Heterotrimeric G proteins and the role of lipids in signaling. John Sondek, Ph.D. Depts. of Pharmacology and Biochemistry & Biophyscis
|
|
|
- Asher Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Heterotrimeric G proteins and the role of lipids in signaling John Sondek, Ph.D. Depts. of Pharmacology and Biochemistry & Biophyscis
2 The GTPase cycle molecular switch
3 A GTPases is NOT a kinase
4
5 Two major regulators of GTPase cycle
6 Specific GEFs and GAPs for heterotrimeric G proteins
7 Active heterotrimer dissociates into a Gα subunit and a Gβγ dimer
8 G protein-coupled receptors as GEFs for heterotrimeric G proteins GPCRs are the largest family of cell-surface receptors for extracellular signals (superfamily of >1000 members) GPCRs respond to a wide range of inputs: hormones, neurotransmitters, odorants, tastants, photons of light, etc. ~60% of all clinical therapeutics act by affecting some aspect of GPCR signaling (e.g., agonist, antagonist, inhibition of natural ligand metabolism)
9 GPCRs are seven transmembrane (7TM) receptors
10 G proteins sense conformational changes of intracellular loops
11 G proteins sense conformational changes of intracellular loops
12 Active receptor stabilized nucleotide-depleted heterotrimer
13 GTP-loading catalyzes heterotrimer dissociation
14 Figure Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
15 Rasmussen et al., Nature 450, 383 (2007)
16 R E G Bockaert & Pin (1999) EMBO J. 18:1732
17 Rhodopsin-like: - dopamine, adrenaline, serotonin (5HT) Ligandbinding pocket DRY -motif critical for G-protein activation IL8, fmlp PAF Thrombin: Special case of protease-activated GPCRs - Irreversible activation by N-terminal cleavage Palmitoylated cysteine Bockaert & Pin (1999) EMBO J. 18:1732
18 High-mol.wt. hormones: Glucagon Metabotropic glutamate/gaba/pheromone: Large Venus flytrap disulfide-linked ectodomain Bockaert & Pin (1999) EMBO J. 18:1732
19 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry G protein-coupled receptor drug membrane Brian Kobilka Brian Kobilka G protein (1994 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine) GDP Robert Lefkowitz
20 The Gα subunit: Lipid modifications for membrane binding Exotoxin from Bordetella pertussis (whooping cough) catalyzes ADP-ribosylation of i-class Gα: Result? De-coupling from receptor Exotoxin from Vibrio cholerae (cholera diarrhea) catalyzes ADP-ribosylation of s-class Gα: Result? Constitutive activity since crippled as a GTPase
21
22
23 Gα contains a Ras-like domain and an all-helical domain Three switch regions have conformations that depend on which nucleotide is bound
24 Gα contains a Ras-like domain and an all-helical domain
25 This image cannot currently be displayed. Arginine finger is critical for GTP hydrolysis. This image cannot currently be displayed. transducin p120 GAP Ras-like domain Ras S3 R789 Helical domain R174 S1 S2 S1 S2 Gαt. GDP. AlF 4 Aluminum tetrafluoride ion mimics third phosphate of GTP and thereby activates GDP-bound Gα subunits. Ras/p120 GAP. GDP. AlF3
26 Arginine finger is critical for GTP hydrolysis Site of cholera activation; R>C mutation activates. Q>L mutation also activates by crippling GTPase function. R789 GDP AlF 4 Q200 Q61 S2 H 2 O R174 Mg 2+ H 2 O S2 GDP Mg 2+ AlF 3 S1 S1 Gαt. GDP. AlF 4 Ras/p120 GAP. GDP. AlF 3 For Ras-like GTPases, arginine finger is supplied in trans by GAPs. For heterotrimeric G proteins, the catalytic arginine is part of the alpha subunit.
27 Primary sequence characteristics of Gβγ dimers
28 Gβ forms a propeller; Gγ is an extended helical peptide. CAAX Sondek et al. Nature (1996) 379: 369
29 The switches of Gα are primary interaction sites with Gβγ (no interactions between Gα and Gγ!) Lambright et al. Nature (1996) 379: 311.
30 The switches of Gα are primary interaction sites with Gβγ (the N-terminal helix of Gα is also used) Lambright et al. Nature (1996) 379: 311.
31 Portions (purple) of all three subunits contact receptor Swap receptor specificity by switching C-termini? Inhibit coupling via C-terminal minigenes? Area of ADP-ribosylation via pertussis toxin (αi-class) Gilchrist et al. (2001) JBC 276:25672
32 Interface defined by structural features and biochemical evidence sugars membrane rhodopsin m retinal N-Myristoyl, S-palmitoyl S-Prenyl (GG or F) GDP Gα S3 S1 S2 Gβγ Regions of protein in purple are implicated in receptor interactions
33 Gα switches (I, II, III) are sensitive to bound nucleotide
34 Gα switch regions (I, II) directly interact with GTP
35 The four families of Gα subunits (-) Pertussis-toxin sensitive Gα subunits Adenylyl cyclase (+) (+) Phospholipase C-beta (+) Rho-GTP
36 Examples of G-protein effector systems G-protein subunit Effector Second messenger Gαs, Gαolf adenylyl cyclase [camp] Gαi1/i2/i3 adenylyl cyclase [camp] Gαq/11 phospholipase-cβ [IP 3 ] & [DAG] Gα12/13 RGS-box RhoGEFs [RhoA-GTP] Gατ (transducin) phospholipase-cε cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase [IP 3 ] & [DAG] [cgmp] Gβγ dimer or adenylyl cyclase or [camp] PLC-β & PLC-ε or ion channel flux [IP 3 ] & [DAG] K+ and Ca2+
37 Four Gβ subunits and one oddball
38 Blake et al. (2001) JBC 276:49267 Plenty o Gγ subunits
39 Gs = stimulatory G-protein linked to adenylyl cyclase activation (2nd-messenger generation) Adenylyl cyclase β2-adrenergic receptor on vasculature of skeletal muscles Adrenaline or Isoproterenol ( 1st messenger ) AC Second messenger + α s GTP γ β camp ATP Net result: Five-fold increase in [camp] i in seconds
40 Gαs GTPγS S3 S2 Complex of Gαs with cytoplasmic portions of Adenylyl cyclase S1 Gαs interacts with cyclase primarily through switches 1 and 2 forskolin Forskolin favors dimerization of cyclase domains IIC2 VC1 Tesmer (1997) Science 278:1907
41 Turning off the signal Multiple levels & multiple time-frames Reuptake/destruction of agonist (~millisec) Hydrolysis of GTP bound to Gα subunit (~sec) Reuptake/destruction of second messenger (~sec) Uncouple receptor from signal machinery (~sec/min) Remove receptor from cell-surface (~min/hr)
42 The R7 family Adapted from Hollinger & Hepler (2002).
43 RGS proteins stabilize the transition state for GTP hydrolysis
44 Figure 10-1 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
45 Figure 10-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
46 Figure 10-3 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
47 Figure 10-4 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
48 Figure 10-5 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
49 Figure 10-7b Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
50 Figure Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
51
52 Figure Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
53 PLCs are phospholipases
54 PLC- β isozymes are classic effectors of heterotrimeric G proteins
MOLECULAR DRUG TARGETS
 MOLECULAR DRUG TARGETS LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of this session student shall be able to: List different types of druggable targets Describe forces involved in drug-receptor interactions Describe theories
MOLECULAR DRUG TARGETS LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of this session student shall be able to: List different types of druggable targets Describe forces involved in drug-receptor interactions Describe theories
Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e Chapter 04
 01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
Receptors and Ion Channels
 Receptors and Ion Channels Laurie Kellaway Senior Lecturer Department of Human Biology Laurie@curie.uct.ac.za Tel. +27 +21 4066 271 What are the two types of Neurotransmitter receptors Ionotropic receptors
Receptors and Ion Channels Laurie Kellaway Senior Lecturer Department of Human Biology Laurie@curie.uct.ac.za Tel. +27 +21 4066 271 What are the two types of Neurotransmitter receptors Ionotropic receptors
Visual pigments. Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019
 Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019 References Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a 127) The
Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019 References Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a 127) The
Visual pigments. Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2015
 Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2015 References Photoreceptors and visual pigments Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a127)
Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2015 References Photoreceptors and visual pigments Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a127)
GPCRs and G Protein Activation
 GPCRs and G Protein Activation 6 Waelbroeck Magali Université Libre de Bruxelles Belgium 1. Introduction An efficient intercellular communication system is essential to allow the correct functioning of
GPCRs and G Protein Activation 6 Waelbroeck Magali Université Libre de Bruxelles Belgium 1. Introduction An efficient intercellular communication system is essential to allow the correct functioning of
Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction 111202 Here we look at the movement of a signal from the outside of a cell to its inside, where it elicits changes within the cell. These changes are usually mediated
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction 111202 Here we look at the movement of a signal from the outside of a cell to its inside, where it elicits changes within the cell. These changes are usually mediated
Identification number: TÁMOP /1/A
 Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
1. Introduction. 1. Introduction. 1.1 Signal transduction
 1. Introduction 1.1 Signal transduction During the evolution of multicellular organisms, highly complex and integrative communication networks have evolved to coordinate growth, differentiation and metabolism
1. Introduction 1.1 Signal transduction During the evolution of multicellular organisms, highly complex and integrative communication networks have evolved to coordinate growth, differentiation and metabolism
Ligand screening system using fusion proteins of G protein coupled receptors with G protein α subunits
 2 Ligand screening system using fusion proteins of G protein coupled receptors with G protein α subunits G protein coupled receptors A key player of signaling transduction. Cell membranes are packed with
2 Ligand screening system using fusion proteins of G protein coupled receptors with G protein α subunits G protein coupled receptors A key player of signaling transduction. Cell membranes are packed with
Modeling signal transduction. Phototransduction from frogs to flies
 Modeling signal transduction Phototransduction from frogs to flies Eye as an evolutionary challenge To suppose that the eye, with all its inimitable contrivances, could have been formed by natural selection,
Modeling signal transduction Phototransduction from frogs to flies Eye as an evolutionary challenge To suppose that the eye, with all its inimitable contrivances, could have been formed by natural selection,
Intercellular communication
 Intercellular communication Dewajani Purnomosari Department of Histology and Cell Biology Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada Outline General principle of intercellular communicabon Signal molecules
Intercellular communication Dewajani Purnomosari Department of Histology and Cell Biology Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada Outline General principle of intercellular communicabon Signal molecules
Signal Transduction Phosphorylation Protein kinases. Misfolding diseases. Protein Engineering Lysozyme variants
 Signal Transduction Phosphorylation Protein kinases Misfolding diseases Protein Engineering Lysozyme variants Cells and Signals Regulation The cell must be able to respond to stimuli Cellular activities
Signal Transduction Phosphorylation Protein kinases Misfolding diseases Protein Engineering Lysozyme variants Cells and Signals Regulation The cell must be able to respond to stimuli Cellular activities
The circle and the basics of signal transduction. Course Outline. Topic #! Topic lecture! Silverthorn! Membranes (pre-requisite material)" "
 Homeostasis 03 The goal of this lecture is to discuss the concept of homeostasis and to introduce basic signal transduction mechanisms involved in homeostatic regulation The sections for this lecture are:
Homeostasis 03 The goal of this lecture is to discuss the concept of homeostasis and to introduce basic signal transduction mechanisms involved in homeostatic regulation The sections for this lecture are:
The EGF Signaling Pathway! Introduction! Introduction! Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3. EGF promotes cell growth
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3 Question of the Day: Who is the son of Sevenless? Introduction! Signal transduction involves the changing of a cell s metabolism or gene
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3 Question of the Day: Who is the son of Sevenless? Introduction! Signal transduction involves the changing of a cell s metabolism or gene
Identification of Functional Amino Acids in the G Protein Alpha-Subunit
 The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine University of Maine Office of Research and Sponsored Programs: Grant Reports Special Collections 7-31-2001 Identification of Functional Amino Acids in the
The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine University of Maine Office of Research and Sponsored Programs: Grant Reports Special Collections 7-31-2001 Identification of Functional Amino Acids in the
GTPASE-ACTIVATING PROTEINS FOR HETEROTRIMERIC GPROTEINS: Regulators of G Protein Signaling (RGS) and RGS-Like Proteins
 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000. 69:795 827 Copyright c 2000 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved GTPASE-ACTIVATING PROTEINS FOR HETEROTRIMERIC GPROTEINS: Regulators of G Protein Signaling (RGS) and RGS-Like
Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000. 69:795 827 Copyright c 2000 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved GTPASE-ACTIVATING PROTEINS FOR HETEROTRIMERIC GPROTEINS: Regulators of G Protein Signaling (RGS) and RGS-Like
Drug interactions. (Efficacy is a measure of the size of response produced by receptor activation)
 Drug interactions Receptor A signal transducer, modifying cell function in response to an extracellular signal. - Membrane proteins e.g. AChR, - Cytoplasmic proteins e.g. steroid receptors Drugs usually
Drug interactions Receptor A signal transducer, modifying cell function in response to an extracellular signal. - Membrane proteins e.g. AChR, - Cytoplasmic proteins e.g. steroid receptors Drugs usually
Reception The target cell s detection of a signal coming from outside the cell May Occur by: Direct connect Through signal molecules
 Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
References on Kinetics and Mechanisms
 References on Kinetics and Mechanisms Excellent reference for all aspects of enzyme kinetics including important elements of Metabolic Control Analysis of relevance to systems analysis of enzyme function
References on Kinetics and Mechanisms Excellent reference for all aspects of enzyme kinetics including important elements of Metabolic Control Analysis of relevance to systems analysis of enzyme function
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
G protein coupled receptors Structure, function, regulation
 G protein coupled receptors Structure, function, regulation Im menschlichen Genom finden sich Gene für ~ 810 G-Protein-gekoppelte Rezeptoren 350 nicht-geruchbildende Rezeptoren 460 Geruchrezeptoren Vielfalt
G protein coupled receptors Structure, function, regulation Im menschlichen Genom finden sich Gene für ~ 810 G-Protein-gekoppelte Rezeptoren 350 nicht-geruchbildende Rezeptoren 460 Geruchrezeptoren Vielfalt
Biochemical bases for energy transformations. Biochemical bases for energy transformations. Nutrition 202 Animal Energetics R. D.
 Biochemical bases for energy transformations Biochemical bases for energy transformations Nutrition 202 Animal Energetics R. D. Sainz Lecture 02 Energy originally from radiant sun energy Captured in chemical
Biochemical bases for energy transformations Biochemical bases for energy transformations Nutrition 202 Animal Energetics R. D. Sainz Lecture 02 Energy originally from radiant sun energy Captured in chemical
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 12, PAGE 1 of 7
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 12, 2009 -- PAGE 1 of 7 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 12, 2009 -- PAGE 1 of 7 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
Bahnson Biochemistry Cume, April 8, 2006 The Structural Biology of Signal Transduction
 Name page 1 of 6 Bahnson Biochemistry Cume, April 8, 2006 The Structural Biology of Signal Transduction Part I. The ion Ca 2+ can function as a 2 nd messenger. Pick a specific signal transduction pathway
Name page 1 of 6 Bahnson Biochemistry Cume, April 8, 2006 The Structural Biology of Signal Transduction Part I. The ion Ca 2+ can function as a 2 nd messenger. Pick a specific signal transduction pathway
Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently become
 Homology Modeling and Docking of Melatonin Receptors Andrew Kohlway, UMBC Jeffry D. Madura, Duquesne University 6/18/04 INTRODUCTION Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently
Homology Modeling and Docking of Melatonin Receptors Andrew Kohlway, UMBC Jeffry D. Madura, Duquesne University 6/18/04 INTRODUCTION Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently
Activation of a receptor. Assembly of the complex
 Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Molecular biology of neural communication
 Molecular biology of neural communication One picture - two information Where do I feel the pain? Real and Virtual Consciousness Almost all neural process is pervaded by the consciousness We not only perceive
Molecular biology of neural communication One picture - two information Where do I feel the pain? Real and Virtual Consciousness Almost all neural process is pervaded by the consciousness We not only perceive
RESEARCH PROPOSAL MODELING A CELLULAR TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING SYSTEM THROUGH INTERACTION WITH G-PROTEINS BY USING CONCURRENT
 RESEARCH PROPOSAL MODELING A CELLULAR TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING SYSTEM THROUGH INTERACTION WITH G-PROTEINS BY USING CONCURRENT CONSTRAINT PROCESS CALCULI BY DIANA-PATRICIA HERMITH-RAMIREZ, B.S. ADVISOR:
RESEARCH PROPOSAL MODELING A CELLULAR TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING SYSTEM THROUGH INTERACTION WITH G-PROTEINS BY USING CONCURRENT CONSTRAINT PROCESS CALCULI BY DIANA-PATRICIA HERMITH-RAMIREZ, B.S. ADVISOR:
ml. ph 7.5 ph 6.5 ph 5.5 ph 4.5. β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS
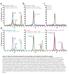 a UV28 absorption (mau) 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS β 2 AR-Gs complex dissociated complex excess nucleotides b 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex
a UV28 absorption (mau) 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS β 2 AR-Gs complex dissociated complex excess nucleotides b 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex
Analysis of correlated mutations in Ras G-domain
 www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Analysis of correlated mutations in Ras G-domain Ekta Pathak * Bioinformatics Department, MMV, Banaras Hindu University. Ekta Pathak - E-mail: ektavpathak@gmail.com;
www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Analysis of correlated mutations in Ras G-domain Ekta Pathak * Bioinformatics Department, MMV, Banaras Hindu University. Ekta Pathak - E-mail: ektavpathak@gmail.com;
Regulation and signaling. Overview. Control of gene expression. Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on
 Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Activation of G Protein Coupled Receptors: Beyond Two-State Models and Tertiary Conformational Changes
 Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008. 48:107 41 First published online as a Review in Advance on September 10, 2007 The Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology is online at http://pharmtox.annualreviews.org
Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008. 48:107 41 First published online as a Review in Advance on September 10, 2007 The Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology is online at http://pharmtox.annualreviews.org
Biosignaling. Molecular mechanisms of signal transduction
 Biosignaling The ability of cells to receive and act on signals from beyond the plasma membrane is fundamental to life. The signals in animals may be autocrine (acting on the same cell that produces them),
Biosignaling The ability of cells to receive and act on signals from beyond the plasma membrane is fundamental to life. The signals in animals may be autocrine (acting on the same cell that produces them),
Phototransduction in Vertebrate Rods and Cones: Molecular Mechanisms of Amplification, Recovery and Light Adaptation
 CHAPTER 5 Phototransduction in Vertebrate Rods and Cones: Molecular Mechanisms of Amplification, Recovery and Light Adaptation E. N. PUGH, Jr T. D. LAMB F. M. Kirby Center for Molecular Ophthalmology,
CHAPTER 5 Phototransduction in Vertebrate Rods and Cones: Molecular Mechanisms of Amplification, Recovery and Light Adaptation E. N. PUGH, Jr T. D. LAMB F. M. Kirby Center for Molecular Ophthalmology,
Minireview: Molecular Structure and Dynamics of Drug Targets
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 109 (2008) No. 2 3, p. 107 112 107) Minireview: Molecular Structure and Dynamics of Drug Targets Dahl S. G., Sylte I. Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Biology,
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 109 (2008) No. 2 3, p. 107 112 107) Minireview: Molecular Structure and Dynamics of Drug Targets Dahl S. G., Sylte I. Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Biology,
GPCR Conformations: Implications for Rational Drug Design
 Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 7-43; doi:10.3390/ph4010007 Review OPEN ACCESS pharmaceuticals ISSN 1424-8247 www.mdpi.com/journal/pharmaceuticals GPCR Conformations: Implications for Rational Drug Design Abby
Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 7-43; doi:10.3390/ph4010007 Review OPEN ACCESS pharmaceuticals ISSN 1424-8247 www.mdpi.com/journal/pharmaceuticals GPCR Conformations: Implications for Rational Drug Design Abby
Raghuram et al PNAS 100:9620
 ION CHANNL MACROMOLCULAR COMPLXS A V I R W c g I S L S R d L L LLL I VA S f L LS HP a b D G C S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 I e V N S6 COOH NH 2 PDZ domains; recognition of short peptides with a COOH terminal hydrophobic
ION CHANNL MACROMOLCULAR COMPLXS A V I R W c g I S L S R d L L LLL I VA S f L LS HP a b D G C S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 I e V N S6 COOH NH 2 PDZ domains; recognition of short peptides with a COOH terminal hydrophobic
Pivotal Role of Extended Linker 2 in the Activation of Gα by G Protein-Coupled Receptor
 JBC Papers in Press. Published on November 20, 2014 as Manuscript M114.608661 The latest version is at http://www.jbc.org/cgi/doi/10.1074/jbc.m114.608661 Huang et al. 1 Pivotal Role of Extended Linker
JBC Papers in Press. Published on November 20, 2014 as Manuscript M114.608661 The latest version is at http://www.jbc.org/cgi/doi/10.1074/jbc.m114.608661 Huang et al. 1 Pivotal Role of Extended Linker
GPROTEIN-coupled, seven-transmembrane segment receptors
 0163-769X/00/$03.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 21(1): 90 113 Copyright 2000 by The Endocrine Society Printed in U.S.A. Uncovering Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Activation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors ULRIK
0163-769X/00/$03.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 21(1): 90 113 Copyright 2000 by The Endocrine Society Printed in U.S.A. Uncovering Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Activation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors ULRIK
The Plant Heterotrimeric G-Protein Complex
 I ANRV310-PP58-12 ARI 26 December 2006 21:34 R E V I E W S First published online as a Review in Advance on January 3, 2007 E C N A D V A N Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007. 58:249 66 The Annual Review of Plant
I ANRV310-PP58-12 ARI 26 December 2006 21:34 R E V I E W S First published online as a Review in Advance on January 3, 2007 E C N A D V A N Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007. 58:249 66 The Annual Review of Plant
University of Warwick institutional repository: A Thesis Submitted for the Degree of PhD at the University of Warwick
 University of Warwick institutional repository: http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap A Thesis Submitted for the Degree of PhD at the University of Warwick http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap/7521 This thesis is made
University of Warwick institutional repository: http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap A Thesis Submitted for the Degree of PhD at the University of Warwick http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap/7521 This thesis is made
Neuropeptide Receptors
 Colloquium series on neuropeptides Series Editors: Lakshmi Devi & Lloyd D. Fricker Neuropeptide Receptors Ivone Gomes Jonathan H. Wardman Steven D. Stockton Jr. Lakshmi A. Devi life sciences Morgan & Claypool
Colloquium series on neuropeptides Series Editors: Lakshmi Devi & Lloyd D. Fricker Neuropeptide Receptors Ivone Gomes Jonathan H. Wardman Steven D. Stockton Jr. Lakshmi A. Devi life sciences Morgan & Claypool
M. Sci. Thesis in Pharmacology RECEPTOR STRUCTURE AND LIGAND INTERACTIONS. Mari Gabrielsen October 2006
 M. Sci. Thesis in Pharmacology THE 5 HT 1E RECEPTOR RECEPTOR STRUCTURE AND LIGAND INTERACTIONS Mari Gabrielsen October 2006 Department of Pharmacology Institute of Medical Biology Faculty of Medicine University
M. Sci. Thesis in Pharmacology THE 5 HT 1E RECEPTOR RECEPTOR STRUCTURE AND LIGAND INTERACTIONS Mari Gabrielsen October 2006 Department of Pharmacology Institute of Medical Biology Faculty of Medicine University
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Protein Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation
 Keep in mind that the original signaling molecule is not physically passed along a signaling pathway; in most cases, it never even enters the cell. When we say that the signal is relayed along a pathway,
Keep in mind that the original signaling molecule is not physically passed along a signaling pathway; in most cases, it never even enters the cell. When we say that the signal is relayed along a pathway,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
Introduction to CNS neurobiology: focus on retina
 Introduction to CNS neurobiology: focus on retina September 27, 2017 The retina is part of the CNS Calloway et al., 2009) 1 Retinal circuits: neurons and synapses Rods and Cones Bipolar cells Horizontal
Introduction to CNS neurobiology: focus on retina September 27, 2017 The retina is part of the CNS Calloway et al., 2009) 1 Retinal circuits: neurons and synapses Rods and Cones Bipolar cells Horizontal
REGULATION OF SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION BY G PROTEIN β SUBUNITS IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE
 REGULATION OF SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION BY G PROTEIN β SUBUNITS IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE Corinne Eileen Zeller A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in
REGULATION OF SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION BY G PROTEIN β SUBUNITS IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE Corinne Eileen Zeller A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
G PROTEINS- TRANSDUCERS OF RECEPTOR-GENERATED SIGNALS
 Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1987. 56. 615-49 Copyright 1987 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved G PROTEINS- TRANSDUCERS OF RECEPTOR-GENERATED SIGNALS Alfred G. Gilman Department of Pharmacology, Southwestern
Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1987. 56. 615-49 Copyright 1987 by Annual Reviews Inc. All rights reserved G PROTEINS- TRANSDUCERS OF RECEPTOR-GENERATED SIGNALS Alfred G. Gilman Department of Pharmacology, Southwestern
Protein Sorting, Intracellular Trafficking, and Vesicular Transport
 Protein Sorting, Intracellular Trafficking, and Vesicular Transport Noemi Polgar, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy, Biochemistry and Physiology Email: polgar@hawaii.edu Phone: 692-1422 Outline Part 1- Trafficking
Protein Sorting, Intracellular Trafficking, and Vesicular Transport Noemi Polgar, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy, Biochemistry and Physiology Email: polgar@hawaii.edu Phone: 692-1422 Outline Part 1- Trafficking
Systems Biology Across Scales: A Personal View XIV. Intra-cellular systems IV: Signal-transduction and networks. Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai
 Systems Biology Across Scales: A Personal View XIV. Intra-cellular systems IV: Signal-transduction and networks Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai Intra-cellular biochemical networks Metabolic networks Nodes:
Systems Biology Across Scales: A Personal View XIV. Intra-cellular systems IV: Signal-transduction and networks Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai Intra-cellular biochemical networks Metabolic networks Nodes:
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters
 Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
Understanding Allosteric Modulation of G-Protein Coupled Receptors
 Clemson University TigerPrints All Dissertations Dissertations 5-2016 Understanding Allosteric Modulation of G-Protein Coupled Receptors Vibhor Agrawal Clemson University, vibhora@clemson.edu Follow this
Clemson University TigerPrints All Dissertations Dissertations 5-2016 Understanding Allosteric Modulation of G-Protein Coupled Receptors Vibhor Agrawal Clemson University, vibhora@clemson.edu Follow this
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Organization of the nervous system. Tortora & Grabowski Principles of Anatomy & Physiology; Page 388, Figure 12.2
 Nervous system Organization of the nervous system Tortora & Grabowski Principles of Anatomy & Physiology; Page 388, Figure 12.2 Autonomic and somatic efferent pathways Reflex arc - a neural pathway that
Nervous system Organization of the nervous system Tortora & Grabowski Principles of Anatomy & Physiology; Page 388, Figure 12.2 Autonomic and somatic efferent pathways Reflex arc - a neural pathway that
Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg Lapets ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2004, 2:
 1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure. You will be given a start time with your exam instructions
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology Date: Thursday, 1st September 2011 Time: 3 hours You will be given a start
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology Date: Thursday, 1st September 2011 Time: 3 hours You will be given a start
Overview of ion channel proteins. What do ion channels do? Three important points:
 Overview of ion channel proteins Protein Structure Membrane proteins & channels Specific channels Several hundred distinct types Organization Evolution We need to consider 1. Structure 2. Functions 3.
Overview of ion channel proteins Protein Structure Membrane proteins & channels Specific channels Several hundred distinct types Organization Evolution We need to consider 1. Structure 2. Functions 3.
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London)
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
1: CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY
 IPC0 6/6/05 3:29 Page : CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY Transmembrane solute transport, 3 Ion channels, 4 Ion ATPases, 6 Resting membrane potential (E m ), 8 Action potential, 0 Second messenger pathways, 2 IPC0 6/6/05
IPC0 6/6/05 3:29 Page : CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY Transmembrane solute transport, 3 Ion channels, 4 Ion ATPases, 6 Resting membrane potential (E m ), 8 Action potential, 0 Second messenger pathways, 2 IPC0 6/6/05
Analysis of Ligand Bias in Functional Studies Involving the Allosteric Modulation of G Protein- Coupled Receptors
 Chapman University Chapman University Digital Commons Biology, Chemistry, and Environmental Sciences Faculty Articles and Research Biology, Chemistry, and Environmental Sciences 5-2014 Analysis of Ligand
Chapman University Chapman University Digital Commons Biology, Chemistry, and Environmental Sciences Faculty Articles and Research Biology, Chemistry, and Environmental Sciences 5-2014 Analysis of Ligand
Supporting Text - Cubic Ternary Complex Activation Model (ctcam)
 Both Ligand- and Cell-Specific Parameters Control Ligand Agonism in a Kinetic Model of G protein Coupled Receptor Signaling by Tamara L. Kinzer-Ursem and Jennifer J. Linderman Supporting Text - Cubic Ternary
Both Ligand- and Cell-Specific Parameters Control Ligand Agonism in a Kinetic Model of G protein Coupled Receptor Signaling by Tamara L. Kinzer-Ursem and Jennifer J. Linderman Supporting Text - Cubic Ternary
Reprogramming what is it? ips. neurones cardiomyocytes. Takahashi K & Yamanaka S. Cell 126, 2006,
 General Mechanisms of Cell Signaling Signaling to Cell Nucleus MUDr. Jan láteník, hd. Somatic cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotent stem cells! fibroblast Reprogramming what is it? is neurones cardiomyocytes
General Mechanisms of Cell Signaling Signaling to Cell Nucleus MUDr. Jan láteník, hd. Somatic cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotent stem cells! fibroblast Reprogramming what is it? is neurones cardiomyocytes
Enzyme Catalysis & Biotechnology
 L28-1 Enzyme Catalysis & Biotechnology Bovine Pancreatic RNase A Biochemistry, Life, and all that L28-2 A brief word about biochemistry traditionally, chemical engineers used organic and inorganic chemistry
L28-1 Enzyme Catalysis & Biotechnology Bovine Pancreatic RNase A Biochemistry, Life, and all that L28-2 A brief word about biochemistry traditionally, chemical engineers used organic and inorganic chemistry
ENZYME KINETICS. Medical Biochemistry, Lecture 24
 ENZYME KINETICS Medical Biochemistry, Lecture 24 Lecture 24, Outline Michaelis-Menten kinetics Interpretations and uses of the Michaelis- Menten equation Enzyme inhibitors: types and kinetics Enzyme Kinetics
ENZYME KINETICS Medical Biochemistry, Lecture 24 Lecture 24, Outline Michaelis-Menten kinetics Interpretations and uses of the Michaelis- Menten equation Enzyme inhibitors: types and kinetics Enzyme Kinetics
From gene to protein. Premedical biology
 From gene to protein Premedical biology Central dogma of Biology, Molecular Biology, Genetics transcription replication reverse transcription translation DNA RNA Protein RNA chemically similar to DNA,
From gene to protein Premedical biology Central dogma of Biology, Molecular Biology, Genetics transcription replication reverse transcription translation DNA RNA Protein RNA chemically similar to DNA,
New G-protein-coupled receptor crystal structures: insights and limitations
 Opinion New G-protein-coupled receptor crystal structures: insights and limitations Brian Kobilka 1 and Gebhard F.X. Schertler 2 1 Departments of Molecular and Cellular Physiology and Medicine, Stanford
Opinion New G-protein-coupled receptor crystal structures: insights and limitations Brian Kobilka 1 and Gebhard F.X. Schertler 2 1 Departments of Molecular and Cellular Physiology and Medicine, Stanford
7.013 Problem Set
 7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as shown below.
7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as shown below.
Ras e la Cascata delle Piccole GTPasi
 Roma 26-27 Giugno 2015 Multidisciplinarietà e Biologia Molecolare applicate alla pratica Clinica i Oncologica: un'opportunità ed un vantaggio per tuttitti Ras e la Cascata delle Piccole GTPasi Alvaro Leone
Roma 26-27 Giugno 2015 Multidisciplinarietà e Biologia Molecolare applicate alla pratica Clinica i Oncologica: un'opportunità ed un vantaggio per tuttitti Ras e la Cascata delle Piccole GTPasi Alvaro Leone
COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF G-PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTOR SCREENING, DIMERIZATION, AND DESENSITIZATION. Peter J. Woolf
 COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF G-PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTOR SCREENING, DIMERIZATION, AND DESENSITIZATION by Peter J. Woolf A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF G-PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTOR SCREENING, DIMERIZATION, AND DESENSITIZATION by Peter J. Woolf A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
Lecture 07, 13 Sept 2005 Chapters 12 and 13. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005
 Lecture 07, 13 Sept 2005 Chapters 12 and 13 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter Vertebrate Physiology 437 Chapter
Lecture 07, 13 Sept 2005 Chapters 12 and 13 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter Vertebrate Physiology 437 Chapter
Gene regulation I Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm February 25, 2005
 Gene regulation I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm February 25, 2005 Principles of gene regulation (cellular versus molecular level) Extracellular signals Chemical (e.g. hormones, growth factors) Environmental
Gene regulation I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm February 25, 2005 Principles of gene regulation (cellular versus molecular level) Extracellular signals Chemical (e.g. hormones, growth factors) Environmental
Module Membrane Biogenesis and Transport Lecture 15 Ion Channels Dale Sanders
 Module 0220502 Membrane Biogenesis and Transport Lecture 15 Ion Channels Dale Sanders 9 March 2009 Aims: By the end of the lecture you should understand The principles behind the patch clamp technique;
Module 0220502 Membrane Biogenesis and Transport Lecture 15 Ion Channels Dale Sanders 9 March 2009 Aims: By the end of the lecture you should understand The principles behind the patch clamp technique;
Ion Channels. 6 th December, Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology
 Ion Channels 6 th December, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Introduction The ion channels of nerve cells are optimally
Ion Channels 6 th December, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Introduction The ion channels of nerve cells are optimally
GPCR Dynamics: Structures in Motion
 This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/cr GPCR
This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/cr GPCR
RHODOPSIN: Insights from Recent Structural Studies
 Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2002. 31:443 84 DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.31.082901.134348 Copyright c 2002 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved RHODOPSIN: Insights from Recent Structural Studies
Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2002. 31:443 84 DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.31.082901.134348 Copyright c 2002 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved RHODOPSIN: Insights from Recent Structural Studies
2: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE BODY
 1 2: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE BODY CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter provides an overview of basic chemical principles that are important to understanding human physiological function and ultimately homeostasis.
1 2: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE BODY CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter provides an overview of basic chemical principles that are important to understanding human physiological function and ultimately homeostasis.
From a biophysical point of view, inwardly
 G Protein Regulation of Inwardly Rectifying K + Channels Andreas Karschin Inwardly rectifying K + (Kir) channels respond to receptor-stimulated signaling cascades that involve G proteins and other cytosolic
G Protein Regulation of Inwardly Rectifying K + Channels Andreas Karschin Inwardly rectifying K + (Kir) channels respond to receptor-stimulated signaling cascades that involve G proteins and other cytosolic
Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor
 Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor Presented by Stephanie Lee Research Mentor: Dr. Rob Coalson Glycine Alpha 1 Receptor (GlyRa1) Member of the superfamily
Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor Presented by Stephanie Lee Research Mentor: Dr. Rob Coalson Glycine Alpha 1 Receptor (GlyRa1) Member of the superfamily
dynamic processes in cells (a systems approach to biology)
 dynamic processes in cells (a systems approach to biology) jeremy gunawardena department of systems biology harvard medical school lecture 11 13 october 2015 the long road to molecular understanding P&M
dynamic processes in cells (a systems approach to biology) jeremy gunawardena department of systems biology harvard medical school lecture 11 13 october 2015 the long road to molecular understanding P&M
Initiation of translation in eukaryotic cells:connecting the head and tail
 Initiation of translation in eukaryotic cells:connecting the head and tail GCCRCCAUGG 1: Multiple initiation factors with distinct biochemical roles (linking, tethering, recruiting, and scanning) 2: 5
Initiation of translation in eukaryotic cells:connecting the head and tail GCCRCCAUGG 1: Multiple initiation factors with distinct biochemical roles (linking, tethering, recruiting, and scanning) 2: 5
active site Region of an enzyme surface to which a substrate molecule binds in order to undergo a catalyzed reaction.
 Glossary acetyl Chemical group derived from acetic acid. Acetyl groups are important in metabolism and are added covalently to some proteins as a posttranslational modification. actin Abundant protein
Glossary acetyl Chemical group derived from acetic acid. Acetyl groups are important in metabolism and are added covalently to some proteins as a posttranslational modification. actin Abundant protein
Examination paper for Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology
 Department of Biology Examination paper for Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology Academic contact during examination: Per Winge Phone: 99369359 Examination date: 20 th December 2017 Examination time (from-to):
Department of Biology Examination paper for Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology Academic contact during examination: Per Winge Phone: 99369359 Examination date: 20 th December 2017 Examination time (from-to):
Mechanisms of Human Health and Disease. Developmental Biology
 Mechanisms of Human Health and Developmental Biology Joe Schultz joe.schultz@nationwidechildrens.org D6 1 Dev Bio: Mysteries How do fertilized eggs become adults? How do adults make more adults? Why and
Mechanisms of Human Health and Developmental Biology Joe Schultz joe.schultz@nationwidechildrens.org D6 1 Dev Bio: Mysteries How do fertilized eggs become adults? How do adults make more adults? Why and
Phospholipase C Isozymes as Effectors of Ras Superfamily GTPases
 Phospholipase C Isozymes as Effectors of Ras Superfamily GTPases T. Kendall Harden 1,2, Stephanie N. Hicks 1, and John Sondek 1,2,3 Department of Pharmacology 1, Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center
Phospholipase C Isozymes as Effectors of Ras Superfamily GTPases T. Kendall Harden 1,2, Stephanie N. Hicks 1, and John Sondek 1,2,3 Department of Pharmacology 1, Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center
Alaa' Alajrami. Hussam Twaissi. Mohammad khatatbeh
 6 Alaa' Alajrami Hussam Twaissi Mohammad khatatbeh Keep smiling stay beautiful,,, We will continue talking about cell membrane and what cause the potential across it. * Proton depended carrier: (secondary
6 Alaa' Alajrami Hussam Twaissi Mohammad khatatbeh Keep smiling stay beautiful,,, We will continue talking about cell membrane and what cause the potential across it. * Proton depended carrier: (secondary
MRP4 and platelets Demokritos C Tsoukatos
 MRP4 and platelets Demokritos C Tsoukatos Laboratory of Biochemistry Department of Chemistry University of Ioannina MRP 4 Multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) is a member of the MRP/ABCC subfamily of
MRP4 and platelets Demokritos C Tsoukatos Laboratory of Biochemistry Department of Chemistry University of Ioannina MRP 4 Multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) is a member of the MRP/ABCC subfamily of
Interrogation of small GTPase Activity. Screening GAPs and GEFs with the PHERAstar FSX from BMG LABTECH and Transcreener Assays from BellBrook Labs
 Interrogation of small GTPase Activity Screening GAPs and GEFs with the PHERAstar FSX from BMG LABTECH and Transcreener Assays from BellBrook Labs Introducing the New PHERAstar FSX Most sensitive reader
Interrogation of small GTPase Activity Screening GAPs and GEFs with the PHERAstar FSX from BMG LABTECH and Transcreener Assays from BellBrook Labs Introducing the New PHERAstar FSX Most sensitive reader
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Energy of Life
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Energy of Life
RNA Synthesis and Processing
 RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
32 Gene regulation, continued Lecture Outline 11/21/05
 32 Gene regulation, continued Lecture Outline 11/21/05 Review the operon concept Repressible operons (e.g. trp) Inducible operons (e.g. lac) Positive regulation of lac () Practice applying the operon concept
32 Gene regulation, continued Lecture Outline 11/21/05 Review the operon concept Repressible operons (e.g. trp) Inducible operons (e.g. lac) Positive regulation of lac () Practice applying the operon concept
Dr. Ketki Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry Heritage IMS, Varanasi
 TRANSPORT MECHANISMS Dr. Ketki Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry Heritage IMS, Varanasi Membrane selectivity allows adjustments of cell composition and function If plasma membrane is relatively
TRANSPORT MECHANISMS Dr. Ketki Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry Heritage IMS, Varanasi Membrane selectivity allows adjustments of cell composition and function If plasma membrane is relatively
Introduction: actin and myosin
 Introduction: actin and myosin Actin Myosin Myosin V and actin 375 residues Found in all eukaryotes Polymeric Forms track for myosin Many other cellular functions 36 nm pseudo-helical repeat Catalytic
Introduction: actin and myosin Actin Myosin Myosin V and actin 375 residues Found in all eukaryotes Polymeric Forms track for myosin Many other cellular functions 36 nm pseudo-helical repeat Catalytic
Drug binding and subtype selectivity in G-protein-coupled receptors
 Drug binding and subtype selectivity in G-protein-coupled receptors Albert C. Pan The Aspect of Time in Drug Design Schloss Rauischholzhausen Marburg, Germany Thursday, March 27 th, 2014 D. E. Shaw Research
Drug binding and subtype selectivity in G-protein-coupled receptors Albert C. Pan The Aspect of Time in Drug Design Schloss Rauischholzhausen Marburg, Germany Thursday, March 27 th, 2014 D. E. Shaw Research
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins
 13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
A Review of camp-dependent Protein Kinase A Catalytic Subunit Structure, Function and Regulation
 A Review of camp-dependent Protein Kinase A Catalytic Subunit Structure, Function and Regulation Kaitlyn McLeod* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA Abstract
A Review of camp-dependent Protein Kinase A Catalytic Subunit Structure, Function and Regulation Kaitlyn McLeod* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA Abstract
Tracking Protein Allostery in Evolution
 Tracking Protein Allostery in Evolution Glycogen phosphorylase frees sugars to provide energy GP orthologs diverged 600,000,000 years can respond to transcription controls, metabolite concentrations and
Tracking Protein Allostery in Evolution Glycogen phosphorylase frees sugars to provide energy GP orthologs diverged 600,000,000 years can respond to transcription controls, metabolite concentrations and
