Microbial and Animal Rhodopsins: Structures, Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
|
|
|
- Lizbeth Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Microbial and Animal Rhodopsins: Structures, Functions and Molecular Mechanisms Oliver P. Ernst 1, David T. Lodowski 2, Marcus Elstner 3, Peter Hegemann 4, Leonid S. Brown 5, and Hideki Kandori 6 1 Departments of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, University of Toronto, 1 King's College Circle, Toronto, Ontario M5S 1A8, Canada, 2 Center for Proteomics and Bioinformatics, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44106, United States, 3 Institute for Physical Chemistry, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Kaiserstrasse 12, Karlsruhe, Germany, 4 Institute of Biology, Experimental Biophysics, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Invalidenstrasse 42, Berlin, Germany, 5 Department of Physics and Biophysics Interdepartmental Group, University of Guelph, 50 Stone Road East, Guelph, Ontario N1G 2W1, Canada, 6 Department of Frontier Materials, Nagoya Institute of Technology, Showa-ku, Nagoya , Japan 1
2 Helix A B B B B C C C C C C C C C D D D E E E F F F F - G G G G G G G # in BR BR M V A M Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G S M Y W Y P W E E F D A K F G H + pump AR1 M V A A Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G S M Y W Y P W E E F D A K F G AR2 M V A A Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G S F Y W Y P W E E F D A K F G AR3 M V A A Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G S M Y W Y P W E E F D A K F G MR? M I A A Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G S F Y W Y P W G E Y D T K F G GPR 1 M I A H Y R Y D W T V P M E S M G S Y Y W Y P Y P L Y D N K F G GPR 2 L V A H Y R Y D W T V P L E T M G G W Y W Y P Y M L Y D N K F G GPR 3 L V A H Y R Y D W T V P L E T M G G W Y W Y P Y M L Y D N K F G BPR 4 M V A H Y R Y D W T V P Q E S M G G W Y W Y P Y F L Y D N K F G BPR 5 M I A H Y R Y D W T V P Q E S M G G W Y W Y P Y L L Y D N K F G GPR 6 L V A H Y R Y D W T V P L E S M G G W Y W Y P Y L L Y D N K F G H + pump GPR 7 L V A H Y R Y D W T V P L E S M G G W Y W Y P Y L L Y D N K F G GR M V A H Y R Y D W T V P L E S M G S F Y W Y P Y L V Y D A K F G XR M V A H Y R Y D W T V P L E A M G S F Y W Y P Y A L Y D A K Y G Ace1 M I A A Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G G L W W Y P W G E M D A K Y A Ace2 M I A A Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G G Q Y W Y P W G E M D A K F G LR M I A S Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G A Y W W Y P W G E Y D A K F G Ph1 A V A A Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G G L Y W Y P W G E Y D A K F G Ph2 M I A S Y R Y D W T T P L D D M G A Y W W Y P W G E Y D A K F G NR? M I A S Y R Y D W T T P L E D M G G Y W W Y P W G E Y D A K F G HsHR A I S S Y R Y T W S T P I A D M G S F S W Y P W E T Y D A K F A Cl - pump NpHR A V S S Y R Y T W S T P I A D M G S F Y W Y P W E T Y D A K F A SrHR A I S S Y R Y T W S T P I A D M G S F Y W Y P W E T Y D A K F T HsSRI L I A S Y R Y D W T T P L Y D M G S H A W Y P W A V Y D A K Y V SrSRI M I A M Y R Y D W T T P L Y D M G S H A W Y P W - I I D A K F V HvSRI F I A S Y R Y D W T T P L F D M G S H A W Y P W E V Y D A K Y V Sensor HsSRII M I A A Y R Y D W T T P I Y D V G G Y Y W Y P W A Y V D S K F V NpSRII M I A A Y R Y D W T T P I F N V G G F Y W Y P W P D I D T K F G HvSRII E I A A Y R Y D W T T P N F Q T G G F Y W Y P W A A V D T K F G ASR M I S A Y R Y D W T T P L S Q V G G F W W Y P W S D F P S K F S CrChR1 S V E K F R Y E W T C P I H D T G G G F W F P F E S H D S K W S VcChR1 S V E K S R Y E W T C P L H D C G S G F W F P F E S H D A K W G Channel MvChR1 S V E I Y R Y E W T C P I A D C G G G W W F P F E S H D S K W G CrChR2 S V E K V R Y E W T C P I H D T G G G F W F P F E S H D S K W G VcChR2 S V E K V R Y E W T C P I H D T G G G F W F P F E S H D S K W G 1) MED134, 2) AND4, 3) SAR11, 4) LC1-200, 5) HOT 75m4, 6) SAR86, 7) HOT 0m1 Supporting Information Figure 1. Conservation of the key amino acids for microbial rhodopsins shown in Figure 9. Despite the varying global sequence identities among microbial rhodopsins (Supporting Information Figure 2), a subset of residues is conserved in sequence and in position in the TM helices, and plays a role in activity and selectivity. The numbering scheme corresponds to the position in BR. Negatively charged residues are shown in red, positively charged in blue, aromatic in yellow, polar in green, non-polar in grey. BR; Bacteriorhodopsin from Archaea (Halobacterium salinarum), AR1; Archaerhodopsin-1 from Archaea (Halorubrum chaoviator), AR2; Archaerhodopsin-2 from Archaea (Halobacterium sp. AUS-2), AR-3; Archaerhodopsin-3 from Archaea (Halorubrum sadomense), MR; Midrhodopsin from Eubacteria (Haloquadratum walsbyi DSM 16790), GPR(1); Green-absorbing Proteorhodopsin from Eubacteria (Dokdonia donghaensis MED134; EAQ40507), GPR(2); Green-absorbing Proteorhodopsin from 2
3 Eubacteria (Vibrio sp. AND4; ZP_ ), GPR(3); Green-absorbing Proteorhodopsin from Eubacteria (Candidatus Pelagibacter ubique HTCC1062, SAR11 group; Q4FMZ3), BPR(4); Blue-absorbing Proteorhodopsin from Eubacteria (Photobacterium sp. LC1-200; BAL68143), BPR(5); Blue-absorbing Proteorhodopsin from uncultured bacterium (HOT 75m4; AAK30179), GPR(6);Green-absorbing Proteorhodopsin from uncultured marine gamma proteobacterium ( SAR86 group; AAG10475), GPR(7); Green-absorbing Proteorhodopsin from uncultured bacterium (HOT 0m1; AAK30176), GR; Gloeobacter Rhodopsin from Eubacteria (Gloeobacter violaceus), XR; Xanthorhodopsin from Eubacteria (Salinibacter ruber DSM 13855), Ace1; Acetabularia Rhodopsin 1 from Eukaryote (Acetabularia acetabulum), Ace2; Acetabularia Rhodopsin 2 from Eukaryote (Acetabularia acetabulum), LR; Leptosphaeria Rhodopsin from Eukaryote (Leptosphaeria maculans), Ph1; Phaeosphaeria Rhodopsin 1 from Eucaryote (Phaeosphaeria nodorum SN15), Ph2; Phaeosphaeria Rhodopsin 2 from Eukaryote (Phaeosphaeria nodorum SN15), NR; Neurospora Rhodopsin from Eukaryote (Neurospora crassa OR74A), HsHR; Halorhodopsin from Archaea (Halobacterium salinarum), NpHR; Halorhodopsin from Archaea (Natronomonas pharaonis), SrHR; Halorhodopsin from Eubacteria (Salinibacter ruber DSM 13855), HsSRI; Sensory Rhodopsin I from Archaea (Halobacterium salinarum), SrSRI; Sensory Rhodopsin I from Eubacteria (Salinibacter ruber M8), HvSRI; Sensory Rhodopsin I from Archaea (Haloarcula vallismortis ATCC 29715), HsSRII; Sensory Rhodopsin II from Archaea (Halobacterium salinarum), NpSRII; Sensory Rhodopsin II from Archaea (Natronomonas pharaonis), HvSRII; Sensory Rhodopsin II from Archaea (Haloarcula vallismortis ATCC 29715), ASR; Anabaena Sensory Rhodopsin from Eubacteria (Nostoc sp. PCC 7120), CrChR1; Channelrhodopsin 1 from Eukaryote (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii), VcChR1; Channelrhodopsin 1 from Eukaryote (Volvox carteri f. nagariensis), MvChR1; Channelrhodopsin 1 from Eukaryote (Mesostigma viride), CrChR2; Channelrhodopsin 2 from Eukaryote (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii), VcChR2; Channelrhodopsin 2 from Eukaryote (Volvox carteri f. nagariensis). 3
4 Supporting Information Figure 2. Pairwise sequence identities for the selected microbial rhodopsins from Figure 9. Despite their similarity of topology and conservation of the key intramembrane residues, especially in the retinal binding pocket, global sequence homology amongst the microbial rhodopsins can be as low as ~15%. 4
5 Supporting Information Figure 3. Asymmetric functional conversion between lightdriven proton and chloride pumps. Light-driven proton pump BR can be converted into a chloride pump by a single amino acid replacement (Asp-to-Thr mutation). In contrast, substituting the BR-like ten amino acids into HR creates a NpHR mutant which is not capable of pumping protons. FTIR spectroscopy revealed that the failure of functional conversion of HR is due to the lack of strongly hydrogen-bonded water(s), the functional determinant of proton pumping.160,301 5
6 N-terminus extracellular S-S bridge EL3 EL3 EL2 C3.25 CEL2 Ret ligand- binding site P6.50 TM7 TM2 TM1 W6.48 P5.50 W4.50 TM5 TM4 (D/E)R3.50Y motif Y5.58 N7.49 Y..F bridge P7.50 Y7.53 TM3 ionic lock Na+ TM1/2/7 network D2.50 N1.50 TM6 F7.63 R3.50 E6.30 K/R5.66 CL2 CL3 H8 CL1 NP7.50xxY(x)5,6Y motif C-terminus intracellular Supporting Information Figure 4. Sequence and motif conservation and ordered water molecules in GPCRs mapped on bovine Rho (PDB ID:1U19) structure (cf. Figure 20). Supplementary Figure 5 Greater Tube thickness indicates greater residue conservation at that position.463 Ordered water molecules (shown in light blue) found by superposition of antagonist Supplementary Figure (4-2) bound GPCR structures. A sodium ion (shown as a black sphere) has been found within 6
7 the A 2A -adenosine and PAR1 receptor structures (PDB ID: 4EIY, 3VW7) in a similar position occupied by water in Rho. TM helices are connected by cytoplasmic (CL1-CL3) and extracellular (EL1-EL3) loops. Asn2 and Asn15 are glycosylated (not shown). Cys322 and Cys323 at end of H8 are palmitoylated (not shown). Cys110 on TM3 and Cys187 in EL2 are linked by a disulfide bridge. Residues Asn , Asp , Arg , Trp , Pro , Pro and Pro are most conserved residues in a TM helix. The superscript relates to Ballesteros Weinstein numbering (cf. ref 521). Conserved motifs are the (D/E)RY motif in TM3 (Glu134-Arg135-Tyr136) and the NPxxY(x) 5,6 F motif in TM7 and H8 (Asn302-Pro303-x-x-Tyr306-x 5,6 -Phe313). The inverse agonist 11-cis retinal is attached to Lys Residues Tyr223 (Y 5.58 ) and Lys231 (K/R 5.66 ) of the Y 5.58 (x) 7 K(R) 5.66 motif in TM5 are microswitches for stabilizing the active receptor state
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal packing of ClR and electron density maps. Crystal packing of type A crystal (a) and type B crystal (b).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal packing of ClR and electron density maps. Crystal packing of type A crystal (a) and type B crystal (b). Crystal contacts at B-C loop are magnified and stereo view of A-weighted
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal packing of ClR and electron density maps. Crystal packing of type A crystal (a) and type B crystal (b). Crystal contacts at B-C loop are magnified and stereo view of A-weighted
Comparison between Bacteriorhodopsin and Halorhodopsin. Halorhodopsin (HR) and Bacteriorhodopsin (BR) belong to a subfamily of
 Comparison between Bacteriorhodopsin and Halorhodopsin Halorhodopsin (HR) and Bacteriorhodopsin (BR) belong to a subfamily of heptahelical membrane proteins, the archaeal rhodopsins. They are found in
Comparison between Bacteriorhodopsin and Halorhodopsin Halorhodopsin (HR) and Bacteriorhodopsin (BR) belong to a subfamily of heptahelical membrane proteins, the archaeal rhodopsins. They are found in
sensors ISSN
 Sensors 2009, 9, 9741-9804; doi:10.3390/s91209741 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 1424-8220 www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors Review Photoreactions and Structural Changes of Anabaena Sensory Rhodopsin Akira Kawanabe
Sensors 2009, 9, 9741-9804; doi:10.3390/s91209741 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 1424-8220 www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors Review Photoreactions and Structural Changes of Anabaena Sensory Rhodopsin Akira Kawanabe
Bahnson Biochemistry Cume, April 8, 2006 The Structural Biology of Signal Transduction
 Name page 1 of 6 Bahnson Biochemistry Cume, April 8, 2006 The Structural Biology of Signal Transduction Part I. The ion Ca 2+ can function as a 2 nd messenger. Pick a specific signal transduction pathway
Name page 1 of 6 Bahnson Biochemistry Cume, April 8, 2006 The Structural Biology of Signal Transduction Part I. The ion Ca 2+ can function as a 2 nd messenger. Pick a specific signal transduction pathway
Ion Translocation Across Biological Membranes. Janos K. Lanyi University of California, Irvine
 Ion Translocation Across Biological Membranes Janos K. Lanyi University of California, Irvine Examples of transmembrane ion pumps Protein Cofactor, substrate, etc. MW Subunits Mitoch. cytochrome oxidase
Ion Translocation Across Biological Membranes Janos K. Lanyi University of California, Irvine Examples of transmembrane ion pumps Protein Cofactor, substrate, etc. MW Subunits Mitoch. cytochrome oxidase
sensors ISSN
 Sensors 2010, 10, 4010-4039; doi:10.3390/s100404010 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 1424-8220 www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors Review Phototactic and Chemotactic Signal Transduction by Transmembrane Receptors and
Sensors 2010, 10, 4010-4039; doi:10.3390/s100404010 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 1424-8220 www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors Review Phototactic and Chemotactic Signal Transduction by Transmembrane Receptors and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
RHODOPSIN: Insights from Recent Structural Studies
 Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2002. 31:443 84 DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.31.082901.134348 Copyright c 2002 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved RHODOPSIN: Insights from Recent Structural Studies
Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2002. 31:443 84 DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.31.082901.134348 Copyright c 2002 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved RHODOPSIN: Insights from Recent Structural Studies
Structure of the light-driven sodium pump KR2 and its implications for optogenetics
 STRUCTURAL SNAPSHOT Structure of the light-driven sodium pump KR2 and its implications for optogenetics Ivan Gushchin 1,2, Vitaly Shevchenko 1,2, Vitaly Polovinkin 1,2,3,4,5, Valentin Borshchevskiy 1,2,
STRUCTURAL SNAPSHOT Structure of the light-driven sodium pump KR2 and its implications for optogenetics Ivan Gushchin 1,2, Vitaly Shevchenko 1,2, Vitaly Polovinkin 1,2,3,4,5, Valentin Borshchevskiy 1,2,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystallization. a, Crystallization constructs of the ET B receptor are shown, with all of the modifications to the human wild-type the ET B receptor indicated. Residues interacting
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystallization. a, Crystallization constructs of the ET B receptor are shown, with all of the modifications to the human wild-type the ET B receptor indicated. Residues interacting
Proteorhodopsin phototrophy in the ocean
 Nature 411, 786-789 (14 June 2001) doi:10.1038/35081051; Received 3 January 2001; Accepted 26 March 2001 Proteorhodopsin phototrophy in the ocean Oded Béjà, Elena N. Spudich, John L. Spudich, Marion Leclerc
Nature 411, 786-789 (14 June 2001) doi:10.1038/35081051; Received 3 January 2001; Accepted 26 March 2001 Proteorhodopsin phototrophy in the ocean Oded Béjà, Elena N. Spudich, John L. Spudich, Marion Leclerc
Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase Cwc27
 Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure. You will be given a start time with your exam instructions
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology Date: Thursday, 1st September 2011 Time: 3 hours You will be given a start
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology Date: Thursday, 1st September 2011 Time: 3 hours You will be given a start
ABSORPTION KINETICS AND ELECTRIC SIGNALS MEASURED ON LEPTOSPHAERIA RHODOPSIN
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 2, No. 3, September 2007, p. 265 269 ABSORPTION KINETICS AND ELECTRIC SIGNALS MEASURED ON LEPTOSPHAERIA RHODOPSIN K. Magyari *, V. Simon, Y. Fan a,
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 2, No. 3, September 2007, p. 265 269 ABSORPTION KINETICS AND ELECTRIC SIGNALS MEASURED ON LEPTOSPHAERIA RHODOPSIN K. Magyari *, V. Simon, Y. Fan a,
Retinal Proteins (Rhodopsins) Vision, Bioenergetics, Phototaxis. Bacteriorhodopsin s Photocycle. Bacteriorhodopsin s Photocycle
 Molecular chanisms of Photoactivation and Spectral Tuning in Retinal Proteins Emad Tajkhorshid Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Molecular chanisms of Photoactivation and Spectral Tuning in Retinal Proteins Emad Tajkhorshid Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Tyr191 Trp265 4-5 Å Tyr268 ~14 Å 4.3 Å 16 17 19 20 4.4 Å 11 15 Lys296 N 8 10 12 14 7.3 Å 18 Tyr191 4-5 Å 18 3.8-4 Å 8 10 12 11 17 16 19 ~ Å ~4 Å Tyr268 5.5-6.3 Å 14 N Lys296 15
Supplementary Figure 1 a Tyr191 Trp265 4-5 Å Tyr268 ~14 Å 4.3 Å 16 17 19 20 4.4 Å 11 15 Lys296 N 8 10 12 14 7.3 Å 18 Tyr191 4-5 Å 18 3.8-4 Å 8 10 12 11 17 16 19 ~ Å ~4 Å Tyr268 5.5-6.3 Å 14 N Lys296 15
β1 Structure Prediction and Validation
 13 Chapter 2 β1 Structure Prediction and Validation 2.1 Overview Over several years, GPCR prediction methods in the Goddard lab have evolved to keep pace with the changing field of GPCR structure. Despite
13 Chapter 2 β1 Structure Prediction and Validation 2.1 Overview Over several years, GPCR prediction methods in the Goddard lab have evolved to keep pace with the changing field of GPCR structure. Despite
Hydration switch model for the proton transfer in the Schiff base region of bacteriorhodopsin
 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1658 (2004) 72 79 Review Hydration switch model for the proton transfer in the Schiff base region of bacteriorhodopsin Hideki Kandori* Department of Materials Science and
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1658 (2004) 72 79 Review Hydration switch model for the proton transfer in the Schiff base region of bacteriorhodopsin Hideki Kandori* Department of Materials Science and
Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently become
 Homology Modeling and Docking of Melatonin Receptors Andrew Kohlway, UMBC Jeffry D. Madura, Duquesne University 6/18/04 INTRODUCTION Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently
Homology Modeling and Docking of Melatonin Receptors Andrew Kohlway, UMBC Jeffry D. Madura, Duquesne University 6/18/04 INTRODUCTION Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently
Secondary Structure. Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2. Structure and Function of Proteins. Further Reading. Φ, Ψ angles alone determine protein structure
 Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound ogm-csf and ogm-csf as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine
 Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound and as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine GM-CSF (slate) with bound GM-CSF in the GIF:GM-CSF complex (GIF: green,
Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound and as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine GM-CSF (slate) with bound GM-CSF in the GIF:GM-CSF complex (GIF: green,
Light-Activated Ion Pumps and Channels for Temporally Precise Optical Control of Activity in Genetically Targeted Neurons 1
 Neuromethods (2012) 67: 305 338 DOI 10.1007/7657_2011_10 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011 Published online: 13 December 2011 Light-Activated Ion Pumps and Channels for Temporally Precise Optical
Neuromethods (2012) 67: 305 338 DOI 10.1007/7657_2011_10 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011 Published online: 13 December 2011 Light-Activated Ion Pumps and Channels for Temporally Precise Optical
Structural Changes of Salinibacter Sensory Rhodopsin I upon Formation of the K and M Photointermediates
 12750 Biochemistry 2008, 47, 12750 12759 Structural Changes of Salinibacter Sensory Rhodopsin I upon Formation of the K and M Photointermediates Daisuke Suzuki, Yuki Sudo, Yuji Furutani, Hazuki Takahashi,
12750 Biochemistry 2008, 47, 12750 12759 Structural Changes of Salinibacter Sensory Rhodopsin I upon Formation of the K and M Photointermediates Daisuke Suzuki, Yuki Sudo, Yuji Furutani, Hazuki Takahashi,
Exam I Answer Key: Summer 2006, Semester C
 1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
Supplementary Figure 3 a. Structural comparison between the two determined structures for the IL 23:MA12 complex. The overall RMSD between the two
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biopanningg and clone enrichment of Alphabody binders against human IL 23. Positive clones in i phage ELISA with optical density (OD) 3 times higher than background are shown for
Supplementary Figure 1. Biopanningg and clone enrichment of Alphabody binders against human IL 23. Positive clones in i phage ELISA with optical density (OD) 3 times higher than background are shown for
Review. Membrane proteins. Membrane transport
 Quiz 1 For problem set 11 Q1, you need the equation for the average lateral distance transversed (s) of a molecule in the membrane with respect to the diffusion constant (D) and time (t). s = (4 D t) 1/2
Quiz 1 For problem set 11 Q1, you need the equation for the average lateral distance transversed (s) of a molecule in the membrane with respect to the diffusion constant (D) and time (t). s = (4 D t) 1/2
Protein Structure. Role of (bio)informatics in drug discovery. Bioinformatics
 Bioinformatics Protein Structure Principles & Architecture Marjolein Thunnissen Dep. of Biochemistry & Structural Biology Lund University September 2011 Homology, pattern and 3D structure searches need
Bioinformatics Protein Structure Principles & Architecture Marjolein Thunnissen Dep. of Biochemistry & Structural Biology Lund University September 2011 Homology, pattern and 3D structure searches need
Potassium channel gating and structure!
 Reading: Potassium channel gating and structure Hille (3rd ed.) chapts 10, 13, 17 Doyle et al. The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K1 Conduction and Selectivity. Science 280:70-77
Reading: Potassium channel gating and structure Hille (3rd ed.) chapts 10, 13, 17 Doyle et al. The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K1 Conduction and Selectivity. Science 280:70-77
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters Guus B. Erkens 1,2, Ronnie P-A. Berntsson 1,2, Faizah Fulyani 1,2, Maria Majsnerowska 1,2, Andreja Vujičić-Žagar
Supplementary information The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters Guus B. Erkens 1,2, Ronnie P-A. Berntsson 1,2, Faizah Fulyani 1,2, Maria Majsnerowska 1,2, Andreja Vujičić-Žagar
Homology Models of Human Adrenergic Receptors
 58 Chapter 4 Homology Models of Human Adrenergic Receptors The increased availability of high-resolution GPCR crystal structures has enabled deeper investigation into homology modeling as a method for
58 Chapter 4 Homology Models of Human Adrenergic Receptors The increased availability of high-resolution GPCR crystal structures has enabled deeper investigation into homology modeling as a method for
Supplementary information for:
 SUPPLEMETARY IFRMATI Supplementary information for: Structure of a β 1 -adrenergic G protein-coupled receptor Tony Warne, Maria J. Serrano-Vega, Jillian G. Baker#, Rouslan Moukhametzianov, Patricia C.
SUPPLEMETARY IFRMATI Supplementary information for: Structure of a β 1 -adrenergic G protein-coupled receptor Tony Warne, Maria J. Serrano-Vega, Jillian G. Baker#, Rouslan Moukhametzianov, Patricia C.
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes. From Alberts et al
 Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
Solutions In each case, the chirality center has the R configuration
 CAPTER 25 669 Solutions 25.1. In each case, the chirality center has the R configuration. C C 2 2 C 3 C(C 3 ) 2 D-Alanine D-Valine 25.2. 2 2 S 2 d) 2 25.3. Pro,, Trp, Tyr, and is, Trp, Tyr, and is Arg,
CAPTER 25 669 Solutions 25.1. In each case, the chirality center has the R configuration. C C 2 2 C 3 C(C 3 ) 2 D-Alanine D-Valine 25.2. 2 2 S 2 d) 2 25.3. Pro,, Trp, Tyr, and is, Trp, Tyr, and is Arg,
Peptides And Proteins
 Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
6 Discussion. 6.1 Bacterial reaction center X-Ray crystallography of RC mutants
 6.1 Bacterial reaction center Proton and electron transfer in bacterial reaction centers were investigated using time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. The effect of sitespecific mutations
6.1 Bacterial reaction center Proton and electron transfer in bacterial reaction centers were investigated using time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. The effect of sitespecific mutations
Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached
 Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached to HpUreI. Urea hydrolysis products 2NH 3 and 1CO 2
Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached to HpUreI. Urea hydrolysis products 2NH 3 and 1CO 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
Steric Constraint in the Primary Photoproduct of Sensory Rhodopsin II Is a Prerequisite for Light-Signal Transfer to HtrII
 6208 Biochemistry 2008, 47, 6208 6215 Steric Constraint in the Primary Photoproduct of Sensory Rhodopsin II Is a Prerequisite for Light-Signal Transfer to HtrII Motohiro Ito, Yuki Sudo,, Yuji Furutani,
6208 Biochemistry 2008, 47, 6208 6215 Steric Constraint in the Primary Photoproduct of Sensory Rhodopsin II Is a Prerequisite for Light-Signal Transfer to HtrII Motohiro Ito, Yuki Sudo,, Yuji Furutani,
Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08 Å resolution: comparison with the Azotobacter vinelandii MoFe protein
 Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
Homology Models of Melatonin Receptors: Challenges and Recent Advances
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8093-8121; doi:10.3390/ijms14048093 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Homology Models of Melatonin Receptors:
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8093-8121; doi:10.3390/ijms14048093 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Homology Models of Melatonin Receptors:
Effects of Chloride Ion Binding on the Photochemical Properties of Salinibacter Sensory Rhodopsin I
 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.06.050 J. Mol. Biol. (2009) 392, 48 62 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Effects of Chloride Ion Binding on the Photochemical Properties of Salinibacter Sensory Rhodopsin
doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.06.050 J. Mol. Biol. (2009) 392, 48 62 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Effects of Chloride Ion Binding on the Photochemical Properties of Salinibacter Sensory Rhodopsin
Sy m posi um-i n-pri nt : P hotoreceptors. Evolutionary Patterns of Retinal-Binding Pockets of Type I Rhodopsins and Their Functionst INTRODUCTION
 Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2006, 82: 1426-1 435 Sy m posi um-i n-pri nt : P hotoreceptors Evolutionary Patterns of Retinal-Binding Pockets of Type Rhodopsins and Their Functionst Larisa Adamian,
Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2006, 82: 1426-1 435 Sy m posi um-i n-pri nt : P hotoreceptors Evolutionary Patterns of Retinal-Binding Pockets of Type Rhodopsins and Their Functionst Larisa Adamian,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.108/nature1099 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Data collection and refinement statistics. Highest resolution shell is shown in parentheses. Structure Data
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.108/nature1099 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Data collection and refinement statistics. Highest resolution shell is shown in parentheses. Structure Data
What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and peptides at aqueous graphene interfaces: Electronic Supplementary
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Central Dogma. modifications genome transcriptome proteome
 entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
Bioinformatics Practical for Biochemists
 Bioinformatics Practical for Biochemists Andrei Lupas, Birte Höcker, Steffen Schmidt WS 2013/14 03. Sequence Features Targeting proteins signal peptide targets proteins to the secretory pathway N-terminal
Bioinformatics Practical for Biochemists Andrei Lupas, Birte Höcker, Steffen Schmidt WS 2013/14 03. Sequence Features Targeting proteins signal peptide targets proteins to the secretory pathway N-terminal
7.012 Problem Set 1. i) What are two main differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
 ame 7.01 Problem Set 1 Section Question 1 a) What are the four major types of biological molecules discussed in lecture? Give one important function of each type of biological molecule in the cell? b)
ame 7.01 Problem Set 1 Section Question 1 a) What are the four major types of biological molecules discussed in lecture? Give one important function of each type of biological molecule in the cell? b)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1737 Supplementary Table 1 variant Description FSEC - 2B12 a FSEC - 6A1 a K d (leucine) c Leucine uptake e K (wild-type like) K (Y18F) K (TS) K (TSY) K288A mutant, lipid facing side chain
doi:1.138/nature1737 Supplementary Table 1 variant Description FSEC - 2B12 a FSEC - 6A1 a K d (leucine) c Leucine uptake e K (wild-type like) K (Y18F) K (TS) K (TSY) K288A mutant, lipid facing side chain
ENZYME MECHANISMS, PROTEASES, STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY
 Supplementary Information SUBJECT AREAS: ENZYME MECHANISMS, PROTEASES, STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to N.T. (ntanaka@pharm.showa-u.ac.jp) or W.O. (owataru@vos.nagaokaut.ac.jp)
Supplementary Information SUBJECT AREAS: ENZYME MECHANISMS, PROTEASES, STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to N.T. (ntanaka@pharm.showa-u.ac.jp) or W.O. (owataru@vos.nagaokaut.ac.jp)
ml. ph 7.5 ph 6.5 ph 5.5 ph 4.5. β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS
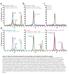 a UV28 absorption (mau) 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS β 2 AR-Gs complex dissociated complex excess nucleotides b 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex
a UV28 absorption (mau) 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS β 2 AR-Gs complex dissociated complex excess nucleotides b 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex
NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile virus NS2B-NS3 protease
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile
Chapter 4: Amino Acids
 Chapter 4: Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. lipid polysaccharide enzyme 1940s 1980s. Lipids membrane 1960s. Polysaccharide Are energy metabolites and many of
Chapter 4: Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. lipid polysaccharide enzyme 1940s 1980s. Lipids membrane 1960s. Polysaccharide Are energy metabolites and many of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 UPPEER ORO doi:10.1038/nature10753 D D D D P E ntracellular C1 W P P C EC1 D Q R H C D W D R C C2 D E D E C R Q Q W P W W R P P EC2 EC3 P C C P W P W W P C W H R C R E C3 P R R P P P C Extracellular embrane
UPPEER ORO doi:10.1038/nature10753 D D D D P E ntracellular C1 W P P C EC1 D Q R H C D W D R C C2 D E D E C R Q Q W P W W R P P EC2 EC3 P C C P W P W W P C W H R C R E C3 P R R P P P C Extracellular embrane
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London)
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
Peptide Syntheses. Illustrative Protection: BOC/ t Bu. A. Introduction. do not acid
 Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptide yntheses from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction do not acid -Met-e- -Met-Met- -e-e- -e-met- dipeptide dipeptide dipeptide dipeptide diketopiperazine
Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptide yntheses from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction do not acid -Met-e- -Met-Met- -e-e- -e-met- dipeptide dipeptide dipeptide dipeptide diketopiperazine
Oxygen Binding in Hemocyanin
 Supporting Information for Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Study of Oxygen Binding in Hemocyanin Toru Saito and Walter Thiel* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung, Kaiser-Wilhelm-Platz 1, D-45470
Supporting Information for Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Study of Oxygen Binding in Hemocyanin Toru Saito and Walter Thiel* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung, Kaiser-Wilhelm-Platz 1, D-45470
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
Salt bridge in the conserved His Asp cluster in Gloeobacter rhodopsin contributes to trimer formation
 FEBS Letters 587 (2013) 322 327 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org Salt bridge in the conserved His Asp cluster in Gloeobacter rhodopsin contributes to trimer formation Takashi Tsukamoto a, Takashi
FEBS Letters 587 (2013) 322 327 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org Salt bridge in the conserved His Asp cluster in Gloeobacter rhodopsin contributes to trimer formation Takashi Tsukamoto a, Takashi
Packing of Secondary Structures
 7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
Exam III. Please read through each question carefully, and make sure you provide all of the requested information.
 09-107 onors Chemistry ame Exam III Please read through each question carefully, and make sure you provide all of the requested information. 1. A series of octahedral metal compounds are made from 1 mol
09-107 onors Chemistry ame Exam III Please read through each question carefully, and make sure you provide all of the requested information. 1. A series of octahedral metal compounds are made from 1 mol
Physiochemical Properties of Residues
 Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Supplement information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physil Chemistry Chemil Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 216 Supplement information Fullerenol C 6 (OH) 16 prevents amyloid fibrillization of Aβ
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physil Chemistry Chemil Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 216 Supplement information Fullerenol C 6 (OH) 16 prevents amyloid fibrillization of Aβ
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
The Microbial Opsin Family of Optogenetic Tools
 The Microbial Opsin Family of Optogenetic Tools The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Zhang,
The Microbial Opsin Family of Optogenetic Tools The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Zhang,
NH 2. Biochemistry I, Fall Term Sept 9, Lecture 5: Amino Acids & Peptides Assigned reading in Campbell: Chapter
 Biochemistry I, Fall Term Sept 9, 2005 Lecture 5: Amino Acids & Peptides Assigned reading in Campbell: Chapter 3.1-3.4. Key Terms: ptical Activity, Chirality Peptide bond Condensation reaction ydrolysis
Biochemistry I, Fall Term Sept 9, 2005 Lecture 5: Amino Acids & Peptides Assigned reading in Campbell: Chapter 3.1-3.4. Key Terms: ptical Activity, Chirality Peptide bond Condensation reaction ydrolysis
Development of a Structure Prediction Method for G-Protein Coupled Receptors
 Development of a Structure Prediction Method for G-Protein Coupled Receptors Thesis by Spencer E. Hall In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute
Development of a Structure Prediction Method for G-Protein Coupled Receptors Thesis by Spencer E. Hall In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute
GPCR Dynamics: Structures in Motion
 This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/cr GPCR
This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/cr GPCR
Identification of Two Antiparallel-sheet Structure of Cobrotoxin in Aqueous Solution by'hnmr
 188 Bulletin of Magnetic Resonance Identification of Two Antiparallel-sheet Structure of Cobrotoxin in Aqueous Solution by'hnmr Chang-Shin Lee and Chin Yu* Department of Chemistry, National Tsing Hua University
188 Bulletin of Magnetic Resonance Identification of Two Antiparallel-sheet Structure of Cobrotoxin in Aqueous Solution by'hnmr Chang-Shin Lee and Chin Yu* Department of Chemistry, National Tsing Hua University
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information A Sensitive Phosphorescent Thiol Chemosensor Based on an Iridium(III) Complex with α,β-unsaturated Ketone Functionalized 2,2 -Bipyridyl Ligand Na Zhao, a Yu-Hui Wu,
Electronic Supplementary Information A Sensitive Phosphorescent Thiol Chemosensor Based on an Iridium(III) Complex with α,β-unsaturated Ketone Functionalized 2,2 -Bipyridyl Ligand Na Zhao, a Yu-Hui Wu,
Membrane Protein Channels
 Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
Protein Structure Marianne Øksnes Dalheim, PhD candidate Biopolymers, TBT4135, Autumn 2013
 Protein Structure Marianne Øksnes Dalheim, PhD candidate Biopolymers, TBT4135, Autumn 2013 The presentation is based on the presentation by Professor Alexander Dikiy, which is given in the course compedium:
Protein Structure Marianne Øksnes Dalheim, PhD candidate Biopolymers, TBT4135, Autumn 2013 The presentation is based on the presentation by Professor Alexander Dikiy, which is given in the course compedium:
Tyr-199 and Charged Residues of pharaonis Phoborhodopsin Are Important for the Interaction with its Transducer
 Biophysical Journal Volume 83 July 2002 427 432 427 Tyr-199 and Charged Residues of pharaonis Phoborhodopsin Are Important for the Interaction with its Transducer Yuki Sudo, Masayuki Iwamoto, Kazumi Shimono,
Biophysical Journal Volume 83 July 2002 427 432 427 Tyr-199 and Charged Residues of pharaonis Phoborhodopsin Are Important for the Interaction with its Transducer Yuki Sudo, Masayuki Iwamoto, Kazumi Shimono,
Esser et al. Crystal Structures of R. sphaeroides bc 1
 Esser et al. Crystal Structures of R. sphaeroides bc Supplementary Information Trivariate Gaussian Probability Analysis The superposition of six structures results in sextets of 3D coordinates for every
Esser et al. Crystal Structures of R. sphaeroides bc Supplementary Information Trivariate Gaussian Probability Analysis The superposition of six structures results in sextets of 3D coordinates for every
GPROTEIN-coupled, seven-transmembrane segment receptors
 0163-769X/00/$03.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 21(1): 90 113 Copyright 2000 by The Endocrine Society Printed in U.S.A. Uncovering Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Activation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors ULRIK
0163-769X/00/$03.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 21(1): 90 113 Copyright 2000 by The Endocrine Society Printed in U.S.A. Uncovering Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Activation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors ULRIK
.crystal structure; KR2; light-driven ion pump;
 Prospects & Overviews The light-driven sodium ion pump: A new player in rhodopsin research Hideaki E. Kato 1), Keiichi Inoue 2)3)4), Hideki Kandori 2)3) and Osamu Nureki 5) Rhodopsins are one of the most
Prospects & Overviews The light-driven sodium ion pump: A new player in rhodopsin research Hideaki E. Kato 1), Keiichi Inoue 2)3)4), Hideki Kandori 2)3) and Osamu Nureki 5) Rhodopsins are one of the most
MOLECULAR DRUG TARGETS
 MOLECULAR DRUG TARGETS LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of this session student shall be able to: List different types of druggable targets Describe forces involved in drug-receptor interactions Describe theories
MOLECULAR DRUG TARGETS LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of this session student shall be able to: List different types of druggable targets Describe forces involved in drug-receptor interactions Describe theories
FW 1 CDR 1 FW 2 CDR 2
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Interface of the E9:Fas structure. The two interfaces formed by V H and V L of E9 with Fas are shown in stereo. The Fas receptor is represented as a surface
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Interface of the E9:Fas structure. The two interfaces formed by V H and V L of E9 with Fas are shown in stereo. The Fas receptor is represented as a surface
A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of
 Questions with Answers- Amino Acids & Peptides A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of 5.0-6.5 (Questions 1-4) 1. Which
Questions with Answers- Amino Acids & Peptides A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of 5.0-6.5 (Questions 1-4) 1. Which
Biological Macromolecules
 Introduction for Chem 493 Chemistry of Biological Macromolecules Dr. L. Luyt January 2008 Dr. L. Luyt Chem 493-2008 1 Biological macromolecules are the molecules of life allow for organization serve a
Introduction for Chem 493 Chemistry of Biological Macromolecules Dr. L. Luyt January 2008 Dr. L. Luyt Chem 493-2008 1 Biological macromolecules are the molecules of life allow for organization serve a
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Active Site Structure and Absorption Spectrum of Channelrhodopsin-2
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Active Site Structure and Absorption Spectrum of Channelrhodopsin-2
Detecting Molecular Interactions that Stabilize Native Bovine Rhodopsin
 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.02.008 J. Mol. Biol. (2006) 358, 255 269 Detecting Molecular Interactions that Stabilize Native Bovine Rhodopsin K. Tanuj Sapra 1, Paul S.-H. Park 2 *, Slawomir Filipek 3, Andreas
doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.02.008 J. Mol. Biol. (2006) 358, 255 269 Detecting Molecular Interactions that Stabilize Native Bovine Rhodopsin K. Tanuj Sapra 1, Paul S.-H. Park 2 *, Slawomir Filipek 3, Andreas
Ligand-receptor interactions
 University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland 11 22 March 2013 Ligand-receptor interactions Dr. Pavel Polishchuk A.V. Bogatsky Physico-Chemical Institute of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine Odessa, Ukraine
University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland 11 22 March 2013 Ligand-receptor interactions Dr. Pavel Polishchuk A.V. Bogatsky Physico-Chemical Institute of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine Odessa, Ukraine
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. MhsT and LeuT architecture.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MhsT and LeuT architecture. a, Cartoon structure representation and topology diagram for MhsT in the occluded inward-facing state and b, LeuT in the occluded outward-facing state
Supplementary Figure 1 MhsT and LeuT architecture. a, Cartoon structure representation and topology diagram for MhsT in the occluded inward-facing state and b, LeuT in the occluded outward-facing state
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Subhodeep Moitra 1, Kalyan C Tirupula 2, Judith Klein-Seetharaman 2* and Christopher James Langmead 1*
 Moitra et al. BMC Biophysics 2012, 5:13 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A minimal ligand binding pocket within a network of correlated mutations identified by multiple sequence and structural analysis of
Moitra et al. BMC Biophysics 2012, 5:13 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A minimal ligand binding pocket within a network of correlated mutations identified by multiple sequence and structural analysis of
Heterotrimeric G proteins and the role of lipids in signaling. John Sondek, Ph.D. Depts. of Pharmacology and Biochemistry & Biophyscis
 Heterotrimeric G proteins and the role of lipids in signaling John Sondek, Ph.D. Depts. of Pharmacology and Biochemistry & Biophyscis The GTPase cycle molecular switch A GTPases is NOT a kinase Two major
Heterotrimeric G proteins and the role of lipids in signaling John Sondek, Ph.D. Depts. of Pharmacology and Biochemistry & Biophyscis The GTPase cycle molecular switch A GTPases is NOT a kinase Two major
CHEM J-9 June 2014
 CEM1611 2014-J-9 June 2014 Alanine (ala) and lysine (lys) are two amino acids with the structures given below as Fischer projections. The pk a values of the conjugate acid forms of the different functional
CEM1611 2014-J-9 June 2014 Alanine (ala) and lysine (lys) are two amino acids with the structures given below as Fischer projections. The pk a values of the conjugate acid forms of the different functional
DOCKING TUTORIAL. A. The docking Workflow
 2 nd Strasbourg Summer School on Chemoinformatics VVF Obernai, France, 20-24 June 2010 E. Kellenberger DOCKING TUTORIAL A. The docking Workflow 1. Ligand preparation It consists in the standardization
2 nd Strasbourg Summer School on Chemoinformatics VVF Obernai, France, 20-24 June 2010 E. Kellenberger DOCKING TUTORIAL A. The docking Workflow 1. Ligand preparation It consists in the standardization
Structural insights into energy regulation of light-harvesting complex from spinach CP29
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Structural insights into energy regulation of light-harvesting complex from spinach CP29 Xiaowei Pan 1, Mei Li 1, Tao Wan 1,2, Longfei Wang 1,2, Chenjun Jia 1,2, Zhiqiang Hou
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Structural insights into energy regulation of light-harvesting complex from spinach CP29 Xiaowei Pan 1, Mei Li 1, Tao Wan 1,2, Longfei Wang 1,2, Chenjun Jia 1,2, Zhiqiang Hou
MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF PHOTOSIGNALING BY ARCHAEAL SENSORY RHODOPSINS
 Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1997. 26:223 58 Copyright c 1997 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF PHOTOSIGNALING BY ARCHAEAL SENSORY RHODOPSINS Wouter D. Hoff, Kwang-Hwan
Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1997. 26:223 58 Copyright c 1997 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF PHOTOSIGNALING BY ARCHAEAL SENSORY RHODOPSINS Wouter D. Hoff, Kwang-Hwan
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. doi: /nature07461
 Figure S1 Electrophysiology. a ph-activation of. Two-electrode voltage clamp recordings of Xenopus oocytes expressing in comparison to waterinjected oocytes. Currents were recorded at 40 mv. The ph of
Figure S1 Electrophysiology. a ph-activation of. Two-electrode voltage clamp recordings of Xenopus oocytes expressing in comparison to waterinjected oocytes. Currents were recorded at 40 mv. The ph of
Basic Principles of Protein Structures
 Basic Principles of Protein Structures Proteins Proteins: The Molecule of Life Proteins: Building Blocks Proteins: Secondary Structures Proteins: Tertiary and Quartenary Structure Proteins: Geometry Proteins
Basic Principles of Protein Structures Proteins Proteins: The Molecule of Life Proteins: Building Blocks Proteins: Secondary Structures Proteins: Tertiary and Quartenary Structure Proteins: Geometry Proteins
Translation. A ribosome, mrna, and trna.
 Translation The basic processes of translation are conserved among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic Translation A ribosome, mrna, and trna. In the initiation of translation in prokaryotes, the Shine-Dalgarno
Translation The basic processes of translation are conserved among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic Translation A ribosome, mrna, and trna. In the initiation of translation in prokaryotes, the Shine-Dalgarno
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I. 1. Of the 20 standard amino acids, only is not optically active. The reason is that its side chain.
 Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
CHMI 2227 EL. Biochemistry I. Test January Prof : Eric R. Gauthier, Ph.D.
 CHMI 2227 EL Biochemistry I Test 1 26 January 2007 Prof : Eric R. Gauthier, Ph.D. Guidelines: 1) Duration: 55 min 2) 14 questions, on 7 pages. For 70 marks (5 marks per question). Worth 15 % of the final
CHMI 2227 EL Biochemistry I Test 1 26 January 2007 Prof : Eric R. Gauthier, Ph.D. Guidelines: 1) Duration: 55 min 2) 14 questions, on 7 pages. For 70 marks (5 marks per question). Worth 15 % of the final
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/243/ra68/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Superbinder SH2 Domains Act as Antagonists of Cell Signaling Tomonori Kaneko, Haiming Huang, Xuan Cao, Xing Li, Chengjun
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/243/ra68/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Superbinder SH2 Domains Act as Antagonists of Cell Signaling Tomonori Kaneko, Haiming Huang, Xuan Cao, Xing Li, Chengjun
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. CRBN binding assay with thalidomide enantiomers.
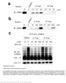 Supplementary Figure 1 CRBN binding assay with thalidomide enantiomers. (a) Competitive elution assay using thalidomide-immobilized beads coupled with racemic thalidomide. Beads were washed three times
Supplementary Figure 1 CRBN binding assay with thalidomide enantiomers. (a) Competitive elution assay using thalidomide-immobilized beads coupled with racemic thalidomide. Beads were washed three times
Chapter V: A Comparison of the Antagonist Binding Sites of the Human Dopamine Receptors
 144 Chapter V: A Comparison of the Antagonist Binding Sites of the Human Dopamine Receptors 145 Chapter V: A Comparison of the Antagonist Binding Sites of the Human Dopamine Receptors Abstract: The dopamine
144 Chapter V: A Comparison of the Antagonist Binding Sites of the Human Dopamine Receptors 145 Chapter V: A Comparison of the Antagonist Binding Sites of the Human Dopamine Receptors Abstract: The dopamine
Model Mélange. Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins
 Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
C H E M I S T R Y N A T I O N A L Q U A L I F Y I N G E X A M I N A T I O N SOLUTIONS GUIDE
 C H E M I S T R Y 2 0 0 0 A T I A L Q U A L I F Y I G E X A M I A T I SLUTIS GUIDE Answers are a guide only and do not represent a preferred method of solving problems. Section A 1B, 2A, 3C, 4C, 5D, 6D,
C H E M I S T R Y 2 0 0 0 A T I A L Q U A L I F Y I G E X A M I A T I SLUTIS GUIDE Answers are a guide only and do not represent a preferred method of solving problems. Section A 1B, 2A, 3C, 4C, 5D, 6D,
