MTX221. Session 33 ENTROPY (CONTROL MASS) Sessie 33 ENTROPIE (KONTROLE MASSA) Dr. Jaco Dirker. These slides also appear on Click-UP
|
|
|
- Kelley Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ses. 33- MTX Sessie 33 ENTROPIE (KONTROLE MASSA) Session 33 ENTROPY (CONTROL MASS) Dr. Jaco Dirker These slides also appear on Click-UP Hierdie skyfies verskyn ook op Click-UP 8 th edition / 8e uitgawe
2 Ses. 33- Die Entropie van n Suiwer Stof 6.3 The Entropy of a Pure Substance Spesifieke entropie Specific entropy is intensive (thus independent of the amount of mass) [kj/kgk] Entropy values are listed in TD tables according to some reference temp. For most refrigerants, -40ºC is used as the reference value in our Tables, BUT can be different for other TD data-sets : BE CAREFUL. (Please note: Negative entropy values are also listed) The term entropy is used for both total entropy, S, [kj/k] and specific entropy, s, [kj/kgk] refer to context. For a two-phase saturated state: s s f xs fg Totale entropie Verwysings temp.
3 Ses Die Entropie van n Suiwer Stof 6.3 The Entropy of a Pure Substance Temperature-Entropy diagrams (T-s diagrams) are of use to visualise the change of state: Another diagram also used is a Enthalpy-Entropy Diagram: Temperatuur-Entropie Diagram Entalpie-Entropie Diagram Vloeist. Liq. Gas Gas
4 Ses Die Entropie van n Suiwer Stof 6.3 The Entropy of a Pure Substance Saamgedrukte / onderverkoelde vloeist Generally for compressed liquid: Entropy is very similar to saturated Gesatureerde vloeist. Liq. entropy at the same given temp. Therefore for compressed liquid: s s f ONLY IF NO ALTERNATIVE DATA SOURCE IS AVAILABLE USE DISCRETION.
5 Ses Remember: Q ds [J/K] T Let us now consider the entropy change during the reversible processes in the Carnot cycle. (We will for now limit ourselves to reversible processes) Remember the Carnot Cycle: Isothermal Expansion Adiabatic Expansion Isothermal Compression Adiabatic Compression rev Isotermiese Uitsetting Adiabatiese Uitsetting Isotermies Samedrukking Adiabatiese Samedrukking Carnot Kringloop
6 Ses Omkeerbare Isotermiese Uitsetting met Hitte-oordrag Reversible Isothermal Expansion with heat transfer: ( ) S S Q T rev Because it is reversible (with const. temp): Note that the Heat transfer can be written as: S S * This is only true for a reversible process T Q Q H T H Q TH S S *
7 Ses Omkeerbare Adiabatiese Uitsetting Reversible Adiabatic Expansion ( 3) Adiabatic means: Q3 0 Thus: We thus have a constant entropy process (S 3 = S ) This is called an isentropic process S Q 3 3 S T rev 0 isentropiese proses
8 Ses Reversible Isothermal Compression with heat transfer: (3 4) Omkeerbare Isotermiese Samedrukking met Hitte-oordrag S Q T Q S3 3 rev T L Remember Q 0, therefore: S 4 S3 0 (Entropy decreases) 3 4
9 Ses Omkeerbare Adiabatiese Samedrukking Reversible Adiabatic Compression (4 ) Q 4 4 T rev S S 0 (Because Q = 0) Isentropic process: isentropiese proses S S 4
10 Ses Summary (Reversible processes) Isothermal Expansion ( ): Isotermiese Uitsetting Adiabatic Expansion ( 3): Adiabatiese Uitsetting Isothermal Compression (3 4): Isotermiese Samedrukking Adiabatic Compression (4 ): Adiabatiese Samedrukking Q S S T H S S 3 S 3 4 S4 S3 T L S4 0 (isentropic) Q 0 (isentropic) isentropies isentropies
11 Ses. 33- Let s plot these processes on a T-s diagram: Area under line represents heat transfer to the system, Q H Area under line 3 4 represents heat transfer from the system, Q L Area 3 4 represents the Work output for this Heat Engine Termiese Rendement: Thermal efficiency: W area _ 3 4 thermal Q area _ b a H Stip op n T-s diagram: Isothermal Adiabatic Entropy increases at T H and decreases at T L Entropie neem toe by T H en neem af by T L Heat Engine Hitte-enjin
12 Ses. 33- If the Heat engine cycle is reversed, we will have a refrigerator / heat pump: Note the change in direction of arrows (counter clockwise) antikloksgewys Entropy decreases at T H and increases at T L (Heat transfer to the system occurs at T L ) Entropie neem af by T H en neem toe by T L Refrigerator / Heat Pump Verkoeler / Hittepomp
13 Ses SPECIAL CASE: Spesiale Geval Omkeerbare hitte-oordrag proses Let s consider a general reversible heat transfer process Consider a system which is internally reversible (no irreversibility inside its boundaries) : Intern omkeerbaar Saturated liquid is heated from state to 3. From state to the process occurs at constant pressure and temperture Konst. druk en temp. Thus: s s s fg m Q T rev But But m q Q T rev mt h h h fg Q (Remember: Q m h h for const. pressure) q T Konst. druk Therefore: s s h T In this case: h s fg h T fg
14 Ses SPECIAL CASE. reversible heat transfer process In this case: h fg s fg T Let s check this: Consider saturated water at 00ºC:. This gives an indication on how entropy change can be calculated, but only for constant pressure, constant temperature processes. Konst. druk en temp ONLY valid for s fg, NOT for s f and s g entropieverandering
15 Ses SPECIAL CASE For process, the heat transfer is given by the area under line What about the heat transferred from to 3? 3 q3 Tds The heat transfer is still equal to the area under line 3. Temp. nie konst. nie T is not constant, thus without the mathematical relation for T (s) this integral can not be obtained directly. IMPORTANT: Heat transfer is only equal to the area under the process line on a T-s diagram if the process is reversible. We will revisit this soon again.
16 Ses Reversible Process Entropy Change Example Based on EX6. (Ed 8), but the following is changed: Working Substance: Ammonia Evaporation temp = -0ºC Condensation temp = 70ºC Mass flow rate = 0.5 kg/s Afrikaans op volgende skyfie Consider a Carnot-cycle heat pump with Ammonia as working fluid. Heat is absorbed into the system at -0ºC (changes from a two-phase state to a saturated vapour). Heat is rejected at 70ºC until the ammonia is a saturated liquid. The Ammonia has a mass flow rate of 0.5 kg/s. Determine the following: a) Pressure after compression before heat rejection b) Quality before evaporation c) Heat receiving rate d) COP of the system.
17 Ses Omkeerbare Proses Entropieverandering Voorbeeld Gebasseer op VB6. (Wge 8), maar met wysigings: Werksvloeier: Ammoniak Verdamping temp = -0ºC Kondensasie temp = 70ºC Massavloei-tempo = 0.5 kg/s English on previous slide Beskou n Carnot-kringloop hittepomp met Ammoniak as werksvloeier. Hitte word ontvang in die stelsel teen -0ºC (verander van tweefase tot n versadigde damp). Hitte word verwerp teen 70ºC tot die ammoniak n versadigde vloeistof is. Die ammoniak het n massavloeitempo van 0.5 kg/s. Bepaal die volgende: a) Die druk na samedrukking, maar voor hitte-verwerping b) Kwaliteit voor verdamping c) Hitte-ontvangstempo d) COP van die stelsel.
MTX221. Session 36 ENTROPY (CONTROL MASS) Sessie 36 ENTROPIE (KONTROLE MASSA) Dr. Jaco Dirker. These slides also appear on Click-UP
 Ses.36- MX Sessie 36 ENROIE (KONROLE MASSA) Session 36 ENROY (CONROL MASS) Dr. Jaco Dirker hese slides also appear on Click-U Hierdie skyfies verskyn ook op Click-U 8 th edition / 8e uitgawe 6.7 6.0 Ses.36-
Ses.36- MX Sessie 36 ENROIE (KONROLE MASSA) Session 36 ENROY (CONROL MASS) Dr. Jaco Dirker hese slides also appear on Click-U Hierdie skyfies verskyn ook op Click-U 8 th edition / 8e uitgawe 6.7 6.0 Ses.36-
MTX221. Sessie 30 DIE KLASSIEKE TWEEDE WET VAN TERMODINAMIKA. Session 30 THE CLASSICAL SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS. Dr.
 Ses. 30-1 Sessie 30 DIE KLASSIEKE TWEEDE WET VAN TERMODINAMIKA MTX221 Hierdie skyfies verskyn ook op Click-UP 8 th edition / 8e uitgawe 5.5 5.7 Session 30 THE CLASSICAL SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Dr.
Ses. 30-1 Sessie 30 DIE KLASSIEKE TWEEDE WET VAN TERMODINAMIKA MTX221 Hierdie skyfies verskyn ook op Click-UP 8 th edition / 8e uitgawe 5.5 5.7 Session 30 THE CLASSICAL SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Dr.
Voorletters en Van Initials and Surname Studente nommer Student number Datum / Date
 Voorletters en Van Initials and Surname Studente nommer Student number Datum / Date MTX221 2011 KLASTOETS 3E / CLASSTES 3E 25 min. (14 punte/marks) *Sal herwerk tot 10 punte vir klaslys doeleindes * Will
Voorletters en Van Initials and Surname Studente nommer Student number Datum / Date MTX221 2011 KLASTOETS 3E / CLASSTES 3E 25 min. (14 punte/marks) *Sal herwerk tot 10 punte vir klaslys doeleindes * Will
Refrigeration. 05/04/2011 T.Al-Shemmeri 1
 Refrigeration is a process of controlled removal of heat from a substance to keep it at a temperature below the ambient condition, often below the freezing point of water (0 O C) 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
Refrigeration is a process of controlled removal of heat from a substance to keep it at a temperature below the ambient condition, often below the freezing point of water (0 O C) 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
Atkins / Paula Physical Chemistry, 8th Edition. Chapter 3. The Second Law
 Atkins / Paula Physical Chemistry, 8th Edition Chapter 3. The Second Law The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 Entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific processes
Atkins / Paula Physical Chemistry, 8th Edition Chapter 3. The Second Law The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 Entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific processes
The Limits of Efficiency. The Limits of Efficiency. The Limits of Efficiency
 The Limits of Efficiency If a perfectly reversible heat engine is used to operate a perfectly reversible refrigerator, the two devices exactly cancel each other. 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 20-1
The Limits of Efficiency If a perfectly reversible heat engine is used to operate a perfectly reversible refrigerator, the two devices exactly cancel each other. 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 20-1
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Unit Workbook 2 - Level 5 ENG U64 Thermofluids 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics II (PY 211) Second Law of Thermodynamics Textbook Reference: Chapter 20 sections 1-4. Second Law of Thermodynamics (Clausius) Heat flows naturally from a hot object to
Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics II (PY 211) Second Law of Thermodynamics Textbook Reference: Chapter 20 sections 1-4. Second Law of Thermodynamics (Clausius) Heat flows naturally from a hot object to
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION. (1X12 = 12 Marks) Answer ONE question from each unit.
 Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
Answer Key THERMODYNAMICS TEST (a) 33. (d) 17. (c) 1. (a) 25. (a) 2. (b) 10. (d) 34. (b) 26. (c) 18. (d) 11. (c) 3. (d) 35. (c) 4. (d) 19.
 HERMODYNAMICS ES Answer Key. (a) 9. (a) 7. (c) 5. (a). (d). (b) 0. (d) 8. (d) 6. (c) 4. (b). (d). (c) 9. (b) 7. (c) 5. (c) 4. (d). (a) 0. (b) 8. (b) 6. (b) 5. (b). (d). (a) 9. (a) 7. (b) 6. (a) 4. (d).
HERMODYNAMICS ES Answer Key. (a) 9. (a) 7. (c) 5. (a). (d). (b) 0. (d) 8. (d) 6. (c) 4. (b). (d). (c) 9. (b) 7. (c) 5. (c) 4. (d). (a) 0. (b) 8. (b) 6. (b) 5. (b). (d). (a) 9. (a) 7. (b) 6. (a) 4. (d).
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics ME 04 BY Dr. Haitham Bahaidarah My Office Office Hours: :00 0:00 am SMW 03:00 04:00 pm UT Location: Building Room # 5.4
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics ME 04 BY Dr. Haitham Bahaidarah My Office Office Hours: :00 0:00 am SMW 03:00 04:00 pm UT Location: Building Room # 5.4
8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 10 Phase Change
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 10 Phase Change
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
10. Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka)
 10 Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka) 1 In this chapter we will discuss how heat devices work Heat devices convert heat into work or work into heat and include heat engines
10 Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka) 1 In this chapter we will discuss how heat devices work Heat devices convert heat into work or work into heat and include heat engines
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
7. Development of the 2nd Law
 7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. (KSK Campus)
 Course File Session-2015 Semester: Fall 2016 MT-24: Thermodynamics for Technologists Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. (KSK Campus) Course File Contents
Course File Session-2015 Semester: Fall 2016 MT-24: Thermodynamics for Technologists Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. (KSK Campus) Course File Contents
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances
 Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
Existing Resources: Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics background and interests:
 Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
THERMODYNAMICS CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS
 THERMODYNAMICS CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS Q-01 Is the heat supplied to a system always equal to the increases in its internal energy? Ans Acc. to first law of thermo- dynamics If heat is supplied in such a manner
THERMODYNAMICS CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS Q-01 Is the heat supplied to a system always equal to the increases in its internal energy? Ans Acc. to first law of thermo- dynamics If heat is supplied in such a manner
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles
 An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
Content. Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas.
 Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
CHEM 305 Solutions for assignment #4
 CEM 05 Solutions for assignment #4 5. A heat engine based on a Carnot cycle does.50 kj of work per cycle and has an efficiency of 45.0%. What are q and q C for one cycle? Since the engine does work on
CEM 05 Solutions for assignment #4 5. A heat engine based on a Carnot cycle does.50 kj of work per cycle and has an efficiency of 45.0%. What are q and q C for one cycle? Since the engine does work on
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
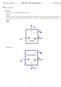 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION
 CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
IS A PARTICULAR PROCESS / REACTION FEASIBLE? TO WHAT EXTENT DOES THE PROCESS / REACTION PROCEED?
 Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
(Refer Slide Time: 00:00:43 min) Welcome back in the last few lectures we discussed compression refrigeration systems.
 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 14 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems (Refer Slide
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 14 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems (Refer Slide
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
ME 200 Final Exam December 14, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas (2)
 1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권
 열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 이번시간에는! 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 물과공기로움직이는기계 사라지지않는에너지 / 증가하는엔트로피 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 [ 학습목차 ] Thermofluids Energy conservation principle Energy Work (boundary work)
열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 이번시간에는! 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 물과공기로움직이는기계 사라지지않는에너지 / 증가하는엔트로피 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 [ 학습목차 ] Thermofluids Energy conservation principle Energy Work (boundary work)
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1
 Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 8 Introduction to Vapour Power Cycle Today, we will continue
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 8 Introduction to Vapour Power Cycle Today, we will continue
Second Law of Thermodynamics -
 Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
V. The Second Law of Thermodynamics. V. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 P V. he Second aw of hermodynamics E. he Carnot Cycle. he reversible heat engine (a piston cylinder device) that operates on a cycle between heat reservoirs at and, as shown below on a P-v diagram, is
P V. he Second aw of hermodynamics E. he Carnot Cycle. he reversible heat engine (a piston cylinder device) that operates on a cycle between heat reservoirs at and, as shown below on a P-v diagram, is
Chapter 7: The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 7: he Second Law of hermodynamics he second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity he first law places no
Chapter 7: he Second Law of hermodynamics he second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity he first law places no
ME 200 Final Exam December 12, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
PROBLEM 6.3. Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property. In each case, locate the state on sketches of the T-v and T-s diagrams.
 PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE NPTEL NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE. Refrigeration and Air-conditioning
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE NPTEL NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Lecture-02 Introduction to Refrigeration with Prof. Ravi Kumar Department of Mechanical
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE NPTEL NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Lecture-02 Introduction to Refrigeration with Prof. Ravi Kumar Department of Mechanical
Thermodynamic Third class Dr. Arkan J. Hadi
 5.5 ENTROPY CHANGES OF AN IDEAL GAS For one mole or a unit mass of fluid undergoing a mechanically reversible process in a closed system, the first law, Eq. (2.8), becomes: Differentiation of the defining
5.5 ENTROPY CHANGES OF AN IDEAL GAS For one mole or a unit mass of fluid undergoing a mechanically reversible process in a closed system, the first law, Eq. (2.8), becomes: Differentiation of the defining
= for reversible < for irreversible
 CHAPER 6 Entropy Copyright he McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. he Clausius Inequality: δ 0 Cyclic integral his inequality is valid for all cycles, reversible
CHAPER 6 Entropy Copyright he McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. he Clausius Inequality: δ 0 Cyclic integral his inequality is valid for all cycles, reversible
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Outline. Property diagrams involving entropy. Heat transfer for internally reversible process
 Outline roperty diagrams involving entropy What is entropy? T-ds relations Entropy change of substances ure substances (near wet dome) Solids and liquids Ideal gases roperty diagrams involving entropy
Outline roperty diagrams involving entropy What is entropy? T-ds relations Entropy change of substances ure substances (near wet dome) Solids and liquids Ideal gases roperty diagrams involving entropy
= for reversible < for irreversible
 CAPER 6 Entropy Copyright he McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. he Clausius Inequality: 0 his inequality is valid for all cycles, reversible or irreversible Cycle
CAPER 6 Entropy Copyright he McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. he Clausius Inequality: 0 his inequality is valid for all cycles, reversible or irreversible Cycle
ENERGY TRANSFER BY WORK: Electrical Work: When N Coulombs of electrical charge move through a potential difference V
 Weight, W = mg Where m=mass, g=gravitational acceleration ENERGY TRANSFER BY WOR: Sign convention: Work done on a system = (+) Work done by a system = (-) Density, ρ = m V kg m 3 Where m=mass, V =Volume
Weight, W = mg Where m=mass, g=gravitational acceleration ENERGY TRANSFER BY WOR: Sign convention: Work done on a system = (+) Work done by a system = (-) Density, ρ = m V kg m 3 Where m=mass, V =Volume
Chapter 6. Using Entropy
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Heat Engines and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Heat Engines and the Second Law of hermodynamics here are three equivalent forms of the second law of thermodynamics; will state all three, discuss: I. (Kelvin-Planck) It is impossible to construct an
Heat Engines and the Second Law of hermodynamics here are three equivalent forms of the second law of thermodynamics; will state all three, discuss: I. (Kelvin-Planck) It is impossible to construct an
SOLUTION: Consider the system to be the refrigerator (shown in the following schematic), which operates over a cycle in normal operation.
 Soln_21 An ordinary household refrigerator operating in steady state receives electrical work while discharging net energy by heat transfer to its surroundings (e.g., the kitchen). a. Is this a violation
Soln_21 An ordinary household refrigerator operating in steady state receives electrical work while discharging net energy by heat transfer to its surroundings (e.g., the kitchen). a. Is this a violation
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Entropy ME 203 (2017) 2 / 27 T037
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
(Refer Slide Time: 0:17)
 (Refer Slide Time: 0:17) Engineering Thermodynamics Professor Jayant K Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 36 Entropy balance in closed system and control
(Refer Slide Time: 0:17) Engineering Thermodynamics Professor Jayant K Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 36 Entropy balance in closed system and control
Irreversible Processes
 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Thermodynamic Processes & Efficiency ME 6101 (2017) 2 / 25 T145 = Q + W cv + i h 2 = h (V2 1 V 2 2)
 Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics P Liquid P x 1 sat P 1 T sat T 2 T x 1 T x 1 T y 1 Liquid Vapour sat P 2 P x 1 P y 1 P y 1 Vapour sat T 1 x, y 1 1 x, y 1 1 Pradeep Ahuja Contents CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics P Liquid P x 1 sat P 1 T sat T 2 T x 1 T x 1 T y 1 Liquid Vapour sat P 2 P x 1 P y 1 P y 1 Vapour sat T 1 x, y 1 1 x, y 1 1 Pradeep Ahuja Contents CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Lecture 12. Refrigerators. Toward Absolute Zero (Ch. 4)
 0 9 0 7 Center of hottest stars Center of Sun, nuclear reactions Lecture. Refrigerators. oward Absolute Zero (Ch. ) emperature, K 0 5 0 0 0-0 - 0-5 Electronic/chemical energy Surface of Sun, hottest boiling
0 9 0 7 Center of hottest stars Center of Sun, nuclear reactions Lecture. Refrigerators. oward Absolute Zero (Ch. ) emperature, K 0 5 0 0 0-0 - 0-5 Electronic/chemical energy Surface of Sun, hottest boiling
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams
 Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Irreversible Processes
 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Chap. 3 The Second Law. Spontaneous change
 Chap. 3 The Second Law Spontaneous change Some things happen naturally; some things don t. the spontaneous direction of change, the direction of change that does not require work to be done to bring it
Chap. 3 The Second Law Spontaneous change Some things happen naturally; some things don t. the spontaneous direction of change, the direction of change that does not require work to be done to bring it
Thermodynamics II. Week 9
 hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 13 June 2007
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
MAE 320 THERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM - Practice. Name: You are allowed three sheets of notes.
 50 MAE 320 THERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM - Practice Name: You are allowed three sheets of notes. 1. Fill in the blanks for each of the two (Carnot) cycles below. (a) 5 a) Heat engine or Heat pump/refrigerator
50 MAE 320 THERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM - Practice Name: You are allowed three sheets of notes. 1. Fill in the blanks for each of the two (Carnot) cycles below. (a) 5 a) Heat engine or Heat pump/refrigerator
Lecture 4. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Lecture 4. The Second Law of Thermodynamics LIMITATION OF THE FIRST LAW: -Does not address whether a particular process is spontaneous or not. -Deals only with changes in energy. Consider this examples:
Lecture 4. The Second Law of Thermodynamics LIMITATION OF THE FIRST LAW: -Does not address whether a particular process is spontaneous or not. -Deals only with changes in energy. Consider this examples:
1. Basic state values of matter
 1. Basic state values of matter Example 1.1 The pressure inside a boiler is p p = 115.10 5 Pa and p v = 9.44.10 4 Pa inside a condenser. Calculate the absolute pressure inside the boiler and condenser
1. Basic state values of matter Example 1.1 The pressure inside a boiler is p p = 115.10 5 Pa and p v = 9.44.10 4 Pa inside a condenser. Calculate the absolute pressure inside the boiler and condenser
November 2005 TYD/TIME: 90 min PUNTE / MARKS: 35 VAN/SURNAME: VOORNAME/FIRST NAMES: STUDENTENOMMER/STUDENT NUMBER: HANDTEKENING/SIGNATURE:
 UNIVERSITEIT VAN PRETORIA / UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA DEPT WISKUNDE EN TOEGEPASTE WISKUNDE DEPT OF MATHEMATICS AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS WTW 263 - NUMERIESE METODES / NUMERICAL METHODS EKSAMEN / EXAMINATION
UNIVERSITEIT VAN PRETORIA / UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA DEPT WISKUNDE EN TOEGEPASTE WISKUNDE DEPT OF MATHEMATICS AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS WTW 263 - NUMERIESE METODES / NUMERICAL METHODS EKSAMEN / EXAMINATION
Laws of Thermodynamics
 Laws of Thermodynamics The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - The first lawof thermodynamics, also called conservation of energy. We can use this knowledge to determine the amount of energy in a system, the
Laws of Thermodynamics The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - The first lawof thermodynamics, also called conservation of energy. We can use this knowledge to determine the amount of energy in a system, the
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law
 Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Zeroth law temperature First law energy Second law - entropy CY1001 2010
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Zeroth law temperature First law energy Second law - entropy CY1001 2010
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES. These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley.
 THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
12 The Laws of Thermodynamics
 June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
Readings for this homework assignment and upcoming lectures
 Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
UNIVERSITEIT VAN PRETORIA / UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA DEPT WISKUNDE EN TOEGEPASTE WISKUNDE DEPT OF MATHEMATICS AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS
 UNIVERSITEIT VAN PRETORIA / UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA DEPT WISKUNDE EN TOEGEPASTE WISKUNDE DEPT OF MATHEMATICS AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS VAN/SURNAME: VOORNAME/FIRST NAMES: WTW 218 - CALCULUS SEMESTERTOETS /
UNIVERSITEIT VAN PRETORIA / UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA DEPT WISKUNDE EN TOEGEPASTE WISKUNDE DEPT OF MATHEMATICS AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS VAN/SURNAME: VOORNAME/FIRST NAMES: WTW 218 - CALCULUS SEMESTERTOETS /
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
Phys 22: Homework 10 Solutions W A = 5W B Q IN QIN B QOUT A = 2Q OUT 2 QOUT B QIN B A = 3Q IN = QIN B QOUT. e A = W A e B W B A Q IN.
 HRK 26.7 Summarizing the information given in the question One way of doing this is as follows. W A = 5W Q IN A = Q IN Q OU A = 2Q OU Use e A = W A Q IN = QIN A QOU Q IN A A A and e = W Q IN = QIN QOU
HRK 26.7 Summarizing the information given in the question One way of doing this is as follows. W A = 5W Q IN A = Q IN Q OU A = 2Q OU Use e A = W A Q IN = QIN A QOU Q IN A A A and e = W Q IN = QIN QOU
Unified Thermodynamics Quiz 1
 Unified Thermodynamics Quiz 1 November 22, 2006 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
Unified Thermodynamics Quiz 1 November 22, 2006 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 5. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
