gravity force buoyancy force drag force where p density of particle density of fluid A cross section perpendicular to the direction of motion
|
|
|
- Letitia Cunningham
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 orce acting on the ettling article SEDIMENTATION gravity force boyancy force drag force In cae of floating: their i zero. f k V g Vg f A where denity of article denity of flid A cro ection erendiclar to the direction of otion Rearrangeent of the eqation Aing herical article of diaeter d, rearrange the eqation, and define (d) and () a: d f Re Re f g d d Generalized ettling lot Y=() againt X=(d) Stoke: lainar region Newton: trblent region, rarely ed becae of the very high ile Aroxiation of the Newton region: X Y 0. Exact forla for the Stoke region: X Y
2 Proble Sandy ldge i ettled in a chanel of bae area 5. Sand denity i 800 /, denity i 00 /, it vicoity i 0 - Pa. a) What i it caacity if the diaeter of allet article to be ettled i 0 -? b) 0 /in of the ae ldge i to be treated in another ettler of bae area 0. What diaeter article will be ettled? c) In the cae of b), i.e. 0 /in of the ae ldge, how any tray are to be alied to ettle ot article with diaeter 50? Soltion: A = 5 = 5 = 800 / k = 00 / k = 0 - Pa d = 0 - = 0-5 V =? a) What i it caacity if the diaeter of allet article to be ettled i 0 -? Caacity of the ettler ean the axi flow rate accetable. irt cote g Pa Then, ince velocity i to be calclated fro known diaeter, calclate (d): 5 X d d Thi fall to Stoke regie (according to the lot), th Y can be calclated with a forla: X 0.58 Y Pa Settling caacity deend on the bae area and the ettling velocity only. V A h b) 0 /in of the ae ldge i to be treated in another ettler of bae area 0. What diaeter article will be ettled? A = 0 V ' = 0 /in
3 Settling velocity (it ini) can be calclated fro the given caacity. V' A' ' 0 V' in ' A' in 0 60 h Now nknown diaeter i to coted fro know velocity. i the ae a earlier becae the aterial i the ae ' Y' ' Pa Thi vale fall to the tranient region, th X' i read fro the lot. X' d' d' d' Th, article with diaeter at leat a large a 0.8 will be ettled. c) In the cae of b), i.e. 0 /in of the ae ldge, how any tray are to be alied to ettle ot article with diaeter 50? A = 0 ' = 0 /in d = 50 = n =? Velocity i to be coted fro known diaeter. X'' d'' d'' Thi vale fall to the tranient region, th Y'' i read fro the lot. Y'' v'' 0. 6 ' ' v'' Pa '' '' How any tray? V V' n A' '' 0 V' n in. A' '' in Th, at leat 5 tray are needed. 5 i ore than. bt no roble if even aller article are alo ettled ot.
4 Proble After grinding of and llock, a fraction of article cale. to.5 have been earated by claifying the article with ieve. a) What velocity t be aintained in a ihon earator in order to earate the two aterial? b) De to an oeration failre, aller article of both kind ha got to the yte. What i the ini article ize at which the earation can be erfored? = 0.95 Pa = 00 / = 00 / llock = 500 / Soltion igre: ótvíz: leent, zén:, eddő: llock a) What velocity t be aintained in a ihon earator in order to earate the two aterial? Soltion ath Velocity relation If d < d and A < then Condition of earation egengedett ebeégtartoány: accetable (feaible) range of velocity Coal i lighter, teherfore it goe throgh wherea the heavier llock ettle ot. Or target i to ettle ot even the allet article of the heavy llock and, in the ae tie, to revent even the larget article of the lighter fro ettling ot.,aller,larg er d,l arg er d,aller in ax in ax
5 Coal Calclate g Pa diaeter velocity: X d d Tranient region, lot: Y. in in Mllock Calclate llock. llock llock g.80 llock diaeter velocity X llock d,larg er Pa Pa d llock tranient region, lot. Y 6. llock ax llock 5 llock ax llock llock llock llock,aller Pa 0.70 Th, velocity of the leent t be ket in the range of 0.05 / < < 0.70 /. 5
6 b) De to an oeration failre, aller article of both kind ha got to the yte. What i the ini article ize at which the earation can be erfored? If rather all article with diaeter d 0 are reent then the following extree itation ay haen: Mini velocity wa deterined in roble a) by the ettling velocity of the larger article of the lighter aterial (). At a velocity aller than thi ini, article of the lighter aterial are alo ettled ot. Now the qetion i what diaeter article of the heavier aterial (llock) will be ettled ot at the earlier ini velocity. in 0.05 d,llock =? Diaeter i to be coted to known velocity. llock i the ae a earlier Y' llock v ' llock. 07 llock Pa tranient region, lot. X' llock d' llock 0. 5 d' llock 0.5 d,llock llock Th, ettling velocity of llock article of diaeter 0.75 eqal the ettling velocity of the larget article. If ch or aller llock article get in the ihon earator then the earation becoe infeaible. 6
7 Proble Maxi tea velociy, deterined exerientally, i N = 0.5 / at an evaoration roce at noral boiling oint. Cro ection of the vaor channel i, and the rere in the evaorator i 666 Pa. What i the a flow rate of the tea ( vaor) leaving the evaorator? Material data at the given and noral rere: 666 Pa 05 Pa t b [ C] [/ ] [Pa] Water: = = 000 /. Note: Solvent i reoved fro a oltion in an evaoration roce. Solvent vaor i reoved and ore concentrated oltion reain in the veel. Dring the boiling and the eergence of vaor, however, liqid drolet are alo dragged by the vaor flow and carried away. or anwering the qetion given in the roble, we ae that the ratio of drolet of different cale are the ae in the two cae if the drolet ize are eqal. Soltion Data: v N = 0,5 / A = Soltion ath Accetable drolet ize carried over by the vaor are the ae at the two rere. N Plot ' Plot ' d d d' ' ' ' Atoheric (noral) rere Calclate. g Pa 7
8 velocity diaeter Y v N Pa tranient region, lot. X d. 5 d.5 d Th, axi accetable drolet ize i Lower rere irt calclate ' ' ' g 9.8 ' diaeter velocity X' d' ' d tranient region, lot. Y' ' ' ' ' Pa ' ' ' ' ' 0.7 Voletric flow rate V' ' A Ma flow rate ' V' ' h Pa 0.6 Th, the vaor velocity t not exceed 779 /h. At a higher velocity larger drolet wold be carried on. Note: Ma flow rate at atoheric rere i V vn A h 8
9 Proble Sandy ldg i to be ettled in a channel of bae area.5 and deth. = 800 / = 000 / = 0 - Pa a) In cae of flow rate 6 /in, how any tray are to be intalled to ettle ot and article larger than 50? In what region i the ettling roce erfored? b) If the tray are intalled a deterined in roble a/ and then the flow rate i dobled then what will be ini diaeter of the ettled artice? In what region i the ettling roce erfored? Data: A =.5 = 9 H = = 800 / = 000 / = 0 - Pa a) In cae of flow rate 6 /in, how any tray are to be intalled to ettle ot and article larger than 50? In what region i the ettling roce erfored? V = 6 /in = 0. / d = 50 = g 9.8 diaeter velocity: 5 X d d Stoke region, forla. X. Y Pa The needed nber of tray, inclding the botto of the channel: V n A 0. V n.5 5 A 9.50 over the botto of the channel.) Pa (Only tray are needed to be intalled 9
10 b) If the tray are intalled a deterined in roble a/ and then the flow rate i dobled then what will be ini diaeter of the ettled artice? In what region i the ettling roce erfored? The total area i changed: A' na 59 5 The new flow rate: V' V 0. Settling velocity deterined fro the flow rate: V' A' ' 0. V' ' A' 5.0 velocity diaeter, doe not change, it deend on the aterial only ' Y' ' Pa Stoke region, forla. X d' Y' d ' Y' ' d d', Th, and article larger than 67. will be ettled ot. 0
Represent each of the following combinations of units in the correct SI form using an appropriate prefix: (a) m/ms (b) μkm (c) ks/mg (d) km μn
 2007 R. C. Hibbeler. Publihed by Pearon Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, J. All right reerved. Thi aterial i protected under all copyright law a they currently exit. o portion of thi aterial ay be
2007 R. C. Hibbeler. Publihed by Pearon Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, J. All right reerved. Thi aterial i protected under all copyright law a they currently exit. o portion of thi aterial ay be
( ) Zp THE VIBRATION ABSORBER. Preamble - A NEED arises: lbf in. sec. X p () t = Z p. cos Ω t. Z p () r. ω np. F o. cos Ω t. X p. δ s.
 THE VIBRATION ABSORBER Preable - A NEED arie: Lui San Andre (c) 8 MEEN 363-617 Conider the periodic forced repone of a yte (Kp-Mp) defined by : 1 1 5 lbf in : 1 3 lb (t) It natural frequency i: : ec F(t)
THE VIBRATION ABSORBER Preable - A NEED arie: Lui San Andre (c) 8 MEEN 363-617 Conider the periodic forced repone of a yte (Kp-Mp) defined by : 1 1 5 lbf in : 1 3 lb (t) It natural frequency i: : ec F(t)
Heat Transfer Enhancement in channel with obstacles
 Proceedings o the nd WSEAS Int. Conerence on Applied and Theoretical Mechanics, Venice, Italy, Noveber 0-, 006 81 eat Transer Enhanceent in channel with obstacles M. Nazari M.. Kayhani Departent o Mechanical
Proceedings o the nd WSEAS Int. Conerence on Applied and Theoretical Mechanics, Venice, Italy, Noveber 0-, 006 81 eat Transer Enhanceent in channel with obstacles M. Nazari M.. Kayhani Departent o Mechanical
Physics 6A. Practice Midterm #2 solutions. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Phyic 6A Practice Midter # olution or apu Learning Aitance Service at USB . A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train forward
Phyic 6A Practice Midter # olution or apu Learning Aitance Service at USB . A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train forward
Boundary layer develops in the flow direction, δ = δ (x) τ
 58:68 Trblent Flos Handot: Bondar Laers Differences to Trblent Channel Flo Bondar laer develops in the flo direction, not knon a priori Oter part of the flo consists of interittent trblent/non-trblent
58:68 Trblent Flos Handot: Bondar Laers Differences to Trblent Channel Flo Bondar laer develops in the flo direction, not knon a priori Oter part of the flo consists of interittent trblent/non-trblent
Physics 6A. Practice Midterm #2 solutions
 Phyic 6A Practice Midter # olution 1. A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train forward at acceleration a. If 3 of the car
Phyic 6A Practice Midter # olution 1. A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train forward at acceleration a. If 3 of the car
By Dr. Salah Salman. Problem (1)
 Chemical Eng. De. Problem ( Solved Problems Samles in Flid Flow 0 A late of size 60 cm x 60 cm slides over a lane inclined to the horizontal at an angle of 0. It is searated from the lane with a film of
Chemical Eng. De. Problem ( Solved Problems Samles in Flid Flow 0 A late of size 60 cm x 60 cm slides over a lane inclined to the horizontal at an angle of 0. It is searated from the lane with a film of
Conditions for equilibrium (both translational and rotational): 0 and 0
 Leon : Equilibriu, Newton econd law, Rolling, Angular Moentu (Section 8.3- Lat tie we began dicuing rotational dynaic. We howed that the rotational inertia depend on the hape o the object and the location
Leon : Equilibriu, Newton econd law, Rolling, Angular Moentu (Section 8.3- Lat tie we began dicuing rotational dynaic. We howed that the rotational inertia depend on the hape o the object and the location
University of Alberta Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering ChE 312 Fluid Mechanics Seminar #1 / Assignment # Sept.
 Univerity of Alberta Departent of Cheical and Material Engineering ChE Flid Mechanic Seinar # / Aignent # -8 Sept. 006 Qetion Note Seinar # Q To be done in einar Aignent # Q, Q, Q4 De :00p, Mon. 8 Sept.
Univerity of Alberta Departent of Cheical and Material Engineering ChE Flid Mechanic Seinar # / Aignent # -8 Sept. 006 Qetion Note Seinar # Q To be done in einar Aignent # Q, Q, Q4 De :00p, Mon. 8 Sept.
Distribution Reservoirs. M5: Distribution and Storage Reservoirs, and Pumps. Types of Distribution and Service. Reservoirs
 M5: Ditribution and Storage Reervoir, and Pu Robert Pitt Univerity of Alabaa and Shirley Clark Penn State - Harriburg Ditribution Reervoir Provide ervice torage to eet widely fluctuating deand ioed on
M5: Ditribution and Storage Reervoir, and Pu Robert Pitt Univerity of Alabaa and Shirley Clark Penn State - Harriburg Ditribution Reervoir Provide ervice torage to eet widely fluctuating deand ioed on
ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D225 TUTORIAL 2 LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM
 ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D5 TUTORIAL LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM On copletion of this ttorial yo shold be able to do the following. State Newton s laws of otion. Define linear
ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D5 TUTORIAL LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM On copletion of this ttorial yo shold be able to do the following. State Newton s laws of otion. Define linear
5. Dimensional Analysis. 5.1 Dimensions and units
 5. Diensional Analysis In engineering the alication of fluid echanics in designs ake uch of the use of eirical results fro a lot of exerients. This data is often difficult to resent in a readable for.
5. Diensional Analysis In engineering the alication of fluid echanics in designs ake uch of the use of eirical results fro a lot of exerients. This data is often difficult to resent in a readable for.
Momentum. Momentum. Impulse. Impulse Momentum Theorem. Deriving Impulse. v a t. Momentum and Impulse. Impulse. v t
 Moentu and Iule Moentu Moentu i what Newton called the quantity of otion of an object. lo called Ma in otion The unit for oentu are: = oentu = a = elocity kg Moentu Moentu i affected by a and elocity eeding
Moentu and Iule Moentu Moentu i what Newton called the quantity of otion of an object. lo called Ma in otion The unit for oentu are: = oentu = a = elocity kg Moentu Moentu i affected by a and elocity eeding
PHYSICS 211 MIDTERM II 12 May 2004
 PHYSIS IDTER II ay 004 Exa i cloed boo, cloed note. Ue only your forula heet. Write all wor and anwer in exa boolet. The bac of page will not be graded unle you o requet on the front of the page. Show
PHYSIS IDTER II ay 004 Exa i cloed boo, cloed note. Ue only your forula heet. Write all wor and anwer in exa boolet. The bac of page will not be graded unle you o requet on the front of the page. Show
Homework #6. 1. Continuum wave equation. Show that for long wavelengths the equation of motion,, reduces to the continuum elastic wave equation dt
 Hoework #6 Continuu wave equation Show that for long wavelength the equation of otion, d u M C( u u u, reduce to the continuu elatic wave equation u u v t x where v i the velocity of ound For a, u u i
Hoework #6 Continuu wave equation Show that for long wavelength the equation of otion, d u M C( u u u, reduce to the continuu elatic wave equation u u v t x where v i the velocity of ound For a, u u i
Application of Newton s Laws. F fr
 Application of ewton Law. A hocey puc on a frozen pond i given an initial peed of 0.0/. It lide 5 before coing to ret. Deterine the coefficient of inetic friction ( μ between the puc and ice. The total
Application of ewton Law. A hocey puc on a frozen pond i given an initial peed of 0.0/. It lide 5 before coing to ret. Deterine the coefficient of inetic friction ( μ between the puc and ice. The total
Conservation of Energy
 Add Iportant Conervation of Energy Page: 340 Note/Cue Here NGSS Standard: HS-PS3- Conervation of Energy MA Curriculu Fraework (006):.,.,.3 AP Phyic Learning Objective: 3.E.., 3.E.., 3.E..3, 3.E..4, 4.C..,
Add Iportant Conervation of Energy Page: 340 Note/Cue Here NGSS Standard: HS-PS3- Conervation of Energy MA Curriculu Fraework (006):.,.,.3 AP Phyic Learning Objective: 3.E.., 3.E.., 3.E..3, 3.E..4, 4.C..,
4.5 Evaporation and Diffusion Evaporation and Diffusion through Quiescent Air (page 286) bulk motion of air and j. y a,2, y j,2 or P a,2, P j,2
 4.5 Evaporation and Diffuion 4.5.4 Evaporation and Diffuion through Quiecent Air (page 86) z bul otion of air and j z diffuion of air (a) diffuion of containant (j) y a,, y j, or P a,, P j, z 1 volatile
4.5 Evaporation and Diffuion 4.5.4 Evaporation and Diffuion through Quiecent Air (page 86) z bul otion of air and j z diffuion of air (a) diffuion of containant (j) y a,, y j, or P a,, P j, z 1 volatile
15 N 5 N. Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. The net force on an object is the vector sum of all forces acting on that object.
 Chapter 4 orce and ewton Law of Motion Goal for Chapter 4 to undertand what i force to tudy and apply ewton irt Law to tudy and apply the concept of a and acceleration a coponent of ewton Second Law to
Chapter 4 orce and ewton Law of Motion Goal for Chapter 4 to undertand what i force to tudy and apply ewton irt Law to tudy and apply the concept of a and acceleration a coponent of ewton Second Law to
AP CHEM WKST KEY: Atomic Structure Unit Review p. 1
 AP CHEM WKST KEY: Atoic Structure Unit Review p. 1 1) a) ΔE = 2.178 x 10 18 J 1 2 nf 1 n 2i = 2.178 x 10 18 1 1 J 2 2 6 2 = 4.840 x 10 19 J b) E = λ hc λ = E hc = (6.626 x 10 34 J )(2.9979 x 10 4.840 x
AP CHEM WKST KEY: Atoic Structure Unit Review p. 1 1) a) ΔE = 2.178 x 10 18 J 1 2 nf 1 n 2i = 2.178 x 10 18 1 1 J 2 2 6 2 = 4.840 x 10 19 J b) E = λ hc λ = E hc = (6.626 x 10 34 J )(2.9979 x 10 4.840 x
Sound Wave as a Particular Case of the Gravitational Wave
 Oen Journal of Acoutic, 1,, 115-1 htt://dx.doi.org/1.436/oja.1.313 Publihed Online Seteber 1 (htt://www.scirp.org/journal/oja) Sound Wave a a Particular ae of the Gravitational Wave Vladiir G. Kirtkhalia
Oen Journal of Acoutic, 1,, 115-1 htt://dx.doi.org/1.436/oja.1.313 Publihed Online Seteber 1 (htt://www.scirp.org/journal/oja) Sound Wave a a Particular ae of the Gravitational Wave Vladiir G. Kirtkhalia
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture 2.3
 PHYSICS 151 Note for Online Lecture.3 riction: The baic fact of acrocopic (everda) friction are: 1) rictional force depend on the two aterial that are liding pat each other. bo liding over a waed floor
PHYSICS 151 Note for Online Lecture.3 riction: The baic fact of acrocopic (everda) friction are: 1) rictional force depend on the two aterial that are liding pat each other. bo liding over a waed floor
Momentum Equation. Necessary because body is not made up of a fixed assembly of particles Its volume is the same however Imaginary
 Momentm Eqation Interest in the momentm eqation: Qantification of proplsion rates esign strctres for power generation esign of pipeline systems to withstand forces at bends and other places where the flow
Momentm Eqation Interest in the momentm eqation: Qantification of proplsion rates esign strctres for power generation esign of pipeline systems to withstand forces at bends and other places where the flow
Synopsis : FRICTION. = μ s R where μ s is called the coefficient of static friction. It depends upon the nature
 FRICTION Synopsis : 1. When a body is in otion over another srace or when an object oves throgh a viscos edi like air or water or when a body rolls over another, there is a resistance to the otion becase
FRICTION Synopsis : 1. When a body is in otion over another srace or when an object oves throgh a viscos edi like air or water or when a body rolls over another, there is a resistance to the otion becase
Second Law of Motion. Force mass. Increasing mass. (Neglect air resistance in this example)
 Newton Law of Motion Moentu and Energy Chapter -3 Second Law of Motion The acceleration of an object i directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, i in the direction of the net force,
Newton Law of Motion Moentu and Energy Chapter -3 Second Law of Motion The acceleration of an object i directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, i in the direction of the net force,
Motion Along a Line. Readings: Chapter 6 (2. nd edition)
 Newton Second Law: Motion Along a Line Reading: Chapter 6 (2 nd edition) 1 1) Object a a particle 2) Identify all the force 3) Find the force (vector u of all individual force) 4) Introduce convenient
Newton Second Law: Motion Along a Line Reading: Chapter 6 (2 nd edition) 1 1) Object a a particle 2) Identify all the force 3) Find the force (vector u of all individual force) 4) Introduce convenient
1. (2.5.1) So, the number of moles, n, contained in a sample of any substance is equal N n, (2.5.2)
 Lecture.5. Ideal gas law We have already discussed general rinciles of classical therodynaics. Classical therodynaics is a acroscoic science which describes hysical systes by eans of acroscoic variables,
Lecture.5. Ideal gas law We have already discussed general rinciles of classical therodynaics. Classical therodynaics is a acroscoic science which describes hysical systes by eans of acroscoic variables,
CAUCHY PROBLEM FOR TECHNOLOGICAL CUMULATIVE CHARGE DESIGN. Christo Christov, Svetozar Botev
 SENS'6 Second Scientific Conference with International Particiation SPACE, ECOLOGY, NANOTECHNOLOGY, SAFETY 4 6 June 6, Varna, Bulgaria ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SENS'6 Second Scientific Conference with International Particiation SPACE, ECOLOGY, NANOTECHNOLOGY, SAFETY 4 6 June 6, Varna, Bulgaria ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8 Pages, 3 Figures, 2 Tables. Table S1: The reagents used for this study, their CAS registry numbers, their sources, and their stated purity levels.
 Suleentary Material for The Feaibility of Photoenitized Reaction with Secondary Organic Aerool Particle in the Preence of Volatile Organic Coound Kurti T. Malecha and Sergey A. Nizkorodov* * nizkorod@uci.edu
Suleentary Material for The Feaibility of Photoenitized Reaction with Secondary Organic Aerool Particle in the Preence of Volatile Organic Coound Kurti T. Malecha and Sergey A. Nizkorodov* * nizkorod@uci.edu
Seat: PHYS 1500 (Fall 2006) Exam #2, V1. After : p y = m 1 v 1y + m 2 v 2y = 20 kg m/s + 2 kg v 2y. v 2x = 1 m/s v 2y = 9 m/s (V 1)
 Seat: PHYS 1500 (Fall 006) Exa #, V1 Nae: 5 pt 1. Two object are oving horizontally with no external force on the. The 1 kg object ove to the right with a peed of 1 /. The kg object ove to the left with
Seat: PHYS 1500 (Fall 006) Exa #, V1 Nae: 5 pt 1. Two object are oving horizontally with no external force on the. The 1 kg object ove to the right with a peed of 1 /. The kg object ove to the left with
Practice Problem Solutions. Identify the Goal The acceleration of the object Variables and Constants Known Implied Unknown m = 4.
 Chapter 5 Newton Law Practice Proble Solution Student Textbook page 163 1. Frae the Proble - Draw a free body diagra of the proble. - The downward force of gravity i balanced by the upward noral force.
Chapter 5 Newton Law Practice Proble Solution Student Textbook page 163 1. Frae the Proble - Draw a free body diagra of the proble. - The downward force of gravity i balanced by the upward noral force.
Name: Answer Key Date: Regents Physics. Energy
 Nae: Anwer Key Date: Regent Phyic Tet # 9 Review Energy 1. Ue GUESS ethod and indicate all vector direction.. Ter to know: work, power, energy, conervation of energy, work-energy theore, elatic potential
Nae: Anwer Key Date: Regent Phyic Tet # 9 Review Energy 1. Ue GUESS ethod and indicate all vector direction.. Ter to know: work, power, energy, conervation of energy, work-energy theore, elatic potential
An alternative approach to evaluate the average Nusselt number for mixed boundary layer conditions in parallel flow over an isothermal flat plate
 An alternative approach to evalate the average Nsselt nber for ied bondary layer conditions in parallel flo over an isotheral flat plate Viacheslav Stetsyk, Krzysztof J. Kbiak, ande i and John C Chai Abstract
An alternative approach to evalate the average Nsselt nber for ied bondary layer conditions in parallel flo over an isotheral flat plate Viacheslav Stetsyk, Krzysztof J. Kbiak, ande i and John C Chai Abstract
3.185 Problem Set 6. Radiation, Intro to Fluid Flow. Solutions
 3.85 Proble Set 6 Radiation, Intro to Fluid Flow Solution. Radiation in Zirconia Phyical Vapor Depoition (5 (a To calculate thi viewfactor, we ll let S be the liquid zicronia dic and S the inner urface
3.85 Proble Set 6 Radiation, Intro to Fluid Flow Solution. Radiation in Zirconia Phyical Vapor Depoition (5 (a To calculate thi viewfactor, we ll let S be the liquid zicronia dic and S the inner urface
[95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER. Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow
![[95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER. Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow [95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER. Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow](/thumbs/81/82687654.jpg) [95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow ABSTRACT The aer discusses a well-known condition [95%/95%],
[95/95] APPROACH FOR DESIGN LIMITS ANALYSIS IN VVER Shishkov L., Tsyganov S. Russian Research Centre Kurchatov Institute Russian Federation, Moscow ABSTRACT The aer discusses a well-known condition [95%/95%],
Chapter 5, Conceptual Questions
 Chapter 5, Conceptual Questions 5.1. Two forces are present, tension T in the cable and gravitational force 5.. F G as seen in the figure. Four forces act on the block: the push of the spring F, sp gravitational
Chapter 5, Conceptual Questions 5.1. Two forces are present, tension T in the cable and gravitational force 5.. F G as seen in the figure. Four forces act on the block: the push of the spring F, sp gravitational
Research on an Axial Magnetic-Field-Modulated Brushless Double Rotor Machine
 Energie 213, 6, 4799-4829; doi:1.339/en694799 Article OPEN ACCESS energie ISSN 1996-173 www.di.co/journal/energie Reearch on an Axial Magnetic-Field-Modulated Bruhle Double Rotor Machine Ping Zheng *,
Energie 213, 6, 4799-4829; doi:1.339/en694799 Article OPEN ACCESS energie ISSN 1996-173 www.di.co/journal/energie Reearch on an Axial Magnetic-Field-Modulated Bruhle Double Rotor Machine Ping Zheng *,
Topic 7 Fuzzy expert systems: Fuzzy inference
 Topic 7 Fuzzy expert yte: Fuzzy inference adani fuzzy inference ugeno fuzzy inference Cae tudy uary Fuzzy inference The ot coonly ued fuzzy inference technique i the o-called adani ethod. In 975, Profeor
Topic 7 Fuzzy expert yte: Fuzzy inference adani fuzzy inference ugeno fuzzy inference Cae tudy uary Fuzzy inference The ot coonly ued fuzzy inference technique i the o-called adani ethod. In 975, Profeor
POSTER PRESENTATION OF A PAPER BY: Alex Shved, Mark Logillo, Spencer Studley AAPT MEETING, JANUARY, 2002, PHILADELPHIA
 POSTER PRESETATIO OF A PAPER BY: Ale Shved, Mar Logillo, Spencer Studley AAPT MEETIG, JAUARY, 00, PHILADELPHIA Daped Haronic Ocillation Uing Air a Drag Force Spencer Studley Ale Shveyd Mar Loguillo Santa
POSTER PRESETATIO OF A PAPER BY: Ale Shved, Mar Logillo, Spencer Studley AAPT MEETIG, JAUARY, 00, PHILADELPHIA Daped Haronic Ocillation Uing Air a Drag Force Spencer Studley Ale Shveyd Mar Loguillo Santa
Concept of Reynolds Number, Re
 Concept of Reynold Nuber, Re Ignore Corioli and Buoyancy and forcing Acceleration Advection Preure Gradient Friction I II III IV u u 1 p i i u ( f u ) b + u t x x x j i i i i i i U U U? U L L If IV <
Concept of Reynold Nuber, Re Ignore Corioli and Buoyancy and forcing Acceleration Advection Preure Gradient Friction I II III IV u u 1 p i i u ( f u ) b + u t x x x j i i i i i i U U U? U L L If IV <
Handout 6 Solutions to Problems from Homework 2
 CS 85/185 Fall 2003 Lower Bounds Handout 6 Solutions to Probles fro Hoewor 2 Ait Charabarti Couter Science Dartouth College Solution to Proble 1 1.2: Let f n stand for A 111 n. To decide the roerty f 3
CS 85/185 Fall 2003 Lower Bounds Handout 6 Solutions to Probles fro Hoewor 2 Ait Charabarti Couter Science Dartouth College Solution to Proble 1 1.2: Let f n stand for A 111 n. To decide the roerty f 3
Fluid Dynamics. Type of Flows Continuity Equation Bernoulli Equation Steady Flow Energy Equation Applications of Bernoulli Equation
 Tye of Flows Continity Eqation Bernolli Eqation Steady Flow Energy Eqation Alications of Bernolli Eqation Flid Dynamics Streamlines Lines having the direction of the flid velocity Flids cannot cross a
Tye of Flows Continity Eqation Bernolli Eqation Steady Flow Energy Eqation Alications of Bernolli Eqation Flid Dynamics Streamlines Lines having the direction of the flid velocity Flids cannot cross a
Physics 6A. Practice Final (Fall 2009) solutions. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Phyic 6A Practice inal (all 009) olution or Capu Learning Aitance Service at UCSB . A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train
Phyic 6A Practice inal (all 009) olution or Capu Learning Aitance Service at UCSB . A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train
Theoretical Fluid Mechanics Turbulent Flow Velocity Profile By James C.Y. Guo, Professor and P.E. Civil Engineering, U. of Colorado at Denver
 Theoretical Flid Mechanics Trblent Flow Velocit Proile B Jaes C.Y. Go, Proessor and P.E. Civil Engineering, U. o Colorado at Denver 1. Concept o Mixing Process in Trblent Flow Far awa ro the solid wall,
Theoretical Flid Mechanics Trblent Flow Velocit Proile B Jaes C.Y. Go, Proessor and P.E. Civil Engineering, U. o Colorado at Denver 1. Concept o Mixing Process in Trblent Flow Far awa ro the solid wall,
THE EFFECT OF SOLID PARTICLE SIZE UPON TIME AND SEDIMENTATION RATE
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 5 (54) No. 1-1 THE EFFECT OF SOLID PARTICLE SIZE UPON TIME AND SEDIMENTATION RATE
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 5 (54) No. 1-1 THE EFFECT OF SOLID PARTICLE SIZE UPON TIME AND SEDIMENTATION RATE
Pressure measurements
 Next Previous 8/6/01 Chapter six + seven Pressure and Flow easureents Laith Batarseh Hoe End Basic concepts Pressure is represented as a force per unit area Absolute pressure refers to the absolute value
Next Previous 8/6/01 Chapter six + seven Pressure and Flow easureents Laith Batarseh Hoe End Basic concepts Pressure is represented as a force per unit area Absolute pressure refers to the absolute value
THE BICYCLE RACE ALBERT SCHUELLER
 THE BICYCLE RACE ALBERT SCHUELLER. INTRODUCTION We will conider the ituation of a cyclit paing a refrehent tation in a bicycle race and the relative poition of the cyclit and her chaing upport car. The
THE BICYCLE RACE ALBERT SCHUELLER. INTRODUCTION We will conider the ituation of a cyclit paing a refrehent tation in a bicycle race and the relative poition of the cyclit and her chaing upport car. The
13 Harmonic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization
 3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
Scale Efficiency in DEA and DEA-R with Weight Restrictions
 Available online at http://ijdea.rbiau.ac.ir Int. J. Data Envelopent Analyi (ISSN 2345-458X) Vol.2, No.2, Year 2014 Article ID IJDEA-00226, 5 page Reearch Article International Journal of Data Envelopent
Available online at http://ijdea.rbiau.ac.ir Int. J. Data Envelopent Analyi (ISSN 2345-458X) Vol.2, No.2, Year 2014 Article ID IJDEA-00226, 5 page Reearch Article International Journal of Data Envelopent
5. The Bernoulli Equation
 5. The Bernolli Eqation [This material relates predominantly to modles ELP034, ELP035] 5. Work and Energy 5. Bernolli s Eqation 5.3 An example of the se of Bernolli s eqation 5.4 Pressre head, velocity
5. The Bernolli Eqation [This material relates predominantly to modles ELP034, ELP035] 5. Work and Energy 5. Bernolli s Eqation 5.3 An example of the se of Bernolli s eqation 5.4 Pressre head, velocity
= s = 3.33 s s. 0.3 π 4.6 m = rev = π 4.4 m. (3.69 m/s)2 = = s = π 4.8 m. (5.53 m/s)2 = 5.
 Seat: PHYS 500 (Fall 0) Exa #, V 5 pt. Fro book Mult Choice 8.6 A tudent lie on a very light, rigid board with a cale under each end. Her feet are directly over one cale and her body i poitioned a hown.
Seat: PHYS 500 (Fall 0) Exa #, V 5 pt. Fro book Mult Choice 8.6 A tudent lie on a very light, rigid board with a cale under each end. Her feet are directly over one cale and her body i poitioned a hown.
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Matheatic Reviion Guide Introduction to Differential Equation Page of Author: Mark Kudlowki MK HOME TUITION Matheatic Reviion Guide Level: A-Level Year DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Verion : Date: 3-4-3 Matheatic
Matheatic Reviion Guide Introduction to Differential Equation Page of Author: Mark Kudlowki MK HOME TUITION Matheatic Reviion Guide Level: A-Level Year DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Verion : Date: 3-4-3 Matheatic
The Realm of Hydrogeology
 The Real of Hydrogeology In class exercise Stagnant Flow Plot hydraulic head and ressure vs. deth for (also indicate the hydrostatic line) Stagnant flow (no flow) Steady downward flow Steady uward flow
The Real of Hydrogeology In class exercise Stagnant Flow Plot hydraulic head and ressure vs. deth for (also indicate the hydrostatic line) Stagnant flow (no flow) Steady downward flow Steady uward flow
PHYS 1443 Section 003 Lecture #21 Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2003 Dr. Mystery Lecturer
 PHYS 443 Section 003 Lecture # Wednesday, Nov. 9, 003 Dr. Mystery Lecturer. Fluid Dyanics : Flow rate and Continuity Equation. Bernoulli s Equation 3. Siple Haronic Motion 4. Siple Bloc-Spring Syste 5.
PHYS 443 Section 003 Lecture # Wednesday, Nov. 9, 003 Dr. Mystery Lecturer. Fluid Dyanics : Flow rate and Continuity Equation. Bernoulli s Equation 3. Siple Haronic Motion 4. Siple Bloc-Spring Syste 5.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR. Mass Spectrometrically-Detected Statistical Aspects of Ligand Populations in Mixed Monolayer Au 25 L 18 Nanoparticles
 SUPPORTIG IFORMATIO FOR Mass Sectroetrically-Detected Statistical Asects of Lig Poulations in Mixed Monolayer Au 25 L 8 anoarticles Aala Dass,,a Kennedy Holt, Joseh F. Parer, Stehen W. Feldberg, Royce
SUPPORTIG IFORMATIO FOR Mass Sectroetrically-Detected Statistical Asects of Lig Poulations in Mixed Monolayer Au 25 L 8 anoarticles Aala Dass,,a Kennedy Holt, Joseh F. Parer, Stehen W. Feldberg, Royce
3 Thermodynamics and Statistical mechanics
 Therodynaics and Statistical echanics. Syste and environent The syste is soe ortion of atter that we searate using real walls or only in our ine, fro the other art of the universe. Everything outside the
Therodynaics and Statistical echanics. Syste and environent The syste is soe ortion of atter that we searate using real walls or only in our ine, fro the other art of the universe. Everything outside the
A Self-adaptive Predictive Congestion Control Model for Extreme Networks
 A Self-adative Predictive Congestion Control Model for Extree etworks Yaqin Li, Min Song, and W. Steven Gray ECE Deartent, Old Doinion University 3 Kafan Hall, orfolk, VA 359 {yli, song, sgray}@od.ed ABSTRACT
A Self-adative Predictive Congestion Control Model for Extree etworks Yaqin Li, Min Song, and W. Steven Gray ECE Deartent, Old Doinion University 3 Kafan Hall, orfolk, VA 359 {yli, song, sgray}@od.ed ABSTRACT
CHAPTER 2 THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPER 2 HERMODYNAMICS 2.1 INRODUCION herodynaics is the study of the behavior of systes of atter under the action of external fields such as teerature and ressure. It is used in articular to describe
CHAPER 2 HERMODYNAMICS 2.1 INRODUCION herodynaics is the study of the behavior of systes of atter under the action of external fields such as teerature and ressure. It is used in articular to describe
Frequency Domain Analysis of Rattle in Gear Pairs and Clutches. Abstract. 1. Introduction
 The 00 International Congress and Exosition on Noise Control Engineering Dearborn, MI, USA. August 9-, 00 Frequency Doain Analysis of Rattle in Gear Pairs and Clutches T. C. Ki and R. Singh Acoustics and
The 00 International Congress and Exosition on Noise Control Engineering Dearborn, MI, USA. August 9-, 00 Frequency Doain Analysis of Rattle in Gear Pairs and Clutches T. C. Ki and R. Singh Acoustics and
Physics 20 Lesson 28 Simple Harmonic Motion Dynamics & Energy
 Phyic 0 Leon 8 Siple Haronic Motion Dynaic & Energy Now that we hae learned about work and the Law of Coneration of Energy, we are able to look at how thee can be applied to the ae phenoena. In general,
Phyic 0 Leon 8 Siple Haronic Motion Dynaic & Energy Now that we hae learned about work and the Law of Coneration of Energy, we are able to look at how thee can be applied to the ae phenoena. In general,
15 Newton s Laws #2: Kinds of Forces, Creating Free Body Diagrams
 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras re is no force of otion acting on an object. Once you have the force or forces
Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras re is no force of otion acting on an object. Once you have the force or forces
Physics Sp Exam #3 Name:
 Phyic 160-0 Sp. 017 Exa #3 Nae: 1) In electrodynaic, a agnetic field produce a force on a oving charged particle that i alway perpendicular to the direction the particle i oving. How doe thi force affect
Phyic 160-0 Sp. 017 Exa #3 Nae: 1) In electrodynaic, a agnetic field produce a force on a oving charged particle that i alway perpendicular to the direction the particle i oving. How doe thi force affect
The Hydrogen Atom. Nucleus charge +Ze mass m 1 coordinates x 1, y 1, z 1. Electron charge e mass m 2 coordinates x 2, y 2, z 2
 The Hydrogen Ato The only ato that can be solved exactly. The results becoe the basis for understanding all other atos and olecules. Orbital Angular Moentu Spherical Haronics Nucleus charge +Ze ass coordinates
The Hydrogen Ato The only ato that can be solved exactly. The results becoe the basis for understanding all other atos and olecules. Orbital Angular Moentu Spherical Haronics Nucleus charge +Ze ass coordinates
USEFUL HINTS FOR SOLVING PHYSICS OLYMPIAD PROBLEMS. By: Ian Blokland, Augustana Campus, University of Alberta
 1 USEFUL HINTS FOR SOLVING PHYSICS OLYMPIAD PROBLEMS By: Ian Bloland, Augustana Capus, University of Alberta For: Physics Olypiad Weeend, April 6, 008, UofA Introduction: Physicists often attept to solve
1 USEFUL HINTS FOR SOLVING PHYSICS OLYMPIAD PROBLEMS By: Ian Bloland, Augustana Capus, University of Alberta For: Physics Olypiad Weeend, April 6, 008, UofA Introduction: Physicists often attept to solve
AP Physics Momentum AP Wrapup
 AP Phyic Moentu AP Wrapup There are two, and only two, equation that you get to play with: p Thi i the equation or oentu. J Ft p Thi i the equation or ipule. The equation heet ue, or oe reaon, the ybol
AP Phyic Moentu AP Wrapup There are two, and only two, equation that you get to play with: p Thi i the equation or oentu. J Ft p Thi i the equation or ipule. The equation heet ue, or oe reaon, the ybol
12.4 Atomic Absorption and Emission Spectra
 Phyic Tool box 12.4 Atoic Abortion and iion Sectra A continuou ectru given off by a heated olid i caued by the interaction between neighbouring ato or olecule. An eiion ectru or line ectru i eitted fro
Phyic Tool box 12.4 Atoic Abortion and iion Sectra A continuou ectru given off by a heated olid i caued by the interaction between neighbouring ato or olecule. An eiion ectru or line ectru i eitted fro
The Lagrangian Method vs. other methods (COMPARATIVE EXAMPLE)
 The Lagrangian ethod vs. other ethods () This aterial written by Jozef HANC, jozef.hanc@tuke.sk Technical University, Kosice, Slovakia For Edwin Taylor s website http://www.eftaylor.co/ 6 January 003 The
The Lagrangian ethod vs. other ethods () This aterial written by Jozef HANC, jozef.hanc@tuke.sk Technical University, Kosice, Slovakia For Edwin Taylor s website http://www.eftaylor.co/ 6 January 003 The
Related Rates section 3.9
 Related Rate ection 3.9 Iportant Note: In olving the related rate proble, the rate of change of a quantity i given and the rate of change of another quantity i aked for. You need to find a relationhip
Related Rate ection 3.9 Iportant Note: In olving the related rate proble, the rate of change of a quantity i given and the rate of change of another quantity i aked for. You need to find a relationhip
4. How a psychrometer works
 1 4. How a sychroeter works Identical theroeters Dry bulb (war Gauze around the wet bulb ool water Wet bulb (cool Saturated air Huidity to be easured T dry at Water being condensated, waring the gauze
1 4. How a sychroeter works Identical theroeters Dry bulb (war Gauze around the wet bulb ool water Wet bulb (cool Saturated air Huidity to be easured T dry at Water being condensated, waring the gauze
A NEW APPROACH FOR INVESTIGATION OF MULTI MACHINE STABILITY IN A POWER SYSTEM
 ISSN: 50-038 (Online) A NEW APPROACH FOR INVESTIGATION OF MULTI MACHINE STABILITY IN A POWER SYSTEM MEENAKSHI DE a, G. DAS b AND K. K. MANDAL c abc Department of Power Engineering, Jadavpr Univerity ABSTRACT
ISSN: 50-038 (Online) A NEW APPROACH FOR INVESTIGATION OF MULTI MACHINE STABILITY IN A POWER SYSTEM MEENAKSHI DE a, G. DAS b AND K. K. MANDAL c abc Department of Power Engineering, Jadavpr Univerity ABSTRACT
s s 1 s = m s 2 = 0; Δt = 1.75s; a =? mi hr
 Flipping Phyic Lecture Note: Introduction to Acceleration with Priu Brake Slaing Exaple Proble a Δv a Δv v f v i & a t f t i Acceleration: & flip the guy and ultiply! Acceleration, jut like Diplaceent
Flipping Phyic Lecture Note: Introduction to Acceleration with Priu Brake Slaing Exaple Proble a Δv a Δv v f v i & a t f t i Acceleration: & flip the guy and ultiply! Acceleration, jut like Diplaceent
Honors Lab 4.5 Freefall, Apparent Weight, and Friction
 Nae School Date Honors Lab 4.5 Freefall, Apparent Weight, and Friction Purpose To investigate the vector nature of forces To practice the use free-body diagras (FBDs) To learn to apply Newton s Second
Nae School Date Honors Lab 4.5 Freefall, Apparent Weight, and Friction Purpose To investigate the vector nature of forces To practice the use free-body diagras (FBDs) To learn to apply Newton s Second
ROOT LOCUS. Poles and Zeros
 Automatic Control Sytem, 343 Deartment of Mechatronic Engineering, German Jordanian Univerity ROOT LOCUS The Root Locu i the ath of the root of the characteritic equation traced out in the - lane a a ytem
Automatic Control Sytem, 343 Deartment of Mechatronic Engineering, German Jordanian Univerity ROOT LOCUS The Root Locu i the ath of the root of the characteritic equation traced out in the - lane a a ytem
Lesson 24: Newton's Second Law (Motion)
 Lesson 24: Newton's Second Law (Motion) To really appreciate Newton s Laws, it soeties helps to see how they build on each other. The First Law describes what will happen if there is no net force. The
Lesson 24: Newton's Second Law (Motion) To really appreciate Newton s Laws, it soeties helps to see how they build on each other. The First Law describes what will happen if there is no net force. The
Physics Sp Exam #4 Name:
 Phyic 160-0 Sp. 017 Ea #4 Nae: 1) A coputer hard dik tart ro ret. It peed up with contant angular acceleration until it ha an angular peed o 700 rp. I it coplete 150 revolution while peeding up, what i
Phyic 160-0 Sp. 017 Ea #4 Nae: 1) A coputer hard dik tart ro ret. It peed up with contant angular acceleration until it ha an angular peed o 700 rp. I it coplete 150 revolution while peeding up, what i
3. Internal Flow General Concepts:
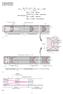 3. Internal Flow General Concet: ρ u u 4 & Re Re, cr 2300 μ ν π μ Re < 2300 lainar 2300 < Re < 4000 tranitional Flow Regie : Re > 4000 turbulent Re > 10,000 fully turbulent (d) 1 (e) Figure 1 Boundary
3. Internal Flow General Concet: ρ u u 4 & Re Re, cr 2300 μ ν π μ Re < 2300 lainar 2300 < Re < 4000 tranitional Flow Regie : Re > 4000 turbulent Re > 10,000 fully turbulent (d) 1 (e) Figure 1 Boundary
FREE BODY DIAGRAMS! For each of the layouts, draw the f.b.d.s for the bodies in the system. (The solutions follow--try each before looking!)! 3.)!
 1.)! FREE BODY DIAGRAMS! For each of the layouts, draw the f.b.d.s for the bodies in the syste. (he solutions follow--try each before looking!)! 3.)!! 1.)! 3.)! 2.)! 4.)!! 2.)! 4.)! 1.) answer 3.) answer!
1.)! FREE BODY DIAGRAMS! For each of the layouts, draw the f.b.d.s for the bodies in the syste. (he solutions follow--try each before looking!)! 3.)!! 1.)! 3.)! 2.)! 4.)!! 2.)! 4.)! 1.) answer 3.) answer!
Work and Energy Problems
 06-08- orce F o trength 0N act on an object o a 3kg a it ove a ditance o 4. I F i perpendicular to the 4 diplaceent, the work done i equal to: Work and Energy Proble a) 0J b) 60J c) 80J d) 600J e) 400J
06-08- orce F o trength 0N act on an object o a 3kg a it ove a ditance o 4. I F i perpendicular to the 4 diplaceent, the work done i equal to: Work and Energy Proble a) 0J b) 60J c) 80J d) 600J e) 400J
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.com
 XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.co https://prootephysics.wordpress.co [MOTION] CHAPTER NO. 3 In this chapter we are going to discuss otion in one diension in which we
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.co https://prootephysics.wordpress.co [MOTION] CHAPTER NO. 3 In this chapter we are going to discuss otion in one diension in which we
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Design of a Transmission Shaft
 Design of a Transission Shaft If power is transferred to and fro the shaft by ygears or sprocket wheels, the shaft is subjected to transverse loading as well as shear loading. Noral stresses due to transverse
Design of a Transission Shaft If power is transferred to and fro the shaft by ygears or sprocket wheels, the shaft is subjected to transverse loading as well as shear loading. Noral stresses due to transverse
MATHEMATICAL MODELS AND OPTICAL INVESTIGATION OF TWO PHASE FLOWS IN WIND TUNNELS
 MATHEMATICAL MODELS AND OPTICAL INESTIGATION OF TWO PHASE FLOWS IN WIND TUNNELS *Central Aerohydrodynaic institute Keywords: wind tunnels, icing in suercooled drolets and non-sherical crystals, otical
MATHEMATICAL MODELS AND OPTICAL INESTIGATION OF TWO PHASE FLOWS IN WIND TUNNELS *Central Aerohydrodynaic institute Keywords: wind tunnels, icing in suercooled drolets and non-sherical crystals, otical
Verification Analysis of the Gravity Wall
 Verification Manal no. Update 0/06 Verification Analysis of the Gravity Wall Progra File Gravity Wall Deo_v_en_0.gtz In this verification anal yo will find hand-ade verification analysis calclations of
Verification Manal no. Update 0/06 Verification Analysis of the Gravity Wall Progra File Gravity Wall Deo_v_en_0.gtz In this verification anal yo will find hand-ade verification analysis calclations of
INCOME AND SUBSTITUTION EFFECTS. Two Demand Functions CHANGES IN INCOME. [See Chapter 5 and 6]
![INCOME AND SUBSTITUTION EFFECTS. Two Demand Functions CHANGES IN INCOME. [See Chapter 5 and 6] INCOME AND SUBSTITUTION EFFECTS. Two Demand Functions CHANGES IN INCOME. [See Chapter 5 and 6]](/thumbs/72/68057710.jpg) INCOME AND SUBSTITUTION EFFECTS [See Chater 5 and 6] Two Deand Functions Marshallian deand i ( n describes how consution varies with rices and incoe. Obtained by aiizing utility subject to the budget constraint.
INCOME AND SUBSTITUTION EFFECTS [See Chater 5 and 6] Two Deand Functions Marshallian deand i ( n describes how consution varies with rices and incoe. Obtained by aiizing utility subject to the budget constraint.
Introduction to Particle Physics I relativistic kinematics. Risto Orava Spring 2017
 Introduction to Particle Phyic I relativitic kineatic Rito Orava Sring 07 Lecture III_ relativitic kineatic outline Lecture I: Introduction the Standard Model Lecture II: Particle detection Lecture III_:
Introduction to Particle Phyic I relativitic kineatic Rito Orava Sring 07 Lecture III_ relativitic kineatic outline Lecture I: Introduction the Standard Model Lecture II: Particle detection Lecture III_:
UNIT V BOUNDARY LAYER INTRODUCTION
 UNIT V BOUNDARY LAYER INTRODUCTION The variation of velocity from zero to free-stream velocity in the direction normal to the bondary takes place in a narrow region in the vicinity of solid bondary. This
UNIT V BOUNDARY LAYER INTRODUCTION The variation of velocity from zero to free-stream velocity in the direction normal to the bondary takes place in a narrow region in the vicinity of solid bondary. This
Lecture 5. Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow Navier-Stockes equation
 Lectre 5 Differential Analsis of Flid Flo Naier-Stockes eqation Differential analsis of Flid Flo The aim: to rodce differential eqation describing the motion of flid in detail Flid Element Kinematics An
Lectre 5 Differential Analsis of Flid Flo Naier-Stockes eqation Differential analsis of Flid Flo The aim: to rodce differential eqation describing the motion of flid in detail Flid Element Kinematics An
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion
 Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Investigation of application of extractive distillation method in chloroform manufacture
 Invetigation of application of etractive ditillation ethod in chlorofor anufacture Proceeding of uropean Congre of Cheical ngineering (CC-6) Copenhagen, 16-20 Septeber 2007 Invetigation of application
Invetigation of application of etractive ditillation ethod in chlorofor anufacture Proceeding of uropean Congre of Cheical ngineering (CC-6) Copenhagen, 16-20 Septeber 2007 Invetigation of application
Section J8b: FET Low Frequency Response
 ection J8b: FET ow Frequency epone In thi ection of our tudie, we re o to reiit the baic FET aplifier confiuration but with an additional twit The baic confiuration are the ae a we etiated ection J6 of
ection J8b: FET ow Frequency epone In thi ection of our tudie, we re o to reiit the baic FET aplifier confiuration but with an additional twit The baic confiuration are the ae a we etiated ection J6 of
4 Conservation of Momentum
 hapter 4 oneration of oentu 4 oneration of oentu A coon itake inoling coneration of oentu crop up in the cae of totally inelatic colliion of two object, the kind of colliion in which the two colliding
hapter 4 oneration of oentu 4 oneration of oentu A coon itake inoling coneration of oentu crop up in the cae of totally inelatic colliion of two object, the kind of colliion in which the two colliding
PY241 Solutions Set 9 (Dated: November 7, 2002)
 PY241 Solutions Set 9 (Dated: Noveber 7, 2002) 9-9 At what displaceent of an object undergoing siple haronic otion is the agnitude greatest for the... (a) velocity? The velocity is greatest at x = 0, the
PY241 Solutions Set 9 (Dated: Noveber 7, 2002) 9-9 At what displaceent of an object undergoing siple haronic otion is the agnitude greatest for the... (a) velocity? The velocity is greatest at x = 0, the
HORIZONTAL MOTION WITH RESISTANCE
 DOING PHYSICS WITH MATLAB MECHANICS HORIZONTAL MOTION WITH RESISTANCE Ian Cooper School of Physics, Uniersity of Sydney ian.cooper@sydney.edu.au DOWNLOAD DIRECTORY FOR MATLAB SCRIPTS ec_fr_b. This script
DOING PHYSICS WITH MATLAB MECHANICS HORIZONTAL MOTION WITH RESISTANCE Ian Cooper School of Physics, Uniersity of Sydney ian.cooper@sydney.edu.au DOWNLOAD DIRECTORY FOR MATLAB SCRIPTS ec_fr_b. This script
Basic Thermodynamic Relations
 Basic herodynaic Relations Isolated syste: this is a syste that does not exchange energy with the surrounding edia. First Postulate (equilibriu theore) : Isolated syste always reaches the equilibriu state
Basic herodynaic Relations Isolated syste: this is a syste that does not exchange energy with the surrounding edia. First Postulate (equilibriu theore) : Isolated syste always reaches the equilibriu state
Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications 3 rd Ed
 Fundaentals of Astrodynaics and Alications 3 rd Ed Errata June 0, 0 This listing is an on-going docuent of corrections and clarifications encountered in the book. I areciate any coents and questions you
Fundaentals of Astrodynaics and Alications 3 rd Ed Errata June 0, 0 This listing is an on-going docuent of corrections and clarifications encountered in the book. I areciate any coents and questions you
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 00 The cgraw-hill Copanies, Inc. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER 8 Principle ECHANICS OF ATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University
00 The cgraw-hill Copanies, Inc. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER 8 Principle ECHANICS OF ATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University
2. What two units of measurement are necessary for describing speed? Ans. Distance and time.
 Conceptual Physics-9 th edition Answers by R. E. Treblay Ch. 3 Pg.51 Review questions. What two units of easureent are necessary for describing speed? Ans. Distance and tie. 3. What kind of speed is registered
Conceptual Physics-9 th edition Answers by R. E. Treblay Ch. 3 Pg.51 Review questions. What two units of easureent are necessary for describing speed? Ans. Distance and tie. 3. What kind of speed is registered
EGN 3353C Fluid Mechanics
 Lecture 4 When nondiensionalizing an equation, nondiensional araeters often aear. Exale Consider an object falling due to gravity in a vacuu d z ays: (1) the conventional diensional aroach, and () diensionless
Lecture 4 When nondiensionalizing an equation, nondiensional araeters often aear. Exale Consider an object falling due to gravity in a vacuu d z ays: (1) the conventional diensional aroach, and () diensionless
CALCULATION of CORONA INCEPTION VOLTAGES in N 2 +SF 6 MIXTURES via GENETIC ALGORITHM
 CALCULATION of COONA INCPTION VOLTAGS in N +SF 6 MIXTUS via GNTIC ALGOITHM. Onal G. Kourgoz e-ail: onal@elk.itu.edu.tr e-ail: guven@itu.edu..edu.tr Istanbul Technical University, Faculty of lectric and
CALCULATION of COONA INCPTION VOLTAGS in N +SF 6 MIXTUS via GNTIC ALGOITHM. Onal G. Kourgoz e-ail: onal@elk.itu.edu.tr e-ail: guven@itu.edu..edu.tr Istanbul Technical University, Faculty of lectric and
The Reynolds analogy. 6.6 The Reynolds analogy. The Reynolds analogy. The Reynolds analogy. Turbulence. 6.7 Turbulent boundary layers.
 6. ainar and trblent e Reynolds analogy 6.6 e Reynolds analogy Integral oent eq. o lat srace lo itot d d 1 y δ [ ( 1] d δ 6.6 e Reynolds analogy Integral energy eq. or te case o const d d φδ 1 ( y d( δ
6. ainar and trblent e Reynolds analogy 6.6 e Reynolds analogy Integral oent eq. o lat srace lo itot d d 1 y δ [ ( 1] d δ 6.6 e Reynolds analogy Integral energy eq. or te case o const d d φδ 1 ( y d( δ
Physics 20 Lesson 16 Friction
 Phyic 0 Leon 16 riction In the previou leon we learned that a rictional orce i any orce that reit, retard or ipede the otion o an object. In thi leon we will dicu how riction reult ro the contact between
Phyic 0 Leon 16 riction In the previou leon we learned that a rictional orce i any orce that reit, retard or ipede the otion o an object. In thi leon we will dicu how riction reult ro the contact between
