Predictive Control of Outer-Rotor Five-Phase BLDC Generators Applicable for Off-Shore. Wind Power Plants
|
|
|
- Claud Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ١ ٢ Predictive Control of Outer-Rotor Five-Phase BLDC Generators Applicable for Off-Shore Wind Power Plants ٣ ٤ Rain SALEHI ARASHLOO Mehdi SALEHIFAR 2 Jose Luis ROMERAL MARINEZ 3 Juan Manuel 4 MORENO ٥ ٦ ٧ CORRESPONDING AUHOR, rain.salehi@cia.upc.edu ٨ 2 ehdi.salehifar@cia.upc.edu ٩ 3 luis.roeral@cia.upc.edu ١٠ 4 anuel.oreno.eguilaz@upc.edu ١١ All Authors are with Electronic Engineering Departent, UPC, Rabla Sant Nebridi, s/n, errassa, Spain, ١٢ el: ١٣ Fax: ١٤ ١٥ ١٦ ١٧ ١٨ ١٩ ٢٠ ٢١ ٢٢ Abstract Model predictive control algoriths have recently gained ore iportance in the field of wind power generators. One of the iportant categories of odel predictive control ethods is iproved deadbeat control in which the reverse odel of generator is used to calculate the appropriate inputs for the next iteration of controlling process. In this paper, a new iproved deadbeat algorith is proposed to control the stator currents of an outer-rotor five-phase BLDC generator. Extended Kalan filter is used in the estiation step of proposed ethod, and generator equations are used to calculate the appropriate voltages for the next odulation period. wo aspects of proposed controlling ethod are evaluated including its sensitivity to generator paraeter variations and its speed in following the reference values of
2 ٢٣ ٢٤ required torque during transient states. Wind power generators are kept in ind, and proposed controlling ethod is both siulated and experientally evaluated on an outer-rotor five-phase BLDC generator. ٢٥ ٢٦ ٢٧ Keywords Multiphase generators, iproved deadbeat control, extended Kalan filter, wind power generators ٢٨ ٢٩ ٣٠ ٣١ ٣٢ ٣٣ ٣٤ ٣٥ ٣٦ ٣٧ ٣٨ ٣٩ ٤٠ ٤١ ٤٢ ٤٣ ٤٤ ٤٥ ٤٦. Introduction Due to their high power density, high efficiency and wide speed range, peranent agnet (PM) generators are receiving ore attention in wind power plants. Aong different topologies of PM generators, brushless direct current (BLDC) generators have the advantage of higher torque density, sipler winding distribution and ore fault tolerance []. As a result, these achines are a practical option for low-aintenance and high power applications such as off-shore wind power fars. Several ethods are proposed in literature to have a better control on stator phase currents of BLDC generators. Aong these algoriths, odel predictive control (MPC) has becoe a suitable option recently. MPC concept is easy to understand, and various constraints and nonlinearities can be directly included in its structure. Moreover, the resulting controller is easy to ipleent [2], [3]. hese types of controllers can be effectively ipleented in generator controlling algorith because linear odels of BLDC generators are quite well known and developed through analytical ethods. In the field of generator power control, MPC algoriths can be generally divided into two ain categories. he first group is an extension of traditional direct-torque control (DC) in which the lookup table is reoved and optiized switching state of the inverter is coputed directly in MPC algorith to iniize a predefined cost function [4][5]. his cost function should be coputed for all possible switching states, and as a result the coputational burden of controlling algorith is relatively high. By appearance of powerful digital processors, it is now possible to use this algorith for fast dynaic
3 ٤٧ ٤٨ ٤٩ ٥٠ ٥١ ٥٢ ٥٣ ٥٤ ٥٥ ٥٦ ٥٧ ٥٨ ٥٩ ٦٠ ٦١ ٦٢ ٦٣ ٦٤ ٦٥ ٦٦ ٦٧ ٦٨ ٦٩ ٧٠ systes such as PM drives [6]. Considering the finite aount of possible switching states in the converter unit, this type of control algorith is also faous as finite set odel predictive control (FS-MPC). On the other hand, the second group can be considered as an extension of traditional field-oriented control of generator. In this group, the inner PI controllers are reoved and replaced by predictive controllers. Moreover, reverse odel of generator is used to calculate appropriate reference voltages, and a odulator is usually used to generate the coputed reference voltages [7]. Model predictive control has also been exained successfully in the case of ultiphase generators [8]. Coparing to standard three-phase generators, ulti-phase structure of a BLDC generator results in several advantages such as lower power per inverter leg, lower current per phase, and lower aplitude and higher frequency of generated torque ripple. However, higher nuber of inverter legs and possible switching states, results in higher coputational burden of MPC algorith in ultiphase generator drives [9][0]. While controlling the stator currents of a ultiphase generator by MPC algoriths, achine odel is directly used to estiate the future values of syste outputs (electrical torque and stator currents) [6]. Consequently, the precision of odel paraeters play an iportant role in final accuracy of the estiated values []. Extended Kalan filter (EKF) is a powerful recursive estiation algorith which can be used to reduce the effect of generator paraeter variation. All available easureents are processed by EKF regardless of their accuracy to provide a fast and precise estiation of all syste states [2]. In [2] and [3] EKF is used to estiate the rotor position and rotor speed of a peranent agnet synchronous achine. Moreover, by coparing final estiations of this algorith with easured values of syste states a fault detection and isolation algorith is developed in [4]. As the atheatical odel of BLDC generator is sufficiently well developed, EKF is ideally suited for the case of five-phase BLDC generator applications.
4 ٧١ ٧٢ ٧٣ ٧٤ ٧٥ ٧٦ ٧٧ ٧٨ ٧٩ ٨٠ ٨١ ٨٢ ٨٣ In this paper, extended Kalan filter based predictive deadbeat control (EKF-PDC) is developed for five-phase BLDC generator. Proposed controlling algorith includes two ain steps naely current estiation step and voltage application step. EKF is developed for five-phase BLDC generator, and is executed during current estiation step to reduce the effect of generator paraeter variation. wo ain aspects of proposed controlling algorith are evaluated both by siulations and experiental tests. hese two aspects are sensitivity respect generator variations, and its ability in following reference currents (and electrical torque) during transient states. he reaining sections of this paper are organized as follows. Electrical odel of five-phase BLDC generator and general concepts of deadbeat current control are explained in section 2. In section 3, EKF theory and its application for iproved predictive deadbeat control of five-phase BLDC generator are developed. Section 4 is dedicated to sensitivity analysis of proposed controlling ethod by eans of siulations. Experiental verifications of proposed deadbeat control are presented in section 5, and finally, section 6 presents a suary of results drawn fro this study. ٨٤ ٨٥ ٨٦ ٨٧ 2. Deadbeat Control of Stator Currents in a Five-Phase BLDC Generator In this section, the electrical odel of a five-phase BLDC generator is briefly reviewed, and after that, general concept of deadbeat control is developed its application. ٨٨ ٨٩ ٩٠ ٩١ ٩٢ 2.. Generator Stator Windings he achine is considered syetric, and oreover, it is assued that there is no iron saturation. he first step of odel developent is the general equation of electrical paraeters in generator windings: v ri t s s s s ()
5 ٩٣ ٩٤ ٩٥ where r s represents stator winding resistance, i s is stator phase currents and v s is stator phase voltages: s an bn cn dn en v v v v v v s a b c d e i i i i i i ٩٦ ٩٧ ٩٨ ٩٩ Moreover, stator winding flux is represented by s which is produced by rotor agnets and stator phase currents: Li s s s p (2) ١٠٠ ١٠١ ١٠٢ ١٠٣ where L s is the stator inductance atrix. In the case of a five-phase BLDC generator, the flux generated by rotor agnets can be estiated by its fundaental and third haronic coponents: (3) ١٠٤ ١٠٥ ١٠٦ ١٠٧ ١٠٨ ١٠٩ ١١٠ sin( ) sin(3 ) sin( ) sin3( ) p psin( 2 ) p3sin 3( 2 ) sin( 3 ) sin 3( 3 ) sin( 4 ) sin 3( 4 ) where is the electrical angle of rotor position, p and p3 coponents of agnet flux in generator windings, and 2 5rad. (4) are fundaental and third haronic Siilar to Park transforation in three-phase systes, it is possible to transfer the electrical paraeters of a five-phase BLDC generator into two rotating reference fraes (naely d q -frae and d 3 q 3 -frae), and one hoopolar axis. Equation (5) presents the transforation atrix for a five-phase syste. ١١١ F d q d q o 3 3 F, abcde
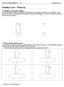
6 ١١٢ ١١٣ ١١٤ cos( ) cos( 2 5) cos( 4 5) cos( 6 5) cos( 8 5) sin( ) sin( 2 5) sin( 4 5) sin( 6 5) sin( 8 5) 2 cos3( ) cos3( 2 5) cos3( 4 5) cos3( 6 5) cos3( 8 5) 5 sin 3( ) sin 3( 2 5) sin 3( 2 5) sin 3( 2 5) sin3( 2 5) Electrical equations of five-phase BLDC generator in two rotating reference fraes are: (5) ١١٥ d vd ri s d Ld id Lqiq (6) dt ١١٦ d vq ri s q Lq iq ( p Ldid) (7) dt ١١٧ d vd3 ri s d3 Ld3 id3 3 Lq3iq3 (8) dt ١١٨ d vq3 ri s q3 Lq3 iq3 3 ( p3 Ld3id3) (9) dt ١١٩ ١٢٠ ١٢١ ١٢٢ d vo ri s o Lo io (0) dt where is the electrical rotational velocity, and L d, L q, L d3, L q3 and L o are the inductance values of stator windings in their corresponding directions. In addition, generated Electrical torque of five-phase BLDC generator in synchronous reference fraes can be calculated as: ١٢٣ e e e3 ١٢٤ 5 P e [ idiq( Ld Lq ) iq] 22 ١٢٥ ١٢٦ 5 P e3 [ 3 id3iq3( Ld3 Lq3) 3 3iq3] 22 () ١٢٧ ١٢٨ ١٢٩ 2.2. General Concept of Deadbeat Current Control for a Five-Phase BLDC Generator In the case of BLDC achine applications, the ain purpose of deadbeat control algorith is to eliinate the stator current errors in the sallest possible nuber of switching periods. As it is shown in
7 ١٣٠ ١٣١ Fig., stator phase currents are sapled at the beginning of k th odulation period. In addition, the duty cycles of each voltage vector are getting updated by the beginning of each odulation period. Modulation Periods V(K) Sapling ties V(K+) tie Ik Iˆk I ( * ) k2 I k ١٣٢ Coputation Voltage Application ١٣٣ ١٣٤ ١٣٥ ١٣٦ ١٣٧ ١٣٨ ١٣٩ Fig. : Deadbeat MPC controlling sequences By knowing the easured values of phase currents (I k ) and applied voltage values (V k ) during k th odulation period, it is possible to calculate the estiated value of stator currents (Î k ) by the end of current odulation period. he ain objective of deadbeat control is to generate reference values of stator currents (I * ) at the end of next odulation period. Considering (6)-(9) and by knowing the estiated value of (Î k ), the desired voltage values for the next odulation period would be: ١٤٠ L V ( k ) ( i iˆ ) riˆ L iˆ d * d d d s d q q ١٤١ L V ( k ) ( i iˆ ) riˆ ( L iˆ ) q * q q q s q d d p ١٤٢ L V ( k ) ( i iˆ ) riˆ 3 L iˆ d 3 * d3 d3 d3 s d3 q3 q3 ١٤٣ ١٤٤ ١٤٥ ١٤٦ L V ( k ) ( i iˆ ) riˆ 3 ( L iˆ ) q3 * q3 q3 q3 s q3 d3 d3 p3 (2) As it can be seen fro (2), calculated values of reference voltages V* dqd3q3 are dependent on estiated values of stator currents in their corresponding directions. As a result, the accuracy of estiation
8 ١٤٧ ١٤٨ ١٤٩ ١٥٠ ethod can affect the final precision of predictive deadbeat control. Extended Kalan Filter is an estiation ethod which can reduce the ipact of syste paraeter variation. In this paper, Extended Kalan Filter is developed for five-phase BLDC achine to estiate the stator phase currents in each direction. his ethod will be explained in the following section. ١٥١ ١٥٢ ١٥٣ ١٥٤ ١٥٥ ١٥٦ 3. Generator Current Estiation In the proposed controlling algorith, EKF is used to estiate generator currents at the end of current odulation period. Due to its ore practical aspects, stationary reference frae is selected in the developent of EKF equations. he transforation atrix between phase- and stationary-reference fraes can be siply derived by setting 0 in (5): ١٥٧ ١٥٨ ١٥٩ ١٦٠ ١٦١ ١٦٢ ١٦٣ F F 33o 0 abcde Nonlinear state odel presentation of five-phase BLDC generator can be written as: where x f( x) Bu() t w() t yt () cxt () vt () (3) (4) ١٦٤ x i i i3 i3 i o e e ١٦٥ u v v v3 v3 v o ١٦٦ ١٦٧ y i i i3 i3 i o (5)
9 ١٦٨ R i L R i L R i L f( x) R i L s p e d Ld s p q Lq s p3 3 d3 Ld3 s p3 3 q3 Lq3 sine ecose 3 esin3 e 3 ecos3 e Rs i o L o 0 e ١٦٩ (6) ١٧٠ Ld L q 0 0 Ld B Lq L o ١٧١ (7) ١٧٢ C ١٧٣ ١٧٤ ١٧٥ ١٧٦ (8) In addition, w(t) represents syste noise vector, and v(t) is the easureent noise vector, and it is assued that w(t) and v(t) are uncorrelated and have zero-ean stochastic values. Ipleented EKF consists of two ain steps. In the first step, a prediction of digitalized syste states ١٧٧ x ) and its covariance ( Pˆk k ) is perfored by knowing the previous estiation of syste states ( ˆk k ١٧٨ ( ˆk k x ) and syste inputs ( uk ) during one sapling period: ١٧٩ xˆ xˆ f( xˆ, u ) kk k k s k k k ١٨٠ ˆ ˆ ˆ P P FP F Q (9) kk k k k k
10 ١٨١ ١٨٢ In the second step, the easured quantities will be used to correct the estiated states and covariance atrix: ١٨٣ ١٨٤ xˆkk xˆk k Kk yk h( xˆkk ) Pˆ Pˆ K HPˆ kk kk k kk ١٨٥ ˆ ( ˆ K P H HP H R) k k k k k ١٨٦ ١٨٧ ١٨٨ ١٨٩ ١٩٠ ١٩١ where H is the easureent atrix and K is faous as Kalan gain [5]. Estiated values of syste states ( x ˆk k ) can now be used in MPC algorith to calculate the required reference voltages of the next odulation period. Figure 2 illustrates the general structure of proposed EKF-based deadbeat control while odulation frequency is 0 khz, and controlling algorith frequency is 4 khz. (20) ١٩٢ * reference current calculation Eq. () * i ( k) d q d q 3 3 iˆ( k) d q d 33 q iˆ( k) 3 3o o 3 3 dqdqo 3 3 Iproved deadbeat control Eq. (2) x ˆk k pˆ kk v * ( k ) o * v ( k ) d q d 3 q khz dqdqo 3 3 o Gain Calculation x Eq. (20) ˆk k k k pˆ kk 3 3 Correction x Eq. (20) ˆk k pˆ kk EKF 3 3o abcde Correction x xˆk k ˆk k Eq. (9) uk pˆ kk pˆ k k v * ( k ) abcde Z vk ( ) abcde ik ( ) abcde 4 khz easureent ١٩٣ 5-phase BLDC v abcde Modulation 0 khz ١٩٤ ١٩٥ ١٩٦ Fig. 2: General structure of proposed EKF-based deadbeat control
11 ١٩٧ ١٩٨ ١٩٩ ٢٠٠ ٢٠١ ٢٠٢ ٢٠٣ 4. Sensitivity of Proposed EKF-PDC - Siulations Siulations are conducted to evaluate the sensitivity of proposed EKF-PDC ethod. Five-phase BLDC generator is siulated at -pu of its rated speed, and while delivering its noinal power. he paraeters of siulated generator are brought in able I which are also correspondent to their real values in laboratory test bench. able I: Electrical (easured) paraeters of five-phase BLDC generator (used both in siulations and experiental evaluations) ٢٠٤ ٢٠٥ Stator Resistance Stator Inductance Noinal orque L aa L ab L ac Noinal Phase Current DC-bus Rated Voltage Peranent Magnet Flux 0. Ω 500 uh 35 uh 42 uh 32 N 9 Ap (rs) 48 V Wb ٢٠٦ ٢٠٧ ٢٠٨ 4.. Siulation Steps Siulations consist of five different steps. In each step a different source of disturbance is introduced to the syste. Five steps of siulations are suarized in able II. ٢٠٩ ٢١٠ able II: Considered paraeters during each siulation est nuber Introduced disturbance Ideal Condition 2 dc-link voltage drop 3 Nonlinear Inverter Characteristics 4 Inaccurate phase resistance 5 Inaccurate PM flux ٢١١
12 ٢١٢ ٢١٣ ٢١٤ ٢١٥ ٢١٦ ٢١٧ ٢١٨ ٢١٩ ٢٢٠ ٢٢١ ٢٢٢ ٢٢٣ ٢٢٤ ٢٢٥ ٢٢٦ he first case (test-) is dedicated to ideal operation. Precise odel of generator is used in the estiation block, and ideal switches are used in inverter block. he second case (test-2) is related to the ipact of dc-bus voltage drop in the inverter block. During test-2, dc-link voltage is reduced to 0.8 its rated value. he third case (test-3) is related to inverter nonlinear characteristics. Considered inverter characteristics include 3us of dead tie, 0.06Ω and 0.04Ω of forward resistance for anti-parallel diodes and IGBs in each leg, and oreover, 2.7 V and.85 V of voltage drop for anti-parallel diodes and IGBs respectively. Generator paraeters are the ain concern of next siulations (tests 4 and test 5). Higher operational teperature and conductor skin effect can lead to higher values of operational stator resistance. During test-4 stator resistance is increased fro 0.Ω to 0.2Ω to study the sensitivity of proposed ethod to resistance changes. High teperatures, aging and echanical stresses can reduce the strength of rotor agnets in a BLDC generator. o evaluate the sensitivity of proposed ethod to agnet flux variations, during test-5 agnetic flux of generator rotor is reduced to 0.8 its rated value. ٢٢٧ ٢٢٨ ٢٢٩ ٢٣٠ ٢٣١ ٢٣٢ ٢٣٣ ٢٣٤ ٢٣٥ 4.2. Siulation Results Under each condition, the behaviour of proposed controlling ethod can be evaluated by easuring stator current errors in different directions. In each siulation test, stator current errors are easured at the end of current estiation step and voltage application step. hat is the error between estiated (Î k ) and easured (I k+ ) current values by the end of current odulation period (e ), and the error between real (I k+2 ) and reference current values (I*) at the end of next odulation period (e 2 ). In each case the energy of e and e 2 are integrated on one period of fundaental frequency under steady states. As a result, during each test E represents the error energy in current estiation step, and E 2 is the energy of stator current errors after copletely executing one round of control algorith:
13 ٢٣٦ E ˆ I j( K) I j( K ) jd, q, d3, q3, o 2 ٢٣٧ * E2 I j I j( K 2) jd, q, d3, q3, o 2 ٢٣٨ ٢٣٩ ٢٤٠ ٢٤١ ٢٤٢ (2) Coputed values of estiation error energy (E ) and voltage application error energy (E 2 ) are suarized in Fig. 3. Moreover, siulated values of generated electrical torque under each condition are suarized in Fig. 4. In all conditions, rated value of torque is generated while the generator is rotating in its noinal speed and under steady state. E (pu) x Estiation Error Energy-E (pu) E2 (pu) otal Error Energy-E2 (pu) ٢٤٣ est Nuber est Nuber ٢٤٤ Fig. 3: Siulated values of current errors in estiation step (E ) and voltage application step (E 2 ) of control algorith ٢٤٥ Steady-State torque ( pu) est Nuber ٢٤٦ ٢٤٧ 0 2Pi 4Pi 6Pi 8Pi 0Pi 2Pi Electrical Angle (rad) Fig. 4: Generated electrical torque of five-phase BLDC generator during test- to test-5 ٢٤٨ ٢٤٩ ٢٥٠ ٢٥١ ٢٥٢ 4.3. Discussion on Siulation Results In each case, the estiation step of control algorith is realized by EKF, and after that, the required reference voltages are directly calculated by using generator equations. As it can be seen fro Fig. 3, ipleentation of EKF in the estiation step leads to lower values of error energy (E ) for all of the
14 ٢٥٣ ٢٥٤ ٢٥٥ ٢٥٦ ٢٥٧ ٢٥٨ ٢٥٩ ٢٦٠ ٢٦١ ٢٦٢ ٢٦٣ siulated tests. Standard deviations of E and E 2 after copleting all of these tests are S =4.007e-004 and S 2 =0.024, respectively. Lower aplitude of S is due to autoatic adaptation of EKF to syste variations in each test. Error energy values of E and E 2 while working with a healthy achine and under ideal conditions are respectively 8.92e-005 and During test 2, the aplitude of dc-link voltage is reduced by 20% while its correspondent value in controlling algorith is not changed. Coparing to healthy conditions, the increent of current error in estiation level (E ) is 22%. However, as generator equations are directly used during voltage application level, the increent of E 2 during this step is higher (08%). Again, the ain reason of less error in the estiation step is adaptation of EKF to syste variations. Equation (2) is used during voltage application step. Considering this equation, in the case of dc-link voltage drop it is possible to write the following equation in d -direction: ٢٦٤ ˆ i ( k 2) i ( k) V ( k ) V ( k ) riˆ ( k) L iˆ ( k) d d d d s d q q L d ٢٦٥ ˆ ( ) ( ) ˆ ( ) ˆ i k V k ri k L i ( k) V ( k ) d d s d q q d L d Ld ٢٦٦ ٢٦٧ ٢٦٨ ٢٦٩ ٢٧٠ ٢٧١ ٢٧٢ i ( k 2) i ( k 2) d nor d where V ( ) k is the iposed voltage in d -direction due to existing error in dc-bus voltage, ( 2) d d nor (22) i k is calculated current aplitude under noral operation, and i ( 2) k is the additional current coponent which is generated due to existing error in dc-link voltage. As it can be seen, increasing the switching frequency (reduction of ) and increasing the stator inductances can directly reduce the error of stator current. However, final aount of current error is also dependent on the aplitude of applied voltage d ٢٧٣ V d (k+) in (k+) th odulation period. Following the sae procedure, stator current error in other ٢٧٤ directions due to dc-link voltage drop can be calculated as: ٢٧٥
15 ٢٧٦ i ( k 2) V ( k ) q q Lq ٢٧٧ i ( k 2) V ( k ) q3 q3 Lq 3 ٢٧٨ i ( k 2) V ( k ) d3 d3 Ld 3 ٢٧٩ ٢٨٠ ٢٨١ ٢٨٢ ٢٨٣ ٢٨٤ ٢٨٥ ٢٨٦ ٢٨٧ ٢٨٨ ٢٨٩ (23) est 3 is dedicated to nonlinear characteristics of the inverter. As it can be seen fro Fig.3, this test is correspondent to the highest aplitude of E and highest torque ripples. In other words, ipleented EKF during estiation step has ore difficulties in adapting the syste to reduce the ipact of inverter nonlinear characteristics. he ain reason of this fact is continuous variation of voltage drop along siulated seiconductors. Forward voltage drops in seiconductors can be considered as a periodic disturbance in dc-link voltage. he aplitude of this voltage disturbance changes each tie the current flow path changes fro an IGB to its anti-parallel diode or vice versa. Siulated values of stator phase currents and applied voltage of phase A are shown in Fig. 5 while nonlinear characteristics of the inverter are included in siulations. As it can be seen, continuous periodic change of applied voltage (while stator current is crossing the zero) is the ain reason of higher estiation error and higher torque ripple. ٢٩٠ ٢٩١ ٢٩٢ I (pu), and V/(Vdc/2) Electrical Angle (rad) Fig. 5: Siulated values of stator phase current including nonlinear characteristics of inverter V I ٢٩٣
16 ٢٩٤ ٢٩٥ ٢٩٦ ٢٩٧ ٢٩٨ ٢٩٩ ٣٠٠ ٣٠١ ٣٠٢ ٣٠٣ ٣٠٤ Nonlinear characteristics of the inverter have also led to higher values of E 2. his tie, generated voltage drops along the conducting seiconductors change the effective value of applied voltages to generator stator phases, and this fact leads to higher values of current error. Siilar to the case of dc-link voltage reduction, in this case higher values of stator inductance and odulation frequency can reduce the aplitude of E 2. During test 4, stator resistance is changed fro 0.Ω to 0.2Ω in generator block while its value is reained fixed in controlling algorith. Copering to test- (ideal operational conditions), E increent is 22% which is uch less than E 2 increent (44%). his fact is due to effective adaptation of EKF respect to resistance change. In addition, a fixed change in stator resistances will not lead to noticeable torque ripples. By the end of each odulation period, stator phase current in d -direction can be calculated as: ٣٠٥ ٣٠٦ ٣٠٧ ٣٠٨ ٣٠٩ ٣١٠ ٣١١ ˆ i ( k 2) i ( k) V ( k ) 2 riˆ ( k) L iˆ ( k) d d d s d q q L d ˆ ( ) ( ) ˆ ( ) ˆ i k V k ri k L i ( k) riˆ ( k) d d s d q q s d Ld Ld i ( k 2) i ( k 2) d nor d where i d (k+2) nor is stator current value in the case of operating under noral conditions, and i ( 2) k d (24) is the error which is iposed to the syste due to higher values of stator phase resistance. his error in other directions can be calculated as: ٣١٢ ٣١٣ i ( k 2) riˆ ( k) L q s q q i ( k 2) riˆ ( k) L d3 s d3 d 3 ٣١٤ i ( k 2) riˆ ( k) L q3 s q3 q3 (25)
17 ٣١٥ ٣١٦ ٣١٧ ٣١٨ ٣١٩ ٣٢٠ ٣٢١ ٣٢٢ ٣٢٣ As it can be seen, generated value of E 2 is directly proportional with stator resistance error and odulation period. Moreover, higher inductance values can lead to less error in stator phase currents. During test 5, generated flux of PM generator is decreased by 20%. his case can happen by aging, high operational teperatures, long-tie echanical vibration or high current aplitudes in d-directions. Although, generated torque ripples are negligible in this case, but coparing to the ideal case (noral operation), both E and E 2 are increased by 22% and 46% respectively. Again the increent of E is not as high as E 2 which is due to autoatic adaptation of estiation step by its ipleented EKF. he ain effect of PM flux variations on proposed controlling algorith will show its effect on q - and q 3 - directions. Considering (2) it is possible to write: ٣٢٤ ٣٢٥ ˆ i ( k 2) i ( k) V ( k ) 2 riˆ ( k) L iˆ ( k) q q q s q d d p p L q ٣٢٦ ˆ ˆ ˆ iq ( k) Vq ( k ) 2 ri s q( k) Ldid( k) p p Lq Lq ٣٢٧ i ( k 2) i ( k 2) q nor q ٣٢٨ (26) ٣٢٩ ˆ i ( k 2) i ( k) V ( k ) 2 riˆ ( k) 3 L iˆ ( k) 3 q3 q3 q3 s q3 d3 d3 p p3 L q3 ٣٣٠ ˆ 3 ˆ ˆ iq ( k) Vq3( k ) 2 ri s q3( k) Ld 3id 3( k) 3 p3 p3 Lq 3 Lq 3 ٣٣١ i ( k 2) i ( k 2) q3 nor q3 ٣٣٢ ٣٣٣ ٣٣٤ ٣٣٥ (27) where i q (k+2) nor and i q3 (k+2) nor are stator current in q - and q 3 -directions by the end of (k+) th odulation period and under noral conditions. In addition, i ( 2) k and i ( 2) 3 k are the introduced error in this direction due to variation of rotor PM flux. q q
18 ٣٣٦ 5. Experiental Evaluation of Proposed EKF-PDC Method ٣٣٧ ٣٣٨ ٣٣٩ 5.. est Bench Structure Experiental tests are conducted in laboratory to evaluate the behaviour of proposed controlling ethod. Figure 6 illustrates the experiental test bench. ٣٤٠ Five-phase inverter dc-power supply Host Coputer Load 5-phase Inverter Gate pulses crio 3-phase PMSM) vk ( ) abcde Encoder (9000-pulses/revolution) dspace ik ( ) abcde orque ransducer DS005 dspace 5-phase BLDC Mechanical link between five-phase otor and load ٣٤١ ٣٤٢ Internal Structure of five-phase BLDC Fig. 6: General configuration of experiental test bench ٣٤٣ ٣٤٤ ٣٤٥ ٣٤٦ ٣٤٧ ٣٤٨ ٣٤٩ Ipleented five-phase BLDC generator incorporates a double-layer winding with fractional-slot structure. Siilar to [6] and [7], induced back-emf wavefor of this achine contain % of 3 rd haronic. A five-leg two-level inverter is used to generate the required voltages. his inverter is controlled by a dspace. he ain three tasks of the dspace odule include ) control algorith execution, 2) five-phase carrier-based odulation, and 3) pulse generation for IGB gate drivers. he frequency of control
19 ٣٥٠ ٣٥١ ٣٥٢ ٣٥٣ ٣٥٤ ٣٥٥ ٣٥٦ ٣٥٧ algorith in dspace is set on 4 khz. his frequency is different fro odulation frequency which is 0 khz. Current easureent signals are generated by five Hall Effect sensors, and rotor position is easured by using an increental encoder with 9000-pulses per revolution. he speed is fixed by the load syste, and generated torque is controlled by five-phase BLDC generator. As a result, developed controlling algoriths for five-phase BLDC generator are equivalent to torque/current control. he load syste is a coercial three-phase servo drive known as SINAMICS- S20. A real-tie controller known as copact Rio (ade by National Instruents) is used to establish the required interference between SINAMICS-S20 and host PC. ٣٥٨ ٣٥٩ ٣٦٠ ٣٦١ ٣٦٢ ٣٦٣ ٣٦٤ ٣٦٥ ٣٦٦ 5.2. Experiental Results and Discussion Measured values of generator stator currents and echanical torque are shown in Fig. 7 while changing the reference value of torque fro 0.33 pu 0.66 pu.0 pu 0.66 pu 0.33 pu. Due to liited nuber of available oscilloscope channels, each part of this figure only contains 4 easureents. In addition, to have a better evaluation on dynaic behaviour of proposed controlling ethod, easured values of echanical torque and stator currents are shown in Fig. 8 for two periods of fundaental current coponent. Proposed current controlling ethod does not include any integrator, and as a result there is alost no overshoot in easured values of stator phase currents and generated torque. ٣٦٧ ٣٦٨ ٣٦٩ ٣٧٠ 5.3. ransient Analysis of Proposed EKF-PDC Method Regarding the deadbeat nature of ipleented control algorith, torque rise tie is expected to be as long as one odulation period (0.25 s). However during transient states, easured value of torque risetie is 0.53 s which is alost 2 ties its expected value.
20 Stator Currents (pu) ٣٧١ ٣٧٢ Electrical Angle (rad) (a).4.2 Generated orque (pu) Reference orque (pu) orque Error (absolute value) orque (pu) ٣٧٣ ٣٧٤ ٣٧٥ ٣٧٦ ٣٧٧ Electrical Angle (rad) (b) Fig. 7: Dynaic behaviour of proposed controlling ethod while changing reference torque fro 0.33 pu 0.66 pu.0 pu 0.66 pu 0.33 pu,), (a) first easureent - generator currents in four phases. Due to liited nuber of oscilloscope channels, I E is not easured directly, (b) second easureent - reference and real values of torque (pu) 0 (pu) 0 ٣٧٨ ٣٧٩ ٣٨٠ ٣٨١ Electrical Angle (rad) Electrical Angle (rad) Fig. 8: Measured value of generated torque during transient states, (a) changing reference torque fro 0.33 pu 0.66 pu, (b) changing reference torque fro 0.66 pu.0 pu. Due to liited value of oscilloscope channels, only I A, I B, I C and torque are shown in each case
21 ٣٨٢ ٣٨٣ ٣٨٤ ٣٨٥ ٣٨٦ ٣٨٧ he ain reason of longer rise-tie is liited value of dc-link voltage. Assuing that the ain coponent of stator currents in each situation is i q and stator currents in the reaining directions are alost zero, the required voltage during transient states in different directions can be calculated fro equation (2) and able II. able III is a suary of required voltages in d q d 3 q 3 -directions during transient states, and their required peak-to-peak voltage in phase reference frae. able III: he required voltage to coplete the transient state in one controlling loop (0.25 s) ransient state V d V q V d3 V q3 V ABCDE (p-p) 0.33 pu 0.66 pu V V 0 V V 58 V 0.66 pu.0 pu V V 0 V V 59 V ٣٨٨ ٣٨٩ ٣٩٠ ٣٩١ ٣٩٢ ٣٩٣ ٣٩٤ ٣٩٥ ٣٩٦ ٣٩٧ ٣٩٨ ٣٩٩ As it can be seen, the required peak-to-peak value of applied voltage during each transient is ore than dc-link value (48 V), which extends the rise-tie to two consecutive controlling loops. It is iportant to note that the controlling algorith is being executed with a frequency of 4 khz while odulator frequency is 0 khz. Higher frequency of odulator is the ain reason of existing ripples during transient states (rise-tie) of stator currents and electrical torque in Fig. 8. Dynaic behaviour of generated torque is also considered. o have an analytical evaluation, the energy of torque error is integrated on four consecutive periods of stator phase currents. Both transient and steady state operation are considered in this evaluation torque saples are easured, and in the case of transients, reference value of torque is changed in the iddle of integration period. Integrated values of torque error are suarized in able IV for each operational condition. able IV: he energy of torque error during different operational conditions orque Error Energy [N 2 ] (pu) Steady State Rated Conditions.08e pu 0.66 pu.83e-005 ransient State 0.66 pu.0 pu.98e-005 ٤٠٠
22 ٤٠١ ٤٠٢ ٤٠٣ ٤٠٤ ٤٠٥ As it can be seen, the iniu value of torque error energy is related to steady-state operation. Under this condition, dc-link voltage is used to cope with stator resistance voltage drop, and induced back-emf. While working in transients, dc-link voltage should also be used to cope with inductance voltage drops in each direction. As it can be seen, the energy of torque error is higher in transient states. he ain reason of higher torque error in transients is dc-link liitations during rise tie periods. ٤٠٦ ٤٠٧ ٤٠٨ ٤٠٩ ٤١٠ ٤١١ ٤١٢ ٤١٣ Sensitivity Analysis of Proposed EKF-PDC Sensitivity of proposed controlling ethod is experientally evaluated respect to various syste changes. Coparing to siulation section, experiental evaluation of sensitivity has soe liitations. he first liitation is related to inverter block. As five-phase BLDC generator is always controlled by an inverter, it is not possible to evaluate the ideal case (no voltage drop in seiconductors and zero value of dead tie). In addition, agnetic flux of rotor agnets is a fixed value during all tests. Conducted tests to evaluate the sensitivity of proposed ethod are suarized in able V. able V: he differences between controlling block assuptions and real situation difference between controlling unit assuption and real situation experient controlling unit Assuption real situation eperient- experient-2 experient-3 Ideal inverter with no voltage drop and no dead tie Ideal inverter and noinal value of dc-link voltage Ideal inverter and rated value of stator resistance (0.Ω) Real inverter Real inverter and 20% voltage drop in dc-link voltage Real inverter and 0.2Ω as stator resistance ٤١٤ ٤١٥ ٤١٦ ٤١٧ In the first experient (experient-), precise values of generator paraeters are used in control algorith. In addition, inverter block is considered ideal and nonlinear characteristics of its seiconductors are not considered in controlling algorith.
23 ٤١٨ ٤١٩ ٤٢٠ ٤٢١ ٤٢٢ ٤٢٣ ٤٢٤ ٤٢٥ In the next step (experient-2), stator phase resistances are changed fro 0.Ω to 0.2Ω by adding external resistances to generator terinals, and at the sae tie, rated values of stator resistances are used in controlling algorith. In the third step (experient-3), the aplitude of dc-link voltage is reduced by 20%, and at the sae tie rated value of dc-link voltage is used in controlling algorith. Siilar to siulation section, in each experient the difference between real and reference values of stator phase currents are easured (current error), and after that, its energy is integrated over one period of fundaental electrical frequency: ٤٢٦ ٤٢٧ ٤٢٨ * E I j I j( K 2) jd, q, d3, q3, o 2 (28) Figure 9 shows the energy of stator current errors for each experient. 0. ٤٢٩ ٤٣٠ otal Eror Energy (pu) Experient Nuber Fig. 9: he energy of current errors during each experient ٤٣١ ٤٣٢ ٤٣٣ ٤٣٤ ٤٣٥ ٤٣٦ ٤٣٧ he iniu energy value of stator current errors is correspondent to experient-. During this experient the ain source of current error is nonlinear characteristics of inverter. As it can be seen fro Fig. 9, the energy of current errors during experient- is ore than 50% its value during other experients (5% its value during experient-2 and 63% its value during experient-3). As electrical achine is always fed by a real inverter, it is possible to write: E 0.5 ( E E dc link ) (29) nonlinear INV nonlinear INV
24 ٤٣٨ and ٤٣٩ E 0.5 ( E E ) nonlinear INV nonlinear INV Rs ٤٤٠ ٤٤١ ٤٤٢ ٤٤٣ (30) while E nonlinear INV, E dc-link, and E Rs are respectively the energy of stator current errors due to nonlinear inverter characteristics, inaccurate dc-link voltage, and stator resistance increent. Equations (29) and (30) respectively result in: ٤٤٤ E nonlinear INV Edc link ٤٤٥ (3) ٤٤٦ and ٤٤٧ E nonlinear INV E Rs ٤٤٨ ٤٤٩ ٤٥٠ ٤٥١ ٤٥٢ ٤٥٣ ٤٥٤ ٤٥٥ ٤٥٦ ٤٥٧ ٤٥٨ (32) In other words, the energy of stator current errors due to inverter nonlinear characteristics is higher than its value due to inaccurate dc-link voltage and inaccurate stator resistance. his result is in accordance with siulation results where the axiu value of stator current errors was due to inverter nonlinear characteristics. In addition, the energy of stator current errors in experient-3 is higher than its value in experient-2. Regarding able V, it is possible to write: ( E E ) ( E E ) nonlinear INV dclink nonlinear INV Rs (33) or E dclink E Rs ٤٥٩ (34)
25 ٤٦٠ ٤٦١ In other words, the energy of stator current errors due to inaccurate dc-link voltage is higher than its value due to inaccurate stator resistance which is again in accordance with siulation results. ٤٦٢ ٤٦٣ ٤٦٤ ٤٦٥ ٤٦٦ ٤٦٧ ٤٦٨ ٤٦٩ ٤٧٠ ٤٧١ ٤٧٢ ٤٧٣ ٤٧٤ ٤٧٥ ٤٧٦. Conclusion Five-phase BLDC generators are becoing ore popular in low aintenance applications of wind power plants. In such applications, fast and robust control of stator phase currents has a high priority. o iprove these two aspects, a new predictive deadbeat controlling ethod is proposed in this paper to control the generated electrical torque and stator currents of a five-phase BLDC generator. Extended Kalan Filter is used in the estiation step of proposed ethod. Siulations are developed to evaluate the sensitivity of proposed ethod respect to different syste variations. In each case, the energy of stator current errors is easured by the end of estiation step and voltage application step of proposed algorith. It is shown that inverter nonlinear characteristics and dc-link voltage drop result in ore current error both in estiation step and voltage application step. In addition, proposed controlling ethod is experientally evaluated on a five-phase BLDC generator. Although the objective of proposed EKF-PDC ethod is to eliinate the stator current errors in one odulation period, but liited values of dc-link capacitor can reduce the speed of proposed controlling ethod. Proposed ethod is able to generate constant torque with no overshoot. ٤٧٧ ٤٧٨ ٤٧٩ ٤٨٠ ٤٨١ ٤٨٢ References [] S. Vaez-Zadeh, A.R. Ghasei, Design optiization of peranent agnet synchronous otors for high torque capability and low agnet volue, Electric Power Systes Research, Vol. 74, No. 2, pp , 2005 [2] Florent Morel, Xuefang Lin-Shi, Jean-Marie Rétif, Bruno Allard, A predictive current control applied to a peranent agnet synchronous achine, coparison with a classical direct torque control, Electric Power Systes Research, Vol. 78, No. 8, pp , 2008
26 ٤٨٣ ٤٨٤ ٤٨٥ ٤٨٦ ٤٨٧ ٤٨٨ ٤٨٩ ٤٩٠ ٤٩١ ٤٩٢ ٤٩٣ ٤٩٤ ٤٩٥ ٤٩٦ ٤٩٧ ٤٩٨ ٤٩٩ ٥٠٠ ٥٠١ ٥٠٢ ٥٠٣ ٥٠٤ ٥٠٥ ٥٠٦ ٥٠٧ ٥٠٨ ٥٠٩ ٥١٠ ٥١١ [3] J.A. Rossiter, Discussion on: Min-ax Model Predictive Control of Nonlinear Systes: A Unifying Overview on Stability, European Journal of Control, Vol. 5, No., pp , 2009 [4]. Geyer, G. Papafotiou, M. Morari, Model predictive direct torque control Part I: Concept, algorith and analysis, IEEE rans. Ind. Electron., vol. 56, no. 6, pp , [5] José A. De Doná, Graha C. Goodwin, María M. Seron, Anti-windup and Model Predictive Control: Reflections and Connections, European Journal of Control, Vol. 6, No. 5, pp , 2000 [6] S. Bolognani, L. Peretti, M. Zigliotto, Design and ipleentation of odel predictive control for electrical otor drives, IEEE rans. Ind. Electron., vol. 56, no. 6, pp , [7] M. Monfared, H. Rastegar, Design and experiental verification of a dead beat power control strategy for low cost three phase PWM converters, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systes, Vol. 42, No., pp , 202 [8] R. Gregor, F. Barrero, S. oral, M. J. Durán, M. R. Arahal, J. Prieto, J. L. Mora, Predictive-SVPWM current control ethod for asyetrical dual-three phase induction otor drives, IE Journal on Electric Power Appl., Vol. 4, No., pp , 200 [9] M.R. Arahal, M.J. Duran, F. Barrero, S.L. oral, Stability analysis of five-phase induction otor drives with variable third haronic injection, Electric Power Systes Research, Vol. 80, No. 2, pp , 200 [0] G.K Singh, Multi-phase induction achine drive research a survey, Electric Power Systes Research, Vol. 6, No. 2, pp , 2002 [] Y. XI, D. LI, S. LIN, Model Predictive Control Status and Challenges, Acta Autoatica Sinica, Vol. 39, No. 3, pp , 203 [2] Lingling Fan, Yasser Wehbe, Extended Kalan filtering based real tie dynaic state and paraeter estiation using PMU data, Electric Power Systes Research, Vol. 03, pp , 203, [3] L. Suerer, J.Y. Keller, M. Darouach, Robust Fault Diagnosis with a wo-stage Kalan Estiator, European Journal of Control, Vol. 3, No. 3, pp , 997 [4] G. Hock Beng Foo, Xinan Zhang, D. M. Vilathgauwa, Interior Peranent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Based on an Extended Kalan Filter, IEEE rans. on Ind. Elec., Vol. 60, No. 8, 203 [5] F. Alonge, F. D'Ippolito, A.Sferlazza, Sensorless Control of Induction-Motor Drive Based on Robust Kalan Filter and Adaptive Speed Estiation,, IEEE rans. on Ind. Elect., Vol. 6, No. 3, pp , 204 [6] S. Dwari, L. Parsa, Fault-olerant Control of Five-Phase Peranent-Magnet Motors with rapezoidal Back EMF, IEEE rans. Ind. Electron., Vol. 58, No. 2, pp , 20
27 ٥١٢ ٥١٣ ٥١٤ [7] A. Mohaadpour, L. Parsa, A Unified Fault-olerant Current Control Approach for Five-Phase PM Motors with rapezoidal Back EMF Under Different Stator Winding Connections, IEEE rans. Power Electron., Vol. 28, No. 7, pp
DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF INDUCTION MACHINES CONSIDERING THE IRON LOSSES
 DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF INDUCTION MACHINES CONSIDERING THE IRON LOSSES TRUC PHAM-DINH A thesis subitted in partial fulfilent of the requireents of Liverpool John Moores University for the degree of Doctor
DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF INDUCTION MACHINES CONSIDERING THE IRON LOSSES TRUC PHAM-DINH A thesis subitted in partial fulfilent of the requireents of Liverpool John Moores University for the degree of Doctor
Sensorless Control of Induction Motor Drive Using SVPWM - MRAS Speed Observer
 Journal of Eerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 2 (3): 509-513 Journal Scholarlink of Eerging Research Trends Institute in Engineering Journals, 2011 and Applied (ISSN: 2141-7016)
Journal of Eerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 2 (3): 509-513 Journal Scholarlink of Eerging Research Trends Institute in Engineering Journals, 2011 and Applied (ISSN: 2141-7016)
Control of Brushless DC Motor with Direct Torque and Indirect Flux using SVPWM Technique
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(2), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i2/71211, Septeber 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Control of Brushless DC Motor with Direct Torque
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(2), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i2/71211, Septeber 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Control of Brushless DC Motor with Direct Torque
Self-Erecting Inverted Pendulum: Swing up and Stabilization Control
 Self-Erecting Inverted Pendulu: Swing up and Stabilization Control S. McGilvray (Winner of the IEEE Life Meber ward for best paper fro the Central Canada Council for the IEEE Student Paper Contest, ) Contents
Self-Erecting Inverted Pendulu: Swing up and Stabilization Control S. McGilvray (Winner of the IEEE Life Meber ward for best paper fro the Central Canada Council for the IEEE Student Paper Contest, ) Contents
An Improved Particle Filter with Applications in Ballistic Target Tracking
 Sensors & ransducers Vol. 72 Issue 6 June 204 pp. 96-20 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co An Iproved Particle Filter with Applications in Ballistic arget racing
Sensors & ransducers Vol. 72 Issue 6 June 204 pp. 96-20 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co An Iproved Particle Filter with Applications in Ballistic arget racing
This is a repository copy of Analytical optimisation of electromagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance motor.
 This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
This is a repository copy of Analytical optiisation of electroagnetic design of a linear (tubular) switched reluctance otor. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/907/
Statistical Logic Cell Delay Analysis Using a Current-based Model
 Statistical Logic Cell Delay Analysis Using a Current-based Model Hanif Fatei Shahin Nazarian Massoud Pedra Dept. of EE-Systes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089 {fatei, shahin,
Statistical Logic Cell Delay Analysis Using a Current-based Model Hanif Fatei Shahin Nazarian Massoud Pedra Dept. of EE-Systes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089 {fatei, shahin,
Zero-Voltage Switching Post Regulation Scheme for Multi-output Forward Converter with Synchronous Switches
 Zero-oltage witching Post Regulation chee for Multi-output Forward Converter with ynchronous witches Jae-Kuk Ki tudent Meber IEEE KAIT Daejeon 305-70 Republic of Korea jaekook@angel.kaist.ac.kr eong-wook
Zero-oltage witching Post Regulation chee for Multi-output Forward Converter with ynchronous witches Jae-Kuk Ki tudent Meber IEEE KAIT Daejeon 305-70 Republic of Korea jaekook@angel.kaist.ac.kr eong-wook
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition. Perceptrons and Support Vector Machines
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley osig 1 Winter Seester 2018 Lesson 6 27 February 2018 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector achines Notation...2 Linear odels...3 Lines, Planes
Model Fitting. CURM Background Material, Fall 2014 Dr. Doreen De Leon
 Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
Model Fitting CURM Background Material, Fall 014 Dr. Doreen De Leon 1 Introduction Given a set of data points, we often want to fit a selected odel or type to the data (e.g., we suspect an exponential
ANALYSIS OF HALL-EFFECT THRUSTERS AND ION ENGINES FOR EARTH-TO-MOON TRANSFER
 IEPC 003-0034 ANALYSIS OF HALL-EFFECT THRUSTERS AND ION ENGINES FOR EARTH-TO-MOON TRANSFER A. Bober, M. Guelan Asher Space Research Institute, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, 3000 Haifa, Israel
IEPC 003-0034 ANALYSIS OF HALL-EFFECT THRUSTERS AND ION ENGINES FOR EARTH-TO-MOON TRANSFER A. Bober, M. Guelan Asher Space Research Institute, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, 3000 Haifa, Israel
Basic Experiments for High-Torque, Low-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor and a Technique for Reducing Cogging Torque
 Basic Experients for High-Torque, Low-Speed Peranent Magnet Synchronous Motor and a Technique for educing Cogging Torque Kouichi Sato, Jung-Seob Shin, Takafui Koseki and Yasuaki Aoyaa Φ Abstract -- Fully
Basic Experients for High-Torque, Low-Speed Peranent Magnet Synchronous Motor and a Technique for educing Cogging Torque Kouichi Sato, Jung-Seob Shin, Takafui Koseki and Yasuaki Aoyaa Φ Abstract -- Fully
System Design of Quadrotor
 Syste Design of Quadrotor Yukai Gong, Weina Mao, Bu Fan, Yi Yang Mar. 29, 2016 A final project of MECHENG 561. Supervised by Prof. Vasudevan. 1 Abstract In this report, an autonoous quadrotor is designed.
Syste Design of Quadrotor Yukai Gong, Weina Mao, Bu Fan, Yi Yang Mar. 29, 2016 A final project of MECHENG 561. Supervised by Prof. Vasudevan. 1 Abstract In this report, an autonoous quadrotor is designed.
Now multiply the left-hand-side by ω and the right-hand side by dδ/dt (recall ω= dδ/dt) to get:
 Equal Area Criterion.0 Developent of equal area criterion As in previous notes, all powers are in per-unit. I want to show you the equal area criterion a little differently than the book does it. Let s
Equal Area Criterion.0 Developent of equal area criterion As in previous notes, all powers are in per-unit. I want to show you the equal area criterion a little differently than the book does it. Let s
Experimental Design For Model Discrimination And Precise Parameter Estimation In WDS Analysis
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Acadeic Works International Conference on Hydroinforatics 8-1-2014 Experiental Design For Model Discriination And Precise Paraeter Estiation In WDS Analysis Giovanna
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Acadeic Works International Conference on Hydroinforatics 8-1-2014 Experiental Design For Model Discriination And Precise Paraeter Estiation In WDS Analysis Giovanna
Mutual capacitor and its applications
 Mutual capacitor and its applications Chun Li, Jason Li, Jieing Li CALSON Technologies, Toronto, Canada E-ail: calandli@yahoo.ca Published in The Journal of Engineering; Received on 27th October 2013;
Mutual capacitor and its applications Chun Li, Jason Li, Jieing Li CALSON Technologies, Toronto, Canada E-ail: calandli@yahoo.ca Published in The Journal of Engineering; Received on 27th October 2013;
Warning System of Dangerous Chemical Gas in Factory Based on Wireless Sensor Network
 565 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 59, 07 Guest Editors: Zhuo Yang, Junie Ba, Jing Pan Copyright 07, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-49-5; ISSN 83-96 The Italian Association
565 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 59, 07 Guest Editors: Zhuo Yang, Junie Ba, Jing Pan Copyright 07, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-49-5; ISSN 83-96 The Italian Association
2nd Workshop on Joints Modelling Dartington April 2009 Identification of Nonlinear Bolted Lap Joint Parameters using Force State Mapping
 Identification of Nonlinear Bolted Lap Joint Paraeters using Force State Mapping International Journal of Solids and Structures, 44 (007) 8087 808 Hassan Jalali, Haed Ahadian and John E Mottershead _ Γ
Identification of Nonlinear Bolted Lap Joint Paraeters using Force State Mapping International Journal of Solids and Structures, 44 (007) 8087 808 Hassan Jalali, Haed Ahadian and John E Mottershead _ Γ
Simplified Thermal Model of a Radial Flux Motor for Electric Vehicle Application
 Journal of Asian Electric Vehicles, Volue 8, Nuber 2, Deceber 2010 Siplified Theral Model of a adial Flux Motor for Electric Vehicle Application Moez Ayadi 1, Hana Kebaili 2, Mohaed Aine Fakhfakh 3, and
Journal of Asian Electric Vehicles, Volue 8, Nuber 2, Deceber 2010 Siplified Theral Model of a adial Flux Motor for Electric Vehicle Application Moez Ayadi 1, Hana Kebaili 2, Mohaed Aine Fakhfakh 3, and
System Modeling and Control of a Clutch Actuator System for Dual Clutch Transmissions
 Syste Modeling and Control of a Clutch Actuator Syste for Dual Clutch Transissions Jinsung Ki *) Seibu B. Choi ) Heerak Lee ) Jiwoo Kang ) Mandae Hur ) ) Departent of Mechanical Engineering, KAIST, 9 Daehak-ro,
Syste Modeling and Control of a Clutch Actuator Syste for Dual Clutch Transissions Jinsung Ki *) Seibu B. Choi ) Heerak Lee ) Jiwoo Kang ) Mandae Hur ) ) Departent of Mechanical Engineering, KAIST, 9 Daehak-ro,
Improved efficiency of a fan drive system without using an encoder or current sensors
 Improved efficiency of a fan drive system without using an encoder or current sensors Tian-Hua Liu, Jyun-Jie Huang Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science Technology,
Improved efficiency of a fan drive system without using an encoder or current sensors Tian-Hua Liu, Jyun-Jie Huang Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science Technology,
CFD-Parametric Study in Stator Heat Transfer of an Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Machine
 World Acadey of Science, Engineering and Technology CFD-Paraetric Study in Stator Heat Transfer of an Axial Flux Peranent Magnet Machine Alireza Rasekh, Peter Sergeant, Jan Vierendeels Abstract This paper
World Acadey of Science, Engineering and Technology CFD-Paraetric Study in Stator Heat Transfer of an Axial Flux Peranent Magnet Machine Alireza Rasekh, Peter Sergeant, Jan Vierendeels Abstract This paper
Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive
 Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive Vikram S. Sathe, Shankar S. Vanamane M. Tech Student, Department of Electrical Engg, Walchand College of Engineering, Sangli. Associate Prof, Department
Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive Vikram S. Sathe, Shankar S. Vanamane M. Tech Student, Department of Electrical Engg, Walchand College of Engineering, Sangli. Associate Prof, Department
A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive
 ISSN 1 746-7, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 4, pp. 87-94 A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive F. Heydari, A. Sheikholeslami, K.
ISSN 1 746-7, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 4, pp. 87-94 A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive F. Heydari, A. Sheikholeslami, K.
Using a De-Convolution Window for Operating Modal Analysis
 Using a De-Convolution Window for Operating Modal Analysis Brian Schwarz Vibrant Technology, Inc. Scotts Valley, CA Mark Richardson Vibrant Technology, Inc. Scotts Valley, CA Abstract Operating Modal Analysis
Using a De-Convolution Window for Operating Modal Analysis Brian Schwarz Vibrant Technology, Inc. Scotts Valley, CA Mark Richardson Vibrant Technology, Inc. Scotts Valley, CA Abstract Operating Modal Analysis
Torsion Experiment. Encoder #3 ( 3 ) Third encoder/disk for Model 205a only. Figure 1: ECP Torsion Experiment
 Torsion Experient Introduction For the Torsion lab, there are two required experients to perfor and one extra credit assignent at the end. In experient 1, the syste paraeters need to be identified so that
Torsion Experient Introduction For the Torsion lab, there are two required experients to perfor and one extra credit assignent at the end. In experient 1, the syste paraeters need to be identified so that
Maximum Power Point Tracking Method for PMSG-based Wind Energy Conversion Systems using Torque Observer
 International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISS 0973-4562 Volue 13, uber 13 (2018) pp. 11295-11304 Research India Publications. http://www.ripublication.co Maxiu Power Point Tracking Method for
International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISS 0973-4562 Volue 13, uber 13 (2018) pp. 11295-11304 Research India Publications. http://www.ripublication.co Maxiu Power Point Tracking Method for
General Properties of Radiation Detectors Supplements
 Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent Yarouk University Chapter 4: General Properties of Radiation Detectors Suppleents Dr. Nidal M. Ershaidat Overview Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent
Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent Yarouk University Chapter 4: General Properties of Radiation Detectors Suppleents Dr. Nidal M. Ershaidat Overview Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent
MSEC MODELING OF DEGRADATION PROCESSES TO OBTAIN AN OPTIMAL SOLUTION FOR MAINTENANCE AND PERFORMANCE
 Proceeding of the ASME 9 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC9 October 4-7, 9, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA MSEC9-8466 MODELING OF DEGRADATION PROCESSES TO OBTAIN AN OPTIMAL
Proceeding of the ASME 9 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC9 October 4-7, 9, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA MSEC9-8466 MODELING OF DEGRADATION PROCESSES TO OBTAIN AN OPTIMAL
Ufuk Demirci* and Feza Kerestecioglu**
 1 INDIRECT ADAPTIVE CONTROL OF MISSILES Ufuk Deirci* and Feza Kerestecioglu** *Turkish Navy Guided Missile Test Station, Beykoz, Istanbul, TURKEY **Departent of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
1 INDIRECT ADAPTIVE CONTROL OF MISSILES Ufuk Deirci* and Feza Kerestecioglu** *Turkish Navy Guided Missile Test Station, Beykoz, Istanbul, TURKEY **Departent of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
Designing a Permanent Magnet Linear Generator Multi Air-gap Structure using the Finite Element Method.
 Designing a Peranent Magnet Linear Generator Multi Air-gap Structure using the Finite Eleent Method. Pierre Kenfack, Daniel Matt, and Philippe Enrici Institute of Electronics and Systes, University Montpellier,
Designing a Peranent Magnet Linear Generator Multi Air-gap Structure using the Finite Eleent Method. Pierre Kenfack, Daniel Matt, and Philippe Enrici Institute of Electronics and Systes, University Montpellier,
Electric Power System Transient Stability Analysis Methods
 1 Electric Power Syste Transient Stability Analysis Methods João Pedro de Carvalho Mateus, IST Abstract In this paper are presented the state of the art of Electric Power Syste transient stability analysis
1 Electric Power Syste Transient Stability Analysis Methods João Pedro de Carvalho Mateus, IST Abstract In this paper are presented the state of the art of Electric Power Syste transient stability analysis
WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN 2011
 WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN 011 WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING 011 SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN WIRELESS
WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN 011 WIRELESS DRIVE OF PIEZOELECTRIC COMPONENTS SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING 011 SATYANARAYAN BHUYAN WIRELESS
9. Operation Principle of the Electric Machines
 9. Operation Principle of the Electric Machines J Electric Machines Operation Principle Ø An electric achine consists of two electric circuits coupled by eans of a agnetic flu, that is linked with both
9. Operation Principle of the Electric Machines J Electric Machines Operation Principle Ø An electric achine consists of two electric circuits coupled by eans of a agnetic flu, that is linked with both
CHAPTER 19: Single-Loop IMC Control
 When I coplete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Recognize that other feedback algoriths are possible Understand the IMC structure and how it provides the essential control features
When I coplete this chapter, I want to be able to do the following. Recognize that other feedback algoriths are possible Understand the IMC structure and how it provides the essential control features
Identical Maximum Likelihood State Estimation Based on Incremental Finite Mixture Model in PHD Filter
 Identical Maxiu Lielihood State Estiation Based on Increental Finite Mixture Model in PHD Filter Gang Wu Eail: xjtuwugang@gail.co Jing Liu Eail: elelj20080730@ail.xjtu.edu.cn Chongzhao Han Eail: czhan@ail.xjtu.edu.cn
Identical Maxiu Lielihood State Estiation Based on Increental Finite Mixture Model in PHD Filter Gang Wu Eail: xjtuwugang@gail.co Jing Liu Eail: elelj20080730@ail.xjtu.edu.cn Chongzhao Han Eail: czhan@ail.xjtu.edu.cn
Lecture 8: Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drives
 1 / 22 Lecture 8: Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 22 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises
1 / 22 Lecture 8: Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 22 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises
Estimation of ADC Nonlinearities from the Measurement in Input Voltage Intervals
 Estiation of ADC Nonlinearities fro the Measureent in Input Voltage Intervals M. Godla, L. Michaeli, 3 J. Šaliga, 4 R. Palenčár,,3 Deptartent of Electronics and Multiedia Counications, FEI TU of Košice,
Estiation of ADC Nonlinearities fro the Measureent in Input Voltage Intervals M. Godla, L. Michaeli, 3 J. Šaliga, 4 R. Palenčár,,3 Deptartent of Electronics and Multiedia Counications, FEI TU of Košice,
A Simplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the Weaving Machines with Automatic Filling Repair
 Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
An Adaptive UKF Algorithm for the State and Parameter Estimations of a Mobile Robot
 Vol. 34, No. 1 ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA January, 2008 An Adaptive UKF Algorith for the State and Paraeter Estiations of a Mobile Robot SONG Qi 1, 2 HAN Jian-Da 1 Abstract For iproving the estiation accuracy
Vol. 34, No. 1 ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA January, 2008 An Adaptive UKF Algorith for the State and Paraeter Estiations of a Mobile Robot SONG Qi 1, 2 HAN Jian-Da 1 Abstract For iproving the estiation accuracy
ESTIMATING AND FORMING CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR EXTREMA OF RANDOM POLYNOMIALS. A Thesis. Presented to. The Faculty of the Department of Mathematics
 ESTIMATING AND FORMING CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR EXTREMA OF RANDOM POLYNOMIALS A Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the Departent of Matheatics San Jose State University In Partial Fulfillent of the Requireents
ESTIMATING AND FORMING CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR EXTREMA OF RANDOM POLYNOMIALS A Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the Departent of Matheatics San Jose State University In Partial Fulfillent of the Requireents
A method to determine relative stroke detection efficiencies from multiplicity distributions
 A ethod to deterine relative stroke detection eiciencies ro ultiplicity distributions Schulz W. and Cuins K. 2. Austrian Lightning Detection and Inoration Syste (ALDIS), Kahlenberger Str.2A, 90 Vienna,
A ethod to deterine relative stroke detection eiciencies ro ultiplicity distributions Schulz W. and Cuins K. 2. Austrian Lightning Detection and Inoration Syste (ALDIS), Kahlenberger Str.2A, 90 Vienna,
Robustness Experiments for a Planar Hopping Control System
 To appear in International Conference on Clibing and Walking Robots Septeber 22 Robustness Experients for a Planar Hopping Control Syste Kale Harbick and Gaurav S. Sukhate kale gaurav@robotics.usc.edu
To appear in International Conference on Clibing and Walking Robots Septeber 22 Robustness Experients for a Planar Hopping Control Syste Kale Harbick and Gaurav S. Sukhate kale gaurav@robotics.usc.edu
CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
 21 CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR 2.1 INTRODUCTION The need for adjustable speed drives in industrial applications has been increasing progressively. The variable speed
21 CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR 2.1 INTRODUCTION The need for adjustable speed drives in industrial applications has been increasing progressively. The variable speed
Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF
 Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF P.Suganya Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Women Salem (DT). Abstract
Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF P.Suganya Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Women Salem (DT). Abstract
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Reading from Young & Freedman: For this topic, read the introduction to chapter 25 and sections 25.1 to 25.3 & 25.6.
 PHY10 Electricity Topic 6 (Lectures 9 & 10) Electric Current and Resistance n this topic, we will cover: 1) Current in a conductor ) Resistivity 3) Resistance 4) Oh s Law 5) The Drude Model of conduction
PHY10 Electricity Topic 6 (Lectures 9 & 10) Electric Current and Resistance n this topic, we will cover: 1) Current in a conductor ) Resistivity 3) Resistance 4) Oh s Law 5) The Drude Model of conduction
Performance Study for High Power Density Three- Phase Vienna PFC Rectifier by Using SVPWM Control Method
 Perforance Study for High Power Density Three- Phase ienna PFC Rectifier by Using SPWM Control Method Ming Zhang, Bin Li, Lijun Hang, Leon M. Tolbert,Zhengyu Lu College of Electrical Engineering,Zhejiang
Perforance Study for High Power Density Three- Phase ienna PFC Rectifier by Using SPWM Control Method Ming Zhang, Bin Li, Lijun Hang, Leon M. Tolbert,Zhengyu Lu College of Electrical Engineering,Zhejiang
Qualitative Modelling of Time Series Using Self-Organizing Maps: Application to Animal Science
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Coputer Science, Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain, Deceber 16-18, 2006 183 Qualitative Modelling of Tie Series Using Self-Organizing Maps:
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Coputer Science, Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain, Deceber 16-18, 2006 183 Qualitative Modelling of Tie Series Using Self-Organizing Maps:
16.512, Rocket Propulsion Prof. Manuel Martinez-Sanchez Lecture 30: Dynamics of Turbopump Systems: The Shuttle Engine
 6.5, Rocket Propulsion Prof. Manuel Martinez-Sanchez Lecture 30: Dynaics of Turbopup Systes: The Shuttle Engine Dynaics of the Space Shuttle Main Engine Oxidizer Pressurization Subsystes Selected Sub-Model
6.5, Rocket Propulsion Prof. Manuel Martinez-Sanchez Lecture 30: Dynaics of Turbopup Systes: The Shuttle Engine Dynaics of the Space Shuttle Main Engine Oxidizer Pressurization Subsystes Selected Sub-Model
Analysis and Implementation of a Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation
 DINAME 27 - Proceedings of the XVII International Syposiu on Dynaic Probles of Mechanics A. T. Fleury, D. A. Rade, P. R. G. Kurka (Editors), ABCM, São Sebastião, SP, Brail, March 5-, 27 Analysis and Ipleentation
DINAME 27 - Proceedings of the XVII International Syposiu on Dynaic Probles of Mechanics A. T. Fleury, D. A. Rade, P. R. G. Kurka (Editors), ABCM, São Sebastião, SP, Brail, March 5-, 27 Analysis and Ipleentation
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measurement Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES
 Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Analysis of ground vibration transmission in high precision equipment by Frequency Based Substructuring
 Analysis of ground vibration transission in high precision equipent by Frequency Based Substructuring G. van Schothorst 1, M.A. Boogaard 2, G.W. van der Poel 1, D.J. Rixen 2 1 Philips Innovation Services,
Analysis of ground vibration transission in high precision equipent by Frequency Based Substructuring G. van Schothorst 1, M.A. Boogaard 2, G.W. van der Poel 1, D.J. Rixen 2 1 Philips Innovation Services,
Homework 3 Solutions CSE 101 Summer 2017
 Hoework 3 Solutions CSE 0 Suer 207. Scheduling algoriths The following n = 2 jobs with given processing ties have to be scheduled on = 3 parallel and identical processors with the objective of iniizing
Hoework 3 Solutions CSE 0 Suer 207. Scheduling algoriths The following n = 2 jobs with given processing ties have to be scheduled on = 3 parallel and identical processors with the objective of iniizing
Department of Electronic and Optical Engineering, Ordnance Engineering College, Shijiazhuang, , China
 6th International Conference on Machinery, Materials, Environent, Biotechnology and Coputer (MMEBC 06) Solving Multi-Sensor Multi-Target Assignent Proble Based on Copositive Cobat Efficiency and QPSO Algorith
6th International Conference on Machinery, Materials, Environent, Biotechnology and Coputer (MMEBC 06) Solving Multi-Sensor Multi-Target Assignent Proble Based on Copositive Cobat Efficiency and QPSO Algorith
Faraday's Law Warm Up
 Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
Condition Monitoring and Fault Detection of Railway Vehicle Suspension using Multiple-Model Approach
 Proceedings of the 17th World Congress The International Federation of Autoatic Control Condition Monitoring and Fault Detection of Railway Vehicle Suspension using Multiple-Model Approach Hitoshi Tsunashia
Proceedings of the 17th World Congress The International Federation of Autoatic Control Condition Monitoring and Fault Detection of Railway Vehicle Suspension using Multiple-Model Approach Hitoshi Tsunashia
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley ENSIAG 2 / osig 1 Second Seester 2012/2013 Lesson 20 2 ay 2013 Kernel ethods and Support Vector achines Contents Kernel Functions...2 Quadratic
Intelligent Systes: Reasoning and Recognition Jaes L. Crowley ENSIAG 2 / osig 1 Second Seester 2012/2013 Lesson 20 2 ay 2013 Kernel ethods and Support Vector achines Contents Kernel Functions...2 Quadratic
Chapter 2: Introduction to Damping in Free and Forced Vibrations
 Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS *
 IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink
 Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink Arun Kumar Yadav 1, Dr. Vinod Kumar Singh 2 1 Reaserch Scholor SVU Gajraula Amroha, U.P. 2 Assistant professor ABSTRACT Induction
Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink Arun Kumar Yadav 1, Dr. Vinod Kumar Singh 2 1 Reaserch Scholor SVU Gajraula Amroha, U.P. 2 Assistant professor ABSTRACT Induction
Design of 25 KA Current Injection Transformer Core with Finite Element Method
 1 Design of 5 KA Current Injection Transforer Core ith Finite Eleent Method HOSSEIN HEYDARI, MOHSEN ARIANNEJAD, FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract.Since Current
1 Design of 5 KA Current Injection Transforer Core ith Finite Eleent Method HOSSEIN HEYDARI, MOHSEN ARIANNEJAD, FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract.Since Current
An Approximate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity Increase in the Intermediate Ballistics Period
 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
EE5900 Spring Lecture 4 IC interconnect modeling methods Zhuo Feng
 EE59 Spring Parallel LSI AD Algoriths Lecture I interconnect odeling ethods Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE59 So far we ve considered only tie doain analyses We ll soon see that it is soeties preferable to odel
EE59 Spring Parallel LSI AD Algoriths Lecture I interconnect odeling ethods Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE59 So far we ve considered only tie doain analyses We ll soon see that it is soeties preferable to odel
Simulation and Analysis of Electromagnetic Transient Characteristics of Controllable Reactor of Transformer Type
 Siulation and Analysis of Electroagnetic Transient Characteristics of Controllable eactor of Transforer Type TIAN MINGXING, ZHAO QIANU, YIN JIANNING, LIU YIBIN Autoation and Electrical Engineering Lanzhou
Siulation and Analysis of Electroagnetic Transient Characteristics of Controllable eactor of Transforer Type TIAN MINGXING, ZHAO QIANU, YIN JIANNING, LIU YIBIN Autoation and Electrical Engineering Lanzhou
HYBRID ADAPTIVE FRICTION COMPENSATION OF INDIRECT DRIVE TRAINS
 Proceedings of the ASME 29 Dynaic Systes and Control Conference DSCC29 October 12-14, 29, Hollywood, California, USA DSCC29-2736 HYBRID ADAPTIVE FRICTION COMPENSATION OF INDIRECT DRIVE TRAINS Wenjie Chen
Proceedings of the ASME 29 Dynaic Systes and Control Conference DSCC29 October 12-14, 29, Hollywood, California, USA DSCC29-2736 HYBRID ADAPTIVE FRICTION COMPENSATION OF INDIRECT DRIVE TRAINS Wenjie Chen
A New Algorithm for Reactive Electric Power Measurement
 A. Abiyev, GAU J. Soc. & Appl. Sci., 2(4), 7-25, 27 A ew Algorith for Reactive Electric Power Measureent Adalet Abiyev Girne Aerican University, Departernt of Electrical Electronics Engineering, Mersin,
A. Abiyev, GAU J. Soc. & Appl. Sci., 2(4), 7-25, 27 A ew Algorith for Reactive Electric Power Measureent Adalet Abiyev Girne Aerican University, Departernt of Electrical Electronics Engineering, Mersin,
th Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Germany, Parallel Connection of Piezoelectric Transformers
 004 35th Annual IEEE ower Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Gerany, 004 arallel Connection of iezoelectric Transforers Svetlana Bronstein, Gregory Ivensky and Sa Ben-Yaakov* ower Electronics Laboratory
004 35th Annual IEEE ower Electronics Specialists Conference Aachen, Gerany, 004 arallel Connection of iezoelectric Transforers Svetlana Bronstein, Gregory Ivensky and Sa Ben-Yaakov* ower Electronics Laboratory
Handwriting Detection Model Based on Four-Dimensional Vector Space Model
 Journal of Matheatics Research; Vol. 10, No. 4; August 2018 ISSN 1916-9795 E-ISSN 1916-9809 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Handwriting Detection Model Based on Four-Diensional Vector
Journal of Matheatics Research; Vol. 10, No. 4; August 2018 ISSN 1916-9795 E-ISSN 1916-9809 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Handwriting Detection Model Based on Four-Diensional Vector
Architectural issues in the control of tall multiple-input multiple-output plants
 Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Autoatic Control Architectural issues in the control of tall ultiple-input ultiple-output plants Pedro Albertos Mario E. Salgado Departent
Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Autoatic Control Architectural issues in the control of tall ultiple-input ultiple-output plants Pedro Albertos Mario E. Salgado Departent
Assessment of wind-induced structural fatigue based on joint probability density function of wind speed and direction
 The 1 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environental, and Materials Research (ACEM 1) eoul, Korea, August 6-3, 1 Assessent of wind-induced structural fatigue based on oint probability density function
The 1 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environental, and Materials Research (ACEM 1) eoul, Korea, August 6-3, 1 Assessent of wind-induced structural fatigue based on oint probability density function
Using Modular Pole for Multi-Objective Design Optimization of a Linear Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
 Using Modular Pole for Multi-Objective Design Optiization of a Linear Peranent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Particle Swar Optiization (PSO) C. Lucas*, Z. Nasiri-Gheidari** and F. Tootoonchian*** Abstract:
Using Modular Pole for Multi-Objective Design Optiization of a Linear Peranent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Particle Swar Optiization (PSO) C. Lucas*, Z. Nasiri-Gheidari** and F. Tootoonchian*** Abstract:
Block designs and statistics
 Bloc designs and statistics Notes for Math 447 May 3, 2011 The ain paraeters of a bloc design are nuber of varieties v, bloc size, nuber of blocs b. A design is built on a set of v eleents. Each eleent
Bloc designs and statistics Notes for Math 447 May 3, 2011 The ain paraeters of a bloc design are nuber of varieties v, bloc size, nuber of blocs b. A design is built on a set of v eleents. Each eleent
Research and Experiments on Electromagnetic Field Induced by Two. Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Inforation Technology (ICMIT 16) Research and Experients on Electroagnetic Field Induced by Two Coaxial Solenoid Coils of Axially Mag-lev Driving Needle
EMPIRICAL COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS OF A MILP-APPROACH FOR OPTIMIZATION OF HYBRID SYSTEMS
 EMPIRICAL COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS OF A MILP-APPROACH FOR OPTIMIZATION OF HYBRID SYSTEMS Jochen Till, Sebastian Engell, Sebastian Panek, and Olaf Stursberg Process Control Lab (CT-AST), University of Dortund,
EMPIRICAL COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS OF A MILP-APPROACH FOR OPTIMIZATION OF HYBRID SYSTEMS Jochen Till, Sebastian Engell, Sebastian Panek, and Olaf Stursberg Process Control Lab (CT-AST), University of Dortund,
Defect-Aware SOC Test Scheduling
 Defect-Aware SOC Test Scheduling Erik Larsson +, Julien Pouget*, and Zebo Peng + Ebedded Systes Laboratory + LIRMM* Departent of Coputer Science Montpellier 2 University Linköpings universitet CNRS Sweden
Defect-Aware SOC Test Scheduling Erik Larsson +, Julien Pouget*, and Zebo Peng + Ebedded Systes Laboratory + LIRMM* Departent of Coputer Science Montpellier 2 University Linköpings universitet CNRS Sweden
Study Committee B5 Colloquium 2005 September Calgary, CANADA
 36 Study oittee B olloquiu Septeber 4-6 algary, ND ero Sequence urrent opensation for Distance Protection applied to Series opensated Parallel Lines TKHRO KSE* PHL G BEUMONT Toshiba nternational (Europe
36 Study oittee B olloquiu Septeber 4-6 algary, ND ero Sequence urrent opensation for Distance Protection applied to Series opensated Parallel Lines TKHRO KSE* PHL G BEUMONT Toshiba nternational (Europe
XV International PhD Workshop OWD 2013, October Limitations Caused by Sampling and Quantization in Position Control of a Single Axis Robot
 XV International PhD Workshop OWD 2013, 19 22 Octoer 2013 Liitations Caused y Sapling and Quantization in Position Control of a Single Axis Root Csaa Budai, Budapest University of Technology and Econoics
XV International PhD Workshop OWD 2013, 19 22 Octoer 2013 Liitations Caused y Sapling and Quantization in Position Control of a Single Axis Root Csaa Budai, Budapest University of Technology and Econoics
IDAN Shock Mount Isolation Vibration Study November 1, The operation of shock and vibration isolation base plate
 dr. Istvan Koller RTD USA BME Laboratory. Background In 998, Real Tie Devices USA, Inc. introduced a novel packaging concept for ebedded PC/04 odules to build Intelligent Data Acquisition Nodes. This syste,
dr. Istvan Koller RTD USA BME Laboratory. Background In 998, Real Tie Devices USA, Inc. introduced a novel packaging concept for ebedded PC/04 odules to build Intelligent Data Acquisition Nodes. This syste,
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Simple Mechanical Systems
 Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
A NEW GEAR FAULT RECOGNITION METHOD USING MUWD SAMPLE ENTROPY AND GREY INCIDENCE
 A NEW GEAR FAULT RECOGNITION METHOD USING MUWD SAMPLE ENTROPY AND GREY INCIDENCE WENBIN ZHANG, 2 JIE MIN, 3 YASONG PU Assoc Prof, College of Engineering, Honghe Univ, Mengzi, Yunnan, 6600, China 2 Lecturer,
A NEW GEAR FAULT RECOGNITION METHOD USING MUWD SAMPLE ENTROPY AND GREY INCIDENCE WENBIN ZHANG, 2 JIE MIN, 3 YASONG PU Assoc Prof, College of Engineering, Honghe Univ, Mengzi, Yunnan, 6600, China 2 Lecturer,
Dimensioning of a permanent magnets motor with double rotor for electric vehicle
 SETIT 007 4 th International Conference: Sciences of Electronic, Technologies of Inforation and Telecounications arch 5-9, 007 TUISIA iensioning of a peranent agnets otor with double rotor for electric
SETIT 007 4 th International Conference: Sciences of Electronic, Technologies of Inforation and Telecounications arch 5-9, 007 TUISIA iensioning of a peranent agnets otor with double rotor for electric
Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction From The Faraday Acyclic Generator
 Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction Fro The Faraday Acyclic Generator July 11, 21 Volt =.2551552 volt 1) If we now consider that the voltage is capable of producing current if the ri of the disk
Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction Fro The Faraday Acyclic Generator July 11, 21 Volt =.2551552 volt 1) If we now consider that the voltage is capable of producing current if the ri of the disk
Ch 12: Variations on Backpropagation
 Ch 2: Variations on Backpropagation The basic backpropagation algorith is too slow for ost practical applications. It ay take days or weeks of coputer tie. We deonstrate why the backpropagation algorith
Ch 2: Variations on Backpropagation The basic backpropagation algorith is too slow for ost practical applications. It ay take days or weeks of coputer tie. We deonstrate why the backpropagation algorith
Feature Extraction Techniques
 Feature Extraction Techniques Unsupervised Learning II Feature Extraction Unsupervised ethods can also be used to find features which can be useful for categorization. There are unsupervised ethods that
Feature Extraction Techniques Unsupervised Learning II Feature Extraction Unsupervised ethods can also be used to find features which can be useful for categorization. There are unsupervised ethods that
Use of PSO in Parameter Estimation of Robot Dynamics; Part One: No Need for Parameterization
 Use of PSO in Paraeter Estiation of Robot Dynaics; Part One: No Need for Paraeterization Hossein Jahandideh, Mehrzad Navar Abstract Offline procedures for estiating paraeters of robot dynaics are practically
Use of PSO in Paraeter Estiation of Robot Dynaics; Part One: No Need for Paraeterization Hossein Jahandideh, Mehrzad Navar Abstract Offline procedures for estiating paraeters of robot dynaics are practically
Model Predictive Control Approach to Design Practical Adaptive Cruise Control for Traffic Jam
 Taku Takahaa et al./international Journal of Autootive Engineering Vol.9, No.3 (218) pp.99-14 Research Paper 218495 Model Predictive Control Approach to Design Practical Adaptive Cruise Control for Traffic
Taku Takahaa et al./international Journal of Autootive Engineering Vol.9, No.3 (218) pp.99-14 Research Paper 218495 Model Predictive Control Approach to Design Practical Adaptive Cruise Control for Traffic
Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyramidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular Cross-Sectional Area
 Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
Non-Parametric Non-Line-of-Sight Identification 1
 Non-Paraetric Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Sinan Gezici, Hisashi Kobayashi and H. Vincent Poor Departent of Electrical Engineering School of Engineering and Applied Science Princeton University, Princeton,
Non-Paraetric Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Sinan Gezici, Hisashi Kobayashi and H. Vincent Poor Departent of Electrical Engineering School of Engineering and Applied Science Princeton University, Princeton,
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT
 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT PACS REFERENCE: 43.5.LJ Krister Larsson Departent of Applied Acoustics Chalers University of Technology SE-412 96 Sweden Tel: +46 ()31 772 22 Fax: +46 ()31
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT PACS REFERENCE: 43.5.LJ Krister Larsson Departent of Applied Acoustics Chalers University of Technology SE-412 96 Sweden Tel: +46 ()31 772 22 Fax: +46 ()31
An improved deadbeat predictive current control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 22, June 2015, pp. 273-282 An improved deadbeat predictive current control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor Mingyi Wang, iyi i, Donghua
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 22, June 2015, pp. 273-282 An improved deadbeat predictive current control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor Mingyi Wang, iyi i, Donghua
Actuators & Mechanisms Actuator sizing
 Course Code: MDP 454, Course Nae:, Second Seester 2014 Actuators & Mechaniss Actuator sizing Contents - Modelling of Mechanical Syste - Mechaniss and Drives The study of Mechatronics systes can be divided
Course Code: MDP 454, Course Nae:, Second Seester 2014 Actuators & Mechaniss Actuator sizing Contents - Modelling of Mechanical Syste - Mechaniss and Drives The study of Mechatronics systes can be divided
Automated Frequency Domain Decomposition for Operational Modal Analysis
 Autoated Frequency Doain Decoposition for Operational Modal Analysis Rune Brincker Departent of Civil Engineering, University of Aalborg, Sohngaardsholsvej 57, DK-9000 Aalborg, Denark Palle Andersen Structural
Autoated Frequency Doain Decoposition for Operational Modal Analysis Rune Brincker Departent of Civil Engineering, University of Aalborg, Sohngaardsholsvej 57, DK-9000 Aalborg, Denark Palle Andersen Structural
DETECTION OF NONLINEARITY IN VIBRATIONAL SYSTEMS USING THE SECOND TIME DERIVATIVE OF ABSOLUTE ACCELERATION
 DETECTION OF NONLINEARITY IN VIBRATIONAL SYSTEMS USING THE SECOND TIME DERIVATIVE OF ABSOLUTE ACCELERATION Masaki WAKUI 1 and Jun IYAMA and Tsuyoshi KOYAMA 3 ABSTRACT This paper shows a criteria to detect
DETECTION OF NONLINEARITY IN VIBRATIONAL SYSTEMS USING THE SECOND TIME DERIVATIVE OF ABSOLUTE ACCELERATION Masaki WAKUI 1 and Jun IYAMA and Tsuyoshi KOYAMA 3 ABSTRACT This paper shows a criteria to detect
Impulsive Control of a Mechanical Oscillator with Friction
 9 Aerican Control Conference Hyatt Regency Riverfront, St. Louis, MO, USA June -, 9 ThC8. Ipulsive Control of a Mechanical Oscillator with Friction Yury Orlov, Raul Santiesteban, and Luis T. Aguilar Abstract
9 Aerican Control Conference Hyatt Regency Riverfront, St. Louis, MO, USA June -, 9 ThC8. Ipulsive Control of a Mechanical Oscillator with Friction Yury Orlov, Raul Santiesteban, and Luis T. Aguilar Abstract
Design of Sliding Mode Stabilizer for Wind Turbine Generator using Dynamic Compensation Observer Technique
 Proceedings of the 6th WSES International Conference on Power Systes, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 6 84 Design of Sliding Mode Stabilizer for Wind urbine Generator using Dynaic Copensation Observer echnique
Proceedings of the 6th WSES International Conference on Power Systes, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 6 84 Design of Sliding Mode Stabilizer for Wind urbine Generator using Dynaic Copensation Observer echnique
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Artificial Neural networks
 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Jaes L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Seester 2017 Lessons 7 20 Dec 2017 Outline Artificial Neural networks Notation...2 Introduction...3 Key Equations... 3 Artificial
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Jaes L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Seester 2017 Lessons 7 20 Dec 2017 Outline Artificial Neural networks Notation...2 Introduction...3 Key Equations... 3 Artificial
Ph 20.3 Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations
 Ph 20.3 Nuerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations Due: Week 5 -v20170314- This Assignent So far, your assignents have tried to failiarize you with the hardware and software in the Physics Coputing
Ph 20.3 Nuerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations Due: Week 5 -v20170314- This Assignent So far, your assignents have tried to failiarize you with the hardware and software in the Physics Coputing
Neural Network Identifier with Iterative Learning for Turbofan Engine Rotor Speed Control System
 Neural Network Identifier with Iterative earning for Turbofan Engine Rotor Speed Control Syste QIAN Kun PANG Xiangping I Bangyuan Departent of Aerial Instruent and Electric Engineering The First Aeronautical
Neural Network Identifier with Iterative earning for Turbofan Engine Rotor Speed Control Syste QIAN Kun PANG Xiangping I Bangyuan Departent of Aerial Instruent and Electric Engineering The First Aeronautical
Adaptive Controller Design for a Synchronous Generator with Unknown Perturbation in Mechanical Power
 308 International Journal of Control Xiaohong Autoation Jiao Yuanzhang and Systes Sun vol and 3 Tielong no (special Shen edition) pp 308-34 June 005 Adaptive Controller Design for a Synchronous Generator
308 International Journal of Control Xiaohong Autoation Jiao Yuanzhang and Systes Sun vol and 3 Tielong no (special Shen edition) pp 308-34 June 005 Adaptive Controller Design for a Synchronous Generator
