From bits to qubits: a quantum leap for computers
|
|
|
- Rudolph Johnston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 From bits to qubits: a quantum leap for computers Susan Coppersmith University of Wisconsin-Madison Department of Physics
2 Susan Coppersmith career path: it felt like I was muddling along. B.S. from MIT Ph.D. from Cornell Postdocs at Brookhaven National Laboratory and AT&T Bell Laboratories Visiting lecturer at Princeton married in grad school husband obtained MD-PhD, then did medical internship, residency, and fellowship Member of Technical Staff at AT&T Bell Laboratories husband finished training Professor at University of Chicago daughter was born Professor at University of Wisconsin-Madison Exposure to a variety of environments has been a big plus. Coordination with family has been challenging but rewarding. Main advice: work with people you like, on things that you find really interesting.
3 Since before 1960, the capabilities of digital electronic devices have grown exponentially Regency TR-1 transistor radio (1954) 4 transistors $49.95, equivalent to $427 today from Wikipedia iphone 5s ~100,000,000 transistors $620 (unlocked)
4 The numbers of transistors in a device has kept increasing because the area per transistor has been shrinking. 1970: ~200 transistors per square millimeter 2011: >1,000,000 transistors per square millimeter
5 Transistor sizes continue to shrink with time. Feature Size K. Kulin, Proceedings of IWCE '09. 13th International Workshop on Computational Electronics, 2009 year New Intel 2013 fab facility: feature sizes of 14 nanometers
6 But transistors cannot shrink indefinitely! Current transistor sizes are only a few times the size of atoms. It is impossible to shrink transistors to be smaller than the size of one silicon atom.
7 Feature sizes cannot shrink past one nanometer, the size of one silicon atom. What happens then? feature size (nanometers) 10, ??? year
8 Eventually, it will not be feasible to make computers faster by shrinking the size of transistors. But at the smallest sizes possible, it may be possible to make computers faster by exploiting the fundamental laws of physics.
9 Behavior on small length scales is governed by the laws of quantum mechanics, which are different from the laws of classical mechanics that govern objects in everyday life. Example: a spin Classical mechanics: a measurement of the value of a component of spin can take any in a range of values. Quantum mechanics: The results of possible measurements are quantized they only take on one of a finite set of values. For an electron: each measurement of the spin yields one of only two values. We ll call them ħ/2 and -ħ/2.
10 Measurements of electron spins yield only two values, ħ/2 and -ħ/2. An experimental procedure can prepare spins, each of which yields the result ħ/2 for a measurement of spin along a certain axis ( the spin is along the z axis ). If you prepare the spins the same way and measure along a perpendicular axis, half the spins will yield the result ħ/2 and half will yield the result -ħ/2. Stern-Gerlach experiment (1922)
11 In quantum mechanics, a measurement changes the quantum state ( the quantum state collapses ) If you prepare a population of electrons, all in a given spin state in which half the electrons, when measured along a certain axis, have spin ħ/2 and the other half have spin -ħ/2. If you measure any of those electrons along that axis a second (or third, or fourth...) time, you will always get the same answer! measurement # electron 1 electron 2 electron 3 electron ħ/2 - ħ/2 - ħ/2 + ħ/2 2 + ħ/2 - ħ/2 - ħ/2 + ħ/2 3 + ħ/2 - ħ/2 - ħ/2 + ħ/2 4 + ħ/2 - ħ/2 - ħ/2 + ħ/2 5 + ħ/2 - ħ/2 - ħ/2 + ħ/2
12 Why care about the laws of quantum physics? A quantum computer that exploits the laws of quantum physics could perform some calculations much faster than the classical computers that we have now.
13 Bits versus qubits: classical versus quantum spins θ φ S y S x ~S = S x î + S y ĵ + S zˆk Classical spin: specified by 3 continuous variables. Can measure Sx, Sy, and Sz simultaneously. Each has a range of possible values.
14 Bits versus qubits: classical versus quantum spins S x θ φ S y ~S = S x î + S y ĵ + S zˆk Quantum spin: can only simultaneously specify S 2 and (say) Sz. Values are quantized. Classical spin: specified by 3 continuous variables. Can measure Sx, Sy, and Sz simultaneously. Each has a range of possible values..., =, all measurements of Sx, Sy, and Sz yield either / or /. Qubit: = =
15 Specifying classical and quantum states of N spins φ 1 θ 1 φ 2 θ 2 φ 3 θ 3 Classical: 2N numbers
16 Specifying classical and quantum states of N spins φ 1 θ 1 φ 2 θ 2 φ 3 θ 3 Classical: 2N numbers ψ = A A A A A A A A Quantum: 2 N numbers Need exponentially more numbers to specify the quantum wavefunction than the classical state.
17 Specifying classical and quantum states of N spins θ 1 θ 2 θ 3 φ 4 θ 4 Classical: 2N numbers φ 1 φ 2 φ 3 Quantum: 2 N numbers Need exponentially more numbers to specify the quantum wavefunction than the classical state.
18 Specifying classical and quantum states of N spins θ 1 θ 2 θ 3 φ 4 θ 4 Classical: 2N numbers φ 1 φ 2 φ 3 Quantum: 2 N numbers Need exponentially more numbers to specify the quantum wavefunction than the classical state. Complication: measurement collapses wavefunction
19 A computer that exploits the laws of quantum mechanics can solve some problems faster than one obeying laws of classical mechanics Quantum simulation (exponential (?)) [Feynman 1982] Shor s factoring algorithm (exponential speedup (?)) [Shor 1994] Grover s database search algorithm ( N versus N) [Grover 1996]
20 To build a quantum computer, one needs to be able to perform all the necessary spin operations without measuring the spins unintentionally. In other words, one must control the quantum evolution without destroying quantum coherence. Figure of merit: coherence time gate operation time Need figure of merit >10 4 for scalable quantum computation. Need fast operations and long coherence times.
21 Several different schemes for quantum computing are being pursued. For example: Trapped ions Superconductors Neutral atoms 14 qubits 4 qubits ~6 qubits
22 Current status: Many different groups are pursuing different physical implementations of quantum computation. The largest coherent quantum computer that has been built so far has 14 qubits. (It can factor 21=3 7.) Need many more qubits to be more powerful than current classical computers. Monz, T. et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, (2011).
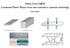
23 UW Si/SiGe quantum dot quantum computer Overview of our approach: quantum dots in Si/SiGe heterostructures confined and controlled with voltages applied using top gates metal gates to confine and control electrons electrons are confined to thin silicon layer sandwiched between silicon-germanium One electron per quantum dot QR L PL T M 200 nm QL R PR IQPC Voltages applied to top gates define electron potentials. Measure system by measuring current through quantum point contact (QPC), which depends on how many electrons are in each quantum dot.
24 UW- Madison Solid- State Quantum Compu;ng Team PI: Mark Eriksson Zhan Shi, Christine Simmons, Dohun Kim, Jon Prance, Dan Ward, Xian Wu, Robert Mohr, Don Savage, Max Lagally, Robert Joynt SNC theory collaborators: Mark Friesen, John Gamble, Xuedong Hu, Teck Seng Koh Sponsored in part by the Army Research Office, the National Science Foundation, and the United States Department of Defense. The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official policies, either expressly or implied, of the U.S. Government.
25 Current status of Si/SiGe quantum dot quantum computer: we just got one qubit to work. X. Shi et al., Nature Communications 5, 3020 (2014); D. Kim et al., arxiv:1401.xxxx Why are we excited about just one qubit? Our methods for fabricating our qubit is similar to those used for classical electronics. So if we can fabricate one high quality qubit, there is a good chance that we can scale up the process. So we need to make the qubit very high quality.
26 Assessing qubit quality look for long-lived quantum oscillations Prepare electron spins in a quantum state where, if it is not measured, it would oscillate between and (spin ħ/2 and spin -ħ/2). Prepare lots of spins the same way, and measure their spin states at different times. The average of the spin state oscillates as a function of time, until it has been measured by its environment. 1.0 gray scale plot of spin value average spin value time 0.4 time 0.2 Need to get >1000 oscillations for a scalable qubit
27 Previous work with highest figure of merit for a quantum dot qubit ~20 oscillations B.M. Maune et al., Nature 481, 344 (2012)
28 Previous work with highest figure of merit for a quantum dot qubit ~20 oscillations B.M. Maune et al., Nature 481, 344 (2012) Our quantum dot qubit now has >100 oscillations (theory predicts that >1000 is achievable) 200 Prob. of Y= tp(s) tp(ns) D. Kim et al., arxiv:1401.xxxx
29 Summary Feature sizes in silicon electronics continue to shrink and in the foreseeable future will become comparable to the size of silicon atoms, where quantum effects become very important. Quantum computers that exploit the laws of quantum physics could perform some calculations much faster than any classical computer. A new quantum dot hybrid qubit that enables faster gating has been developed. Initial experiments on hybrid quantum dot qubit are promising.
30 Thank you!
31 Thank you! Questions?
32 Our new hybrid quantum dot qubit enables fast qubit operations in a relatively simple (and hence relatively easy-to-fabricate) architecture Z. Shi et. al, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, (2012) T.S. Koh et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, (2012) device (top view) manipulation voltage pulse T 200 nm QR QL V L Vp tp IQPC L PL M PR R t tp ~ 100ps - 4 ns
33 A hybrid 3-electron qubit: T S Z. Shi et. al, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, (2012) J. Gamble et al., Phys. Rev. B 86, (2012).
34 Gates for hybrid qubit are fast because all gate operations are controlled electrically Singlet Triplet
35 Gates for hybrid qubit are fast because all gate operations are controlled electrically Singlet Triplet
36 Gates for hybrid qubit are fast because all gate operations are controlled electrically Singlet Triplet
37 Gates for hybrid qubit are fast because all gate operations are controlled electrically Singlet Triplet
38 Gates for hybrid qubit are fast because all gate operations are controlled electrically Singlet Triplet Charge transitions change the spin state in the left dot from singlet to triplet.
39 Our theoretical calculations yield a coherence time of hybrid qubit of ~1μs in Si (versus < 1ns for charge qubit). J. Gamble et al., Phys. Rev. B 86, (2012) Theory predicts that hybrid qubit gate operations can be performed at ~10 GHz Figure of merit of 10 4 (if theory is correct).
Building a quantum computer using quantum dots in silicon. Susan Coppersmith. University of Wisconsin-Madison Department of Physics
 Building a quantum computer using quantum dots in silicon Susan Coppersmith University of Wisconsin-Madison Department of Physics UW-Madison Solid-State Quantum Compu5ng Team PI: Mark Eriksson Sam Neyens,
Building a quantum computer using quantum dots in silicon Susan Coppersmith University of Wisconsin-Madison Department of Physics UW-Madison Solid-State Quantum Compu5ng Team PI: Mark Eriksson Sam Neyens,
Quantum Computing. The Future of Advanced (Secure) Computing. Dr. Eric Dauler. MIT Lincoln Laboratory 5 March 2018
 The Future of Advanced (Secure) Computing Quantum Computing This material is based upon work supported by the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering and the Office of the Director
The Future of Advanced (Secure) Computing Quantum Computing This material is based upon work supported by the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering and the Office of the Director
Magnetic semiconductors. (Dilute) Magnetic semiconductors
 Magnetic semiconductors We saw last time that: We d like to do spintronics in semiconductors, because semiconductors have many nice properties (gateability, controllable spin-orbit effects, long spin lifetimes).
Magnetic semiconductors We saw last time that: We d like to do spintronics in semiconductors, because semiconductors have many nice properties (gateability, controllable spin-orbit effects, long spin lifetimes).
phys4.20 Page 1 - the ac Josephson effect relates the voltage V across a Junction to the temporal change of the phase difference
 Josephson Effect - the Josephson effect describes tunneling of Cooper pairs through a barrier - a Josephson junction is a contact between two superconductors separated from each other by a thin (< 2 nm)
Josephson Effect - the Josephson effect describes tunneling of Cooper pairs through a barrier - a Josephson junction is a contact between two superconductors separated from each other by a thin (< 2 nm)
Single Electron Transistor (SET)
 Single Electron Transistor (SET) SET: e - e - dot A single electron transistor is similar to a normal transistor (below), except 1) the channel is replaced by a small dot. C g 2) the dot is separated from
Single Electron Transistor (SET) SET: e - e - dot A single electron transistor is similar to a normal transistor (below), except 1) the channel is replaced by a small dot. C g 2) the dot is separated from
Supercondcting Qubits
 Supercondcting Qubits Patricia Thrasher University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195 Superconducting qubits are electrical circuits based on the Josephson tunnel junctions and have the ability to
Supercondcting Qubits Patricia Thrasher University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195 Superconducting qubits are electrical circuits based on the Josephson tunnel junctions and have the ability to
CMSC 33001: Novel Computing Architectures and Technologies. Lecture 06: Trapped Ion Quantum Computing. October 8, 2018
 CMSC 33001: Novel Computing Architectures and Technologies Lecturer: Kevin Gui Scribe: Kevin Gui Lecture 06: Trapped Ion Quantum Computing October 8, 2018 1 Introduction Trapped ion is one of the physical
CMSC 33001: Novel Computing Architectures and Technologies Lecturer: Kevin Gui Scribe: Kevin Gui Lecture 06: Trapped Ion Quantum Computing October 8, 2018 1 Introduction Trapped ion is one of the physical
Quantum Dot Spin QuBits
 QSIT Student Presentations Quantum Dot Spin QuBits Quantum Devices for Information Technology Outline I. Double Quantum Dot S II. The Logical Qubit T 0 III. Experiments I. Double Quantum Dot 1. Reminder
QSIT Student Presentations Quantum Dot Spin QuBits Quantum Devices for Information Technology Outline I. Double Quantum Dot S II. The Logical Qubit T 0 III. Experiments I. Double Quantum Dot 1. Reminder
Quantum Computation 650 Spring 2009 Lectures The World of Quantum Information. Quantum Information: fundamental principles
 Quantum Computation 650 Spring 2009 Lectures 1-21 The World of Quantum Information Marianna Safronova Department of Physics and Astronomy February 10, 2009 Outline Quantum Information: fundamental principles
Quantum Computation 650 Spring 2009 Lectures 1-21 The World of Quantum Information Marianna Safronova Department of Physics and Astronomy February 10, 2009 Outline Quantum Information: fundamental principles
Introduction to Superconductivity. Superconductivity was discovered in 1911 by Kamerlingh Onnes. Zero electrical resistance
 Introduction to Superconductivity Superconductivity was discovered in 1911 by Kamerlingh Onnes. Zero electrical resistance Meissner Effect Magnetic field expelled. Superconducting surface current ensures
Introduction to Superconductivity Superconductivity was discovered in 1911 by Kamerlingh Onnes. Zero electrical resistance Meissner Effect Magnetic field expelled. Superconducting surface current ensures
News from NBIA. Condensed Matter Physics: from new materials to quantum technology. time. Mark Rudner
 News from NBIA Condensed Matter Physics: from new materials to quantum technology Mark Rudner time ~100 years after Bohr, the basic laws and players are established 1913 2013 Image from www.periodni.com
News from NBIA Condensed Matter Physics: from new materials to quantum technology Mark Rudner time ~100 years after Bohr, the basic laws and players are established 1913 2013 Image from www.periodni.com
Solid-State Spin Quantum Computers
 Solid-State Spin Quantum Computers 1 NV-Centers in Diamond P Donors in Silicon Kane s Computer (1998) P- doped silicon with metal gates Silicon host crystal + 31 P donor atoms + Addressing gates + J- coupling
Solid-State Spin Quantum Computers 1 NV-Centers in Diamond P Donors in Silicon Kane s Computer (1998) P- doped silicon with metal gates Silicon host crystal + 31 P donor atoms + Addressing gates + J- coupling
Deterministic Coherent Writing and Control of the Dark Exciton Spin using Short Single Optical Pulses
 Deterministic Coherent Writing and Control of the Dark Exciton Spin using Short Single Optical Pulses Ido Schwartz, Dan Cogan, Emma Schmidgall, Liron Gantz, Yaroslav Don and David Gershoni The Physics
Deterministic Coherent Writing and Control of the Dark Exciton Spin using Short Single Optical Pulses Ido Schwartz, Dan Cogan, Emma Schmidgall, Liron Gantz, Yaroslav Don and David Gershoni The Physics
Silicon-based Quantum Computing:
 Silicon-based Quantum Computing: The path from the laboratory to industrial manufacture Australian National Fabrication Facility Andrew Dzurak UNSW - Sydney a.dzurak@unsw.edu.au Leti Innovation Days, Grenoble,
Silicon-based Quantum Computing: The path from the laboratory to industrial manufacture Australian National Fabrication Facility Andrew Dzurak UNSW - Sydney a.dzurak@unsw.edu.au Leti Innovation Days, Grenoble,
1.0 Introduction to Quantum Systems for Information Technology 1.1 Motivation
 QSIT09.V01 Page 1 1.0 Introduction to Quantum Systems for Information Technology 1.1 Motivation What is quantum mechanics good for? traditional historical perspective: beginning of 20th century: classical
QSIT09.V01 Page 1 1.0 Introduction to Quantum Systems for Information Technology 1.1 Motivation What is quantum mechanics good for? traditional historical perspective: beginning of 20th century: classical
Design Considerations for Integrated Semiconductor Control Electronics for a Large-scale Solid State Quantum Processor
 Design Considerations for Integrated Semiconductor Control Electronics for a Large-scale Solid State Quantum Processor Hendrik Bluhm Andre Kruth Lotte Geck Carsten Degenhardt 1 0 Ψ 1 Quantum Computing
Design Considerations for Integrated Semiconductor Control Electronics for a Large-scale Solid State Quantum Processor Hendrik Bluhm Andre Kruth Lotte Geck Carsten Degenhardt 1 0 Ψ 1 Quantum Computing
State-conditional coherent charge qubit oscillations in a Si/SiGe quadruple quantum dot
 www.nature.com/npjqi ARTICLE OPEN State-conditional coherent charge qubit oscillations in a Si/SiGe quadruple quantum dot Daniel R Ward 1,2,5, Dohun Kim 1,3,5, Donald E Savage 4, Max G Lagally 4, Ryan
www.nature.com/npjqi ARTICLE OPEN State-conditional coherent charge qubit oscillations in a Si/SiGe quadruple quantum dot Daniel R Ward 1,2,5, Dohun Kim 1,3,5, Donald E Savage 4, Max G Lagally 4, Ryan
Some Introductory Notes on Quantum Computing
 Some Introductory Notes on Quantum Computing Markus G. Kuhn http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/ Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge 2000-04-07 1 Quantum Computing Notation Quantum Computing is best
Some Introductory Notes on Quantum Computing Markus G. Kuhn http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/ Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge 2000-04-07 1 Quantum Computing Notation Quantum Computing is best
Promise of Quantum Computation
 Quantum Computation, and Epilog: The Future of Computing 1 Promise of Quantum Computation Classical computers have their limitations: Factoring large numbers takes exponential time. No faster algorithm
Quantum Computation, and Epilog: The Future of Computing 1 Promise of Quantum Computation Classical computers have their limitations: Factoring large numbers takes exponential time. No faster algorithm
MA 3260 Lecture 10 - Boolean Algebras (cont.) Friday, October 19, 2018.
 MA 3260 Lecture 0 - Boolean Algebras (cont.) Friday, October 9, 208. Objectives: Boolean algebras on { 0, }. Before we move on, I wanted to give you a taste of what the connection between Boolean algebra
MA 3260 Lecture 0 - Boolean Algebras (cont.) Friday, October 9, 208. Objectives: Boolean algebras on { 0, }. Before we move on, I wanted to give you a taste of what the connection between Boolean algebra
quantum mechanics is a hugely successful theory... QSIT08.V01 Page 1
 1.0 Introduction to Quantum Systems for Information Technology 1.1 Motivation What is quantum mechanics good for? traditional historical perspective: beginning of 20th century: classical physics fails
1.0 Introduction to Quantum Systems for Information Technology 1.1 Motivation What is quantum mechanics good for? traditional historical perspective: beginning of 20th century: classical physics fails
 Image courtesy of Keith Schwab http://www.lbl.gov/science-articles/archive/afrd Articles/Archive/AFRD-quantum-logic.html http://www.wmi.badw.de/sfb631/tps/dqd2.gif http://qist.lanl.gov/qcomp_map.shtml
Image courtesy of Keith Schwab http://www.lbl.gov/science-articles/archive/afrd Articles/Archive/AFRD-quantum-logic.html http://www.wmi.badw.de/sfb631/tps/dqd2.gif http://qist.lanl.gov/qcomp_map.shtml
Two-qubit Gate of Combined Single Spin Rotation and Inter-dot Spin Exchange in a Double Quantum Dot
 Two-qubit Gate of Combined Single Spin Rotation and Inter-dot Spin Exchange in a Double Quantum Dot R. Brunner 1,2, Y.-S. Shin 1, T. Obata 1,3, M. Pioro-Ladrière 4, T. Kubo 5, K. Yoshida 1, T. Taniyama
Two-qubit Gate of Combined Single Spin Rotation and Inter-dot Spin Exchange in a Double Quantum Dot R. Brunner 1,2, Y.-S. Shin 1, T. Obata 1,3, M. Pioro-Ladrière 4, T. Kubo 5, K. Yoshida 1, T. Taniyama
Quantum Information Processing
 Quantum Information Processing Jonathan Jones http://nmr.physics.ox.ac.uk/teaching The Information Age Communication Shannon Computation Turing Current approaches are essentially classical which is wrong
Quantum Information Processing Jonathan Jones http://nmr.physics.ox.ac.uk/teaching The Information Age Communication Shannon Computation Turing Current approaches are essentially classical which is wrong
Post Von Neumann Computing
 Post Von Neumann Computing Matthias Kaiserswerth Hasler Stiftung (formerly IBM Research) 1 2014 IBM Corporation Foundation Purpose Support information and communication technologies (ICT) to advance Switzerland
Post Von Neumann Computing Matthias Kaiserswerth Hasler Stiftung (formerly IBM Research) 1 2014 IBM Corporation Foundation Purpose Support information and communication technologies (ICT) to advance Switzerland
INTRODUCTORY NOTES ON QUANTUM COMPUTATION
 INTRODUCTORY NOTES ON QUANTUM COMPUTATION Keith Hannabuss Balliol College, Oxford Hilary Term 2009 Notation. In these notes we shall often use the physicists bra-ket notation, writing ψ for a vector ψ
INTRODUCTORY NOTES ON QUANTUM COMPUTATION Keith Hannabuss Balliol College, Oxford Hilary Term 2009 Notation. In these notes we shall often use the physicists bra-ket notation, writing ψ for a vector ψ
Lecture 2: Double quantum dots
 Lecture 2: Double quantum dots Basics Pauli blockade Spin initialization and readout in double dots Spin relaxation in double quantum dots Quick Review Quantum dot Single spin qubit 1 Qubit states: 450
Lecture 2: Double quantum dots Basics Pauli blockade Spin initialization and readout in double dots Spin relaxation in double quantum dots Quick Review Quantum dot Single spin qubit 1 Qubit states: 450
The Future. Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers.
 Quantum Computing Moore s Law The Future Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers. The Future Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers. When gate lengths
Quantum Computing Moore s Law The Future Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers. The Future Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers. When gate lengths
Quantum Computing. Vraj Parikh B.E.-G.H.Patel College of Engineering & Technology, Anand (Affiliated with GTU) Abstract HISTORY OF QUANTUM COMPUTING-
 Quantum Computing Vraj Parikh B.E.-G.H.Patel College of Engineering & Technology, Anand (Affiliated with GTU) Abstract Formerly, Turing Machines were the exemplar by which computability and efficiency
Quantum Computing Vraj Parikh B.E.-G.H.Patel College of Engineering & Technology, Anand (Affiliated with GTU) Abstract Formerly, Turing Machines were the exemplar by which computability and efficiency
Lecture Quantum Information Processing II: Implementations. spring term (FS) 2017
 Lecture Quantum Information Processing II: Implementations spring term (FS) 2017 Lectures & Exercises: Andreas Wallraff, Christian Kraglund Andersen, Christopher Eichler, Sebastian Krinner Please take
Lecture Quantum Information Processing II: Implementations spring term (FS) 2017 Lectures & Exercises: Andreas Wallraff, Christian Kraglund Andersen, Christopher Eichler, Sebastian Krinner Please take
Experimental Quantum Computing: A technology overview
 Experimental Quantum Computing: A technology overview Dr. Suzanne Gildert Condensed Matter Physics Research (Quantum Devices Group) University of Birmingham, UK 15/02/10 Models of quantum computation Implementations
Experimental Quantum Computing: A technology overview Dr. Suzanne Gildert Condensed Matter Physics Research (Quantum Devices Group) University of Birmingham, UK 15/02/10 Models of quantum computation Implementations
Quantum Computing An Overview
 Quantum Computing An Overview NAS Division NASA Ames Research Center TR Govindan Program Manager, QIS U.S. Army Research Office Outline Motivation Essentials of the Quantum Computing (QC) model Challenges
Quantum Computing An Overview NAS Division NASA Ames Research Center TR Govindan Program Manager, QIS U.S. Army Research Office Outline Motivation Essentials of the Quantum Computing (QC) model Challenges
Algorithms, Logic and Complexity. Quantum computation. basic explanations! &! survey of progress
 Algorithms, Logic and Complexity Quantum computation basic explanations! &! survey of progress Index Why Quantum Computation?! Quantum mechanics! D-wave! Quantum programming «If you think you understand
Algorithms, Logic and Complexity Quantum computation basic explanations! &! survey of progress Index Why Quantum Computation?! Quantum mechanics! D-wave! Quantum programming «If you think you understand
Computers of the Future? Moore s Law Ending in 2018?
 Computers of the Future? CS 221 Moore s Law Ending in 2018? Moore s Law: Processor speed / number transistors doubling approximately 18 months 1 Moore s Law Moore s Law Recent research predicts an end
Computers of the Future? CS 221 Moore s Law Ending in 2018? Moore s Law: Processor speed / number transistors doubling approximately 18 months 1 Moore s Law Moore s Law Recent research predicts an end
Lecture 8, April 12, 2017
 Lecture 8, April 12, 2017 This week (part 2): Semiconductor quantum dots for QIP Introduction to QDs Single spins for qubits Initialization Read-Out Single qubit gates Book on basics: Thomas Ihn, Semiconductor
Lecture 8, April 12, 2017 This week (part 2): Semiconductor quantum dots for QIP Introduction to QDs Single spins for qubits Initialization Read-Out Single qubit gates Book on basics: Thomas Ihn, Semiconductor
Electrical control of spin relaxation in a quantum dot. S. Amasha et al., condmat/
 Electrical control of spin relaxation in a quantum dot S. Amasha et al., condmat/07071656 Spin relaxation In a magnetic field, spin states are split b the Zeeman energ = g µ B B Provides a two-level sstem
Electrical control of spin relaxation in a quantum dot S. Amasha et al., condmat/07071656 Spin relaxation In a magnetic field, spin states are split b the Zeeman energ = g µ B B Provides a two-level sstem
Quantum Computing. Separating the 'hope' from the 'hype' Suzanne Gildert (D-Wave Systems, Inc) 4th September :00am PST, Teleplace
 Quantum Computing Separating the 'hope' from the 'hype' Suzanne Gildert (D-Wave Systems, Inc) 4th September 2010 10:00am PST, Teleplace The Hope All computing is constrained by the laws of Physics and
Quantum Computing Separating the 'hope' from the 'hype' Suzanne Gildert (D-Wave Systems, Inc) 4th September 2010 10:00am PST, Teleplace The Hope All computing is constrained by the laws of Physics and
The effect of surface conductance on lateral gated quantum devices in Si/SiGe heterostructures
 The effect of surface conductance on lateral gated quantum devices in Si/SiGe heterostructures The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
The effect of surface conductance on lateral gated quantum devices in Si/SiGe heterostructures The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
The Development of a Quantum Computer in Silicon
 The Development of a Quantum Computer in Silicon Professor Michelle Simmons Director, Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology, Sydney, Australia December 4th, 2013 Outline
The Development of a Quantum Computer in Silicon Professor Michelle Simmons Director, Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology, Sydney, Australia December 4th, 2013 Outline
ECE 340 Lecture 31 : Narrow Base Diode Class Outline:
 ECE 340 Lecture 31 : Narrow Base Diode Class Outline: Narrow-Base Diodes Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is a narrow-base diode? How does current flow in a narrow-base diode? Quick
ECE 340 Lecture 31 : Narrow Base Diode Class Outline: Narrow-Base Diodes Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is a narrow-base diode? How does current flow in a narrow-base diode? Quick
Let's Build a Quantum Computer!
 Let's Build a Quantum Computer! 31C3 29/12/2014 Andreas Dewes Acknowledgements go to "Quantronics Group", CEA Saclay. R. Lauro, Y. Kubo, F. Ong, A. Palacios-Laloy, V. Schmitt PhD Advisors: Denis Vion,
Let's Build a Quantum Computer! 31C3 29/12/2014 Andreas Dewes Acknowledgements go to "Quantronics Group", CEA Saclay. R. Lauro, Y. Kubo, F. Ong, A. Palacios-Laloy, V. Schmitt PhD Advisors: Denis Vion,
Coherent Control of a Single Electron Spin with Electric Fields
 Coherent Control of a Single Electron Spin with Electric Fields Presented by Charulata Barge Graduate student Zumbühl Group Department of Physics, University of Basel Date:- 9-11-2007 Friday Group Meeting
Coherent Control of a Single Electron Spin with Electric Fields Presented by Charulata Barge Graduate student Zumbühl Group Department of Physics, University of Basel Date:- 9-11-2007 Friday Group Meeting
Electrical Control of Single Spins in Semiconductor Quantum Dots Jason Petta Physics Department, Princeton University
 Electrical Control of Single Spins in Semiconductor Quantum Dots Jason Petta Physics Department, Princeton University g Q 2 m T + S Mirror U 3 U 1 U 2 U 3 Mirror Detector See Hanson et al., Rev. Mod. Phys.
Electrical Control of Single Spins in Semiconductor Quantum Dots Jason Petta Physics Department, Princeton University g Q 2 m T + S Mirror U 3 U 1 U 2 U 3 Mirror Detector See Hanson et al., Rev. Mod. Phys.
MITOCW ocw lec8
 MITOCW ocw-5.112-lec8 The following content is provided by MIT OpenCourseWare under a Creative Commons license. Additional information about our license and MIT OpenCourseWare in general is available at
MITOCW ocw-5.112-lec8 The following content is provided by MIT OpenCourseWare under a Creative Commons license. Additional information about our license and MIT OpenCourseWare in general is available at
Manipulating and characterizing spin qubits based on donors in silicon with electromagnetic field
 Network for Computational Nanotechnology (NCN) Purdue, Norfolk State, Northwestern, MIT, Molecular Foundry, UC Berkeley, Univ. of Illinois, UTEP Manipulating and characterizing spin qubits based on donors
Network for Computational Nanotechnology (NCN) Purdue, Norfolk State, Northwestern, MIT, Molecular Foundry, UC Berkeley, Univ. of Illinois, UTEP Manipulating and characterizing spin qubits based on donors
Building Quantum Computers: Is the end near for the silicon chip?
 Building Quantum Computers: Is the end near for the silicon chip? Presented by Dr. Suzanne Gildert University of Birmingham 09/02/2010 What is inside your mobile phone? What is inside your mobile phone?
Building Quantum Computers: Is the end near for the silicon chip? Presented by Dr. Suzanne Gildert University of Birmingham 09/02/2010 What is inside your mobile phone? What is inside your mobile phone?
Lecture 2, March 1, 2018
 Lecture 2, March 1, 2018 Last week: Introduction to topics of lecture Algorithms Physical Systems The development of Quantum Information Science Quantum physics perspective Computer science perspective
Lecture 2, March 1, 2018 Last week: Introduction to topics of lecture Algorithms Physical Systems The development of Quantum Information Science Quantum physics perspective Computer science perspective
Measurement theory for phase qubits
 Measurement theory for phase qubits Co-P.I. Alexander Korotkov, UC Riverside The team: 1) Qin Zhang, graduate student ) Dr. Abraham Kofman, researcher (started in June 005) 3) Alexander Korotkov, associate
Measurement theory for phase qubits Co-P.I. Alexander Korotkov, UC Riverside The team: 1) Qin Zhang, graduate student ) Dr. Abraham Kofman, researcher (started in June 005) 3) Alexander Korotkov, associate
400 nm Solid State Qubits (1) Daniel Esteve GROUP. SPEC, CEA-Saclay
 400 nm Solid State Qubits (1) S D Daniel Esteve QUAN UM ELECT RONICS GROUP SPEC, CEA-Saclay From the Copenhagen school (1937) Max Planck front row, L to R : Bohr, Heisenberg, Pauli,Stern, Meitner, Ladenburg,
400 nm Solid State Qubits (1) S D Daniel Esteve QUAN UM ELECT RONICS GROUP SPEC, CEA-Saclay From the Copenhagen school (1937) Max Planck front row, L to R : Bohr, Heisenberg, Pauli,Stern, Meitner, Ladenburg,
All optical quantum computation by engineering semiconductor. macroatoms. Irene D Amico. Dept. of Physics, University of York
 All optical quantum computation by engineering semiconductor macroatoms Irene D Amico Dept. of Physics, University of York (Institute for Scientific Interchange, Torino) GaAs/AlAs, GaN/AlN Eliana Biolatti
All optical quantum computation by engineering semiconductor macroatoms Irene D Amico Dept. of Physics, University of York (Institute for Scientific Interchange, Torino) GaAs/AlAs, GaN/AlN Eliana Biolatti
Measurement Based Quantum Computing, Graph States, and Near-term Realizations
 Measurement Based Quantum Computing, Graph States, and Near-term Realizations Miami 2018 Antonio Russo Edwin Barnes S. E. Economou 17 December 2018 Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University A.
Measurement Based Quantum Computing, Graph States, and Near-term Realizations Miami 2018 Antonio Russo Edwin Barnes S. E. Economou 17 December 2018 Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University A.
Lecture 2, March 2, 2017
 Lecture 2, March 2, 2017 Last week: Introduction to topics of lecture Algorithms Physical Systems The development of Quantum Information Science Quantum physics perspective Computer science perspective
Lecture 2, March 2, 2017 Last week: Introduction to topics of lecture Algorithms Physical Systems The development of Quantum Information Science Quantum physics perspective Computer science perspective
The Quantum Landscape
 The Quantum Landscape Computational drug discovery employing machine learning and quantum computing Contact us! lucas@proteinqure.com Or visit our blog to learn more @ www.proteinqure.com 2 Applications
The Quantum Landscape Computational drug discovery employing machine learning and quantum computing Contact us! lucas@proteinqure.com Or visit our blog to learn more @ www.proteinqure.com 2 Applications
Reversible and Quantum computing. Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2015/2016
 Reversible and Quantum computing Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2015/2016 Reversible computing A process is said to be logically reversible if the transition function that maps old computational states to
Reversible and Quantum computing Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2015/2016 Reversible computing A process is said to be logically reversible if the transition function that maps old computational states to
Quantum Computing: the Majorana Fermion Solution. By: Ryan Sinclair. Physics 642 4/28/2016
 Quantum Computing: the Majorana Fermion Solution By: Ryan Sinclair Physics 642 4/28/2016 Quantum Computation: The Majorana Fermion Solution Since the introduction of the Torpedo Data Computer during World
Quantum Computing: the Majorana Fermion Solution By: Ryan Sinclair Physics 642 4/28/2016 Quantum Computation: The Majorana Fermion Solution Since the introduction of the Torpedo Data Computer during World
The Quantum Supremacy Experiment
 The Quantum Supremacy Experiment John Martinis, Google & UCSB New tests of QM: Does QM work for 10 15 Hilbert space? Does digitized error model also work? Demonstrate exponential computing power: Check
The Quantum Supremacy Experiment John Martinis, Google & UCSB New tests of QM: Does QM work for 10 15 Hilbert space? Does digitized error model also work? Demonstrate exponential computing power: Check
Quantum Information Science (QIS)
 Quantum Information Science (QIS) combination of three different fields: Quantum Physics QIS Computer Science Information Theory Lecture 1 - Outline 1. Quantum Mechanics 2. Computer Science History 3.
Quantum Information Science (QIS) combination of three different fields: Quantum Physics QIS Computer Science Information Theory Lecture 1 - Outline 1. Quantum Mechanics 2. Computer Science History 3.
Carbon Nanotube Synaptic Transistor Network for. Pattern Recognition. Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Carbon Nanotube Synaptic Transistor Network for Pattern Recognition Sungho Kim 1, Jinsu Yoon 2, Hee-Dong Kim 1 & Sung-Jin Choi 2,* 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Sejong
Supporting Information for Carbon Nanotube Synaptic Transistor Network for Pattern Recognition Sungho Kim 1, Jinsu Yoon 2, Hee-Dong Kim 1 & Sung-Jin Choi 2,* 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Sejong
2.0 Basic Elements of a Quantum Information Processor. 2.1 Classical information processing The carrier of information
 QSIT09.L03 Page 1 2.0 Basic Elements of a Quantum Information Processor 2.1 Classical information processing 2.1.1 The carrier of information - binary representation of information as bits (Binary digits).
QSIT09.L03 Page 1 2.0 Basic Elements of a Quantum Information Processor 2.1 Classical information processing 2.1.1 The carrier of information - binary representation of information as bits (Binary digits).
+ - Indirect excitons. Exciton: bound pair of an electron and a hole.
 Control of excitons in multi-layer van der Waals heterostructures E. V. Calman, C. J. Dorow, M. M. Fogler, L. V. Butov University of California at San Diego, S. Hu, A. Mishchenko, A. K. Geim University
Control of excitons in multi-layer van der Waals heterostructures E. V. Calman, C. J. Dorow, M. M. Fogler, L. V. Butov University of California at San Diego, S. Hu, A. Mishchenko, A. K. Geim University
3/10/2013. Lecture #1. How small is Nano? (A movie) What is Nanotechnology? What is Nanoelectronics? What are Emerging Devices?
 EECS 498/598: Nanocircuits and Nanoarchitectures Lecture 1: Introduction to Nanotelectronic Devices (Sept. 5) Lectures 2: ITRS Nanoelectronics Road Map (Sept 7) Lecture 3: Nanodevices; Guest Lecture by
EECS 498/598: Nanocircuits and Nanoarchitectures Lecture 1: Introduction to Nanotelectronic Devices (Sept. 5) Lectures 2: ITRS Nanoelectronics Road Map (Sept 7) Lecture 3: Nanodevices; Guest Lecture by
Measuring Spin-Lattice Relaxation Time
 WJP, PHY381 (2009) Wabash Journal of Physics v4.0, p.1 Measuring Spin-Lattice Relaxation Time L.W. Lupinski, R. Paudel, and M.J. Madsen Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated:
WJP, PHY381 (2009) Wabash Journal of Physics v4.0, p.1 Measuring Spin-Lattice Relaxation Time L.W. Lupinski, R. Paudel, and M.J. Madsen Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated:
Coherent Coupling between 4300 Superconducting Flux Qubits and a Microwave Resonator
 : A New Era in Quantum Information Processing Technologies Coherent Coupling between 4300 Superconducting Flux Qubits and a Microwave Resonator Yuichiro Matsuzaki, Kosuke Kakuyanagi, Hiraku Toida, Hiroshi
: A New Era in Quantum Information Processing Technologies Coherent Coupling between 4300 Superconducting Flux Qubits and a Microwave Resonator Yuichiro Matsuzaki, Kosuke Kakuyanagi, Hiraku Toida, Hiroshi
Information processing in nanoscale systems
 Information processing in nanoscale systems Mark Rudner Niels Bohr International Academy Image from: www.upscale.utoronto.ca 100 years after Bohr, the basic laws and players are established 1913 2013 Image
Information processing in nanoscale systems Mark Rudner Niels Bohr International Academy Image from: www.upscale.utoronto.ca 100 years after Bohr, the basic laws and players are established 1913 2013 Image
Quantum computation and quantum information
 Quantum computation and quantum information Chapter 7 - Physical Realizations - Part 2 First: sign up for the lab! do hand-ins and project! Ch. 7 Physical Realizations Deviate from the book 2 lectures,
Quantum computation and quantum information Chapter 7 - Physical Realizations - Part 2 First: sign up for the lab! do hand-ins and project! Ch. 7 Physical Realizations Deviate from the book 2 lectures,
Martes cuántico Zaragoza, 8 th October Atomic and molecular spin qubits. Fernando LUIS Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón
 Martes cuántico Zaragoza, 8 th October 2013 Atomic and molecular spin qubits Fernando LUIS Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón Outline Quantum information with spins 1 0 Atomic defects in semiconductors
Martes cuántico Zaragoza, 8 th October 2013 Atomic and molecular spin qubits Fernando LUIS Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón Outline Quantum information with spins 1 0 Atomic defects in semiconductors
Developing Quantum Logic Gates: Spin-Resonance-Transistors
 Developing Quantum Logic Gates: Spin-Resonance-Transistors H. W. Jiang (UCLA) SRT: a Field Effect Transistor in which the channel resistance monitors electron spin resonance, and the resonance frequency
Developing Quantum Logic Gates: Spin-Resonance-Transistors H. W. Jiang (UCLA) SRT: a Field Effect Transistor in which the channel resistance monitors electron spin resonance, and the resonance frequency
Modeling Schottky barrier SINIS junctions
 Modeling Schottky barrier SINIS junctions J. K. Freericks, B. Nikolić, and P. Miller * Department of Physics, Georgetown University, Washington, DC 20057 * Department of Physics, Brandeis University, Waltham,
Modeling Schottky barrier SINIS junctions J. K. Freericks, B. Nikolić, and P. Miller * Department of Physics, Georgetown University, Washington, DC 20057 * Department of Physics, Brandeis University, Waltham,
!. 2) 3. '45 ( !"#!$%!&&' 9,.. : Cavity QED . / 3., /*. Ion trap 6..,%, Magnetic resonance Superconductor
 0 1!"#!$%!&&' ()*+,-! 2) 3 '45 ( 0 9, : 3, * 6,%, -73 35 8 Cavity QED Magnetic resonance Ion trap Superconductor 7 : ) :; 1 ( 6 7? 2 + ' - < 75 @ *6 97
0 1!"#!$%!&&' ()*+,-! 2) 3 '45 ( 0 9, : 3, * 6,%, -73 35 8 Cavity QED Magnetic resonance Ion trap Superconductor 7 : ) :; 1 ( 6 7? 2 + ' - < 75 @ *6 97
Tuning a short coherence length Josephson junction through a metal-insulator transition
 Tuning a short coherence length Josephson junction through a metal-insulator transition J. K. Freericks, B. Nikolić, and P. Miller * Department of Physics, Georgetown University, Washington, DC 20057 *
Tuning a short coherence length Josephson junction through a metal-insulator transition J. K. Freericks, B. Nikolić, and P. Miller * Department of Physics, Georgetown University, Washington, DC 20057 *
ION TRAPS STATE OF THE ART QUANTUM GATES
 ION TRAPS STATE OF THE ART QUANTUM GATES Silvio Marx & Tristan Petit ION TRAPS STATE OF THE ART QUANTUM GATES I. Fault-tolerant computing & the Mølmer- Sørensen gate with ion traps II. Quantum Toffoli
ION TRAPS STATE OF THE ART QUANTUM GATES Silvio Marx & Tristan Petit ION TRAPS STATE OF THE ART QUANTUM GATES I. Fault-tolerant computing & the Mølmer- Sørensen gate with ion traps II. Quantum Toffoli
*WILEY- Quantum Computing. Joachim Stolze and Dieter Suter. A Short Course from Theory to Experiment. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.
 Joachim Stolze and Dieter Suter Quantum Computing A Short Course from Theory to Experiment Second, Updated and Enlarged Edition *WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XIII 1 Introduction
Joachim Stolze and Dieter Suter Quantum Computing A Short Course from Theory to Experiment Second, Updated and Enlarged Edition *WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XIII 1 Introduction
Physics 351 Wednesday, January 10, 2018
 Physics 351 Wednesday, January 10, 2018 Chapers 1 5 mostly review freshman physics, so we ll go through them very quickly in the first few days of class. Read Chapters 1+2 for Friday. Read Chapter 3 (momentum
Physics 351 Wednesday, January 10, 2018 Chapers 1 5 mostly review freshman physics, so we ll go through them very quickly in the first few days of class. Read Chapters 1+2 for Friday. Read Chapter 3 (momentum
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Apr 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Apr 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Apr 2016](/thumbs/71/66197100.jpg) State-conditional coherent charge qubit oscillations in a Si/SiGe quadruple quantum dot arxiv:164.7956v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Apr 216 D. R. Ward, 1, 2, Dohun Kim, 1, 3, D. E. Savage, 4 M. G. Lagally,
State-conditional coherent charge qubit oscillations in a Si/SiGe quadruple quantum dot arxiv:164.7956v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 27 Apr 216 D. R. Ward, 1, 2, Dohun Kim, 1, 3, D. E. Savage, 4 M. G. Lagally,
Adiabatic quantum computation a tutorial for computer scientists
 Adiabatic quantum computation a tutorial for computer scientists Itay Hen Dept. of Physics, UCSC Advanced Machine Learning class UCSC June 6 th 2012 Outline introduction I: what is a quantum computer?
Adiabatic quantum computation a tutorial for computer scientists Itay Hen Dept. of Physics, UCSC Advanced Machine Learning class UCSC June 6 th 2012 Outline introduction I: what is a quantum computer?
Superconducting Qubits Lecture 4
 Superconducting Qubits Lecture 4 Non-Resonant Coupling for Qubit Readout A. Blais, R.-S. Huang, A. Wallraff, S. M. Girvin, and R. J. Schoelkopf, PRA 69, 062320 (2004) Measurement Technique Dispersive Shift
Superconducting Qubits Lecture 4 Non-Resonant Coupling for Qubit Readout A. Blais, R.-S. Huang, A. Wallraff, S. M. Girvin, and R. J. Schoelkopf, PRA 69, 062320 (2004) Measurement Technique Dispersive Shift
Semiconductors: Applications in spintronics and quantum computation. Tatiana G. Rappoport Advanced Summer School Cinvestav 2005
 Semiconductors: Applications in spintronics and quantum computation Advanced Summer School 1 I. Background II. Spintronics Spin generation (magnetic semiconductors) Spin detection III. Spintronics - electron
Semiconductors: Applications in spintronics and quantum computation Advanced Summer School 1 I. Background II. Spintronics Spin generation (magnetic semiconductors) Spin detection III. Spintronics - electron
Experimental Realization of Shor s Quantum Factoring Algorithm
 Experimental Realization of Shor s Quantum Factoring Algorithm M. Steffen1,2,3, L.M.K. Vandersypen1,2, G. Breyta1, C.S. Yannoni1, M. Sherwood1, I.L.Chuang1,3 1 IBM Almaden Research Center, San Jose, CA
Experimental Realization of Shor s Quantum Factoring Algorithm M. Steffen1,2,3, L.M.K. Vandersypen1,2, G. Breyta1, C.S. Yannoni1, M. Sherwood1, I.L.Chuang1,3 1 IBM Almaden Research Center, San Jose, CA
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS February 21, 2017
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS February 21, 2017 Content Questions How do you place a single arsenic atom with the ratio 1 in 100 million? Sounds difficult to get evenly spread throughout. Yes, techniques
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS February 21, 2017 Content Questions How do you place a single arsenic atom with the ratio 1 in 100 million? Sounds difficult to get evenly spread throughout. Yes, techniques
Parity-Protected Josephson Qubits
 Parity-Protected Josephson Qubits Matthew Bell 1,2, Wenyuan Zhang 1, Lev Ioffe 1,3, and Michael Gershenson 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University, New Jersey 2 Department of Electrical
Parity-Protected Josephson Qubits Matthew Bell 1,2, Wenyuan Zhang 1, Lev Ioffe 1,3, and Michael Gershenson 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University, New Jersey 2 Department of Electrical
AFRL-RI-RS-TR
 AFRL-RI-RS-TR-2015-013 HYBRID CIRCUIT QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS: COUPLING A SINGLE SILICON SPIN QUBIT TO A PHOTON PRINCETON UNIVERSITY JANUARY 2015 FINAL TECHNICAL REPORT APPROVED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE; DISTRIBUTION
AFRL-RI-RS-TR-2015-013 HYBRID CIRCUIT QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS: COUPLING A SINGLE SILICON SPIN QUBIT TO A PHOTON PRINCETON UNIVERSITY JANUARY 2015 FINAL TECHNICAL REPORT APPROVED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE; DISTRIBUTION
simulations of the Polarization dependence of the light Potential equation in quantum ComPUting
 simulations of the Polarization dependence of the light Potential equation in quantum ComPUting bert david Copsey, student author dr. Katharina gillen, research advisor abstract Many methods of quantum
simulations of the Polarization dependence of the light Potential equation in quantum ComPUting bert david Copsey, student author dr. Katharina gillen, research advisor abstract Many methods of quantum
Lecture 1: Introduction to Quantum Computing
 Lecture 1: Introduction to Quantum Computing Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur Whenever the word Quantum Computing is uttered in public, there are many reactions. The first one is of surprise, mostly pleasant, and
Lecture 1: Introduction to Quantum Computing Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur Whenever the word Quantum Computing is uttered in public, there are many reactions. The first one is of surprise, mostly pleasant, and
Lecture 18: 3D Review, Examples
 Lecture 18: 3D Review, Examples A real (2D) quantum dot http://pages.unibas.ch/physmeso/pictures/pictures.html Lecture 18, p 1 Lect. 16: Particle in a 3D Box (3) The energy eigenstates and energy values
Lecture 18: 3D Review, Examples A real (2D) quantum dot http://pages.unibas.ch/physmeso/pictures/pictures.html Lecture 18, p 1 Lect. 16: Particle in a 3D Box (3) The energy eigenstates and energy values
Coherent control and charge echo in a GaAs charge qubit
 LETTER Coherent control and charge echo in a GaAs charge qubit To cite this article: Bao-Chuan Wang et al 2017 EPL 117 57006 View the article online for updates and enhancements. Related content - Arbitrary
LETTER Coherent control and charge echo in a GaAs charge qubit To cite this article: Bao-Chuan Wang et al 2017 EPL 117 57006 View the article online for updates and enhancements. Related content - Arbitrary
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 26 Feb 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 26 Feb 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 26 Feb 2004](/thumbs/72/66342523.jpg) Voltage Control of Exchange Coupling in Phosphorus Doped Silicon arxiv:cond-mat/42642v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 26 Feb 24 C.J. Wellard a, L.C.L. Hollenberg a, L.M. Kettle b and H.-S. Goan c Centre for Quantum
Voltage Control of Exchange Coupling in Phosphorus Doped Silicon arxiv:cond-mat/42642v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 26 Feb 24 C.J. Wellard a, L.C.L. Hollenberg a, L.M. Kettle b and H.-S. Goan c Centre for Quantum
Non-linear driving and Entanglement of a quantum bit with a quantum readout
 Non-linear driving and Entanglement of a quantum bit with a quantum readout Irinel Chiorescu Delft University of Technology Quantum Transport group Prof. J.E. Mooij Kees Harmans Flux-qubit team visitors
Non-linear driving and Entanglement of a quantum bit with a quantum readout Irinel Chiorescu Delft University of Technology Quantum Transport group Prof. J.E. Mooij Kees Harmans Flux-qubit team visitors
Optically-controlled controlled quantum dot spins for quantum computers
 Optically-controlled controlled quantum dot spins for quantum computers David Press Yamamoto Group Applied Physics Department Ph.D. Oral Examination April 28, 2010 1 What could a Quantum Computer do? Simulating
Optically-controlled controlled quantum dot spins for quantum computers David Press Yamamoto Group Applied Physics Department Ph.D. Oral Examination April 28, 2010 1 What could a Quantum Computer do? Simulating
Decodiy for surface. Quantum Error Correction. path integral. theory versus. Decoding for GKP code. experiment. Correcting
 Quantum Error Correction 1 3X 1100 ( 230 ntro : theory versus experiment Quantum Error i Bosonic Codes # } \ Correcting Conditions stalilizer Codes ( including conthuoqsoyueagjask \ # Decoding Decoding
Quantum Error Correction 1 3X 1100 ( 230 ntro : theory versus experiment Quantum Error i Bosonic Codes # } \ Correcting Conditions stalilizer Codes ( including conthuoqsoyueagjask \ # Decoding Decoding
Topological Quantum Computation. George Toh 11/6/2017
 Topological Quantum Computation George Toh 11/6/2017 Contents Quantum Computing Comparison of QC vs TQC Topological Quantum Computation How to implement TQC? Examples, progress Industry investment Future
Topological Quantum Computation George Toh 11/6/2017 Contents Quantum Computing Comparison of QC vs TQC Topological Quantum Computation How to implement TQC? Examples, progress Industry investment Future
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 3 Numbers and Units
 Numbers in Physics PHYSICS 107 Lecture 3 Numbers and Units We've seen already that even 2500 years ago Aristotle recognized that lengths and times are magnitudes, meaning that any length or time can be
Numbers in Physics PHYSICS 107 Lecture 3 Numbers and Units We've seen already that even 2500 years ago Aristotle recognized that lengths and times are magnitudes, meaning that any length or time can be
Quantum Computing. Joachim Stolze and Dieter Suter. A Short Course from Theory to Experiment. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA
 Joachim Stolze and Dieter Suter Quantum Computing A Short Course from Theory to Experiment Second, Updated and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Preface XIII 1 Introduction and
Joachim Stolze and Dieter Suter Quantum Computing A Short Course from Theory to Experiment Second, Updated and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Preface XIII 1 Introduction and
Quantum computing. Jan Černý, FIT, Czech Technical University in Prague. České vysoké učení technické v Praze. Fakulta informačních technologií
 České vysoké učení technické v Praze Fakulta informačních technologií Katedra teoretické informatiky Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-MVI Methods of Computational Intelligence(2010/2011)
České vysoké učení technické v Praze Fakulta informačních technologií Katedra teoretické informatiky Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-MVI Methods of Computational Intelligence(2010/2011)
Implementing Competitive Learning in a Quantum System
 Implementing Competitive Learning in a Quantum System Dan Ventura fonix corporation dventura@fonix.com http://axon.cs.byu.edu/dan Abstract Ideas from quantum computation are applied to the field of neural
Implementing Competitive Learning in a Quantum System Dan Ventura fonix corporation dventura@fonix.com http://axon.cs.byu.edu/dan Abstract Ideas from quantum computation are applied to the field of neural
Physics of Semiconductors
 Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Controlling Spin Qubits in Quantum Dots. C. M. Marcus Harvard University
 Controlling Spin Qubits in Quantum Dots C. M. Marcus Harvard University 1 Controlling Spin Qubits in Quantum Dots C. M. Marcus Harvard University GaAs Experiments: David Reilly (Univ. Sydney) Edward Laird
Controlling Spin Qubits in Quantum Dots C. M. Marcus Harvard University 1 Controlling Spin Qubits in Quantum Dots C. M. Marcus Harvard University GaAs Experiments: David Reilly (Univ. Sydney) Edward Laird
Coherent Manipulation of Coupled Electron Spins in Semiconductor Quantum Dots
 Coherent Manipulation of Coupled Electron Spins in Semiconductor Quantum Dots J. R. Petta 1, A. C. Johnson 1, J. M. Taylor 1, E. A. Laird 1, A. Yacoby, M. D. Lukin 1, C. M. Marcus 1, M. P. Hanson 3, A.
Coherent Manipulation of Coupled Electron Spins in Semiconductor Quantum Dots J. R. Petta 1, A. C. Johnson 1, J. M. Taylor 1, E. A. Laird 1, A. Yacoby, M. D. Lukin 1, C. M. Marcus 1, M. P. Hanson 3, A.
Summary of Hyperion Research's First QC Expert Panel Survey Questions/Answers. Bob Sorensen, Earl Joseph, Steve Conway, and Alex Norton
 Summary of Hyperion Research's First QC Expert Panel Survey Questions/Answers Bob Sorensen, Earl Joseph, Steve Conway, and Alex Norton Hyperion s Quantum Computing Program Global Coverage of R&D Efforts
Summary of Hyperion Research's First QC Expert Panel Survey Questions/Answers Bob Sorensen, Earl Joseph, Steve Conway, and Alex Norton Hyperion s Quantum Computing Program Global Coverage of R&D Efforts
MAA509: Quantum Computing and Information Introduction
 MAA509: Quantum Computing and Information Introduction November 7, 2016 November 7, 2016 1 / 19 Why make computers? Computation by hand is difficult and not very stimulating. Why not make a machine do
MAA509: Quantum Computing and Information Introduction November 7, 2016 November 7, 2016 1 / 19 Why make computers? Computation by hand is difficult and not very stimulating. Why not make a machine do
Single Spin Qubits, Qubit Gates and Qubit Transfer with Quantum Dots
 International School of Physics "Enrico Fermi : Quantum Spintronics and Related Phenomena June 22-23, 2012 Varenna, Italy Single Spin Qubits, Qubit Gates and Qubit Transfer with Quantum Dots Seigo Tarucha
International School of Physics "Enrico Fermi : Quantum Spintronics and Related Phenomena June 22-23, 2012 Varenna, Italy Single Spin Qubits, Qubit Gates and Qubit Transfer with Quantum Dots Seigo Tarucha
