RESISTANCE OF AMECRC SYSTEMATIC SERLES. HIGH SPEED DISPLACEMENT HULL FoRMs
|
|
|
- Gabriel Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IV SYMPOSIUM ON HIGH SPEED MARINE VEHICLES March 1997, Naples, Italy RESISTANCE OF AMECRC SYSTEMATIC SERLES OF HIGH SPEED DISPLACEMENT HULL FoRMs Predrag Bojovic Australian Maritime Engineering CRC Ltd. P.O. Box 986, Launceston, Tasmania 7250, Australia Sununary The high-speed displacement vessels of round-bilge, transom-stem hull form have been widely used for various naval application. Inspired by industry interest, systematic research leading to the better performance prediction of these vessels has been conducted at the Australian Maritime Engineering Cooperative Research Centre (AMECRC). This paper presents the analysis of the calm water experiments of the AMECRC systematic series of high-speed displacement monohulls. The series consists of 14 models based on the MARIN HSDHF systematic series. Speed independent regression analysis was performed and two independent sets of regression equations were derived from the same set of experimental data. The regression analysis was developed using a 'classical', multiple linear regression analysis, as well as a novel technique - nonlinear estimation. The latter presents a generalization of the former and enables any form of regression model and loss function to be explored. The nonlinear estimation approach proved to be superior. Evaluation of the developed prediction methods is presented, together with some regression equations regarding the series' geometry. A unique data presentation method, particularly useful for systematic series data is presented. It enables single-chart visualisation of multiparameter variations.
2 Resistance of AMECRC Systematic Series of High-speed Displacement Hull Forms Predrag Bojovic, Research Fellow AMECRC Ltd., P.O. Box 986, Launceston, Tasmania 7250, Australia i INTRODUCTION 1.1 Round-bilge hulls As described in Bailey (1974), semi-displacement hulls have a characteristic underwater shape distinguished by curvature between the bottom and sides, known as round bilge or soft chine. They have straight entrance waterlines, straight buttock lines and a transom stem. Their application is in the workboat, launch, frigate and corvette field. The extremes of the range are the heavy displacement, low speed workboat and the light displacement, fast patrol boat. The same author suggests that for Fn below 1.05 this type of form consistently offers a better performance in calm water than hard chine vessels. More detailed recommendation regarding this comparison could be found in Blount (1995). In recent years completely new types of high-speed vessels have been designed and built. However, in naval and many other applications, the well proven high-speed monohull vessels still dominate, as stated in Lahtiharju et al. (1991). In comment to this paper, S avitsky outlines that the maj or interest of the maritime community for round-bilge hull forms is exemplified by the impressive growth in the number of high-speed ferries, and special purpose marine vehicles which utilise these hull forms. The resistance per unit weight of these craft is significantly less than for planing hulls, and they have substantially larger useful load fractions. A comprehensive review of the related literature could be found in Lewis (1988), with some additional references listed at the end of the paper. 1.2 Systematic Series A systematic series of models is obtained when parameters of one or more parent hulls are varied in a systematic manner. Usually not more than four parameters are varied. Data of this kind provide the designer with very valuable information regarding the parameter variation influence on the vessel's performance. Systematic series data can be presented by design charts or, more commonly nowadays, in mathematical form using regression equations. Again, a comprehensive literature review is presented in Lewis (1988), with some additional references in the reference list. i
3 1.3 Regression Analysis Regression analysis has been successfully used to analyse resistance data for both random hull form data and systematic series. The reliability of random hull data analysis is based on the large database, where the database limits present the limits of the prediction method's applicability. Less randomness in database selection leads to more constrained database limits, but also increases the prediction accuracy. Using a very homogenous database, like a systematic series, very accurate predictions could be obtained, but only within the series limits. These limits are defined by the limits of the varied series' parameters, while most of the other hull parameters have a prescribed, constant value. In any case, users should avoid predictions outside the limits, as considerable inaccuracies may occur. A detailed historical review of regression analysis in resistance predictions could be found in Fung (1991) and Farlie-Clark (1975). In regression analysis of ship resistance data many different mathematical models have been used. They could be broadly categorised into the two groups: speed-independent and speed-dependent models. Fung et al. (1993) provided a detailed discussion of these two types of models with their associated strengths and weaknesses. Briefly, speed independent models do not include ship speed as an independent variable and a separate analysis has to be performed at each of the analysed speeds. In speed-dependent regression models, ship speed is explicitly included as an independent variable and the mathematical model reflects the natural variation of resistance with speed (i.e. humps and hollows). For naval engineering applications, the multiple linear regression analysis is most commonly used. It tries to identify the subset of the given set of independent variables which provides the best cause-effect explanation among the analysed data. This is a very tedious process, even using computers, and automated procedures are available. The most common ones are 'backward elimination' and 'forward selection' procedures, while more complex variations also exist. These selection procedures are based on preset selection criteria, which should be appropriately set to match the purpose of the analysis. Detailed descriptions could be found in Fung (1991) and StatSoft (1994). The multiple linear regression model is presented in Equation 1. By including some transformations of independent variables (i.e. X2=X12, X3=X13,...), the model known as 'nonlinear in variables' could be obtained. The regression equation coefficients are obtained by least squares minimisation. The statistical package used provided numerous methods for data analysis. Apart from the multiple regression approach, another suitable method was identified: nonlinear estimation. This method actually presents the generalisation of the multiple regression analysis. It enables any relationships between the dependent and independent variables to be explored, as in Equation 2, unlike linear ones as in Equation 1. It is also possible to use any form of loss function. In other words, if a linear model (Equation 1) and least square loss function are used in nonlinear estimation, the results will be the same as in the multiple regression analysis. The comparison between multiple regression analysis and nonlinear estimation is discussed further in the paper. Y=a+b1X1+b2X,+... +b.x (1) Y=F(x,x2,...,x) (2) 2
4 2 AMECRC SYSTEMATIC SERIES 2.1 Background The Australian Maritime Engineering Cooperative Research Centre (AMECRC) systematic series is based on the High Speed Displacement Hull Form systematic series (HSDHF) developed at the Maritime Research Institute Netherlands (MARIN). The HSDHF project was a major research project on combatant vessels design, jointly sponsored by the Royal Netherlands Navy, the United States Navy, the Royal Australian Navy and MARIN. It was initiated by the growing belief that a significant improvement in the performance of transom stern, round-bilge monohulls could be obtained, especially with regard to their seakeeping characteristics. The various aspects of HSDHF series development and extensive testing in calm water and waves are described in Blok, et al. (1984), Van Oossanen, et al. (1985), Koops (1985), Robson (1987), MARIN Reports (1982, 1987, 1989). Briefly, the series parent hull was selected because of its superior motion characteristics in waves, and the series was obtained by systematic variations of LIB, B/T and CB parameters over the parameter ranges described in Figure 2.1 and Table 2.1. About forty models were tested. The hull geometry and the tests results have not been published to date, except for the parent design Figure MARIN systematic series parameter space HSDHF AMECRC L/B B/T CB Table Ranges of varied parameters for MARIN and AMECRC systematic series 3
5 2.2 Series Establishment AIvIECRC is one of sixty-two Cooperative Research Centres established around Australia in the government initiative to enable closer interactions between industry and research. In one of the many industry driven projects the initiative was taken to perform research similar to the MARIN HSDHF project. Industry involvement included all major Australian naval vessel shipbuilding companies, who identified the range of parameters (parameter space) relevant to their needs, as outlined in Table 2.1. The AMECRC series parent hull is identical to HSDHF series parent hull; the body plan is presented in Figure 2.2. The systematic series parameter space is illustrated in Figure 2.3, from which the parameters of each of the models can be identified. The parameters which were kept constant throughout the series are presented in Table 2.2. Figure Parent hull of AMECRC systematic series Figure AMECRC systematic series parameter space The AMECRC series used a different CB transformation procedure than in the HSDHF series. A hull with CB = 0.55 was derived from the parent hull (CB = 0.40) and a software was developed which is capable of generating any hull with intermediate CB value. 4
6 2.3 Testing Procedure Cp AT/AX BT/BX CM CPXCB LCB 44.6% from transom Table Hull parameters common for all series' models The models were tested in the Ship Hydrodynamics Centre at the Australian Maritime College. The towing tank has length, width and depth of 60, 3.5 and 1.5 m respectively. All models were constructed with a waterline length of 1.6 m. Calm water tests were conducted at speeds from 0.4 to 4 mis, corresponding to Fn from 0.1 to 1.0. During testing, the models were free to sink and trim, and resistance, trim and rise of centre of gravity were recorded. Tests in regular head waves were conducted at Froude numbers 0.285, 0.57 and 0.856, over a frequency range Hz. Pitch, heave, vertical accelerations and added drag were recorded. 3. DATA PRESENTATION 3.1 Data Plotting Any data analysis, at some stage, involves data plotting. With the computer power now available, data plotting is more flexible and easier than ever. It is quite straight-forward when the analysed data is based on one or two independent variables. However, with more independent variables, data presentation becomes more complex, as a data must be presented as a set of charts. The number of data charts significantly increases with an increase in the number of independent variables, especially if the influence of each of independent variables is to be clearly presented. For example, in Marwood et al. (1969), the NPL series' model test data (resistancedisplacement ratio and dynamic wetted surface area) were presented as functions of three independent variables: length-displacement ratio, length-beam ratio and Froude volume number. Each presentation consisted of four plots (one plot for each of the following L/B values: 6.25, 5.41, 4.55 and 3.33). Contours of length displacement ratio (marked as circular- M on the chart) and Froude volume number were plotted on each plot, as in Figure 3.1. This way of data presentation seems to be very comprehensive. However, its deficiency is revealed as soon as the effect of L/B variation is analysed. In order to do so, it is necessary to either generate new plots which will contain LIB contours or to invest mental effort to extract this information from existing plots. For refined conclusions regarding the possible nonlinearities, the former seems to be necessary. 5
7 WETTED SURFACE COEFFICIENT L/ Figure Coefficient of dynamic wetted surface area for LIB = 4.55 (Fig. 33 from Marwood et al. 1969) In the case of the AMECRC systematic series, the effects of four independent variables (LIB, BIT, CB and nondimensional speed) were analysed. Trying to cover every aspect of their variation would result in an impractical number of charts. Therefore, a way was sought to reduce the number of charts, while preserving the amount of information. The outcome of this search is presented in next chapter. When presenting systematic series data, it should be noted that number of models is small (less than 50, often less then 20). The variation of a single series parameter is usually represented by not more than three models. Trying to clearly present the influence of every parameter may result in too many plots with not much data on each. This data fragmentation may result in failure to extract all of the available information. 3.2 Multiparameter Data Presentation Looking at Figure 3.1, it is interesting to note that this plot does not have any particular parameter on its X-axis. Imagine that the ranges of circular-m and Fnv are represented by a rectangle in the horizontal plane. Corresponding dynamic WSA values would then present a surface above this rectangle. If both the rectangle and the surface are rotated around the vertical axis and projected onto the vertical plane, the outcome would be the plot as in Figure 3.1. Tn this way, the dependent variable, dynamic WSA, is plotted against the function based on both independent variables and the angle of the mentioned rotation. In general, this idea could be expanded further in order to obtain a function, not of two, but of three or even more independent variables, against which the values of the analysed dependent variable could be plotted. Figure 3.2 illustrates how to obtain such a function for three independent variables. The idea is to produce a plot, one for each different Fnv value, which will present the influence of each of the series parameters, LIB, B/T and CB, on the dependent variable, for example RR/W. 6
8 Figure Creation of four-dimensional RR/W (LIB, BIT, CB) plot for particular Fnv The cube on top of Figure 3.2 presents the series parameter space and is free to rotate around any of its axes. Different line types, used for its edges, represent variation of different independent parameters. The cube is first projected onto the 'horizontal' plane. This projection is then projected onto the horizontal axis of the intended plot. In this way, a function of L'B, BIT' and CB (and the angles of rotations) is obtained, against which the RR/W values are plotted. When the RR/W values are connected by line types corresponding to the ones used in the parameter cube, the influence of the parameters' variation is clearly illustrated and a plot as in Figure 3.3 is obtained. 07 BIT X MoieI 412.5/0.396 Figure RRIW plot for Fnv =
9 It is suggested to mark one of the models on the plot, the parent hull or the model with the lowest/highest values of all independent parameters, in order to enable easy determination of the direction of parameter changes. For example, in Figure 3.3 the model with the lowest parameters (L/B = 4, BIT =2.5, CB=O.395) is marked and each line that starts from it represents an increase of that parameter. Therefore, it could be seen from this Figure that, at this particular Fn, the increase of JIB, B/T and CB results in respective decrease, decrease and increase of RR/W. Also, it could be seen that the effect of changes in B/T and CB is less pronounced for higher L/B values. Presentation of data in this way resulted in a significantly reduced number of charts, equal to the number of different Fn being analysed, while arguably more compact and complete data visualisation was obtained. In the analysis of the AlvIECRC series' data, the multiparameter charts lead to better understanding of the influences and interactions of the analysed parameters. Initially it was expected that these charts could be used as an ultimate performance prediction tool. This would be possible for linear effect of independent parameter changes. The consequent data regression analysis revealed nonlinear effects which could not be accurately predicted from the chart. For example, Figure 3.4 presents the regression model, described in Chapter 4, fitted to the data from Figure 3.3. However, the multiparameter charts provided comprehensive data visualisation which supported decision making in various stages of the regression analysis. Figure Regression model for RR/W at Fn = 1.05 The multiparameter chart is used in Figure 4.6 to present the influence of the series' parameters on the wetted surface area, as well as the comparison between the regression equation and actual values. 8
10 4. REGRESSION ANALYSIS 4.1 Development A speed independent regression model was used in the analysis of the AMECRC series calm water resistance data. This means that a separate data analysis was performed at each of the nondimensional speeds. In the literature, speed-independent regression models are either of CR-Fn or RR/W- Fnv form. The relationship between these formats is presented by Equations 3 and 4. CR RR RR V213 -.p.s.v2 = W +.S.Fî4 Fn- Fn Although a clear correlation between nondimensional parameters exists, the combinations of these parameters are completely independent. This means that the performance of any model at any speed will be linked to two independent data sets, on the basis of the nondimensional speeds. The consequent analyses will lead to independent conclusions. The importance of this approach is in the fact that more than one set of independent conclusions could be derived from the same set of data. The initial data analysis used as independent variables L'B, B/T, CB, L.JT and VV"3, and their square and reciprocal values. It should be noted that the length-volume ratio, known to be the best performance descriptor for this type of vessel, is a function of LIB, B/T and CB: L VI'3 = (L2 B C8 T The encouraging outcome of this analysis had the following form: R/Weight=b +b,l/v"3+b3 L/V"3 i This form of regression equation agreed well with the literature. But, still this form was suggesting that the performance of the analysed vessels is proportional both to VV"3 and to its reciprocal value. That left the feeling that more specific conclusions could be extracted from the analysed data. It was decided to conduct more aggressive data analysis, as it was believed that the regression model from Equation 6 actually was suggesting that the best predictor has the following form: 9
11 (L"tm' 1Bm J The final set of independent variables consisted of 86 variables of the form presented in Equation 7, where: _O in1 _, _O in, m3 = These variables were used in the 'classical' approach, using multiple regression analysis (MRA). At the same time, two additional mathematical models were developed using nonlinear estimation technique. They attempted to fit the following mathematical model to the analysed data: b1+b2.) "L"' (B'\" ;J 6 3 B (7) 3 3 (8) by minimising two different loss functions, described in Equations 10 and 11. Equation 10 presents the least squares function which is also 'built into' the multiple regression analysis model. Minimising of this function minimises absolute prediction errors, but results in larger relative errors for the models with lower values of resistance coefficients. Therefore the loss function, which minimises the relative prediction error, as in Equation 11, was used. These two models are marked as NLE 1 and NLE2 in Figures 4.1 and 4.2. (observed - predicted)2 (10) (observed - predicted "j2 L observed ) Z 9g B-NLEI N LE Z I) Figure CR-Fn predictions - relative R2 10
12 J S k -OMRA fo-- NLS1 O NLE2 g Fnv 2.5 Figure RR/W- Fny predictions- relative R2 The comparison of six developed mathematical models was performed on the basis of R2 value based on the relative prediction differences and is presented in Figures 4.1 and 4.2. Based on this, it was concluded that the nonlinear estimation model, with the loss function based on the relative errors, provides the best estimation. Also, it could be seen that both formats (CR-Fn and RRIW- Fnv) demonstrate a similar level of accuracy. 4.2 Evaluation The best way to evaluate a regression equation is to use it to predict the performance of a model not used in its development. The two most accurate regression equations, as identified above, were regenerated without model #13 data. This model has parameters in the middle of the series' parameter space, Figure 2.3. The newly obtained performance prediction equations were then compared with the test results of the model #13. The comparison is presented in Figures 4.3 and 4.4. They have demonstrated the accuracy of about ±2% for prediction of residuary resistance, which implies higher accuracy for the total resistance prediction. The regression equations generated with and without model #13 were compared to explore the sensitivity of the mathematical models to the database selection. The differences were within 1.5%. o CRirtflOSlS O CR(RRMhIspS&.fO CR RPM PRE) Figure Predictions of model #13 performance - GR-Fn plot li
13 o o. J! R0N (CR.ln«d( o RWWflO.00rd RR4(nLECR) Nil RR'N Fn, Figure Predictions of model #13 performance - RR/W- Ffl plot 4.3 Software implementation Two sets of regression equations were developed, as described above. The CR-Fn set covers a range of Fn from 0.3 to 1.0, and RR/W- Fn a range of Ffl from 0.6 to They were implemented as an easy-to-use spreadsheet application. In order to obtain maximum benefits from the model test data, a prediction correction was implemented in the software application. It is based on the difference between performance prediction and the test results for the series' model with the closest lengthvolume ratio. 4.4 Discussion of Results As mentioned in previous chapters, the length-volume ratio is the best descriptor of the performance of round-bilge monohulls. That was confirmed by the mathematical model obtained from the initial regression analysis, presented in Equation 6. In that mathematical model the influence of series parameters on the calm water resistance was actually described by their influence on the length-volume ratio, as per Equation 5. Further data analysis showed that even more subtle effects of series' parameters on vessel's performance could be identified. This enabled the evaluation of the series' parameters influence even for the vessels with the same value of length-volume ratio. This is illustrated in Figure 4.5, for Fri = 1.65, where test result are plotted together with the lines which describe the performance along the edges of the systematic series' cube. Actually, with a lot of imagination, a severely distorted series' 'cube' could be seen in this Figure. 4.5 Regression Analysis of Wetted Surface Area The regression equations described in previous chapters deal with calm water performance from the point of view of predicting the model's residuary resistance. In order to predict the total resistance it is necessary to obtain an estimate of frictional resistance. It is 12
14 LI V' Figure AMECRC series performance at Fn = 1.65 calculated using the following formula: (12) where CF is calculated according to the ITTC 1957 formula, described by Lewis (1988). It is obvious that an accurate estimation of the wetted surface area is needed in order to evaluate this formula. Dynamic wetted surface area was not recorded during the tests, but regression analysis of the wetted surface area at rest was performed. In order to increase the prediction accuracy, additional models were computer generated, so that the hull database for this analysis consisted of 27 models. The analysis was performed using both the multiple regression analysis and nonlinear estimation approaches. The equations developed for Cs = S / V2'3 are presented in Equations 13 and 14. The respective values for MRA and NLE methods are respectively and , resulting in prediction accuracy of ±0.4% for the NLE method. The influence of the series' basic parameters on the wetted surface area coefficient could be seen in Figure 4.6. In general, the increase of LIB, B/T and C8 leads to respective increase, increase and decrease of Cs. C = V L/B2'3 C2' BIT. CB LIB2'3 BIT CB' L/B3. C BIT"3. C13113 (13) Cs = L/B B/T''7' CB C«'23- L/B03812 (14) 13
15 Figure NLE prediction of Cs - prediction vs actual values Equations 15 and 16 present two very useful formulas in the initial stages of design. They describe the position of the vertical centre of buoyancy and the metacentric radius. For a known vertical position of the centre of gravity, these equations enable an estimate of the initial metacentric height. KB/T=O O CB (15) BM.CBT/B2=O (16) 5 CONCLUDING REMARKS This paper describes the work done so far in the area of the calm water resistance of the AMECRC systematic series of round-bilge monohulls. Based on the same set of test values, two independent sets of regression equations were developed, in CR-Ffl and RR/W- Fn formats. Each set was generated using two different regression techniques - 'classical', multiple regression analysis and a novel, nonlinear estimation method. The later proved to be superior. Also, a data presentation method is presented which enables single chart visualisation of multiparameter changes. This method is particularly useful for presentation of systematic series data. 14
16 6 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The author wishes to acknowledge the support of the Australian shipbuilding industry which this project has had over the years. Many enthusiastic people from the AMECRC industry participants were actively involved in the model testing. Their work is much appreciated, as well as the work of the towing tank staff. Special acknowledgments go to Messrs. Michael Rikard-Bell and Garry Goetz for their early work in the AMECRC systematic series establishment. 7 NOTATION A1/Ax Ratio of area at transom and maximal sectional area B Beam on waterline BM Metacentric radius BTIBX Ratio of beam at transom and maximal beam CB Block coefficient CF Coefficient of frictional resistance (ITTC 1957) CM Midship section coefficient C Prismatic coefficient CR Coefficient of residuary resistance Cs Wetted surface area coefficient Waterplane area coefficient Fn Froude number based on length Fn Froude number based on volume L Waterline length LCB Longitudinal centre of buoyancy S Wetted surface area RR Residuary resistance T Draft W Model weight WSA Wetted surface area V Model volume 8 REFERENCES Bailey, D., 1976, The NPL High Speed Round Bilge Displacement Hull Series, RINA, Maritime Technology Monograph No.4 Blok, J.J., Beukelman, W., 1984, The High-Speed Displacement Ship Systematic Series Hull Forms - Seakeeping Characteristics, Transactions SNAME, Vol. 92 Blount D.L., 1995, 'Factors Influencing the Selection of a Hard Chine or Round-Bilge Hull for High Froude Numbers', Proceedings Third International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation (FAST '95), Schiffbautechnische Gesellschaft, Vol. 1 15
17 Fairlie-Clarke, A.C., 1975, 'Regression Analysis of Ship Data', International Shipbuilding Progress, Vol.22. Fung, S.c., 1991, Resistance and Powering Prediction for Transom Stern Hull Forms During Early Stage Ship Design, Transactions SNAME, Vol. 99 Fung, S. C., Leibman, L., 1993, Statistically-Based Speed-Dependent Powering Predictions For High-Speed Transom Stern Hull Forms, NAVSEA 05 l-05h3-tn-0 100, March Koops, A., 1985, Hull Form Definition And Computer Aided Design, Computer Applications in the Automation of Shipyard Operaion and Ship Design V, Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. Kracht, A.M., 1992, D-Series Systematic Experiments With Models of Fast Twin-Screw Displacement Ships, Transactions SNAME, Vol. 100 Lahtiharju, E., Karppinen, T., Hellevaara, M., Aitta, T., 1991, Resistance And Seakeeping Characteristics Of Fast Transom Stern Hulls With Systematically Varied Form, Transactions SNAME, Vol.99 Lewis, E.V., 1988, Principles of Naval Architecture, SNAIvIE, Vol. II Lin, W-C, Day, W-G, Koh, I-Y, 1987, Statistical Prediction of Ship's Effective Power Using Theoretical Formulation and Historic Data, Marine Technology, Vol. 24, July MARIN Internal Report No. 11, 1982, High Speed Huliforms, July MARIN Internal Report No. 30, 1987, MARIN High Speed Displacement Hull Form Designs, December MARIN Report No. 35, 1989, High Speed Hull Form series project in final stage, February Marwood, W.J., Bailey, D., 1969, Design Data for High -Speed Displacement Hulls of Round Bilge Form, National Physical Laboratory, Ship Division, Report 99 Robson, B.L., 1987, Systematic Series of High Speed Displacement Hull Forms for Naval Combatants, Transactions RINA, Vol. 130 StatSoftTM, 1994, STATISTICA for Windows, (software manuals), Vol. II and III Van Oossanen, P., Pieffers, J.B.M., 1985, NSMB - Systematic Series of High Speed Displacement Forms, Workshop on Developments in Hull Form Design, Wageningen 16
THIRD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT FOR MARINE APPLICATIONS. 5-8 May 1997, Newport, Rhode Island, USA
 THIRD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT FOR MARINE APPLICATIONS 5-8 May 997, Newport, Rhode Island, USA REGRESSION ANALYSIS OF SYSTEMATIC SERIES CALM WATER PERFORMANCE Predrag Bojovic
THIRD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT FOR MARINE APPLICATIONS 5-8 May 997, Newport, Rhode Island, USA REGRESSION ANALYSIS OF SYSTEMATIC SERIES CALM WATER PERFORMANCE Predrag Bojovic
Wave Resistance Prediction of Hard-Chine Catamarans through. Regression Analysis
 Wave Resistance Prediction of Hard-Chine Catamarans through Xuan P. Pham Research Student Dept. of Naval Architecture & Ocean Engineering Australian Maritime College PO Box 986, Launceston, TAS 7250, Australia.
Wave Resistance Prediction of Hard-Chine Catamarans through Xuan P. Pham Research Student Dept. of Naval Architecture & Ocean Engineering Australian Maritime College PO Box 986, Launceston, TAS 7250, Australia.
Welcome to the Ship Resistance Predictor! The total calm water resistance is given by:
 Welcome to the Ship Resistance Predictor! What does this Excel Sheet do? This Excel sheet helps you calculate the Total Calm Water Resistance for a Ship at a given forward speed It also calculates from
Welcome to the Ship Resistance Predictor! What does this Excel Sheet do? This Excel sheet helps you calculate the Total Calm Water Resistance for a Ship at a given forward speed It also calculates from
Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Influence of the Transom-Hollow Length on Wave Resistance
 Summary Influence of the Transom-Hollow Length on Wave Resistance Lawrence J. Doctors The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia Email: L.Doctors@UNSW.edu.au Previous experimental data
Summary Influence of the Transom-Hollow Length on Wave Resistance Lawrence J. Doctors The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia Email: L.Doctors@UNSW.edu.au Previous experimental data
Estimating Maneuvering and Seakeeping Characteristics with Neural Networks
 070131-071 1 Estimating Maneuvering and Seakeeping Characteristics with Neural Networks Paulo Triunfante Martins 1, Victor Lobo 2, Member, IEEE Maneuvering and seakeeping are two very important naval architecture
070131-071 1 Estimating Maneuvering and Seakeeping Characteristics with Neural Networks Paulo Triunfante Martins 1, Victor Lobo 2, Member, IEEE Maneuvering and seakeeping are two very important naval architecture
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM
 DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
Ship Resistance And Propulsion Prof. Dr. P. Krishnankutty Ocean Department Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Ship Resistance And Propulsion Prof. Dr. P. Krishnankutty Ocean Department Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 14 Ship Resistance Prediction Methods II We have been discussing about resistance
Ship Resistance And Propulsion Prof. Dr. P. Krishnankutty Ocean Department Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 14 Ship Resistance Prediction Methods II We have been discussing about resistance
A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew Dominic J. Taunton Dominic A.
 A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew, Dominic J. Taunton, Dominic A. Hudson Fluid Structure Interactions Group, University of Southampton ss17e111@soton.ac.uk
A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew, Dominic J. Taunton, Dominic A. Hudson Fluid Structure Interactions Group, University of Southampton ss17e111@soton.ac.uk
Motions and Resistance of a Ship in Regular Following Waves
 Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
Resistance Prediction for Hard Chine Hulls in the Pre-Planing Regime
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(82) 2014 Vol 21; pp. 9-26 10.2478/pomr-2014-0014 Resistance Prediction for Hard Chine Hulls in the Pre-Planing Regime Dejan Radojcic 1), Ph. D., Antonio Zgradic 2), M. Sc., Milan
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(82) 2014 Vol 21; pp. 9-26 10.2478/pomr-2014-0014 Resistance Prediction for Hard Chine Hulls in the Pre-Planing Regime Dejan Radojcic 1), Ph. D., Antonio Zgradic 2), M. Sc., Milan
Formation Design Systems' Maxsurf Stability Tank Table Generator: Verification and Validation Study
 Formation Design Systems' Maxsurf Stability Tank Table Generator: Verification and Validation Study Edward Dawson Maritime Division Defence Science and Technology Organisation DSTO-TR-2968 ABSTRACT A verification
Formation Design Systems' Maxsurf Stability Tank Table Generator: Verification and Validation Study Edward Dawson Maritime Division Defence Science and Technology Organisation DSTO-TR-2968 ABSTRACT A verification
Aalto University School of Engineering
 Aalto University School of Engineering Kul-24.4140 Ship Dynamics (P) Lecture 9 Loads Where is this lecture on the course? Design Framework Lecture 5: Equations of Motion Environment Lecture 6: Strip Theory
Aalto University School of Engineering Kul-24.4140 Ship Dynamics (P) Lecture 9 Loads Where is this lecture on the course? Design Framework Lecture 5: Equations of Motion Environment Lecture 6: Strip Theory
Research and application of 2-D water entry simulation (constant velocity)
 Research and application of 2-D water entry simulation (constant velocity) College of Shipbuilding and Engineering Harbin Engineering University ------------- Zhu Xin Supervisor: Prof. Duan Wen-yang 1
Research and application of 2-D water entry simulation (constant velocity) College of Shipbuilding and Engineering Harbin Engineering University ------------- Zhu Xin Supervisor: Prof. Duan Wen-yang 1
ITTC Recommended Procedures Testing and Extrapolation Methods Resistance Resistance Test
 -0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
-0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
Hull loads and response, hydroelasticity
 Transactions on the Built Environment vol 1, 1993 WIT Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 1743-3509 Hull loads and response, hydroelasticity effects on fast monohulls E. Jullumstr0 & J.V. Aarsnes Division of
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 1, 1993 WIT Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 1743-3509 Hull loads and response, hydroelasticity effects on fast monohulls E. Jullumstr0 & J.V. Aarsnes Division of
Seakeeping characteristics of intact and damaged ship in the Adriatic Sea
 Towards Green Marine Technology and Transport Guedes Soares, Dejhalla & Pavleti (Eds) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02887-6 Seakeeping characteristics of intact and damaged ship in
Towards Green Marine Technology and Transport Guedes Soares, Dejhalla & Pavleti (Eds) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02887-6 Seakeeping characteristics of intact and damaged ship in
Simple Estimation of Wave Added Resistance from Experiments in Transient and Irregular Water Waves
 Simple Estimation of Wave Added Resistance from Experiments in Transient and Irregular Water Waves by Tsugukiyo Hirayama*, Member Xuefeng Wang*, Member Summary Experiments in transient water waves are
Simple Estimation of Wave Added Resistance from Experiments in Transient and Irregular Water Waves by Tsugukiyo Hirayama*, Member Xuefeng Wang*, Member Summary Experiments in transient water waves are
Effects of hull form parameters on seakeeping for YTU gulet series with cruiser stern
 csnk, 04 Int. J. Nav. rchit. Ocean Eng. (04) 6:700~74 http://dx.doi.org/0.478/ijnoe-03-006 pissn: 09-678, eissn: 09-6790 Effects of hull form parameters on seakeeping for YTU gulet series with cruiser
csnk, 04 Int. J. Nav. rchit. Ocean Eng. (04) 6:700~74 http://dx.doi.org/0.478/ijnoe-03-006 pissn: 09-678, eissn: 09-6790 Effects of hull form parameters on seakeeping for YTU gulet series with cruiser
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
 Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Teaching sessions week 40
 Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE
 N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
Requirements for Computational Methods to be sed for the IMO Second Generation Intact Stability Criteria
 Proceedings of the 1 th International Conference on the Stability of Ships and Ocean Vehicles, 14-19 June 15, Glasgow, UK Requirements for Computational Methods to be sed for the IMO Second Generation
Proceedings of the 1 th International Conference on the Stability of Ships and Ocean Vehicles, 14-19 June 15, Glasgow, UK Requirements for Computational Methods to be sed for the IMO Second Generation
RESISTANCE PREDICTION OF SEMIPLANING TRANSOM STERN HULLS
 Nenad, VARDA, University of Zagreb, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, I. Lučića 5, 10000 Zagreb Nastia, DEGIULI, University of Zagreb, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval
Nenad, VARDA, University of Zagreb, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, I. Lučića 5, 10000 Zagreb Nastia, DEGIULI, University of Zagreb, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval
Slamming and Whipping Analysis in Preliminary Structural Design
 Slamming and Whipping Analysis in Preliminary Structural Design Bruce L. Hutchison, P.E., (FSNAME, The Glosten Associates, Inc.) Justin M. Morgan, P.E., (MSNAME, The Glosten Associates, Inc.) Low-order
Slamming and Whipping Analysis in Preliminary Structural Design Bruce L. Hutchison, P.E., (FSNAME, The Glosten Associates, Inc.) Justin M. Morgan, P.E., (MSNAME, The Glosten Associates, Inc.) Low-order
Optimal Design of FPSO Vessels
 November 2, 201 Optimal Design of FPSO Vessels Ezebuchi Akandu PhD, MTech, BTech, COREN, RINA, MNSE Department of Marine Engineering, Rivers State University, Port Harcourt, Nigeria akandu.ezebuchi@ust.edu.ng
November 2, 201 Optimal Design of FPSO Vessels Ezebuchi Akandu PhD, MTech, BTech, COREN, RINA, MNSE Department of Marine Engineering, Rivers State University, Port Harcourt, Nigeria akandu.ezebuchi@ust.edu.ng
Mooring Model for Barge Tows in Lock Chamber
 Mooring Model for Barge Tows in Lock Chamber by Richard L. Stockstill BACKGROUND: Extensive research has been conducted in the area of modeling mooring systems in sea environments where the forcing function
Mooring Model for Barge Tows in Lock Chamber by Richard L. Stockstill BACKGROUND: Extensive research has been conducted in the area of modeling mooring systems in sea environments where the forcing function
VALIDATION OF A TIME DOMAIN PANEL CODE FOR PREDICTING THE SEAKEEPING BEHAVIOUR OF A RIGID HULL INFLATABLE BOAT
 F(1ST2017 N\TES-FRNCE VLIDTION OF TIME DOMIN PNEL CODE FOR PREDICTING THE SEKEEPING BEHVIOUR OF RIGID HULL INFLTBLE BOT Callan Bird - Defence Science and Teclinology Group (DST), Melbourne, ustralia Frans
F(1ST2017 N\TES-FRNCE VLIDTION OF TIME DOMIN PNEL CODE FOR PREDICTING THE SEKEEPING BEHVIOUR OF RIGID HULL INFLTBLE BOT Callan Bird - Defence Science and Teclinology Group (DST), Melbourne, ustralia Frans
INVESTIGATION OF MOTIONS OF CATAMARANS IN REGULAR WAVES II
 Pergaoion cean Engng, Vol. 24, No. 10, pp. 949-966, 1997 1997 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain 0029-8018/97 $17.00 + 0.00 PII: S0029-8018(97)00056-X INVESTIGATIN F MTINS
Pergaoion cean Engng, Vol. 24, No. 10, pp. 949-966, 1997 1997 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain 0029-8018/97 $17.00 + 0.00 PII: S0029-8018(97)00056-X INVESTIGATIN F MTINS
ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Bare Hull Resistance Prediction Based on the Delft Systematic Yacht Hull Series
 Bare Hull Resistance Prediction Based on the Delft Systematic Yacht Hull Series Copyright Ulrich Remmlinger, Germany, August 4 Abstract. A regression analysis yields a new formula for the prediction of
Bare Hull Resistance Prediction Based on the Delft Systematic Yacht Hull Series Copyright Ulrich Remmlinger, Germany, August 4 Abstract. A regression analysis yields a new formula for the prediction of
Ship Project A ASSIGNMENT ONE RAN XIAO & THEIR TOMAS
 2014 Ship Project A ASSIGNMENT ONE RAN XIAO 467643 & THEIR TOMAS 224051 Resistance estimation Methodology brief As our ship concept is in form of catamaran, it is not proper to simply introduce the method
2014 Ship Project A ASSIGNMENT ONE RAN XIAO 467643 & THEIR TOMAS 224051 Resistance estimation Methodology brief As our ship concept is in form of catamaran, it is not proper to simply introduce the method
Measurement of speed loss due to waves
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Measurement of speed loss due to waves Sverre Steen 1 and Zhenju Chuang 1 1 Department of Marine Technology,
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Measurement of speed loss due to waves Sverre Steen 1 and Zhenju Chuang 1 1 Department of Marine Technology,
Chapter IV. (Ship Hydro-Statics & Dynamics) Floatation & Stability
 Chapter V (Ship Hydro-Statics & Dynamics) Floatation & Stability 4.1 mportant Hydro-Static Curves or Relations (see Fig. 4.11 at p44 & handout) Displacement Curves (displacement [molded, total] vs. draft,
Chapter V (Ship Hydro-Statics & Dynamics) Floatation & Stability 4.1 mportant Hydro-Static Curves or Relations (see Fig. 4.11 at p44 & handout) Displacement Curves (displacement [molded, total] vs. draft,
Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos
 Session 7 Stability of Damaged Ships Numerical Simulation of Progressive Flooding and Capsize Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos Qiuxin Gao and Dracos
Session 7 Stability of Damaged Ships Numerical Simulation of Progressive Flooding and Capsize Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos Qiuxin Gao and Dracos
Powering for Medium Speed Wave-Piercing Catamarans comparing Waterjet and Screw Propeller Performance using Model Testing
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Powering for Medium Speed Wave-Piercing Catamarans comparing Waterjet and Screw Propeller Performance using Model
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Powering for Medium Speed Wave-Piercing Catamarans comparing Waterjet and Screw Propeller Performance using Model
Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods
 ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Study on Motions of a Floating Body under Composite External Loads
 137 Study on Motions of a Floating Body under Composite External Loads by Kunihiro Ikegami*, Member Masami Matsuura*, Member Summary In the field of marine engineering, various types of floating bodies
137 Study on Motions of a Floating Body under Composite External Loads by Kunihiro Ikegami*, Member Masami Matsuura*, Member Summary In the field of marine engineering, various types of floating bodies
Bare Hull Upright Resistance Prediction Based on the Delft Systematic Yacht Hull Series
 Bare Hull Upright Resistance Prediction Based on the Delft Systematic Yacht Hull Series Copyright Ulrich Remmlinger, Germany, 4, last revision September 6 Abstract. A regression analysis yields a new formula
Bare Hull Upright Resistance Prediction Based on the Delft Systematic Yacht Hull Series Copyright Ulrich Remmlinger, Germany, 4, last revision September 6 Abstract. A regression analysis yields a new formula
STABILITY AND TRIM OF MARINE VESSELS. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Subject 2.017
 STABILITY AND TRIM OF MARINE VESSELS Concept of Mass Center for a Rigid Body Centroid the point about which moments due to gravity are zero: 6 g m i (x g x i )= 0 Æ x = 6m i x i / 6m i = 6m i x i / M g
STABILITY AND TRIM OF MARINE VESSELS Concept of Mass Center for a Rigid Body Centroid the point about which moments due to gravity are zero: 6 g m i (x g x i )= 0 Æ x = 6m i x i / 6m i = 6m i x i / M g
Nonlinear Feedback Stabilization of High-Speed Planing Vessels by A Controllable Transom Flap
 2 American Control Conference June 8-1, 2. Portland, OR, USA FrB11.2 Nonlinear Feedback Stabilization of High-Speed Planing Vessels by A Controllable Transom Flap Handa Xi and Jing Sun Department of Naval
2 American Control Conference June 8-1, 2. Portland, OR, USA FrB11.2 Nonlinear Feedback Stabilization of High-Speed Planing Vessels by A Controllable Transom Flap Handa Xi and Jing Sun Department of Naval
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
Università degli studi di Napoli Federico II
 Università degli studi di Napoli Federico II SCUOLA DI DOTTORATO IN INGEGNERIA NAVALE, AEROSPAZIALE E DELLA QUALITA XXIV CICLO Experimental Study on Interceptor's Effectiveness TUTOR CANDIDATE Prof. CLAUDIO
Università degli studi di Napoli Federico II SCUOLA DI DOTTORATO IN INGEGNERIA NAVALE, AEROSPAZIALE E DELLA QUALITA XXIV CICLO Experimental Study on Interceptor's Effectiveness TUTOR CANDIDATE Prof. CLAUDIO
CFD Based Hull Hydrodynamic Forces for Simulation of Ship Manoeuvres
 International Journal on Marine avigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 3 umber 1 March 9 Based Hull Hydrodynamic Forces for Simulation of Ship Manoeuvres T. Tabaczek, T. Gornicz & J. Kulczyk
International Journal on Marine avigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 3 umber 1 March 9 Based Hull Hydrodynamic Forces for Simulation of Ship Manoeuvres T. Tabaczek, T. Gornicz & J. Kulczyk
Development of formulas allowing to predict hydrodynamic responses of inland vessels operated within the range of navigation 0.6 Hs 2.
 Gian Carlo Matheus Torres 6 th EMship cycle: October 2015 February 2017 Master Thesis Development of formulas allowing to predict hydrodynamic responses of inland vessels operated within the range of navigation
Gian Carlo Matheus Torres 6 th EMship cycle: October 2015 February 2017 Master Thesis Development of formulas allowing to predict hydrodynamic responses of inland vessels operated within the range of navigation
Computation of the wavemaking resistance of a Harley surface effect ship
 Proceedings of the Sixteenth Seventeenth (2007) (2007) International Offshore and and Polar Polar Engineering Conference Lisbon, Portugal, July 1-6, 2007 Copyright 2007 by The International Society of
Proceedings of the Sixteenth Seventeenth (2007) (2007) International Offshore and and Polar Polar Engineering Conference Lisbon, Portugal, July 1-6, 2007 Copyright 2007 by The International Society of
ROLL MOTION OF A RORO-SHIP IN IRREGULAR FOLLOWING WAVES
 38 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 9, o. 1, pp. 38-44 (2001) ROLL MOTIO OF A RORO-SHIP I IRREGULAR FOLLOWIG WAVES Jianbo Hua* and Wei-Hui Wang** Keywords: roll motion, parametric excitation,
38 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 9, o. 1, pp. 38-44 (2001) ROLL MOTIO OF A RORO-SHIP I IRREGULAR FOLLOWIG WAVES Jianbo Hua* and Wei-Hui Wang** Keywords: roll motion, parametric excitation,
Experimental studies of springing and whipping of container vessels
 Experimental studies of springing and whipping of container vessels Ole Andreas Hermundstad CeSOS Highlights and AMOS Visions Conference 27-29th May 2013 in Trondheim Outline Background and motivation
Experimental studies of springing and whipping of container vessels Ole Andreas Hermundstad CeSOS Highlights and AMOS Visions Conference 27-29th May 2013 in Trondheim Outline Background and motivation
THE LEVEL OF CONFIDENCE FOR A SHIP HULL GIRDER
 94 Paper present at International Conference on Diagnosis and Prediction in Mechanical Engineering Systems (DIPRE 07) 26-27 October 2007, Galati, Romania THE LEVEL OF CONFIDENCE FOR A SHIP HULL GIRDER
94 Paper present at International Conference on Diagnosis and Prediction in Mechanical Engineering Systems (DIPRE 07) 26-27 October 2007, Galati, Romania THE LEVEL OF CONFIDENCE FOR A SHIP HULL GIRDER
EFFECT OF HULL FORM COEFFICIENTS ON THE VESSEL SEA-KEEPING PERFORMANCE
 594 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 21, No. 5, pp. 594-604 (2013) DOI: 1119/JMST-013-0117-2 EFFECT OF HULL FORM COEFFICIENTS ON THE VESSEL SEA-KEEPING PERFORMANCE Mohsen Khosravi Babadi
594 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 21, No. 5, pp. 594-604 (2013) DOI: 1119/JMST-013-0117-2 EFFECT OF HULL FORM COEFFICIENTS ON THE VESSEL SEA-KEEPING PERFORMANCE Mohsen Khosravi Babadi
INVESTIGATION OF TRIMARAN INTERFERENCE EFFECTS. Brendan Carr Robert Dvorak
 INVESTIGATION OF TRIMARAN INTERFERENCE EFFECTS by Brendan Carr Robert Dvorak A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Bachelor of Science Degree in Naval Architecture and Marine
INVESTIGATION OF TRIMARAN INTERFERENCE EFFECTS by Brendan Carr Robert Dvorak A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Bachelor of Science Degree in Naval Architecture and Marine
Mt Introduction. 2. Governing gphysics. 3. Decomposition of resistance. 4. Similarity laws and scaling
 1. Introduction 2. Governing gphysics 3. Decomposition of resistance 4. Similarity laws and scaling Mt 527 Importance of proper power-speed prediction Resistance, prop. efficiency, power Wake field Experimental,
1. Introduction 2. Governing gphysics 3. Decomposition of resistance 4. Similarity laws and scaling Mt 527 Importance of proper power-speed prediction Resistance, prop. efficiency, power Wake field Experimental,
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method
 Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
1 POTENTIAL FLOW THEORY Formulation of the seakeeping problem
 1 POTENTIAL FLOW THEORY Formulation of the seakeeping problem Objective of the Chapter: Formulation of the potential flow around the hull of a ship advancing and oscillationg in waves Results of the Chapter:
1 POTENTIAL FLOW THEORY Formulation of the seakeeping problem Objective of the Chapter: Formulation of the potential flow around the hull of a ship advancing and oscillationg in waves Results of the Chapter:
AN APPROXIMATE POWER PREDICTION METHOD. J. Holtrop* and G.G.J. Mennen* R TR. can be used.
 166 AN APPROXIMATE POWER PREDICTION METHOD by J. Holtrop* and G.G.J. Mennen* 1. Introduction In a recent publication [ 1 ] a statistical method was presented f the determination of the required propulsive
166 AN APPROXIMATE POWER PREDICTION METHOD by J. Holtrop* and G.G.J. Mennen* 1. Introduction In a recent publication [ 1 ] a statistical method was presented f the determination of the required propulsive
On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
 International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 1 March 28 On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 1 March 28 On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on Pump Performance
 11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
Study of the hydrodynamic flow around a 70m sailing boat for powering, wave pattern and propeller efficiency prediction
 Study of the hydrodynamic flow around a 70m sailing boat for powering, wave pattern and propeller efficiency prediction Romain Baudson Supervisor: Prof. Dario Boote (UNIGE) External Reviewer: Prof. Pierre
Study of the hydrodynamic flow around a 70m sailing boat for powering, wave pattern and propeller efficiency prediction Romain Baudson Supervisor: Prof. Dario Boote (UNIGE) External Reviewer: Prof. Pierre
FRICTION IN SHIP RESISTANCE - A DIFFERENT APPROACH
 5th WSEAS International Conference on FLUID MECHANICS (FLUIDS'08) Acapulco, Mexico, January 5-7, 008 FRICTION IN SHIP RESISTANCE - A DIFFERENT APPROACH EBERHARD WOLFF Departamento de Metal Mecanica Instituto
5th WSEAS International Conference on FLUID MECHANICS (FLUIDS'08) Acapulco, Mexico, January 5-7, 008 FRICTION IN SHIP RESISTANCE - A DIFFERENT APPROACH EBERHARD WOLFF Departamento de Metal Mecanica Instituto
DEVELOPMENT OF A SQUAT FORMULA BASED ON NUMERICAL CALCULATIONS
 4th MASHCON, Hamburg - Uliczka et al. (eds) - 6 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-9393-38- (Online) DOI:.845/978-3-9393-38-_3 DEVELOPMENT OF A SQUAT FORMULA BASED ON NUMERICAL CALCULATIONS A Gronarz,
4th MASHCON, Hamburg - Uliczka et al. (eds) - 6 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-9393-38- (Online) DOI:.845/978-3-9393-38-_3 DEVELOPMENT OF A SQUAT FORMULA BASED ON NUMERICAL CALCULATIONS A Gronarz,
SPECIAL CONDITION. Water Load Conditions. SPECIAL CONDITION Water Load Conditions
 Doc. No. : SC-CVLA.051-01 Issue : 1d Date : 04-Aug-009 Page : 1 of 13 SUBJECT : CERTIFICATION SPECIFICATION : VLA.51 PRIMARY GROUP / PANEL : 03 (Structure) SECONDARY GROUPE / PANEL : -- NATURE : SCN VLA.51
Doc. No. : SC-CVLA.051-01 Issue : 1d Date : 04-Aug-009 Page : 1 of 13 SUBJECT : CERTIFICATION SPECIFICATION : VLA.51 PRIMARY GROUP / PANEL : 03 (Structure) SECONDARY GROUPE / PANEL : -- NATURE : SCN VLA.51
StAt 5,- - IHR COPY -'~~- 4 II. by- ' i, S ' -.
 StAt 5,- - MQW-a½ S. CIF 4 II I IHR COPY -'~~- by- X A ' i, S ' -. MODEL TEST RESULTS AND PREDICTED EHP FOR AN 86-FOOT PERSONNEL BOAT, FROM TESTS OF MODEL 4675 by Eugene P. Clement and Charles W. Tate,
StAt 5,- - MQW-a½ S. CIF 4 II I IHR COPY -'~~- by- X A ' i, S ' -. MODEL TEST RESULTS AND PREDICTED EHP FOR AN 86-FOOT PERSONNEL BOAT, FROM TESTS OF MODEL 4675 by Eugene P. Clement and Charles W. Tate,
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
NOVEL USES OF CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEMS FOR STRUCTURE CONDITION ASSESSMENT. James A. Ellor Elzly Technology Corporation Reston, VA
 NOVEL USES OF CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEMS FOR STRUCTURE CONDITION ASSESSMENT James A. Ellor Elzly Technology Corporation Reston, VA jellor@elzly.com And Andrew D. Seelinger Naval Sea Systems Command Washington,
NOVEL USES OF CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEMS FOR STRUCTURE CONDITION ASSESSMENT James A. Ellor Elzly Technology Corporation Reston, VA jellor@elzly.com And Andrew D. Seelinger Naval Sea Systems Command Washington,
On the evaluation quadratic forces on stationary bodies
 On the evaluation quadratic forces on stationary bodies Chang-Ho Lee AMIT Inc., Chestnut Hill MA, USA June 9, 006 Abstract. Conservation of momentum is applied to finite fluid volume surrounding a body
On the evaluation quadratic forces on stationary bodies Chang-Ho Lee AMIT Inc., Chestnut Hill MA, USA June 9, 006 Abstract. Conservation of momentum is applied to finite fluid volume surrounding a body
SIMPLIFICATION BY MATHEMATIC MODEL TO SOLVE THE EXPERIMENTAL OF SLOSHING EFFECT ON THE FPSO VESSEL
 European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 3 No. 5 June, 2014 SIMPLIFICATION BY MATHEMATIC MODEL TO SOLVE THE EXPERIMENTAL OF SLOSHING EFFECT ON THE FPSO VESSEL LuhutTumpalParulianSinaga
European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 3 No. 5 June, 2014 SIMPLIFICATION BY MATHEMATIC MODEL TO SOLVE THE EXPERIMENTAL OF SLOSHING EFFECT ON THE FPSO VESSEL LuhutTumpalParulianSinaga
Safetrans Safe design and operation of marine transports
 Safetrans Safe design and operation of marine transports CONTENTS General Voyage Motion Climate Monte Carlo Simulations Calculation of Ship Motions Weather Databases User Group References 2 SAFETRANS Safetrans
Safetrans Safe design and operation of marine transports CONTENTS General Voyage Motion Climate Monte Carlo Simulations Calculation of Ship Motions Weather Databases User Group References 2 SAFETRANS Safetrans
Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering Graduate Study Specialization in Ocean Engineering. Written Preliminary Examination Information
 Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering Graduate Study Specialization in Ocean Engineering Written Preliminary Examination Information Faculty: Professors W. Neu, O. Hughes, A. Brown, M. Allen Test
Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering Graduate Study Specialization in Ocean Engineering Written Preliminary Examination Information Faculty: Professors W. Neu, O. Hughes, A. Brown, M. Allen Test
Analysis of the resistance due to waves in ships
 Analysis of the resistance due to waves in ships Treball Final de Grau Facultat de Nàutica de Barcelona Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Treball realitzat per: Rafael Pacheco Blàzquez Dirigit per:
Analysis of the resistance due to waves in ships Treball Final de Grau Facultat de Nàutica de Barcelona Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Treball realitzat per: Rafael Pacheco Blàzquez Dirigit per:
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results
 Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
A method of calculation of ship resistance on calm water useful at preliminary stages of ship design
 Scientific Journals Maritime University of Szczecin Zeszyty Naukowe Akademia Morska w Szczecinie 14, 38(11) pp. 15 13 14, 38(11) s. 15 13 ISSN 1733-867 A method of calculation of ship resistance on calm
Scientific Journals Maritime University of Szczecin Zeszyty Naukowe Akademia Morska w Szczecinie 14, 38(11) pp. 15 13 14, 38(11) s. 15 13 ISSN 1733-867 A method of calculation of ship resistance on calm
A Quadratic, Time-Domain Strip Theory Method for Predicting Global Ship Structure Response in Waves
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Senior Honors Theses Undergraduate Showcase 5-217 A Quadratic, Time-Domain Strip Theory Method for Predicting Global Ship Structure Response in Waves Kyle Elias
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Senior Honors Theses Undergraduate Showcase 5-217 A Quadratic, Time-Domain Strip Theory Method for Predicting Global Ship Structure Response in Waves Kyle Elias
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Wave Resistance Prediction of a Cataaran by Linearised Theory M.INSEL Faculty of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Istanbul Technical University, TURKEY A.F.MOLLAND, J.F.WELLICOME Departent of
Wave Resistance Prediction of a Cataaran by Linearised Theory M.INSEL Faculty of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Istanbul Technical University, TURKEY A.F.MOLLAND, J.F.WELLICOME Departent of
Master Thesis. Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations
 Master Thesis Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations Author: Erik Rotteveel Supervisor: Frans Quadvlieg Graduation report
Master Thesis Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations Author: Erik Rotteveel Supervisor: Frans Quadvlieg Graduation report
COLD REGIONS SCIENCE AND MARINE TECHNOLOGY Vol II - Ice Breaking And Ship Modelling - Karl-Heinz Rupp
 ICE BREAKING AND SHIP MODELLING Karl-Heinz Rupp Hamburg, Germany Keywords: Ice breaking, Hull shape, Ice thickness, Friction, Resistance astern, Stability control, Ice floes, ice cake, brash ice, Rafted
ICE BREAKING AND SHIP MODELLING Karl-Heinz Rupp Hamburg, Germany Keywords: Ice breaking, Hull shape, Ice thickness, Friction, Resistance astern, Stability control, Ice floes, ice cake, brash ice, Rafted
Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further.
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further. Gerasimos Politis 1,Theodoros Ioannou
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further. Gerasimos Politis 1,Theodoros Ioannou
WATERJET PROPULSION SYSEM FOR HIGH SPEED CRAFTS
 ARAB ACADEMY FOR SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND MARITIME TRANSPORT COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY WATERJET PROPULSION SYSEM FOR HIGH SPEED CRAFTS Thesis Submitted to The Marine Engineering Department In
ARAB ACADEMY FOR SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND MARITIME TRANSPORT COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY WATERJET PROPULSION SYSEM FOR HIGH SPEED CRAFTS Thesis Submitted to The Marine Engineering Department In
Ship Hydrodynamics, Ship Propeller Acoustics and Cavitation.
 Ship Hydrodynamics, Ship Propeller Acoustics and Cavitation. Dr.l.noordzij@leennoordzij.nl www.leennoordzij.me Content Introduction.... 1 The Cavitation Tunnel.... 2 The Depressurized Towing Tank... 4
Ship Hydrodynamics, Ship Propeller Acoustics and Cavitation. Dr.l.noordzij@leennoordzij.nl www.leennoordzij.me Content Introduction.... 1 The Cavitation Tunnel.... 2 The Depressurized Towing Tank... 4
Simplified formulas of heave added mass coefficients at high frequency for various two-dimensional bodies in a finite water depth
 csnak, 2015 Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. (2015) 7:115~127 http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/ijnaoe-2015-0009 pissn: 2092-6782, eissn: 2092-6790 Simplified formulas of heave added mass coefficients at high frequency
csnak, 2015 Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. (2015) 7:115~127 http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/ijnaoe-2015-0009 pissn: 2092-6782, eissn: 2092-6790 Simplified formulas of heave added mass coefficients at high frequency
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic. FEMAP & NX Nastran
 Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
ITTC Circular Letter
 ITTC Circular Letter May, 2016 Load variation tests The speed/power sea trials procedures, ITTC Recommended rocedures 7.5-04-01-01.1 and -01.2, and IO15016:2015 require that load variation tests are performed
ITTC Circular Letter May, 2016 Load variation tests The speed/power sea trials procedures, ITTC Recommended rocedures 7.5-04-01-01.1 and -01.2, and IO15016:2015 require that load variation tests are performed
AN EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY OF A HIGH SPEED PLANING CRAFT WITH FULL-SCALE VALIDATION
 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 26, No. 5, pp. 617-628 (2018) 617 DOI: 10.6119/JMST.201810_26(5).0001 AN EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY OF A HIGH SPEED PLANING CRAFT WITH FULL-SCALE VALIDATION
Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 26, No. 5, pp. 617-628 (2018) 617 DOI: 10.6119/JMST.201810_26(5).0001 AN EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY OF A HIGH SPEED PLANING CRAFT WITH FULL-SCALE VALIDATION
Final Exam TTK4190 Guidance and Control
 Trondheim Department of engineering Cybernetics Contact person: Professor Thor I. Fossen Phone: 73 59 43 61 Cell: 91 89 73 61 Email: tif@itk.ntnu.no Final Exam TTK4190 Guidance and Control Friday May 15,
Trondheim Department of engineering Cybernetics Contact person: Professor Thor I. Fossen Phone: 73 59 43 61 Cell: 91 89 73 61 Email: tif@itk.ntnu.no Final Exam TTK4190 Guidance and Control Friday May 15,
Proceedings of the ASME th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France
 Proceedings of the ASME 2011 32th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France OMAE2013-10124 APPLYING STRIP THEORY BASED LINEAR SEAKEEPING
Proceedings of the ASME 2011 32th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France OMAE2013-10124 APPLYING STRIP THEORY BASED LINEAR SEAKEEPING
Slope stability software for soft soil engineering. D-Geo Stability. Verification Report
 Slope stability software for soft soil engineering D-Geo Stability Verification Report D-GEO STABILITY Slope stability software for soft soil engineering Verification Report Version: 16.2 Revision: 00
Slope stability software for soft soil engineering D-Geo Stability Verification Report D-GEO STABILITY Slope stability software for soft soil engineering Verification Report Version: 16.2 Revision: 00
Calculations of the Heave and Pitch RAO s for Three Different Ship s Hull Forms
 August 5, 5 Calculations of the Heave and Pitch RAO s for Three Different Ship s Hull Forms Hassan Ghassemi, a,*, Sohrab Majdfar, b and Valiollah Gill, b a) Department of Maritime Engineering, Amirkabir
August 5, 5 Calculations of the Heave and Pitch RAO s for Three Different Ship s Hull Forms Hassan Ghassemi, a,*, Sohrab Majdfar, b and Valiollah Gill, b a) Department of Maritime Engineering, Amirkabir
SHIP BUOYANCY AND STABILITY
 SHIP BUOYANCY AND STABILITY Lecture 04 Ship stability-z curve 09/11/2017 Ship Buoyancy and Stability 1 Literature J. Matusiak: Laivan kelluvuus ja vakavuus Biran A. B., Ship Hydrostatics and Stability,
SHIP BUOYANCY AND STABILITY Lecture 04 Ship stability-z curve 09/11/2017 Ship Buoyancy and Stability 1 Literature J. Matusiak: Laivan kelluvuus ja vakavuus Biran A. B., Ship Hydrostatics and Stability,
Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions
 DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 2010 Thrusters Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions Michael Palm,
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 2010 Thrusters Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions Michael Palm,
Transport Analysis Report Full Stability Analysis. Project EXAMPLE PROJECT DEMO RUN FOR REVIEW. Client ORCA OFFSHORE
 ONLINE MARINE ENGINEERING Transport Analysis Report Full Stability Analysis Project EXAMPLE PROJECT DEMO RUN FOR REVIEW Client ORCA OFFSHORE Issue Date 18/11/2010 Report reference number: Herm-18-Nov-10-47718
ONLINE MARINE ENGINEERING Transport Analysis Report Full Stability Analysis Project EXAMPLE PROJECT DEMO RUN FOR REVIEW Client ORCA OFFSHORE Issue Date 18/11/2010 Report reference number: Herm-18-Nov-10-47718
ITTC Recommended Procedures Testing and Extrapolation Methods Ice Testing Resistance Test in Level Ice
 TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 1 of 7 evision CONTENTS 1 PUPOSE OF POCEDUE CE ESSTANCE TESTS N LEVEL CE 3 PAAMETES 3.1 Ship model parameters 3. ce parameters to be measured 4
TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 1 of 7 evision CONTENTS 1 PUPOSE OF POCEDUE CE ESSTANCE TESTS N LEVEL CE 3 PAAMETES 3.1 Ship model parameters 3. ce parameters to be measured 4
Hydrostatic and Stability IN A NUTSHELL. of Floating Structures. Compendium. Relevant to Questions in Exam. Robert Bronsart
 Hydrostatic and Stability of Floating Structures IN A NUTSHELL Compendium Relevant to Questions in Exam Robert Bronsart Version Date Comment 2.21 September 2015 minor corrections Author: Robert Bronsart
Hydrostatic and Stability of Floating Structures IN A NUTSHELL Compendium Relevant to Questions in Exam Robert Bronsart Version Date Comment 2.21 September 2015 minor corrections Author: Robert Bronsart
APPROXIMATING THE ADDED RESISTANCE COEFFICIENT FOR A BULK CARRIER SAILING IN HEAD SEA CONDITIONS BASED ON ITS GEOMETRICAL PARAMETERS AND SPEED
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 4 (92) 2016 Vol. 23; pp. 8-15 10.1515/pomr-2016-0066 APPROXIMATING THE ADDED RESISTANCE COEFFICIENT FOR A BULK CARRIER SAILING IN HEAD SEA CONDITIONS BASED ON ITS GEOMETRICAL PARAMETERS
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 4 (92) 2016 Vol. 23; pp. 8-15 10.1515/pomr-2016-0066 APPROXIMATING THE ADDED RESISTANCE COEFFICIENT FOR A BULK CARRIER SAILING IN HEAD SEA CONDITIONS BASED ON ITS GEOMETRICAL PARAMETERS
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power
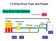 7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
ADDED RESISTANCE IN WAVES OF INTACT AND DAMAGED SHIP IN THE ADRIATIC SEA
 Brodogradnja/Shipbilding Volume 66 Number, 15 Ivana Martić Nastia Degiuli ISSN 7-15X eissn 1845-5859 ADDED RESISTANCE IN WAVES OF INTACT AND DAMAGED SHIP IN THE ADRIATIC SEA Summary UDC 69.5.15.4(6.3)
Brodogradnja/Shipbilding Volume 66 Number, 15 Ivana Martić Nastia Degiuli ISSN 7-15X eissn 1845-5859 ADDED RESISTANCE IN WAVES OF INTACT AND DAMAGED SHIP IN THE ADRIATIC SEA Summary UDC 69.5.15.4(6.3)
BMO Round 2 Problem 3 Generalisation and Bounds
 BMO 2007 2008 Round 2 Problem 3 Generalisation and Bounds Joseph Myers February 2008 1 Introduction Problem 3 (by Paul Jefferys) is: 3. Adrian has drawn a circle in the xy-plane whose radius is a positive
BMO 2007 2008 Round 2 Problem 3 Generalisation and Bounds Joseph Myers February 2008 1 Introduction Problem 3 (by Paul Jefferys) is: 3. Adrian has drawn a circle in the xy-plane whose radius is a positive
Computational Analysis of Added Resistance in Short Waves
 13 International Research Exchange Meeting of Ship and Ocean Engineering in Osaka -1 December, Osaka, Japan Computational Analysis of Added Resistance in Short Waves Yonghwan Kim, Kyung-Kyu Yang and Min-Guk
13 International Research Exchange Meeting of Ship and Ocean Engineering in Osaka -1 December, Osaka, Japan Computational Analysis of Added Resistance in Short Waves Yonghwan Kim, Kyung-Kyu Yang and Min-Guk
New Artificial Intelligence Technology Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing CO 2 Emissions of Ships through Use of Operational Big Data
 New Artificial Intelligence Technology Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing CO 2 Emissions of Ships through Use of Operational Big Data Taizo Anan Hiroyuki Higuchi Naoki Hamada Fuel cost and CO 2 emissions
New Artificial Intelligence Technology Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing CO 2 Emissions of Ships through Use of Operational Big Data Taizo Anan Hiroyuki Higuchi Naoki Hamada Fuel cost and CO 2 emissions
