15 Newton s Laws #2: Kinds of Forces, Creating Free Body Diagrams
|
|
|
- Lorena Patrick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras re is no force of otion acting on an object. Once you have the force or forces exerted on the object by everything (including any force-per-ass field at the location of the object) that is touching the object, you have all the forces. Do not add a bogus force of otion to your free body diagra. It is especially tepting to add a bogus force when there are no actual forces in the direction in which an object is going. eep in ind, however, that an object does not need a force on it to keep going in the direction in which it is going; oving along at a constant velocity is what an object does when there is no net force on it. ow that you ve had soe practice using free body diagras it is tie to discuss how to create the. As you draw a free body diagra, there are a couple of things you need to keep in ind: (1) Include only those forces acting O the object whose free body diagra you are drawing. Any force exerted BY the object on soe other object belongs on the free body diagra of the other object. (2) All forces are contact forces and every force has an agent. agent is that which is exerting the force. In other words, the agent is the life for or thing that is doing the pushing or pulling on the object. o agent can exert a force on an object without being in contact with the object. (We are using the field point of view, rather than the action-at-adistance point of view for the fundaental forces of nature. Thus, for instance, it is the earth s gravitational field at the location of the object, rather than the aterial earth itself, that exerts the gravitational force on an object.) We are going to introduce the various kinds of forces by eans of exaples. Here is the first exaple: Exaple 15-1 A rock is thrown up into the air by a person. Draw the free body diagra of the rock while it is up in the air. (Your free body diagra is applicable for any tie after the rock leaves the thrower s hand, until the last instant before the rock akes contact with whatever it is destined to hit.) eglect any forces that ight be exerted on the rock by the air. If you see the rock flying through the air, it ay very well look to you like there is nothing touching the rock. But the earth s gravitational field is everywhere in the vicinity of the earth. It can t be blocked. It can t be shielded. It is in the air, in the water, even in the dirt. It is in direct contact with everything in the vicinity of the earth. It exerts a force on every object near the surface of the earth. We call that force the gravitational force. You have already studied the gravitational force. We give a brief synopsis of it here. 86
2 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras Exerted on Objects ear the urface of the Earth. Because it has ass, the earth has a gravitational field. gravitational field is a force-per-ass field. It is invisible. It is not atter. It is an infinite set of force-per-ass vectors, one at every point in space in the vicinity of the surface of the earth. Each forceper-ass vector is directed downward, toward the center of the earth and, near the surface of the earth, has a agnitude of sybol used to represent the earth s kg gravitational field vector at any point where it exists is g. Thus, g = 9.80 Downward. effect of the earth s gravitational field is to exert a force on kg any object that is in the earth s gravitational field. force is called the gravitational force and is equal to the product of the ass of the object and the earth s gravitational field vector: = g. agnitude of the gravitational force is given by g = g (15-1) where g = 9.80 is the agnitude of the earth s gravitational field vector. kg direction of the near-earth s-surface gravitational force is downward, toward the center of the earth. Here is the free body diagra and the corresponding table of forces for Exaple 15-1: a Table of s ybol =? ae Agent Victi Earth s = g Rock ield ote: 1) only thing touching the object while it is up in the air (neglecting the air itself) is the earth s gravitational field. o there is only one force on the object, naely the gravitational force. arrow representing the force vector is drawn so that the tail of the arrow is touching the object, and the arrow extends away fro the object in the direction of the force. 2) Unless otherwise stipulated and labeled on the diagra, upward is toward the top of the page and downward is toward the botto of the page. 3) arrow representing the acceleration ust be near but not touching the object. (If it is touching the object, one ight istake it for a force.) 4) re is no velocity inforation on a free body diagra. 87
3 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras 5) re is no force of the hand acting on the object because, at the instant in question, the hand is no longer touching the object. When you draw a free body diagra, only forces that are acting on the object at the instant depicted in the diagra are included. acceleration of the object depends only on the currently-acting forces on the object. force of the hand is of historical interest only. 6) Regarding the table of forces: a) Make sure that for any free body diagra you draw, you are capable of aking a coplete table of forces. You are not required to provide a table of forces with every free body diagra you draw, but you should expect to be called upon to create a table of forces ore than once. b) In the table of forces, the agent is the life for or thing that is exerting the force and the victi is the object on which the force is being exerted. Make sure that, in every case, the victi is the object for which the free body diagra is being drawn. c) In the case at hand, there is only one force so there is only one entry in the table of forces. d) or any object near the surface of the earth, the agent of the gravitational force is the earth s gravitational field. It is okay to abbreviate that to Earth because the gravitational field of the earth can be considered to be an invisible part of the earth, but it is OT okay to call it gravity. Gravity is a subject heading corresponding to the kind of force the gravitational force is, gravity is not an agent. Exaple 15-2 A ball of ass hangs at rest, suspended by a string. Draw the free body diagra for the ball, and create the corresponding table of forces. To do this proble, you need the following inforation about strings: Exerted by a Taut tring on an Object to Which it is Affixed (This also applies to ropes, cables, chains, and the like.) force exerted by a string, on an object to which it is attached, is always directed away fro the object, along the length of the string. ote that the force in question is exerted by the string, not for instance, by soe person pulling on the other end of the string. force exerted by a string on an object is referred to as a tension force and its agnitude is conventionally represented by the sybol T. ote: re is no forula to tell you what the tension force is. If it is not given, the only way to get it is to use ewton s 2 nd Law. 88
4 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras Here is the free body diagra of the ball, and the corresponding table of forces for Exaple 15-2: T a = 0 Table of s ybol=? ae Agent Victi Tension T tring Ball =g Earth s ield Ball Exaple 15-3 A sled of ass is being pulled forward over a horizontal frictionless surface by eans of a horizontal rope attached to the front of the sled. Draw the free body diagra of the sled and provide the corresponding table of forces. Aside fro the rope and the earth s gravitational field, the sled is in contact with a solid surface. surface exerts a kind of force that we need to know about in order to create the free body diagra for this exaple. oral When an object is in contact with a surface, that surface exerts a force on the object. surface presses on the object. force on the object is away fro the surface, and it is perpendicular to the surface. force is called the noral force because noral eans perpendicular, and as entioned, the force is perpendicular to the surface. We use the sybol to represent the agnitude of the noral force. ote: re is no forula to tell you what the noral force is. If it is not given, the only way to get it is to use ewton s 2 nd Law. Here is the free body diagra of the sled as well as the corresponding table of forces. a T Table of s ybol=? ae Agent Victi oral Horizontal led urface T =g Tension Rope Earth s ield led led 89
5 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras ote: word ree in ree Body Diagra refers to the fact that the object is drawn free of its surroundings. Do not include the surroundings (such as the horizontal surface on which the sled is sliding in the case at hand) in your ree Body Diagra. Exaple 15-4 A block of ass rests on a frictionless horizontal surface. block is due west of a west-facing wall. block is attached to the wall by an ideal assless uncopressed/unstretched spring whose force constant is k. spring is perpendicular to the wall. A person pulls the block a distance x directly away fro the wall and releases it fro rest. Draw the free body diagra of the block appropriate for the first instant after release. Provide the corresponding table of forces. ow, for the first tie, we have a spring exerting a force on the object for which we are drawing the free body diagra. o, we need to know about the force exerted by a spring. Exerted by a pring force exerted by an ideal assless spring on an object in contact with one end of the spring is directed along the length of the spring, and away fro the object if the spring is stretched, toward the object if the spring is copressed. or the spring to exert a force on the object in the stretched-spring case, the object ust be attached to the end of the spring. ot so in the copressed-spring case. spring can push on an object whether or not the spring is attached to the object. force depends on the aount x by which the spring is stretched or copressed, and on a easure of the stiffness of the spring known as the force constant of the spring a.k.a. the spring constant and represented by the sybol k. agnitude of the spring force is typically represented by the sybol. spring force is directly proportional to the aount of stretch x. spring constant k is the constant of proportionality. Thus, = k x (15-2) Here is the free body diagra of the block, and the corresponding table of forces for Exaple 15-4: 90
6 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras UP a EAT BEWARE: By chance, in the exaples provided in this chapter, the noral force is upward. ever assue it to be upward. noral force is perpendicular to, and away fro, the surface exerting it. It happens to be upward in the exaples because the object is in contact with the top of a horizontal surface. If the surface is a wall, the noral force is horizontal; if it is a ceiling, downward; if an incline, perpendicular to and away fro the incline. ever assue the noral force to be upward. Table of s ybol=? ae Agent Victi oral Horizontal urface Block = k x pring pring Block =g Earth s ield Block Exaple 15-5 ro your vantage point, a crate of ass is sliding rightward on a flat level concrete floor. othing solid is in contact with the crate except for the floor. Draw the free body diagra of the crate. Provide the corresponding table of forces. ro our experience with objects sliding on concrete floors, we know that the crate is slowing down at the instant under consideration. It is slowing because of kinetic friction. inetic riction A surface, upon which an object is sliding, exerts (in addition to the noral force) a retarding force on that object. retarding force is in the direction opposite that of the velocity of the object. In the case of an object sliding on a dry surface of a solid body (such as a floor) we call the retarding force a kinetic frictional force. inetic eans otion and we include the adjective kinetic to ake it clear that we are dealing with an object that is in otion. kinetic frictional forula given below is an epirical result. This eans that it is 91
7 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras derived directly fro experiental results. It works only in the case of objects sliding on dry surfaces. It does not apply, for instance, to the case of an object sliding on a greased surface. We use the sybol k f for the kinetic friction force. kinetic frictional forula reads k f = µ (15-3) is the agnitude of the noral force. Its presence in the forula indicates that the ore strongly the surface is pressing on the object, the greater the frictional force. µ (u-sub-) is called the coefficient of kinetic friction. Its value depends on the aterials of which both the object and the surface are ade as well as the soothness of the two contact surfaces. It has no units. It is just a nuber. agnitude of the kinetic frictional force is soe fraction of the agnitude of the noral force; µ is that fraction. Values of µ for various pairs of aterials can be found in handbooks. y tend to fall between 0 and 1. actual value for a given pair of aterials depends on the soothness of the surface and is typically quoted with but a single significant digit. IMPORTAT: µ is a coefficient (with no units) used in calculating the frictional force. It is not a force itself. Here is the free body diagra and the table of forces for the case at hand. crate is oving rightward and slowing down it has a leftward acceleration. a k f Table of s ybol ae Agent Victi Concrete oral loor Crate k f = µ inetic Concrete riction loor Crate Earth s = g Crate ield ote: ot every object has a noral ( perpendicular-to-the-surface ) force acting on it. If the object is not in contact with a surface, then there is no noral force acting on the object. 92
8 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras Exaple 15-6 A person has pushed a brick along a tile floor toward an eastward-facing wall trapping a spring of unstretched length Lo and force constant k between the wall and the end of the brick that is facing the wall. That end of the brick is a distance d fro the wall. person has released the brick, but the spring is unable to budge it the brick reains exactly where it was when the person released it. Draw the free body diagra for the brick and provide the corresponding table of forces. A frictional force is acting on an object at rest. Typically, an object at rest clings ore strongly to the surface with which it is in contact than the sae object does when it is sliding across the sae surface. What we have here is a case of static friction. tatic riction A surface that is not frictionless can exert a static friction force on an object that is in contact with that surface. force of static friction is parallel to the surface. It is in the direction opposite the direction of ipending otion of the stationary object. direction of ipending otion is the direction in which the object would accelerate if there was no static friction. In general, there is no forula for calculating static friction to solve for the force of static friction, you use ewton s 2 nd Law. force of static friction is whatever it has to be to ake the net parallel-to-the-surface force zero. We use the sybol sf to represent the agnitude of the static friction force. PECIAL CAE: Iagine trying to push a refrigerator across the floor. Iagine that you push horizontally, and that you gradually increase the force with which you are pushing. Initially, the harder you push, the bigger the force of static friction. But it can t grow forever. re is a axiu possible static friction force agnitude for any such case. Once the agnitude of your force exceeds that, the refrigerator will start sliding. axiu possible force of static friction is given by: = µ (15-4) ax possible sf unitless quantity µ is the coefficient of static friction specific to the type of surface the object is sliding on and the nature of the surface of the object. Values of µ tend to fall between 0 and 1. or a particular pair of surfaces, µ is at least as large as, and typically larger than, µ. 93
9 Chapter 15 ewton s Laws #2: inds of s, Creating ree Body Diagras ax possible Clearly, this forula ( = µ ) is only applicable when the sf question is about the axiu possible force of static friction. You can use this forula if the object is said to be on the verge of slipping, or if the question is about how hard one ust push to budge an object. It also coes in handy when you want to know whether or not an object will stay put. In such a case you would use ewton s 2 nd to find out the agnitude of the force of static friction needed to keep the object fro accelerating. n you would copare that agnitude with the axiu possible agnitude of the force of static friction. Here is the free body diagra of the brick and the table of forces for Exaple 15-6: Up a=0 East sf Table of s ybol=? ae Agent Victi oral Tile loor Brick sf tatic riction Tile loor Brick = g Earth s ield = k x pring pring Brick Brick 94
For a situation involving gravity near earth s surface, a = g = jg. Show. that for that case v 2 = v 0 2 g(y y 0 ).
 Reading: Energy 1, 2. Key concepts: Scalar products, work, kinetic energy, work-energy theore; potential energy, total energy, conservation of echanical energy, equilibriu and turning points. 1.! In 1-D
Reading: Energy 1, 2. Key concepts: Scalar products, work, kinetic energy, work-energy theore; potential energy, total energy, conservation of echanical energy, equilibriu and turning points. 1.! In 1-D
Chapter 5, Conceptual Questions
 Chapter 5, Conceptual Questions 5.1. Two forces are present, tension T in the cable and gravitational force 5.. F G as seen in the figure. Four forces act on the block: the push of the spring F, sp gravitational
Chapter 5, Conceptual Questions 5.1. Two forces are present, tension T in the cable and gravitational force 5.. F G as seen in the figure. Four forces act on the block: the push of the spring F, sp gravitational
Name Period. What force did your partner s exert on yours? Write your answer in the blank below:
 Nae Period Lesson 7: Newton s Third Law and Passive Forces 7.1 Experient: Newton s 3 rd Law Forces of Interaction (a) Tea up with a partner to hook two spring scales together to perfor the next experient:
Nae Period Lesson 7: Newton s Third Law and Passive Forces 7.1 Experient: Newton s 3 rd Law Forces of Interaction (a) Tea up with a partner to hook two spring scales together to perfor the next experient:
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 05: FRICTION, INCLINES, SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.co INTRO TO FRICTION Friction happens when two surfaces are in contact f = μ =. KINETIC FRICTION (v 0 *): STATIC FRICTION (v 0 *): - Happens when ANY object slides/skids/slips. * = Point
!! www.clutchprep.co INTRO TO FRICTION Friction happens when two surfaces are in contact f = μ =. KINETIC FRICTION (v 0 *): STATIC FRICTION (v 0 *): - Happens when ANY object slides/skids/slips. * = Point
Physics 140 D100 Midterm Exam 2 Solutions 2017 Nov 10
 There are 10 ultiple choice questions. Select the correct answer for each one and ark it on the bubble for on the cover sheet. Each question has only one correct answer. (2 arks each) 1. An inertial reference
There are 10 ultiple choice questions. Select the correct answer for each one and ark it on the bubble for on the cover sheet. Each question has only one correct answer. (2 arks each) 1. An inertial reference
Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW QUICK REFERENCE. Important Terms
 Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW Dynaics is the study o the causes o otion, in particular, orces. A orce is a push or a pull. We arrange our knowledge o orces into three laws orulated
Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW Dynaics is the study o the causes o otion, in particular, orces. A orce is a push or a pull. We arrange our knowledge o orces into three laws orulated
A 30 o 30 o M. Homework #4. Ph 231 Introductory Physics, Sp-03 Page 1 of 4
 Hoework #4. Ph 231 Introductory Physics, Sp-03 Page 1 o 4 4-1A. A particle o ass 2 kg is initially at rest at the origin x = 0. I the only orce acting on the particle is a constant 4 in the x-direction,
Hoework #4. Ph 231 Introductory Physics, Sp-03 Page 1 o 4 4-1A. A particle o ass 2 kg is initially at rest at the origin x = 0. I the only orce acting on the particle is a constant 4 in the x-direction,
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.com
 XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.co https://prootephysics.wordpress.co [MOTION] CHAPTER NO. 3 In this chapter we are going to discuss otion in one diension in which we
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.co https://prootephysics.wordpress.co [MOTION] CHAPTER NO. 3 In this chapter we are going to discuss otion in one diension in which we
F = 0. x o F = -k x o v = 0 F = 0. F = k x o v = 0 F = 0. x = 0 F = 0. F = -k x 1. PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture 2.4.
 PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture.4 Springs, Strings, Pulleys, and Connected Objects Hook s Law F = 0 F = -k x 1 x = 0 x = x 1 Let s start with a horizontal spring, resting on a frictionless table.
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture.4 Springs, Strings, Pulleys, and Connected Objects Hook s Law F = 0 F = -k x 1 x = 0 x = x 1 Let s start with a horizontal spring, resting on a frictionless table.
Systems of Masses. 1. Ignoring friction, calculate the acceleration of the system below and the tension in the rope. and (4.0)(9.80) 39.
 Systes of Masses. Ignoring friction, calculate the acceleration of the syste below and the tension in the rope. Drawing individual free body diagras we get 4.0kg 7.0kg g 9.80 / s a?? g and g (4.0)(9.80)
Systes of Masses. Ignoring friction, calculate the acceleration of the syste below and the tension in the rope. Drawing individual free body diagras we get 4.0kg 7.0kg g 9.80 / s a?? g and g (4.0)(9.80)
Lesson 24: Newton's Second Law (Motion)
 Lesson 24: Newton's Second Law (Motion) To really appreciate Newton s Laws, it soeties helps to see how they build on each other. The First Law describes what will happen if there is no net force. The
Lesson 24: Newton's Second Law (Motion) To really appreciate Newton s Laws, it soeties helps to see how they build on each other. The First Law describes what will happen if there is no net force. The
Experiment 2: Hooke s Law
 COMSATS Institute of Inforation Technology, Islaabad Capus PHYS-108 Experient 2: Hooke s Law Hooke s Law is a physical principle that states that a spring stretched (extended) or copressed by soe distance
COMSATS Institute of Inforation Technology, Islaabad Capus PHYS-108 Experient 2: Hooke s Law Hooke s Law is a physical principle that states that a spring stretched (extended) or copressed by soe distance
NB1140: Physics 1A - Classical mechanics and Thermodynamics Problem set 2 - Forces and energy Week 2: November 2016
 NB1140: Physics 1A - Classical echanics and Therodynaics Proble set 2 - Forces and energy Week 2: 21-25 Noveber 2016 Proble 1. Why force is transitted uniforly through a assless string, a assless spring,
NB1140: Physics 1A - Classical echanics and Therodynaics Proble set 2 - Forces and energy Week 2: 21-25 Noveber 2016 Proble 1. Why force is transitted uniforly through a assless string, a assless spring,
Question 1. [14 Marks]
![Question 1. [14 Marks] Question 1. [14 Marks]](/thumbs/88/116022373.jpg) 6 Question 1. [14 Marks] R r T! A string is attached to the dru (radius r) of a spool (radius R) as shown in side and end views here. (A spool is device for storing string, thread etc.) A tension T is
6 Question 1. [14 Marks] R r T! A string is attached to the dru (radius r) of a spool (radius R) as shown in side and end views here. (A spool is device for storing string, thread etc.) A tension T is
The Laws of Motion. Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples
 The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
FREE BODY DIAGRAMS! For each of the layouts, draw the f.b.d.s for the bodies in the system. (The solutions follow--try each before looking!)! 3.)!
 1.)! FREE BODY DIAGRAMS! For each of the layouts, draw the f.b.d.s for the bodies in the syste. (he solutions follow--try each before looking!)! 3.)!! 1.)! 3.)! 2.)! 4.)!! 2.)! 4.)! 1.) answer 3.) answer!
1.)! FREE BODY DIAGRAMS! For each of the layouts, draw the f.b.d.s for the bodies in the syste. (he solutions follow--try each before looking!)! 3.)!! 1.)! 3.)! 2.)! 4.)!! 2.)! 4.)! 1.) answer 3.) answer!
For more Study Material and Latest Questions related to IIT-JEE visit
 or ore Study Material and Latest Questions related to IIT-JEE visit www. ICTION Introduction If we slide or try to slide a body over a surface, the otion is resisted by a bonding between the body and the
or ore Study Material and Latest Questions related to IIT-JEE visit www. ICTION Introduction If we slide or try to slide a body over a surface, the otion is resisted by a bonding between the body and the
26 Impulse and Momentum
 6 Ipulse and Moentu First, a Few More Words on Work and Energy, for Coparison Purposes Iagine a gigantic air hockey table with a whole bunch of pucks of various asses, none of which experiences any friction
6 Ipulse and Moentu First, a Few More Words on Work and Energy, for Coparison Purposes Iagine a gigantic air hockey table with a whole bunch of pucks of various asses, none of which experiences any friction
1. The property of matter that causes an object to resist changes in its state of motion is called:
 SPH3U Exa Review 1. The property of atter that causes an object to resist changes in its state of otion is called: A. friction B. inertia C. the noral force D. tension 1. The property of atter that causes
SPH3U Exa Review 1. The property of atter that causes an object to resist changes in its state of otion is called: A. friction B. inertia C. the noral force D. tension 1. The property of atter that causes
3/10/2019. What Is a Force? What Is a Force? Tactics: Drawing Force Vectors
 What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
Physics 6A. Practice Midterm #2 solutions
 Phyic 6A Practice Midter # olution 1. A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train forward at acceleration a. If 3 of the car
Phyic 6A Practice Midter # olution 1. A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train forward at acceleration a. If 3 of the car
What Is a Force? Slide Pearson Education, Inc.
 What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Physics I Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass:
Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Physics I Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass:
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapter 5 Force and Motion Chapter Goal: To establish a connection between force and motion. Slide 5-2 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-3 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-4 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-5 Chapter 5 Preview
Chapter 5 Force and Motion Chapter Goal: To establish a connection between force and motion. Slide 5-2 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-3 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-4 Chapter 5 Preview Slide 5-5 Chapter 5 Preview
8.1 Force Laws Hooke s Law
 8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
15 N 5 N. Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. The net force on an object is the vector sum of all forces acting on that object.
 Chapter 4 orce and ewton Law of Motion Goal for Chapter 4 to undertand what i force to tudy and apply ewton irt Law to tudy and apply the concept of a and acceleration a coponent of ewton Second Law to
Chapter 4 orce and ewton Law of Motion Goal for Chapter 4 to undertand what i force to tudy and apply ewton irt Law to tudy and apply the concept of a and acceleration a coponent of ewton Second Law to
NAME NUMBER SEC. PHYCS 101 SUMMER 2001/2002 FINAL EXAME:24/8/2002. PART(I) 25% PART(II) 15% PART(III)/Lab 8% ( ) 2 Q2 Q3 Total 40%
 NAME NUMER SEC. PHYCS 101 SUMMER 2001/2002 FINAL EXAME:24/8/2002 PART(I) 25% PART(II) 15% PART(III)/Lab 8% ( ) 2.5 Q1 ( ) 2 Q2 Q3 Total 40% Use the followings: Magnitude of acceleration due to gravity
NAME NUMER SEC. PHYCS 101 SUMMER 2001/2002 FINAL EXAME:24/8/2002 PART(I) 25% PART(II) 15% PART(III)/Lab 8% ( ) 2.5 Q1 ( ) 2 Q2 Q3 Total 40% Use the followings: Magnitude of acceleration due to gravity
PHYSICS. Chapter 5 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
Physics 20 Lesson 18 Pulleys and Systems
 Physics 20 Lesson 18 Pulleys and Systes I. Pulley and syste probles In this lesson we learn about dynaics probles that involve several asses that are connected and accelerating together. Using the pulley
Physics 20 Lesson 18 Pulleys and Systes I. Pulley and syste probles In this lesson we learn about dynaics probles that involve several asses that are connected and accelerating together. Using the pulley
What is a Force? Free-Body diagrams. Contact vs. At-a-Distance 11/28/2016. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion What is a Force? In generic terms: a force is a push or a pull exerted on an object that could cause one of the following to occur: A linear acceleration of the object
Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion What is a Force? In generic terms: a force is a push or a pull exerted on an object that could cause one of the following to occur: A linear acceleration of the object
Physics 6A. Practice Midterm #2 solutions. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Phyic 6A Practice Midter # olution or apu Learning Aitance Service at USB . A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train forward
Phyic 6A Practice Midter # olution or apu Learning Aitance Service at USB . A locootive engine of a M i attached to 5 train car, each of a M. The engine produce a contant force that ove the train forward
Q5 We know that a mass at the end of a spring when displaced will perform simple m harmonic oscillations with a period given by T = 2!
 Chapter 4.1 Q1 n oscillation is any otion in which the displaceent of a particle fro a fixed point keeps changing direction and there is a periodicity in the otion i.e. the otion repeats in soe way. In
Chapter 4.1 Q1 n oscillation is any otion in which the displaceent of a particle fro a fixed point keeps changing direction and there is a periodicity in the otion i.e. the otion repeats in soe way. In
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued 4.9 Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface forces can act on the objects. The component of this force acting
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued 4.9 Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface forces can act on the objects. The component of this force acting
PHYSICS. Chapter 5 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Free Response Question #1 - AP Physics Exam Solutions
 2015 FRQ #1 Free Response Question #1 - AP Physics 1-2015 Exa Solutions (a) First off, we know both blocks have a force of gravity acting downward on the. et s label the F & F. We also know there is a
2015 FRQ #1 Free Response Question #1 - AP Physics 1-2015 Exa Solutions (a) First off, we know both blocks have a force of gravity acting downward on the. et s label the F & F. We also know there is a
Forces and Newton s Laws Notes
 Forces and Newton s Laws Notes Force An action exerted on an object which can change the motion of the object. The SI unit for force is the Newton (N) o N = (kg m)/s 2 o Pound is also a measure of force
Forces and Newton s Laws Notes Force An action exerted on an object which can change the motion of the object. The SI unit for force is the Newton (N) o N = (kg m)/s 2 o Pound is also a measure of force
Section /07/2013. PHY131H1F University of Toronto Class 9 Preclass Video by Jason Harlow. Based on Knight 3 rd edition Ch. 5, pgs.
 PHY131H1F University of Toronto Class 9 Preclass Video by Jason Harlow Based on Knight 3 rd edition Ch. 5, pgs. 116-133 Section 5.1 A force is a push or a pull What is a force? What is a force? A force
PHY131H1F University of Toronto Class 9 Preclass Video by Jason Harlow Based on Knight 3 rd edition Ch. 5, pgs. 116-133 Section 5.1 A force is a push or a pull What is a force? What is a force? A force
UNIT 4 NEWTON S THIRD LAW, FORCE DIAGRAMS AND FORCES. Objectives. To understand and be able to apply Newton s Third Law
 UNIT 4 NEWTON S THIRD LAW, FORCE DIAGRAMS AND FORCES Objectives To understand and be able to apply Newton s Third Law To be able to determine the object that is exerting a particular force To understand
UNIT 4 NEWTON S THIRD LAW, FORCE DIAGRAMS AND FORCES Objectives To understand and be able to apply Newton s Third Law To be able to determine the object that is exerting a particular force To understand
Chapter 4. Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion. That is, describing why objects move
 Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal orce, Tension, riction ree-body
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal orce, Tension, riction ree-body
Note-A-Rific: Mechanical
 Note-A-Rific: Mechanical Kinetic You ve probably heard of inetic energy in previous courses using the following definition and forula Any object that is oving has inetic energy. E ½ v 2 E inetic energy
Note-A-Rific: Mechanical Kinetic You ve probably heard of inetic energy in previous courses using the following definition and forula Any object that is oving has inetic energy. E ½ v 2 E inetic energy
Physics 2A Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Physics 2A Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare It s not what happens to you that determines how far you will
Physics 2A Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare It s not what happens to you that determines how far you will
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion Observation #1 An object at rest remains at rest, unless something makes it move. Observation #2 A object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity, unless something
Newton s Laws of Motion Observation #1 An object at rest remains at rest, unless something makes it move. Observation #2 A object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity, unless something
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems. Force & Motion I
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 5 Force & Motion I Newton s Laws Vertical motion Horizontal motion Mixed forces Contact forces Inclines General problems 1. A 5.0-kg block is lowered with a downward
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 5 Force & Motion I Newton s Laws Vertical motion Horizontal motion Mixed forces Contact forces Inclines General problems 1. A 5.0-kg block is lowered with a downward
Physics 1A Lecture 4B. "Fig Newton: The force required to accelerate a fig inches per second. --J. Hart
 Physics 1A Lecture 4B "Fig Newton: The force required to accelerate a fig 39.37 inches per second. --J. Hart Types of Forces There are many types of forces that we will apply in this class, let s discuss
Physics 1A Lecture 4B "Fig Newton: The force required to accelerate a fig 39.37 inches per second. --J. Hart Types of Forces There are many types of forces that we will apply in this class, let s discuss
Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass: Section 5.1
Lecture 7 Chapter 5 Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 5: Force, Mass: Section 5.1
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Forces I. Newtons Laws
 Forces I Newtons Laws Kinematics The study of how objects move Dynamics The study of why objects move Newton s Laws and Forces What is force? What are they? Force A push or a pull Symbol is F Unit is N
Forces I Newtons Laws Kinematics The study of how objects move Dynamics The study of why objects move Newton s Laws and Forces What is force? What are they? Force A push or a pull Symbol is F Unit is N
Physics 120 Final Examination
 Physics 120 Final Exaination 12 August, 1998 Nae Tie: 3 hours Signature Calculator and one forula sheet allowed Student nuber Show coplete solutions to questions 3 to 8. This exaination has 8 questions.
Physics 120 Final Exaination 12 August, 1998 Nae Tie: 3 hours Signature Calculator and one forula sheet allowed Student nuber Show coplete solutions to questions 3 to 8. This exaination has 8 questions.
Chapter 5. The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The Laws of Motion The description of an object in motion included its position, velocity, and acceleration. There was no consideration of what might influence that motion.
Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The Laws of Motion The description of an object in motion included its position, velocity, and acceleration. There was no consideration of what might influence that motion.
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Quiz 3 4.7 The Gravitational Force Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Quiz 3 4.7 The Gravitational Force Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other
CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION
 62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
62 CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION CHAPTER 4 NEWTON S LAWS O MOTION 63 Up to now we have described the motion of particles using quantities like displacement, velocity and acceleration. These quantities
Unit 5 Forces I- Newtonʼ s First & Second Law
 Unit 5 orces I- Newtonʼ s irst & Second Law Unit is the NEWTON(N) Is by definition a push or a pull Does force need a Physical contact? Can exist during physical contact(tension, riction, Applied orce)
Unit 5 orces I- Newtonʼ s irst & Second Law Unit is the NEWTON(N) Is by definition a push or a pull Does force need a Physical contact? Can exist during physical contact(tension, riction, Applied orce)
2. Which of the following best describes the relationship between force and potential energy?
 Work/Energy with Calculus 1. An object oves according to the function x = t 5/ where x is the distance traveled and t is the tie. Its kinetic energy is proportional to (A) t (B) t 5/ (C) t 3 (D) t 3/ (E)
Work/Energy with Calculus 1. An object oves according to the function x = t 5/ where x is the distance traveled and t is the tie. Its kinetic energy is proportional to (A) t (B) t 5/ (C) t 3 (D) t 3/ (E)
m A 1 m mgd k m v ( C) AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Oscillations
 P Physics Multiple Choice Practice Oscillations. ass, attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is.
P Physics Multiple Choice Practice Oscillations. ass, attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is.
= 1.49 m/s m. 2 kg. 2 kg
 5.6. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex5.6. Solve: For the diagra on the left, three of the vectors lie along the axes of the tilted coordinate sste. Notice that the angle between the 3 N force and the
5.6. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex5.6. Solve: For the diagra on the left, three of the vectors lie along the axes of the tilted coordinate sste. Notice that the angle between the 3 N force and the
Phys101 Second Major-131 Zero Version Coordinator: Dr. A. A. Naqvi Sunday, November 03, 2013 Page: 1
 Coordinator: Dr. A. A. Naqvi Sunday, November 03, 2013 Page: 1 Q1. Two forces are acting on a 2.00 kg box. In the overhead view of Figure 1 only one force F 1 and the acceleration of the box are shown.
Coordinator: Dr. A. A. Naqvi Sunday, November 03, 2013 Page: 1 Q1. Two forces are acting on a 2.00 kg box. In the overhead view of Figure 1 only one force F 1 and the acceleration of the box are shown.
Physics Mechanics. Lecture 11 Newton s Laws - part 2
 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 11 Newton s Laws - part 2 Newton s Second Law of Motion An object may have several forces acting on it; the acceleration is due to the net force: Newton s Second Law of
Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 11 Newton s Laws - part 2 Newton s Second Law of Motion An object may have several forces acting on it; the acceleration is due to the net force: Newton s Second Law of
Newton s 3 Laws of Motion
 Newton s 3 Laws of Motion 1. If F = 0 No change in motion 2. = ma Change in motion Fnet 3. F = F 1 on 2 2 on 1 Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Newton s 3 Laws of Motion 1. If F = 0 No change in motion 2. = ma Change in motion Fnet 3. F = F 1 on 2 2 on 1 Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
PHYSICS 231 Laws of motion PHY 231
 PHYSICS 231 Laws of motion 1 Newton s Laws First Law: If the net force exerted on an object is zero the object continues in its original state of motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was
PHYSICS 231 Laws of motion 1 Newton s Laws First Law: If the net force exerted on an object is zero the object continues in its original state of motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was
In the session you will be divided into groups and perform four separate experiments:
 Mechanics Lab (Civil Engineers) Nae (please print): Tutor (please print): Lab group: Date of lab: Experients In the session you will be divided into groups and perfor four separate experients: (1) air-track
Mechanics Lab (Civil Engineers) Nae (please print): Tutor (please print): Lab group: Date of lab: Experients In the session you will be divided into groups and perfor four separate experients: (1) air-track
The Concept of Force Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames Mass Newton s Second Law The Gravitational Force and Weight Newton s Third Law Analysis
 The Laws of Motion The Concept of Force Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames Mass Newton s Second Law The Gravitational Force and Weight Newton s Third Law Analysis Models using Newton s Second Law Forces
The Laws of Motion The Concept of Force Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames Mass Newton s Second Law The Gravitational Force and Weight Newton s Third Law Analysis Models using Newton s Second Law Forces
Name: Unit 4 Newton s 1 st & 3 rd Law
 Name: Period: Table #: Unit 4 Newton s 1 st & 3 rd Law 1 UNIT IV: Reading - Force Diagrams The analysis of a problem in dynamics usually involves the selection and analysis of the relevant forces acting
Name: Period: Table #: Unit 4 Newton s 1 st & 3 rd Law 1 UNIT IV: Reading - Force Diagrams The analysis of a problem in dynamics usually involves the selection and analysis of the relevant forces acting
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Departent of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 MIDTERM TEST October 22, 2008 Tie: 90 inutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Departent of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 MIDTERM TEST October 22, 2008 Tie: 90 inutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
Student Book pages
 Chapter 7 Review Student Boo pages 390 39 Knowledge. Oscillatory otion is otion that repeats itself at regular intervals. For exaple, a ass oscillating on a spring and a pendulu swinging bac and forth..
Chapter 7 Review Student Boo pages 390 39 Knowledge. Oscillatory otion is otion that repeats itself at regular intervals. For exaple, a ass oscillating on a spring and a pendulu swinging bac and forth..
Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: b) c)
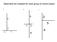 Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: a) b) c) 8 8 2 5-3 3 7-3 2-8 -8 a) 11 8 3 4 Magnitude 11.7 Direction: 70 degrees North of East -3 7 b) 8-3 2-8 1 Magnitude: 1 Direction: West c)
Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: a) b) c) 8 8 2 5-3 3 7-3 2-8 -8 a) 11 8 3 4 Magnitude 11.7 Direction: 70 degrees North of East -3 7 b) 8-3 2-8 1 Magnitude: 1 Direction: West c)
4.2. Visualize: Assess: Note that the climber does not touch the sides of the crevasse so there are no forces from the crevasse walls.
 4.1. Solve: A force is basically a push or a pull on an object. There are five basic characteristics of forces. (i) A force has an agent that is the direct and immediate source of the push or pull. (ii)
4.1. Solve: A force is basically a push or a pull on an object. There are five basic characteristics of forces. (i) A force has an agent that is the direct and immediate source of the push or pull. (ii)
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE B F BA. repulsion between two negatively charged objects. attraction between a negative charge and a positive charge
 HSC PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES Electrostatic force (force mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance) the attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A B BA
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES Electrostatic force (force mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance) the attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A B BA
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Departent of Physics and Engineering Physics 017 Saskatchewan High School Physics Scholarship Copetition Wednesday May 10, 017 Tie allowed: 90 inutes This copetition is based
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Departent of Physics and Engineering Physics 017 Saskatchewan High School Physics Scholarship Copetition Wednesday May 10, 017 Tie allowed: 90 inutes This copetition is based
Physics 11 HW #6 Solutions
 Physics HW #6 Solutions Chapter 6: Focus On Concepts:,,, Probles: 8, 4, 4, 43, 5, 54, 66, 8, 85 Focus On Concepts 6- (b) Work is positive when the orce has a coponent in the direction o the displaceent.
Physics HW #6 Solutions Chapter 6: Focus On Concepts:,,, Probles: 8, 4, 4, 43, 5, 54, 66, 8, 85 Focus On Concepts 6- (b) Work is positive when the orce has a coponent in the direction o the displaceent.
Simple Harmonic Motion of Spring
 Nae P Physics Date iple Haronic Motion and prings Hooean pring W x U ( x iple Haronic Motion of pring. What are the two criteria for siple haronic otion? - Only restoring forces cause siple haronic otion.
Nae P Physics Date iple Haronic Motion and prings Hooean pring W x U ( x iple Haronic Motion of pring. What are the two criteria for siple haronic otion? - Only restoring forces cause siple haronic otion.
Chapter 3 The Laws of motion. The Laws of motion
 Chapter 3 The Laws of motion The Laws of motion The Concept of Force. Newton s First Law. Newton s Second Law. Newton s Third Law. Some Applications of Newton s Laws. 1 5.1 The Concept of Force Force:
Chapter 3 The Laws of motion The Laws of motion The Concept of Force. Newton s First Law. Newton s Second Law. Newton s Third Law. Some Applications of Newton s Laws. 1 5.1 The Concept of Force Force:
Chapter 11 Simple Harmonic Motion
 Chapter 11 Siple Haronic Motion "We are to adit no ore causes of natural things than such as are both true and sufficient to explain their appearances." Isaac Newton 11.1 Introduction to Periodic Motion
Chapter 11 Siple Haronic Motion "We are to adit no ore causes of natural things than such as are both true and sufficient to explain their appearances." Isaac Newton 11.1 Introduction to Periodic Motion
PHYSICS 211 MIDTERM II 12 May 2004
 PHYSIS IDTER II ay 004 Exa i cloed boo, cloed note. Ue only your forula heet. Write all wor and anwer in exa boolet. The bac of page will not be graded unle you o requet on the front of the page. Show
PHYSIS IDTER II ay 004 Exa i cloed boo, cloed note. Ue only your forula heet. Write all wor and anwer in exa boolet. The bac of page will not be graded unle you o requet on the front of the page. Show
Honors Lab 4.5 Freefall, Apparent Weight, and Friction
 Nae School Date Honors Lab 4.5 Freefall, Apparent Weight, and Friction Purpose To investigate the vector nature of forces To practice the use free-body diagras (FBDs) To learn to apply Newton s Second
Nae School Date Honors Lab 4.5 Freefall, Apparent Weight, and Friction Purpose To investigate the vector nature of forces To practice the use free-body diagras (FBDs) To learn to apply Newton s Second
AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions - Chapter 4
 1 Which of ewton's Three Laws of Motion is best expressed by the equation F=ma? a ewton's First Law b ewton's Second Law c ewton's Third Law d one of the above 4.1 2 A person is running on a track. Which
1 Which of ewton's Three Laws of Motion is best expressed by the equation F=ma? a ewton's First Law b ewton's Second Law c ewton's Third Law d one of the above 4.1 2 A person is running on a track. Which
Two Hanging Masses. ) by considering just the forces that act on it. Use Newton's 2nd law while
 Student View Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Edit Assignment Settings per Student Exam 2 - Forces [ Print ] Due: 11:59pm on Tuesday, November 1, 2011 Note: To underst how points are
Student View Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Edit Assignment Settings per Student Exam 2 - Forces [ Print ] Due: 11:59pm on Tuesday, November 1, 2011 Note: To underst how points are
Review: Newton s Laws
 More force was needed to stop the rock Review: Newton s Laws F r 1 F r F r 3 F r 4 2 Newton s First Law The velocity of an object does not change unless a force acts on the object Newton s Second Law:
More force was needed to stop the rock Review: Newton s Laws F r 1 F r F r 3 F r 4 2 Newton s First Law The velocity of an object does not change unless a force acts on the object Newton s Second Law:
1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) m 3 B) m 3 C) m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3
 1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) 2.1 10 5 m 3 B) 9.1 10 4 m 3 C) 3.6 10 3 m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3 2. A 25-N crate slides down a frictionless incline that is 25 above the horizontal.
1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) 2.1 10 5 m 3 B) 9.1 10 4 m 3 C) 3.6 10 3 m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3 2. A 25-N crate slides down a frictionless incline that is 25 above the horizontal.
4.1.1 Extra Practice 4.1 Analyze the effects of a uniform force (magnitude and direction.)
 4.1.1 Extra Practice 4.1 Analyze the effects of a uniform force (magnitude and direction.) Frictional Forces LEVEL 2 1. (HRW 6-3) A bedroom bureau with a mass of 45 kg, including drawers and clothing,
4.1.1 Extra Practice 4.1 Analyze the effects of a uniform force (magnitude and direction.) Frictional Forces LEVEL 2 1. (HRW 6-3) A bedroom bureau with a mass of 45 kg, including drawers and clothing,
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Midterm Examination Tuesday March
 EN4: Dynaics and Vibrations Midter Exaination Tuesday March 8 16 School of Engineering Brown University NAME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is peritted on this exaination. You ay bring
EN4: Dynaics and Vibrations Midter Exaination Tuesday March 8 16 School of Engineering Brown University NAME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is peritted on this exaination. You ay bring
y scalar component x scalar component A. 770 m 250 m file://c:\users\joe\desktop\physics 2A\PLC Assignments - F10\2a_PLC7\index.
 Page 1 of 6 1. A certain string just breaks when it is under 400 N of tension. A boy uses this string to whirl a 10-kg stone in a horizontal circle of radius 10. The boy continuously increases the speed
Page 1 of 6 1. A certain string just breaks when it is under 400 N of tension. A boy uses this string to whirl a 10-kg stone in a horizontal circle of radius 10. The boy continuously increases the speed
F on stone by rope F on box by rope. F on stone by Earth
 B3-SCT70: HANGING STONE CONNECTED TO BOX FREE-BODY DIAGRAS A massless rope connects a box on a horizontal surface and a hanging stone as shown below. The rope passes over a massless, frictionless pulley.
B3-SCT70: HANGING STONE CONNECTED TO BOX FREE-BODY DIAGRAS A massless rope connects a box on a horizontal surface and a hanging stone as shown below. The rope passes over a massless, frictionless pulley.
1 k. 1 m. m A. AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Work-Energy
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Wor-Energy 1. A ass attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Wor-Energy 1. A ass attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Physics Fall Term = # v x. t " =0. are the values at t = 0.
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Physics Fall Term 2012 Exam 1: Practice Problems! d r!! d v! One-Dimensional Kinematics: v =, a = dt dt t " =t v x (t)! v x,0 = # a x (
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Physics Fall Term 2012 Exam 1: Practice Problems! d r!! d v! One-Dimensional Kinematics: v =, a = dt dt t " =t v x (t)! v x,0 = # a x (
You may use g = 10 m/s 2, sin 60 = 0.87, and cos 60 = 0.50.
 1. A child pulls a 15kg sled containing a 5kg dog along a straight path on a horizontal surface. He exerts a force of a 55N on the sled at an angle of 20º above the horizontal. The coefficient of friction
1. A child pulls a 15kg sled containing a 5kg dog along a straight path on a horizontal surface. He exerts a force of a 55N on the sled at an angle of 20º above the horizontal. The coefficient of friction
Physically Based Modeling CS Notes Spring 1997 Particle Collision and Contact
 Physically Based Modeling CS 15-863 Notes Spring 1997 Particle Collision and Contact 1 Collisions with Springs Suppose we wanted to ipleent a particle siulator with a floor : a solid horizontal plane which
Physically Based Modeling CS 15-863 Notes Spring 1997 Particle Collision and Contact 1 Collisions with Springs Suppose we wanted to ipleent a particle siulator with a floor : a solid horizontal plane which
General Physics I Spring Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 General Physics I Spring 2011 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion 1 Forces and Interactions The central concept in understanding why things move is force. If a tractor pushes or pulls a trailer, the tractor
General Physics I Spring 2011 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion 1 Forces and Interactions The central concept in understanding why things move is force. If a tractor pushes or pulls a trailer, the tractor
Chapters 5-6. Dynamics: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. Applications
 Chapters 5-6 Dynamics: orces and Newton s Laws of Motion. Applications That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal,
Chapters 5-6 Dynamics: orces and Newton s Laws of Motion. Applications That is, describing why objects move orces Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law Examples of orces: Weight, Normal,
2009 Academic Challenge
 009 Acadeic Challenge PHYSICS TEST - REGIONAL This Test Consists of 5 Questions Physics Test Production Tea Len Stor, Eastern Illinois University Author/Tea Leader Doug Brandt, Eastern Illinois University
009 Acadeic Challenge PHYSICS TEST - REGIONAL This Test Consists of 5 Questions Physics Test Production Tea Len Stor, Eastern Illinois University Author/Tea Leader Doug Brandt, Eastern Illinois University
27 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring
 Chapter 7 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring 7 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring If a siple haronic oscillation proble does not involve the tie, you should probably be using conservation
Chapter 7 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring 7 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring If a siple haronic oscillation proble does not involve the tie, you should probably be using conservation
Physics B Newton s Laws AP Review Packet
 Force A force is a push or pull on an object. Forces cause an object to accelerate To speed up To slow down To change direction Unit: Newton (SI system) Newton s First Law The Law of Inertia. A body in
Force A force is a push or pull on an object. Forces cause an object to accelerate To speed up To slow down To change direction Unit: Newton (SI system) Newton s First Law The Law of Inertia. A body in
m potential kinetic forms of energy.
 Spring, Chapter : A. near the surface of the earth. The forces of gravity and an ideal spring are conservative forces. With only the forces of an ideal spring and gravity acting on a ass, energy F F will
Spring, Chapter : A. near the surface of the earth. The forces of gravity and an ideal spring are conservative forces. With only the forces of an ideal spring and gravity acting on a ass, energy F F will
PHYSICS 1 Forces & Newton s Laws
 Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Forces & Newton s Laws Presenter 2014-2015 Forces & Newton s Laws What I Absolutel Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Force is an push or pull. It is a vector. Newton s Second
Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Forces & Newton s Laws Presenter 2014-2015 Forces & Newton s Laws What I Absolutel Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Force is an push or pull. It is a vector. Newton s Second
HW 6 - Solutions Due November 20, 2017
 Conteporary Physics I HW 6 HW 6 - Solutions Due Noveber 20, 2017 1. A 4 kg block is attached to a spring with a spring constant k 200N/, and is stretched an aount 0.2 [5 pts each]. (a) Sketch the potential
Conteporary Physics I HW 6 HW 6 - Solutions Due Noveber 20, 2017 1. A 4 kg block is attached to a spring with a spring constant k 200N/, and is stretched an aount 0.2 [5 pts each]. (a) Sketch the potential
Common Exam 2 Physics 111 Fall 2006 Name A
 Coon Ea Physics Fall 006 Nae A Total Nuber of Points is 5 (Multiple Choice and Worout Probles). Multiple Choice Probles are Point per Question..) A toy car oving at constant speed copletes one lap around
Coon Ea Physics Fall 006 Nae A Total Nuber of Points is 5 (Multiple Choice and Worout Probles). Multiple Choice Probles are Point per Question..) A toy car oving at constant speed copletes one lap around
Web practice Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Web practice Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If we know an object is moving at
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Web practice Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If we know an object is moving at
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 3 - Solutions Wednesday February 2, 2011
 Phsics 18 Spring 2011 Hoework 3 - s Wednesda Februar 2, 2011 Make sure our nae is on our hoework, and please bo our final answer. Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attept all the probles,
Phsics 18 Spring 2011 Hoework 3 - s Wednesda Februar 2, 2011 Make sure our nae is on our hoework, and please bo our final answer. Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attept all the probles,
Isaac Newton ( ) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity
 Isaac Newton (1642-1727) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Isaac Newton (1642-1727) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 6 Dynamics I: Motion Along a Line
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 6 Dynamics I: Motion Along a Line Spring, 008 Ho Jung Paik Applications of Newton s Law Objects can be modeled as particles Masses of strings or ropes are negligible
Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 6 Dynamics I: Motion Along a Line Spring, 008 Ho Jung Paik Applications of Newton s Law Objects can be modeled as particles Masses of strings or ropes are negligible
