Output high order sliding mode control of unity-power-factor in three-phase AC/DC Boost Converter
|
|
|
- Blake Sanders
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Output high order sliding mode control of unity-power-factor in three-phase AC/DC Boost Converter JianXing Liu, Salah Laghrouche, Maxim Wack Laboratoire Systèmes Et Transports (SET) Laboratoire SeT
2 Contents of the presentation Introduction Problem Formulation Second order sliding mode controller design Second order sliding mode observer design Simulation results with proposed controller Conclusions
3 AC-DC power conversion The electric utility grid has a sinusoidal waveform, and most electronic equipment needs a DC power supply. AC-DC power conversion is required by all electronic devices virtually MOSFET, IGBT, are commonly used for AC-DC Converters
4 AC-DC power conversion Problem:. The performance and efficiency of power converters with unknown varying load and internal uncertainties. Minimize the number of the sensors Power factor reflects the efficiency and quality of such process. Different control algorithms have been used to achieve unity power factor. An output second order sliding mode control is designed here.
5 Model of three phase AC/DC converter The circuit of three phase AC/DC boost converter i link Fig Three phase boost type AC/DC converter
6 Model Model in Phase Coordinate Frame: di r U U 0 = i ( u u u 3) + dt L 6L L di r U U 0 = i ( u u u ) + dt L 6L L di U 3 r U i 0 = 3 ( u 3 u u ) + dt L 6L L du U ( ) 0 0 = + ui + ui + ui 33 dt RlC C g g g3
7 Model in (d,q) Coordinate Frame It is convenient to design the control in the rotating reference frame synchronized with the supply frequency. Transformation Matrix: cos( ) cos( ) cos( ) x x ωt ωt π ωt+ π d 3 3 x x = q 3 sin( ωt) sin( ωt π) sin( ωt π) + x Define: C cos( ) cos( ) cos( ) ωt ωt π ωt+ π 3 3 = 3 sin( ωt) sin( ωt π) sin( ωt π) + 3 3
8 Model in (d,q) Coordinate Frame di r U U d 0 = i + ω i u + dt L d q L d L di r U U q = i ω i 0 u + dt L q d L q L du U 3 0 = 0 + ( iu + iu ) dt R C 4C d d q q l Where ω is the source frequency gd gq
9 Control objectives Unity power factor Ripple free output voltage with desired level i d i * * tracks id, q tracks i q Satisfy Power Balance Equation 3 ( U i + U i ) = U U * * 0 gd d gq q 0REF Rl Considering unity power factor, the desired currents are as follows: * d i = i = 0 U U * 0REF 0 q 3U R gq l
10 Control structure Observer-based control structure is shown is fig. Fig Observer-based control structure
11 Super-Twisting sliding mode x= f(,) xt + bxtu (,) y = Design sx ( ) where x, f, b! n Control Objective: Force sx ( ) to zero. The relative degree with respect to Advantages: Robustness property with respect to perturbations and parametric uncertainties. Smoother than the classic sliding mode control sx ( ) is equal to one. u = υ(), s υ() s = λs sign() s + αsign() s dt,( λα, > 0)
12 Step:Sliding manifolds design Design the switching functions: s = i * i d d d = * q q q s i i To find a domain in the system space from which any state trajectory converges to the sliding manifold(s d =0,s q =0). U * r gd u d d q s i i ωi d L L U u 0 d fd U0 = + C u = + U u * r gq L q fq L s q iq iq ωi + d u 3 L L
13 Step: Control design Super twisting sliding mode controller can be designed: u - υ(s ) u = - υ(s ) u 3 - υ(s 3) υ( e) = λe sign( e) + αsign( e) dt,( λα, > 0) The transformed vector s should be designed such that, under the above controller, s d and s q will vanish in finite time. s L 3 s T d s = C U0 s q s 3
14 Super-Twisting Observation Design Assuming that only the output voltage(u 0 ) is measured, a supertwisting sliding observer is constructed as a copy of the original system. di r d U U i i 0 gd = d+ ω q u d + k υ( e 3) dt L L L diq r U U i i 0 gq = u k q ω d q + υ( e 3) dt L L L du0 U0 3 = + ( iu d d + iu q q ) k3υ ( e3 ) dt RlC 4C Where Define observation error: e = id id e = iq iq e = U U υ( e ) = λe sign( e ) + αsign( e ) dt,( λα, > 0)
15 Super-Twisting Observation Design The estimation error dynamics are: de r ud = e + ω e e 3 k υ( e 3) dt L L u q de = r e ω e e 3 k υ( e 3) dt L L de3 3 = e3+ ( ue d + ue q ) k3υ ( e3 ) dt RlC 4C The sliding surface defined as s=e 3 =0. Choosing a large positive constant k 3 can assure the convergence of s(e 3 =0) in finite time.
16 Observer convergence proof Dynamics on the sliding manifold The equivalent switching function is: υ ( e3) = ( ue d + ue q ) kc 3 Substitute into the two equations of error dynamics, r r e ω ~ L e k k ud uq e ω L k k ud uq, A, A, U = = = dq = r e kc 3 k k 0 0 e r k k 0 0 e ω ω L e ψ ( e ) L As A is a Hurwitz matrix, there exists a unique positive definite symmetric matrix P that satisfies the equation with positive definite symmetric matrix Q. T PA + A P = Q The Lyapunov function is given as: V ( e ) = e Pe T
17 Observer convergence proof The derivative of V(e ) is V V V ( e ) = Ae + ( e ) e ψ e The first term: V Ae T T T = e ( PA + A P ) e = e Qe λmin ( Q ) e e The second term can be expressed as: V T ( e ) ep ( e ) P e ( e ) e ψ ψ ψ ~ η ψ( e ) A U dq e ρ e, ρ = kc kc 3 3 ~ ~ T ~ A λmax( A A) ( k k ) η = = = + If ρ < λmin ( Q) λ ( P) max V( e ) λ ( Q) e + ρλ ( P) e min max,the origin is globally exponentially stable.
18 Observation of Source Phase Voltage A link current sensor is used to estimate the source phase voltage. if u u = u link if u u = u3 Design the sliding mode observer: i3 if u3 u = u di r U0 i ( u u u 3) M ( e = + υ ), r Ug Mυ( e) dt L 6L L e= e+ L L υ( e) = λ e sign( e) + αsign( e) dt, e = ui link i Ug = Mυ( e) i 3 = i Choose sufficiently large observer gain M, the sliding mode will be enforced in finite time. i
19 Observation of Load Resistance du0 U0 = + ( ui + ui + ui 33 ) dt RlC C du0 U0 = + ( ui + ui + ui 33 ) + kυ ( e ) dt RC C l υ( e) = λ e sign( e) + αsign( e) dt, e = U U 0 0 Error dynamics: U U e= k e 0 0 ( ) υ( ) RC l RC l Choose sufficiently large observer gain k, sliding mode will be enforced. υ e U = Rl = kcυ ( e) + R U 0 ( ) ( ) kc R Rl l l 0
20 Power Factor Calculation I I PF = PFh PFd = cos( φ) I main current harmonic PFh harmonic distortion I total current RMS φ phase shift between input current and main voltage T RMS( i( t)) = i( τ) dτ T is the period of i(t) T 0 Remark: Using Fourier analysis, harmonic distortion measurement, trigonometric modules in matlab, the power factor of the system can easily be obtained.
21 Simulation Results Parameter Value Description R Load Resistance Ω r 0.0 Parasitic phase resistance Ω L e-3 Phase inductor H C 00e-6 Output capacitance F E 50 Amplitude of source voltage V f t=.5s t=.0s Source voltage frequency Hz U 0ref 650 Desired output DC voltage V; V(0)=V Load resistance and frequency are varied to test controller s ability to handle with varying load and frequency.
22 Input current in phase with source voltage Figure Input current and source voltage in case of super-twisting SMC Figure Input current and source voltage in case of traditional SMC Traditional SMC results in higher harmonics compared with super-twisting SMC.
23 Source Voltage Estimation Figure3 Source voltage U g estimation within the windows when i link is equal to i Source voltage can be reconstructed with super-twisting observer without designing a low-pass filter.
24 Load Resistance Estimation Figure4 Load resistance R estimator performance Figure4 shows the performance of load resistance estimation.
25 The performance of observer Figure5 Output voltage estimator performance U 0 Figure6 Current estimator performance i q
26 The performance of observer Figure7 Phase Current estimator performance Figure5-7 show the performance of the observer. i a
27 The performance of output voltage Figure8 Output voltage performance with super-twisting control Figure9 Output voltage performance with traditional sliding mode control A bit higher than the desired voltage level and more oscillating compared with super-twisting SMC.
28 Power Factor Figure0 Power factor with super-twisting control Figure Power factor with Traditional SMC Less value and more oscillations compared with supertwisting control. The super-twisting control was able to produce a power factor that was more than 99%, and can withstand the changing conditions.
29 Conclusions The proposed control method can achieve a power factor close to unity. Power Balance Condition is taken into account to achieve the desired performance of the system. The proposed super-twisting observer demonstrates its robustness to the change in operational conditions. Source Voltage Estimation is achieved with i link via super-twisting method without using low-pass filter.
30 Thanks! If you have any questions, I would be pleased to answer them!
Grid-connected photovoltaic systems based on nonlinear control.
 University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2018 Grid-connected photovoltaic systems based on nonlinear control. Pablo
University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2018 Grid-connected photovoltaic systems based on nonlinear control. Pablo
Inductance, Inductors, RL Circuits & RC Circuits, LC, and RLC Circuits
 Inductance, Inductors, RL Circuits & RC Circuits, LC, and RLC Circuits Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the timevarying
Inductance, Inductors, RL Circuits & RC Circuits, LC, and RLC Circuits Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the timevarying
Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3.
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
TSTE25 Power Electronics. Lecture 3 Tomas Jonsson ICS/ISY
 TSTE25 Power Electronics Lecture 3 Tomas Jonsson ICS/ISY 2016-11-09 2 Outline Rectifiers Current commutation Rectifiers, cont. Three phase Inrush and short circuit current Exercises 5-5, 5-8, 3-100, 3-101,
TSTE25 Power Electronics Lecture 3 Tomas Jonsson ICS/ISY 2016-11-09 2 Outline Rectifiers Current commutation Rectifiers, cont. Three phase Inrush and short circuit current Exercises 5-5, 5-8, 3-100, 3-101,
EM Oscillations. David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 212
 I ve got an oscillating fan at my house. The fan goes back and forth. It looks like the fan is saying No. So I like to ask it questions that a fan would say no to. Do you keep my hair in place? Do you
I ve got an oscillating fan at my house. The fan goes back and forth. It looks like the fan is saying No. So I like to ask it questions that a fan would say no to. Do you keep my hair in place? Do you
Chapter 4 Transients. Chapter 4 Transients
 Chapter 4 Transients Chapter 4 Transients 1. Solve first-order RC or RL circuits. 2. Understand the concepts of transient response and steady-state response. 1 3. Relate the transient response of first-order
Chapter 4 Transients Chapter 4 Transients 1. Solve first-order RC or RL circuits. 2. Understand the concepts of transient response and steady-state response. 1 3. Relate the transient response of first-order
Handout 10: Inductance. Self-Inductance and inductors
 1 Handout 10: Inductance Self-Inductance and inductors In Fig. 1, electric current is present in an isolate circuit, setting up magnetic field that causes a magnetic flux through the circuit itself. This
1 Handout 10: Inductance Self-Inductance and inductors In Fig. 1, electric current is present in an isolate circuit, setting up magnetic field that causes a magnetic flux through the circuit itself. This
Power Electronics
 Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
Prof. Dr. Ing. Joachim Böcker Power Electronics 3.09.06 Last Name: Student Number: First Name: Study Program: Professional Examination Performance Proof Task: (Credits) (0) (0) 3 (0) 4 (0) Total (80) Mark
Lecture 11 - AC Power
 - AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
- AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
Inductance, RL and RLC Circuits
 Inductance, RL and RLC Circuits Inductance Temporarily storage of energy by the magnetic field When the switch is closed, the current does not immediately reach its maximum value. Faraday s law of electromagnetic
Inductance, RL and RLC Circuits Inductance Temporarily storage of energy by the magnetic field When the switch is closed, the current does not immediately reach its maximum value. Faraday s law of electromagnetic
Prof. Anyes Taffard. Physics 120/220. Voltage Divider Capacitor RC circuits
 Prof. Anyes Taffard Physics 120/220 Voltage Divider Capacitor RC circuits Voltage Divider The figure is called a voltage divider. It s one of the most useful and important circuit elements we will encounter.
Prof. Anyes Taffard Physics 120/220 Voltage Divider Capacitor RC circuits Voltage Divider The figure is called a voltage divider. It s one of the most useful and important circuit elements we will encounter.
MODULE I. Transient Response:
 Transient Response: MODULE I The Transient Response (also known as the Natural Response) is the way the circuit responds to energies stored in storage elements, such as capacitors and inductors. If a capacitor
Transient Response: MODULE I The Transient Response (also known as the Natural Response) is the way the circuit responds to energies stored in storage elements, such as capacitors and inductors. If a capacitor
Figure Circuit for Question 1. Figure Circuit for Question 2
 Exercises 10.7 Exercises Multiple Choice 1. For the circuit of Figure 10.44 the time constant is A. 0.5 ms 71.43 µs 2, 000 s D. 0.2 ms 4 Ω 2 Ω 12 Ω 1 mh 12u 0 () t V Figure 10.44. Circuit for Question
Exercises 10.7 Exercises Multiple Choice 1. For the circuit of Figure 10.44 the time constant is A. 0.5 ms 71.43 µs 2, 000 s D. 0.2 ms 4 Ω 2 Ω 12 Ω 1 mh 12u 0 () t V Figure 10.44. Circuit for Question
EXP. NO. 3 Power on (resistive inductive & capacitive) load Series connection
 OBJECT: To examine the power distribution on (R, L, C) series circuit. APPARATUS 1-signal function generator 2- Oscilloscope, A.V.O meter 3- Resisters & inductor &capacitor THEORY the following form for
OBJECT: To examine the power distribution on (R, L, C) series circuit. APPARATUS 1-signal function generator 2- Oscilloscope, A.V.O meter 3- Resisters & inductor &capacitor THEORY the following form for
EE 230 Lecture 40. Data Converters. Amplitude Quantization. Quantization Noise
 EE 230 Lecture 40 Data Converters Amplitude Quantization Quantization Noise Review from Last Time: Time Quantization Typical ADC Environment Review from Last Time: Time Quantization Analog Signal Reconstruction
EE 230 Lecture 40 Data Converters Amplitude Quantization Quantization Noise Review from Last Time: Time Quantization Typical ADC Environment Review from Last Time: Time Quantization Analog Signal Reconstruction
Project Components. MC34063 or equivalent. Bread Board. Energy Systems Research Laboratory, FIU
 Project Components MC34063 or equivalent Bread Board PSpice Software OrCAD designer Lite version http://www.cadence.com/products/orcad/pages/downloads.aspx#pspice More Details on the Introduction CONVERTER
Project Components MC34063 or equivalent Bread Board PSpice Software OrCAD designer Lite version http://www.cadence.com/products/orcad/pages/downloads.aspx#pspice More Details on the Introduction CONVERTER
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor. The solution of this differential equation is
 RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
RLC Circuit (3) We can then write the differential equation for charge on the capacitor The solution of this differential equation is (damped harmonic oscillation!), where 25 RLC Circuit (4) If we charge
Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency
 Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency 3.1. The dc transformer model 3.2. Inclusion of inductor copper loss 3.3. Construction of equivalent circuit model 3.4. How to
Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency 3.1. The dc transformer model 3.2. Inclusion of inductor copper loss 3.3. Construction of equivalent circuit model 3.4. How to
Module 25: Outline Resonance & Resonance Driven & LRC Circuits Circuits 2
 Module 25: Driven RLC Circuits 1 Module 25: Outline Resonance & Driven LRC Circuits 2 Driven Oscillations: Resonance 3 Mass on a Spring: Simple Harmonic Motion A Second Look 4 Mass on a Spring (1) (2)
Module 25: Driven RLC Circuits 1 Module 25: Outline Resonance & Driven LRC Circuits 2 Driven Oscillations: Resonance 3 Mass on a Spring: Simple Harmonic Motion A Second Look 4 Mass on a Spring (1) (2)
Single-Phase Synchronverter for DC Microgrid Interface with AC Grid
 The First Power Electronics and Renewable Energy Workshop (PEREW 2017) March 1-2, 2017- Aswan Faculty of Engineering, Aswan Egypt Single-Phase Synchronverter for Microgrid Interface with AC Grid Presenter:
The First Power Electronics and Renewable Energy Workshop (PEREW 2017) March 1-2, 2017- Aswan Faculty of Engineering, Aswan Egypt Single-Phase Synchronverter for Microgrid Interface with AC Grid Presenter:
Lecture 39. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 39 PHYC 161 Fall 016 Announcements DO THE ONLINE COURSE EVALUATIONS - response so far is < 8 % Magnetic field energy A resistor is a device in which energy is irrecoverably dissipated. By contrast,
Lecture 39 PHYC 161 Fall 016 Announcements DO THE ONLINE COURSE EVALUATIONS - response so far is < 8 % Magnetic field energy A resistor is a device in which energy is irrecoverably dissipated. By contrast,
1 Phasors and Alternating Currents
 Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Handout 11: AC circuit. AC generator
 Handout : AC circuit AC generator Figure compares the voltage across the directcurrent (DC) generator and that across the alternatingcurrent (AC) generator For DC generator, the voltage is constant For
Handout : AC circuit AC generator Figure compares the voltage across the directcurrent (DC) generator and that across the alternatingcurrent (AC) generator For DC generator, the voltage is constant For
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
EE 435. Lecture 30. Data Converters. Spectral Performance
 EE 435 Lecture 30 Data Converters Spectral Performance . Review from last lecture. INL Often Not a Good Measure of Linearity Four identical INL with dramatically different linearity X OUT X OUT X REF X
EE 435 Lecture 30 Data Converters Spectral Performance . Review from last lecture. INL Often Not a Good Measure of Linearity Four identical INL with dramatically different linearity X OUT X OUT X REF X
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Electromagnetic Oscillations Physics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 8! We have been working with circuits that have a constant current a current that increases to a constant current
Electromagnetic Oscillations Physics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 8! We have been working with circuits that have a constant current a current that increases to a constant current
C R. Consider from point of view of energy! Consider the RC and LC series circuits shown:
 ircuits onsider the R and series circuits shown: ++++ ---- R ++++ ---- Suppose that the circuits are formed at t with the capacitor charged to value. There is a qualitative difference in the time development
ircuits onsider the R and series circuits shown: ++++ ---- R ++++ ---- Suppose that the circuits are formed at t with the capacitor charged to value. There is a qualitative difference in the time development
EN Power Electronics and Machines
 EN 206 - Power Electronics and Machines Phase Controlled Rectifiers Suryanarayana Doolla Department of Energy Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay suryad@iitb.ac.in Prof. Doolla
EN 206 - Power Electronics and Machines Phase Controlled Rectifiers Suryanarayana Doolla Department of Energy Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay suryad@iitb.ac.in Prof. Doolla
Lecture 24. Impedance of AC Circuits.
 Lecture 4. Impedance of AC Circuits. Don t forget to complete course evaluations: https://sakai.rutgers.edu/portal/site/sirs Post-test. You are required to attend one of the lectures on Thursday, Dec.
Lecture 4. Impedance of AC Circuits. Don t forget to complete course evaluations: https://sakai.rutgers.edu/portal/site/sirs Post-test. You are required to attend one of the lectures on Thursday, Dec.
Active Figure 32.3 (SLIDESHOW MODE ONLY)
 RL Circuit, Analysis An RL circuit contains an inductor and a resistor When the switch is closed (at time t = 0), the current begins to increase At the same time, a back emf is induced in the inductor
RL Circuit, Analysis An RL circuit contains an inductor and a resistor When the switch is closed (at time t = 0), the current begins to increase At the same time, a back emf is induced in the inductor
Electronic Circuits Summary
 Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
Solutions to Problems in Chapter 4
 Solutions to Problems in Chapter 4 Problems with Solutions Problem 4. Fourier Series of the Output Voltage of an Ideal Full-Wave Diode Bridge Rectifier he nonlinear circuit in Figure 4. is a full-wave
Solutions to Problems in Chapter 4 Problems with Solutions Problem 4. Fourier Series of the Output Voltage of an Ideal Full-Wave Diode Bridge Rectifier he nonlinear circuit in Figure 4. is a full-wave
Modeling Buck Converter by Using Fourier Analysis
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 8, 2010 705 Modeling Buck Converter by Using Fourier Analysis Mao Zhang 1, Weiping Zhang 2, and Zheng Zhang 2 1 School of Computing, Engineering and Physical Sciences, University
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 8, 2010 705 Modeling Buck Converter by Using Fourier Analysis Mao Zhang 1, Weiping Zhang 2, and Zheng Zhang 2 1 School of Computing, Engineering and Physical Sciences, University
To find the step response of an RC circuit
 To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design
 EE C45 ME C18 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 008 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 9470 Lecture 6: Output
EE C45 ME C18 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 008 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 9470 Lecture 6: Output
Coupled Electrical Oscillators Physics Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 2018 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 5/24/2018
 Coupled Electrical Oscillators Physics 3600 - Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 08 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 5/4/08 I. INTRODUCTION The objectives of this experiment are: () explore the properties
Coupled Electrical Oscillators Physics 3600 - Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 08 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 5/4/08 I. INTRODUCTION The objectives of this experiment are: () explore the properties
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits
 Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Inductance, RL Circuits, LC Circuits, RLC Circuits
 Inductance, R Circuits, C Circuits, RC Circuits Inductance What happens when we close the switch? The current flows What does the current look like as a function of time? Does it look like this? I t Inductance
Inductance, R Circuits, C Circuits, RC Circuits Inductance What happens when we close the switch? The current flows What does the current look like as a function of time? Does it look like this? I t Inductance
Lecture 4: R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits
 Lecture 4: R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits RLC series circuit: What's V R? Simplest way to solve for V is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation: V X L X C V R = in R R + X C + X L L
Lecture 4: R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits RLC series circuit: What's V R? Simplest way to solve for V is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation: V X L X C V R = in R R + X C + X L L
The output voltage is given by,
 71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
Chapter 32. Inductance
 Chapter 32 Inductance Joseph Henry 1797 1878 American physicist First director of the Smithsonian Improved design of electromagnet Constructed one of the first motors Discovered self-inductance Unit of
Chapter 32 Inductance Joseph Henry 1797 1878 American physicist First director of the Smithsonian Improved design of electromagnet Constructed one of the first motors Discovered self-inductance Unit of
ECE 201 Fall 2009 Final Exam
 ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the time-varying current.
 Inductance Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the time-varying current. Basis of the electrical circuit element called an
Inductance Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the time-varying current. Basis of the electrical circuit element called an
Repetitive control : Power Electronics. Applications
 Repetitive control : Power Electronics Applications Ramon Costa Castelló Advanced Control of Energy Systems (ACES) Instituto de Organización y Control (IOC) Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) Barcelona,
Repetitive control : Power Electronics Applications Ramon Costa Castelló Advanced Control of Energy Systems (ACES) Instituto de Organización y Control (IOC) Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) Barcelona,
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE
 EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 20 121101 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Chapters 1-3 Circuit Analysis Techniques Chapter 10 Diodes Ideal Model
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 20 121101 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Chapters 1-3 Circuit Analysis Techniques Chapter 10 Diodes Ideal Model
Prof. Dr. Erol KURT Nonlinear Problems in Piezoelectric Harvesters
 Prof. Dr. Erol KURT Nonlinear Problems in Piezoelectric Harvesters 1 This chapter focuses on the nonlinear problems in the piezoelectric harvester systems under the magnetic field. In this manner, the
Prof. Dr. Erol KURT Nonlinear Problems in Piezoelectric Harvesters 1 This chapter focuses on the nonlinear problems in the piezoelectric harvester systems under the magnetic field. In this manner, the
Novel DC-AC Converter Topology for Multilevel Battery Energy Storage Systems. Mario Gommeringer, Felix Kammerer, Johannes Kolb, Michael Braun
 Elektrotechnisches Institut (ETI) Prof. Dr.-Ing. Michael Braun Prof. Dr.-Ing. Martin Doppelbauer Prof. Dr.-Ing. Marc Hiller Kaiserstr.12. 76131 Karlsruhe 13. Sept. 216 Title: Novel DC-C Converter Topology
Elektrotechnisches Institut (ETI) Prof. Dr.-Ing. Michael Braun Prof. Dr.-Ing. Martin Doppelbauer Prof. Dr.-Ing. Marc Hiller Kaiserstr.12. 76131 Karlsruhe 13. Sept. 216 Title: Novel DC-C Converter Topology
Power Factor Improvement
 Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits
 P517/617 Lec4, P1 R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits Consider the following RLC series circuit What's R? Simplest way to solve for is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation. X L X C in 0
P517/617 Lec4, P1 R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits Consider the following RLC series circuit What's R? Simplest way to solve for is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation. X L X C in 0
Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work Solutions
 Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work s 21.1 Problem 21.11 What is the time constant of the circuit in Figure (21.19). 10 Ω 10 Ω 5.0 Ω 2.0µF 2.0µF 2.0µF 3.0µF Figure 21.19: Given: The circuit
Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work s 21.1 Problem 21.11 What is the time constant of the circuit in Figure (21.19). 10 Ω 10 Ω 5.0 Ω 2.0µF 2.0µF 2.0µF 3.0µF Figure 21.19: Given: The circuit
Introduction to CMOS RF Integrated Circuits Design
 V. Voltage Controlled Oscillators Fall 2012, Prof. JianJun Zhou V-1 Outline Phase Noise and Spurs Ring VCO LC VCO Frequency Tuning (Varactor, SCA) Phase Noise Estimation Quadrature Phase Generator Fall
V. Voltage Controlled Oscillators Fall 2012, Prof. JianJun Zhou V-1 Outline Phase Noise and Spurs Ring VCO LC VCO Frequency Tuning (Varactor, SCA) Phase Noise Estimation Quadrature Phase Generator Fall
Chapter 21: RLC Circuits. PHY2054: Chapter 21 1
 Chapter 21: RC Circuits PHY2054: Chapter 21 1 Voltage and Current in RC Circuits AC emf source: driving frequency f ε = ε sinωt ω = 2π f m If circuit contains only R + emf source, current is simple ε ε
Chapter 21: RC Circuits PHY2054: Chapter 21 1 Voltage and Current in RC Circuits AC emf source: driving frequency f ε = ε sinωt ω = 2π f m If circuit contains only R + emf source, current is simple ε ε
EA2.3 - Electronics 2 1
 In the previous lecture, I talked about the idea of complex frequency s, where s = σ + jω. Using such concept of complex frequency allows us to analyse signals and systems with better generality. In this
In the previous lecture, I talked about the idea of complex frequency s, where s = σ + jω. Using such concept of complex frequency allows us to analyse signals and systems with better generality. In this
Converter System Modeling via MATLAB/Simulink
 Converter System Modeling via MATLAB/Simulink A powerful environment for system modeling and simulation MATLAB: programming and scripting environment Simulink: block diagram modeling environment that runs
Converter System Modeling via MATLAB/Simulink A powerful environment for system modeling and simulation MATLAB: programming and scripting environment Simulink: block diagram modeling environment that runs
Chapter 32. Inductance
 Chapter 32 Inductance Inductance Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the time-varying current. Basis of the electrical circuit
Chapter 32 Inductance Inductance Self-inductance A time-varying current in a circuit produces an induced emf opposing the emf that initially set up the time-varying current. Basis of the electrical circuit
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2003 Experiment 17: RLC Circuit (modified 4/15/2003) OBJECTIVES
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 7: R Circuit (modified 4/5/3) OBJECTIVES. To observe electrical oscillations, measure their frequencies, and verify energy
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 7: R Circuit (modified 4/5/3) OBJECTIVES. To observe electrical oscillations, measure their frequencies, and verify energy
ω 0 = 2π/T 0 is called the fundamental angular frequency and ω 2 = 2ω 0 is called the
 he ime-frequency Concept []. Review of Fourier Series Consider the following set of time functions {3A sin t, A sin t}. We can represent these functions in different ways by plotting the amplitude versus
he ime-frequency Concept []. Review of Fourier Series Consider the following set of time functions {3A sin t, A sin t}. We can represent these functions in different ways by plotting the amplitude versus
Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System Simulation *
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com AASRI Procedia 3 (2012 ) 262 269 2012 AASRI Conference on Modeling, Identification and Control Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com AASRI Procedia 3 (2012 ) 262 269 2012 AASRI Conference on Modeling, Identification and Control Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System
Basics of Electric Circuits
 António Dente Célia de Jesus February 2014 1 Alternating Current Circuits 1.1 Using Phasors There are practical and economic reasons justifying that electrical generators produce emf with alternating and
António Dente Célia de Jesus February 2014 1 Alternating Current Circuits 1.1 Using Phasors There are practical and economic reasons justifying that electrical generators produce emf with alternating and
Section 4. Nonlinear Circuits
 Section 4 Nonlinear Circuits 1 ) Voltage Comparators V P < V N : V o = V ol V P > V N : V o = V oh One bit A/D converter, Practical gain : 10 3 10 6 V OH and V OL should be far apart enough Response Time:
Section 4 Nonlinear Circuits 1 ) Voltage Comparators V P < V N : V o = V ol V P > V N : V o = V oh One bit A/D converter, Practical gain : 10 3 10 6 V OH and V OL should be far apart enough Response Time:
Lecture 23: NorCal 40A Power Amplifier. Thermal Modeling.
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 23 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 23: NorCal 40A Power Amplifier. Thermal Modeling. Recall from the last lecture that the NorCal 40A uses a Class C power amplifier. From Fig. 10.3(b) the collector
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 23 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 23: NorCal 40A Power Amplifier. Thermal Modeling. Recall from the last lecture that the NorCal 40A uses a Class C power amplifier. From Fig. 10.3(b) the collector
Basic RL and RC Circuits R-L TRANSIENTS: STORAGE CYCLE. Engineering Collage Electrical Engineering Dep. Dr. Ibrahim Aljubouri
 st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
Circuit Analysis-III. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 3 Friday 06 th April, 18
 Circuit Analysis-III Sinusoids Example #1 ü Find the amplitude, phase, period and frequency of the sinusoid: v (t ) =12cos(50t +10 ) Signal Conversion ü From sine to cosine and vice versa. ü sin (A ± B)
Circuit Analysis-III Sinusoids Example #1 ü Find the amplitude, phase, period and frequency of the sinusoid: v (t ) =12cos(50t +10 ) Signal Conversion ü From sine to cosine and vice versa. ü sin (A ± B)
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012
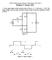 ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
11. AC Circuit Power Analysis
 . AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
. AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE
 EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 14 121011 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review Steady-State Analysis RC Circuits RL Circuits 3 DC Steady-State
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 14 121011 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review Steady-State Analysis RC Circuits RL Circuits 3 DC Steady-State
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 . W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 2.4 Cuk converter example L 1 C 1 L 2 Cuk converter, with ideal switch i 1 i v 1 2 1 2 C 2 v 2 Cuk
. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 2.4 Cuk converter example L 1 C 1 L 2 Cuk converter, with ideal switch i 1 i v 1 2 1 2 C 2 v 2 Cuk
EE 435. Lecture 28. Data Converters Linearity INL/DNL Spectral Performance
 EE 435 Lecture 8 Data Converters Linearity INL/DNL Spectral Performance Performance Characterization of Data Converters Static characteristics Resolution Least Significant Bit (LSB) Offset and Gain Errors
EE 435 Lecture 8 Data Converters Linearity INL/DNL Spectral Performance Performance Characterization of Data Converters Static characteristics Resolution Least Significant Bit (LSB) Offset and Gain Errors
Physics 115. AC: RL vs RC circuits Phase relationships RLC circuits. General Physics II. Session 33
 Session 33 Physics 115 General Physics II AC: RL vs RC circuits Phase relationships RLC circuits R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 6/2/14 1
Session 33 Physics 115 General Physics II AC: RL vs RC circuits Phase relationships RLC circuits R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 6/2/14 1
GATE EE Topic wise Questions SIGNALS & SYSTEMS
 www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
AC Circuits Homework Set
 Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Switched-Capacitor Circuits David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto
 Switched-Capacitor Circuits David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) University of Toronto 1 of 60 Basic Building Blocks Opamps Ideal opamps usually
Switched-Capacitor Circuits David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) University of Toronto 1 of 60 Basic Building Blocks Opamps Ideal opamps usually
Control of Wind Turbine Generators. James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University
 Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
Solutions to these tests are available online in some places (but not all explanations are good)...
 The Physics GRE Sample test put out by ETS https://www.ets.org/s/gre/pdf/practice_book_physics.pdf OSU physics website has lots of tips, and 4 additional tests http://www.physics.ohiostate.edu/undergrad/ugs_gre.php
The Physics GRE Sample test put out by ETS https://www.ets.org/s/gre/pdf/practice_book_physics.pdf OSU physics website has lots of tips, and 4 additional tests http://www.physics.ohiostate.edu/undergrad/ugs_gre.php
Some of the different forms of a signal, obtained by transformations, are shown in the figure. jwt e z. jwt z e
 Transform methods Some of the different forms of a signal, obtained by transformations, are shown in the figure. X(s) X(t) L - L F - F jw s s jw X(jw) X*(t) F - F X*(jw) jwt e z jwt z e X(nT) Z - Z X(z)
Transform methods Some of the different forms of a signal, obtained by transformations, are shown in the figure. X(s) X(t) L - L F - F jw s s jw X(jw) X*(t) F - F X*(jw) jwt e z jwt z e X(nT) Z - Z X(z)
Homework Assignment 08
 Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Chapter 7 DC-DC Switch-Mode Converters
 Chapter 7 DC-DC Switch-Mode Converters dc-dc converters for switch-mode dc power supplies and dc-motor drives 7-1 Block Diagram of DC-DC Converters Functional block diagram 7-2 Stepping Down a DC Voltage
Chapter 7 DC-DC Switch-Mode Converters dc-dc converters for switch-mode dc power supplies and dc-motor drives 7-1 Block Diagram of DC-DC Converters Functional block diagram 7-2 Stepping Down a DC Voltage
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
Interconnection of LTI Systems
 EENG226 Signals and Systems Chapter 2 Time-Domain Representations of Linear Time-Invariant Systems Interconnection of LTI Systems Prof. Dr. Hasan AMCA Electrical and Electronic Engineering Department (ee.emu.edu.tr)
EENG226 Signals and Systems Chapter 2 Time-Domain Representations of Linear Time-Invariant Systems Interconnection of LTI Systems Prof. Dr. Hasan AMCA Electrical and Electronic Engineering Department (ee.emu.edu.tr)
EE 40: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 2008: Midterm 2
 EE 4: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 8: Midterm Venkat Anantharam 3/9/8 Total Time Allotted : min Total Points:. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed to bring two pages
EE 4: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 8: Midterm Venkat Anantharam 3/9/8 Total Time Allotted : min Total Points:. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed to bring two pages
8. Electric Currents
 8. Electric Currents S. G. Rajeev January 30, 2011 An electric current is produced by the movement of electric charges. In most cases these are electrons. A conductor is a material through which an electric
8. Electric Currents S. G. Rajeev January 30, 2011 An electric current is produced by the movement of electric charges. In most cases these are electrons. A conductor is a material through which an electric
Part II Converter Dynamics and Control
 Part II Converter Dynamics and Control 7. AC equivalent circuit modeling 8. Converter transfer functions 9. Controller design 10. Ac and dc equivalent circuit modeling of the discontinuous conduction mode
Part II Converter Dynamics and Control 7. AC equivalent circuit modeling 8. Converter transfer functions 9. Controller design 10. Ac and dc equivalent circuit modeling of the discontinuous conduction mode
Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03
![Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03](/thumbs/94/118747664.jpg) EE 4 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 016 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS NETWORK ANALYSIS Time: Three Hours Answer Question
EE 4 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 016 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS NETWORK ANALYSIS Time: Three Hours Answer Question
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Self-paced Course
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Self-paced Course MODULE 26 APPLICATIONS TO ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS Module Topics 1. Complex numbers and alternating currents 2. Complex impedance 3.
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Self-paced Course MODULE 26 APPLICATIONS TO ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS Module Topics 1. Complex numbers and alternating currents 2. Complex impedance 3.
Module 24: Outline. Expt. 8: Part 2:Undriven RLC Circuits
 Module 24: Undriven RLC Circuits 1 Module 24: Outline Undriven RLC Circuits Expt. 8: Part 2:Undriven RLC Circuits 2 Circuits that Oscillate (LRC) 3 Mass on a Spring: Simple Harmonic Motion (Demonstration)
Module 24: Undriven RLC Circuits 1 Module 24: Outline Undriven RLC Circuits Expt. 8: Part 2:Undriven RLC Circuits 2 Circuits that Oscillate (LRC) 3 Mass on a Spring: Simple Harmonic Motion (Demonstration)
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors)
 Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
ECE Spring 2017 Final Exam
 ECE 20100 Spring 2017 Final Exam May 2, 2017 Section (circle below) Qi (12:30) 0001 Tan (10:30) 0004 Hosseini (7:30) 0005 Cui (1:30) 0006 Jung (11:30) 0007 Lin (9:30) 0008 Peleato-Inarrea (2:30) 0009 Name
ECE 20100 Spring 2017 Final Exam May 2, 2017 Section (circle below) Qi (12:30) 0001 Tan (10:30) 0004 Hosseini (7:30) 0005 Cui (1:30) 0006 Jung (11:30) 0007 Lin (9:30) 0008 Peleato-Inarrea (2:30) 0009 Name
Mixing Problems. Solution of concentration c 1 grams/liter flows in at a rate of r 1 liters/minute. Figure 1.7.1: A mixing problem.
 page 57 1.7 Modeling Problems Using First-Order Linear Differential Equations 57 For Problems 33 38, use a differential equation solver to determine the solution to each of the initial-value problems and
page 57 1.7 Modeling Problems Using First-Order Linear Differential Equations 57 For Problems 33 38, use a differential equation solver to determine the solution to each of the initial-value problems and
AC Circuits III. Physics 2415 Lecture 24. Michael Fowler, UVa
 AC Circuits III Physics 415 Lecture 4 Michael Fowler, UVa Today s Topics LC circuits: analogy with mass on spring LCR circuits: damped oscillations LCR circuits with ac source: driven pendulum, resonance.
AC Circuits III Physics 415 Lecture 4 Michael Fowler, UVa Today s Topics LC circuits: analogy with mass on spring LCR circuits: damped oscillations LCR circuits with ac source: driven pendulum, resonance.
Physics 11b Lecture #15
 Physics 11b ecture #15 and ircuits A ircuits S&J hapter 3 & 33 Administravia Midterm # is Thursday If you can t take midterm, you MUST let us (me, arol and Shaun) know in writing before Wednesday noon
Physics 11b ecture #15 and ircuits A ircuits S&J hapter 3 & 33 Administravia Midterm # is Thursday If you can t take midterm, you MUST let us (me, arol and Shaun) know in writing before Wednesday noon
AC analysis. EE 201 AC analysis 1
 AC analysis Now we turn to circuits with sinusoidal sources. Earlier, we had a brief look at sinusoids, but now we will add in capacitors and inductors, making the story much more interesting. What are
AC analysis Now we turn to circuits with sinusoidal sources. Earlier, we had a brief look at sinusoids, but now we will add in capacitors and inductors, making the story much more interesting. What are
Power semiconductor devices
 Electrical Engineering Division Page 1 of 10 Power semiconductor devices Power semiconductor devices constitute the heart of modern power electronic apparatus. The main function of the power semiconductor
Electrical Engineering Division Page 1 of 10 Power semiconductor devices Power semiconductor devices constitute the heart of modern power electronic apparatus. The main function of the power semiconductor
Lecture 4, Noise. Noise and distortion
 Lecture 4, Noise Noise and distortion What did we do last time? Operational amplifiers Circuit-level aspects Simulation aspects Some terminology Some practical concerns Limited current Limited bandwidth
Lecture 4, Noise Noise and distortion What did we do last time? Operational amplifiers Circuit-level aspects Simulation aspects Some terminology Some practical concerns Limited current Limited bandwidth
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 2
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 2
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA
 EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
Lecture 05 Power in AC circuit
 CA2627 Building Science Lecture 05 Power in AC circuit Instructor: Jiayu Chen Ph.D. Announcement 1. Makeup Midterm 2. Midterm grade Grade 25 20 15 10 5 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Grade Jiayu Chen, Ph.D. 2
CA2627 Building Science Lecture 05 Power in AC circuit Instructor: Jiayu Chen Ph.D. Announcement 1. Makeup Midterm 2. Midterm grade Grade 25 20 15 10 5 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Grade Jiayu Chen, Ph.D. 2
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
