ITTC Recommended Procedures Testing and Extrapolation Methods Ice Testing Resistance Test in Level Ice
|
|
|
- Lydia Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 1 of 7 evision CONTENTS 1 PUPOSE OF POCEDUE CE ESSTANCE TESTS N LEVEL CE 3 PAAMETES 3.1 Ship model parameters 3. ce parameters to be measured 4 VALDATON Uncertainty Analysis 4. Comparison with full-scale data 4.3 Benchmark Tests Updated by Approved Specialist Committee: ce of 3 rd TTC 3 rd TTC Date Date
2 TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page of 7 evision esistance Test in Level ce 1 PUPOSE OF POCEDUE The main reason for the towed resistance tests for ships in level ice is to determine the effectiveness of the hull-form in breaking ice and progressing through it. The specific results from these tests include: ce resistance at certain speeds and ice thickness The ship performance diagram (i.e. speed versus ice thickness) Limiting ice thickness for a continuous motion. CE ESSTANCE TESTS N LEVEL CE ce resistance tests are not always sufficient for the above tasks and additional propulsion tests are required. The propulsion tests, described in procedure , are needed to obtain a more complete view of the ship s performance in ice. However, the level ice resistance remains the basic element in describing the ship operability in ice. The ice resistance tests may be carried out either by towing the model with a constant towing force or at constant speed through ice. The use of constant force is more realistic in view of the constant thrust given by the propeller in full scale. The constant force tests are very difficult to perform and are susceptible to vibrations in the towing system originating from the variation in ice resistance due to the breaking pattern of ice. Also the speed cannot be set eactly in advance in constant force tests. For this reason the constant speed test is the common ice resistance test. When performing constant speed tests, a counterweight is sometimes used in order to keep the towing wire in tension. There are four forces acting on the model (Fig. 1). The use of the counterweight eliminates oscillations of the model in the ice-free areas where the resistance is very low. The total resistance of the vessel is: = F W (1) T When a rigid system is used, the total resistance is the measured towing force. Fig. 1 Forces acting on a model in a resistance test. The towing method and arrangement should be recorded to ensure a repeatability of the tests. The parameters which need to be measured in an ice resistance test, with their associated priority, are given below. The velocity of the model and the towing force are the main parameters and the main result from a resistance test. When reporting ice resistance model tests, the entire instrumen-
3 TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 3 of 7 evision tation should be described. The digital sampling rate should be high enough to capture variations in ice breaking. The total ice resistance is defined as the time average of the longitudinal force resisting the forward (or astern) motion of the ship, see Fig. : T = t 1 t t 1 t 1 F () t dt () Due to the quasi-steady nature of ice resistance, the time interval has to be long enough. The time when the test begins should be the time when the aft end of the vessel enters the level ice sheet. The integral of the towing force is a straight line when the resistance does not include any transient effects. Usually, it is recommended to allow the ship to proceed at least two ship lengths in level ice of uniform thickness to get a reliable resistance value. Therefore the above time dependent equation can be presented in a distance dependent form T / v 1 = F 1 1 / v d V where V = the towing speed. (3) The conventional rule (rule of thumb) for the minimum test length is: 1 > L WL. The total ice resistance is divided into components for the purposes of correcting small deviations of ice parameters from the target values. The net ice resistance is defined as the difference between the total ice resistance and the open water resistance, for the same speed: = T OW (4) Fig. The measured towing force and its integral The difference between the total and net ice resistance is small in low speeds but increases very quickly with increasing speeds. Therefore, at higher speeds the difference between total and net ice resistance can be substantial. Note that sometimes the open water resistance is determined in the track left in ice when the broken ice pieces are removed from it. n this case, the surrounding ice influences the resistance and the resistance is called, resistance in ice free water. This resistance differs from open water resistance, but the distinction is small and usually can be ignored.
4 TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 4 of 7 evision Often the velocities used in ice model tests are low, and consequently, the open water resistance is low. n this case, wave-making resistance is small, and the open water resistance can be as approimated by the viscous drag. Sometimes, the open water resistance is measured in the ice-free section before the model enters the ice. This method should be avoided if the speed is high enough to make wavemaking resistance noticeable. The ice resistance tests commonly have a target ice fleural strength and ice thickness, they are design parameters of the vessel. The model ice preparation process may result in small deviations from the target values of ice thickness or strength. The results obtained from the slightly different ice sheet are then corrected to the target values. A relationship for ice resistance, ice thickness and ice strength is available. Some tanks use for the ice thickness correction the following simple equation: H 15. (5) Another methodology to obtain corrections is to assume that the ice resistance is dependent on the strength and the thickness of the ice: into the parametric dependence is usually required. The classic way to do the corrections is to use a component breakdown of the ice resistance. (Jones & al. 1994, iska & al. 1994, zumiyama & Uto 1995) = (7) B + V where B is the breaking component and V is usually termed as the speed dependent part of the ice resistance. This division is not strictly correct, as the breaking part is also somewhat speed dependent. Further, the speed dependent part is sometimes divided into submergence part and frictional part. A better way to do the division could be given by the division into components due to tangential and normal forces but this has not been widely applied yet. The breaking component can be determined by means of a test in presawn ice. n this type of test ice is cut beforehand in a similar pattern as can be observed in the level ice test. This way B is eliminated from the total resistance, and therefore, B can be defined as the difference between the resistance measured in level ice and in the presawn ice, for the same speed: ( ) σ ( ) ρ = a v H + b v H. (6) i i B = = (8) T. levelice T. presawnice v. where the speed dependent constants (a and b) are determined by regression analysis. Similar equations have been presented (see e.g. Alekseev & Sasonov 1994) but the drawback of these methods is that usually not many measurement points are available. Some insight The speed of the model was considered constant in all of the above equations (3.3 to 3.8). f tests in level ice and presawn ice are performed at several speeds, the effect of speed on B can be determined. Two speeds in presawn ice suffice as the resistance in presawn ice may be considered linear with speed Fig. 3 shows that F = V/ gh. H
5 TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 5 of 7 evision An adjustment (correction) of the results to the targeted ice strength and ice thickness may be needed. The ice resistance is assumed to depend on the ice thickness according to a power law. Thus the corrected resistance is: =, meas H H meas, (10) Fig. 3 The resistance in presawn ice versus the ice thickness based Froude Number. The pattern of ice pieces in the presawn ice field should resemble the real breaking pattern. Some compromises are, however, usually made and a typical pattern shown in procedure The centreline of the model should coincide with the centreline of the presawn ice field. The recommendation for the length of the presawn area is the same as for the level ice section. t is important that the presawn area is slightly broader than the waterline breadth of the model ship. The breadth of the presawn area may be defined by the formula: BPS = BWL + nh (9) where the constant n should be between 3 and 4. f the air temperature is below the freezing point, or the ice is very cold, the ice pieces may freeze together. Therefore it is important to minimise the time lag between the tests and preparation of the presawn field. where the eponent depends on the hull shape and the model ice. n most cases, =1.5 to.0. f the ice resistance is measured in two clearly different ice thicknesses, the eponent can be calculated as: ( 1) ( H H ) = ln / ln / 1 (11) Eperience has shown that the eponent may be different in level ice and in presawn ice. Moderate deviations in ice fleural strength from target values can be corrected by assuming that the breaking resistance depends linearly on the fleural strength. Thus,the final corrected ice resistance is: = + v, meas B, meas σ f σ H H f, meas meas, (1 Finally, the etrapolation from model scale results to full scale is achieved by the formula: = λ 3 (13), p. where λ is the geometric scale factor and the subscript p refers to the prototype.
6 TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 6 of 7 evision The friction coefficient is important for the ice resistance. f the surface treatment of the model does not result in a desired friction between the model and the ice, some further corrections are needed. The best correction is to repaint the model to the desired surface roughness. However, if the difference between the measured friction coefficient and the target value is small, instead of a new surface treatment, a friction correction coefficient may be applied. The friction coefficient may be taken into account by the following equation: esistance tests can be performed with or without appendages, but in the former case all appendages have to be mentioned (reported). f consecutive tests are performed, it is recommended to remove all ice pieces that are remaining under the model before the net test. ce removal is impossible, if the tests are run by increasing the speed stepwise. n some cases large ice floes, resulting especially from low speed tests, may get trapped (e.g. between two rudders) and may cause additional resistance. f this kind of situation has taken place, it should be reported. = C µ. (14) corr, p, The friction correction coefficient can be based on the coefficient of the measured model ice friction and a comparisons between fullscale tests results and model tests with different model/ice-friction coefficients. Actual test results (Fig. 4) can be used to derive the friction correction coefficient. f the correction is assumed to be linearly proportional to the coefficient of friction, then from Fig. 4 the following formula is obtained: 3 λ m,, p 1 = = a+ fd. b (15) C µ where f D is the dynamic model ice friction coefficient and a and b are empirical coefficients (From Fig. 4, a = 0.8 and b = 5.8). This formula is valid for a new ship with a hull surface in good condition. Fig. 4 The ratio between etrapolated model scale ice resistance and measured full scale ice resistance plotted versus the coefficient of friction in model scale (Liukkonen 1989). The above equations present just one type of correction procedure, which is based on the division of resistance in ice into different components. As long as no ideal model ice material eists, some kind of correction methods is needed to handle the differences between measured and target values of ice thickness, fleural strength, buoyancy and other parameters that are substantial in ice breaking. f any kind of data correction method is used, it is
7 TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 7 of 7 evision very important to present the detailed principles of the method. 4. Comparison with full-scale data None 3 PAAMETES 3.1 Ship model parameters Parameter Priority Towing velocity 1 Type of restraints 1 Towing Force 1 Location of towing point 1 Pitch angle oll angle Heave Natural frequency of the towing system 3. ce parameters to be measured Parameter Priority ce thickness 1 Broken channel width 1 Piece size, breaking pattern 1 Model ice type 1 Elastic modulus 1 Fleural strength 1 Compressive strength 1 Underwater photography 1 ce density 1 ce crystal structure Fracture toughness Water density 4 VALDATON Uncertainty Analysis Not treated yet 4.3 Benchmark Tests 1. eport of Committee on Ships in ce Covered Water (16th 1981 pp ). Catalogue of Available Model and Full Scale Test Data (16th 1981 pp ) (1) Standard Model Tests (17th TTC 1984) () Model Tests with -Class cebreaker (3) Propulsion Tests (4) Full Scale Prediction. eanalysis of Full Scale -Class cebreaker Trial esults (18th TTC pp ) to Get eliable Full-Scale - Class Data CCGS "Pierre adisson and CCGS Franklin 3. etest of -Class cebreaker Model at a Different Friction Level (18th TTC 1987, pp ) a) esistance Tests (18th 1987 pp ) b) Self Propulsion Test (18th 1987 pp ) 8. Comparative Test Program with -Class Model (19th 1990 pp ) 9. Comparative Test Program with Basic Offshore Model Structure (19th 1990 pp ) and Basic Cylinder Tests (0th TTC pp ) 10. epeatability Tests for Quality Control (0th TTC 1993 pp )
ITTC Recommended Procedures Testing and Extrapolation Methods Resistance Resistance Test
 -0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
-0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines Testing and Extrapolation Methods Propulsion, Performance Propulsion Test
 7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines Performance, Propulsion 1978 ITTC Performance Prediction Method
 I ecommended 1978 I erformance rediction ethod 7.5 0 age 1 of 9 008 evision able of ontents 1978 I erformance rediction ethod... 1. UOE OF OEUE.... EIION OF OEUE....1 Introduction.... efinition of the
I ecommended 1978 I erformance rediction ethod 7.5 0 age 1 of 9 008 evision able of ontents 1978 I erformance rediction ethod... 1. UOE OF OEUE.... EIION OF OEUE....1 Introduction.... efinition of the
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
Motions and Resistance of a Ship in Regular Following Waves
 Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page 1 of 15 Table of Contents Ship Resistance in Ice Tank Testing... 1. PURPOSE OF THE PROCEDURE.... INTRODUCTION... 3. EXPERIMENTAL DATA... 3 4. EXPERIMENTAL UNCERTAINTY ANALYSIS BASIC EQUATIONS... 4
Page 1 of 15 Table of Contents Ship Resistance in Ice Tank Testing... 1. PURPOSE OF THE PROCEDURE.... INTRODUCTION... 3. EXPERIMENTAL DATA... 3 4. EXPERIMENTAL UNCERTAINTY ANALYSIS BASIC EQUATIONS... 4
ITTC Recommended Procedures
 Example for est 7.5-0 -0-0 Page of 7 00 ONENS PUPOSE O POEDUE EXAMPLE O ESISANE ES. est Design. Measurement Systems and Procedure. Uncertainty Analysis.. ias Limit... Hull Geometry (Model Length and Wetted
Example for est 7.5-0 -0-0 Page of 7 00 ONENS PUPOSE O POEDUE EXAMPLE O ESISANE ES. est Design. Measurement Systems and Procedure. Uncertainty Analysis.. ias Limit... Hull Geometry (Model Length and Wetted
COLD REGIONS SCIENCE AND MARINE TECHNOLOGY Vol II - Ice Breaking And Ship Modelling - Karl-Heinz Rupp
 ICE BREAKING AND SHIP MODELLING Karl-Heinz Rupp Hamburg, Germany Keywords: Ice breaking, Hull shape, Ice thickness, Friction, Resistance astern, Stability control, Ice floes, ice cake, brash ice, Rafted
ICE BREAKING AND SHIP MODELLING Karl-Heinz Rupp Hamburg, Germany Keywords: Ice breaking, Hull shape, Ice thickness, Friction, Resistance astern, Stability control, Ice floes, ice cake, brash ice, Rafted
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
CEE 3310 Dimensional Analysis & Similitude, Oct. 22,
 CEE 3310 Dimensional Analysis & Similitude, Oct., 018 115 5.5 Review vorticity twice the local rotation rate: ω x = w y v z, ω y = u z w x, ω z = v x u y Dimensional Analysis Buckingham Pi Theorem: k =
CEE 3310 Dimensional Analysis & Similitude, Oct., 018 115 5.5 Review vorticity twice the local rotation rate: ω x = w y v z, ω y = u z w x, ω z = v x u y Dimensional Analysis Buckingham Pi Theorem: k =
Estimating Maneuvering and Seakeeping Characteristics with Neural Networks
 070131-071 1 Estimating Maneuvering and Seakeeping Characteristics with Neural Networks Paulo Triunfante Martins 1, Victor Lobo 2, Member, IEEE Maneuvering and seakeeping are two very important naval architecture
070131-071 1 Estimating Maneuvering and Seakeeping Characteristics with Neural Networks Paulo Triunfante Martins 1, Victor Lobo 2, Member, IEEE Maneuvering and seakeeping are two very important naval architecture
CFD Based Hull Hydrodynamic Forces for Simulation of Ship Manoeuvres
 International Journal on Marine avigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 3 umber 1 March 9 Based Hull Hydrodynamic Forces for Simulation of Ship Manoeuvres T. Tabaczek, T. Gornicz & J. Kulczyk
International Journal on Marine avigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 3 umber 1 March 9 Based Hull Hydrodynamic Forces for Simulation of Ship Manoeuvres T. Tabaczek, T. Gornicz & J. Kulczyk
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 ITT Recommended 7.5-0 -0-0 Page of 8 00 Table of ontents PURPOSE OF PROEDURE... EXAMPLE FOR RESISTANE TEST. Test Design.... Measurement Systems and Procedure.... Uncertainty Analysis...4.. ias Limit...5...
ITT Recommended 7.5-0 -0-0 Page of 8 00 Table of ontents PURPOSE OF PROEDURE... EXAMPLE FOR RESISTANE TEST. Test Design.... Measurement Systems and Procedure.... Uncertainty Analysis...4.. ias Limit...5...
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page 1 of 9 CONTENTS Model Test Experiments... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Model Parameters... 3 2.2 Environmental Parameters... 3 2.3 Operation of Thrusters... 3 2.3.1 Thruster-Current
Page 1 of 9 CONTENTS Model Test Experiments... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Model Parameters... 3 2.2 Environmental Parameters... 3 2.3 Operation of Thrusters... 3 2.3.1 Thruster-Current
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis
 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
ITTC Recommended Procedures
 7.5-0 -03-0. Page of 6 CONTENTS PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE EXAMPLE FOR OPEN WATER TEST. Test Design. Measurement System and Procedure.3 Uncertainty Analysis.3. ias Limit.3.. Propeller Geometry.3.. Speed of advance
7.5-0 -03-0. Page of 6 CONTENTS PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE EXAMPLE FOR OPEN WATER TEST. Test Design. Measurement System and Procedure.3 Uncertainty Analysis.3. ias Limit.3.. Propeller Geometry.3.. Speed of advance
FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTIONS PREAMBLE. There are two types of vibrations: resonance and instability.
 FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTIONS PREAMBLE There are two types of vibrations: resonance and instability. Resonance occurs when a structure is excited at a natural frequency. When damping is low, the structure
FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTIONS PREAMBLE There are two types of vibrations: resonance and instability. Resonance occurs when a structure is excited at a natural frequency. When damping is low, the structure
Dead-Downwind Faster Than The Wind (DDWFTTW) Analysis
 Dead-Downwind Faster Than The Wind (DDWFTTW) Analysis Mark Drela Jan 09 Nomenclature boat speed W wind speed F t drag force on water turbine thrust force on air prop P t shaft power of water turbine P
Dead-Downwind Faster Than The Wind (DDWFTTW) Analysis Mark Drela Jan 09 Nomenclature boat speed W wind speed F t drag force on water turbine thrust force on air prop P t shaft power of water turbine P
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
 Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Chapter 7 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE Because so few real flows can be solved exactly by analytical methods alone, the development of fluid
 Chapter 7 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE Because so few real flows can be solved exactly by analytical methods alone, the development of fluid mechanics has depended heavily on experimental results.
Chapter 7 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE Because so few real flows can be solved exactly by analytical methods alone, the development of fluid mechanics has depended heavily on experimental results.
1.The pressure drop per unit length that develops due to friction cannot generally be solved analytically. A. True B. False
 CHAPTER 07 1.The pressure drop per unit length that develops due to friction cannot generally be solved analytically. 2.A qualitative description of physical quantities can be given in terms of. YOUR ANSWER:
CHAPTER 07 1.The pressure drop per unit length that develops due to friction cannot generally be solved analytically. 2.A qualitative description of physical quantities can be given in terms of. YOUR ANSWER:
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
Hull loads and response, hydroelasticity
 Transactions on the Built Environment vol 1, 1993 WIT Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 1743-3509 Hull loads and response, hydroelasticity effects on fast monohulls E. Jullumstr0 & J.V. Aarsnes Division of
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 1, 1993 WIT Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 1743-3509 Hull loads and response, hydroelasticity effects on fast monohulls E. Jullumstr0 & J.V. Aarsnes Division of
Flow and Transport. c(s, t)s ds,
 Flow and Transport 1. The Transport Equation We shall describe the transport of a dissolved chemical by water that is traveling with uniform velocity ν through a long thin tube G with uniform cross section
Flow and Transport 1. The Transport Equation We shall describe the transport of a dissolved chemical by water that is traveling with uniform velocity ν through a long thin tube G with uniform cross section
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power
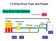 7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
VINTERSJÖFARTSFORSKNING ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE CHANNEL PROFILE VALIDATING THE POWER REQUIREMENT IN THE FINNISH-SWEDISH ICE CLASS RULES
 STYRELSEN FÖR VINTERSJÖFARTSFORSKNING WINTER NAVIGATION RESEARCH OARD Research Report No 66 Hanna Ritvanen ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE CHANNEL PROFILE VALIDATING THE POWER REQUIREMENT IN THE FINNISH-SWEDISH
STYRELSEN FÖR VINTERSJÖFARTSFORSKNING WINTER NAVIGATION RESEARCH OARD Research Report No 66 Hanna Ritvanen ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE CHANNEL PROFILE VALIDATING THE POWER REQUIREMENT IN THE FINNISH-SWEDISH
Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Ship Project A ASSIGNMENT ONE RAN XIAO & THEIR TOMAS
 2014 Ship Project A ASSIGNMENT ONE RAN XIAO 467643 & THEIR TOMAS 224051 Resistance estimation Methodology brief As our ship concept is in form of catamaran, it is not proper to simply introduce the method
2014 Ship Project A ASSIGNMENT ONE RAN XIAO 467643 & THEIR TOMAS 224051 Resistance estimation Methodology brief As our ship concept is in form of catamaran, it is not proper to simply introduce the method
Welcome to the Ship Resistance Predictor! The total calm water resistance is given by:
 Welcome to the Ship Resistance Predictor! What does this Excel Sheet do? This Excel sheet helps you calculate the Total Calm Water Resistance for a Ship at a given forward speed It also calculates from
Welcome to the Ship Resistance Predictor! What does this Excel Sheet do? This Excel sheet helps you calculate the Total Calm Water Resistance for a Ship at a given forward speed It also calculates from
Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships
 (August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
(August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 24, 1997 WIT Press, ISSN
 Comparison of model test with ship sea trial results for a given vessel series C.Behrendt & T.Kucharski Institute of Marine Plant Operation, Maritime University of Szczecin, 70-500 Szczecin, Poland Abstract
Comparison of model test with ship sea trial results for a given vessel series C.Behrendt & T.Kucharski Institute of Marine Plant Operation, Maritime University of Szczecin, 70-500 Szczecin, Poland Abstract
Interaction of Ships within Navigable Ice Channel
 RescOp - Development of rescue operations in the Gulf of Finland International Seminar: MARITIME SAFETY IN THE GULF OF FINLAND Interaction of Ships within Navigable Ice Channel Vadim K. Goncharov Department
RescOp - Development of rescue operations in the Gulf of Finland International Seminar: MARITIME SAFETY IN THE GULF OF FINLAND Interaction of Ships within Navigable Ice Channel Vadim K. Goncharov Department
13.42 LECTURE 13: FLUID FORCES ON BODIES. Using a two dimensional cylinder within a two-dimensional flow we can demonstrate some of the principles
 13.42 LECTURE 13: FLUID FORCES ON BODIES SPRING 2003 c A. H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Morrison s Equation Using a two dimensional cylinder within a two-dimensional flow we can demonstrate some of
13.42 LECTURE 13: FLUID FORCES ON BODIES SPRING 2003 c A. H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Morrison s Equation Using a two dimensional cylinder within a two-dimensional flow we can demonstrate some of
Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods
 ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
Master Thesis. Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations
 Master Thesis Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations Author: Erik Rotteveel Supervisor: Frans Quadvlieg Graduation report
Master Thesis Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations Author: Erik Rotteveel Supervisor: Frans Quadvlieg Graduation report
MEC-E2001 Ship Hydrodynamics. Prof. Z. Zong Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, Espoo
 MEC-E2001 Ship Hydrodynamics Prof. Z. Zong zhi.zong@aalto.fi Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, 02510 Espoo Teacher: Prof. Z. Zong, zhi.zong@aalto.fi Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, 02510 Espoo Teaching
MEC-E2001 Ship Hydrodynamics Prof. Z. Zong zhi.zong@aalto.fi Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, 02510 Espoo Teacher: Prof. Z. Zong, zhi.zong@aalto.fi Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, 02510 Espoo Teaching
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew Dominic J. Taunton Dominic A.
 A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew, Dominic J. Taunton, Dominic A. Hudson Fluid Structure Interactions Group, University of Southampton ss17e111@soton.ac.uk
A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew, Dominic J. Taunton, Dominic A. Hudson Fluid Structure Interactions Group, University of Southampton ss17e111@soton.ac.uk
Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses
 (Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
(Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
Objectives: After completion of this module, you should be able to:
 Chapter 12 Objectives: After completion of this module, you should be able to: Demonstrate your understanding of elasticity, elastic limit, stress, strain, and ultimate strength. Write and apply formulas
Chapter 12 Objectives: After completion of this module, you should be able to: Demonstrate your understanding of elasticity, elastic limit, stress, strain, and ultimate strength. Write and apply formulas
Study of the hydrodynamic flow around a 70m sailing boat for powering, wave pattern and propeller efficiency prediction
 Study of the hydrodynamic flow around a 70m sailing boat for powering, wave pattern and propeller efficiency prediction Romain Baudson Supervisor: Prof. Dario Boote (UNIGE) External Reviewer: Prof. Pierre
Study of the hydrodynamic flow around a 70m sailing boat for powering, wave pattern and propeller efficiency prediction Romain Baudson Supervisor: Prof. Dario Boote (UNIGE) External Reviewer: Prof. Pierre
Turbulent Boundary Layers: Roughness Effects
 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 2005 Lecture 19 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Turbulent Boundary Layers: Roughness Effects So far, we have assumed a hydraulically smooth surface. In practice,
2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 2005 Lecture 19 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Turbulent Boundary Layers: Roughness Effects So far, we have assumed a hydraulically smooth surface. In practice,
General Physics I. Lecture 12: Applications of Oscillatory Motion. Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 )
 General Physics I Lecture 1: Applications of Oscillatory Motion Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) inwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~inwan/ Outline The pendulum Comparing simple harmonic motion and uniform circular
General Physics I Lecture 1: Applications of Oscillatory Motion Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) inwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~inwan/ Outline The pendulum Comparing simple harmonic motion and uniform circular
Mt Introduction. 2. Governing gphysics. 3. Decomposition of resistance. 4. Similarity laws and scaling
 1. Introduction 2. Governing gphysics 3. Decomposition of resistance 4. Similarity laws and scaling Mt 527 Importance of proper power-speed prediction Resistance, prop. efficiency, power Wake field Experimental,
1. Introduction 2. Governing gphysics 3. Decomposition of resistance 4. Similarity laws and scaling Mt 527 Importance of proper power-speed prediction Resistance, prop. efficiency, power Wake field Experimental,
UNIT V : DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND MODEL STUDIES
 UNIT V : DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND MODEL STUDIES 1. Define dimensional analysis. Dimensional analysis is a mathematical technique which makes use of the study of dimensions as an aid to solution of several
UNIT V : DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND MODEL STUDIES 1. Define dimensional analysis. Dimensional analysis is a mathematical technique which makes use of the study of dimensions as an aid to solution of several
Free surface flows over submerged obstructions
 Free surface flows over submerged obstructions A thesis submitted to the School of Computing Sciences of the University of East Anglia in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Free surface flows over submerged obstructions A thesis submitted to the School of Computing Sciences of the University of East Anglia in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Simple Estimation of Wave Added Resistance from Experiments in Transient and Irregular Water Waves
 Simple Estimation of Wave Added Resistance from Experiments in Transient and Irregular Water Waves by Tsugukiyo Hirayama*, Member Xuefeng Wang*, Member Summary Experiments in transient water waves are
Simple Estimation of Wave Added Resistance from Experiments in Transient and Irregular Water Waves by Tsugukiyo Hirayama*, Member Xuefeng Wang*, Member Summary Experiments in transient water waves are
ROLLER BEARING FAILURES IN REDUCTION GEAR CAUSED BY INADEQUATE DAMPING BY ELASTIC COUPLINGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIONS
 ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
Deliverable D.6.1. Application of CFD tools to the development of a novel propulsion concept
 TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 Proceedings of COBEM 2007 Copyright 2007 by ABCM 19th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 5-9, 2007, Brasília, DF VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Luiz
Proceedings of COBEM 2007 Copyright 2007 by ABCM 19th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 5-9, 2007, Brasília, DF VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Luiz
Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further.
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further. Gerasimos Politis 1,Theodoros Ioannou
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further. Gerasimos Politis 1,Theodoros Ioannou
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM
 DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
Effects of hull form parameters on seakeeping for YTU gulet series with cruiser stern
 csnk, 04 Int. J. Nav. rchit. Ocean Eng. (04) 6:700~74 http://dx.doi.org/0.478/ijnoe-03-006 pissn: 09-678, eissn: 09-6790 Effects of hull form parameters on seakeeping for YTU gulet series with cruiser
csnk, 04 Int. J. Nav. rchit. Ocean Eng. (04) 6:700~74 http://dx.doi.org/0.478/ijnoe-03-006 pissn: 09-678, eissn: 09-6790 Effects of hull form parameters on seakeeping for YTU gulet series with cruiser
Fluid Mechanics. du dy
 FLUID MECHANICS Technical English - I 1 th week Fluid Mechanics FLUID STATICS FLUID DYNAMICS Fluid Statics or Hydrostatics is the study of fluids at rest. The main equation required for this is Newton's
FLUID MECHANICS Technical English - I 1 th week Fluid Mechanics FLUID STATICS FLUID DYNAMICS Fluid Statics or Hydrostatics is the study of fluids at rest. The main equation required for this is Newton's
Ship Hydrodynamics, Ship Propeller Acoustics and Cavitation.
 Ship Hydrodynamics, Ship Propeller Acoustics and Cavitation. Dr.l.noordzij@leennoordzij.nl www.leennoordzij.me Content Introduction.... 1 The Cavitation Tunnel.... 2 The Depressurized Towing Tank... 4
Ship Hydrodynamics, Ship Propeller Acoustics and Cavitation. Dr.l.noordzij@leennoordzij.nl www.leennoordzij.me Content Introduction.... 1 The Cavitation Tunnel.... 2 The Depressurized Towing Tank... 4
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Consideration of medium-speed four-stroke engines in ship vibration analyses I. Asmussen, A. Muller-Schmerl GermanischerLloyd, P.O. Box 111606, 20416Hamburg, Germany Abstract Vibration problems were recently
Consideration of medium-speed four-stroke engines in ship vibration analyses I. Asmussen, A. Muller-Schmerl GermanischerLloyd, P.O. Box 111606, 20416Hamburg, Germany Abstract Vibration problems were recently
AE3610 Experiments in Fluid and Solid Mechanics TRANSIENT MEASUREMENTS OF HOOP STRESSES FOR A THIN-WALL PRESSURE VESSEL
 Objective AE3610 Experiments in Fluid and Solid Mechanics TRANSIENT MEASUREMENTS OF OOP STRESSES FOR A TIN-WA PRESSURE VESSE This experiment will allow you to investigate hoop and axial stress/strain relations
Objective AE3610 Experiments in Fluid and Solid Mechanics TRANSIENT MEASUREMENTS OF OOP STRESSES FOR A TIN-WA PRESSURE VESSE This experiment will allow you to investigate hoop and axial stress/strain relations
7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory
 7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory In this section, problems involving long and slender beams are addressed. s with pressure vessels, the geometry of the beam, and the specific type of loading which will be
7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory In this section, problems involving long and slender beams are addressed. s with pressure vessels, the geometry of the beam, and the specific type of loading which will be
Time domain assessment of nonlinear coupled ship motions and sloshing in free surface tanks
 Time domain assessment of nonlinear coupled ship motions and sloshing in free surface tanks 1 outline 1.Motivation & state-of-the-art 2.Simulation approach 1.SHIXDOF: nonlinear ship motion TD 6DOF 2.AQUAgpusph:
Time domain assessment of nonlinear coupled ship motions and sloshing in free surface tanks 1 outline 1.Motivation & state-of-the-art 2.Simulation approach 1.SHIXDOF: nonlinear ship motion TD 6DOF 2.AQUAgpusph:
AP Physics B Summer Assignment
 BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
THE LEVEL OF CONFIDENCE FOR A SHIP HULL GIRDER
 94 Paper present at International Conference on Diagnosis and Prediction in Mechanical Engineering Systems (DIPRE 07) 26-27 October 2007, Galati, Romania THE LEVEL OF CONFIDENCE FOR A SHIP HULL GIRDER
94 Paper present at International Conference on Diagnosis and Prediction in Mechanical Engineering Systems (DIPRE 07) 26-27 October 2007, Galati, Romania THE LEVEL OF CONFIDENCE FOR A SHIP HULL GIRDER
Hydraulic Engineering
 PDHonline Course H146 (4 PDH) Hydraulic Engineering Instructor: Mohamed Elsanabary, Ph.D., Prov. Lic. Engineering. 2013 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax:
PDHonline Course H146 (4 PDH) Hydraulic Engineering Instructor: Mohamed Elsanabary, Ph.D., Prov. Lic. Engineering. 2013 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax:
Measurement of speed loss due to waves
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Measurement of speed loss due to waves Sverre Steen 1 and Zhenju Chuang 1 1 Department of Marine Technology,
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Measurement of speed loss due to waves Sverre Steen 1 and Zhenju Chuang 1 1 Department of Marine Technology,
ITTC Circular Letter
 ITTC Circular Letter May, 2016 Load variation tests The speed/power sea trials procedures, ITTC Recommended rocedures 7.5-04-01-01.1 and -01.2, and IO15016:2015 require that load variation tests are performed
ITTC Circular Letter May, 2016 Load variation tests The speed/power sea trials procedures, ITTC Recommended rocedures 7.5-04-01-01.1 and -01.2, and IO15016:2015 require that load variation tests are performed
ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller
 voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change. Chapter 12: States of Matter
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
Modelling stray current interference to shipboard cathodic protection system
 Paper No. 215-6631 Modelling stray current interference to shipboard cathodic protection system Yueping Wang Defence Research and Development Canada Atlantic Research Centre CFB Halifax, Bldg D-2 P.O.
Paper No. 215-6631 Modelling stray current interference to shipboard cathodic protection system Yueping Wang Defence Research and Development Canada Atlantic Research Centre CFB Halifax, Bldg D-2 P.O.
Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos
 Session 7 Stability of Damaged Ships Numerical Simulation of Progressive Flooding and Capsize Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos Qiuxin Gao and Dracos
Session 7 Stability of Damaged Ships Numerical Simulation of Progressive Flooding and Capsize Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos Qiuxin Gao and Dracos
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1887 Diverse calving patterns linked to glacier geometry J. N. Bassis and S. Jacobs 1. Supplementary Figures (a) (b) (c) Supplementary Figure S1 Schematic of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1887 Diverse calving patterns linked to glacier geometry J. N. Bassis and S. Jacobs 1. Supplementary Figures (a) (b) (c) Supplementary Figure S1 Schematic of
τ = (Force)(lever arm) #
 EXPERIMENT: MOMENT OF INERTIA OBJECTIVES : 1) To familiarize yourself with the concept of the moment of inertia, I, which plays the same role in the description of the rotation of the rigid body as the
EXPERIMENT: MOMENT OF INERTIA OBJECTIVES : 1) To familiarize yourself with the concept of the moment of inertia, I, which plays the same role in the description of the rotation of the rigid body as the
SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE
 N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
Computation of the wavemaking resistance of a Harley surface effect ship
 Proceedings of the Sixteenth Seventeenth (2007) (2007) International Offshore and and Polar Polar Engineering Conference Lisbon, Portugal, July 1-6, 2007 Copyright 2007 by The International Society of
Proceedings of the Sixteenth Seventeenth (2007) (2007) International Offshore and and Polar Polar Engineering Conference Lisbon, Portugal, July 1-6, 2007 Copyright 2007 by The International Society of
Teaching sessions week 40
 Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems
 Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Uniaxial Compression
Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Uniaxial Compression
Force, Mass, and Acceleration
 Introduction Force, Mass, and Acceleration At this point you append you knowledge of the geometry of motion (kinematics) to cover the forces and moments associated with any motion (kinetics). The relations
Introduction Force, Mass, and Acceleration At this point you append you knowledge of the geometry of motion (kinematics) to cover the forces and moments associated with any motion (kinetics). The relations
developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati Presented by: BENZOHRA Abdelmalek
 Master Thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the double degree: Advanced Master in Naval Architecture conferred by University of Liege "Master of Sciences in Applied Mechanics,
Master Thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the double degree: Advanced Master in Naval Architecture conferred by University of Liege "Master of Sciences in Applied Mechanics,
Hydromechanics: Course Summary
 Hydromechanics: Course Summary Hydromechanics VVR090 Material Included; French: Chapters to 9 and 4 + Sample problems Vennard & Street: Chapters 8 + 3, and (part of it) Roberson & Crowe: Chapter Collection
Hydromechanics: Course Summary Hydromechanics VVR090 Material Included; French: Chapters to 9 and 4 + Sample problems Vennard & Street: Chapters 8 + 3, and (part of it) Roberson & Crowe: Chapter Collection
The distortion observed in the bottom channel of Figure 1 can be predicted from the full transport equation, C t + u C. y D C. z, (1) x D C.
 1 8. Shear Dispersion. The transport models and concentration field solutions developed in previous sections assume that currents are spatially uniform, i.e. u f(,y,). However, spatial gradients of velocity,
1 8. Shear Dispersion. The transport models and concentration field solutions developed in previous sections assume that currents are spatially uniform, i.e. u f(,y,). However, spatial gradients of velocity,
MASTER THESIS PRESENTATION
 MASTER THESIS PRESENTATION TURBULENT FLOW SEPARATION AROUND A ROV BODY Presented by: KOFFI Danoh Kouassi Ange Gatien Outline 1- Introduction 2- Numerical modeling of the ROV 3- Choice of the turbulence
MASTER THESIS PRESENTATION TURBULENT FLOW SEPARATION AROUND A ROV BODY Presented by: KOFFI Danoh Kouassi Ange Gatien Outline 1- Introduction 2- Numerical modeling of the ROV 3- Choice of the turbulence
A model of an aircraft towing a cable-body system
 ANZIAM J. 47 (EMAC2005) pp.c615 C632, 2007 C615 A model of an aircraft towing a cable-body system C. K. H. Chin R. L. May (Received 2 November 2005; revised 31 January 2007) Abstract We integrate together
ANZIAM J. 47 (EMAC2005) pp.c615 C632, 2007 C615 A model of an aircraft towing a cable-body system C. K. H. Chin R. L. May (Received 2 November 2005; revised 31 January 2007) Abstract We integrate together
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
ITTC Recommended Procedures
 I Recommended Analysis in Resistance ests 7.5- -- Page of 0. PURPOSE O GUIDELINE... able of ontents 3.5 Data Reduction... 6. MEASURANDS... 3. UNERAINY SOURES... 3. Model Geometry... 3 3. est Installation...
I Recommended Analysis in Resistance ests 7.5- -- Page of 0. PURPOSE O GUIDELINE... able of ontents 3.5 Data Reduction... 6. MEASURANDS... 3. UNERAINY SOURES... 3. Model Geometry... 3 3. est Installation...
IIT JEE PAPER The question paper consists of 3 parts (Chemistry, Mathematics and Physics). Each part has 4 sections.
 IIT JEE - 2009 PAPER 2 A. Question paper format: 1. The question paper consists of 3 parts (Chemistry, Mathematics and Physics). Each part has 4 sections. 2. Section I contains 4 multiple choice questions.
IIT JEE - 2009 PAPER 2 A. Question paper format: 1. The question paper consists of 3 parts (Chemistry, Mathematics and Physics). Each part has 4 sections. 2. Section I contains 4 multiple choice questions.
CE FLUID MECHANICS AND MECHINERY UNIT I
 CE 6451- FLUID MECHANICS AND MECHINERY UNIT I 1. Define specific volume of a fluid and write its unit. [N/D-14] Volume per unit mass of a fluid is called specific volume. Unit: m3 / kg. 2. Name the devices
CE 6451- FLUID MECHANICS AND MECHINERY UNIT I 1. Define specific volume of a fluid and write its unit. [N/D-14] Volume per unit mass of a fluid is called specific volume. Unit: m3 / kg. 2. Name the devices
Dense Solid-Liquid Suspensions in Top-Covered Unbaffled Stirred Vessels
 Dense Solid-Liquid Suspensions in Top-Covered Unbaffled Stirred Vessels Alessandro Tamburini*, Andrea Cipollina, Giorgio Micale, Alberto Brucato Dipartimento di Ingegneria Chimica, Gestionale, Informatica,
Dense Solid-Liquid Suspensions in Top-Covered Unbaffled Stirred Vessels Alessandro Tamburini*, Andrea Cipollina, Giorgio Micale, Alberto Brucato Dipartimento di Ingegneria Chimica, Gestionale, Informatica,
Sound. Measure the speed of sound in air by means of resonance in a tube; Measure the speed of sound in a metal rod using Kundt s tube.
 Sound Purpose Problem 1 Problem 2 Measure the speed of sound in air by means of resonance in a tube; Measure the speed of sound in a metal rod using Kundt s tube. Introduction and Theory When a vibrating
Sound Purpose Problem 1 Problem 2 Measure the speed of sound in air by means of resonance in a tube; Measure the speed of sound in a metal rod using Kundt s tube. Introduction and Theory When a vibrating
Problem Set Number 01, MIT (Winter-Spring 2018)
 Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
The challenge of supplying antifouling coatings to reduce emission of greenhouse gases
 The challenge of supplying antifouling coatings to reduce emission of greenhouse gases Erik Risberg Jotun A/S Outline The complex technology situation Boundary layers and their influence on frictional
The challenge of supplying antifouling coatings to reduce emission of greenhouse gases Erik Risberg Jotun A/S Outline The complex technology situation Boundary layers and their influence on frictional
Lecture 19. Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
7. Basics of Turbulent Flow Figure 1.
 1 7. Basics of Turbulent Flow Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. The ratio of inertial to viscous forces is the Reynolds
1 7. Basics of Turbulent Flow Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. The ratio of inertial to viscous forces is the Reynolds
Experimental studies of springing and whipping of container vessels
 Experimental studies of springing and whipping of container vessels Ole Andreas Hermundstad CeSOS Highlights and AMOS Visions Conference 27-29th May 2013 in Trondheim Outline Background and motivation
Experimental studies of springing and whipping of container vessels Ole Andreas Hermundstad CeSOS Highlights and AMOS Visions Conference 27-29th May 2013 in Trondheim Outline Background and motivation
Interaction of Ships while Opposing Navigation among Small Ice Floes
 ARCTIC OI RECOVERY EXERCISE 05 KEMI ARCTIC 05 Conference Interaction of Ships while Opposing Navigation among Small Ice Floes Vadim K. Goncharov Professor Department of Oceantechnics and Marine Technology
ARCTIC OI RECOVERY EXERCISE 05 KEMI ARCTIC 05 Conference Interaction of Ships while Opposing Navigation among Small Ice Floes Vadim K. Goncharov Professor Department of Oceantechnics and Marine Technology
VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION OF RESISTANCE AND PROPULSION COMPUTATION
 VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION OF RESISTANCE AND PROPULSION COMPUTATION G. Deng, A. Leroyer, E. Guilmineau, P. Queutey, M. Visonneau & J. Wackers (ECN-LHEEA,CNRS, France) A. del Toro Llorens (Spanish Institution
VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION OF RESISTANCE AND PROPULSION COMPUTATION G. Deng, A. Leroyer, E. Guilmineau, P. Queutey, M. Visonneau & J. Wackers (ECN-LHEEA,CNRS, France) A. del Toro Llorens (Spanish Institution
Solutions for Tutorial 5 Dynamic Behavior of Typical Dynamic Systems
 olutions for Tutorial 5 Dynamic Behavior of Typical Dynamic ystems 5.1 First order ystem: A model for a first order system is given in the following equation. dy dt X in X out (5.1.1) What conditions have
olutions for Tutorial 5 Dynamic Behavior of Typical Dynamic ystems 5.1 First order ystem: A model for a first order system is given in the following equation. dy dt X in X out (5.1.1) What conditions have
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO
 SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO Half-Yearly Exam 2013 Subject: Physics Level: Advanced Time: 3hrs Name: Course: Year: 1st This paper carries 200 marks which are 80% of
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO Half-Yearly Exam 2013 Subject: Physics Level: Advanced Time: 3hrs Name: Course: Year: 1st This paper carries 200 marks which are 80% of
Stability and Control
 Stability and Control Introduction An important concept that must be considered when designing an aircraft, missile, or other type of vehicle, is that of stability and control. The study of stability is
Stability and Control Introduction An important concept that must be considered when designing an aircraft, missile, or other type of vehicle, is that of stability and control. The study of stability is
