Chapter 14 Molecular Model of Matter
|
|
|
- Mark Cummings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 14 Molecular Model of Matter GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and use it in an operational definition: rms velocity surface tension adhesion capillarity cohesion osmosis Molecular Model Explain the properties of fluids using the molecular model. Problems Solve problems that relate the gas laws to the properties of the gas and that involve surface tension, capilarity, and osmosis. PREREQUISITES Before beginning this chapter you should have achieved the goals of Chapter 4, Forces and Newton's Laws, Chapter 5, Energy, Chapter 6, Momentum and Impulse, Chapter 10, Temperature and Heat, and Chapter 13, Elastic Properties of Materials 118
2 Chapter 14 Molecular Model of Matter OVERVIEW - Molecules are extremely small. Only the very largest molecules have been photographed and only with indirect methods using an electron microscope. The model scientists use to describe molecules and their movements and interactions is only an ideal representation. However, this model helps us gain an understanding for phenomena we can observe for a large number of molecules acting together. SUGGESTED STUDY PROCEDURE - Begin this chapter by reading the following Chapter Goals: Definitions, Molecular Model, and Problems. For additional discussion of the terms listed under the goal of Definitions, turn to the Definitions section of this Study Guide chapter. Now, continue by reading text sections In section 14.3 you may have difficulties following all the assumptions and mathematical steps. Even though this may be the case, pay close attention to the results as expressed by equations (14.14), (14.15), and (14.18). The example on page 312 will help clarify the use of the results derived in this section. At the end of the chapter, read the Chapter Summary and complete Summary Exercises Check your answers carefully against those provided. Next, do Algorithmic Problems 1-8 again checking your answers with those provided. Now do Exercises and Problems 1, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, and 12. For additional work on the contents of this chapter, see the Examples section of this Study Guide chapter. Now you should be prepared to attempt the Practice Test on Molecular Model of Matter provided at the end of this Study Guide chapter. If you have difficulties with any of the concepts involved, please refer to the appropriate section of the text or this for more assistance. This study procedure is outlined below Chapter Goals Suggested Summary Algorithmic Exercises Text Readings Exercises Problems & Problems Definitions 14.1,14.6, Molecular Model 14.2,14.3,14.4, Problems 14.8,14.9, ,4,5,6, 9,10,12 119
3 DEFINITIONS ROOT MEAN SQUARE VELOCITY - The square root of the sum of the squares of the velocities divided by the number of the particles. If we have two particles, one with a velocity of -20 m/s and the other with +20 m/s, their mean velocity is zero; their rms is +20 m/s. If we have two particles, one with velocity +50 m/s, the other with a velocity of +100 m/s; their mean velocity is +75m/s; their rms velocity is 56 m/s. ADHESION - Attraction of unlike molecules. The new epoxy cements have brought a whole era of adhesives for daily use. COHESION - Attraction of like molecules. Cohesive forces in solids are stronger than cohesive forces in liquids. SURFACE TENSION - Force necessary to break a unit length of surface. Have you ever seen a water spider "skate" along on the surface of a pond? CAPILLARITY - The rise of water in a capillary above the water level in the surrounding area. This arises when a liquid adheres to the walls of a narrow tube. OSMOSIS - Motion of fluid through a semipermeable membrane until the potential energy on the two sides of the membrane is the same. Osmosis is extremely common in biological systems. EXAMPLES KINETIC THEORY OF GASES 1. Assume that all the molecules in a gas are travelling in the x direction (1/2 of the molecules are headed in the plus x direction and 1/2 of the molecules are headed in the minus x direction). Assume that all the molecules have the same magnitude of velocity, v, and that n molecules strike a wall of area A in a time t. (a) From what volume do the molecules come that reach the area A of the wall in time t? (Sketch this volume on the figure below.) (b) Assume that all n molecules strike the wall head-on, are perfectly elastic, and rebound with a velocity v in the opposite (or - x) direction. What is the impulse imparted to the wall? (mass of each molecule = m) (c) What is the pressure on the wall? (d) In part (a) above, what is the number of molecules per unit volume that produce the bombardment of the wall? (e) In a closed container which has a volume V and contains a total of N molecules the number of molecules per unit volume is N/V. Make the correct substitution into your answer of part (c) and find an expression for the pressure of a gas in terms of N and V as well as m and v. 120
4 What Data Are Given? There are n molecules of mass m travelling with velocity v in the positive x direction that strike an area A of the wall perpendicular to the x-axis in a time of t. What Data Are Implied? The molecules are perfectly elastic and obey the laws of classical physics during the motion and collisions. What Physics Principles Are Involved? The fundamental laws of motion and collisions will be needed. What Equations Are to be Used? distance = velocity time impulse = change in momentum = force time pressure = force/area Algebraic Solution (a) In a time t, the molecules moving with a velocity v will travel a distance of vt. So the n molecules that hit the wall in time t had to be within a distance vt of the wall. (b) For each molecule p = -mv = (mv) = -2mv Impulse of wall on molecule = -2mv Impulse of a molecule on wall = +2mv Total impulse on the wall = n(2mv) = 2nmv (c) Pressure = force / area = (Impulse/time)/area = (2nmv)/(At) (d) Number per unit volume = number/volume = (rn)/(avt) = rn then pressure = 2rnmv 2 (1) (e) In a closed container only 1/6 of the molecules will have a positive x component of velocity since there are six equivalent orthogonal directions, +x, -x, +y, -y, +z, -z. So the r in Equation (1) is only 1/6 N/V; thus pressure = 2 (1/6 x N/V)mv 2 = 1/3 ((Nmv 2 ) / (v)) (2) 2. By the middle of the nineteenth century, the ideal gas law was written as PV = nrt (3) where the three variables are the pressure P (dynes/cm 2 ), the volume V(cm 3 ), and the temperature T ( ø K). The quantity n is the number of moles of gas in the sample (dimensionless) and R is a universal constant simply called the gas constant. The experimental value of the gas constant R is R = 8.31 x 10 7 ergs/ ø K where an erg = 1 dyne cm Later work by Avogadro led to a re-expression of the same law as PV = N k T (4) where the quantity N is the total number of molecules in the sample of gas and k is Boltzmann's constant. The experimental value for k is k = 1.38 x ergs/ ø K (a) Derive an expression for N in terms of k, n, and R. (b) Avogadro's number, N o, is the number of molecules in a mole (N/n). From the above data, determine the numerical value of N o. Thinking About This Problem The problem does not involve any profound knowledge of physics; rather straightforward manipulation of Equations (3) and (4) is all that is necessary. pv = nrt = NkT (a) so N = nr/k (b) Avogadro's number No = N/n = R/k = (8.31 x 10 7 ergs/ ø K)/(1.38 x ergs/ ø K) = 6.02 x
5 PRACTICE TEST 1. In an interesting physics demonstration, a young physics teacher placed a thin film of water between two flat panes of glass. The result is a bond which holds the two pieces of glass firmly together. Is this an example of adhesion or cohesion? Explain your answer as if you were teaching the class. 2. The rms speed of oxygen (O 2 ) molecules at 27 ø C is 482 m/sec. Assume that this is an ideal gas for the following questions. (The Boltzmann constant is 1.38 x J/molecule- ø k) a. Find the mass of the oxygen molecule in kilograms. b. Calculate the energy of an individual oxygen molecule. c. If the energy is to be reduced by a factor of 3, what reduction in temperature is required? 3. The surface tension of an unknown liquid is measured at room temperature with the apparatus shown below. First the system is balanced using a small counter balance m. After the ring of radius r (10 cm) is placed in the unknown liquid, an additional mass of Δm must be added to pull the circular wire from the liquid. If m = 50.2 grams and Δm = 18.8 grams, calculate the surface tension of the liquid at room temperature. (Express your answer in dynes/cm.) ANSWERS: 1. Adhesion. Water molecules adhere (are attracted) to glass molecules. The forces between individual water molecules are cohesive forces x kg, 6.2 x Joule, Reduce temperature by 200 ø K dynes/cm 122
Revision Guide for Chapter 13
 Matter: very simple Revision Guide for Chapter Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes Ideal gas... Ideal gas laws... Assumptions of kinetic theory of gases... 5 Internal energy... 6 Specific thermal
Matter: very simple Revision Guide for Chapter Contents Student s Checklist Revision Notes Ideal gas... Ideal gas laws... Assumptions of kinetic theory of gases... 5 Internal energy... 6 Specific thermal
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
 LECTURE 8 KINETIC THEORY OF GASES Text Sections 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7 Sample Problems 0.4 Suggested Questions Suggested Problems Summary None 45P, 55P Molecular model for pressure Root mean square (RMS) speed
LECTURE 8 KINETIC THEORY OF GASES Text Sections 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7 Sample Problems 0.4 Suggested Questions Suggested Problems Summary None 45P, 55P Molecular model for pressure Root mean square (RMS) speed
Chapter 14. The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number To facilitate comparison of the mass of one atom with another, a mass scale know as the atomic mass
Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number To facilitate comparison of the mass of one atom with another, a mass scale know as the atomic mass
Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter
 Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter To understand the mole and Avogadro's number. To understand equations of state. To study the kinetic theory of ideal gas. To understand heat capacity. To learn and
Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter To understand the mole and Avogadro's number. To understand equations of state. To study the kinetic theory of ideal gas. To understand heat capacity. To learn and
Slide 1-2. Slide 3-4. Slide 5-6. Review from Physics 114. Gasses. Three possible mechanisms that explain how the alcohol disappears
 Slide 1-2 Review from Physics 114 Gasses Physics 115 Eyres Draw force diagrams (FBDs) (Section 2.1). Use Newton's second and third laws to analyze interactions of objects (Section 2.8). Use the impulse-momentum
Slide 1-2 Review from Physics 114 Gasses Physics 115 Eyres Draw force diagrams (FBDs) (Section 2.1). Use Newton's second and third laws to analyze interactions of objects (Section 2.8). Use the impulse-momentum
Lecture 3. The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
 Lecture 3. The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases THE IDEAL GAS LAW: A purely empirical law solely the consequence of experimental observations Explains the behavior of gases over a limited range of conditions
Lecture 3. The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases THE IDEAL GAS LAW: A purely empirical law solely the consequence of experimental observations Explains the behavior of gases over a limited range of conditions
Lecture 24. Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
17-1 Ideal Gases. Gases are the easiest state of matter to describe - All ideal gases exhibit similar behavior.
 17-1 Ideal Gases Gases are the easiest state of matter to describe - All ideal gases exhibit similar behavior. An ideal gas is one that is thin enough, that the interactions between molecules can be ignored.
17-1 Ideal Gases Gases are the easiest state of matter to describe - All ideal gases exhibit similar behavior. An ideal gas is one that is thin enough, that the interactions between molecules can be ignored.
Lecture 24. Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
Kinetic Model of Gases
 Kinetic Model of Gases Section 1.3 of Atkins, 6th Ed, 24.1 of Atkins, 7th Ed. 21.1 of Atkins, 8th Ed., and 20.1 of Atkins, 9th Ed. Basic Assumptions Molecular Speeds RMS Speed Maxwell Distribution of Speeds
Kinetic Model of Gases Section 1.3 of Atkins, 6th Ed, 24.1 of Atkins, 7th Ed. 21.1 of Atkins, 8th Ed., and 20.1 of Atkins, 9th Ed. Basic Assumptions Molecular Speeds RMS Speed Maxwell Distribution of Speeds
Physics 161 Lecture 14 Kinetic Theory of Gas. October 18, 2018
 Physics 161 Lecture 14 Kinetic Theory of Gas October 18, 2018 1 Exam 1, Thursday 18 Oct The exam will start promptly at 10:00pm. You will be permitted to open your exam at 10:00pm. You will have until
Physics 161 Lecture 14 Kinetic Theory of Gas October 18, 2018 1 Exam 1, Thursday 18 Oct The exam will start promptly at 10:00pm. You will be permitted to open your exam at 10:00pm. You will have until
Lecture Outline Chapter 17. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 17 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 17 Phases and Phase Changes Ideal Gases Kinetic Theory Units of Chapter 17 Solids and Elastic Deformation Phase Equilibrium and
Lecture Outline Chapter 17 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 17 Phases and Phase Changes Ideal Gases Kinetic Theory Units of Chapter 17 Solids and Elastic Deformation Phase Equilibrium and
Kinetic Theory: Atomic and Molecular Explanation of Pressure and Temperature
 Kinetic Theory: Atomic and Molecular Explanation of Pressure and Temperature Bởi: OpenStaxCollege We have developed macroscopic definitions of pressure and temperature. Pressure is the force divided by
Kinetic Theory: Atomic and Molecular Explanation of Pressure and Temperature Bởi: OpenStaxCollege We have developed macroscopic definitions of pressure and temperature. Pressure is the force divided by
Chapter 17 Temperature & Kinetic Theory of Gases 1. Thermal Equilibrium and Temperature
 Chapter 17 Temperature & Kinetic Theory of Gases 1. Thermal Equilibrium and Temperature Any physical property that changes with temperature is called a thermometric property and can be used to measure
Chapter 17 Temperature & Kinetic Theory of Gases 1. Thermal Equilibrium and Temperature Any physical property that changes with temperature is called a thermometric property and can be used to measure
Ideal Gases. 247 minutes. 205 marks. theonlinephysicstutor.com. facebook.com/theonlinephysicstutor. Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments:
 Ideal Gases Name: Class: Date: Time: 247 minutes Marks: 205 marks Comments: Page 1 of 48 1 Which one of the graphs below shows the relationship between the internal energy of an ideal gas (y-axis) and
Ideal Gases Name: Class: Date: Time: 247 minutes Marks: 205 marks Comments: Page 1 of 48 1 Which one of the graphs below shows the relationship between the internal energy of an ideal gas (y-axis) and
Temperature, Thermal Expansion and the Gas Laws
 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and the Gas Laws z x Physics 053 Lecture Notes Temperature,Thermal Expansion and the Gas Laws Temperature and Thermometers Thermal Equilibrium Thermal Expansion The Ideal
Temperature, Thermal Expansion and the Gas Laws z x Physics 053 Lecture Notes Temperature,Thermal Expansion and the Gas Laws Temperature and Thermometers Thermal Equilibrium Thermal Expansion The Ideal
Physics 1501 Lecture 35
 Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
Molecular Motion and Gas Laws
 Molecular Motion and Gas Laws What is the connection between the motion of molecules (F = ma and K = mv 2 /2) and the thermodynamics of gases (pv = nrt and U = 3nRT/2)? In this lab, you will discover how
Molecular Motion and Gas Laws What is the connection between the motion of molecules (F = ma and K = mv 2 /2) and the thermodynamics of gases (pv = nrt and U = 3nRT/2)? In this lab, you will discover how
Rate of Heating and Cooling
 Rate of Heating and Cooling 35 T [ o C] Example: Heating and cooling of Water E 30 Cooling S 25 Heating exponential decay 20 0 100 200 300 400 t [sec] Newton s Law of Cooling T S > T E : System S cools
Rate of Heating and Cooling 35 T [ o C] Example: Heating and cooling of Water E 30 Cooling S 25 Heating exponential decay 20 0 100 200 300 400 t [sec] Newton s Law of Cooling T S > T E : System S cools
Chapter 14. The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number To facilitate comparison of the mass of one atom with another, a mass scale know as the atomic mass
Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number To facilitate comparison of the mass of one atom with another, a mass scale know as the atomic mass
Chapter 14. The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number The atomic number of an element is the # of protons in its nucleus. Isotopes of an element have different
Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number The atomic number of an element is the # of protons in its nucleus. Isotopes of an element have different
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 19: KINETIC THEORY OF IDEAL GASSES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ATOMIC VIEW OF AN IDEAL GAS Remember! A gas is a type of fluid whose volume can change to fill a container - What makes a gas ideal? An IDEAL GAS is a gas whose particles
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ATOMIC VIEW OF AN IDEAL GAS Remember! A gas is a type of fluid whose volume can change to fill a container - What makes a gas ideal? An IDEAL GAS is a gas whose particles
Thermal Properties of Matter (Microscopic models)
 Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matter (Microscopic models) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 6_18_2012
Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matter (Microscopic models) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 6_18_2012
Ch. 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Ch. 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases In this chapter we consider the physics of gases. If the atoms or molecules that make up a gas collide with the walls of their container, they exert a pressure p on
Ch. 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases In this chapter we consider the physics of gases. If the atoms or molecules that make up a gas collide with the walls of their container, they exert a pressure p on
Chapter 13: Temperature, Kinetic Theory and Gas Laws
 Chapter 1: Temperature, Kinetic Theory and Gas Laws Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics (law of equilibrium): If objects A and B are separately in thermal equilibrium with a third object C, then A and B are in
Chapter 1: Temperature, Kinetic Theory and Gas Laws Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics (law of equilibrium): If objects A and B are separately in thermal equilibrium with a third object C, then A and B are in
Revision Guide for Chapter 13
 Matter: very simple Revision Guide for Chapter Contents Revision Checklist Revision Notes Ideal gas... 4 Ideal gas laws... 4 Assumptions of kinetic theory of gases... 5 Internal energy... 6 Specific thermal
Matter: very simple Revision Guide for Chapter Contents Revision Checklist Revision Notes Ideal gas... 4 Ideal gas laws... 4 Assumptions of kinetic theory of gases... 5 Internal energy... 6 Specific thermal
Although different gasses may differ widely in their chemical properties, they share many physical properties
 IV. Gases (text Chapter 9) A. Overview of Chapter 9 B. Properties of gases 1. Ideal gas law 2. Dalton s law of partial pressures, etc. C. Kinetic Theory 1. Particulate model of gases. 2. Temperature and
IV. Gases (text Chapter 9) A. Overview of Chapter 9 B. Properties of gases 1. Ideal gas law 2. Dalton s law of partial pressures, etc. C. Kinetic Theory 1. Particulate model of gases. 2. Temperature and
Lesson 12. Luis Anchordoqui. Physics 168. Tuesday, November 28, 17
 Lesson 12 Physics 168 1 Temperature and Kinetic Theory of Gases 2 Atomic Theory of Matter On microscopic scale, arrangements of molecules in solids, liquids, and gases are quite different 3 Temperature
Lesson 12 Physics 168 1 Temperature and Kinetic Theory of Gases 2 Atomic Theory of Matter On microscopic scale, arrangements of molecules in solids, liquids, and gases are quite different 3 Temperature
E6 PROPERTIES OF GASES Flow-times, density, phase changes, solubility
 E6 PROPERTIES OF GASES Flow-times, density, phase changes, solubility Introduction Kinetic-Molecular Theory The kinetic energy of an object is dependent on its mass and its speed. The relationship, given
E6 PROPERTIES OF GASES Flow-times, density, phase changes, solubility Introduction Kinetic-Molecular Theory The kinetic energy of an object is dependent on its mass and its speed. The relationship, given
Exercises. Pressure. CHAPTER 5 GASES Assigned Problems
 For Review 7. a. At constant temperature, the average kinetic energy of the He gas sample will equal the average kinetic energy of the Cl 2 gas sample. In order for the average kinetic energies to be the
For Review 7. a. At constant temperature, the average kinetic energy of the He gas sample will equal the average kinetic energy of the Cl 2 gas sample. In order for the average kinetic energies to be the
Chapter 12. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips
 (a) v esc = gr = (.6 740 0 3 ) ½ = 400 m s (370 m s to 3 sig figs) (b) (i) Mean kinetic energy = 3_ kt =.5.38 0 3 400 = 8.3 0 J (ii) Mass of an oxygen molecule m= molar mass/n A 0.03 = kg 6.0 0 3 Rearranging
(a) v esc = gr = (.6 740 0 3 ) ½ = 400 m s (370 m s to 3 sig figs) (b) (i) Mean kinetic energy = 3_ kt =.5.38 0 3 400 = 8.3 0 J (ii) Mass of an oxygen molecule m= molar mass/n A 0.03 = kg 6.0 0 3 Rearranging
PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I
 Welcome back to PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I Photo: J. M. Schwarz Announcements In class today we will finish Chapter 20 (sections 3, 4, and 7). and then move to Chapter 13 (the first six sections).
Welcome back to PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I Photo: J. M. Schwarz Announcements In class today we will finish Chapter 20 (sections 3, 4, and 7). and then move to Chapter 13 (the first six sections).
Kinetic Theory: Atomic and Molecular Explanation of Pressure and Temperature
 OpenStax-CNX module: m55236 1 Kinetic Theory: Atomic and Molecular Explanation of Pressure and Temperature OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m55236 1 Kinetic Theory: Atomic and Molecular Explanation of Pressure and Temperature OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
First Law of Thermodynamics Second Law of Thermodynamics Mechanical Equivalent of Heat Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Expansion of Solids
 Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
Slide 1 / 66 1 What is the name of the following statement: "When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other"? A B C D E First Law
Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matter
 Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matter In this section we define the thermodynamic state variables and their relationship to each other, called the equation of state. The system of interest (most of the
Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matter In this section we define the thermodynamic state variables and their relationship to each other, called the equation of state. The system of interest (most of the
PV = n R T = N k T. Measured from Vacuum = 0 Gauge Pressure = Vacuum - Atmospheric Atmospheric = 14.7 lbs/sq in = 10 5 N/m
 PV = n R T = N k T P is the Absolute pressure Measured from Vacuum = 0 Gauge Pressure = Vacuum - Atmospheric Atmospheric = 14.7 lbs/sq in = 10 5 N/m V is the volume of the system in m 3 often the system
PV = n R T = N k T P is the Absolute pressure Measured from Vacuum = 0 Gauge Pressure = Vacuum - Atmospheric Atmospheric = 14.7 lbs/sq in = 10 5 N/m V is the volume of the system in m 3 often the system
ε tran ε tran = nrt = 2 3 N ε tran = 2 3 nn A ε tran nn A nr ε tran = 2 N A i.e. T = R ε tran = 2
 F1 (a) Since the ideal gas equation of state is PV = nrt, we can equate the right-hand sides of both these equations (i.e. with PV = 2 3 N ε tran )and write: nrt = 2 3 N ε tran = 2 3 nn A ε tran i.e. T
F1 (a) Since the ideal gas equation of state is PV = nrt, we can equate the right-hand sides of both these equations (i.e. with PV = 2 3 N ε tran )and write: nrt = 2 3 N ε tran = 2 3 nn A ε tran i.e. T
Kinetic theory of the ideal gas
 Appendix H Kinetic theory of the ideal gas This Appendix contains sketchy notes, summarizing the main results of elementary kinetic theory. The students who are not familiar with these topics should refer
Appendix H Kinetic theory of the ideal gas This Appendix contains sketchy notes, summarizing the main results of elementary kinetic theory. The students who are not familiar with these topics should refer
Chapter 21 Electrical Properties of Matter
 Chapter 21 Electrical Properties of Matter GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and
Chapter 21 Electrical Properties of Matter GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and
Gases, Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
 Chapter 6 Gases, Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces Solids: The particles of a solid have fixed positions and exhibit motions of vibration. Liquids: The particles of a liquid are free to move within
Chapter 6 Gases, Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces Solids: The particles of a solid have fixed positions and exhibit motions of vibration. Liquids: The particles of a liquid are free to move within
(A) 0 (B) mv (C) 2mv (D) 2mv sin θ (E) 2mv cos θ
 Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 5 GASES INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 5 GASES 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 5 GASES Properties of Gases Pressure History and Application of the Gas Laws Partial Pressure Stoichiometry of
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 5 GASES 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 5 GASES Properties of Gases Pressure History and Application of the Gas Laws Partial Pressure Stoichiometry of
Handout 11: Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat. Ideal gas law
 Handout : Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat Ideal gas law For a gas at pressure p, volume V and absolute temperature T, ideal gas law states that pv = nrt, where n is the number of moles and R
Handout : Ideal gas, internal energy, work and heat Ideal gas law For a gas at pressure p, volume V and absolute temperature T, ideal gas law states that pv = nrt, where n is the number of moles and R
Chapter 10. Gases. The Gas Laws
 Page 1 of 12 10.1 Characteristics of Gases. Chapter 10. Gases. All substances have three phases; solid, liquid and gas. Substances that are liquids or solids under ordinary conditions may also exist as
Page 1 of 12 10.1 Characteristics of Gases. Chapter 10. Gases. All substances have three phases; solid, liquid and gas. Substances that are liquids or solids under ordinary conditions may also exist as
An ideal gas. Ideal gas equation.
 S t r o n a 1 Autor: Ryszard Świda An ideal gas. Ideal gas equation. To facilitate the application of physical theories, various physicals models are created and used. A physical model is a hypothetical
S t r o n a 1 Autor: Ryszard Świda An ideal gas. Ideal gas equation. To facilitate the application of physical theories, various physicals models are created and used. A physical model is a hypothetical
Chapter 13. liquids. gases. 1) Fluids exert pressure. a) because they're made up of matter with forces applied between (I.M.F.)
 \ Chapter 13 Fluids 1) Fluids exert pressure a) because they're made up of matter with forces applied between (I.M.F.) liquids gases b) they are made of matter in constant motion colliding with other matter
\ Chapter 13 Fluids 1) Fluids exert pressure a) because they're made up of matter with forces applied between (I.M.F.) liquids gases b) they are made of matter in constant motion colliding with other matter
Physics. Assignment-1(UNITS AND MEASUREMENT)
 Assignment-1(UNITS AND MEASUREMENT) 1. Define physical quantity and write steps for measurement. 2. What are fundamental units and derived units? 3. List the seven basic and two supplementary physical
Assignment-1(UNITS AND MEASUREMENT) 1. Define physical quantity and write steps for measurement. 2. What are fundamental units and derived units? 3. List the seven basic and two supplementary physical
Kinetic Theory of Aether Particles
 Chapter 2 Kinetic Theory of Aether Particles 2.1 Basic Concepts and Assumptions This chapter will derive energy density and pressure from particles collision on a surface based on kinetic theory. Kinetic
Chapter 2 Kinetic Theory of Aether Particles 2.1 Basic Concepts and Assumptions This chapter will derive energy density and pressure from particles collision on a surface based on kinetic theory. Kinetic
Quantitative Exercise 9.4. Tip 9/14/2015. Quantitative analysis of an ideal gas
 Chapter 9 - GASES 9. Quantitative analysis of gas 9.4 emperature 9.5 esting the ideal gas Quantitative analysis of an ideal gas We need more simplifying assumptions. Assume that the particles do not collide
Chapter 9 - GASES 9. Quantitative analysis of gas 9.4 emperature 9.5 esting the ideal gas Quantitative analysis of an ideal gas We need more simplifying assumptions. Assume that the particles do not collide
PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I. Photo: J. M. Schwarz
 PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I Photo: J. M. Schwarz Announcements We will be talking about the laws of thermodynamics today, which will help get you ready for next week s lab on the Stirling engine.
PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I Photo: J. M. Schwarz Announcements We will be talking about the laws of thermodynamics today, which will help get you ready for next week s lab on the Stirling engine.
(a) (i) One of the assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases is that molecules make elastic collisions. State what is meant by an elastic collision.
 1 (a) (i) One of the assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases is that molecules make elastic collisions. State what is meant by an elastic collision. State two more assumptions that are made in the kinetic
1 (a) (i) One of the assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases is that molecules make elastic collisions. State what is meant by an elastic collision. State two more assumptions that are made in the kinetic
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
14 The IDEAL GAS LAW. and KINETIC THEORY Molecular Mass, The Mole, and Avogadro s Number. Atomic Masses
 14 The IDEAL GAS LAW and KINETIC THEORY 14.1 Molecular Mass, The Mole, and Avogadro s Number Atomic Masses The SI Unit of mass: An atomic mass unit is de ned as a unit of mass equal to 1/12 of the mass
14 The IDEAL GAS LAW and KINETIC THEORY 14.1 Molecular Mass, The Mole, and Avogadro s Number Atomic Masses The SI Unit of mass: An atomic mass unit is de ned as a unit of mass equal to 1/12 of the mass
Module 5: Rise and Fall of the Clockwork Universe. You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of:
 OCR B Physics H557 Module 5: Rise and Fall of the Clockwork Universe You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 5.2: Matter Particle model: A gas consists of many very small, rapidly
OCR B Physics H557 Module 5: Rise and Fall of the Clockwork Universe You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 5.2: Matter Particle model: A gas consists of many very small, rapidly
Center of Mass & Linear Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
Fluid Mechanics Introduction
 Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
Lesson 1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Red Sox - Yankees. Baseball can not get more exciting than these games. Physics 121, April 17, Kinetic theory of gases.
 Red Sox - Yankees. Baseball can not get more exciting than these games. Physics 121, April 17, 2008. Kinetic theory of gases. http://eml.ou.edu/physics/module/thermal/ketcher/idg4.avi Physics 121. April
Red Sox - Yankees. Baseball can not get more exciting than these games. Physics 121, April 17, 2008. Kinetic theory of gases. http://eml.ou.edu/physics/module/thermal/ketcher/idg4.avi Physics 121. April
10 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL EXPANSION, IDEAL GAS LAW, AND KINETIC THEORY OF GASES.
 10 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL EXPANSION, IDEAL GAS LAW, AND KINETIC THEORY OF GASES. Key words: Atoms, Molecules, Atomic Theory of Matter, Molecular Mass, Solids, Liquids, and Gases, Thermodynamics, State Variables,
10 TEMPERATURE, THERMAL EXPANSION, IDEAL GAS LAW, AND KINETIC THEORY OF GASES. Key words: Atoms, Molecules, Atomic Theory of Matter, Molecular Mass, Solids, Liquids, and Gases, Thermodynamics, State Variables,
Thermodynamics. Atoms are in constant motion, which increases with temperature.
 Thermodynamics SOME DEFINITIONS: THERMO related to heat DYNAMICS the study of motion SYSTEM an object or set of objects ENVIRONMENT the rest of the universe MICROSCOPIC at an atomic or molecular level
Thermodynamics SOME DEFINITIONS: THERMO related to heat DYNAMICS the study of motion SYSTEM an object or set of objects ENVIRONMENT the rest of the universe MICROSCOPIC at an atomic or molecular level
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 2 (*) (1)
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. (a) pressure (*) Pa or N m volume m (*) (*) (not allow kpa) number of moles mol (or none) molar gas constant J K 1 mol 1 (mol 1 implies molar) temperature K 4 (b) (i) W(=
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. (a) pressure (*) Pa or N m volume m (*) (*) (not allow kpa) number of moles mol (or none) molar gas constant J K 1 mol 1 (mol 1 implies molar) temperature K 4 (b) (i) W(=
Chapter 15. simple harmonic motion
 Chapter 15 Simple Harmonic Motion GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and use it
Chapter 15 Simple Harmonic Motion GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and use it
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion
 Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
This is a statistical treatment of the large ensemble of molecules that make up a gas. We had expressed the ideal gas law as: pv = nrt (1)
 1. Kinetic Theory of Gases This is a statistical treatment of the large ensemble of molecules that make up a gas. We had expressed the ideal gas law as: pv = nrt (1) where n is the number of moles. We
1. Kinetic Theory of Gases This is a statistical treatment of the large ensemble of molecules that make up a gas. We had expressed the ideal gas law as: pv = nrt (1) where n is the number of moles. We
Chapter 11 Thermal Transport
 Chapter 11 Thermal Transport GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define the following terms, and use them in an operational
Chapter 11 Thermal Transport GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define the following terms, and use them in an operational
Proper&es of Water. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 2.2 Properties of Water
 Lesson Overview Proper&es of Water Lesson Overview 2.2 Properties of Water THINK ABOUT IT Looking back at Earth from space, an astronaut called it the blue planet, referring to the oceans of water that
Lesson Overview Proper&es of Water Lesson Overview 2.2 Properties of Water THINK ABOUT IT Looking back at Earth from space, an astronaut called it the blue planet, referring to the oceans of water that
Introduction Matter has three possible states: - Solid - Liquid - Gas. Chem101 - Lecture 6
 Chem101 - Lecture 6 States of Matter Introduction Matter has three possible states: - Solid - Liquid - Gas We will investigate the differences in the physical properties exhibited by each of these states
Chem101 - Lecture 6 States of Matter Introduction Matter has three possible states: - Solid - Liquid - Gas We will investigate the differences in the physical properties exhibited by each of these states
Downloaded from
 Chapter 13 (Kinetic Theory) Q1. A cubic vessel (with face horizontal + vertical) contains an ideal gas at NTP. The vessel is being carried by a rocket which is moving at a speed of500 ms in vertical direction.
Chapter 13 (Kinetic Theory) Q1. A cubic vessel (with face horizontal + vertical) contains an ideal gas at NTP. The vessel is being carried by a rocket which is moving at a speed of500 ms in vertical direction.
Chemistry of Life: Water and Solutions
 Chemistry of Life: Water and Solutions Unit Objective I can describe the role of organic and inorganic chemicals important to living things. During this unit, we will answer the following very important
Chemistry of Life: Water and Solutions Unit Objective I can describe the role of organic and inorganic chemicals important to living things. During this unit, we will answer the following very important
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change. Chapter 12: States of Matter
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
Gases! n Properties! n Kinetic Molecular Theory! n Variables! n The Atmosphere! n Gas Laws!
 Gases n Properties n Kinetic Molecular Theory n Variables n The Atmosphere n Gas Laws Properties of a Gas n No definite shape or volume n Gases expand to fill any container n Thus they take the shape of
Gases n Properties n Kinetic Molecular Theory n Variables n The Atmosphere n Gas Laws Properties of a Gas n No definite shape or volume n Gases expand to fill any container n Thus they take the shape of
(k = force constant of the spring)
 Lecture 10: Potential Energy, Momentum and Collisions 1 Chapter 7: Conservation of Mechanical Energy in Spring Problems The principle of conservation of Mechanical Energy can also be applied to systems
Lecture 10: Potential Energy, Momentum and Collisions 1 Chapter 7: Conservation of Mechanical Energy in Spring Problems The principle of conservation of Mechanical Energy can also be applied to systems
Ideal Gas Behavior. NC State University
 Chemistry 331 Lecture 6 Ideal Gas Behavior NC State University Macroscopic variables P, T Pressure is a force per unit area (P= F/A) The force arises from the change in momentum as particles hit an object
Chemistry 331 Lecture 6 Ideal Gas Behavior NC State University Macroscopic variables P, T Pressure is a force per unit area (P= F/A) The force arises from the change in momentum as particles hit an object
van der Waals Isotherms near T c
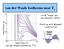 van der Waals Isotherms near T c v d W loops are not physical. Why? Patch up with Maxwell construction van der Waals Isotherms, T/T c van der Waals Isotherms near T c Look at one of the van der Waals isotherms
van der Waals Isotherms near T c v d W loops are not physical. Why? Patch up with Maxwell construction van der Waals Isotherms, T/T c van der Waals Isotherms near T c Look at one of the van der Waals isotherms
 Kinetic Molecular Model of Gas 1. The kinetic gas equation for 1 mole of a gas 1 mc PV ) 1 1 PV MC ) C 1 mc PV ) PV. At the same temperature and pressure which of the following gas will have highest K.E
Kinetic Molecular Model of Gas 1. The kinetic gas equation for 1 mole of a gas 1 mc PV ) 1 1 PV MC ) C 1 mc PV ) PV. At the same temperature and pressure which of the following gas will have highest K.E
A Level Physics G484 PHYSICS DEPARTMENT. Assessment. Assessed with a 1 hour 15 minute, 60 mark paper where all questions are answered.
 A Level Physics G484 Assessment Assessed with a 1 hour 15 minute, 60 mark paper where all questions are answered. Useful Data Gravitational constant, G 6.67 x 10-11 N m 2 kg -2 Avogadro constant, N A 6.02
A Level Physics G484 Assessment Assessed with a 1 hour 15 minute, 60 mark paper where all questions are answered. Useful Data Gravitational constant, G 6.67 x 10-11 N m 2 kg -2 Avogadro constant, N A 6.02
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry
 Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third system (such
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third system (such
If the position of a molecule is measured after increments of 10, 100, 1000 steps, what will the distribution of measured steps look like?
 If the position of a molecule is measured after increments of 10, 100, 1000 steps, what will the distribution of measured steps look like? (1) No longer Gaussian (2) Identical Gaussians (3) Gaussians with
If the position of a molecule is measured after increments of 10, 100, 1000 steps, what will the distribution of measured steps look like? (1) No longer Gaussian (2) Identical Gaussians (3) Gaussians with
KINETICE THEROY OF GASES
 INTRODUCTION: Kinetic theory of gases relates the macroscopic properties of gases (like pressure, temperature, volume... etc) to the microscopic properties of the gas molecules (like speed, momentum, kinetic
INTRODUCTION: Kinetic theory of gases relates the macroscopic properties of gases (like pressure, temperature, volume... etc) to the microscopic properties of the gas molecules (like speed, momentum, kinetic
Think-Pair-Share. Linear Momentum (Ch 9) Linear Momentum, cont. Newton and Momentum
 Linear Momentum (Ch 9) The linear momentum of a particle or an object that can be modeled as a particle of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined to be the product of the mass and velocity: p = m v
Linear Momentum (Ch 9) The linear momentum of a particle or an object that can be modeled as a particle of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined to be the product of the mass and velocity: p = m v
LBS 172 Exam 1 Review
 Chapter 12- Gases LBS 172 Exam 1 Review I. What is a gas? a. Properties i. Non-definite volume, fills container, can flow, spread out, can be compressed b. Air is a gas composed of many gases i. Relatively
Chapter 12- Gases LBS 172 Exam 1 Review I. What is a gas? a. Properties i. Non-definite volume, fills container, can flow, spread out, can be compressed b. Air is a gas composed of many gases i. Relatively
Chapter 10, Thermal Physics
 CHAPTER 10 1. If it is given that 546 K equals 273 C, then it follows that 400 K equals: a. 127 C b. 150 C c. 473 C d. 1 200 C 2. A steel wire, 150 m long at 10 C, has a coefficient of linear expansion
CHAPTER 10 1. If it is given that 546 K equals 273 C, then it follows that 400 K equals: a. 127 C b. 150 C c. 473 C d. 1 200 C 2. A steel wire, 150 m long at 10 C, has a coefficient of linear expansion
Chapter 10. Solids and Fluids
 Chapter 10 Solids and Fluids Surface Tension Net force on molecule A is zero Pulled equally in all directions Net force on B is not zero No molecules above to act on it Pulled toward the center of the
Chapter 10 Solids and Fluids Surface Tension Net force on molecule A is zero Pulled equally in all directions Net force on B is not zero No molecules above to act on it Pulled toward the center of the
17-6 The Gas Laws and Absolute Temperature
 17-6 The Gas Laws and Absolute Temperature The relationship between the volume, pressure, temperature, and mass of a gas is called an equation of state. We will deal here with gases that are not too dense.
17-6 The Gas Laws and Absolute Temperature The relationship between the volume, pressure, temperature, and mass of a gas is called an equation of state. We will deal here with gases that are not too dense.
Chapter 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS
 Chapter 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass Systems with Changing
Chapter 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass Systems with Changing
Atomic Mass and Atomic Mass Number. Moles and Molar Mass. Moles and Molar Mass
 Atomic Mass and Atomic Mass Number The mass of an atom is determined primarily by its most massive constituents: protons and neutrons in its nucleus. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons is called
Atomic Mass and Atomic Mass Number The mass of an atom is determined primarily by its most massive constituents: protons and neutrons in its nucleus. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons is called
Fluids Bernoulli s equation conclusion
 Chapter 11 Fluids Bernoulli s equation conclusion 11.9 Bernoulli s Equation W NC = ( P 2! P 1 )V W NC = E 1! E 2 = 1 mv 2 + mgy 2 1 1 ( )! ( 1 "v 2 + "gy 2 2 2 ) ( P 2! P 1 ) = 1 "v 2 + "gy 2 1 1 NC Work
Chapter 11 Fluids Bernoulli s equation conclusion 11.9 Bernoulli s Equation W NC = ( P 2! P 1 )V W NC = E 1! E 2 = 1 mv 2 + mgy 2 1 1 ( )! ( 1 "v 2 + "gy 2 2 2 ) ( P 2! P 1 ) = 1 "v 2 + "gy 2 1 1 NC Work
Chapter 14 Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 Kinetic Theory Kinetic Theory of Gases A remarkable triumph of molecular theory was showing that the macroscopic properties of an ideal gas are related to the molecular properties. This is the
Chapter 14 Kinetic Theory Kinetic Theory of Gases A remarkable triumph of molecular theory was showing that the macroscopic properties of an ideal gas are related to the molecular properties. This is the
Fluids Bernoulli s equation conclusion
 Chapter 11 Fluids Bernoulli s equation conclusion 11.9 Bernoulli s Equation W NC = ( P 2! P 1 )V W NC = E 1! E 2 = 1 mv 2 + mgy 2 1 1 ( )! ( 1 "v 2 + "gy 2 2 2 ) ( P 2! P 1 ) = 1 "v 2 + "gy 2 1 1 NC Work
Chapter 11 Fluids Bernoulli s equation conclusion 11.9 Bernoulli s Equation W NC = ( P 2! P 1 )V W NC = E 1! E 2 = 1 mv 2 + mgy 2 1 1 ( )! ( 1 "v 2 + "gy 2 2 2 ) ( P 2! P 1 ) = 1 "v 2 + "gy 2 1 1 NC Work
Liquids & Solids: Section 12.3
 Liquids & Solids: Section 12.3 MAIN IDEA: The particles in and have a range of motion and are not easily. Why is it more difficult to pour syrup that is stored in the refrigerator than in the cabinet?
Liquids & Solids: Section 12.3 MAIN IDEA: The particles in and have a range of motion and are not easily. Why is it more difficult to pour syrup that is stored in the refrigerator than in the cabinet?
Flow of fluids 1. Prof. Ferenc Bari. Department of Medical Physics and Informatics
 Flow of fluids 1 Prof Ferenc Bari Department of Medical Physics and Informatics 20 th October 2016 Prof Ferenc Bari (SZTE DMI) Flow of fluids 1 20 th October 2016 1 / 71 Contents 1 Overview 2 Gases Overview
Flow of fluids 1 Prof Ferenc Bari Department of Medical Physics and Informatics 20 th October 2016 Prof Ferenc Bari (SZTE DMI) Flow of fluids 1 20 th October 2016 1 / 71 Contents 1 Overview 2 Gases Overview
2017 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN
 2017 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN Topics: Forces Motion Momentum Gravity Electrostatics DATE: TIME: ROOM: PROCTOR: YOU ARE REQUIRED TO BRING: 1. CALCULATOR (YOUR OWN NO SHARING) 2. PENCIL
2017 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN Topics: Forces Motion Momentum Gravity Electrostatics DATE: TIME: ROOM: PROCTOR: YOU ARE REQUIRED TO BRING: 1. CALCULATOR (YOUR OWN NO SHARING) 2. PENCIL
Chapter 10. Thermal Physics
 Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER 1 XI PHYSICS
 TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER 1 XI PHYSICS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions (a) All questions are compulsory. (b) There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry one mark each, questions
TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER 1 XI PHYSICS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions (a) All questions are compulsory. (b) There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry one mark each, questions
CHEMISTRY XL-14A GASES. August 6, 2011 Robert Iafe
 CHEMISTRY XL-14A GASES August 6, 2011 Robert Iafe Chemistry in the News 2 Polymer nicotine trap is composed of a porphyrin derivative (black), in which amide pincers (green) are attached to the zinc (violet)
CHEMISTRY XL-14A GASES August 6, 2011 Robert Iafe Chemistry in the News 2 Polymer nicotine trap is composed of a porphyrin derivative (black), in which amide pincers (green) are attached to the zinc (violet)
Chapter 11 Gases 1 Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009
 Chapter 11 Gases Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 11.1 Properties of Gases The properties of a gas are almost independent of its identity. (Gas molecules behave as if no other molecules are present.) Compressible
Chapter 11 Gases Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 11.1 Properties of Gases The properties of a gas are almost independent of its identity. (Gas molecules behave as if no other molecules are present.) Compressible
PHYSICS. Chapter 20 Lecture 4/E FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 20 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 20 The Micro/Macro Connection IN THIS CHAPTER, you will see how macroscopic
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 20 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 20 The Micro/Macro Connection IN THIS CHAPTER, you will see how macroscopic
Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter
 Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter Learning Goals: Students will be able to describe matter in terms of particle motion. The description should include Diagrams to support the
Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter Learning Goals: Students will be able to describe matter in terms of particle motion. The description should include Diagrams to support the
Unit Outline. I. Introduction II. Gas Pressure III. Gas Laws IV. Gas Law Problems V. Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases VI.
 Unit 10: Gases Unit Outline I. Introduction II. Gas Pressure III. Gas Laws IV. Gas Law Problems V. Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases VI. Real Gases I. Opening thoughts Have you ever: Seen a hot air balloon?
Unit 10: Gases Unit Outline I. Introduction II. Gas Pressure III. Gas Laws IV. Gas Law Problems V. Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases VI. Real Gases I. Opening thoughts Have you ever: Seen a hot air balloon?
NY Times 11/25/03 Physics L 22 Frank Sciulli slide 1
 NY Times /5/03 slide Thermodynamics and Gases Last Time specific heats phase transitions Heat and Work st law of thermodynamics heat transfer conduction convection radiation Today Kinetic Theory of Gases
NY Times /5/03 slide Thermodynamics and Gases Last Time specific heats phase transitions Heat and Work st law of thermodynamics heat transfer conduction convection radiation Today Kinetic Theory of Gases
