Performance Assessment of the Waterjet Propulsion System through a Combined Analytical and Numerical Approach
|
|
|
- Osborn Harrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Physics, 013, Vol. 1, No., -7 Available online at Science and Education Publishing DOI: /ijp-1--1 Performance Assessment of the Waterjet Propulsion System through a Combined Analytical and Numerical Approach Parviz Ghadimi *, Roya Shademani, Mahdi Yousefi Fard Department of Marine Technology, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran *Corresponding author: pghadimi@aut.ac.ir Received December 13, 01; Revised April 1, 013; Accepted April 4, 013 Abstract The application of waterjets is rapidly growing and they are increasingly being chosen for propulsion in high-speed crafts. Waterjet as a propulsion system of a vessel is also favorable when it comes to maneuvering, appendage drag, draft and fuel consumption at high speeds. Furthermore, waterjet system has recently gained more credibility for its acceptable efficiency because of the advent of more efficient and large pumps. This type of propulsion system consists of many components working together harmoniously, thus establishing a complex system. A significant problem facing designers when predicting performance of the waterjet is the interaction between the hull and the waterjet. This paper describes the powering performance of a vessel equipped with a waterjet system. The interaction between the hull and waterjet is studied in order to predict the powering characteristics. The work starts with an introduction of the waterjet and a review of its current status in design and analysis. Subsequently, hydrodynamic properties of its components are computed and interactions among them are analyzed. Finally, numerical computation is performed for acquiring pressure distribution by a two dimensional computer code in the suction area of the waterjet inlet to predict the possible occurrence of cavitation for the inlet duct. Keywords: waterjet, inlet flow, numerical analysis, cavitation, propulsion system 1. Introduction In 16 Th century, Toogood and Hays for the first time proposed waterjet propulsion system, as reported by J.S. Carlton [1]. At that period of time, waterjet propulsions were used in high-speed pleasure craft and work boats. However, in recent years, this system has been considered for large high-speed crafts. Accordingly, many huge waterjet units have been used in wide range of ships such as passenger and naval crafts. The waterjet propulsion is a complex system. On the contrary, the screw propellers are simpler, lighter and more efficient than waterjet system. However, the arrival of more efficient pumps, the necessity for timely delivering the critical commercial cargoes, and the required maneuverability for particular vessels have made the usage of waterjets more attractive. It is normal to divide this type of propulsion system into a hull and a waterjet. It has been demonstrated that waterjet-hull interaction can affect the overall efficiency more than 0% []. Usually, waterjet system is broken down into subsystems and an explicit modular approach is applied to analyze them. In order to assess the interaction between the hull and the jet, a parametric method is used. In 1980, an early contribution related to the jet-hull interaction is attributed to Etter et al. [3]. A complete review of the existing relations for waterjet-hull performance is presented by Allison [4]. Van Terwisga [] proposed a parametric propulsion prediction method for the waterjet driven craft. Several numerical methods were devoted to study the flow behavior in every part of waterjet system by many researchers whose works were submitted to the ITT Conference [5]. A complete design method that utilized the numerical scheme for the analysis of system parts has been used by CCDOTT 1 [6]. N.W.H. Bulten [7] used CFD methods to design and analyze the whole jet system. Also, a flushtype waterjet propulsion unit was designed with different inner diameter impellers by Moon et al. [8]. In a related work, analysis of a waterjet axial pump was performed numerically [9]. They investigated the performance of the axial-flow-type waterjet based on the variation of the impeller tip clearance. The main distinction between the procedure implemented here and the previous methods is that the present method applies the empirical, analytical and numerical methods simultaneously to reach a conceptual design of the waterjet system. By numerical analysis, inlet design parameters that describe model geometry have been specified. Moreover, a simple -dimensional inlet model has been used here instead of a complex 3-D geometry. By this method, we have an acceptable propulsion system in a short time. Accordingly, a complete jet system design code has been developed that combines the empirical, analytical and numerical methods. 1 Center for the Commercial Deployment of Transportation Technologies
2 International Journal of Physics 3 By considering the ship geometry limitations and hydrodynamic properties, this software proposes suitable jet conceptual design parameters. Consequently, by using simple -D domain for inlet duct and computed pressure distributions for different inlet angles, an optimum inlet has been proposed which leads to minimum losses and maximum efficiency.. Basic Theory of System Waterjet propulsion system has three main components: Inlet, Pump and Nozzle. Figure 1 shows typical waterjet arrangement while Figure demonstrates the idealized profile of the jet system. Sea water enters the system with the velocity V in and leaves it with a different velocityv jet. The mass flow rate of the water through the waterjet is given by A jet jet (1) m A V where jet and are the area of nozzle outlet and density of water, respectively. The thrust produced by the system is equal to the rate of change of momentum: T A V V V () jet jet jet in Hence, the effective propulsion power delivered by the system is given by E S S jet in (3) P TV mv V V Figure 1. Typical waterjet general arrangement [1] Figure. Idealized waterjet arrangement [1] In Figure, the energy equation between points 1 and can be written as 1 1 P P V P V H H hloss (4) g g g g where H P : Pump head H : Vertical distance between inlet and outlet h loss : Total head loss. The jet efficiency is defined as jet P E PE Losses (5) This indicates that the jet efficiency is equal to the ratio of useful power to the total power absorbed by the system. Because of the effect of hull and geometry of the inlet duct, the inlet velocity is different from ship velocity. Hence, the inlet velocity ratio is defined as follows: IVR V in (6) V S The inlet has an optimal inlet velocity ratio at which jet has minimum losses at that point. This optimum point has been found by studying a range of velocity ratio and computing related system efficiency. Head losses in the duct inlet and outlet are functions of squared velocity [1]: Inlet in (7) h V g Outlet jet (8) h V g where and are empirical coefficients. These parameters can be assumed as fixed values depending on the inlet and outlet geometries [1]. Power input to the system (received by the pump) is given by 1 P m V V g h h pump jet in j loss (9) where h j is the vertical distance between the outlet nozzle and the water line. By separating system losses and applying loss coefficients, we obtain (10) m P [ pump V jet Vs ghj ] By using equation (10) and assuming the velocity ratio as V S V, equation (5) can be written as jet (1 (1 ) ) j gh 1 (1 )(1 ) i Vs (11) Jet efficiency can be calculated from equation (11). Other design parameters have been found based on the velocity ratios. Figure 3 shows that jet outlet diameter increases at high velocity ratio, while the maximum value of jet efficiency is observed to occur at high velocity ratio. Thus, to achieve high efficiency, a large jet diameter should be selected. However, the aft geometry of ship makes limitations for jet diameter. Therefore, a specified jet diameter is selected and other design parameters are assessed based on this main restriction. On the other hand, the optimum velocity ratio is found by setting the derivative of equation (11) with respect to equal to zero to obtain: where is given by opt (1)
3 Head [m] Mass Flow [Ton/s] Efficiency Jet Diameter [m] 4 International Journal of Physics gh j VS (13) By using the pump and hull efficiencies, the total efficiency is defined by the following equation:.. OA Pump Hull jet (14) Hull 1 t (15) 1 where Hull, and t are the hull efficiency, wake and thrust deduction factors, respectively. Wake factor can be estimated by the boundary layer theory which will be explained in the next section Efficiency Jet Diameter Figure 3. Efficiency and jet diameter as a function of velocity ratio Figure 4. shows how the pump head is inversely proportional to the mass flow rate of the jet system. Therefore, for a specified velocity ratio, a pump should be selected as such that its head and mass flow rate correspond to those values obtained from the plots in Figure 4 at that designated velocity ratio. On the other hand, the engine and propulsion system spaces have dimensional limitations, since mixed flow pumps is a better option than other types like axial pumps Head Mass Flow Figure 4. System head and flow rate as a function of velocity ratio 3. Assessment of Wake Parameter The waterjet inlet provides flow from beneath the ship to the waterjet pump. The waterjet inlet is located near the stern area of the ship, and as a result inflow to the flush waterjet inlets will include a significant amount of hull boundary layer flow. This means that for a flush waterjet inlet, the flow entering the waterjet inlet has a momentum velocity, U m, which is less than the ship speed, V S, due to the inclusion of hull boundary layer flow. The amount of the hull boundary layer flow which is included in the inlet flow is important as it can impact the size, performance, and propulsive efficiency of the waterjet pump and must be taken into consideration during the design phase of a waterjet pump. Prediction of the inlet momentum velocity requires a thorough understanding of the boundary layer velocity profile which is instrumental for estimation of the boundary layer thickness,. Svenson et al. [10] presented data for hull boundary layer thickness for high Reynolds number applications, as: where x L Re (16) Re x U Lx x (17) Accordingly, velocity at any point in the boundary layer region is given by: where U U y 1 n (18) n log10 Rex (19) A standard method of expressing the impact of the inlet momentum velocity is the inlet wake fraction or factor given as: U 1 m U which can be conversely written as: Um (0) 1 U (1) where U, is the uniform speed at far stream (in this case is considered to be the ship-speed V S ) and U m is the velocity inside the boundary layer (but here, it is the flow speed at the inlet due to the boundary layer). Figure 5 shows the computed values of wake parameter and the boundary layer thickness as functions of ship velocity. It is quite obvious that these two significant parameters decline as ship velocity increases. However, the value of wake parameter is about 0.9 and this parameter could be considered as a constant quantity. 4. Validation of Design Parameters As mentioned before, main results of the current code in the form of mass flow rate, pump head and power have been compared with the available results of design software and model test [6]. A range of data made available by the current code was compared with that provided by the CCDOTT software [6]. Furthermore, comparison was made between the results of the current code with the CCDOTT experiment for the design point shown in figures 6, 7, and 8. WJ sign in comparison
4 Flow Rate Power [HP] Wake δ [m] Head Rise International Journal of Physics 5 figures shows the results of the present method. Figure 6 shows the comparison of the mass flow rate for the experimental design point, the current method and fast ferry computed results which was offered by CCDOTT [6]. Also, figures 7 and 8 present the same comparisons for system head and power, respectively. These figures demonstrate that the existing errors between the results of the current code and the experimental data are generally lower than 5%. Based on the presented validations, it can be concluded that the off-design results are quite reliable. The off-design results become particularly important when the high-speed craft tends to reach a maximum speed over the main hump of the speed-resistance curve, because the power which is produced by the engine in off-design condition is sometimes lower than the required value separation could occur at two points at different inlet velocity ratios [11]. Figures 10 and 11 show the positions of the cavitation and separation phenomena at low and high inlet velocity ratios, respectively. The probability of cavitation occurrence was shown by the current work to be a function of the inlet angle, ramp radius among other design parameters. In the meantime, Inlet angle was found to be the most influential parameter which affects the cavitation occurrence and as such, the best inlet angle was determined. Based on this observation, it was decided that controlling of the cavitation occurrence be done through variation of the inlet angle while keeping other parameters constant CCDOTT WJ Design Point δ [m] ω Figure 7. Comparison of system head results Ship Velocity (Knot) Figure 5. Boundary layer thickness and wake factor as a function of ship velocity WJ Design Point CCDOTT WJ Design Point Figure 8. Comparison of system power results Figure 6. Comparison of flow rate results 5. Analysis of the Inlet Design Parameters The current code is capable to compute the inlet area and pump diameter from momentum equation and geometry limits. Based on these computed results, empirical theory was used to predict the system losses and basic geometrical parameters. It was found that elliptical inlets have more advantages than the rectangular inlets. Experiments show that elliptical inlet geometry with aspect ratio of 1.3 is the best inlet form for flush type jet []. Figure 9 shows the parameterized geometry of the inlet profile. Obviously, a fair inlet profile has many advantages, but sometimes transom geometry and aft form of ship impose limitations. To survey the inlet profile shape and to analyze the flow over this domain, some geometrical parameters have been defined. Cavitation and Figure 9. Inlet design parameters Figure 10. Cavitation (point A) and separation (point B) at low Inlet velocity ratio (IVR)
5 σ 6 International Journal of Physics Figure 14 presents the cavitation number at the centerline of the system for two different inlet angles. These figures could furthermore indicate how and where the cavitation could occur. Figure 14 shows how the system will operate at a design speed range without cavitation at the inlet ramp when the inlet angle becomes 6 degrees. Figure 11. Separation (point A) and cavitation (point B) at high Inlet velocity ratio (IVR) 6. Numerical Analysis of the Inlet Duct When designing a high-speed waterjet inlet, it is difficult to achieve an optimum design that is both efficient and has low drag. This is because cavitation occurs in the water that is unfavorable to both drag and efficiency. Cavitation generally occurs when the local pressure on a body moving in a fluid drops to or below the vapor pressure of the fluid. When reaching the vapor pressure, small bubbles or cavities are produced. These cavities will collapse when they reach a higher-pressure region and cause a small water hammer to form. This phenomenon is called cavitation. Cavitation can produce the negative effects of noise, vibration, and erosion or damage to the inlet, and therefore, must be avoided in order to safeguard the efficiency and the drag. RANS code has been used to find pressure distribution around the inlet duct. Two-dimensional geometry of waterjet inlet duct has been modeled. Additionally, a rectangular region is constructed around the hull to represent the boundaries of the ocean. Since the ocean is not actually bounded, those boundaries will have to either be placed adequately far away from the ship hull and defined as a wall, or placed closer to the hull to reduce the size of the problem and defined as an opening. Once the modeling was accomplished, an inlet duct was analyzed for four different inlet angles ranging from 6 to 34 degrees, and minimum pressure at the given inlet angles were compared against the numerical findings of CCDOTT group [6]. This comparison in Figure 1 shows a good agreement between the validation base and numerical calculations. Selection of the inlet angle was done based on two different design considerations; suitable length of propulsion system and avoidance of cavitation. Finding the optimum inlet angle requires a trial and error progress. Accordingly, a large angle was selected and possibility of cavitation was examined, needless to say that assuming a proper safety factor is very important in this progress. Cavitation number is defined as: p pv () 1 U When 0, cavitation starts. This implies that high cavitation numbers give less risk for cavitation. Figure 13 shows contours of cavitation numbers in XY plane while Reynolds Averaged Navier Stokes Figure 1. Comparison of minimum pressure for different inlet angles Figure 13. Cavitation number around inlet duct (Inlet angle 6 ) Inlet Angle=8 Inlet Angle= Figure 14. Cavitation number on top inlet wall at two inlet angle (see Figure 9) 3-D analysis of inlet duct which was done by CCDOTT shows that the minimum pressure occurs at the centerline. On the other hand, the results of the current study have good conformity with those of the mentioned 3D analysis. Thus, Figure 14 could be considered as a reliable source for designing the inlet duct. 7. Conclusion Simultaneous accomplishment of the conceptual and basic design as well as the analysis of waterjet propulsion system in a single process is a cumbersome task. Many analytic and empirical methods have been proposed to evaluate the influential parameters of this system. Numerical methods are used for the analysis of the system X[m]
6 International Journal of Physics 7 performance, albeit not in a design process. In the current work, a particular method has been presented which covers all stages of the design and the analysis of waterjet propulsion system which has also been validated by reliable results. Two different codes have been developed, one for the analytical assessment of the main waterjet propulsion system parameters and the other of numerical investigation of the inlet duct impacts. In the current scheme, a practical method is used to predict the powering characteristics of systems. Prediction of the performance of the waterjet system at the design point starts with determination of the required thrust, jet diameter, shaft horsepower, and RPM which is done by a developed computer program. During the detailed hydrodynamic optimization study, the RPM, radial blade loading distribution, and other parameters of the waterjet were varied to arrive at the optimum design for this power level. Computed values of flow rate, head rise, and power versus the velocity ratio were compared against earlier reported experimental and numerical results. These comparisons demonstrated good agreements indicating that the separate handling of the waterjet and hull designing process appears to be quite possible. The adopted approach leads to a set of parametric relations that describes the interaction between the hull and the waterjet system. Because of this modular approach, the results can simply be refined during the design process of the vessel. Empirical relations have been used for preliminary estimation of the required power for the vessel. From this calculated thrust and the assessed internal losses in the waterjet system, the required pump power can be found. Possible cavitation at the inlet duct leads to erosion or vibrations which must be avoided. In this paper, cavitation characteristics at the inlet were found by looking at the pressure distribution of the water around the inlet opening. Accordingly, the possibility of cavitation was investigated and controlled by close scrutiny of the cavitation number. Along the same line, optimum inlet geometry was found based on the observation of pressure distributions at different inlet angles. This whole process was achieved by a -D numerical code written for the flow investigation at the inlet of the waterjet system. Numerical findings of the current -D code compared with the earlier results of the 3-D modeling show an excellent match between the pressure distributions. As a result, one may conclude that a lengthy process of 3-D computation can indeed be avoided and that similar results can easily be achieved by a -D analysis which is a less laborious process and saves much computational time. Main geometrical parameters for the design of waterjet propulsion system have been determined by the present method. By utilizing these important parameters, a designer is able to predict the waterjet performance on a ship before arriving at the basic design stage. Needless to say that there are other considerations that must be taken into account which include necessary number of jets, position of the propulsion system, and the effect of the system on compartmental arrangement of the ship. Nomenclature m : Mass flow rate ρ: Density A jet : Area of nozzle outlet V jet : Jet velocity T: System thrust V in : Inlet velocity P E : Effective power V S : Ship speed H P : Pump head h loss : Total head losses η jet : Jet efficiency IVR : Inlet h Inlet : Inlet head losses h Outlet : Outlet head losses ξ : Inlet losses coefficient ψ : Outlet losses coefficient P Pump : Pump power h j : jet height from waterline ω : Wake factor µ : Velocity ratio η Pump : Pump efficiency η Hull : Hull efficiency t : Trust reduction factor δ : Boundary layer thickness L X : Distance from bow Re x : Reynolds number υ : Kinematical viscosity y : Vertical distance from hull U : Uniform flow velocity (ship speed) U m : Flow speed at the inlet due to boundary layer σ : Cavitation number p : Fluid pressure p v : Fluid vapor pressure References [1] Carlton.J.S. (John S.), Marine Propeller and Propulsion, Oxford, Butterworth-Heinemann, 1994T.J.C. Van Terwisga, A Parametric Propulsion Prediction Method For Waterjet Driven Craft, Fast 97 Conference, paper No. 151, [] T.J.C. Van Terwisga, A Parametric Propulsion Prediction Method For Waterjet Driven Craft, Fast 97 Conference, paper No. 151, [3] Etter, R.J., Krishnamoorthy, V. and Sherer, J.O., Model Testing of waterjet Propelled Draft, Proceedings of the 19 th ATTC, [4] Allison, J.L., Marine Waterjet Propulsion, SNAME Annual meeting, New York, [5] ITTC, The Specialist Committee on Waterjets, th ITTC, International Towing Tank Conference, [6] Stanley Wheatley, Development of a High-speed Sealift Waterjet Propulsion System, Final Report, Center for the Commercial Deployment of Transportation Technologies California State University, Long Beach Foundation, September 30, 003. [7] Bulten, N.W.H., Numerical Analysis of Waterjet Propulsion System, PhD Thesis, Technical University of Eindhoven, 006. [8] Moon-Chan Kim, Ho-Hwan Chun, Experimental Investigation into the performance of the Axial-Flow-Type Waterjet according to the Variation of Impeller Tip Clearance, Ocean Engineering 34, pp.75-83, 007. [9] Hong Gao, Wanlai Lim, Zhaohui Du, Numerical Flow and Performance Analysis of a Waterjet Axial Flow Pump, Ocean Engineering 35, pp , 008. [10] Svensson, R., etal., Trial Results Including Wake Measurements from the World s Largest Waterjet Installation, RINA International Conference on Waterjet Propulsion, Amsterdam, - 3 October [11] Donald M. MacPherson, A Universal Parametric Model for Waterjet performance, FAST '99, Aug 1999.
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Management TECHNOLOGY (ICETEM14) (IJDMT) 30-31,December, 2014, Ernakulam,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Management TECHNOLOGY (ICETEM14) (IJDMT) 30-31,December, 2014, Ernakulam,
Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of a Wake Equalizing Duct
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
Teaching sessions week 40
 Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using CFD
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on Pump Performance
 11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder
 A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder Hassan Ghassemi, a,* and Farzam Allafchi, a a ) Department of Ocean Engineering, Amirkabir
A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder Hassan Ghassemi, a,* and Farzam Allafchi, a a ) Department of Ocean Engineering, Amirkabir
Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Full scale thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
ENGR 4011 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships Assignment 5: A dimensional analysis of propeller thrust starting with the functional expression
 ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Workshop: Propeller performance Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description Ulf Barkmann 1, Hans-Jürgen
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Workshop: Propeller performance Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description Ulf Barkmann 1, Hans-Jürgen
Fluid structure interaction dynamic analysis of a mixed-flow waterjet pump
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Fluid structure interaction dynamic analysis of a mixed-flow waterjet pump To cite this article: X W Pan et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Fluid structure interaction dynamic analysis of a mixed-flow waterjet pump To cite this article: X W Pan et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.:
Numerical analysis of a waterjet propulsion system
 Numerical analysis of a waterjet propulsion system Bulten, N.W.H. DOI: 10.6100/IR614907 Published: 01/01/2006 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version of Record (includes final page, issue
Numerical analysis of a waterjet propulsion system Bulten, N.W.H. DOI: 10.6100/IR614907 Published: 01/01/2006 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version of Record (includes final page, issue
WATERJET PROPULSION SYSEM FOR HIGH SPEED CRAFTS
 ARAB ACADEMY FOR SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND MARITIME TRANSPORT COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY WATERJET PROPULSION SYSEM FOR HIGH SPEED CRAFTS Thesis Submitted to The Marine Engineering Department In
ARAB ACADEMY FOR SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND MARITIME TRANSPORT COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY WATERJET PROPULSION SYSEM FOR HIGH SPEED CRAFTS Thesis Submitted to The Marine Engineering Department In
Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA
 Research Article Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA Kiam Beng Yeo, Wai Heng Choong and Wen Yen Hau ABSTRACT The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of marine propeller blade stress
Research Article Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA Kiam Beng Yeo, Wai Heng Choong and Wen Yen Hau ABSTRACT The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of marine propeller blade stress
Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer To cite this article: C Ning et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 72 032025
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer To cite this article: C Ning et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 72 032025
An Overview of Impellers, Velocity Profile and Reactor Design
 An Overview of s, Velocity Profile and Reactor Design Praveen Patel 1, Pranay Vaidya 1, Gurmeet Singh 2 1 Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India 1 Indian Oil Corporation Limited, R&D Centre Faridabad
An Overview of s, Velocity Profile and Reactor Design Praveen Patel 1, Pranay Vaidya 1, Gurmeet Singh 2 1 Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India 1 Indian Oil Corporation Limited, R&D Centre Faridabad
Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN
 ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF WATERJET PROPELLED DELFT CATAMARANS
 11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF WATERJET PROPELLED DELFT CATAMARANS Manivannan Kandasamy
11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF WATERJET PROPELLED DELFT CATAMARANS Manivannan Kandasamy
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines Testing and Extrapolation Methods Propulsion, Performance Propulsion Test
 7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
STUDY ON TIP LEAKAGE VORTEX IN AN AXIAL FLOW PUMP BASED ON MODIFIED SHEAR STRESS TRANSPORT k-ω TURBULENCE MODEL
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 213, Vol. 17, No. 5, pp. 1551-1555 1551 STUDY ON TIP AKAGE VORX IN AN AXIAL FLOW PUMP BASED ON MODIFIED SHEAR STRE TRANSPORT k-ω TURBUNCE MODEL Introduction by Desheng ZHANG *, Dazhi
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 213, Vol. 17, No. 5, pp. 1551-1555 1551 STUDY ON TIP AKAGE VORX IN AN AXIAL FLOW PUMP BASED ON MODIFIED SHEAR STRE TRANSPORT k-ω TURBUNCE MODEL Introduction by Desheng ZHANG *, Dazhi
Contents. 1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines Overview of Turbomachinery Nomenclature...9
 Preface page xv 1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines...1 Definition 1 Advantages of Gas-Turbine Engines 1 Applications of Gas-Turbine Engines 3 The Gas Generator 3 Air Intake and Inlet Flow Passage 3
Preface page xv 1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines...1 Definition 1 Advantages of Gas-Turbine Engines 1 Applications of Gas-Turbine Engines 3 The Gas Generator 3 Air Intake and Inlet Flow Passage 3
Cavitations Analysis on Impeller Blades of Thai-made Irrigation Pump by Computational Fluid Dynamic technique
 Cavitations Analysis on Impeller Blades of Thai-made Irrigation Pump by Computational Fluid Dynamic technique Benya Kasantikul 1 and Santi Laksitanonta 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty
Cavitations Analysis on Impeller Blades of Thai-made Irrigation Pump by Computational Fluid Dynamic technique Benya Kasantikul 1 and Santi Laksitanonta 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty
Performance characteristics of turbo blower in a refuse collecting system according to operation conditions
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1896~1901 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-008-0729-6 Performance characteristics
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1896~1901 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-008-0729-6 Performance characteristics
Thrusters. Numerical Analysis of Flow Around a Thruster
 Thrusters Numerical Analysis of Flow Around a Thruster Norbert W. H. Bulten Wärtsilä Propulson, Netherlands October 17-18, 2006 Return to Session Directory Numerical Analysis of Flow around a Thruster
Thrusters Numerical Analysis of Flow Around a Thruster Norbert W. H. Bulten Wärtsilä Propulson, Netherlands October 17-18, 2006 Return to Session Directory Numerical Analysis of Flow around a Thruster
Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further.
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further. Gerasimos Politis 1,Theodoros Ioannou
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further. Gerasimos Politis 1,Theodoros Ioannou
ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
International Journal of Research in Advent Technology Available Online at:
 A COMPUTER PROGRAMMED DESIGN OPTIMISATION AND ANALYSIS OF COMPRESSOR IMPELLER G. Naga Malleshwar Rao 1, Dr. S.L.V. Prasad 2, Dr. S. Sudhakarbabu 3 1, 2 Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Shri Shirdi
A COMPUTER PROGRAMMED DESIGN OPTIMISATION AND ANALYSIS OF COMPRESSOR IMPELLER G. Naga Malleshwar Rao 1, Dr. S.L.V. Prasad 2, Dr. S. Sudhakarbabu 3 1, 2 Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Shri Shirdi
Study on Extrapolation Method for Self-Propulsion Test with Pre-Swirl Device *
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Study on Extrapolation Method for Self-Propulsion Test with Pre-Swirl Device * Moon-Chan Kim 1, Yong-Jin Shin 1, Won-Joon
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Study on Extrapolation Method for Self-Propulsion Test with Pre-Swirl Device * Moon-Chan Kim 1, Yong-Jin Shin 1, Won-Joon
Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics to Practical Design and Performance Analysis of Turbomachinery
 10 Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics to Practical Design and Performance Analysis of Turbomachinery Hyoung Woo OH Chungju National University Korea 1. Introduction Over the past several decades,
10 Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics to Practical Design and Performance Analysis of Turbomachinery Hyoung Woo OH Chungju National University Korea 1. Introduction Over the past several decades,
Prediction of induced vibrations for a passenger - car ferry
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Prediction of induced vibrations for a passenger - car ferry To cite this article: L Crudu et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Prediction of induced vibrations for a passenger - car ferry To cite this article: L Crudu et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
CHAPTER EIGHT P U M P I N G O F L I Q U I D S
 CHAPTER EIGHT P U M P I N G O F L I Q U I D S Pupmps are devices for supplying energy or head to a flowing liquid in order to overcome head losses due to friction and also if necessary, to raise liquid
CHAPTER EIGHT P U M P I N G O F L I Q U I D S Pupmps are devices for supplying energy or head to a flowing liquid in order to overcome head losses due to friction and also if necessary, to raise liquid
DETERMINING OPTIMUM GEOMETRY FOR A BOW THRUSTER PROPELLER
 DEERMINING OPIMUM GEOMERY FOR A BOW HRUSER PROPELLER Y.H. OZDEMIR, S. BAYRAKAR,. YILMAZ, M.GUNER Yildiz echnical University, Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, 34349 Besiktas, Istanbul,
DEERMINING OPIMUM GEOMERY FOR A BOW HRUSER PROPELLER Y.H. OZDEMIR, S. BAYRAKAR,. YILMAZ, M.GUNER Yildiz echnical University, Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, 34349 Besiktas, Istanbul,
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM
 DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
A simplified method for calculating propeller thrust decrease for a ship sailing on a given shipping lane
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(82) 2014 Vol 21; pp. 27-33 10.2478/pomr-2014-0015 A simplified method for calculating propeller thrust decrease for a ship sailing on a given shipping lane Katarzyna Zelazny,
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(82) 2014 Vol 21; pp. 27-33 10.2478/pomr-2014-0015 A simplified method for calculating propeller thrust decrease for a ship sailing on a given shipping lane Katarzyna Zelazny,
Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions
 DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 2010 Thrusters Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions Michael Palm,
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 2010 Thrusters Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions Michael Palm,
Deliverable D.6.1. Application of CFD tools to the development of a novel propulsion concept
 TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Performances of Marine Propeller
 Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Performances of Marine Propeller Master Thesis developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati in the framework of the EMSHIP Erasmus Mundus Master Course
Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Performances of Marine Propeller Master Thesis developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati in the framework of the EMSHIP Erasmus Mundus Master Course
NUMERIC SIMULATION OF ULTRA-HIGH PRESSURE ROTARY ATOMIZING WATERJET FLOW FIELD
 2005 WJTA American Waterjet Conference August 21-23, 2005 Houston, Texas Paper 6A-4 NUMERIC SIMULATION OF ULTRA-HIGH PRESSURE ROTARY ATOMIZING WATERJET FLOW FIELD Xue Shengxiong, Li Jiangyun *, Peng Haojun,
2005 WJTA American Waterjet Conference August 21-23, 2005 Houston, Texas Paper 6A-4 NUMERIC SIMULATION OF ULTRA-HIGH PRESSURE ROTARY ATOMIZING WATERJET FLOW FIELD Xue Shengxiong, Li Jiangyun *, Peng Haojun,
The Numerical Investigation on Hydrodynamic Performance of Twisted Rudder during Self-propulsion
 The Numerical Investigation on Hydrodynamic Performance of Twisted Rudder during Self-propulsion Cong Liu *, Jianhua Wang,Decheng Wan State Key Laboratory of Ocean Engineering, School of Naval Architecture,
The Numerical Investigation on Hydrodynamic Performance of Twisted Rudder during Self-propulsion Cong Liu *, Jianhua Wang,Decheng Wan State Key Laboratory of Ocean Engineering, School of Naval Architecture,
Introduction to Turbomachinery
 1. Coordinate System Introduction to Turbomachinery Since there are stationary and rotating blades in turbomachines, they tend to form a cylindrical form, represented in three directions; 1. Axial 2. Radial
1. Coordinate System Introduction to Turbomachinery Since there are stationary and rotating blades in turbomachines, they tend to form a cylindrical form, represented in three directions; 1. Axial 2. Radial
On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
Powering for Medium Speed Wave-Piercing Catamarans comparing Waterjet and Screw Propeller Performance using Model Testing
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Powering for Medium Speed Wave-Piercing Catamarans comparing Waterjet and Screw Propeller Performance using Model
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Powering for Medium Speed Wave-Piercing Catamarans comparing Waterjet and Screw Propeller Performance using Model
Hydro-Structure Analysis of Composite Marine Propeller under Pressure Hydrodynamic Loading
 American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
Numerical Simulation of Underwater Propeller Noise
 Numerical Simulation of Underwater Propeller Noise Bagheri M.R, a*, Seif M.S, a and Mehdigholi H, a a) Sharif University of Technology, Center of Excellence in Hydrodynamic and Dynamic of Marine Vehicles,
Numerical Simulation of Underwater Propeller Noise Bagheri M.R, a*, Seif M.S, a and Mehdigholi H, a a) Sharif University of Technology, Center of Excellence in Hydrodynamic and Dynamic of Marine Vehicles,
Chapter 5 Control Volume Approach and Continuity Equation
 Chapter 5 Control Volume Approach and Continuity Equation Lagrangian and Eulerian Approach To evaluate the pressure and velocities at arbitrary locations in a flow field. The flow into a sudden contraction,
Chapter 5 Control Volume Approach and Continuity Equation Lagrangian and Eulerian Approach To evaluate the pressure and velocities at arbitrary locations in a flow field. The flow into a sudden contraction,
DESIGN AND CFD ANALYSIS OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
 DESIGN AND CFD ANALYSIS OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP 1 CH.YADAGIRI, 2 P.VIJAYANAND 1 Pg Scholar, Department of MECH, Holymary Institute of Technology, Ranga Reddy, Telangana, India. 2 Assistant Professor, Department
DESIGN AND CFD ANALYSIS OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP 1 CH.YADAGIRI, 2 P.VIJAYANAND 1 Pg Scholar, Department of MECH, Holymary Institute of Technology, Ranga Reddy, Telangana, India. 2 Assistant Professor, Department
Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines
 Contents 1- Introduction. - Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Contents 1- Introduction. - Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Improved Model for Meanline Analysis of Centrifugal Compressors with a Large Tip Clearance
 Improved Model for Meanline Analysis of Centrifugal Compressors with a Large Tip Clearance Andrey Sherbina 1, Ivan Klimov 2 and Leonid Moroz 3 SoftInWay Inc., 1500 District Avenue, Burlington, MA, 01803,
Improved Model for Meanline Analysis of Centrifugal Compressors with a Large Tip Clearance Andrey Sherbina 1, Ivan Klimov 2 and Leonid Moroz 3 SoftInWay Inc., 1500 District Avenue, Burlington, MA, 01803,
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power
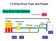 7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation
 CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation S. Ramakrishna* GVP College of Engineering (A) Visakhapatnam V. Ramakrishna Scientist D N S T L Visakhapatnam A. Ramakrishna Professor A U C E (A) Visakhapatnam
CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation S. Ramakrishna* GVP College of Engineering (A) Visakhapatnam V. Ramakrishna Scientist D N S T L Visakhapatnam A. Ramakrishna Professor A U C E (A) Visakhapatnam
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
 Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results
 Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
Mt Introduction. 2. Governing gphysics. 3. Decomposition of resistance. 4. Similarity laws and scaling
 1. Introduction 2. Governing gphysics 3. Decomposition of resistance 4. Similarity laws and scaling Mt 527 Importance of proper power-speed prediction Resistance, prop. efficiency, power Wake field Experimental,
1. Introduction 2. Governing gphysics 3. Decomposition of resistance 4. Similarity laws and scaling Mt 527 Importance of proper power-speed prediction Resistance, prop. efficiency, power Wake field Experimental,
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines
 Contents 1- Introduction. 2- Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Contents 1- Introduction. 2- Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics Anirban Bhattacharyya 1, Jan Clemens
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics Anirban Bhattacharyya 1, Jan Clemens
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller
 voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
1. Starting of a project and entering of basic initial data.
 PROGRAM VISIMIX TURBULENT SV. Example 1. Contents. 1. Starting of a project and entering of basic initial data. 1.1. Opening a Project. 1.2. Entering dimensions of the tank. 1.3. Entering baffles. 1.4.
PROGRAM VISIMIX TURBULENT SV. Example 1. Contents. 1. Starting of a project and entering of basic initial data. 1.1. Opening a Project. 1.2. Entering dimensions of the tank. 1.3. Entering baffles. 1.4.
Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(78) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 13-20 10.2478/pomr-2013-0012 Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle Hassan
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(78) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 13-20 10.2478/pomr-2013-0012 Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle Hassan
Facilities: CHL (Computational Hydrodynamics Laboratory) in ECJ 8.502
 Ocean Engineering Group (OEG)/EWRE (August 28, 2018) Spyros A. Kinnas Professor and Director of OTRC s UT Office (Offshore Technology Research Center) Kinnas Home Page @SpyrosKinnas on twitter Research
Ocean Engineering Group (OEG)/EWRE (August 28, 2018) Spyros A. Kinnas Professor and Director of OTRC s UT Office (Offshore Technology Research Center) Kinnas Home Page @SpyrosKinnas on twitter Research
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW ANALYSIS THROUGH A DOUBLE-SUCTION IMPELLER OF A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
 Proceedings of the Fortieth National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power December 12-14, 2013, NIT Hamirpur, Himachal Pradesh, India FMFP2013_141 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW ANALYSIS THROUGH A DOUBLE-SUCTION
Proceedings of the Fortieth National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power December 12-14, 2013, NIT Hamirpur, Himachal Pradesh, India FMFP2013_141 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW ANALYSIS THROUGH A DOUBLE-SUCTION
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 7.5 02 Page 1 of 21 Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 2 2 ITTC DICTIONARY OF SHIP HYDRODYNAMICS PROPELLER SECTION... 2 COMMENTS OF THE PROPULSION COMMITTEE OF 22 nd ITTC Several of the symbols and definitions
7.5 02 Page 1 of 21 Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 2 2 ITTC DICTIONARY OF SHIP HYDRODYNAMICS PROPELLER SECTION... 2 COMMENTS OF THE PROPULSION COMMITTEE OF 22 nd ITTC Several of the symbols and definitions
Impact of a Jet. Experiment 4. Purpose. Apparatus. Theory. Symmetric Jet
 Experiment 4 Impact of a Jet Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate and verify the integral momentum equation. The force generated by a jet of water deflected by an impact surface is
Experiment 4 Impact of a Jet Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate and verify the integral momentum equation. The force generated by a jet of water deflected by an impact surface is
Study on the Performance of a Sirocco Fan (Flow Around the Runner Blade)
 Rotating Machinery, 10(5): 415 424, 2004 Copyright c Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1023-621X print / 1542-3034 online DOI: 10.1080/10236210490474629 Study on the Performance of a Sirocco Fan (Flow Around
Rotating Machinery, 10(5): 415 424, 2004 Copyright c Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1023-621X print / 1542-3034 online DOI: 10.1080/10236210490474629 Study on the Performance of a Sirocco Fan (Flow Around
Cavitation Control on Hydrofoils
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Prague, Czech Republic, August 11-12, 2014 Paper No. 181 Cavitation Control on Hydrofoils Mohammad Mortezazadeh, Ali Katal, Khodayar
Proceedings of the International Conference on Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Prague, Czech Republic, August 11-12, 2014 Paper No. 181 Cavitation Control on Hydrofoils Mohammad Mortezazadeh, Ali Katal, Khodayar
Experimental and numerical analysis of eight different volutes with the same impeller in a squirrel-cage fan
 Experimental and numerical analysis of eight different volutes with the same impeller in a squirrel-cage fan SINA SAMARBAKHSH, JAVAD ALINEJAD Azmoon Pardazesh Research Institute, Malekloo St., Farjam St.,
Experimental and numerical analysis of eight different volutes with the same impeller in a squirrel-cage fan SINA SAMARBAKHSH, JAVAD ALINEJAD Azmoon Pardazesh Research Institute, Malekloo St., Farjam St.,
Fluid Mechanics III. 1. Dimensional analysis and similarity
 Fluid Mechanics III 1. Dimensional analysis and similarity Similarity The real world is non-dimensional. The proposition the Eiffel Tower is tall has no sense unless we state what is the object we compare
Fluid Mechanics III 1. Dimensional analysis and similarity Similarity The real world is non-dimensional. The proposition the Eiffel Tower is tall has no sense unless we state what is the object we compare
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE. October 13-14, Thrusters. Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels
 Return to Session Directory DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 13-14, 2009 Thrusters Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels Dirk Jürgens, Michael Palm
Return to Session Directory DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 13-14, 2009 Thrusters Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels Dirk Jürgens, Michael Palm
HYDRODYNAMIC PREDICTION OF THE DUCTED PROPELLER BY CFD SOLVER
 68 ournal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 5, No. 3, pp. 68-75 (17) DOI: 1.6119/MST-16-114- HYDRODYNAMIC PREDICTION OF THE DUCTED PROPELLER BY CFD SOLVER Sohrab Majdfar, Hassan Ghassemi 1, Hamid
68 ournal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 5, No. 3, pp. 68-75 (17) DOI: 1.6119/MST-16-114- HYDRODYNAMIC PREDICTION OF THE DUCTED PROPELLER BY CFD SOLVER Sohrab Majdfar, Hassan Ghassemi 1, Hamid
Calculation of Power and Flow Capacity of Rotor / Stator Devices in VisiMix RSD Program.
 Calculation of Power and Flow Capacity of Rotor / Stator Devices in VisiMix RSD Program. L.N.Braginsky, D.Sc. (Was invited to be presented on the CHISA 2010-13th Conference on Process Integration, Modelling
Calculation of Power and Flow Capacity of Rotor / Stator Devices in VisiMix RSD Program. L.N.Braginsky, D.Sc. (Was invited to be presented on the CHISA 2010-13th Conference on Process Integration, Modelling
PROPELLER INDUCED STRUCTURAL VIBRATION THROUGH THE THRUST BEARING
 PROPELLER INDUCED TRUCTURAL VIBRATION THROUGH THE THRUT BEARING Jie Pan, Nabil Farag, Terry Lin and Ross Juniper* DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL AND MATERIAL ENGINEERING THE UNIVERITY OF WETERN AUTRALIA 35 TIRLING
PROPELLER INDUCED TRUCTURAL VIBRATION THROUGH THE THRUT BEARING Jie Pan, Nabil Farag, Terry Lin and Ross Juniper* DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL AND MATERIAL ENGINEERING THE UNIVERITY OF WETERN AUTRALIA 35 TIRLING
The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory
 J. Marine Sci. Appl. (2012) 11: 164-168 DOI: 10.1007/s11804-012-1118-1 The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory Qiuxin Gao *, Wei Jin and Dracos Vassalos Department of
J. Marine Sci. Appl. (2012) 11: 164-168 DOI: 10.1007/s11804-012-1118-1 The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory Qiuxin Gao *, Wei Jin and Dracos Vassalos Department of
A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew Dominic J. Taunton Dominic A.
 A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew, Dominic J. Taunton, Dominic A. Hudson Fluid Structure Interactions Group, University of Southampton ss17e111@soton.ac.uk
A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew, Dominic J. Taunton, Dominic A. Hudson Fluid Structure Interactions Group, University of Southampton ss17e111@soton.ac.uk
3 Energy Exchange in Turbomachines
 3 Energy Exchange in Turbomachines Problem 1 The solved and unsolved examples of this chapter are meant to illustrate the various forms of velocity triangles and the variety of the turbomachines. In addition,
3 Energy Exchange in Turbomachines Problem 1 The solved and unsolved examples of this chapter are meant to illustrate the various forms of velocity triangles and the variety of the turbomachines. In addition,
mixing of fluids MIXING AND AGITATION OF FLUIDS
 Levenspiel [2] considered when two fluids are mixed together, the molecular behavior of the dispersed fluid falls between two extremes. If molecules are completely free to move about, the dispersed fluid
Levenspiel [2] considered when two fluids are mixed together, the molecular behavior of the dispersed fluid falls between two extremes. If molecules are completely free to move about, the dispersed fluid
SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -11. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before. attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook. THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 Fluid Flow
 Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 REFERENCES REFERENCES Streeter, Victor L., Fluid Mechanics, 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, ISBN 07-062191-9.
Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 REFERENCES REFERENCES Streeter, Victor L., Fluid Mechanics, 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, ISBN 07-062191-9.
DESIGN OF A HYBRID POWER/TORQUE THRUSTER CONTROLLER WITH LOSS ESTIMATION. Øyvind N. Smogeli, Asgeir J. Sørensen and Thor I. Fossen
 DESIGN OF A HYBRID POWER/TORQUE THRUSTER CONTROLLER WITH LOSS ESTIMATION Øyvind N. Smogeli, Asgeir J. Sørensen and Thor I. Fossen Department of Marine Technology Norwegian University of Science and Technology
DESIGN OF A HYBRID POWER/TORQUE THRUSTER CONTROLLER WITH LOSS ESTIMATION Øyvind N. Smogeli, Asgeir J. Sørensen and Thor I. Fossen Department of Marine Technology Norwegian University of Science and Technology
Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump To cite this article: Y Y Liu et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 032023
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump To cite this article: Y Y Liu et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 032023
Effect of modification to tongue and basic circle diameter on vibration in a double-suction centrifugal pump
 5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 2015) Effect of modification to tongue and basic circle diameter on vibration in a double-suction centrifugal
5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 2015) Effect of modification to tongue and basic circle diameter on vibration in a double-suction centrifugal
ITTC Recommended Procedures Testing and Extrapolation Methods Resistance Resistance Test
 -0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
-0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PERFORMANCE OF KAPLAN TURBINE WITH DRAFT TUBE
 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PERFORMANCE OF KAPLAN TURBINE WITH DRAFT TUBE Mohamed Adel and Nabil H. Mostafa ABSTRACT Mechanical Power Engineering Department, Engineering Faculty Zagazig University, Zagazig,
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PERFORMANCE OF KAPLAN TURBINE WITH DRAFT TUBE Mohamed Adel and Nabil H. Mostafa ABSTRACT Mechanical Power Engineering Department, Engineering Faculty Zagazig University, Zagazig,
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method
 Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
Simplified Model of WWER-440 Fuel Assembly for ThermoHydraulic Analysis
 1 Portál pre odborné publikovanie ISSN 1338-0087 Simplified Model of WWER-440 Fuel Assembly for ThermoHydraulic Analysis Jakubec Jakub Elektrotechnika 13.02.2013 This work deals with thermo-hydraulic processes
1 Portál pre odborné publikovanie ISSN 1338-0087 Simplified Model of WWER-440 Fuel Assembly for ThermoHydraulic Analysis Jakubec Jakub Elektrotechnika 13.02.2013 This work deals with thermo-hydraulic processes
New Artificial Intelligence Technology Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing CO 2 Emissions of Ships through Use of Operational Big Data
 New Artificial Intelligence Technology Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing CO 2 Emissions of Ships through Use of Operational Big Data Taizo Anan Hiroyuki Higuchi Naoki Hamada Fuel cost and CO 2 emissions
New Artificial Intelligence Technology Improving Fuel Efficiency and Reducing CO 2 Emissions of Ships through Use of Operational Big Data Taizo Anan Hiroyuki Higuchi Naoki Hamada Fuel cost and CO 2 emissions
ITTC Circular Letter
 ITTC Circular Letter May, 2016 Load variation tests The speed/power sea trials procedures, ITTC Recommended rocedures 7.5-04-01-01.1 and -01.2, and IO15016:2015 require that load variation tests are performed
ITTC Circular Letter May, 2016 Load variation tests The speed/power sea trials procedures, ITTC Recommended rocedures 7.5-04-01-01.1 and -01.2, and IO15016:2015 require that load variation tests are performed
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering CVNG 1001: Mechanics of Fluids
 INTRODUCTION Hydrodynamic Machines A hydromachine is a device used either for extracting energy from a fluid or to add energy to a fluid. There are many types of hydromachines and Figure 1 below illustrates
INTRODUCTION Hydrodynamic Machines A hydromachine is a device used either for extracting energy from a fluid or to add energy to a fluid. There are many types of hydromachines and Figure 1 below illustrates
Dynamic Responses of Composite Marine Propeller in Spatially Wake
 Dynamic Responses of Composite Marine Propeller in Spatially Wake Dynamic Responses of Composite Marine Propeller in Spatially Wake Y. Hong a, X.D. He a,*, R.G. Wang a, Y.B. Li a, J.Z. Zhang a, H.M. Zhang
Dynamic Responses of Composite Marine Propeller in Spatially Wake Dynamic Responses of Composite Marine Propeller in Spatially Wake Y. Hong a, X.D. He a,*, R.G. Wang a, Y.B. Li a, J.Z. Zhang a, H.M. Zhang
Resistance and Propulsion
 MSc. Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering Resistance and Propulsion 0-0 Project Propeller Design with the Lifting Line Theory - Program PROPINFAC Resistance and Propulsion Project Propeller Design
MSc. Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering Resistance and Propulsion 0-0 Project Propeller Design with the Lifting Line Theory - Program PROPINFAC Resistance and Propulsion Project Propeller Design
AN OVERVIEW OF IMPELLERS, VELOCITY PROFILES AND REACTOR DESIGN
 AN OVERVIEW OF IMPELLERS, VELOCITY PROFILES AND REACTOR DESIGN Instructor: Gurmeet Singh (Department Manager of Polymer and Processing Department IOCL R&D center, Faridabad) 1 Presented by: Pranay. K.
AN OVERVIEW OF IMPELLERS, VELOCITY PROFILES AND REACTOR DESIGN Instructor: Gurmeet Singh (Department Manager of Polymer and Processing Department IOCL R&D center, Faridabad) 1 Presented by: Pranay. K.
Efficient runner safety assessment during early design phase and root cause analysis
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Efficient runner safety assessment during early design phase and root cause analysis To cite this article: Q W Liang et al 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Efficient runner safety assessment during early design phase and root cause analysis To cite this article: Q W Liang et al 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth
A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION
 A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION Written by: J.D. van Manen (Whale Tail Development, The Netherlands) and T. van Terwisga (MARIN, The Netherlands) Presented on 34 th WEGEMT School by: M.X.
A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION Written by: J.D. van Manen (Whale Tail Development, The Netherlands) and T. van Terwisga (MARIN, The Netherlands) Presented on 34 th WEGEMT School by: M.X.
Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships
 (August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
(August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
Confined water effects on the viscous flow around a tanker with propeller and rudder
 International Shipbuilding Progress 60 (2013) 309 343 309 DOI 10.3233/ISP-130101 IOS Press Confined water effects on the viscous flow around a tanker with propeller and rudder L. Zou and L. Larsson Chalmers
International Shipbuilding Progress 60 (2013) 309 343 309 DOI 10.3233/ISP-130101 IOS Press Confined water effects on the viscous flow around a tanker with propeller and rudder L. Zou and L. Larsson Chalmers
Motions and Resistance of a Ship in Regular Following Waves
 Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
