Refrigeration. 05/04/2011 T.Al-Shemmeri 1
|
|
|
- Barnaby Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Refrigeration is a process of controlled removal of heat from a substance to keep it at a temperature below the ambient condition, often below the freezing point of water (0 O C) 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
2 Refrigeration In principle, It is based on the fact that when a liquid is allowed to evaporate, it will absorb heat from its surroundings. 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
3 Domestic: fridges, freezers. Transportation: refrigerated containers Industrial: dairies, brewing, ice cream, Commercial: supermarkets, hotels and restaurants. Air-conditioning: hospitals, offices, aeroplanes, trains, cars. Leisure and Sports : ice rinks. 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 3
4 The principle of a Heat Engine in which fuel is burnt to produce work (drive the car), the exhaust rejects lower quality heat to the ambient. = Q - Q according to the first law of thermodynamics HOT RESERVOIR Q HEAT ENGINE COLD RESERVOIR Q 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 4
5 The principle of a Heat Pump in which work (motor), is used to drive a compressor pumping the gas to a higher pressure, then let it through a condenser to loose heat, and finally suddenly drop its pressure allowing to vapourise and hence absorb heat from its surroundings, hence Q = Q - according to the first law of thermodynamics HOT RESERVOIR Q HOT RESERVOIR Q HEAT PUMP HEAT ENGINE COLD RESERVOIR Q COLD RESERVOIR Q 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 5
6 The reason this is known as Heat Pump because it is possible to utilise both heat terms Q and Q. HOT RESERVOIR Q HEAT PUMP COLD RESERVOIR Q 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 6
7 Both COP are related to each other, According to Energy Conservation : Q Q = Or Q = Q + Divide equation by, to get : Q / = Q / + COP H = COP R + 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 7
8 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 8
9 Simple Refrigeration cycle: 4 processes: - Isentropic compression 3 CONDENSER - 3 Condensation at constant pressure 3-4 Throttling at constant enthalpy EVAPORATOR 4 - Evaporation at constant pressure 4 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 9
10 3 CONDENSER P 3 EVAPORATOR 4 4 h 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 0
11 Calculations for ideal compression, 00% isentropic: 3 Input ork = m r ( h h ) Refrigeration Effect Q 4 = m r ( h h 4 ) Heating Effect Q 3 = m r (h h 3 ) If the Refrigerant mass is not specified, calculate on kg/s basis. Q COP = 3 H 4 h Q COP = 4 R 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
12 Calculations for irreverible compression, less than 00%: 3 if h is the actual enthalpy after compression, and h is the ideal value, at constant entropy curve. Then the compressor s isentropic efficiency is defined as: η c 4 = h h ' h h h 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
13 Calculations for irreverible compression, less than 00%: 3 Input ork = m r ( h h ) Refrigeration Effect Q 4 = m r ( h h 4 ) Heating Effect Q 3 = m r (h h 3 ) If the Refrigerant mass is not specified, calculate on kg/s basis. Q COP = 4 R 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 3 4 h Q COP = 3 H
14 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 4
15 Enthalpy h (kj/kg) Pressure P( bar ) X- axis Y-axis Temp T ( C) on inside of the Curve Volume v( m 3 /kg) lines ( curves ) at 0 o to horizontal Entropy s (kj/kgk) lines ( curves ) at o to horizontal 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 5
16 3 condenser 4 Heat Exchanger 5 6 evaporator compressor p Expansion Valve h 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 6
17 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 7
18 SOLVED EXAMPLE A heat pump is used to heat a factory during winter with average outside temperature being 0 o C and the factory temperature is to be maintained at 0 o C. The building heating load is estimated as 00 k. Determine the minimum power requirement to drive the HP unit for this application. 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 8
19 SOLUTION EXAMPLE COP but H COP hence min max = = T / T 73/ 93 = H max = = Q COP Q max L = H = 6. 8 k /04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 9
20 SOLVED EXAMPLE A refrigerator using R as the working fluid. The refrigerant enters the compressor as saturated vapour at bar and on leaving the condenser it is saturated liquid at 8 bar (absolute). Assume that the compression process is 00% isentropic, and that there is no superheating or subcooling effects and that pressure losses are negligible. Calculate using the chart: the work of compression, the refrigerating effect, the coefficient of performance - compare this value with the Carnot performance Solution: Construct the cycle on the P-h chart find h=45 kj/kg h=70 kj/kg h3 = h4 = 30 kj/kg Hence: ork of compressor c = h-h=4 kj/kg Refrigeration effect RE = h-h4=6 kj/kg COP R = RE/c=4.83 Note that COP ideal T = T T 60 = =. 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri 0
21 SOLVED EXAMPLE 3 A refrigerator using R34a as a Retrofit working fluid to replace R in the system of example 7.5. The refrigerant enters the compressor as saturated vapour at bar and on leaving the condenser it is saturated liquid at 8 bar (absolute). Assume that the compression process is 00% isentropic, and that there is no superheating or subcooling effects and that pressure looses are negligible. Calculate using the chart: the work of compression, the refrigerating effect, the coefficient of performance. Solution: Construct the cycle on the P-h chart, find enthalpies at key state points: h =95 kj/kg h =35 kj/kg h3 = h4 =45 kj/kg Hence: ork of compressor c= h-h=30 kj/kg Refrigeration effect RE=h-h4=50 kj/kg Coefficient of Performance COP R =RE/c= 5.0 which is better than that for R but still not as good as the ideal value of /04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Unit Workbook 2 - Level 5 ENG U64 Thermofluids 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Readings for this homework assignment and upcoming lectures
 Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002
 10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Test 2 Solution Problem 1 (35 points) High pressure steam (stream 1) at a rate of 1000 kg/h initially at 3.5 MPa and 350 ºC is expanded in a turbine
10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Test 2 Solution Problem 1 (35 points) High pressure steam (stream 1) at a rate of 1000 kg/h initially at 3.5 MPa and 350 ºC is expanded in a turbine
Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 10 Phase Change
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.21 The Physics of Energy Fall 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 8.21 Lecture 10 Phase Change
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Common Terms, Definitions and Conversion Factors
 1 Common Terms, Definitions and Conversion Factors 1. Force: A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object s interaction with another object. It is defined as Where F = m a F = Force
1 Common Terms, Definitions and Conversion Factors 1. Force: A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object s interaction with another object. It is defined as Where F = m a F = Force
Spring_#7. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
7. Development of the 2nd Law
 7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION. (1X12 = 12 Marks) Answer ONE question from each unit.
 Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION
 CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
ME 200 Final Exam December 14, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
(Refer Slide Time: 00:00:43 min) Welcome back in the last few lectures we discussed compression refrigeration systems.
 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 14 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems (Refer Slide
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 14 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems (Refer Slide
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number: Instructions
 ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1
 Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
Second Law of Thermodynamics -
 Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
SOLUTION: Consider the system to be the refrigerator (shown in the following schematic), which operates over a cycle in normal operation.
 Soln_21 An ordinary household refrigerator operating in steady state receives electrical work while discharging net energy by heat transfer to its surroundings (e.g., the kitchen). a. Is this a violation
Soln_21 An ordinary household refrigerator operating in steady state receives electrical work while discharging net energy by heat transfer to its surroundings (e.g., the kitchen). a. Is this a violation
Brown Hills College of Engineering & Technology
 UNIT 4 Flow Through Nozzles Velocity and heat drop, Mass discharge through a nozzle, Critical pressure ratio and its significance, Effect of friction, Nozzle efficiency, Supersaturated flow, Design pressure
UNIT 4 Flow Through Nozzles Velocity and heat drop, Mass discharge through a nozzle, Critical pressure ratio and its significance, Effect of friction, Nozzle efficiency, Supersaturated flow, Design pressure
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
w = -nrt hot ln(v 2 /V 1 ) nrt cold ln(v 1 /V 2 )[sincev/v 4 3 = V 1 /V 2 ]
![w = -nrt hot ln(v 2 /V 1 ) nrt cold ln(v 1 /V 2 )[sincev/v 4 3 = V 1 /V 2 ] w = -nrt hot ln(v 2 /V 1 ) nrt cold ln(v 1 /V 2 )[sincev/v 4 3 = V 1 /V 2 ]](/thumbs/85/91320285.jpg) Chemistry 433 Lecture 9 Entropy and the Second Law NC State University Spontaneity of Chemical Reactions One might be tempted based on the results of thermochemistry to predict that all exothermic reactions
Chemistry 433 Lecture 9 Entropy and the Second Law NC State University Spontaneity of Chemical Reactions One might be tempted based on the results of thermochemistry to predict that all exothermic reactions
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION. 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance in thermodynamics.
 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES. These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley.
 THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
Thermodynamic Analysis of the Effect of Generator Temperature on the Performance of a Single-Effect Absorption Refrigeration Cycle
 Thermodynamic Analysis of the Effect of Generator Temperature on the Performance of a Single-Effect Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Abstract Debendra Nath Sarkar 1, Dipankar Narayan Basu 2 1 UG 4 th Year
Thermodynamic Analysis of the Effect of Generator Temperature on the Performance of a Single-Effect Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Abstract Debendra Nath Sarkar 1, Dipankar Narayan Basu 2 1 UG 4 th Year
10 minutes reading time is allowed for this paper.
 EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
ME 200 Final Exam December 12, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
In the next lecture...
 16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
Existing Resources: Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics background and interests:
 Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Thermodynamic Processes & Efficiency ME 6101 (2017) 2 / 25 T145 = Q + W cv + i h 2 = h (V2 1 V 2 2)
 Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
First Steps in Thermodynamics: Absolute Beginners
 2 First Steps in Thermodynamics: Absolute Beginners Abstract: The purpose of this chapter is to discuss key concepts which should be presented to absolute beginners in order to enable them to understand
2 First Steps in Thermodynamics: Absolute Beginners Abstract: The purpose of this chapter is to discuss key concepts which should be presented to absolute beginners in order to enable them to understand
Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall 2006
 FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
5.2. The Rankine Cycle
 Figure 5.1. Illustration of a Carnot cycle based on steam in T-S coordinates. The Carnot cycle has a major advantage over other cycles. It operates at the highest temperature available for as long as possible,
Figure 5.1. Illustration of a Carnot cycle based on steam in T-S coordinates. The Carnot cycle has a major advantage over other cycles. It operates at the highest temperature available for as long as possible,
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
1. j&& 100 &o 2. %4k%-ig#3g%m+~%%a*&4+s 5fl~J6?~+* O
 1. j&& 100 &o 2. %4k%-ig#3g%m+~%%a*&4+s 5fl~J6?~+* O 3. Mathematical and governing equations are listed in page 6. Problem 1. &$Fa ( ff- 10 /J.% 9 $./J.% 2 @ ff- 20 %) ( ) 1. Compressibility factor, Z,
1. j&& 100 &o 2. %4k%-ig#3g%m+~%%a*&4+s 5fl~J6?~+* O 3. Mathematical and governing equations are listed in page 6. Problem 1. &$Fa ( ff- 10 /J.% 9 $./J.% 2 @ ff- 20 %) ( ) 1. Compressibility factor, Z,
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
MAE 11. Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018
 MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Chapter 20 Second Law of Thermodynamics. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Second Law of Thermodynamics It is easy to produce thermal energy using work, but how does one produce work using thermal energy? This is a heat engine; mechanical energy can be obtained from
Chapter 20 Second Law of Thermodynamics It is easy to produce thermal energy using work, but how does one produce work using thermal energy? This is a heat engine; mechanical energy can be obtained from
Elements of Mechanical Engineering
 2011 Elements of Mechanical Engineering AMRAT PATEL Asst. Professor 1/17/2011 Smt Shantaben Haribhai Gajera Charitable Trust, Surat LAXMI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, SARIGAM BE I, Sem I (Section: A, B & C)
2011 Elements of Mechanical Engineering AMRAT PATEL Asst. Professor 1/17/2011 Smt Shantaben Haribhai Gajera Charitable Trust, Surat LAXMI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, SARIGAM BE I, Sem I (Section: A, B & C)
RECORD AND ANALYSE THE PRESSURE-ENTHALPY DIAGRAM FOR A COMPRESSION HEAT PUMP
 Thermodynamics Heat cycles Heat Pump RECORD AND ANALYSE THE PRESSURE-ENTHALPY DIAGRAM FOR A COMPRESSION HEAT PUMP Demonstrate how an electric compression heat pump works Quantitatively investigate of the
Thermodynamics Heat cycles Heat Pump RECORD AND ANALYSE THE PRESSURE-ENTHALPY DIAGRAM FOR A COMPRESSION HEAT PUMP Demonstrate how an electric compression heat pump works Quantitatively investigate of the
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles
 An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6301-ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems
 ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 10 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A VAPOUR ABSORPTION REFRIGERATION UNIT
 ISSN 1726-4529 Int j simul model 9 (2010) 2, 86-97 Original scientific paper MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A VAPOUR ABSORPTION REFRIGERATION UNIT Micallef, D. & Micallef, C. University of Malta, Department of
ISSN 1726-4529 Int j simul model 9 (2010) 2, 86-97 Original scientific paper MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A VAPOUR ABSORPTION REFRIGERATION UNIT Micallef, D. & Micallef, C. University of Malta, Department of
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Basic thermodynamics. heat to the high temperature reservoir.
 Consider a heat engine that is operating in a cyclic process takes heat (QH) from a high temperature reservoir & converts completely into work (W), violating the Kelvin Planck statement. Let the work W,
Consider a heat engine that is operating in a cyclic process takes heat (QH) from a high temperature reservoir & converts completely into work (W), violating the Kelvin Planck statement. Let the work W,
Laws of Thermodynamics
 Laws of Thermodynamics The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - The first lawof thermodynamics, also called conservation of energy. We can use this knowledge to determine the amount of energy in a system, the
Laws of Thermodynamics The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - The first lawof thermodynamics, also called conservation of energy. We can use this knowledge to determine the amount of energy in a system, the
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
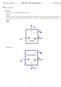 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
Availability and Irreversibility
 Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002
 16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
1. Basic state values of matter
 1. Basic state values of matter Example 1.1 The pressure inside a boiler is p p = 115.10 5 Pa and p v = 9.44.10 4 Pa inside a condenser. Calculate the absolute pressure inside the boiler and condenser
1. Basic state values of matter Example 1.1 The pressure inside a boiler is p p = 115.10 5 Pa and p v = 9.44.10 4 Pa inside a condenser. Calculate the absolute pressure inside the boiler and condenser
Thermodynamics Lecture Series
 Thermodynamics Lecture Series Second Law uality of Energy Applied Sciences Education Research Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@hotmail.com http://www.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj.html
Thermodynamics Lecture Series Second Law uality of Energy Applied Sciences Education Research Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@hotmail.com http://www.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj.html
Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology New Delhi II Semester MEL 140 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 PROBLEM SET 1: Review of Basics Problem 1: Define Work. Explain how the force is generated in an automobile. Problem 2: Define and classify Energy and explain the relation between a body and energy. Problem
PROBLEM SET 1: Review of Basics Problem 1: Define Work. Explain how the force is generated in an automobile. Problem 2: Define and classify Energy and explain the relation between a body and energy. Problem
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
Investigations on Performance of an Auto-Cascade Absorption Refrigeration System Operating with Mixed Refrigerants
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Investigations on Performance of an Auto-Cascade Absorption Refrigeration
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Investigations on Performance of an Auto-Cascade Absorption Refrigeration
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Air is a mixture of several gases, but it is considered to be a pure
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES PURE SUBSTANCE Pure substance: A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout. Air is a mixture of several gases, but it is considered to be a pure
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles
 Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
Chapter 7. Dr Ali Jawarneh. Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University
 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
ME 2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW
 ME 2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW 1. What is thermodynamics? It is a basic science that deals with energy and its transformations. The
ME 2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW 1. What is thermodynamics? It is a basic science that deals with energy and its transformations. The
Ttions, and its relation to states of matter. This chapter covers the
 Related Commercial Resources CHAPTER 1 THERMODYNAMICS AND REFRIGERATION CYCLES THERMODYNAMICS... 1.1 First Law of Thermodynamics... 1.2 Second Law of Thermodynamics... 1.2 Thermodynamic Analysis of Refrigeration
Related Commercial Resources CHAPTER 1 THERMODYNAMICS AND REFRIGERATION CYCLES THERMODYNAMICS... 1.1 First Law of Thermodynamics... 1.2 Second Law of Thermodynamics... 1.2 Thermodynamic Analysis of Refrigeration
ME 200 Exam 2 October 16, :30 p.m. to 7:30 p.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Solution Last Name 7:30 am 8:30 am 10:30 am 11:30 am Joglekar Bae Gore Abraham 1:30 pm 3:30 pm 4:30 pm Naik Naik Cheung ME 200 Exam 2 October 16, 2013 6:30 p.m. to
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Solution Last Name 7:30 am 8:30 am 10:30 am 11:30 am Joglekar Bae Gore Abraham 1:30 pm 3:30 pm 4:30 pm Naik Naik Cheung ME 200 Exam 2 October 16, 2013 6:30 p.m. to
THE METHOD OF THE WORKING FLUID SELECTION FOR ORGANIC RANKINE CYCLE (ORC) SYSTEM WITH VOLUMETRIC EXPANDER. * Corresponding Author ABSTRACT
 Paper ID: 79, Page 1 THE METHOD OF THE WORKING FLUID SELECTION FOR ORGANIC RANKINE CYCLE (ORC) SYSTEM WITH VOLUMETRIC EXPANDER Piotr Kolasiński* 1 1 Wrocław University of Technology, Department of Thermodynamics,
Paper ID: 79, Page 1 THE METHOD OF THE WORKING FLUID SELECTION FOR ORGANIC RANKINE CYCLE (ORC) SYSTEM WITH VOLUMETRIC EXPANDER Piotr Kolasiński* 1 1 Wrocław University of Technology, Department of Thermodynamics,
Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy
 Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy The second law of thermodynamics The first law relates heat energy, work and the internal thermal energy of a system, and is essentially a statement
Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy The second law of thermodynamics The first law relates heat energy, work and the internal thermal energy of a system, and is essentially a statement
Mathematical Modelling for Refrigerant Flow in Diabatic Capillary Tube
 Mathematical Modelling for Refrigerant Flow in Diabatic Capillary Tube Jayant Deshmukh Department of Mechanical Engineering Sagar Institute of Research and Technology, Bhopal, M.P., India D.K. Mudaiya
Mathematical Modelling for Refrigerant Flow in Diabatic Capillary Tube Jayant Deshmukh Department of Mechanical Engineering Sagar Institute of Research and Technology, Bhopal, M.P., India D.K. Mudaiya
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number:
 ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
IS A PARTICULAR PROCESS / REACTION FEASIBLE? TO WHAT EXTENT DOES THE PROCESS / REACTION PROCEED?
 Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 5. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams
 Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
Part III: Planes, Trains, and Automobiles: Making Heat Work for You
 Contents at a Glance Introduction... 1 Part I: Covering the Basics in Thermodynamics... 7 Chapter 1: Thermodynamics in Everyday Life...9 Chapter 2: Laying the Foundation of Thermodynamics...15 Chapter
Contents at a Glance Introduction... 1 Part I: Covering the Basics in Thermodynamics... 7 Chapter 1: Thermodynamics in Everyday Life...9 Chapter 2: Laying the Foundation of Thermodynamics...15 Chapter
