acceleration. E. A. Startsev and C. J. McKinstrie. Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U.
 Particle-in-Cell Simulations of Particle Acceleration E. A. Startsev and C. J. McKinstrie Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester Previous analytical calculations suggest that a preaccelerated
Particle-in-Cell Simulations of Particle Acceleration E. A. Startsev and C. J. McKinstrie Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester Previous analytical calculations suggest that a preaccelerated
Anomalous Stimulated Raman Scattering and Electron Acoustic Waves in Laser-Produced Plasmas: A Linear Model
 Anomalous Stimulated Raman Scattering and Electron Acoustic Waves in Laser-Produced Plasmas: A Linear Model Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS, an instability in which light is scattered by and amplifies
Anomalous Stimulated Raman Scattering and Electron Acoustic Waves in Laser-Produced Plasmas: A Linear Model Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS, an instability in which light is scattered by and amplifies
A Model of Laser Imprinting. V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V.
 A Model of Laser Imprinting V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V. Gotchev Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester The control of
A Model of Laser Imprinting V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V. Gotchev Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester The control of
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
Measurement of Long-Scale-Length Plasma Density Profiles for Two-Plasmon Decay Studies
 Measurement of Long-Scale-Length Plasma Density Profiles for Two-Plasmon Decay Studies Plasma density scale length at 10 21 cm 3 (nm) 350 300 250 200 150 100 0 Flat foil 2 4 6 8 10 100 Target diameter
Measurement of Long-Scale-Length Plasma Density Profiles for Two-Plasmon Decay Studies Plasma density scale length at 10 21 cm 3 (nm) 350 300 250 200 150 100 0 Flat foil 2 4 6 8 10 100 Target diameter
Calculation of Half-Harmonic Emission Generated by the Two-Plasmon Decay Instability at exit boundary
 Calculation of Half-Harmonic Emission Generated by the wo-plasmon Decay Instability ^ h E D~ at exit boundary Arbitrary units 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.0 inear conversion Nonlinear conversion homson down-scattering
Calculation of Half-Harmonic Emission Generated by the wo-plasmon Decay Instability ^ h E D~ at exit boundary Arbitrary units 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.0 inear conversion Nonlinear conversion homson down-scattering
Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility
 Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility R (mm) 1 8 6 4 End of acceleration phase r(g/cc) 7.5 3.5.5 Gain 4 3 2 1 1 2 2 s (mm) 5 25 25 5 Z (mm) P. W. McKenty
Analysis of a Direct-Drive Ignition Capsule Design for the National Ignition Facility R (mm) 1 8 6 4 End of acceleration phase r(g/cc) 7.5 3.5.5 Gain 4 3 2 1 1 2 2 s (mm) 5 25 25 5 Z (mm) P. W. McKenty
D- 3 He Protons as a Diagnostic for Target ρr
 D- 3 He Protons as a Diagnostic for Target ρr Areal density (ρr) is an important parameter for measuring compression in ICF experiments. Several diagnostics employing nuclear particles have been considered
D- 3 He Protons as a Diagnostic for Target ρr Areal density (ρr) is an important parameter for measuring compression in ICF experiments. Several diagnostics employing nuclear particles have been considered
Parametric Instabilities in Laser/Matter Interaction: From Noise Levels to Relativistic Regimes
 UCRL-ID-133227 Parametric Instabilities in Laser/Matter Interaction: From Noise Levels to Relativistic Regimes H. A. Baldis C. Labaune W. L. Kruer February 11, 1999 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
UCRL-ID-133227 Parametric Instabilities in Laser/Matter Interaction: From Noise Levels to Relativistic Regimes H. A. Baldis C. Labaune W. L. Kruer February 11, 1999 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Polymath Research Inc.
 Can We Really Control Stimulated Raman and Brillouin Backscattering by Surposing Large Amplitude Waves onto the Plasma an Making it an Inhospitable Environment for Their Growth? Bedros Afeyan & M.Mardirian
Can We Really Control Stimulated Raman and Brillouin Backscattering by Surposing Large Amplitude Waves onto the Plasma an Making it an Inhospitable Environment for Their Growth? Bedros Afeyan & M.Mardirian
Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale
 Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale Laser intensity ( 1 15 W/cm 2 ) 5 4 3 2 1 Laser spike is replaced with hot-electron spike 2 4 6 8 1 Gain 2 15 1 5 1. 1.2 1.4
Two-Dimensional Simulations of Electron Shock Ignition at the Megajoule Scale Laser intensity ( 1 15 W/cm 2 ) 5 4 3 2 1 Laser spike is replaced with hot-electron spike 2 4 6 8 1 Gain 2 15 1 5 1. 1.2 1.4
Parametric Studies of Kinetically-Enhanced Raman Backscatter and Electron Acoustic Thomson Scattering
 Parametric Studies of Kinetically-Enhanced Raman Backscatter and Electron Acoustic Thomson Scattering D. J. Strozzi 1, E. A. Williams 1, A. B. Langdon 1, A. Bers 2 1 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory,
Parametric Studies of Kinetically-Enhanced Raman Backscatter and Electron Acoustic Thomson Scattering D. J. Strozzi 1, E. A. Williams 1, A. B. Langdon 1, A. Bers 2 1 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory,
Cross-Beam Energy Transport in Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments
 Cross-Beam Energy Transport in Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments 35 3 Laser pulse Power (TW) 25 2 15 1 Modeled scattered light Measured 5 D. H. Edgell University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.5
Cross-Beam Energy Transport in Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments 35 3 Laser pulse Power (TW) 25 2 15 1 Modeled scattered light Measured 5 D. H. Edgell University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.5
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA
 An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
An Overview of Laser-Driven Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion on OMEGA 4 compression beams MIFEDS coils B z ~ 1 T Preheat beam from P9 1 mm Ring 3 Rings 4 Ring 3 Target support Fill-tube pressure transducer
Two-Plasmon Decay Driven by Multiple Incoherent Laser Beams
 Two-Plasmon Decay Driven by Multiple Incoherent Laser Beams 2 # # E^xyt,, h dy dy^arbitrary h n Two coherent e /n c plane waves Dm = 8.8 Å Dm = 17.6 Å.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27 2 Arbitrary
Two-Plasmon Decay Driven by Multiple Incoherent Laser Beams 2 # # E^xyt,, h dy dy^arbitrary h n Two coherent e /n c plane waves Dm = 8.8 Å Dm = 17.6 Å.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27.19.21.23.25.27 2 Arbitrary
Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions
 Modelisation and Numerical Methods for Hot Plasmas Talence, October 14, 2015 Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions V. T. Tikhonchuk, A. Colaïtis, A. Vallet, E. Llor
Modelisation and Numerical Methods for Hot Plasmas Talence, October 14, 2015 Physics of Laser-Plasma Interaction and Shock Ignition of Fusion Reactions V. T. Tikhonchuk, A. Colaïtis, A. Vallet, E. Llor
PHYSICS OF HOT DENSE PLASMAS
 Chapter 6 PHYSICS OF HOT DENSE PLASMAS 10 26 10 24 Solar Center Electron density (e/cm 3 ) 10 22 10 20 10 18 10 16 10 14 10 12 High pressure arcs Chromosphere Discharge plasmas Solar interior Nd (nω) laserproduced
Chapter 6 PHYSICS OF HOT DENSE PLASMAS 10 26 10 24 Solar Center Electron density (e/cm 3 ) 10 22 10 20 10 18 10 16 10 14 10 12 High pressure arcs Chromosphere Discharge plasmas Solar interior Nd (nω) laserproduced
Monochromatic 8.05-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets
 Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
Monochromatic 8.5-keV Flash Radiography of Imploded Cone-in-Shell Targets y position (nm) y position (nm) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 66381 undriven 66393, 3.75 ns 66383, 3.82 ns Au Al 66391, 3.93 ns 66386, 4.5 ns 66389,
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers
 Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
Scaling Hot-Electron Generation to High-Power, Kilojoule-Class Lasers 75 nm 75 75 5 nm 3 copper target Normalized K b /K a 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 Cold material 1 ps 10 ps 0.2 10 3 10 4 Heating 2.1 kj, 10
A Tunable (1100-nm to 1500-nm) 50-mJ Laser Enables a Pump-Depleting Plasma-Wave Amplifier
 A Tunable (1100-nm to 1500-nm) 50-mJ Laser Enables a Pump-Depleting Plasma-Wave Amplifier Focused intensity (W/cm 2 ) 10 30 10 25 10 20 10 15 10 10 Nonlinear quantum electrodynamics (QED) Ultrarelativistic
A Tunable (1100-nm to 1500-nm) 50-mJ Laser Enables a Pump-Depleting Plasma-Wave Amplifier Focused intensity (W/cm 2 ) 10 30 10 25 10 20 10 15 10 10 Nonlinear quantum electrodynamics (QED) Ultrarelativistic
First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA
 First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA MIT 1 mm 1 mm 100 µm C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division
First Results from Cryogenic-Target Implosions on OMEGA MIT 1 mm 1 mm 100 µm C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division
Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA
 Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA In-flight aspect ratio OMEGA cryogenic ignition hydro-equivalent design tr = 3 mg/cm 2, V imp = 3.7 7 cm/s 3 3 2 14 m = 48 ng
Mitigation of Cross-Beam Energy Transfer in Direct-Drive Implosions on OMEGA In-flight aspect ratio OMEGA cryogenic ignition hydro-equivalent design tr = 3 mg/cm 2, V imp = 3.7 7 cm/s 3 3 2 14 m = 48 ng
Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks. 26 June 2009
 PSFC/JA-8-8 Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks J. R. Rygg, J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Seguin, R. D. Petrasso, F.J. Marshalli, J. A. Delettrez, J.P. Knauer, D.D.
PSFC/JA-8-8 Observations of the collapse of asymmetrically driven convergent shocks J. R. Rygg, J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Seguin, R. D. Petrasso, F.J. Marshalli, J. A. Delettrez, J.P. Knauer, D.D.
Capsule-areal-density asymmetries inferred from 14.7-MeV deuterium helium protons in direct-drive OMEGA implosions a
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 10, NUMBER 5 MAY 2003 Capsule-areal-density asymmetries inferred from 14.7-MeV deuterium helium protons in direct-drive OMEGA implosions a C. K. Li, b) F. H. Séguin, J. A. Frenje,
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 10, NUMBER 5 MAY 2003 Capsule-areal-density asymmetries inferred from 14.7-MeV deuterium helium protons in direct-drive OMEGA implosions a C. K. Li, b) F. H. Séguin, J. A. Frenje,
Integrated Modeling of Fast Ignition Experiments
 Integrated Modeling of Fast Ignition Experiments Presented to: 9th International Fast Ignition Workshop Cambridge, MA November 3-5, 2006 R. P. J. Town AX-Division Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Integrated Modeling of Fast Ignition Experiments Presented to: 9th International Fast Ignition Workshop Cambridge, MA November 3-5, 2006 R. P. J. Town AX-Division Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Scattering of Electromagnetic Radiation. References:
 Scattering of Electromagnetic Radiation References: Plasma Diagnostics: Chapter by Kunze Methods of experimental physics, 9a, chapter by Alan Desilva and George Goldenbaum, Edited by Loveberg and Griem.
Scattering of Electromagnetic Radiation References: Plasma Diagnostics: Chapter by Kunze Methods of experimental physics, 9a, chapter by Alan Desilva and George Goldenbaum, Edited by Loveberg and Griem.
Progress in Vlasov-Fokker- Planck simulations of laserplasma
 Progress in Vlasov-Fokker- Planck simulations of laserplasma interactions C. P. Ridgers, M. W. Sherlock, R. J. Kingham, A.Thomas, R. Evans Imperial College London Outline Part 1 simulations of long-pulse
Progress in Vlasov-Fokker- Planck simulations of laserplasma interactions C. P. Ridgers, M. W. Sherlock, R. J. Kingham, A.Thomas, R. Evans Imperial College London Outline Part 1 simulations of long-pulse
What is. Inertial Confinement Fusion?
 What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
Thomson Scattering from Nonlinear Electron Plasma Waves
 Thomson Scattering from Nonlinear Electron Plasma Waves A. DAVIES, 1 J. KATZ, 1 S. BUCHT, 1 D. HABERBERGER, 1 J. BROMAGE, 1 J. D. ZUEGEL, 1 J. D. SADLER, 2 P. A. NORREYS, 3 R. BINGHAM, 4 R. TRINES, 5 L.O.
Thomson Scattering from Nonlinear Electron Plasma Waves A. DAVIES, 1 J. KATZ, 1 S. BUCHT, 1 D. HABERBERGER, 1 J. BROMAGE, 1 J. D. ZUEGEL, 1 J. D. SADLER, 2 P. A. NORREYS, 3 R. BINGHAM, 4 R. TRINES, 5 L.O.
Multibeam Laser Plasma Interactions in Inertial Confinement Fusion
 Multibeam Laser Plasma Interactions in Inertial Confinement Fusion Polar drive X-ray drive 1 n e /n c n e /n c 1 mm.25. n e /n c 3.5 mm J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics
Multibeam Laser Plasma Interactions in Inertial Confinement Fusion Polar drive X-ray drive 1 n e /n c n e /n c 1 mm.25. n e /n c 3.5 mm J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics
Measuring the Refractive Index of a Laser-Plasma System
 Measuring the Refractive Index of a Laser-Plasma System 1 dh ( 10 4 ) 0 1 J (dh) R (dh) 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 D. Turnbull University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Dm (Å) 58th Annual Meeting of the
Measuring the Refractive Index of a Laser-Plasma System 1 dh ( 10 4 ) 0 1 J (dh) R (dh) 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 D. Turnbull University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Dm (Å) 58th Annual Meeting of the
Dynamo on the OMEGA laser and kinetic problems of proton radiography
 Dynamo on the OMEGA laser and kinetic problems of proton radiography Archie Bott, Alex Rigby, Tom White, Petros Tzeferacos, Don Lamb, Gianluca Gregori, Alex Schekochihin (and many others ) 2 th August
Dynamo on the OMEGA laser and kinetic problems of proton radiography Archie Bott, Alex Rigby, Tom White, Petros Tzeferacos, Don Lamb, Gianluca Gregori, Alex Schekochihin (and many others ) 2 th August
High-Intensity Laser Interactions with Solid Targets and Implications for Fast-Ignition Experiments on OMEGA EP
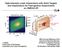 n n High-Intensity Laser Interactions with Solid Targets and Implications for Fast-Ignition Experiments on OMEGA EP a n n n n J. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual
n n High-Intensity Laser Interactions with Solid Targets and Implications for Fast-Ignition Experiments on OMEGA EP a n n n n J. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual
Energetic neutral and negative ion beams accelerated from spray target irradiated with ultra-short, intense laser pulses
 Energetic neutral and negative ion beams accelerated from spray target irradiated with ultra-short, intense laser pulses Sargis Ter-Avetisyan ELI - Extreme Light Infrastructure Science and Technology with
Energetic neutral and negative ion beams accelerated from spray target irradiated with ultra-short, intense laser pulses Sargis Ter-Avetisyan ELI - Extreme Light Infrastructure Science and Technology with
Physics of Radiotherapy. Lecture II: Interaction of Ionizing Radiation With Matter
 Physics of Radiotherapy Lecture II: Interaction of Ionizing Radiation With Matter Charge Particle Interaction Energetic charged particles interact with matter by electrical forces and lose kinetic energy
Physics of Radiotherapy Lecture II: Interaction of Ionizing Radiation With Matter Charge Particle Interaction Energetic charged particles interact with matter by electrical forces and lose kinetic energy
Development of a WDM platform for chargedparticle stopping experiments
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Development of a WDM platform for chargedparticle stopping experiments To cite this article: A B Zylstra et al 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 717 12118
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Development of a WDM platform for chargedparticle stopping experiments To cite this article: A B Zylstra et al 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 717 12118
Determination of Hot-Electron Conversion Efficiencies and Isochoric Heating of Low-Mass Targets Irradiated by the Multi-Terawatt Laser
 Determination of Hot-Electron Conversion Efficiencies and Isochoric Heating of Low-Mass Targets Irradiated by the Multi-Terawatt Laser 1.2 Total energy K a /laser energy 1 3 1 4 Refluxing No refluxing
Determination of Hot-Electron Conversion Efficiencies and Isochoric Heating of Low-Mass Targets Irradiated by the Multi-Terawatt Laser 1.2 Total energy K a /laser energy 1 3 1 4 Refluxing No refluxing
The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition
 The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition Normalized intensity 1..8.6.4.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Core self-emission. 3 2 1
The 1-D Campaign on OMEGA: A Systematic Approach to Find the Path to Ignition Normalized intensity 1..8.6.4.2 R. Betti University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Core self-emission. 3 2 1
Two-Plasmon-Decay Hot Electron Generation and Reheating in OMEGA Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments
 Two-Plasmon-Decay Hot Electron Generation and Reheating in OMEGA Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments r 1/4 ~500 nm Ne To sheath e Laser r e To core 20 nm J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for
Two-Plasmon-Decay Hot Electron Generation and Reheating in OMEGA Direct-Drive-Implosion Experiments r 1/4 ~500 nm Ne To sheath e Laser r e To core 20 nm J. F. Myatt University of Rochester Laboratory for
Relativistic Electron Heating in Focused Multimode Laser Fields with Stochastic Phase Purturbations
 1 Relativistic Electron Heating in Focused Multimode Laser Fields with Stochastic Phase Purturbations Yu.A.Mikhailov, L.A.Nikitina, G.V.Sklizkov, A.N.Starodub, M.A.Zhurovich P.N.Lebedev Physical Institute,
1 Relativistic Electron Heating in Focused Multimode Laser Fields with Stochastic Phase Purturbations Yu.A.Mikhailov, L.A.Nikitina, G.V.Sklizkov, A.N.Starodub, M.A.Zhurovich P.N.Lebedev Physical Institute,
Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I. R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 2009
 Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 009 Light of the night sky We learn of the universe around us from EM radiation, neutrinos,
Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics I R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 18 May 009 Light of the night sky We learn of the universe around us from EM radiation, neutrinos,
Spectral analysis of K-shell X-ray emission of magnesium plasma produced by ultrashort high-intensity laser pulse irradiation
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 365 371 Spectral analysis of K-shell X-ray emission of magnesium plasma produced by ultrashort high-intensity laser
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 365 371 Spectral analysis of K-shell X-ray emission of magnesium plasma produced by ultrashort high-intensity laser
Framed X-Ray Imaging of Cryogenic Target Implosion Cores on OMEGA
 Framed X-Ray Imaging of Cryogenic Target Implosion Cores on OMEGA KBFRAMED optic assembly KBFRAMED core image OMEGA cryogenic DT target implosion shot 77064 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory
Framed X-Ray Imaging of Cryogenic Target Implosion Cores on OMEGA KBFRAMED optic assembly KBFRAMED core image OMEGA cryogenic DT target implosion shot 77064 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory
Exploration of the Feasibility of Polar Drive on the LMJ. Lindsay M. Mitchel. Spencerport High School. Spencerport, New York
 Exploration of the Feasibility of Polar Drive on the LMJ Lindsay M. Mitchel Spencerport High School Spencerport, New York Advisor: Dr. R. S. Craxton Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester
Exploration of the Feasibility of Polar Drive on the LMJ Lindsay M. Mitchel Spencerport High School Spencerport, New York Advisor: Dr. R. S. Craxton Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester
Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion Advanced Ignition Techniques
 Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion Advanced Ignition Techniques R. Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta Presented at the Canadian Workshop on Fusion Energy
Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion Advanced Ignition Techniques R. Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta Presented at the Canadian Workshop on Fusion Energy
Electron-Acoustic Wave in a Plasma
 Electron-Acoustic Wave in a Plasma 0 (uniform ion distribution) For small fluctuations, n ~ e /n 0
Electron-Acoustic Wave in a Plasma 0 (uniform ion distribution) For small fluctuations, n ~ e /n 0
SHIELDING CALCULATIONS FOR THE HARD X-RAY GENERATED BY LCLS MEC LASER SYSTEM R. QIU, J. C. LIU, S. H. ROKNI AND A. A. PRINZ
 SLAC-PUB-14159 SHIELDING CALCULATIONS FOR THE HARD X-RAY GENERATED BY LCLS MEC LASER SYSTEM R. QIU, J. C. LIU, S. H. ROKNI AND A. A. PRINZ SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory: 2575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo
SLAC-PUB-14159 SHIELDING CALCULATIONS FOR THE HARD X-RAY GENERATED BY LCLS MEC LASER SYSTEM R. QIU, J. C. LIU, S. H. ROKNI AND A. A. PRINZ SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory: 2575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo
Using the X-FEL to understand X-ray Thomson scattering for partially ionized plasmas
 LLNL-PROC-564720 Using the X-FEL to understand X-ray Thomson scattering for partially ionized plasmas J. Nilsen, W. R. Johnson, K. T. Cheng July 17, 2012 13th International Conference on X-ray Lasers Paris,
LLNL-PROC-564720 Using the X-FEL to understand X-ray Thomson scattering for partially ionized plasmas J. Nilsen, W. R. Johnson, K. T. Cheng July 17, 2012 13th International Conference on X-ray Lasers Paris,
Multibeam Stimulated Brillouin Scattering from Hot Solid-Target Plasmas
 Multibeam Stimulated Brillouin Scattering from Hot Solid-Target Plasmas Introduction We report on the first multibeam laser plasma interaction experiments with a critical density surface present at all
Multibeam Stimulated Brillouin Scattering from Hot Solid-Target Plasmas Introduction We report on the first multibeam laser plasma interaction experiments with a critical density surface present at all
An Alternative Laser-Speckle-Smoothing Scheme for the NIF
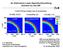 An Alternative Laser-Speckle-Smoothing Scheme for the NIF 1.5-MJ CH-foam target; end of acceleration 1-D SSD, 1.8 Å 1-D MultiFM, 8 Å 2-D SSD, 11 Å 1-D SSD 1-D, multiple-fm SSD 2-D SSD Density (g cm 3 )
An Alternative Laser-Speckle-Smoothing Scheme for the NIF 1.5-MJ CH-foam target; end of acceleration 1-D SSD, 1.8 Å 1-D MultiFM, 8 Å 2-D SSD, 11 Å 1-D SSD 1-D, multiple-fm SSD 2-D SSD Density (g cm 3 )
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008
 Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
Ultrafast X-Ray-Matter Interaction and Damage of Inorganic Solids October 10, 2008 Richard London rlondon@llnl.gov Workshop on Interaction of Free Electron Laser Radiation with Matter Hamburg This work
Determination of the Flux Limiter in CH Targets from Experiments on the OMEGA Laser
 Determination of the Flux Limiter in CH Targets from Experiments on the OMEGA Laser f = 0.070 Neutron rate (1/s) Exp. f = 0.065 f = 0.060 J. A. Delettrez et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser
Determination of the Flux Limiter in CH Targets from Experiments on the OMEGA Laser f = 0.070 Neutron rate (1/s) Exp. f = 0.065 f = 0.060 J. A. Delettrez et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser
High Gain Direct Drive Target Designs and Supporting Experiments with KrF )
 High Gain Direct Drive Target Designs and Supporting Experiments with KrF ) Max KARASIK, Yefim AGLITSKIY 1), Jason W. BATES, Denis G. COLOMBANT 4), David M. KEHNE, Wallace M. MANHEIMER 2), Nathan METZLER
High Gain Direct Drive Target Designs and Supporting Experiments with KrF ) Max KARASIK, Yefim AGLITSKIY 1), Jason W. BATES, Denis G. COLOMBANT 4), David M. KEHNE, Wallace M. MANHEIMER 2), Nathan METZLER
Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF
 Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF OMEGA polar-drive geometry 21.4 Backlit x-ray image OMEGA polar-drive implosion 21.4 58.2 77.8 42. 58.8 CR ~ 5 R = 77 nm 4 nm 4 nm P. B. Radha University of Rochester Laboratory
Polar Drive on OMEGA and the NIF OMEGA polar-drive geometry 21.4 Backlit x-ray image OMEGA polar-drive implosion 21.4 58.2 77.8 42. 58.8 CR ~ 5 R = 77 nm 4 nm 4 nm P. B. Radha University of Rochester Laboratory
Modeling the Effects Mix at the Hot Spot Surface in 1-D Simulations of Cryogenic All-DT Ignition Capsule Implosions
 Modeling the Effects Mix at the Hot Spot Surface in 1-D Simulations of Cryogenic All-DT Ignition Capsule Implosions 14 Time = 1.4 ns 25 Ion temperature (kev) 12 1 8 6 4 2 22.2 8.7 1.5 Gain =.45 2 15 1
Modeling the Effects Mix at the Hot Spot Surface in 1-D Simulations of Cryogenic All-DT Ignition Capsule Implosions 14 Time = 1.4 ns 25 Ion temperature (kev) 12 1 8 6 4 2 22.2 8.7 1.5 Gain =.45 2 15 1
ULTRA-INTENSE LASER PLASMA INTERACTIONS RELATED TO FAST IGNITOR IN INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION
 ULTRA-INTENSE LASER PLASMA INTERACTIONS RELATED TO FAST IGNITOR IN INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION R. KODAMA, H. FUJITA, N. IZUMI, T. KANABE, Y. KATO*, Y. KITAGAWA, Y. SENTOKU, S. NAKAI, M. NAKATSUKA, T. NORIMATSU,
ULTRA-INTENSE LASER PLASMA INTERACTIONS RELATED TO FAST IGNITOR IN INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION R. KODAMA, H. FUJITA, N. IZUMI, T. KANABE, Y. KATO*, Y. KITAGAWA, Y. SENTOKU, S. NAKAI, M. NAKATSUKA, T. NORIMATSU,
arxiv: v4 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v4 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Nov 2018 arxiv: v4 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Nov 2018](/thumbs/89/100953439.jpg) arxiv:1809.10490v4 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Nov 2018 Absolute instability modes due to rescattering of stimulated Raman scattering in a large nonuniform plasma Yao Zhao 1,, Zhengming Sheng 2,3,4,5, Suming
arxiv:1809.10490v4 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Nov 2018 Absolute instability modes due to rescattering of stimulated Raman scattering in a large nonuniform plasma Yao Zhao 1,, Zhengming Sheng 2,3,4,5, Suming
Measurements of fuel and shell areal densities of OMEGA capsule implosions using elastically scattered protons
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 9, NUMBER 11 NOVEMBER 2002 Measurements of fuel and shell areal densities of OMEGA capsule implosions using elastically scattered protons J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Séguin,
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 9, NUMBER 11 NOVEMBER 2002 Measurements of fuel and shell areal densities of OMEGA capsule implosions using elastically scattered protons J. A. Frenje, C. K. Li, F. H. Séguin,
Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled, cone-in-shell, fast-ignitor targets on the OMEGA Laser
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (25) B859 B867 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:1.188/741-3335/47/12b/s68 Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled,
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (25) B859 B867 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:1.188/741-3335/47/12b/s68 Direct-drive fuel-assembly experiments with gas-filled,
Laser trigged proton acceleration from ultrathin foil
 Laser trigged proton acceleration from ultrathin foil A.V. Brantov 1, V. Yu. Bychenkov 1, D. V. Romanov 2, A. Maksimchuk 3 1 P. N. Lebedev Physics Institute RAS, Moscow 119991, Russia 2 All-Russia Research
Laser trigged proton acceleration from ultrathin foil A.V. Brantov 1, V. Yu. Bychenkov 1, D. V. Romanov 2, A. Maksimchuk 3 1 P. N. Lebedev Physics Institute RAS, Moscow 119991, Russia 2 All-Russia Research
T T Fusion Neutron Spectrum Measured in Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiment
 T T Fusion Neutron Spectrum Measured in Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiment V. Yu. Glebov University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
T T Fusion Neutron Spectrum Measured in Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiment V. Yu. Glebov University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
Spatial Intensity Nonuniformities of an OMEGA Beam due to Nonlinear Beam Propagation
 Spatial Intensity Nonuniformities of an OMEGA Beam due to Nonlinear Beam Propagation Several applications require that a laser beam maintain a high degree of wavefront quality after propagating a long
Spatial Intensity Nonuniformities of an OMEGA Beam due to Nonlinear Beam Propagation Several applications require that a laser beam maintain a high degree of wavefront quality after propagating a long
Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiments & Modeling
 Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiments & Modeling Using X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy of Thin Tracer Layers to Diagnose the Time-Dependent Properties of ICF Ablator Materials David Cohen (Swarthmore College,
Inertial Confinement Fusion Experiments & Modeling Using X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy of Thin Tracer Layers to Diagnose the Time-Dependent Properties of ICF Ablator Materials David Cohen (Swarthmore College,
Magnetized High-Energy-Density Plasma
 LLNL PRES 446057 Magnetized High-Energy-Density Plasma D.D. Ryutov Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94551, USA Presented at the 2010 Science with High-Power Lasers and Pulsed Power
LLNL PRES 446057 Magnetized High-Energy-Density Plasma D.D. Ryutov Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94551, USA Presented at the 2010 Science with High-Power Lasers and Pulsed Power
Inertial Confinement Fusion DR KATE LANCASTER YORK PLASMA INSTITUTE
 Inertial Confinement Fusion DR KATE LANCASTER YORK PLASMA INSTITUTE In the beginning In the late fifties, alternative applications of nuclear explosions were being considered the number one suggestion
Inertial Confinement Fusion DR KATE LANCASTER YORK PLASMA INSTITUTE In the beginning In the late fifties, alternative applications of nuclear explosions were being considered the number one suggestion
Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets
 Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets v rms of tr (mg/cm )..6 Si [4.%] Si [7.4%] Ge [.9%] DRACO simulations..4 Time (ns) S. X. Hu University
Analysis of Laser-Imprinting Reduction in Spherical-RT Experiments with Si-/Ge-Doped Plastic Targets v rms of tr (mg/cm )..6 Si [4.%] Si [7.4%] Ge [.9%] DRACO simulations..4 Time (ns) S. X. Hu University
High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry
 High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry Low intensity High intensity 4 nm CH 3 nm Mo 138 nm quartz VISAR SOP Simulated peak pressure (Mbar) 1 5 Laser backscatter 17.5 kev Mo K a Hard
High-Intensity Shock-Ignition Experiments in Planar Geometry Low intensity High intensity 4 nm CH 3 nm Mo 138 nm quartz VISAR SOP Simulated peak pressure (Mbar) 1 5 Laser backscatter 17.5 kev Mo K a Hard
Experimental Demonstration of X-Ray Drive Enhancement with Rugby-Shaped Hohlraums
 Experimental Demonstration of X-Ray Drive Enhancement with Rugby-Shaped Hohlraums The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Experimental Demonstration of X-Ray Drive Enhancement with Rugby-Shaped Hohlraums The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Lecture 3: Optical Properties of Insulators, Semiconductors, and Metals. 5 nm
 Metals Lecture 3: Optical Properties of Insulators, Semiconductors, and Metals 5 nm Course Info Next Week (Sept. 5 and 7) no classes First H/W is due Sept. 1 The Previous Lecture Origin frequency dependence
Metals Lecture 3: Optical Properties of Insulators, Semiconductors, and Metals 5 nm Course Info Next Week (Sept. 5 and 7) no classes First H/W is due Sept. 1 The Previous Lecture Origin frequency dependence
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL Monterey, California THESIS
 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL Monterey, California THESIS ION DENSITY FLUCTUATIONS IN PLASMA AND THEIR EFFECTS ON HOT ELECTRON GENERATION by Marty Wallace June 2002 Thesis Advisor: Second Reader: William L.
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL Monterey, California THESIS ION DENSITY FLUCTUATIONS IN PLASMA AND THEIR EFFECTS ON HOT ELECTRON GENERATION by Marty Wallace June 2002 Thesis Advisor: Second Reader: William L.
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA
 Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Advanced Ignition Experiments on OMEGA C. Stoeckl University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 5th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics Dallas, TX 17 21
Light Interaction with Small Structures
 Light Interaction with Small Structures Molecules Light scattering due to harmonically driven dipole oscillator Nanoparticles Insulators Rayleigh Scattering (blue sky) Semiconductors...Resonance absorption
Light Interaction with Small Structures Molecules Light scattering due to harmonically driven dipole oscillator Nanoparticles Insulators Rayleigh Scattering (blue sky) Semiconductors...Resonance absorption
Kinetics of the Raman Instability in a Laser Plasma
 WDS'05 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 383 390, 2005. ISBN 80-86732-59-2 MATFYZPRESS Kinetics of the Raman Instability in a Laser Plasma M. Mašek and K. Rohlena Institute of Physics, Academy
WDS'05 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 383 390, 2005. ISBN 80-86732-59-2 MATFYZPRESS Kinetics of the Raman Instability in a Laser Plasma M. Mašek and K. Rohlena Institute of Physics, Academy
Heating and current drive: Radio Frequency
 Heating and current drive: Radio Frequency Dr Ben Dudson Department of Physics, University of York Heslington, York YO10 5DD, UK 13 th February 2012 Dr Ben Dudson Magnetic Confinement Fusion (1 of 26)
Heating and current drive: Radio Frequency Dr Ben Dudson Department of Physics, University of York Heslington, York YO10 5DD, UK 13 th February 2012 Dr Ben Dudson Magnetic Confinement Fusion (1 of 26)
Simulation of Plasma Wakefields and Weibel Instability of Electron Beams in Plasma Using Codes LSP and OSIRIS
 Simulation of Plasma Wakefields and Weibel Instability of Electron Beams in Plasma Using Codes and OSIRIS 15 Electron density Beam density Plasma density 4 6 4 A. Solodov, C. Ren, J. Myatt, and R. Betti
Simulation of Plasma Wakefields and Weibel Instability of Electron Beams in Plasma Using Codes and OSIRIS 15 Electron density Beam density Plasma density 4 6 4 A. Solodov, C. Ren, J. Myatt, and R. Betti
Interaction of particles with matter - 2. Silvia Masciocchi, GSI and University of Heidelberg SS2017, Heidelberg May 3, 2017
 Interaction of particles with matter - 2 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI and University of Heidelberg SS2017, Heidelberg May 3, 2017 Energy loss by ionization (by heavy particles) Interaction of electrons with
Interaction of particles with matter - 2 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI and University of Heidelberg SS2017, Heidelberg May 3, 2017 Energy loss by ionization (by heavy particles) Interaction of electrons with
Answers to questions on exam in laser-based combustion diagnostics on March 10, 2006
 Answers to questions on exam in laser-based combustion diagnostics on March 10, 2006 1. Examples of advantages and disadvantages with laser-based combustion diagnostic techniques: + Nonintrusive + High
Answers to questions on exam in laser-based combustion diagnostics on March 10, 2006 1. Examples of advantages and disadvantages with laser-based combustion diagnostic techniques: + Nonintrusive + High
Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width
 Introduction Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width A. B. Zylstra, M. Rosenberg, N. Sinenian, C. Li, F. Seguin, J. Frenje, R. Petrasso (MIT) R. Rygg, D. Hicks, S. Friedrich,
Introduction Diagnosing OMEGA and NIF Implosions Using the D 3 He Spectrum Line Width A. B. Zylstra, M. Rosenberg, N. Sinenian, C. Li, F. Seguin, J. Frenje, R. Petrasso (MIT) R. Rygg, D. Hicks, S. Friedrich,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/319/5867/1223/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Proton Radiography of Inertial Fusion Implosions J. R. Rygg, F. H. Séguin, C. K. Li, J. A. Frenje, M. J.-E. Manuel,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/319/5867/1223/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Proton Radiography of Inertial Fusion Implosions J. R. Rygg, F. H. Séguin, C. K. Li, J. A. Frenje, M. J.-E. Manuel,
Science and code validation program to secure ignition on LMJ
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Science and code validation program to secure ignition on LMJ Related content - Inertial fusion with the LMJ C Cavailler To cite this article: E
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Science and code validation program to secure ignition on LMJ Related content - Inertial fusion with the LMJ C Cavailler To cite this article: E
Fukuoka, Japan. 23 August National Ignition Facility (NIF) Laboratory for Laser Energetics (OPERA)
 Fukuoka, Japan 23 August 2012 National Ignition Facility (NIF) LLNL-PRES-562760 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under
Fukuoka, Japan 23 August 2012 National Ignition Facility (NIF) LLNL-PRES-562760 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under
Study of Laser Plasma Interactions Using an Eulerian Vlasov Code
 PSFC/JA-04-6 Study of Laser Plasma Interactions Using an Eulerian Vlasov Code D. J. Strozzi, M. M. Shoucri*, and A. Bers March 2004 Plasma Science and Fusion Center Massachusetts Institute of Technology
PSFC/JA-04-6 Study of Laser Plasma Interactions Using an Eulerian Vlasov Code D. J. Strozzi, M. M. Shoucri*, and A. Bers March 2004 Plasma Science and Fusion Center Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Larmor Formula (Chapters 18-19)
 2017-02-28 Dispersive Media, Lecture 12 - Thomas Johnson 1 The Larmor Formula (Chapters 18-19) T. Johnson Outline Brief repetition of emission formula The emission from a single free particle - the Larmor
2017-02-28 Dispersive Media, Lecture 12 - Thomas Johnson 1 The Larmor Formula (Chapters 18-19) T. Johnson Outline Brief repetition of emission formula The emission from a single free particle - the Larmor
The Plasma Phase. Chapter 1. An experiment - measure and understand transport processes in a plasma. Chapter 2. An introduction to plasma physics
 The Plasma Phase Chapter 1. An experiment - measure and understand transport processes in a plasma Three important vugraphs What we have just talked about The diagnostics Chapter 2. An introduction to
The Plasma Phase Chapter 1. An experiment - measure and understand transport processes in a plasma Three important vugraphs What we have just talked about The diagnostics Chapter 2. An introduction to
Explanation of prompt growth of ECE signal in tokamak runaway electron experiments
 Chang Liu et al. 2nd IAEA TM on the Fusion Data Processing, Validation and Analysis 1 Explanation of prompt growth of ECE signal in tokamak runaway electron experiments Chang Liu 1, Lei Shi 2, Eero Hirvijoki
Chang Liu et al. 2nd IAEA TM on the Fusion Data Processing, Validation and Analysis 1 Explanation of prompt growth of ECE signal in tokamak runaway electron experiments Chang Liu 1, Lei Shi 2, Eero Hirvijoki
arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 12 Aug 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 12 Aug 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 12 Aug 2013](/thumbs/87/96806811.jpg) Laser-plasma interactions for fast ignition arxiv:1308.2628v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 12 Aug 2013 A J Kemp 1, F Fiuza 1,2, A Debayle 3, T Johzaki 4, W B Mori 5, P K Patel 1, Y Sentoku 6, L O Silva 2 1 Lawrence
Laser-plasma interactions for fast ignition arxiv:1308.2628v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 12 Aug 2013 A J Kemp 1, F Fiuza 1,2, A Debayle 3, T Johzaki 4, W B Mori 5, P K Patel 1, Y Sentoku 6, L O Silva 2 1 Lawrence
Announcements. Fast => v~c c= the velocity of light
 Announcements 2402 Lab will be started this week Lab manual is available on the course web page HW: Chapter.2 70, 75, 76, 87, 92, 97*, 99, 104, 111 1 st Quiz: 9/18 (Ch.2) Nonclassical Physics *** Course
Announcements 2402 Lab will be started this week Lab manual is available on the course web page HW: Chapter.2 70, 75, 76, 87, 92, 97*, 99, 104, 111 1 st Quiz: 9/18 (Ch.2) Nonclassical Physics *** Course
Neutral Beam-Ion Prompt Loss Induced by Alfvén Eigenmodes in DIII-D
 Neutral Beam-Ion Prompt Loss Induced by Alfvén Eigenmodes in DIII-D by X. Chen,1 M.E. Austin,2 R.K. Fisher,3 W.W. Heidbrink,1 G.J. Kramer,4 R. Nazikian,4 D.C. Pace,3 C.C. Petty,3 M.A. Van Zeeland3 1University
Neutral Beam-Ion Prompt Loss Induced by Alfvén Eigenmodes in DIII-D by X. Chen,1 M.E. Austin,2 R.K. Fisher,3 W.W. Heidbrink,1 G.J. Kramer,4 R. Nazikian,4 D.C. Pace,3 C.C. Petty,3 M.A. Van Zeeland3 1University
M o n o e n e r g e t i c A c c e l e r a t i o n o f E l e c t r o n s b y L a s e r - D r i v e n P l a s m a W a v e
 USj-WS on HIF & HEDP at Utsunomiya 29 Sep,. 2005 M o n o e n e r g e t i c A c c e l e r a t i o n o f E l e c t r o n s b y L a s e r - D r i v e n P l a s m a W a v e Kazuyoshi KOYAMA, Takayuki WATANABE
USj-WS on HIF & HEDP at Utsunomiya 29 Sep,. 2005 M o n o e n e r g e t i c A c c e l e r a t i o n o f E l e c t r o n s b y L a s e r - D r i v e n P l a s m a W a v e Kazuyoshi KOYAMA, Takayuki WATANABE
X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering
 X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering What we can learn from data depend on our understanding of various X-ray emission, scattering, and absorption processes. We will discuss some basic processes:
X-ray Radiation, Absorption, and Scattering What we can learn from data depend on our understanding of various X-ray emission, scattering, and absorption processes. We will discuss some basic processes:
Magnetic Reconnection and Plasma Dynamics in Two-Beam Laser Solid Interactions
 Magnetic Reconnection and Plasma Dynamics in Two-Beam Laser Solid Interactions P. M. Nilson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
Magnetic Reconnection and Plasma Dynamics in Two-Beam Laser Solid Interactions P. M. Nilson University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 48th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society
X-Ray Spectral Measurements of Cryogenic Capsules Imploded by OMEGA
 X-Ray Spectral Measurements of Cryogenic Capsules Imploded by OMEGA 1 15 1 14 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics kt =.65 kev 48386 (v ice = 1.5 nm) 2 48385 (v ice =
X-Ray Spectral Measurements of Cryogenic Capsules Imploded by OMEGA 1 15 1 14 F. J. Marshall University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics kt =.65 kev 48386 (v ice = 1.5 nm) 2 48385 (v ice =
Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil
 Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil Matthew Allen Department of Nuclear Engineering UC Berkeley mallen@nuc.berkeley.edu March 15, 2004 8th Nuclear Energy
Ion Acceleration from the Interaction of Ultra-Intense Laser Pulse with a Thin Foil Matthew Allen Department of Nuclear Engineering UC Berkeley mallen@nuc.berkeley.edu March 15, 2004 8th Nuclear Energy
Fast Ignition Experimental and Theoretical Researches toward Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX)
 1 Fast Ignition Experimental and Theoretical Researches toward Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX) K. Mima 1), H. Azechi 1), H. Fujita 1), Y. Izawa 1), T. Jitsuno 1), T. Johzaki 1), Y. Kitagawa
1 Fast Ignition Experimental and Theoretical Researches toward Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX) K. Mima 1), H. Azechi 1), H. Fujita 1), Y. Izawa 1), T. Jitsuno 1), T. Johzaki 1), Y. Kitagawa
The MIT Accelerator for development of ICF diagnostics at OMEGA / OMEGA-EP and the NIF
 Introduction The MIT Accelerator for development of ICF diagnostics at OMEGA / OMEGA-EP and the NIF SBDs d + or 3 He +(2+) D or 3 He target Present MIT Graduate Students and the MIT Accelerator OLUG 21
Introduction The MIT Accelerator for development of ICF diagnostics at OMEGA / OMEGA-EP and the NIF SBDs d + or 3 He +(2+) D or 3 He target Present MIT Graduate Students and the MIT Accelerator OLUG 21
