Numerical Investigation of the Performance of Voith Schneider Propulsion
|
|
|
- Aleesha Hill
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Journal of Marine Science, 214, Vol. 2, No. 3, Available online at Science and Education Publishing DOI:12691/marine Numerical Investigation of the Performance of Voith Schneider Propulsion Ehsan Esmailian *, Hassan Ghassemi, Seyyed Abbas Heidari Department of Ocean Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran *Corresponding author: Received December 2, 214; Revised December 16, 214; Accepted December 24, 214 Abstract The research explained in this article was carried out to investigate the numerical hydrodynamic characteristics of the Voith Schneider Propeller (VSP) system. The system has four vertical blades connected to the horizontal disk. Each blade has two speeds, one around a disk and second local rational along its axis. The method is finite volume CFD code (Fluent v14) with RNG k-ε turbulence model. For the purposes of this research, a VSP with 4 blades is analyzed at various operating conditions. Hydrodynamic characteristic parameters including moment, thrust and efficiency are presented as functions of advance velocity coefficients at three different pitch rations. Keywords: Voith Schneider Propeller, CFD, RNG turbulence model, hydrodynamic performance Cite This Article: Ehsan Esmailian, Hassan Ghassemi, and Seyyed Abbas Heidari, Numerical Investigation of the Performance of Voith Schneider Propulsion. American Journal of Marine Science, vol. 2, no. 3 (214): doi: 12691/marine Introduction VSP was developed as a high performance drive system by Australian engineer Ernst Schneider and came into operation in It is used primarily for ships that have to satisfy particularly demanding safety and maneuverability requirements [1]. The thrust is generated by separately oscillating, balanced propeller blades. VSP permits continuously variable thrust adjustment through 36. Thus, the VSP has no preferential direction of thrust and allows infinite variation in the magnitude and direction of thrust [2,3]. A significant difference between the VSP and the screw propeller is the direction of the axis of rotation relative to the direction of thrust. In the case of screw propeller, the axis of rotation and the direction of thrust are identical, on the VSP they are perpendicular to one another. The VSPs operate at a comparatively low rotational speed and are therefore notable for their long service life and very low maintenance [5]. Since the VSP simultaneously generates propulsion and steering forces, there is no need for additional appendages such as propeller brackets, rudders, pods, shafts, etc. Blades of VSP are symmetric. In certain installation conditions, the rectangular swept area of a VSP is approximately twice as large as that of a screw propeller. Thus, generated thrust force in the VSP is more than a screw propeller. The perpendiculars of the chords of the profiles intersect at a single point, the steering center N, as the blades revolve. The pitch of VSP can be varied within a range e.8. Propellers with a pitch e>1 are known as trochoidal propellers. The Kirsten-Boeing propeller is a special casewith a pitch of e=1 [5,7]. Rotation speed in VSP is one fourth of typical propellers. Their diameter varies between 1.2 and 3.8 meters and the input power to them is up to 41 kw. Parameters affecting hydrodynamic performance of VSP are angle of attack during rotation of the rotor, geometry of blades profile, ratio of blade chord length to diameter of rotor, position of blade shafts, relative thickness of blades, tail-end flap of blades and ratio of blade length (span) todiameter of rotor. The tail-end flap in blades can lower the induced drag force [8,9,1]. Assessment of cavitation behavior shows that the sheet cavitation is more common in these propellers. Sheet cavitation has no erosion and corrosion on the blades. VSPs are mainly used in Offshore Support Vessels (OSV), Voith Water Tractor (VWT), Tugs, Mine Countermeasures Vessels (MCMV) and Double-Ended Ferries (DEF) [11,12]. Design improvement is an important phase of the engineering design process. In reference[4],the numerical optimization and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), in particular the Vortex-Lattice Method for the optimization of VSP is used. In reference[21], the Automatic Differentiation method is used for the optimization of the VoithSchneiderPropeller. In reference[22], a new vertical axis propulsion system with orbital paddles which is constituted by a pair of contra-rotating impellers is proposed.here, the effect of pitch ratio on efficiency and other hydrodynamic characteristics is investigated. It will be shown that the efficiency increases with pitch ratio. 2. Component of Rotor in VSP The energy required to generate the thrust is supplied to the rotor casing (1) via the flanged-on reduction gear (7) and the bevel gear (6) (Figure 1). Gland bearings or
2 American Journal of Marine Science 59 special roller bearing are used to support the blade shaft. The rotor casing is axially supported by the thrust plate (1) and centered radially by the roller bearing (11). Due to the kinematic system (3), the blades (2) perform an oscillating. Figure 1. Components of VSP [5] The amplitude and phase of blade motion is determined by the position of the steering center and hence the magnitude and direction of thrust are varied by means of the control rod [13,14,15]. The control rod is actuated by two orthogonally arranged servo motors (5). The propulsion servo motor (aservo motor is a rotary actuator that allows for precise control of angular position, velocity and acceleration) isused to adjust the pitch for longitudinal thrust (forward and reverse motion of the ship). The rudder servo motor is usedfor transverse thrust(motion to port and starboard). The two servo motorspermit steering according to Cartesian X/Y coordinates (identical with the principal axes of the ship). Controlled changes in thrust are possible via the thrust-free condition. For example, its direction can be changed from full ahead to full astern at a constant speed of rotation without creating disturbing transverse forces [16,17]. Fitting the VSP with mechanical controls for the servo motors and an oil pump (12) flanged to the input gear results in a self-contained propulsion and maneuvering system which, apart from the torque input, requires no other source of power. Various mechanical kinematic systems and hydraulic blade actuating systems were developed and used in the course of development [18]. The blades of the VSP move along a circular path while simultaneously performing a superimposed pivoting motion. The perpendicular of the chord of the profiles intersects at single point, the steering center N. 3. Geometrical Equations in VSP The eccentricity (e) refers to as pitch of the VSP and is defined as: ON e =, (1) D 2 where D is the blade orbit diameter.pointn, as shown in Figure 2, is the control point of the all blades which is related to the pitch angle of the VSP. The advance coefficient () of the VSP is the ratio of inflow velocity of the propeller (V A ) to the circumferential velocity u of the blades (u): V = A (2) u The circumferential velocity u at the blade circle, with rotor speed (n) and blade orbit diameter (D), is given by u = π nd (3) The motion of the blade relative to a stationary observer arises from the superimposition of the rotary movement and a straight line representing the forward motion of the vessel. The blade follows a curve of a cycloid. The rolling radius of the cycloid is D 2. In one revolution, the propeller travels a distance D 2 π in the direction of motion of the ship. Because the blades travel along a cycloidal path, the VSP is also referred to as cycloidal propeller [19]. There is continuous variation in the lift during each revolution owing to the non-stationary inflow to the propeller blades. The force-components acting transversely to the desired direction of thrust cancel each other out, while the force-components in the direction of thrust add up over the circumference of propeller [7]. Figure 2. Forces on the blade in various angular positions [7] 4. Hydrodynamic Characteristic of VSP The hydrodynamic characteristics of VSP are represented by dimensionless coefficients which, as a result of the historical development of the system, differ by constant factors from those of screw propeller [2]. Hydrodynamic equations of the VSP are defined as follows: Thrust Torque Thrust coefficient Torque coefficient T M = Li (4) = Di (5) T KS = (6) 2.5ρDLV 4M = (7) 2 ρd LV KS Open water efficiency η = (8)
3 6 American Journal of Marine Science where D, ρ, L,, nare the diameter of the propeller, the density of water, the length of the blades, advance coefficient and the number of revolutions of the propeller, respectively. The Reynolds number for VSPs, based on the mean chord length c of a profile, is defined as follows [12]: c 2 2 Re = V A + u ν (9) where ν and care the kinematic viscosity and chord length, respectively. The hydrodynamic properties of VSPs are primarily influenced by the following parameters: Blade angle of attack during revolution. Profile geometry. Ratio of chord length c to blade circle diameter D, (c/d). Relative thickness of the profile. Blade shaft position. Ratio of blade length L to blade orbit diameter D (L/D). Shape of blade outline. Design of the blade ends [14-18]. The thrust coefficient and efficiency are a function of the advance coefficient and pitch e. there is a qualitative shift in the coefficients as a function of and e, as is familiar from screw propellers with variable pitch. The efficiency increases with pitch. In addition, the fewer the number of blades has higher efficiency. On today s VSPs, the number of blades is much less significant since the hydrodynamic interactions between the blades on the front and rear halves of the rotor are reduced by modification of the blade angle curve. The side thrust of VSP increases with the advance coefficient. As the advance ratio increases and the propeller speed remains the same, the steering forces also increase, as do the torques [7]. This study used the finite volume code FLUENT v14 to solve the incompressible continuity and momentum equation in two dimensions. For the turbulent flow cases, the equations were Reynolds-averaged and the k ε model was used for turbulence closure. This study adopted the re-normalization group (RNG) extension of the k ε model. Figure 3. Mesh and details of the profile mesh 5. Principal Tug Particulars The main particulars of a tug are shown in Table 1. This will be usedfor estimateof the lift, drag, pressure and velocity distributions in VSPs. Figure 4. Velocity vector around the blade of the VSP at α=15 Table 1. Principal tug particulars Parameter Value [unit] Length of waterline LWL 14 [m] Beam B 3.3 [m] Draft T 1.9 [m] Block coefficient C B.41 [-] Speed V 12 [Knot] Total resistance R T [kn] The present VSP has 4 blades and the blade orbit diameter is 1.5 m. The rotor speed is 15rpm. NACA 12 blade section is selected that has a symmetric section. The blade dimensions are defined: Chord length= 1 m, Span length= 1.2 m, Relative thickness =.2 m. 6. Numerical Results Figure 5. Pressure distribution on blade at α=15
4 American Journal of Marine Science 61 The most important of VSP characteristics of the VSP are hydrodynamic coefficients. These coefficients are thrust, moment and efficiency. The VSP is a variable pitch propeller. These calculations are carried out for various pitches.3,.4 and.5. Hydrodynamic characteristics (thrust, moment and efficiency) are shown in Figure 9- Figure 11. The efficiency increases with thepitch. Advance velocity coefficient ( ) can play an important role in the hydrodynamic performance. Maximum efficiency is around 7% for pitch ratio of.5 at =.7 and hasreasonable value based on the experimental data as shown in reference [5]. Figure 6. Pressure distribution on blade at α=3 Ks.8 e=.3.7 e=.4.6 e= Figure 9. Thrust coefficient at different pitch ratios e=.3 e=.4 e=.5 Figure 7. Lift coefficients as a function of α Figure 1. Torque coefficient at different pitch ratios Figure 8. Drag coefficients as a function of α Here, the numerical results of the blade of VSP are presented. The results are velocity vector, pressure distributions on blade of VSP, lift and drag at various angles of attack ( α ). Figure 3 shows the mesh and its domain. Numerical results for pressure, velocity, lift and drag are shown in Figure 4-Figure Hydrodynamic Characteristic Results η e=.3.2 e=.4 e= Conclusions Figure 11. Efficiency at different pitch ratios The hydrodynamic analysis of a VSP at various operating conditions was investigated. A finite volume
5 62 American Journal of Marine Science based RANS solver (Fluent) has been used to evaluate the performance of these systems. Based on the numerical results, the following conclusions can be drawn: 1. When the point N (means control point) is changed the resultant velocity entering to the blade and its angle are determined. Therefore, especial emphasis should be applied to determine the physical and geometrical blades operating conditions. 2. Physical characteristics of one blade at various angles of attack is investigated in order to get the lift and drag of the blade. 3. Hydrodynamic characteristics of the VSP( KS,, η ) are calculated at three different pitch rations. It is concluded that with increasing the pitch of the blade, efficiency is increased. Acknowledgement This research was supported by the Marine Research Center of Amirkabir University of Technology whose works are greatly acknowledged. Nomenclature B Beam, m c Chord length, m C B Block coefficient C L Lift coefficient C D Drag coefficient D Blade orbit diameter, m e Pitch K s Thrust coefficient K D Torque coefficient L length of the blades, m LWL Length of waterline, m M Torque, kn n Propeller rotational speed, rps N Steering center O Center of VSPs Re Reynolds number R T Total resistance, kn T Thrust, kn T 1 Draft, m u Circumferential velocity, ms -1 V Speed of ship, Knot V A Inflow velocity of propeller, ms -1 Advance coefficient ν Kinematic viscosity, m 2 s -1 α angles of attack, degree ρ Density of water, kg m -3 References [1] [2] [3] Dirk Jürgens, Michael Palm, VSP - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels, Voith Turbo Schneider Propulsions, October 29. [4] Dirk Jurgens, Michael Palm, Sebastian Singer, Karsten Urban, Numerical optimization of the Voith-Schneider Propeller, Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, October 27. [5] Jens-Erk Bartels, Dirk Jürgens, The Voith Schneider Propeller: Current Applications and New Developments, Voith Turbo Marine GmbH & Company KG, 26 [6] [7] Dirk Jürgens, Torsten Moltrecht, Marcel Flipse, Cycloidal propulsion the Quiet Maneuvering propulsion for Large Motor Yachts, Paper to 18th International HISWA, Symposium on Yacht Design and yacht Construction, November 15-16, 24 [8] [9] Jürgens, Birgit; Fork, Faszination, Voith Schneider propeller, Geschichte und technik, Humburg 22. [1] Kirsten, F.K., The Cycloidal propeller in marine Application. University of Washington, 195 [11] Coton, F.N, Galbraith, A.McD, An Experiment study of dynamic stall on a finite wing. Aeronautical Journal, p , may, 1999 [12] Ficken, N.L, Dickerson, M.C., Experimental performance and steering Characteristic of cycloidal propeller, NSRDC report 2983, Washington, 1969 [13] Zhu, D.M., A Computational Method for Cycloidal propeller. I.S.P., vol.28, No.321, [14] Isay, W.H., Moderene probleme der Propeller theorie. Berlin, Heidelberg, Springer-Verlag London Ltd, New York 197. [15] Streckwall, H.:An unsteady Vortex-lattice method for ships propeller, shipbuilding symposium in rostock, [16] Ferziger, J, H. Peric, M., Computational methods for fluid dynamics, Springer, Third edition, Berlin, Heidelberg, 213. [17] Bartels, J.-E. Voith Schneider propulsion systems for double ended ferries, Log s ferries 93 conference, Florida,.march 1993 [18] Jürgens, D, Theoretical and experimental studies of unsteady flows around blades and development of calculation method for vertical axis rotors, Dissertation, Rostock University 1994 [19] Sturmhoefel, U; Bartels, J.-E.: Voith, J. M, Basic requirements for safe escort vessels-theoretical consideration and model measurements, RINA, Escort Tugs design, construction and handling-the way ahead.london, [2] Mott, H.J, Kirstensen, D.H. laible, D.H., Thompson, T.,Stone,M.; Acquisition of tanker escort and assist tugs for Newfoundland Transshipment, SNAME, [21] Ralf Leidenberger, Karsten Urban, Automatic differentiation for the optimization of a ship propulsion and steering system: a proof of concept, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, 21 [22] Piergiorgio Pasetto, Leslie Barnabà, Matteo Miletto Bracco, Igor Zotti, A NEW PROPOSAL OF A VERTICAL AXIS PROPELLER, International Conference IDS213 Amazonia, July 213.
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller
 voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE. October 13-14, Thrusters. Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels
 Return to Session Directory DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 13-14, 2009 Thrusters Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels Dirk Jürgens, Michael Palm
Return to Session Directory DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 13-14, 2009 Thrusters Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels Dirk Jürgens, Michael Palm
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
ENGR 4011 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships Assignment 4: 2017
 Question 1a. Values of forward speed, propeller thrust and torque measured during a propeller open water performance test are presented in the table below. The model propeller was 0.21 meters in diameter
Question 1a. Values of forward speed, propeller thrust and torque measured during a propeller open water performance test are presented in the table below. The model propeller was 0.21 meters in diameter
Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions
 DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 2010 Thrusters Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions Michael Palm,
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 2010 Thrusters Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions Michael Palm,
A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using CFD
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
2 Hydrodynamic characteristics of propeller blades in curvilinear motion. Let, the vertical axis propeller moves ahead with a constant speed V p
 Hydrodynamic characteristics of propeller blades in curvilinear motion Practical application of such methods is of some interest for a straight line motion of the wing. But for calculating dynamic characteristics
Hydrodynamic characteristics of propeller blades in curvilinear motion Practical application of such methods is of some interest for a straight line motion of the wing. But for calculating dynamic characteristics
Deliverable D.6.1. Application of CFD tools to the development of a novel propulsion concept
 TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION
 A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION Written by: J.D. van Manen (Whale Tail Development, The Netherlands) and T. van Terwisga (MARIN, The Netherlands) Presented on 34 th WEGEMT School by: M.X.
A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION Written by: J.D. van Manen (Whale Tail Development, The Netherlands) and T. van Terwisga (MARIN, The Netherlands) Presented on 34 th WEGEMT School by: M.X.
Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Rotor reference axis
 Rotor reference axis So far we have used the same reference axis: Z aligned with the rotor shaft Y perpendicular to Z and along the blade (in the rotor plane). X in the rotor plane and perpendicular do
Rotor reference axis So far we have used the same reference axis: Z aligned with the rotor shaft Y perpendicular to Z and along the blade (in the rotor plane). X in the rotor plane and perpendicular do
The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory
 J. Marine Sci. Appl. (2012) 11: 164-168 DOI: 10.1007/s11804-012-1118-1 The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory Qiuxin Gao *, Wei Jin and Dracos Vassalos Department of
J. Marine Sci. Appl. (2012) 11: 164-168 DOI: 10.1007/s11804-012-1118-1 The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory Qiuxin Gao *, Wei Jin and Dracos Vassalos Department of
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH TWIST ANGLE IN BLADES
 Eleventh International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 7-9 December 05 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH TWIST ANGLE IN BLADES
Eleventh International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 7-9 December 05 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE WITH TWIST ANGLE IN BLADES
ENGR 4011 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships Assignment 5: A dimensional analysis of propeller thrust starting with the functional expression
 ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 2012/13
 Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 212/13 Exam 2ª época, 2 February 213 Name : Time : 8: Number: Duration : 3 hours 1 st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed 2 nd Part :
Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 212/13 Exam 2ª época, 2 February 213 Name : Time : 8: Number: Duration : 3 hours 1 st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed 2 nd Part :
CHAPTER 4 OPTIMIZATION OF COEFFICIENT OF LIFT, DRAG AND POWER - AN ITERATIVE APPROACH
 82 CHAPTER 4 OPTIMIZATION OF COEFFICIENT OF LIFT, DRAG AND POWER - AN ITERATIVE APPROACH The coefficient of lift, drag and power for wind turbine rotor is optimized using an iterative approach. The coefficient
82 CHAPTER 4 OPTIMIZATION OF COEFFICIENT OF LIFT, DRAG AND POWER - AN ITERATIVE APPROACH The coefficient of lift, drag and power for wind turbine rotor is optimized using an iterative approach. The coefficient
APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS ON RUDDERS
 Proceedings of ASME 25 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE 25 May 3 - June 5, 25, St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada OMAE25-4796 APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS
Proceedings of ASME 25 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE 25 May 3 - June 5, 25, St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada OMAE25-4796 APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN
 ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(78) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 13-20 10.2478/pomr-2013-0012 Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle Hassan
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(78) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 13-20 10.2478/pomr-2013-0012 Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle Hassan
A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder
 A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder Hassan Ghassemi, a,* and Farzam Allafchi, a a ) Department of Ocean Engineering, Amirkabir
A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder Hassan Ghassemi, a,* and Farzam Allafchi, a a ) Department of Ocean Engineering, Amirkabir
Performance Analysis and Design of Vertical Axis Tidal Stream Turbine
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 2 (2012) 191-200 D DAVID PUBLISHING Performance Analysis and Design of Vertical Axis Tidal Stream Turbine Beom-Soo Hyun, Da-Hye Choi, Jun-Seon Han and Ji-Yuan
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 2 (2012) 191-200 D DAVID PUBLISHING Performance Analysis and Design of Vertical Axis Tidal Stream Turbine Beom-Soo Hyun, Da-Hye Choi, Jun-Seon Han and Ji-Yuan
Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses
 (Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
(Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Workshop: Propeller performance Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description Ulf Barkmann 1, Hans-Jürgen
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Workshop: Propeller performance Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description Ulf Barkmann 1, Hans-Jürgen
Performance Assessment of the Waterjet Propulsion System through a Combined Analytical and Numerical Approach
 International Journal of Physics, 013, Vol. 1, No., -7 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/1//1 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.1691/ijp-1--1 Performance Assessment of the Waterjet
International Journal of Physics, 013, Vol. 1, No., -7 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/1//1 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.1691/ijp-1--1 Performance Assessment of the Waterjet
ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF A TURBIVO COMPRESSOR FOR MVR APPLICATIONS. Abstract 1. INTRODUCTION
 1275, Page 1 ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF A TURBIVO COMPRESSOR FOR MVR APPLICATIONS Elias BOULAWZ KSAYER, Denis CLODIC Center for Energy and Processes, Ecole des Mines de Paris 60, boulevard Saint Michel
1275, Page 1 ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF A TURBIVO COMPRESSOR FOR MVR APPLICATIONS Elias BOULAWZ KSAYER, Denis CLODIC Center for Energy and Processes, Ecole des Mines de Paris 60, boulevard Saint Michel
Fluid structure interaction dynamic analysis of a mixed-flow waterjet pump
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Fluid structure interaction dynamic analysis of a mixed-flow waterjet pump To cite this article: X W Pan et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Fluid structure interaction dynamic analysis of a mixed-flow waterjet pump To cite this article: X W Pan et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 015 IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS Jan Rosłanowski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering Morska Street 81-87,
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 015 IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS Jan Rosłanowski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering Morska Street 81-87,
Full scale thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method
 Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines Testing and Extrapolation Methods Propulsion, Performance Propulsion Test
 7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
Cams. 774 l Theory of Machines
 774 l Theory of Machines 0 Fea eatur tures es 1. Introduction.. Classification of Followers. 3. Classification of Cams. 4. Terms used in Radial cams. 5. Motion of the Follower. 6. Displacement, Velocity
774 l Theory of Machines 0 Fea eatur tures es 1. Introduction.. Classification of Followers. 3. Classification of Cams. 4. Terms used in Radial cams. 5. Motion of the Follower. 6. Displacement, Velocity
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
Teaching sessions week 40
 Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
ANALYSIS OF HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINES WITH LIFTING LINE THEORY
 ANALYSIS OF HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINES WITH LIFTING LINE THEORY Daniela Brito Melo daniela.brito.melo@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal December, 2016 ABSTRACT
ANALYSIS OF HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINES WITH LIFTING LINE THEORY Daniela Brito Melo daniela.brito.melo@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal December, 2016 ABSTRACT
Performance characteristics of turbo blower in a refuse collecting system according to operation conditions
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1896~1901 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-008-0729-6 Performance characteristics
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1896~1901 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-008-0729-6 Performance characteristics
GyroRotor program : user manual
 GyroRotor program : user manual Jean Fourcade January 18, 2016 1 1 Introduction This document is the user manual of the GyroRotor program and will provide you with description of
GyroRotor program : user manual Jean Fourcade January 18, 2016 1 1 Introduction This document is the user manual of the GyroRotor program and will provide you with description of
Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes.
 13.012 Marine Hydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Fall 2004 Quiz #2 Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes. For the problems in Section A, fill
13.012 Marine Hydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Fall 2004 Quiz #2 Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes. For the problems in Section A, fill
ANALYSIS OF CURRENT CLOSE TO THE SURFACE OF NET STRUCTURES Mathias Paschen, University of Rostock, Germany
 ANALYSIS OF CURRENT CLOSE TO THE SURFACE OF NET STRUCTURES Mathias Paschen, University of Rostock, Germany mathias.paschen@uni-rostock.de Abstract The development of the theory of (pelagic) trawls is stagnating
ANALYSIS OF CURRENT CLOSE TO THE SURFACE OF NET STRUCTURES Mathias Paschen, University of Rostock, Germany mathias.paschen@uni-rostock.de Abstract The development of the theory of (pelagic) trawls is stagnating
Viscous investigation of a flapping foil propulsor
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Viscous investigation of a flapping foil propulsor To cite this article: Attapol Posri et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Viscous investigation of a flapping foil propulsor To cite this article: Attapol Posri et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 7.5 02 Page 1 of 21 Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 2 2 ITTC DICTIONARY OF SHIP HYDRODYNAMICS PROPELLER SECTION... 2 COMMENTS OF THE PROPULSION COMMITTEE OF 22 nd ITTC Several of the symbols and definitions
7.5 02 Page 1 of 21 Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 2 2 ITTC DICTIONARY OF SHIP HYDRODYNAMICS PROPELLER SECTION... 2 COMMENTS OF THE PROPULSION COMMITTEE OF 22 nd ITTC Several of the symbols and definitions
DETERMINING OPTIMUM GEOMETRY FOR A BOW THRUSTER PROPELLER
 DEERMINING OPIMUM GEOMERY FOR A BOW HRUSER PROPELLER Y.H. OZDEMIR, S. BAYRAKAR,. YILMAZ, M.GUNER Yildiz echnical University, Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, 34349 Besiktas, Istanbul,
DEERMINING OPIMUM GEOMERY FOR A BOW HRUSER PROPELLER Y.H. OZDEMIR, S. BAYRAKAR,. YILMAZ, M.GUNER Yildiz echnical University, Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, 34349 Besiktas, Istanbul,
Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Wind Tunnel Tests of the Counter-Rotating Propeller of. Stratospheric Airship. Peiqing Liu 1, a, Jingwei Sun 2,b and Zhihao Tang 3,c
 Wind Tunnel Tests of the Counter-Rotating Propeller of Stratospheric Airship Peiqing Liu 1, a, Jingwei Sun 2,b and Zhihao Tang 3,c School of Aeronautic Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Aeronautics
Wind Tunnel Tests of the Counter-Rotating Propeller of Stratospheric Airship Peiqing Liu 1, a, Jingwei Sun 2,b and Zhihao Tang 3,c School of Aeronautic Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Aeronautics
Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 2015/16
 Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics st Semester 05/6 Exam st season, 8 January 06 Name : Time : 8:30 Number: Duration : 3 hours st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed nd Part : Textbooks allowed
Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics st Semester 05/6 Exam st season, 8 January 06 Name : Time : 8:30 Number: Duration : 3 hours st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed nd Part : Textbooks allowed
Performance evaluation of composite marine propeller using L 8 orthogonal array
 Performance evaluation of composite marine propeller using L 8 orthogonal array S.Solomon Raj Dr.P.Ravinder Reddy 2. Assistant professor, department of mechanical engineering, chaitanya bharathi institute
Performance evaluation of composite marine propeller using L 8 orthogonal array S.Solomon Raj Dr.P.Ravinder Reddy 2. Assistant professor, department of mechanical engineering, chaitanya bharathi institute
ZIG-ZAG MANEUVER SIMULATION BY CFD FOR A TANKER LIKE VESSEL
 V International Conference on Computational Methods in Marine Engineering MARINE 2013 B. Brinkmann and P. Wriggers (Eds) ZIG-ZAG MANEUVER SIMULATION BY CFD FOR A TANKER LIKE VESSEL G. DUBBIOSO, D. DURANTE,
V International Conference on Computational Methods in Marine Engineering MARINE 2013 B. Brinkmann and P. Wriggers (Eds) ZIG-ZAG MANEUVER SIMULATION BY CFD FOR A TANKER LIKE VESSEL G. DUBBIOSO, D. DURANTE,
Balancing of Masses. 1. Balancing of a Single Rotating Mass By a Single Mass Rotating in the Same Plane
 lecture - 1 Balancing of Masses Theory of Machine Balancing of Masses A car assembly line. In this chapter we shall discuss the balancing of unbalanced forces caused by rotating masses, in order to minimize
lecture - 1 Balancing of Masses Theory of Machine Balancing of Masses A car assembly line. In this chapter we shall discuss the balancing of unbalanced forces caused by rotating masses, in order to minimize
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Two-Dimensional Aerodynamic Models of Insect Flight for Robotic Flapping Wing Mechanisms of Maximum Efficiency
 Journal of Bionic Engineering 5 (2008) 1 11 Two-Dimensional Aerodynamic Models of Insect Flight for Robotic Flapping Wing Mechanisms of Maximum Efficiency Thien-Tong Nguyen 1, Doyoung Byun 2 1. Department
Journal of Bionic Engineering 5 (2008) 1 11 Two-Dimensional Aerodynamic Models of Insect Flight for Robotic Flapping Wing Mechanisms of Maximum Efficiency Thien-Tong Nguyen 1, Doyoung Byun 2 1. Department
ScienceDirect. Experimental Validation on Lift Increment of a Flapping Rotary Wing with Boring-hole Design
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 99 (2015 ) 1543 1547 APISAT2014, 2014 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Aerospace Technology, APISAT2014 Experimental
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 99 (2015 ) 1543 1547 APISAT2014, 2014 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Aerospace Technology, APISAT2014 Experimental
Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of a Wake Equalizing Duct
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
Numerical Investigation of the Fluid Flow around and Past a Circular Cylinder by Ansys Simulation
 , pp.49-58 http://dx.doi.org/10.1457/ijast.016.9.06 Numerical Investigation of the Fluid Flow around and Past a Circular Cylinder by Ansys Simulation Mojtaba Daneshi Department of Mechanical Engineering,
, pp.49-58 http://dx.doi.org/10.1457/ijast.016.9.06 Numerical Investigation of the Fluid Flow around and Past a Circular Cylinder by Ansys Simulation Mojtaba Daneshi Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships
 (August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
(August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA
 Research Article Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA Kiam Beng Yeo, Wai Heng Choong and Wen Yen Hau ABSTRACT The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of marine propeller blade stress
Research Article Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA Kiam Beng Yeo, Wai Heng Choong and Wen Yen Hau ABSTRACT The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of marine propeller blade stress
CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation
 CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation S. Ramakrishna* GVP College of Engineering (A) Visakhapatnam V. Ramakrishna Scientist D N S T L Visakhapatnam A. Ramakrishna Professor A U C E (A) Visakhapatnam
CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation S. Ramakrishna* GVP College of Engineering (A) Visakhapatnam V. Ramakrishna Scientist D N S T L Visakhapatnam A. Ramakrishna Professor A U C E (A) Visakhapatnam
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Confined water effects on the viscous flow around a tanker with propeller and rudder
 International Shipbuilding Progress 60 (2013) 309 343 309 DOI 10.3233/ISP-130101 IOS Press Confined water effects on the viscous flow around a tanker with propeller and rudder L. Zou and L. Larsson Chalmers
International Shipbuilding Progress 60 (2013) 309 343 309 DOI 10.3233/ISP-130101 IOS Press Confined water effects on the viscous flow around a tanker with propeller and rudder L. Zou and L. Larsson Chalmers
Effect of Blade Number on a Straight-Bladed Vertical-Axis Darreius Wind Turbine
 Effect of Blade Number on a Straight-Bladed Vertical-Axis Darreius Wind Turbine Marco Raciti Castelli, Stefano De Betta and Ernesto Benini Abstract This paper presents a mean for reducing the torque variation
Effect of Blade Number on a Straight-Bladed Vertical-Axis Darreius Wind Turbine Marco Raciti Castelli, Stefano De Betta and Ernesto Benini Abstract This paper presents a mean for reducing the torque variation
Effect of Blade Number on a Straight-Bladed Vertical-Axis Darreius Wind Turbine
 Effect of Blade Number on a Straight-Bladed Vertical-Axis Darreius Wind Turbine Marco Raciti Castelli, Stefano De Betta and Ernesto Benini Abstract This paper presents a mean for reducing the torque variation
Effect of Blade Number on a Straight-Bladed Vertical-Axis Darreius Wind Turbine Marco Raciti Castelli, Stefano De Betta and Ernesto Benini Abstract This paper presents a mean for reducing the torque variation
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? 20cm T =? 20kg
 1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
An Essential Requirement in CV Based Industrial Appliances.
 Measurement of Flow P M V Subbarao Professor Mechanical Engineering Department An Essential Requirement in CV Based Industrial Appliances. Mathematics of Flow Rate The Scalar Product of two vectors, namely
Measurement of Flow P M V Subbarao Professor Mechanical Engineering Department An Essential Requirement in CV Based Industrial Appliances. Mathematics of Flow Rate The Scalar Product of two vectors, namely
1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils
 1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils Two-dimensional flow around a streamlined shape Foces on an airfoil Distribution of pressue coefficient over an airfoil The variation of the lift coefficient with the
1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils Two-dimensional flow around a streamlined shape Foces on an airfoil Distribution of pressue coefficient over an airfoil The variation of the lift coefficient with the
Performance Characteristics of Static and Dynamic Azimuthing Podded Propulsor
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Performance Characteristics of Static and Dynamic Azimuthing Podded Propulsor Mohammed F. Islam 1, Ayhan Akinturk,
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Performance Characteristics of Static and Dynamic Azimuthing Podded Propulsor Mohammed F. Islam 1, Ayhan Akinturk,
Makoto Uchida. Yuuki Matsumoto
 ADVANCED EDUCATION AND RESEARCH ON MARINE PROPULSION EXPERIMENTAL S TUDY ON PROPELLER AIR-DRAWINGS AND BEARING FORCES Makoto Uchida Professor, Dr. Faculty of Maritime Sciences, Kobe University 5-1-1 Fukae-Minami,
ADVANCED EDUCATION AND RESEARCH ON MARINE PROPULSION EXPERIMENTAL S TUDY ON PROPELLER AIR-DRAWINGS AND BEARING FORCES Makoto Uchida Professor, Dr. Faculty of Maritime Sciences, Kobe University 5-1-1 Fukae-Minami,
Numerical Study on Performance of Innovative Wind Turbine Blade for Load Reduction
 Numerical Study on Performance of Innovative Wind Turbine Blade for Load Reduction T. Maggio F. Grasso D.P. Coiro This paper has been presented at the EWEA 011, Brussels, Belgium, 14-17 March 011 ECN-M-11-036
Numerical Study on Performance of Innovative Wind Turbine Blade for Load Reduction T. Maggio F. Grasso D.P. Coiro This paper has been presented at the EWEA 011, Brussels, Belgium, 14-17 March 011 ECN-M-11-036
Research on Prediction of Ship Manoeuvrability
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (08 30-35 doi 0.765/59-5879/08.0.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Research on Prediction of Ship Manoeuvrability CUI Jian, WU Zixin and CHEN Weimin Shanghai Ship and Shipping
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (08 30-35 doi 0.765/59-5879/08.0.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Research on Prediction of Ship Manoeuvrability CUI Jian, WU Zixin and CHEN Weimin Shanghai Ship and Shipping
developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati Presented by: BENZOHRA Abdelmalek
 Master Thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the double degree: Advanced Master in Naval Architecture conferred by University of Liege "Master of Sciences in Applied Mechanics,
Master Thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the double degree: Advanced Master in Naval Architecture conferred by University of Liege "Master of Sciences in Applied Mechanics,
Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Performances of Marine Propeller
 Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Performances of Marine Propeller Master Thesis developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati in the framework of the EMSHIP Erasmus Mundus Master Course
Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Performances of Marine Propeller Master Thesis developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati in the framework of the EMSHIP Erasmus Mundus Master Course
Experiments with Podded Propulsors in Static Azimuthing Conditions
 Experiments with Podded Propulsors in Static Azimuthing Conditions Islam M. F 1, Veitch B 1, Akinturk A 2, Bose N 3 and Liu P 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University of Newfoundland
Experiments with Podded Propulsors in Static Azimuthing Conditions Islam M. F 1, Veitch B 1, Akinturk A 2, Bose N 3 and Liu P 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University of Newfoundland
S.E. (Mech.) (First Sem.) EXAMINATION, (Common to Mech/Sandwich) FLUID MECHANICS (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 8 Seat No. [4262]-113 S.E. (Mech.) (First Sem.) EXAMINATION, 2012 (Common to Mech/Sandwich) FLUID MECHANICS (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 8 Seat No. [4262]-113 S.E. (Mech.) (First Sem.) EXAMINATION, 2012 (Common to Mech/Sandwich) FLUID MECHANICS (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum
Lecture-4. Flow Past Immersed Bodies
 Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results
 Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
DP MAINTENANCE TRAINING
 DP MAINTENANCE TRAINING SINGAPORE Topics Day 2 Review Introduction to Serial Communications Serial Interface Cards Using the Workstation Diagnostics Screens Practical Applications Discussion of AMC Topics
DP MAINTENANCE TRAINING SINGAPORE Topics Day 2 Review Introduction to Serial Communications Serial Interface Cards Using the Workstation Diagnostics Screens Practical Applications Discussion of AMC Topics
VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 Proceedings of COBEM 2007 Copyright 2007 by ABCM 19th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 5-9, 2007, Brasília, DF VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Luiz
Proceedings of COBEM 2007 Copyright 2007 by ABCM 19th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 5-9, 2007, Brasília, DF VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Luiz
Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer To cite this article: C Ning et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 72 032025
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer To cite this article: C Ning et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 72 032025
Study of the hydrodynamic flow around a 70m sailing boat for powering, wave pattern and propeller efficiency prediction
 Study of the hydrodynamic flow around a 70m sailing boat for powering, wave pattern and propeller efficiency prediction Romain Baudson Supervisor: Prof. Dario Boote (UNIGE) External Reviewer: Prof. Pierre
Study of the hydrodynamic flow around a 70m sailing boat for powering, wave pattern and propeller efficiency prediction Romain Baudson Supervisor: Prof. Dario Boote (UNIGE) External Reviewer: Prof. Pierre
Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods
 ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF H-DARRIEUS VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE.
 NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF H-DARRIEUS VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE Normunds Jekabsons 1, Sabine Upnere 1, Janis Kleperis 2,3 1 Ventspils University College, Latvia; 2 SIA Multipla Energy,
NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF H-DARRIEUS VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE Normunds Jekabsons 1, Sabine Upnere 1, Janis Kleperis 2,3 1 Ventspils University College, Latvia; 2 SIA Multipla Energy,
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF NACA 4 SERIES AIRFOILS
 54 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF NACA 4 SERIES AIRFOILS The baseline characteristics and analysis of NACA 4 series airfoils are presented in this chapter in detail. The correlations for coefficient of lift and
54 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF NACA 4 SERIES AIRFOILS The baseline characteristics and analysis of NACA 4 series airfoils are presented in this chapter in detail. The correlations for coefficient of lift and
Analysis of Dynamic Stability of a Fast Single Craft Being Chased
 Applied Engineering 017; 1(1): 37-43 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ae doi: 10.11648/j.ae.0170101.15 Analysis of Dynamic Stability of a Fast Single raft Being hased Mohammad Reza Moghoomi 1, *,
Applied Engineering 017; 1(1): 37-43 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ae doi: 10.11648/j.ae.0170101.15 Analysis of Dynamic Stability of a Fast Single raft Being hased Mohammad Reza Moghoomi 1, *,
Aerodynamic Design of VTOL MAV
 Aerodynamic Design of VTOL MAV Sergey Shkarayev The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA Jean-Marc Moschetta and Boris Bataille SUPAERO, Toulouse, France This work is sponsored by AFRL, Eglin AFB and
Aerodynamic Design of VTOL MAV Sergey Shkarayev The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA Jean-Marc Moschetta and Boris Bataille SUPAERO, Toulouse, France This work is sponsored by AFRL, Eglin AFB and
Effect of modification to tongue and basic circle diameter on vibration in a double-suction centrifugal pump
 5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 2015) Effect of modification to tongue and basic circle diameter on vibration in a double-suction centrifugal
5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 2015) Effect of modification to tongue and basic circle diameter on vibration in a double-suction centrifugal
Mathematical Modeling of the Flow behind Propeller
 Studies in Engineering and Technology Vol. 2, No. 1; August 2015 ISSN 2330-2038 E-ISSN 2330-2046 Published by Redfame Publishing URL: http://set.redfame.com Mathematical Modeling of the Flow behind Propeller
Studies in Engineering and Technology Vol. 2, No. 1; August 2015 ISSN 2330-2038 E-ISSN 2330-2046 Published by Redfame Publishing URL: http://set.redfame.com Mathematical Modeling of the Flow behind Propeller
Fig. 6.1 Plate or disk cam.
 CAMS INTRODUCTION A cam is a mechanical device used to transmit motion to a follower by direct contact. The driver is called the cam and the driven member is called the follower. In a cam follower pair,
CAMS INTRODUCTION A cam is a mechanical device used to transmit motion to a follower by direct contact. The driver is called the cam and the driven member is called the follower. In a cam follower pair,
Optimizing Centrifugal Pump Performance by Different Blade Configuration Patterns
 American Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering 2018; 3(1): 1-14 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajmie doi: 10.11648/j.ajmie.20180301.11 ISSN: 2575-6079 (Print); ISSN: 2575-6060 (Online)
American Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering 2018; 3(1): 1-14 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajmie doi: 10.11648/j.ajmie.20180301.11 ISSN: 2575-6079 (Print); ISSN: 2575-6060 (Online)
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
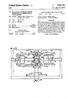 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
Study on Strut Effect on Turning Characteristics of LNG Carrier
 Study on Strut Effect on Turning Characteristics of LNG Carrier Mohd Amirul Hamdi Bin Mohd Alwi, a Jaswar Koto, a, b,* and Zulkarnain, b a) Department of Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering,Mechanical
Study on Strut Effect on Turning Characteristics of LNG Carrier Mohd Amirul Hamdi Bin Mohd Alwi, a Jaswar Koto, a, b,* and Zulkarnain, b a) Department of Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering,Mechanical
STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS
 Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
Analysis of Crashback Forces Compared with Experimental Results
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 09, Trondheim, Norway, une 2009 Analysis of Crashback Forces Compared with Experimental Results Scott Black and Susan Swithenbank Naval Surface Warfare
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 09, Trondheim, Norway, une 2009 Analysis of Crashback Forces Compared with Experimental Results Scott Black and Susan Swithenbank Naval Surface Warfare
MASTER THESIS PRESENTATION
 MASTER THESIS PRESENTATION TURBULENT FLOW SEPARATION AROUND A ROV BODY Presented by: KOFFI Danoh Kouassi Ange Gatien Outline 1- Introduction 2- Numerical modeling of the ROV 3- Choice of the turbulence
MASTER THESIS PRESENTATION TURBULENT FLOW SEPARATION AROUND A ROV BODY Presented by: KOFFI Danoh Kouassi Ange Gatien Outline 1- Introduction 2- Numerical modeling of the ROV 3- Choice of the turbulence
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer
 CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
Hydro-Structure Analysis of Composite Marine Propeller under Pressure Hydrodynamic Loading
 American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
1 Introduction. Minho Lee 1 Jihoon Lee 1 Gunhee Jang 1
 DOI 10.1007/s005-015-5-5 TECHNICAL PAPER Stability analysis of a whirling rigid rotor supported by stationary grooved FDBs considering the five degrees of freedom of a general rotor bearing system Minho
DOI 10.1007/s005-015-5-5 TECHNICAL PAPER Stability analysis of a whirling rigid rotor supported by stationary grooved FDBs considering the five degrees of freedom of a general rotor bearing system Minho
Robust shaft design to compensate deformation in the hub press fitting and disk clamping process of 2.5 HDDs
 DOI 10.1007/s00542-016-2850-2 TECHNICAL PAPER Robust shaft design to compensate deformation in the hub press fitting and disk clamping process of 2.5 HDDs Bumcho Kim 1,2 Minho Lee 3 Gunhee Jang 3 Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00542-016-2850-2 TECHNICAL PAPER Robust shaft design to compensate deformation in the hub press fitting and disk clamping process of 2.5 HDDs Bumcho Kim 1,2 Minho Lee 3 Gunhee Jang 3 Received:
Numerical Investigation on the Performance of Double Layered H-Rotor Darrieus Turbine
 Numerical Investigation on the Performance of Double Layered H-Rotor Darrieus Turbine Submitted by S.M. Rakibul Hassan Student ID: 0413102055 Supervisor Dr. Mohammad Ali Professor Department of Mechanical
Numerical Investigation on the Performance of Double Layered H-Rotor Darrieus Turbine Submitted by S.M. Rakibul Hassan Student ID: 0413102055 Supervisor Dr. Mohammad Ali Professor Department of Mechanical
Chapter three. Two-dimensional Cascades. Laith Batarseh
 Chapter three Two-dimensional Cascades Laith Batarseh Turbo cascades The linear cascade of blades comprises a number of identical blades, equally spaced and parallel to one another cascade tunnel low-speed,
Chapter three Two-dimensional Cascades Laith Batarseh Turbo cascades The linear cascade of blades comprises a number of identical blades, equally spaced and parallel to one another cascade tunnel low-speed,
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology
 Science and Technology An Experimental Study on the Darrieus-Savonius Turbine for the Tidal Current Power Generation * Yusaku KYOZUKA ** **Faculty of Engineering Sciences, Kyushu University 6-1 Kasuga
Science and Technology An Experimental Study on the Darrieus-Savonius Turbine for the Tidal Current Power Generation * Yusaku KYOZUKA ** **Faculty of Engineering Sciences, Kyushu University 6-1 Kasuga
WORK SHEET FOR MEP311
 EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
