Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
|
|
|
- Abigail Sharlene Ray
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The driver applied the as soon as she approached the hotel where she wanted to take a. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) brake, break (C) brake, brake (B) break, break (D) break, brake Q.2 It is no surprise that every society has had codes of behaviour; however, the nature of these codes is often. The word that best fills the blank in the above sentence is (A) unpredictable (B) simple (C) expected (D) strict Q.3 Hema s age is 5 years more than twice Hari s age. Suresh s age is 13 years less than 10 times Hari s age. If Suresh is 3 times as old as Hema, how old is Hema? (A) 14 (B) 17 (C) 18 (D) 19 Q.4 Tower A is 90 m tall and tower B is 140 m tall. They are 100 m apart. A horizontal skywalk connects the floors at 70 m in both the towers. If a taut rope connects the top of tower A to the bottom of tower B, at what distance (in meters) from tower A will the rope intersect the skywalk? (A) (B) 50 (C) (D) Q.5 The temperature T in a room varies as a function of the outside temperature T 0 and the number of persons in the room p, according to the relation T = Κ (Θp + T 0 ), where Θ and Κ are constants. What would be the value of Θ given the following data? T 0 p T (A) 0.8 (B) 1.0 (C) 2.0 (D) 10.0 GA 1/3
2 GATE 2018 Q. 6 Q. 10 carry two marks each. General Aptitude (GA) Set-7 Q.6 A fruit seller sold a basket of fruits at 12.5% loss. Had he sold it for Rs. 108 more, he would have made a 10% gain. What is the loss in Rupees incurred by the fruit seller? (A) 48 (B) 52 (C) 60 (D) 108 Q.7 The price of a wire made of a superalloy material is proportional to the square of its length. The price of 10 m length of the wire is Rs What would be the total price (in Rs.) of two wires of lengths 4 m and 6m? (A) 768 (B) 832 (C) 1440 (D) 1600 Q.8 Which of the following function(s) is an accurate description of the graph for the range(s) indicated? (i) y = 2x + 4 for 3 x 1 (ii) y = x 1 for 1 x 2 (iii) y = x 1 for 1 x 2 (iv) y = 1 for 2 x 3 (A) (i), (ii) and (iii) only. (B) (i), (ii) and (iv) only. (C) (i) and (iv) only. (D) (ii) and (iv) only. Q.9 Consider a sequence of numbers a 1, a 2, a 3,, a n where a n = 1 n 1 n > 0. What is the sum of the first 50 terms? n+2, for each integer (A) (1 + 1 ) (B) (1 + 1 ) (C) (1 + 1 ) ( ) (D) 1 ( ) GA 2/3
3 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-7 Q.10 Each of the letters arranged as below represents a unique integer from 1 to 9. The letters are positioned in the figure such that (A B C), (B G E) and (D E F) are equal. Which integer among the following choices cannot be represented by the letters A, B, C, D, E, F or G? A D B G E C F (A) 4 (B) 5 (C) 6 (D) 9 END OF THE QUESTION PAPER GA 3/3
4 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Which one of the following matrices is singular? (A) (B) (C) (D) Q.2 For the given orthogonal matrix Q, 3/7 2/7 6/7 Q = [ 6/7 3/7 2/7 ] 2/7 6/7 3/7 The inverse is 3/7 2/7 6/7 (A) [ 6/7 3/7 2/7 ] 2/7 6/7 3/7 3/7 2/7 6/7 (B) [ 6/7 3/7 2/7] 2/7 6/7 3/7 3/7 6/7 2/7 (C) [ 2/7 3/7 6/7 ] 6/7 2/7 3/7 3/7 6/7 2/7 (D) [ 2/7 3/7 6/7] 6/7 2/7 3/7 Q.3 At the point x = 0, the function f(x) = x 3 has (A) local maximum (B) local minimum (C) both local maximum and minimum (D) neither local maximum nor local minimum Q.4 A column of height h with a rectangular cross-section of size a 2a has a buckling load of P. If the cross-section is changed to 0.5a 3a and its height changed to 1.5h, the buckling load of the redesigned column will be (A) P/12 (B) P/4 (C) P/2 (D) 3P/4 CE 1/11
5 Q.5 A steel column of ISHB kg/m is subjected to a factored axial compressive load of 2000 kn. The load is transferred to a concrete pedestal of grade M20 through a square base plate. Consider bearing strength of concrete as 0.45fck, where fck is the characteristic strength of concrete. Using limit state method and neglecting the self weight of base plate and steel column, the length of a side of the base plate to be provided is (A) 39 cm (B) 42 cm (C) 45 cm (D) 48 cm Q.6 The Le Chatelier apparatus is used to determine (A) compressive strength of cement (C) setting time of cement Q.7 The deformation in concrete due to sustained loading is (B) fineness of cement (D) soundness of cement (A) creep (B) hydration (C) segregation (D) shrinkage Q.8 A solid circular beam with radius of 0.25 m and length of 2 m is subjected to a twisting moment of 20 knm about the z-axis at the free end, which is the only load acting as shown in the figure. The shear stress component τ xy at Point M in the cross-section of the beam at a distance of 1 m from the fixed end is 20 knm (A) 0.0 MPa (B) 0.51 MPa (C) MPa (D) 2.0 MPa Q.9 Two rectangular under-reinforced concrete beam sections X and Y are similar in all aspects except that the longitudinal compression reinforcement in section Y is 10% more. Which one of the following is the correct statement? (A) Section X has less flexural strength and is less ductile than section Y (B) Section X has less flexural strength but is more ductile than section Y (C) Sections X and Y have equal flexural strength but different ductility (D) Sections X and Y have equal flexural strength and ductility Q.10 The percent reduction in the bearing capacity of a strip footing resting on sand under flooding condition (water level at the base of the footing) when compared to the situation where the water level is at a depth much greater than the width of footing, is approximately (A) 0 (B) 25 (C) 50 (D) 100 CE 2/11
6 Q.11 The width of a square footing and the diameter of a circular footing are equal. If both the footings are placed on the surface of sandy soil, the ratio of the ultimate bearing capacity of circular footing to that of square footing will be (A) 4/3 (B) 1 (C) 3/4 (D) 2/3 Q.12 Bernoulli s equation is applicable for (A) viscous and compressible fluid flow (B) inviscid and compressible fluid flow (C) inviscid and incompressible fluid flow (D) viscous and incompressible fluid flow Q.13 There are 20,000 vehicles operating in a city with an average annual travel of 12,000 km per vehicle. The NOx emission rate is 2.0 g/km per vehicle. The total annual release of NOx will be (A) 4,80,000 kg (B) 4,800 kg (C) 480 kg (D) 48 kg Q.14 A bitumen sample has been graded as VG30 as per IS : The 30 in the grade means that (A) penetration of bitumen at 25 C is between 20 and 40 (B) viscosity of bitumen at 60 C is between 2400 and 3600 Poise (C) ductility of bitumen at 27 C is more than 30 cm (D) elastic recovery of bitumen at 15 C is more than 30% Q.15 The speed-density relationship for a road section is shown in the figure. Speed Density The shape of the flow-density relationship is (A) piecewise linear (B) parabolic (C) initially linear then parabolic (D) initially parabolic then linear Q.16 A well-designed signalized intersection is one in which the (A) crossing conflicts are increased (B) total delay is minimized (C) cycle time is equal to the sum of red and green times in all phases (D) cycle time is equal to the sum of red and yellow times in all phases CE 3/11
7 Q.17 A flow field is given by u = y 2, v = xy, w = 0. Value of the z-component of the angular velocity (in radians per unit time, up to two decimal places) at the point (0, 1, 1) is Q.18 The frequency distribution of the compressive strength of 20 concrete cube specimens is given in the table. f (MPa) Number of specimens with compressive strength equal to f If μ is the mean strength of the specimens and σ is the standard deviation, the number of specimens (out of 20) with compressive strength less than μ 3σ is Q.19 In a fillet weld, the direct shear stress and bending tensile stress are 50 MPa and 150 MPa, respectively. As per IS 800: 2007, the equivalent stress (in MPa, up to two decimal places) will be Q.20 In a shrinkage limit test, the volume and mass of a dry soil pat are found to be 50 cm 3 and 88 g, respectively. The specific gravity of the soil solids is 2.71 and the density of water is 1 g/cc. The shrinkage limit (in %, up to two decimal places) is Q.21 A core cutter of 130 mm height has inner and outer diameters of 100 mm and 106 mm, respectively. The area ratio of the core cutter (in %, up to two decimal places) is Q.22 A 1:50 model of a spillway is to be tested in the laboratory. The discharge in the prototype spillway is 1000 m 3 /s. The corresponding discharge (in m 3 /s, up to two decimal places) to be maintained in the model, neglecting variation in acceleration due to gravity, is Q.23 A 10 m wide rectangular channel carries a discharge of 20 m 3 /s under critical condition. Using g = 9.81 m/s 2, the specific energy (in m, up to two decimal places) is Q.24 For routing of flood in a given channel using the Muskingum method, two of the routing coefficients are estimated as C and C The value of the third coefficient C2 would be Q.25 A city generates kg of municipal solid waste (MSW) per year, out of which only 10% is recovered/recycled and the rest goes to landfill. The landfill has a single lift of 3 m height and is compacted to a density of 550 kg/m 3. If 80% of the landfill is assumed to be MSW, the landfill area (in m 2, up to one decimal place) required would be CE 4/11
8 Q. 26 Q. 55 carry two marks each. π Q.26 The value of the integral x cos 2 x dx 0 (A) π 2 /8 (B) π 2 /4 (C) π 2 /2 (D) π 2 is Q.27 A cantilever beam of length 2 m with a square section of side length 0.1 m is loaded vertically at the free end. The vertical displacement at the free end is 5 mm. The beam is made of steel with Young s modulus of N/m 2. The maximum bending stress at the fixed end of the cantilever is (A) 20.0 MPa (B) 37.5 MPa (C) 60.0 MPa (D) 75.0 MPa Q.28 A cylinder of radius 250 mm and weight, W = 10 kn is rolled up an obstacle of height 50 mm by applying a horizontal force P at its centre as shown in the figure. All interfaces are assumed frictionless. The minimum value of P is (A) 4.5 kn (B) 5.0 kn (C) 6.0 kn (D) 7.5 kn Q.29 A plate in equilibrium is subjected to uniform stresses along its edges with magnitude σ xx = 30 MPa and σ yy = 50 MPa as shown in the figure. The Young s modulus of the material is N/m 2 and the Poisson s ratio is 0.3. If σ zz is negligibly small and assumed to be zero, then the strain ε zz is (A) (B) (C) 0.0 (D) CE 5/11
9 Q.30 The figure shows a simply supported beam PQ of uniform flexural rigidity EI carrying two moments M and 2M. The slope at P will be (A) 0 (B) ML/(9EI) (C) ML/(6EI) (D) ML/(3EI) Q.31 A 0.5 m 0.5 m square concrete pile is to be driven in a homogeneous clayey soil having undrained shear strength, cu = 50 kpa and unit weight, γ = 18.0 kn/m 3. The design capacity of the pile is 500 kn. The adhesion factor α is given as The length of the pile required for the above design load with a factor of safety of 2.0 is (A) 5.2 m (B) 5.8 m (C) 11.8 m (D) 12.5 m Q.32 A closed tank contains 0.5 m thick layer of mercury (specific gravity = 13.6) at the bottom. A 2.0 m thick layer of water lies above the mercury layer. A 3.0 m thick layer of oil (specific gravity = 0.6) lies above the water layer. The space above the oil layer contains air under pressure. The gauge pressure at the bottom of the tank is kn/m 2. The density of water is 1000 kg/m 3 and the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s 2. The value of pressure in the air space is (A) kn/m 2 (B) kn/m 2 (C) kn/m 2 (D) kn/m 2 Q.33 A rapid sand filter comprising a number of filter beds is required to produce 99 MLD of potable water. Consider water loss during backwashing as 5%, rate of filtration as 6.0 m/h and length to width ratio of filter bed as The width of each filter bed is to be kept equal to 5.2 m. One additional filter bed is to be provided to take care of break-down, repair and maintenance. The total number of filter beds required will be (A) 19 (B) 20 (C) 21 (D) 22 Q.34 A priority intersection has a single-lane one-way traffic road crossing an undivided twolane two-way traffic road. The traffic stream speed on the single-lane road is 20 kmph and the speed on the two-lane road is 50 kmph. The perception-reaction time is 2.5 s, coefficient of longitudinal friction is 0.38 and acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s 2. A clear sight triangle has to be ensured at this intersection. The minimum lengths of the sides of the sight triangle along the two-lane road and the single-lane road, respectively will be (A) 50 m and 20 m (C) 111 m and 15 m (B) 61 m and 18 m (D) 122 m and 36 m CE 6/11
10 Q.35 The following details refer to a closed traverse: Line Consecutive coordinate Northing (m) Southing (m) Easting (m) Westing (m) PQ QR RS SP The length and direction (whole circle bearing) of closure, respectively are (A) 1 m and 90 (B) 2 m and 90 (C) 1 m and 270 (D) 2 m and 270 Q.36 A square area (on the surface of the earth) with side 100 m and uniform height, appears as 1 cm 2 on a vertical aerial photograph. The topographic map shows that a contour of 650 m passes through the area. If focal length of the camera lens is 150 mm, the height from which the aerial photograph was taken, is (A) 800 m (B) 1500 m (C) 2150 m (D) 3150 m Q.37 The solution at x = 1, t = 1 of the partial differential equation 2 u = 25 2 u subject to x 2 t2 initial conditions of u(0) = 3x and u (0) = 3 is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 4 (D) 6 t Q.38 The solution (up to three decimal places) at x = 1 of the differential equation d 2 y + 2 dy dx 2 dx dy + y = 0 subject to boundary conditions y(0) = 1 and (0) = 1 is dx Q.39 Variation of water depth (y) in a gradually varied open channel flow is given by the first order differential equation dy dx = 1 10 e 3 ln(y) e 3ln(y) Given initial condition: y(x = 0) = 0.8 m. The depth (in m, up to three decimal places) of flow at a downstream section at x = 1 m from one calculation step of Single Step Euler Method is Q.40 An RCC short column (with lateral ties) of rectangular cross section of 250 mm 300 mm is reinforced with four numbers of 16 mm diameter longitudinal bars. The grades of steel and concrete are Fe415 and M20, respectively. Neglect eccentricity effect. Considering limit state of collapse in compression (IS 456 : 2000), the axial load carrying capacity of the column (in kn, up to one decimal place), is CE 7/11
11 Q.41 An RCC beam of rectangular cross section has factored shear of 200 kn at its critical section. Its width b is 250 mm and effective depth d is 350 mm. Assume design shear strength τ c of concrete as 0.62 N/mm 2 and maximum allowable shear stress τ c,max in concrete as 2.8 N/mm 2. If two legged 10 mm diameter vertical stirrups of Fe250 grade steel are used, then the required spacing (in cm, up to one decimal place) as per limit state method will be Q.42 The dimensions of a symmetrical welded I-section are shown in the figure (All dimensions are in mm) The plastic section modulus about the weaker axis (in cm 3, up to one decimal place) is CE 8/11
12 Q.43 Consider the deformable pin-jointed truss with loading, geometry and section properties as shown in the figure. Given that E = N/m 2, A = 10 mm 2, L = 1 m and P = 1 kn. The horizontal displacement of Joint C (in mm, up to one decimal place) is Q.44 At a construction site, a contractor plans to make an excavation as shown in the figure. 30 Elevation (in m) Proposed Excavation Clay, Unit weight, γ = 20 kn/m 3 Highly Pervious Sand Elevation: +20 m River The water level in the adjacent river is at an elevation of m. Unit weight of water is 10 kn/m 3. The factor of safety (up to two decimal places) against sand boiling for the proposed excavation is Q.45 A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 kpa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kpa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kpa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kpa, the pore pressure developed (in kpa, up to one decimal place) is CE 9/11
13 Q.46 The void ratio of a soil is 0.55 at an effective normal stress of 140 kpa. The compression index of the soil is In order to reduce the void ratio to 0.4, an increase in the magnitude of effective normal stress (in kpa, up to one decimal place) should be Q.47 A rigid smooth retaining wall of height 7 m with vertical backface retains saturated clay as backfill. The saturated unit weight and undrained cohesion of the backfill are 17.2 kn/m 3 and 20 kpa, respectively. The difference in the active lateral forces on the wall (in kn per meter length of wall, up to two decimal places), before and after the occurrence of tension cracks is Q.48 Rainfall depth over a watershed is monitored through six number of well distributed rain gauges. Gauged data are given below Rain Gauge Number Rainfall Depth (mm) Area of Thiessen Polygon ( 10 4 m 2 ) The Thiessen mean value (in mm, up to one decimal place) of the rainfall is Q.49 The infiltration rate f in a basin under ponding condition is given by f = e 2t, where, f is in mm/h and t is time in hour. Total depth of infiltration (in mm, up to one decimal place) during the last 20 minutes of a storm of 30 minutes duration is Q.50 In a laboratory, a flow experiment is performed over a hydraulic structure. The measured values of discharge and velocity are 0.05 m 3 /s and 0.25 m/s, respectively. If the full scale structure (30 times bigger) is subjected to a discharge of 270 m 3 /s, then the time scale (model to full scale) value (up to two decimal places) is Q.51 A water sample analysis data is given below. Ion Concentration, mg/l Atomic Weight Ca Mg HCO The carbonate hardness (expressed as mg/l of CaCO3, up to one decimal place) for the water sample is CE 10/11
14 Q.52 The ultimate BOD (L 0 ) of a wastewater sample is estimated as 87% of COD. The COD of this wastewater is 300 mg/l. Considering first order BOD reaction rate constant k (use natural log) = 0.23 per day and temperature coefficient θ = 1.047, the BOD value (in mg/l, up to one decimal place) after three days of incubation at 27 o C for this wastewater will be Q.53 A waste activated sludge (WAS) is to be blended with green waste (GW). The carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) contents, per kg of WAS and GW, on dry basis are given in the table. Parameter WAS GW Carbon (g) Nitrogen (g) 10 6 The ratio of WAS to GW required (up to two decimal places) to achieve a blended C:N ratio of 20:1 on dry basis is Q.54 Given the following data: design life n = 15 years, lane distribution factor D = 0.75, annual rate of growth of commercial vehicles r = 6%, vehicle damage factor F = 4 and initial traffic in the year of completion of construction = 3000 Commercial Vehicles Per Day (CVPD). As per IRC: , the design traffic in terms of cumulative number of standard axles (in million standard axles, up to two decimal places) is Q.55 An aircraft approaches the threshold of a runway strip at a speed of 200 km/h. The pilot decelerates the aircraft at a rate of m/s 2 and takes 18 s to exit the runway strip. If the deceleration after exiting the runway is 1 m/s 2, then the distance (in m, up to one decimal place) of the gate position from the location of exit on the runway is END OF THE QUESTION PAPER CE 11/11
Section-I: General Ability. 1. Hema s age is 5 years more than twice Hari s age. Suresh s age is 13 years less than 10 times Hari s
 CE-GATE 018 Section-I: General Ability 1. Hema s age is 5 years more than twice Hari s age. Suresh s age is 1 years less than 10 times Hari s Key: (D) age. If Suresh is times as old as Hema, how old is
CE-GATE 018 Section-I: General Ability 1. Hema s age is 5 years more than twice Hari s age. Suresh s age is 1 years less than 10 times Hari s Key: (D) age. If Suresh is times as old as Hema, how old is
GATE SOLUTIONS E N G I N E E R I N G
 GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
Entrance exam Master Course
 - 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
- 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
1.The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method,
 EXAM-1 1.The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method, is equal to : A. the degree of statistical indeterminacy B. the degree of kinematic indeterminacy C. the number
EXAM-1 1.The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method, is equal to : A. the degree of statistical indeterminacy B. the degree of kinematic indeterminacy C. the number
CE : CIVIL ENGINEERING
 2009 CE : CIVIL ENGINEERING Duration : Three Hours Read the following instructions carefully. l. This question paper contains 16 printed pages including pages for rough work. Please check all pages and
2009 CE : CIVIL ENGINEERING Duration : Three Hours Read the following instructions carefully. l. This question paper contains 16 printed pages including pages for rough work. Please check all pages and
2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
1. Two forces P and Q are acting at an angle as shown in the figure. In terms of these quantities, what are values of R and respectively?
 1. Two forces P and Q are acting at an angle as shown in the figure. In terms of these quantities, what are values of R and respectively? Q R P a) Qsin P Q PQ cos and tan 1 P Q cos b) Qsin P Q PQ cos and
1. Two forces P and Q are acting at an angle as shown in the figure. In terms of these quantities, what are values of R and respectively? Q R P a) Qsin P Q PQ cos and tan 1 P Q cos b) Qsin P Q PQ cos and
Chapter. Materials. 1.1 Notations Used in This Chapter
 Chapter 1 Materials 1.1 Notations Used in This Chapter A Area of concrete cross-section C s Constant depending on the type of curing C t Creep coefficient (C t = ε sp /ε i ) C u Ultimate creep coefficient
Chapter 1 Materials 1.1 Notations Used in This Chapter A Area of concrete cross-section C s Constant depending on the type of curing C t Creep coefficient (C t = ε sp /ε i ) C u Ultimate creep coefficient
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL
 SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Necessity of studying Shear Strength of soils : Soil failure usually occurs in the form of shearing along internal surface within the soil. Shear Strength: Thus, structural strength
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Necessity of studying Shear Strength of soils : Soil failure usually occurs in the form of shearing along internal surface within the soil. Shear Strength: Thus, structural strength
Mechanical Properties of Materials
 Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
DESIGN AND DETAILING OF COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL
 DESIGN AND DETAILING OF COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL When the height of the retaining wall exceeds about 6 m, the thickness of the stem and heel slab works out to be sufficiently large and the design becomes
DESIGN AND DETAILING OF COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL When the height of the retaining wall exceeds about 6 m, the thickness of the stem and heel slab works out to be sufficiently large and the design becomes
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS-I. Unit-1. Simple stresses and strains
 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS-I Unit-1 Simple stresses and strains 1. What is the Principle of surveying 2. Define Magnetic, True & Arbitrary Meridians. 3. Mention different types of chains 4. Differentiate between
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS-I Unit-1 Simple stresses and strains 1. What is the Principle of surveying 2. Define Magnetic, True & Arbitrary Meridians. 3. Mention different types of chains 4. Differentiate between
Name :. Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.TECH (CE-NEW)/SEM-3/CE-301/ SOLID MECHANICS
 Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
Sub. Code:
 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
The University of Melbourne Engineering Mechanics
 The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
Theory of Shear Strength
 MAJ 1013 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 Strength of different materials Steel Concrete Soil Tensile strength Compressive strength Shear strength Complex behavior
MAJ 1013 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 Strength of different materials Steel Concrete Soil Tensile strength Compressive strength Shear strength Complex behavior
Civil Engineering Design (1) Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns 2006/7
 Civil Engineering Design (1) Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns 2006/7 Dr. Colin Caprani, Chartered Engineer 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Background... 3 1.2 Failure Modes... 5 1.3 Design Aspects...
Civil Engineering Design (1) Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns 2006/7 Dr. Colin Caprani, Chartered Engineer 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Background... 3 1.2 Failure Modes... 5 1.3 Design Aspects...
Mechanical Engineering Ph.D. Preliminary Qualifying Examination Solid Mechanics February 25, 2002
 student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
Unit III Theory of columns. Dr.P.Venkateswara Rao, Associate Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg., SVCE, Sriperumbudir
 Unit III Theory of columns 1 Unit III Theory of Columns References: Punmia B.C.,"Theory of Structures" (SMTS) Vol II, Laxmi Publishing Pvt Ltd, New Delhi 2004. Rattan.S.S., "Strength of Materials", Tata
Unit III Theory of columns 1 Unit III Theory of Columns References: Punmia B.C.,"Theory of Structures" (SMTS) Vol II, Laxmi Publishing Pvt Ltd, New Delhi 2004. Rattan.S.S., "Strength of Materials", Tata
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
ME Final Exam. PROBLEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) M (x) y. z (neutral axis) beam cross-sec+on. 20 kip ft. 0.2 ft. 10 ft. 0.1 ft.
 ME 323 - Final Exam Name December 15, 2015 Instructor (circle) PROEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) Krousgrill 11:30AM-12:20PM Ghosh 2:30-3:20PM Gonzalez 12:30-1:20PM Zhao 4:30-5:20PM M (x) y 20 kip ft 0.2
ME 323 - Final Exam Name December 15, 2015 Instructor (circle) PROEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) Krousgrill 11:30AM-12:20PM Ghosh 2:30-3:20PM Gonzalez 12:30-1:20PM Zhao 4:30-5:20PM M (x) y 20 kip ft 0.2
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad. Chapter (7)
 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
Theory of Shear Strength
 SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 SOIL STRENGTH DEFINITION Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces The maximum or
SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 SOIL STRENGTH DEFINITION Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces The maximum or
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in
 Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
1.8 Unconfined Compression Test
 1-49 1.8 Unconfined Compression Test - It gives a quick and simple measurement of the undrained strength of cohesive, undisturbed soil specimens. 1) Testing method i) Trimming a sample. Length-diameter
1-49 1.8 Unconfined Compression Test - It gives a quick and simple measurement of the undrained strength of cohesive, undisturbed soil specimens. 1) Testing method i) Trimming a sample. Length-diameter
SEM-2016(01HI CIVIL ENGINEERING. Paper Answer all questions. Question No. 1 does not have internal choice,
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 5 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(01HI CIVIL ENGINEERING Paper - 11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions to
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 5 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(01HI CIVIL ENGINEERING Paper - 11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions to
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1
 ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
1. ARRANGEMENT. a. Frame A1-P3. L 1 = 20 m H = 5.23 m L 2 = 20 m H 1 = 8.29 m L 3 = 20 m H 2 = 8.29 m H 3 = 8.39 m. b. Frame P3-P6
 Page 3 Page 4 Substructure Design. ARRANGEMENT a. Frame A-P3 L = 20 m H = 5.23 m L 2 = 20 m H = 8.29 m L 3 = 20 m H 2 = 8.29 m H 3 = 8.39 m b. Frame P3-P6 L = 25 m H 3 = 8.39 m L 2 = 3 m H 4 = 8.5 m L
Page 3 Page 4 Substructure Design. ARRANGEMENT a. Frame A-P3 L = 20 m H = 5.23 m L 2 = 20 m H = 8.29 m L 3 = 20 m H 2 = 8.29 m H 3 = 8.39 m b. Frame P3-P6 L = 25 m H 3 = 8.39 m L 2 = 3 m H 4 = 8.5 m L
Downloaded from Downloaded from / 1
 PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
16 Rainfall on a Slope
 Rainfall on a Slope 16-1 16 Rainfall on a Slope 16.1 Problem Statement In this example, the stability of a generic slope is analyzed for two successive rainfall events of increasing intensity and decreasing
Rainfall on a Slope 16-1 16 Rainfall on a Slope 16.1 Problem Statement In this example, the stability of a generic slope is analyzed for two successive rainfall events of increasing intensity and decreasing
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
Design of Beams (Unit - 8)
 Design of Beams (Unit - 8) Contents Introduction Beam types Lateral stability of beams Factors affecting lateral stability Behaviour of simple and built - up beams in bending (Without vertical stiffeners)
Design of Beams (Unit - 8) Contents Introduction Beam types Lateral stability of beams Factors affecting lateral stability Behaviour of simple and built - up beams in bending (Without vertical stiffeners)
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
Q.1 The lecture was attended by quite students, so the hall was not very. (A) a few, quite (B) few, quiet (C) a few, quiet (D) few, quite
 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The lecture was attended by quite students, so the hall was not very. (A) a few, quite (B) few, quiet (C) a few, quiet (D) few,
GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The lecture was attended by quite students, so the hall was not very. (A) a few, quite (B) few, quiet (C) a few, quiet (D) few,
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Civil Engineering
GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Civil Engineering
Soil strength. the strength depends on the applied stress. water pressures are required
 Soil Strength Soil strength u Soils are essentially frictional materials the strength depends on the applied stress u Strength is controlled by effective stresses water pressures are required u Soil strength
Soil Strength Soil strength u Soils are essentially frictional materials the strength depends on the applied stress u Strength is controlled by effective stresses water pressures are required u Soil strength
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test.
 (d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
(d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
Samantha Ramirez, MSE. Stress. The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. F 2
 Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 2 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2015
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 2 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2015
Mechanics of Materials II. Chapter III. A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection
 Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
CIVIL DEPARTMENT MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES- ASSIGNMENT NO 1. Brach: CE YEAR:
 MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES- ASSIGNMENT NO 1 SEMESTER: V 1) Find the least moment of Inertia about the centroidal axes X-X and Y-Y of an unequal angle section 125 mm 75 mm 10 mm as shown in figure 2) Determine
MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES- ASSIGNMENT NO 1 SEMESTER: V 1) Find the least moment of Inertia about the centroidal axes X-X and Y-Y of an unequal angle section 125 mm 75 mm 10 mm as shown in figure 2) Determine
9.5 Compression Members
 9.5 Compression Members This section covers the following topics. Introduction Analysis Development of Interaction Diagram Effect of Prestressing Force 9.5.1 Introduction Prestressing is meaningful when
9.5 Compression Members This section covers the following topics. Introduction Analysis Development of Interaction Diagram Effect of Prestressing Force 9.5.1 Introduction Prestressing is meaningful when
NCEES Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Examination CIVIL EXAM SPECIFICATIONS
 NCEES Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Examination CIVIL EXAM SPECIFICATIONS Effective Beginning with the April 2009 Examinations The FE examination is an 8-hour supplied-reference examination: 120 questions
NCEES Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Examination CIVIL EXAM SPECIFICATIONS Effective Beginning with the April 2009 Examinations The FE examination is an 8-hour supplied-reference examination: 120 questions
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA
 SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
Design of AAC wall panel according to EN 12602
 Design of wall panel according to EN 160 Example 3: Wall panel with wind load 1.1 Issue Design of a wall panel at an industrial building Materials with a compressive strength 3,5, density class 500, welded
Design of wall panel according to EN 160 Example 3: Wall panel with wind load 1.1 Issue Design of a wall panel at an industrial building Materials with a compressive strength 3,5, density class 500, welded
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses.
 8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
Advanced Structural Analysis EGF Section Properties and Bending
 Advanced Structural Analysis EGF316 3. Section Properties and Bending 3.1 Loads in beams When we analyse beams, we need to consider various types of loads acting on them, for example, axial forces, shear
Advanced Structural Analysis EGF316 3. Section Properties and Bending 3.1 Loads in beams When we analyse beams, we need to consider various types of loads acting on them, for example, axial forces, shear
Engineering Science OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 4 COLUMNS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/10 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL COLUMNS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering systems
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/10 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL COLUMNS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering systems
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
SECTION A. 8 kn/m. C 3 m 3m
 SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
GATE question paper Civil Engineering (CE) 2005
 GATE question paper Civil Engineering (CE) 005 GATE question paper Civil Engineering 005 Q.1- Q.30 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Consider the matrices X (4 3) Y (4-3) and P ( 3). The order of [P(X T Y) -1 P
GATE question paper Civil Engineering (CE) 005 GATE question paper Civil Engineering 005 Q.1- Q.30 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Consider the matrices X (4 3) Y (4-3) and P ( 3). The order of [P(X T Y) -1 P
FE Fluids Review March 23, 2012 Steve Burian (Civil & Environmental Engineering)
 Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
Seismic Pushover Analysis Using AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design
 Seismic Pushover Analysis Using AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design Elmer E. Marx, Alaska Department of Transportation and Public Facilities Michael Keever, California Department
Seismic Pushover Analysis Using AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design Elmer E. Marx, Alaska Department of Transportation and Public Facilities Michael Keever, California Department
Reinforced Soil Structures Reinforced Soil Walls. Prof K. Rajagopal Department of Civil Engineering IIT Madras, Chennai
 Geosynthetics and Reinforced Soil Structures Reinforced Soil Walls continued Prof K. Rajagopal Department of Civil Engineering IIT Madras, Chennai e-mail: gopalkr@iitm.ac.inac in Outline of the Lecture
Geosynthetics and Reinforced Soil Structures Reinforced Soil Walls continued Prof K. Rajagopal Department of Civil Engineering IIT Madras, Chennai e-mail: gopalkr@iitm.ac.inac in Outline of the Lecture
NAME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: Law of Sines:
 NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
Chapter (12) Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad
 Chapter (12) Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter Outlines Shear strength in soils Direct shear test Unconfined Compression Test Tri-axial Test Shear Strength The strength of a material is the
Chapter (12) Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter Outlines Shear strength in soils Direct shear test Unconfined Compression Test Tri-axial Test Shear Strength The strength of a material is the
Chapter (5) Allowable Bearing Capacity and Settlement
 Chapter (5) Allowable Bearing Capacity and Settlement Introduction As we discussed previously in Chapter 3, foundations should be designed for both shear failure and allowable settlement. So the allowable
Chapter (5) Allowable Bearing Capacity and Settlement Introduction As we discussed previously in Chapter 3, foundations should be designed for both shear failure and allowable settlement. So the allowable
SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1. State and prove the relationship between shearing stress and rate of change of bending moment at a section in a loaded beam.
 ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
: APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS)
 BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
Centrifuge Shaking Table Tests and FEM Analyses of RC Pile Foundation and Underground Structure
 Centrifuge Shaking Table s and FEM Analyses of RC Pile Foundation and Underground Structure Kenji Yonezawa Obayashi Corporation, Tokyo, Japan. Takuya Anabuki Obayashi Corporation, Tokyo, Japan. Shunichi
Centrifuge Shaking Table s and FEM Analyses of RC Pile Foundation and Underground Structure Kenji Yonezawa Obayashi Corporation, Tokyo, Japan. Takuya Anabuki Obayashi Corporation, Tokyo, Japan. Shunichi
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
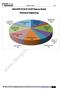 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS
 7-1 7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS 7.1 THE MOHR CIRCLE The discussions in Chapters and 5 were largely concerned with vertical stresses. A more detailed examination of soil behaviour requires a knowledge
7-1 7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS 7.1 THE MOHR CIRCLE The discussions in Chapters and 5 were largely concerned with vertical stresses. A more detailed examination of soil behaviour requires a knowledge
UNIT II SHALLOW FOUNDATION
 Introduction UNIT II SHALLOW FOUNDATION A foundation is a integral part of the structure which transfer the load of the superstructure to the soil. A foundation is that member which provides support for
Introduction UNIT II SHALLOW FOUNDATION A foundation is a integral part of the structure which transfer the load of the superstructure to the soil. A foundation is that member which provides support for
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Cambridge, MA Problem Set 14
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Cambridge, MA 02139 16.01/16.02 Unified Engineering I, II Fall 2003 Problem Set 14 Name: Due Date: 12/9/03 F18 F19 F20 M19
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Cambridge, MA 02139 16.01/16.02 Unified Engineering I, II Fall 2003 Problem Set 14 Name: Due Date: 12/9/03 F18 F19 F20 M19
1. Replace the given system of forces acting on a body as shown in figure 1 by a single force and couple acting at the point A.
 Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 STATICS AND MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr, John T. DeWolf David E Mazurek \Cawect Mc / iur/» Craw SugomcT Hilt Introduction 1 1.1 What is Mechanics? 2 1.2 Fundamental
STATICS AND MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr, John T. DeWolf David E Mazurek \Cawect Mc / iur/» Craw SugomcT Hilt Introduction 1 1.1 What is Mechanics? 2 1.2 Fundamental
2017 Soil Mechanics II and Exercises Final Exam. 2017/7/26 (Wed) 10:00-12:00 Kyotsu 4 Lecture room
 2017 Soil Mechanics II and Exercises Final Exam 2017/7/26 (Wed) 10:00-12:00 Kyotsu 4 Lecture room Attention: The exam consists of five questions for which you are provided with five answer sheets. Write
2017 Soil Mechanics II and Exercises Final Exam 2017/7/26 (Wed) 10:00-12:00 Kyotsu 4 Lecture room Attention: The exam consists of five questions for which you are provided with five answer sheets. Write
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
CHAPTER 8 ANALYSES OF THE LATERAL LOAD TESTS AT THE ROUTE 351 BRIDGE
 CHAPTER ANALYSES OF THE LATERAL LOAD TESTS AT THE ROUTE 351 BRIDGE.1 INTRODUCTION An important objective of this research is to determine whether accurate analyses of the lateral load-deflection behavior
CHAPTER ANALYSES OF THE LATERAL LOAD TESTS AT THE ROUTE 351 BRIDGE.1 INTRODUCTION An important objective of this research is to determine whether accurate analyses of the lateral load-deflection behavior
Evaluation of dynamic behavior of culverts and embankments through centrifuge model tests and a numerical analysis
 Computer Methods and Recent Advances in Geomechanics Oka, Murakami, Uzuoka & Kimoto (Eds.) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-00148-0 Evaluation of dynamic behavior of culverts and embankments
Computer Methods and Recent Advances in Geomechanics Oka, Murakami, Uzuoka & Kimoto (Eds.) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-00148-0 Evaluation of dynamic behavior of culverts and embankments
Structural Analysis I Chapter 4 - Torsion TORSION
 ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
CHAPTER 6: ULTIMATE LIMIT STATE
 CHAPTER 6: ULTIMATE LIMIT STATE 6.1 GENERAL It shall be in accordance with JSCE Standard Specification (Design), 6.1. The collapse mechanism in statically indeterminate structures shall not be considered.
CHAPTER 6: ULTIMATE LIMIT STATE 6.1 GENERAL It shall be in accordance with JSCE Standard Specification (Design), 6.1. The collapse mechanism in statically indeterminate structures shall not be considered.
OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS. You should judge your progress by completing the self assessment exercises. CONTENTS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/1404 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/1404 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL
 Soil Failure Criteria SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Knowledge about the shear strength of soil important for the analysis of: Bearing capacity of foundations, Slope stability, Lateral pressure on retaining structures,
Soil Failure Criteria SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Knowledge about the shear strength of soil important for the analysis of: Bearing capacity of foundations, Slope stability, Lateral pressure on retaining structures,
3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No.
 *17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
*17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS
 Subject with Code : SM-1(15A01303) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES
Subject with Code : SM-1(15A01303) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES
2. (a) Explain different types of wing structures. (b) Explain the advantages and disadvantages of different materials used for aircraft
 Code No: 07A62102 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations,May 2010 Aerospace Vehicle Structures -II Aeronautical Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE
Code No: 07A62102 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech II Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations,May 2010 Aerospace Vehicle Structures -II Aeronautical Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
EQUIVALENT FRACTURE ENERGY CONCEPT FOR DYNAMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF PROTOTYPE RC GIRDERS
 EQUIVALENT FRACTURE ENERGY CONCEPT FOR DYNAMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF PROTOTYPE RC GIRDERS Abdul Qadir Bhatti 1, Norimitsu Kishi 2 and Khaliq U Rehman Shad 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Structural Engineering,
EQUIVALENT FRACTURE ENERGY CONCEPT FOR DYNAMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF PROTOTYPE RC GIRDERS Abdul Qadir Bhatti 1, Norimitsu Kishi 2 and Khaliq U Rehman Shad 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Structural Engineering,
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 51 Module 4: Lecture 2 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-coulomb failure
51 Module 4: Lecture 2 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-coulomb failure
Hardened Concrete. Lecture No. 16
 Hardened Concrete Lecture No. 16 Fatigue strength of concrete Modulus of elasticity, Creep Shrinkage of concrete Stress-Strain Plot of Concrete At stress below 30% of ultimate strength, the transition
Hardened Concrete Lecture No. 16 Fatigue strength of concrete Modulus of elasticity, Creep Shrinkage of concrete Stress-Strain Plot of Concrete At stress below 30% of ultimate strength, the transition
FINAL EXAMINATION. (CE130-2 Mechanics of Materials)
 UNIVERSITY OF CLIFORNI, ERKELEY FLL SEMESTER 001 FINL EXMINTION (CE130- Mechanics of Materials) Problem 1: (15 points) pinned -bar structure is shown in Figure 1. There is an external force, W = 5000N,
UNIVERSITY OF CLIFORNI, ERKELEY FLL SEMESTER 001 FINL EXMINTION (CE130- Mechanics of Materials) Problem 1: (15 points) pinned -bar structure is shown in Figure 1. There is an external force, W = 5000N,
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Lecture Slides
 Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Foundation Analysis LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE
 Foundation Analysis LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE INTRODUCTION Vertical or near-vertical slopes of soil are supported by retaining walls, cantilever sheet-pile walls, sheet-pile bulkheads, braced cuts, and other
Foundation Analysis LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE INTRODUCTION Vertical or near-vertical slopes of soil are supported by retaining walls, cantilever sheet-pile walls, sheet-pile bulkheads, braced cuts, and other
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS
 1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
MATERIALS FOR CIVIL AND CONSTRUCTION ENGINEERS
 MATERIALS FOR CIVIL AND CONSTRUCTION ENGINEERS 3 rd Edition Michael S. Mamlouk Arizona State University John P. Zaniewski West Virginia University Solution Manual FOREWORD This solution manual includes
MATERIALS FOR CIVIL AND CONSTRUCTION ENGINEERS 3 rd Edition Michael S. Mamlouk Arizona State University John P. Zaniewski West Virginia University Solution Manual FOREWORD This solution manual includes
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING ECG 503 LECTURE NOTE ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF RETAINING STRUCTURES
 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING ECG 503 LECTURE NOTE 07 3.0 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF RETAINING STRUCTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Learning outcomes: At the end of this lecture/week the students would be able to: Understand
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING ECG 503 LECTURE NOTE 07 3.0 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF RETAINING STRUCTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Learning outcomes: At the end of this lecture/week the students would be able to: Understand
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA
 EGC373 (F) / Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UK DEGREE TRANSFER PROGRAMME INTI ADELAIDE TRANSFER PROGRAMME EGC 373: FOUNDATION ENGINEERING FINAL EXAMINATION : AUGUST 00 SESSION This paper consists of
EGC373 (F) / Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UK DEGREE TRANSFER PROGRAMME INTI ADELAIDE TRANSFER PROGRAMME EGC 373: FOUNDATION ENGINEERING FINAL EXAMINATION : AUGUST 00 SESSION This paper consists of
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading
 MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science Zhe Cheng (2018) 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading Statics
MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science Zhe Cheng (2018) 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading Statics
