Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description
|
|
|
- Merilyn Atkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Workshop: Propeller performance Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description Ulf Barkmann 1, Hans-Jürgen Heinke 1, Lars Lübke 1 1 SVA, Potsdam Model Basin, Germany 1 AIM OF WORKSHOP The purpose of the workshop is in-force the development of numerical methods for calculation of the performance of marine propulsors in cavitating and non-cavitating flows. The high demand for improving the accuracy and the quality of the numerical methods should be assess by providing high qualitative and intensive experimental validation data. The SVA Potsdam GmbH supported the smp organisation committee in monitoring the performance and accuracy of available numerical methods by offering test and validation data for a controllable pitch propeller SVA-VP1304. The test results are published in course of the propeller workshop of the Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors 2011 (smp 11). The geometry and results of the propeller are presented under the name PPTC, an acronym for Potsdam Propeller Test Case. The experimental results were unknown for the participants of the workshop. The experimental investigation includes open water test, velocity field measurements and cavitation tests. Different operation conditions were investigated. A detailed description of the open water tests conducted at the towing tank of the SVA is presented in the SVA report 3752 [1], which can be down loaded from the website (sva-potsdam.de). 2 GEOMETRY OF THE POTSDAM PROPELLER TEST CASE The propeller is a controllable pitch propeller. This affects the propeller blade design near the hub and results in a 0.3 mm gap between hub and the root of the propeller blade near the leading and trailing edge. The hub cap and aft fairing where designed according to the 22 nd ITTC (1999) proceedings. The gap between aft fairing and hub has a width of 3 mm. Also a dummy hub, having the same dimensions and mass as the propeller hub, was manufactured. The main data of the propeller is given in Table 1. The propeller geometry can be down loaded from the website (sva-potsdam.de). 3 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS 3.1 Open Water Performance Test Conditions The propeller is investigated in a pull configuration in the towing tank of the SVA. For the open water tests the dynamometer H39 from Kempf & Remmers has been used. During the tests the propeller shaft is submerged by 1.5 D. Measurements with a dummy hub were conducted, in order to get data of the idle torque, the force in the gap between the hub and the aft fairing and the resistance of the hub cap. The open water tests were carried out at two different numbers of revolutions to evaluate the dependency on the Reynolds number. However for the evaluation of the computational results solely the tests with n = 15 s -1 are taken into account. The details of experimental setup and test conditions are given in table 2 and Requested Computations It was requested to calculate the open water characteristics of the propeller for the advanced coefficients J = 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.4. The computations should be conducted according to the operation conditions given in Table 4. The thrust and torque of the propeller should be made dimensionless employing the rate of revolution n, the propeller diameter D and the density of water as follows: Advance coefficient Thrust coefficient Torque coefficient VA J n D K T K Q T n Q n 2 D 4 2 D 5
2 Open water efficiency 0 J K 2 K T Q The axial velocities are defined positive in flow direction, the radial velocities for increasing radii and the tangential velocities in direction of rotation. with V A being the advance speed, T the thrust and Q the propeller torque Open Water Test Results The measured values in the open water tests were corrected with the values of the idle torque and the gap force. The measured and corrected open water characteristics for the five requested advance coefficients are given in Table 4 for the number of revolutions n = 15 s Velocity Field Test Conditions The velocity field was measured by means of LDV in the cavitation tunnel K 15 A (Kempf & Remmers) of the SVA Potsdam, utilising a test section with the length of 2600 mm and a cross section of 600x600 mm. The dynamometer J25 from Kempf & Remmers was arranged in front of the propeller model. The shaft inclination was zero degrees. A 2D-LDV measuring system from TSI was used for the velocity measurements. Angular based measurements of the transient flow field behind the rotating propeller operating in homogeneous inflow were carried out. Special attention was laid upon resolving the tip vortex. The velocity field around the model propeller VP1304 was measured in seven planes x/d = -0.2, 0.094, 0.10, 0.11, 0.13, 0.16 and 0.20, with respect to the propeller plane as shown in Table 5. One revolution of the propeller was resolved within 1440 angle classes, giving an angular resolution of The resolution in radial direction is shown in Table 6. All measurements were conducted for the same working point, given in Table 7. The test conditions are given in Table 8. The LDV measurements were carried out along a line of constant angular position = 225. The data is than related to the zero degree position, being defined as the 12 o clock position. The tests were conducted with a non-cavitating propeller. Test results are summarized in in SVA report [2] Requested Computations It was requested to calculate the velocity field around the propeller for the working point and test conditions given in Table 4 and 5. The calculations should be conducted according to the thrust identity. Four different evaluations were requested. The velocity distribution should be provided on three different radii each for two planes located 0.1 and 0.2 propeller diameters behind the propeller plane, see Table 9. The velocity components for Case shall be made dimensionless by means of the inflow velocity, as follows 1-(V x /V A ), V t /V A and V r /V A. 3.3 Cavitation Test Conditions The cavitation tests were conducted in the cavitation tunnel K 15 A (Kempf & Remmers) of the SVA Potsdam. For the tests a test section with the length of 2600 mm and a cross section of 600 x 600 mm was used. The dynamometer J25 from Kempf & Remmers was arranged in front of the propeller model. The shaft inclination was zero degrees. The propeller characteristic in the cavitation tunnel had been measured at the numbers of revolutions n = 15, 20 and 25 s -1. Cavitation buckets were measured with the number of revolutions n = 25 s -1. Two blades had been selected for the cavitation tests. The cavitation behaviour of the propeller was observed in three working points, corresponding to the test conditions required for test case Test results are summarized in SVA report [3] Requested Computations It was requested to calculate the propeller cavitation for three working point, given in Table 10. The calculation shall be conducted according to the thrust identity. For the three working points it was requested to visualize the cavity surface for vapor fractions of 20, 50 and 80%. For case and case it was requested to look upon the suction side, while for case on the pressure side of the propeller. In order to quantify the thrust deduction it was additionally requested to provide the thrust coefficient of the propeller in cavitating condition. It was also requested to provide the pressure distribution, made dimensionless with the section advance speed, on the propeller radii r/r = 0.7, 0.97 and 1.00 with and without cavitation. The data is made dimensionless as follows: Cavitation number with respect to n: n Pressure coefficient: c P pv 2 p 0. 5 nd p p V 2 n r with D P being the propeller diameter, T the propeller thrust, Q the propeller torque, p the tunnel pressure, p v the vapour pressure, p 0 the static pressure and r the radius. 2
3 REFERENCES [1]Barkmann, U., Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) - Open Water Tests with the Model Propeller VP1304, Report 3752, Schiffbau- Versuchsanstalt Potsdam, April 2011 [2]Mach, K., Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC), LDV with the Model Propeller VP1304, Report 3754, Schiffbau-Versuchsanstalt Potsdam, April 2011 (unpublished) [3]Heinke, H.-J., Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC), Cavitation Tests with the Model Propeller VP1304, Report 3753, Schiffbau- Versuchsanstalt Potsdam, April 2011
4 TABLES Table 1: Main data of model propeller VP1304 VP1304 Diameter D [m] Pitch ratio r/r = 0.7 P 0.7 /D [ ] Area ratio A E /A 0 [ ] Chord length r/r = 0.7 c 0.7 [m] Skew θ EXT [ ] Hub ratio d h /D [ ] Number of blades Z [ ] 5 Sense of rotation [ ] right Type [ ] controllable pitch propeller PPTC Towing tank Table 2: Details of model tests Dimensions of towing tank 280 x 9 x 4.5 m Propeller: Propeller type Material of model propeller Diameter of the propeller Sense of rotation VP1304 controllable pitch propeller brass 0.25 m right (looking on pressure side) Arrangement: Shaft inclination 0 Dynamometer shaft behind the propeller Measuring equipment: dynamometer H39 n max = 60 s -1 T max = 1 kn Q max = 50 Nm
5 Table 3: Operation conditions Water density (t W = 17.5 C) [kg/m³] Kinematic viscosity (t W = 17.5 C) [m²/s] 1.070E-06 Number of revolutions n [1/s] Table 4: Measured open water characteristics (by polynomials) J K T 10K Q η O Table 5: LDV Measuring planes x-position x/d [ ] x-position x [mm] Table 6: LDV Positions of the measuring points measuring plane start radius end radius distance r/r r/r r/r [mm] in front of the propeller x/d = behind the propeller x/d = 0.094, 0.10, 0.11, 0.13, 0.16, Table 7: Working point for the LDV measurements Inflow speed V A [m/s] Number of revolutions n [s -1 ] 23 Advance coefficient J [ ] Thrust coefficient K T [ ] Torque coefficient 10K Q [ ] Water density (for t w = 24.7 C) [kg/m 3 ] Kinematic viscosity of water (for t w = 24.7 C) [m²/s] 0.903E-6
6 Table 8: Test conditions for the LDV measurements Water density (for t w = 24.7 C) [kg/m 3 ] Kinematic viscosity of water (for t w = 24.7 C) [m²/s] 0.903E-6 Table 9: Requested Computations r/r [-] x/d [-] [ ] Case , Case , Case , Case , 0.2 Table 10: Working points for the cavitation tests Case Case Case Advanced coefficient J [-] Cavitation number based on n n [-] Thrust coefficient (non-cavitating!) K T [-] Number of revolutions n [1/s] Water density (for t w = 23.2 C) [kg/m 3 ] Kinematic viscosity water (for [m²/s] t w = 23.2 C) Vapour pressure (for t w = 23.2 C) p v [Pa] Air content / s [%]
ITTC Propeller Benchmark
 ITTC Propeller Benchmark PPTC PPTC, Propeller P1727 - VP1304 Report 4488 Potsdam, March April 2016 2016 Schiffbau-Versuchsanstalt Potsdam GmbH, Marquardter Chaussee 100, 14469 Potsdam Tel. +49 331 56712-0,
ITTC Propeller Benchmark PPTC PPTC, Propeller P1727 - VP1304 Report 4488 Potsdam, March April 2016 2016 Schiffbau-Versuchsanstalt Potsdam GmbH, Marquardter Chaussee 100, 14469 Potsdam Tel. +49 331 56712-0,
ENGR 4011 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships Assignment 4: 2017
 Question 1a. Values of forward speed, propeller thrust and torque measured during a propeller open water performance test are presented in the table below. The model propeller was 0.21 meters in diameter
Question 1a. Values of forward speed, propeller thrust and torque measured during a propeller open water performance test are presented in the table below. The model propeller was 0.21 meters in diameter
ITTC Propeller Benchmark
 ITTC Propeller Benchmark Tip Rake PPTC, Propeller P1727 - P1727 Report 4487 Potsdam, March April 2016 2016 Schiffbau-Versuchsanstalt Potsdam GmbH, Marquardter Chaussee 100, 14469 Potsdam Tel. +49 331 56712-0,
ITTC Propeller Benchmark Tip Rake PPTC, Propeller P1727 - P1727 Report 4487 Potsdam, March April 2016 2016 Schiffbau-Versuchsanstalt Potsdam GmbH, Marquardter Chaussee 100, 14469 Potsdam Tel. +49 331 56712-0,
Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a CP Propeller Unsteady Cavitation at Different Pitch Settings
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 211 Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a CP Propeller Unsteady Cavitation at Different Pitch Settings Daniele
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 211 Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a CP Propeller Unsteady Cavitation at Different Pitch Settings Daniele
Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics Anirban Bhattacharyya 1, Jan Clemens
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics Anirban Bhattacharyya 1, Jan Clemens
Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 7.5 02 Page 1 of 21 Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 2 2 ITTC DICTIONARY OF SHIP HYDRODYNAMICS PROPELLER SECTION... 2 COMMENTS OF THE PROPULSION COMMITTEE OF 22 nd ITTC Several of the symbols and definitions
7.5 02 Page 1 of 21 Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 2 2 ITTC DICTIONARY OF SHIP HYDRODYNAMICS PROPELLER SECTION... 2 COMMENTS OF THE PROPULSION COMMITTEE OF 22 nd ITTC Several of the symbols and definitions
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines Testing and Extrapolation Methods Propulsion, Performance Propulsion Test
 7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
Analysis of Crashback Forces Compared with Experimental Results
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 09, Trondheim, Norway, une 2009 Analysis of Crashback Forces Compared with Experimental Results Scott Black and Susan Swithenbank Naval Surface Warfare
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 09, Trondheim, Norway, une 2009 Analysis of Crashback Forces Compared with Experimental Results Scott Black and Susan Swithenbank Naval Surface Warfare
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation
 CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation S. Ramakrishna* GVP College of Engineering (A) Visakhapatnam V. Ramakrishna Scientist D N S T L Visakhapatnam A. Ramakrishna Professor A U C E (A) Visakhapatnam
CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation S. Ramakrishna* GVP College of Engineering (A) Visakhapatnam V. Ramakrishna Scientist D N S T L Visakhapatnam A. Ramakrishna Professor A U C E (A) Visakhapatnam
ITTC Recommended Procedures
 7.5-0 -03-0. Page of 6 CONTENTS PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE EXAMPLE FOR OPEN WATER TEST. Test Design. Measurement System and Procedure.3 Uncertainty Analysis.3. ias Limit.3.. Propeller Geometry.3.. Speed of advance
7.5-0 -03-0. Page of 6 CONTENTS PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE EXAMPLE FOR OPEN WATER TEST. Test Design. Measurement System and Procedure.3 Uncertainty Analysis.3. ias Limit.3.. Propeller Geometry.3.. Speed of advance
Resistance and Propulsion
 MSc. Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering Resistance and Propulsion 0-0 Project Propeller Design with the Lifting Line Theory - Program PROPINFAC Resistance and Propulsion Project Propeller Design
MSc. Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering Resistance and Propulsion 0-0 Project Propeller Design with the Lifting Line Theory - Program PROPINFAC Resistance and Propulsion Project Propeller Design
DDES of Wetted and Cavitating Marine Propeller for CHA Underwater Noise Assessment
 Article DDES of Wetted and Cavitating Marine Propeller for CHA Underwater Noise Assessment Ville M. Viitanen 1, *, Antti Hynninen 1, Tuomas Sipilä 1 and Timo Siikonen 2 ID 1 VTT Technical Research Centre
Article DDES of Wetted and Cavitating Marine Propeller for CHA Underwater Noise Assessment Ville M. Viitanen 1, *, Antti Hynninen 1, Tuomas Sipilä 1 and Timo Siikonen 2 ID 1 VTT Technical Research Centre
Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(78) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 13-20 10.2478/pomr-2013-0012 Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle Hassan
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(78) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 13-20 10.2478/pomr-2013-0012 Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle Hassan
Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of a Wake Equalizing Duct
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
Fan Stage Broadband Noise Benchmarking Programme
 Fan Stage Broadband Noise Benchmarking Programme Specification of Fundamental Test Case 3 (FC3) Version 1 : 26 January 2015 Test Case Coordinator John Coupland ISVR University of Southampton UK E-mail
Fan Stage Broadband Noise Benchmarking Programme Specification of Fundamental Test Case 3 (FC3) Version 1 : 26 January 2015 Test Case Coordinator John Coupland ISVR University of Southampton UK E-mail
Full scale thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
Large Eddy Simulation of Crashback in Marine Propellers
 26th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Rome, Italy, 17 22 September 2006 Large Eddy Simulation of Crashback in Marine Propellers Martin Vyšohlíd, Krishnan Mahesh (Aerospace Engineering & Mechanics, University
26th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Rome, Italy, 17 22 September 2006 Large Eddy Simulation of Crashback in Marine Propellers Martin Vyšohlíd, Krishnan Mahesh (Aerospace Engineering & Mechanics, University
Performance evaluation of composite marine propeller using L 8 orthogonal array
 Performance evaluation of composite marine propeller using L 8 orthogonal array S.Solomon Raj Dr.P.Ravinder Reddy 2. Assistant professor, department of mechanical engineering, chaitanya bharathi institute
Performance evaluation of composite marine propeller using L 8 orthogonal array S.Solomon Raj Dr.P.Ravinder Reddy 2. Assistant professor, department of mechanical engineering, chaitanya bharathi institute
Aerodynamic Performance 1. Figure 1: Flowfield of a Wind Turbine and Actuator disc. Table 1: Properties of the actuator disk.
 Aerodynamic Performance 1 1 Momentum Theory Figure 1: Flowfield of a Wind Turbine and Actuator disc. Table 1: Properties of the actuator disk. 1. The flow is perfect fluid, steady, and incompressible.
Aerodynamic Performance 1 1 Momentum Theory Figure 1: Flowfield of a Wind Turbine and Actuator disc. Table 1: Properties of the actuator disk. 1. The flow is perfect fluid, steady, and incompressible.
On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN
 ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE. October 13-14, Thrusters. Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels
 Return to Session Directory DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 13-14, 2009 Thrusters Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels Dirk Jürgens, Michael Palm
Return to Session Directory DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 13-14, 2009 Thrusters Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels Dirk Jürgens, Michael Palm
Numerical Investigation of a Cavitating Model Propeller Including Compressible Shock Wave Dynamics
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 5, Austin, Texas, USA, June, 25 Numerical Investigation of a Cavitating Model Propeller Including Compressible Shock Wave Dynamics Bernd Budich,
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 5, Austin, Texas, USA, June, 25 Numerical Investigation of a Cavitating Model Propeller Including Compressible Shock Wave Dynamics Bernd Budich,
Introduction to Turbomachinery
 1. Coordinate System Introduction to Turbomachinery Since there are stationary and rotating blades in turbomachines, they tend to form a cylindrical form, represented in three directions; 1. Axial 2. Radial
1. Coordinate System Introduction to Turbomachinery Since there are stationary and rotating blades in turbomachines, they tend to form a cylindrical form, represented in three directions; 1. Axial 2. Radial
Propeller Analysis Using RANS/BEM Coupling Accounting for Blade Blockage
 DRDC-RDDC-2015-N005 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Propeller Analysis Using RANS/BEM Coupling Accounting for Blade Blockage David Hally 1 1 Defence
DRDC-RDDC-2015-N005 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Propeller Analysis Using RANS/BEM Coupling Accounting for Blade Blockage David Hally 1 1 Defence
CHAPTER 4 OPTIMIZATION OF COEFFICIENT OF LIFT, DRAG AND POWER - AN ITERATIVE APPROACH
 82 CHAPTER 4 OPTIMIZATION OF COEFFICIENT OF LIFT, DRAG AND POWER - AN ITERATIVE APPROACH The coefficient of lift, drag and power for wind turbine rotor is optimized using an iterative approach. The coefficient
82 CHAPTER 4 OPTIMIZATION OF COEFFICIENT OF LIFT, DRAG AND POWER - AN ITERATIVE APPROACH The coefficient of lift, drag and power for wind turbine rotor is optimized using an iterative approach. The coefficient
IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 015 IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS Jan Rosłanowski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering Morska Street 81-87,
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 015 IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS Jan Rosłanowski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering Morska Street 81-87,
Propeller geometry optimization for pressure pulses reduction: an analysis of the influence of the rake distribution
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 217 Propeller geometry optimization for pressure pulses reduction: an analysis of the influence of the rake distribution
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 217 Propeller geometry optimization for pressure pulses reduction: an analysis of the influence of the rake distribution
λ (1) optimization, blade element momentum theory Abstract The objectives of this contribution is an enhanced
 Multi-Objective Optimization of Blades for Fixed Pitch Horizontal Axis Tidal Stream Turbines with Variable Speed Control Nicholas Kaufmann #, Thomas H. Carolus #2, Ralf Starzmann *3 # Institute for Fluid-
Multi-Objective Optimization of Blades for Fixed Pitch Horizontal Axis Tidal Stream Turbines with Variable Speed Control Nicholas Kaufmann #, Thomas H. Carolus #2, Ralf Starzmann *3 # Institute for Fluid-
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page 1 of 9 CONTENTS Model Test Experiments... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Model Parameters... 3 2.2 Environmental Parameters... 3 2.3 Operation of Thrusters... 3 2.3.1 Thruster-Current
Page 1 of 9 CONTENTS Model Test Experiments... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Model Parameters... 3 2.2 Environmental Parameters... 3 2.3 Operation of Thrusters... 3 2.3.1 Thruster-Current
A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using CFD
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 11, 1995 WIT Press, ISSN
 An experimental and numerical investigation of turbulent flows around a ship-like body with and without propeller M. Abdel-Maksoud*, H. Brandt*, H.Nowackf, G. Tzabiras* *Schiffbau-VersucksanstaltPotsdam
An experimental and numerical investigation of turbulent flows around a ship-like body with and without propeller M. Abdel-Maksoud*, H. Brandt*, H.Nowackf, G. Tzabiras* *Schiffbau-VersucksanstaltPotsdam
Two medium size cavitation tunnel hydro-acoustic benchmark experiment comparisons as part of a round robin test campaign
 Two medium size cavitation tunnel hydro-acoustic benchmark experiment comparisons as part of a round robin test campaign Giorgio Tani 1, Batuhan Aktas 2,*, Michele Viviani 1, Mehmet Atlar 2 1 Department
Two medium size cavitation tunnel hydro-acoustic benchmark experiment comparisons as part of a round robin test campaign Giorgio Tani 1, Batuhan Aktas 2,*, Michele Viviani 1, Mehmet Atlar 2 1 Department
A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder
 A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder Hassan Ghassemi, a,* and Farzam Allafchi, a a ) Department of Ocean Engineering, Amirkabir
A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder Hassan Ghassemi, a,* and Farzam Allafchi, a a ) Department of Ocean Engineering, Amirkabir
Investigation of Reynolds Number Scale Effects on Propeller Tip Vortex Cavitation and Propeller-Induced Hull Pressure Fluctuations
 th International Symposium on Cavitation CAV28 Baltimore, Maryland, USA, 4 6 May 28 Investigation of Reynolds Number Scale Effects on Propeller Tip Vortex Cavitation and Propeller-Induced Hull Pressure
th International Symposium on Cavitation CAV28 Baltimore, Maryland, USA, 4 6 May 28 Investigation of Reynolds Number Scale Effects on Propeller Tip Vortex Cavitation and Propeller-Induced Hull Pressure
Analysis of Unsteady Propeller Blade Forces by RANS
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 2009 Analysis of Unsteady Propeller Blade Forces by Vladimir Krasilnikov 1, Zhirong Zhang 2 and Fangwen Hong 2 1 Norwegian
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 2009 Analysis of Unsteady Propeller Blade Forces by Vladimir Krasilnikov 1, Zhirong Zhang 2 and Fangwen Hong 2 1 Norwegian
CFD Analysis of Scale Effects on Conventional and Tip-Modified Propellers
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 CFD Analysis of Scale Effects on Conventional and Tip-Modified Propellers Keun Woo Shin 1, Poul Andersen 2 1 Propeller
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 CFD Analysis of Scale Effects on Conventional and Tip-Modified Propellers Keun Woo Shin 1, Poul Andersen 2 1 Propeller
APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS ON RUDDERS
 Proceedings of ASME 25 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE 25 May 3 - June 5, 25, St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada OMAE25-4796 APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS
Proceedings of ASME 25 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE 25 May 3 - June 5, 25, St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada OMAE25-4796 APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS
Performance Investigation of Ducted Aerodynamic Propulsors
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors Smp 9, Trondheim, Norway, June 29 Performance Investigation of Ducted Aerodynamic Propulsors Naipei P. Bi, Kevin R. Kimmel, David J. Haas Naval Surface
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors Smp 9, Trondheim, Norway, June 29 Performance Investigation of Ducted Aerodynamic Propulsors Naipei P. Bi, Kevin R. Kimmel, David J. Haas Naval Surface
Turbine Blade Design of a Micro Gas Turbine
 Turbine Blade Design of a Micro Gas Turbine Bhagawat Yedla Vellore Institute of Technlogy, Vellore 632014, India Sanchit Nawal Vellore Institute of Technlogy, Vellore 632014, India Shreehari Murali Vellore
Turbine Blade Design of a Micro Gas Turbine Bhagawat Yedla Vellore Institute of Technlogy, Vellore 632014, India Sanchit Nawal Vellore Institute of Technlogy, Vellore 632014, India Shreehari Murali Vellore
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power
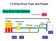 7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller
 voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
Yiran Su 1, Seungnam Kim 1, Weikang Du 1, Spyros A. Kinnas 2, Mikael Grekula 3, Jan Hallander 3, Da- Qing Li 3
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Prediction of the Propeller-induced Hull Pressure Fluctuation via a Potential-based Method: Study of the Rudder Effect
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Prediction of the Propeller-induced Hull Pressure Fluctuation via a Potential-based Method: Study of the Rudder Effect
Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Performances of Marine Propeller
 Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Performances of Marine Propeller Master Thesis developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati in the framework of the EMSHIP Erasmus Mundus Master Course
Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Performances of Marine Propeller Master Thesis developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati in the framework of the EMSHIP Erasmus Mundus Master Course
Rate-Dependent Hydroelastic Response of Self-Adaptive Composite Propellers in Fully Wetted and Cavitating Flows
 Proceedings of the 7 th International Symposium on Cavitation CAV2009 Paper No. 60 August 17-22, 2009, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA Rate-Dependent Hydroelastic Response of Self-Adaptive Composite Propellers
Proceedings of the 7 th International Symposium on Cavitation CAV2009 Paper No. 60 August 17-22, 2009, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA Rate-Dependent Hydroelastic Response of Self-Adaptive Composite Propellers
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
Comparison of experimental measurements and numerical calculations for a propeller in axial cylinder
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Comparison of experimental measurements and numerical calculations for a propeller in axial cylinder Gaggero Stefano
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Comparison of experimental measurements and numerical calculations for a propeller in axial cylinder Gaggero Stefano
Facilities: CHL (Computational Hydrodynamics Laboratory) in ECJ 8.502
 Ocean Engineering Group (OEG)/EWRE (August 28, 2018) Spyros A. Kinnas Professor and Director of OTRC s UT Office (Offshore Technology Research Center) Kinnas Home Page @SpyrosKinnas on twitter Research
Ocean Engineering Group (OEG)/EWRE (August 28, 2018) Spyros A. Kinnas Professor and Director of OTRC s UT Office (Offshore Technology Research Center) Kinnas Home Page @SpyrosKinnas on twitter Research
Interactive Program System for the Design/Analysis of Marine Propulsors
 ISNAOE'03 - Shanghai, China - Sept 23-26, 2003 Interactive Program System for the Design/Analysis of Marine Propulsors Vladimir I. Krasilnikov, PhD, esearch Scientist, Aage Berg, MSc, Senior esearch Engineer
ISNAOE'03 - Shanghai, China - Sept 23-26, 2003 Interactive Program System for the Design/Analysis of Marine Propulsors Vladimir I. Krasilnikov, PhD, esearch Scientist, Aage Berg, MSc, Senior esearch Engineer
Nominal vs. Effective Wake Fields and Their Influence on Propeller Cavitation Performance
 Journal of Marine Science and Engineering Article Nominal vs. Effective Wake Fields and Their Influence on Propeller Cavitation Performance Pelle Bo Regener 1, * ID, Yasaman Mirsadraee 1,2 ID and Poul
Journal of Marine Science and Engineering Article Nominal vs. Effective Wake Fields and Their Influence on Propeller Cavitation Performance Pelle Bo Regener 1, * ID, Yasaman Mirsadraee 1,2 ID and Poul
Unsteady Analysis of a Horizontal Axis Marine Current Turbine in Yawed Inflow Conditions With a Panel Method
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 2009 Unsteady Analysis of a Horizontal Axis Marine Current Turbine in Yawed Inflow Conditions With a J. Baltazar, J.A.C.
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 2009 Unsteady Analysis of a Horizontal Axis Marine Current Turbine in Yawed Inflow Conditions With a J. Baltazar, J.A.C.
Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA
 Research Article Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA Kiam Beng Yeo, Wai Heng Choong and Wen Yen Hau ABSTRACT The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of marine propeller blade stress
Research Article Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA Kiam Beng Yeo, Wai Heng Choong and Wen Yen Hau ABSTRACT The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of marine propeller blade stress
Lecture-10 Tutorial -2 Solved Problems and Tutorial Problems On Three Dimensional flow in Axial Flow Compressor
 1 Lecture-10 Tutorial -2 Solved Problems and Tutorial Problems On Three Dimensional flow in Axial Flow Compressor 2 Recap of simple 3-D flow theories (These are mainly used for design) Lect-10 1)Free Vortex
1 Lecture-10 Tutorial -2 Solved Problems and Tutorial Problems On Three Dimensional flow in Axial Flow Compressor 2 Recap of simple 3-D flow theories (These are mainly used for design) Lect-10 1)Free Vortex
AN EXPLORATORY STUDY ON THE WORKING PRINCIPLES OF ENERGY SAVING DEVICES (ESDS) PIV, CFD INVESTIGATIONS AND ESD DESIGN GUIDELINES
 Proceedings of the 3 st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE22 July -6, 22, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil OMAE22-8353 AN EXPLORATORY STUDY ON THE WORKING PRINCIPLES OF ENERGY
Proceedings of the 3 st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE22 July -6, 22, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil OMAE22-8353 AN EXPLORATORY STUDY ON THE WORKING PRINCIPLES OF ENERGY
Contents. 1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines Overview of Turbomachinery Nomenclature...9
 Preface page xv 1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines...1 Definition 1 Advantages of Gas-Turbine Engines 1 Applications of Gas-Turbine Engines 3 The Gas Generator 3 Air Intake and Inlet Flow Passage 3
Preface page xv 1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines...1 Definition 1 Advantages of Gas-Turbine Engines 1 Applications of Gas-Turbine Engines 3 The Gas Generator 3 Air Intake and Inlet Flow Passage 3
Numerical Analysis of Azimuth Propulsor Performance in Seaways: Influence of Oblique Inflow and Free Surface
 Journal of Marine Science and Engineering Article Numerical Analysis of Azimuth Propulsor Performance in Seaways: Influence of Oblique Inflow and Free Surface Nabila Berchiche, Vladimir I. Krasilnikov
Journal of Marine Science and Engineering Article Numerical Analysis of Azimuth Propulsor Performance in Seaways: Influence of Oblique Inflow and Free Surface Nabila Berchiche, Vladimir I. Krasilnikov
Performance Assessment of the Waterjet Propulsion System through a Combined Analytical and Numerical Approach
 International Journal of Physics, 013, Vol. 1, No., -7 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/1//1 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.1691/ijp-1--1 Performance Assessment of the Waterjet
International Journal of Physics, 013, Vol. 1, No., -7 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/1//1 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.1691/ijp-1--1 Performance Assessment of the Waterjet
Cavitating Flow Calculations for the E779A Propeller in Open Water and Behind Conditions: Code Comparison and Solution Validation
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 5, Austin, Texas, USA, June 5 Cavitating Flow Calculations for the E779A Propeller in Open Water and Behind Conditions: Code Comparison and Solution
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 5, Austin, Texas, USA, June 5 Cavitating Flow Calculations for the E779A Propeller in Open Water and Behind Conditions: Code Comparison and Solution
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr.
 Reading Assignments Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr. Sert) Study Set 1 You can find the answers of some of the following
Reading Assignments Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr. Sert) Study Set 1 You can find the answers of some of the following
An Extrapolation Method Suitable for Scaling of Propellers of any Design
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 5, Austin, Texas, USA, June 205 An Extrapolation Method Suitable for Scaling of Propellers of any Design Dr. Stephan Helma Stone Marine Propulsion
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 5, Austin, Texas, USA, June 205 An Extrapolation Method Suitable for Scaling of Propellers of any Design Dr. Stephan Helma Stone Marine Propulsion
Efficient Prediction of Crashback Performance of Controllable Pitch Propellers
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 217 Efficient Prediction of Crashback Performance of Controllable Pitch Propellers Markus Pergande, Keqi Wang, Jan Clemens
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 217 Efficient Prediction of Crashback Performance of Controllable Pitch Propellers Markus Pergande, Keqi Wang, Jan Clemens
On predicting the sound from a cavitating marine propeller in a tunnel
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On predicting the sound from a cavitating marine propeller in a tunnel Antti Hynninen, 1 Jukka Tanttari, 1 Ville M.
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On predicting the sound from a cavitating marine propeller in a tunnel Antti Hynninen, 1 Jukka Tanttari, 1 Ville M.
Analysis of Wind Turbine Pressure Distribution and 3D Flows Visualization on Rotating Condition
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 02 (February. 2016), V1 PP 18-30 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Wind Turbine Pressure Distribution and 3D Flows
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 02 (February. 2016), V1 PP 18-30 www.iosrjen.org Analysis of Wind Turbine Pressure Distribution and 3D Flows
Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships
 (August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
(August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on Pump Performance
 11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
ENGR 4011 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships Assignment 5: A dimensional analysis of propeller thrust starting with the functional expression
 ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
Experiments with Podded Propulsors in Static Azimuthing Conditions
 Experiments with Podded Propulsors in Static Azimuthing Conditions Islam M. F 1, Veitch B 1, Akinturk A 2, Bose N 3 and Liu P 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University of Newfoundland
Experiments with Podded Propulsors in Static Azimuthing Conditions Islam M. F 1, Veitch B 1, Akinturk A 2, Bose N 3 and Liu P 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University of Newfoundland
Simulation-driven Design of a Rim Drive for an Autonomous Vehicle
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Simulation-driven Design of a Rim Drive for an Autonomous Vehicle Heinrich Grümmer 1, Stefan Harries 2 and Andrés Cura
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Simulation-driven Design of a Rim Drive for an Autonomous Vehicle Heinrich Grümmer 1, Stefan Harries 2 and Andrés Cura
Deliverable D.6.1. Application of CFD tools to the development of a novel propulsion concept
 TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
 Ventilation 5 Fans Vladimír Zmrhal (room no. 814) http://users.fs.cvut.cz/~zmrhavla/index.htm Dpt. Of Environmental Engineering 1 Introduction Fans air pump that creates a pressure difference and causes
Ventilation 5 Fans Vladimír Zmrhal (room no. 814) http://users.fs.cvut.cz/~zmrhavla/index.htm Dpt. Of Environmental Engineering 1 Introduction Fans air pump that creates a pressure difference and causes
Performance Characteristics of Static and Dynamic Azimuthing Podded Propulsor
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Performance Characteristics of Static and Dynamic Azimuthing Podded Propulsor Mohammed F. Islam 1, Ayhan Akinturk,
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Performance Characteristics of Static and Dynamic Azimuthing Podded Propulsor Mohammed F. Islam 1, Ayhan Akinturk,
An Overview of Impellers, Velocity Profile and Reactor Design
 An Overview of s, Velocity Profile and Reactor Design Praveen Patel 1, Pranay Vaidya 1, Gurmeet Singh 2 1 Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India 1 Indian Oil Corporation Limited, R&D Centre Faridabad
An Overview of s, Velocity Profile and Reactor Design Praveen Patel 1, Pranay Vaidya 1, Gurmeet Singh 2 1 Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India 1 Indian Oil Corporation Limited, R&D Centre Faridabad
Investigation on the influence of scaling effects in propeller testing through the use of theoretical prediction codes
 Master of Science Thesis Investigation on the influence of scaling effects in propeller testing through the use of theoretical prediction codes Thomas De Leeuw... 2013 Delft University of Technology Dept.
Master of Science Thesis Investigation on the influence of scaling effects in propeller testing through the use of theoretical prediction codes Thomas De Leeuw... 2013 Delft University of Technology Dept.
A simplified model for a small propeller with different airfoils along the blade
 A simplified model for a small propeller with different airfoils along the blade Kamal A. R. Ismail 1) and *Célia V. A. G. Rosolen 2) 1), 2) State University of Campinas, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
A simplified model for a small propeller with different airfoils along the blade Kamal A. R. Ismail 1) and *Célia V. A. G. Rosolen 2) 1), 2) State University of Campinas, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Rotor reference axis
 Rotor reference axis So far we have used the same reference axis: Z aligned with the rotor shaft Y perpendicular to Z and along the blade (in the rotor plane). X in the rotor plane and perpendicular do
Rotor reference axis So far we have used the same reference axis: Z aligned with the rotor shaft Y perpendicular to Z and along the blade (in the rotor plane). X in the rotor plane and perpendicular do
Marine Propulsors. Design Methodology for Subcavitating. Archief
 TECHNLSCBE UNIVERSITEIT Scheepshydromechanica Archief Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft Te1:015-2786873/Fax:2781836 NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS DEPARTMENT OF NAVAL ARCHITECTURE AND MARINE ENGINEERING
TECHNLSCBE UNIVERSITEIT Scheepshydromechanica Archief Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft Te1:015-2786873/Fax:2781836 NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS DEPARTMENT OF NAVAL ARCHITECTURE AND MARINE ENGINEERING
Modeling of Cavitating Flow through Waterjet Propulsors
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsion smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Modeling of Cavitating Flow through Waterjet Propulsors Jules W. Lindau, Christopher Pena, Warren J. Baker, James
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsion smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Modeling of Cavitating Flow through Waterjet Propulsors Jules W. Lindau, Christopher Pena, Warren J. Baker, James
Measurement of Axial Thrust Number in Various Agitation Flow Regimes
 Measurement of Axial Thrust Number in Various Agitation Flow Regimes Matthew A. Reilly Abstract Structural design of agitators requires a detailed knowledge of the relationship between mixing strength
Measurement of Axial Thrust Number in Various Agitation Flow Regimes Matthew A. Reilly Abstract Structural design of agitators requires a detailed knowledge of the relationship between mixing strength
Interactive Optimization Programs for Initial Propeller Design
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 12-20-2009 Interactive Optimization Programs for Initial Propeller Design Richard
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 12-20-2009 Interactive Optimization Programs for Initial Propeller Design Richard
Teaching sessions week 40
 Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Lect-36. In this lecture... Tutorial on radial flow turbines. Prof. Bhaskar Roy, Prof. A M Pradeep, Department of Aerospace, IIT Bombay
 Lect- 36 1 In this lecture... Lect-36 Tutorial on radial flow turbines 2 Problem # 1 Lect-36 The rotor of an IFR turbine, which is designed to operate at the nominal condition, is 23.76 cm in diameter
Lect- 36 1 In this lecture... Lect-36 Tutorial on radial flow turbines 2 Problem # 1 Lect-36 The rotor of an IFR turbine, which is designed to operate at the nominal condition, is 23.76 cm in diameter
DUAL-MODE CONTRAPROPELLER WITH CURVE STACKING LINE FOR BLADE
 Anatolij-Branko R. Togunjac, Ph.D, Research and Design Institute for Fishing Fleet, GIPRORYBFLOT, M. Morskaya str.,18-20, St. Petersburg, 190000 Russia Leonid I. Vishnevsky, D.Sc,Krylov Shipbuilding Research
Anatolij-Branko R. Togunjac, Ph.D, Research and Design Institute for Fishing Fleet, GIPRORYBFLOT, M. Morskaya str.,18-20, St. Petersburg, 190000 Russia Leonid I. Vishnevsky, D.Sc,Krylov Shipbuilding Research
Hydro-Structure Analysis of Composite Marine Propeller under Pressure Hydrodynamic Loading
 American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
Chapter three. Two-dimensional Cascades. Laith Batarseh
 Chapter three Two-dimensional Cascades Laith Batarseh Turbo cascades The linear cascade of blades comprises a number of identical blades, equally spaced and parallel to one another cascade tunnel low-speed,
Chapter three Two-dimensional Cascades Laith Batarseh Turbo cascades The linear cascade of blades comprises a number of identical blades, equally spaced and parallel to one another cascade tunnel low-speed,
Study of the Losses in Fluid Machinery with the Help of Entropy
 Study of the Losses in Fluid Machinery with the Help of Entropy Martin Böhle 1, Annika Fleder 1, Matthias Mohr 1 * SYMPOSIA ON ROTATING MACHINERY ISROMAC 16 International Symposium on Transport Phenomena
Study of the Losses in Fluid Machinery with the Help of Entropy Martin Böhle 1, Annika Fleder 1, Matthias Mohr 1 * SYMPOSIA ON ROTATING MACHINERY ISROMAC 16 International Symposium on Transport Phenomena
FEDSM AERODYNAMIC NOISE SIMULATION OF PROPELLER FAN BY LARGE EDDY SIMULATION
 Proceedings of FEDSM27 5th Joint ASME/JSME Fluids Engineering Conference July 3-August 2, 27 San Diego, California USA FEDSM27-37145 AERODYNAMIC NOISE SIMULATION OF PROPELLER FAN BY LARGE EDDY SIMULATION
Proceedings of FEDSM27 5th Joint ASME/JSME Fluids Engineering Conference July 3-August 2, 27 San Diego, California USA FEDSM27-37145 AERODYNAMIC NOISE SIMULATION OF PROPELLER FAN BY LARGE EDDY SIMULATION
Contents. 2 Basic Components Aerofoils Force Generation Performance Parameters xvii
 Contents 1 Working Principles... 1 1.1 Definition of a Turbomachine... 1 1.2 Examples of Axial Turbomachines... 2 1.2.1 Axial Hydraulic Turbine... 2 1.2.2 Axial Pump... 4 1.3 Mean Line Analysis... 5 1.4
Contents 1 Working Principles... 1 1.1 Definition of a Turbomachine... 1 1.2 Examples of Axial Turbomachines... 2 1.2.1 Axial Hydraulic Turbine... 2 1.2.2 Axial Pump... 4 1.3 Mean Line Analysis... 5 1.4
Makoto Uchida. Yuuki Matsumoto
 ADVANCED EDUCATION AND RESEARCH ON MARINE PROPULSION EXPERIMENTAL S TUDY ON PROPELLER AIR-DRAWINGS AND BEARING FORCES Makoto Uchida Professor, Dr. Faculty of Maritime Sciences, Kobe University 5-1-1 Fukae-Minami,
ADVANCED EDUCATION AND RESEARCH ON MARINE PROPULSION EXPERIMENTAL S TUDY ON PROPELLER AIR-DRAWINGS AND BEARING FORCES Makoto Uchida Professor, Dr. Faculty of Maritime Sciences, Kobe University 5-1-1 Fukae-Minami,
Dynamic Analysis of Composite Propeller of Ship using FEA P. NARASAIAH 1, PROF. S.S. BASARKOD 2
 ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.27 September-2014, Pages:5467-5472 www.ijsetr.com Dynamic Analysis of Composite Propeller of Ship using FEA P. NARASAIAH 1, PROF. S.S. BASARKOD 2 Abstract: Ships and under water
ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.27 September-2014, Pages:5467-5472 www.ijsetr.com Dynamic Analysis of Composite Propeller of Ship using FEA P. NARASAIAH 1, PROF. S.S. BASARKOD 2 Abstract: Ships and under water
Scaling of Tip Vortex Cavitation Inception for a Marine Open Propeller
 27 th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Seoul, Korea, 5-10 October 2008 Scaling of Tip Vortex Cavitation Inception for a Marine Open Propeller C.-T. Hsiao and G. L. Chahine (DYNAFLOW, INC., USA) ABSTRACT
27 th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Seoul, Korea, 5-10 October 2008 Scaling of Tip Vortex Cavitation Inception for a Marine Open Propeller C.-T. Hsiao and G. L. Chahine (DYNAFLOW, INC., USA) ABSTRACT
ROLLER BEARING FAILURES IN REDUCTION GEAR CAUSED BY INADEQUATE DAMPING BY ELASTIC COUPLINGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIONS
 ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
Dynamometry Tutorial IMECE
 Dynamometry Tutorial IMECE2013-62800 2013 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Diego, California Dr. Michael L. Jonson The Pennsylvania State University Applied Research Laboratory
Dynamometry Tutorial IMECE2013-62800 2013 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Diego, California Dr. Michael L. Jonson The Pennsylvania State University Applied Research Laboratory
3D hot-wire measurements of a wind turbine wake
 1 3D hot-wire measurements of a wind turbine wake Pål Egil Eriksen PhD candidate, NTNU/NOWITECH Per-Åge Krogstad NTNU 2 Outline of the presentation Experimental setup Measurement technique Time averaged
1 3D hot-wire measurements of a wind turbine wake Pål Egil Eriksen PhD candidate, NTNU/NOWITECH Per-Åge Krogstad NTNU 2 Outline of the presentation Experimental setup Measurement technique Time averaged
Cavitation instabilities in hydraulic machines
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Cavitation instabilities in hydraulic machines To cite this article: Y Tsujimoto 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 012005 View
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Cavitation instabilities in hydraulic machines To cite this article: Y Tsujimoto 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 012005 View
Drag and Torque on Locked Screw Propeller
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 8 Number 3 September 24 DOI:.276/.8.3.6 Drag and Torque on Locked Screw Propeller T. Tabaczek
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 8 Number 3 September 24 DOI:.276/.8.3.6 Drag and Torque on Locked Screw Propeller T. Tabaczek
