Atsc final Equations: page 1/6
|
|
|
- Chad Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Atsc final Equations: page 1/6 Answer each of these 7 questions (note weight). Show all your work on all questions (needed for partial credit). Be sure to put your name on any detached pages. 1. (10) Starting from (33) show that for a flat sheet of liquid water in equilibrium with vapor, g l = g v. According to (33): dg sdt + αdp (1) where we are talking about the mixture of liquid and vapor and specifying that water is neither entering or leaving the system. If dt=0 and dp=0 then dg can only be negative or zero, so in equilibrium g=constant. But we also know that :G = m v g v + m l g l and since neither g v = h v T s v and g l = h l T s l will change if T and p are constant, we ve got: dg = 0 = g v dm v + g l dm l (2) Next, since water is conserved we know that dm v = dm l, plug those in and we get g l = g v 2. (12) Suppose you measure a drizzle size distribution with radii between mm that takes the form: n(r) = 700r 3 (3) where n(r) is the number density in m 3 mm 1. For the mm size range find The total number concentration N in m 3 In [4]: -0.5*(700)*((1./r[1])**2. - (1./r[0])**2.) Out[4]: #m^-3 The mean radius r in mm In [6]: (-700)*((1./r[1]) - (1./r[0]))/ Out[6]: The rain rate, in mm/hr, given a fall speed of V (r) = 6r, where V (r) is in m/s and r is in mm. The rainrate R in meters/second is:
2 Atsc final Equations: page 2/6 R = π r r 3 6rdr (4) 0.2 = π r = π (4 0.04) m/s = m/s = mm/hr (5) Matlab script to do this numerically spacing=0.0001; %mm r=0.2:spacing:2;%mm number=700*(r).^(-3).*spacing;% m^{-3} concentration in each bin tot_num=sum(number); out_mesg={ \ntotal number is %8.4f m^{-3}\n }; fprintf(strcat(out_mesg{:}),tot_num); mean_rad=sum(number.*r)/tot_num; out_mesg={ \nmean radius is %8.4f mm\n }; fprintf(strcat(out_mesg{:}),mean_rad); Vfall=6*r; %m/s rmeter=r*1.e-3; % meters Volume=4./3.*pi*rmeter.^3.; R=sum(number.*Volume.*Vfall); %m/s R=R*1000*3600.; %mm/hour out_mesg={ \nrain rate is %8.2f mm/hour\n }; fprintf(strcat(out_mesg{:}),r); When run this prints out: total number is m^{-3} mean radius is mm rain rate is mm/hour 3. (6) Use Taylor series to show that: log θ e 1 θ e (6) θ e for sufficiently small θ e. let y = log θ e so that y (θ e ) = 1 θ e now expand about θ e1 using a first order Taylor series:
3 Atsc final Equations: page 3/6 y 2 = log θ e2 = log θ e1 + 1 θ e1 (θ e2 θ e1 ) (7) log θ e2 log θ e1 = log θ e = 1 θ e θ e (8) 4. (15) Moist adiabat Describe how you would calculate a set of (temperature, pressure) coordinates that could be used to draw a single moist adiabat on a tephigram using matlab. Do it in two ways: ( ) (a) With fzero: use the relationship θ e = θ exp l vw s c pt (first show how integrating equation (25) gives this expression). (b) With ode45: Derive an equation for dt/dp from (24), assuming hydrostatic balance and also assuming that you can call functions that will give you w w and dw s /dt for any temperature and pressure. In each case describe how you would start and stop the calculation, and write out the routines in pseudo-code that doesn t have to run, but should translate roughly line for line to Matlab. 5. (6) Conservation laws Prove using (19) that the moist static energy h m defined by (24) is conserved for adiabatic motion in a hydrostatic atmosphere. Use this to show that h m for a mixture of two parcels is just the sum of the moist static energies of the two parcels: h mc = h ma + h mb.
4 Atsc final Equations: page 4/6 6. (11) Köhler curve The figure shows two droplets with radii of 0.2 µm and 1 µm at a environmental relative humidity of about (a) (3) Both droplets lie on a curved line called the Koehler curve. What do points on this line represent? i.e. what is it that all points lying on this line have in common? (b) (4) Suppose the relative humidity increases from to Describe qualitatively what happens to the two drops. (c) (4) Quantitatively, what is the initial evaporation/growth rate of droplet 2 in microns/second, assuming a RH of 1.002, temperature T=280, esat(t)=10 hpa. 7. (6) Show with the help of a figure why: ρ v t = D 2 ρ v (9)
5 Atsc final Equations: page 5/6 Equation sheet du = q dt w dt = q dt p dα (10) dw v = w ( v p ) p e e de dp (27) e = ρ v R v T (11) p = ρ R d T v (12) f(x) = f(x 0 ) + f (x 0 )(x x 0 ) + f (x 0 ) (x x 0 ) (28) 2 w dt = p dα (13) h = u + p α (14) T v = T ( w v w l ) (15) l v = T (s v s l ) (29) de s dt = l ve s R v T 2 (30) e s w vs = ρ s /ρ d = ɛ (16) p e s dh = c px dt (dry air or liquid) (17) dh = c p dt + l v dw v (air/water mixture) (18) h l = c l (T T p ) h v = l v0 + c pv (T T p ) s d = c pd log T R d log p d s l = c l ln T T p s v = c pv ln T R v ln e + l v0 T p e s0 T p (31a) (31b) (31c) (31d) (31e) dh = T ds + α dp (reversible) (19) dθ ds = c p θ = c dt p T R dp d p ds q dt T (20) (21) l v = h v h l (22) e g = u + pα T s = h T s (32) dg sdt + αdp (33) E = m v g v + m l g l + 4πσr 2 (34) ( ) S d(g l g v ) R v T ln a we s a w (35) dp = ρ g dz (23) dh m = c p dt + l v dw v + g dz (24) e r = e s (T )(n w /(n w + n s )) exp(a/r) = e s (T )(1 + a r b r 3 ) (36) ds = c p dθ es θ es ds = c p dθ l θ l dθ = c p θ + l v dw s T dθ = c p θ l v dw l T (25) (26) ( ) 4a 3 1/2 s crit = b (37) ( ) 1/2 3b r crit = a (38)
6 Atsc final Equations: page 6/6 c p dθ e θ e = dm m h m T = dm m s = c p dm m log θ e (39) 1 dm m dt = λ (40) dw T dz = (w w T )ˆλ (41) dm = πr 2 E c (V (R) V (r))w l (42) dt where V(r) 0 and V(R) JR (with J=6000 s 1, Rin m) dm dt = 4πrD(ρ v ρ vr ) (43) dr dt = 1 Dρ v [e e r ] (44) r ρ l e n dm dt = DC ɛ 0 (ρ v ρ vc ) (45) N(D ) = D n(d)dd (46) 2σ a ρ l R vt imm b w (4/3)M sπρ σ J m 2 ρ l 1000 kg m 3 c pd 1006 J kg 1 K 1 c vd 719 J kg 1 K 1 c pv 1870 J kg 1 K 1 c vv 1408 J kg 1 K 1 c l 4190 J kg 1 K 1 D m 2 s 1 R d 287 J kg 1 K 1 R v 461 J kg 1 K 1 k J K 1 molecule 1 l v J kg at 0 deg C
2σ e s (r,t) = e s (T)exp( rr v ρ l T ) = exp( ) 2σ R v ρ l Tln(e/e s (T)) e s (f H2 O,r,T) = f H2 O
 Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
Formulas/Constants, Physics/Oceanography 4510/5510 B Atmospheric Physics II N A = 6.02 10 23 molecules/mole (Avogadro s number) 1 mb = 100 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N/m 2 Γ d = 9.8 o C/km (dry adiabatic lapse rate)
Clouds associated with cold and warm fronts. Whiteman (2000)
 Clouds associated with cold and warm fronts Whiteman (2000) Dalton s law of partial pressures! The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases equals the sum of the partial pressure of the gases! Partial
Clouds associated with cold and warm fronts Whiteman (2000) Dalton s law of partial pressures! The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases equals the sum of the partial pressure of the gases! Partial
ATMO 551a Moist Adiabat Fall Change in internal energy: ΔU
 Enthalpy and the Moist Adiabat We have described the dry adiabat where an air parcel is lifted rapidly causing the air parcel to expand as the environmental pressure decreases and the air parcel does work
Enthalpy and the Moist Adiabat We have described the dry adiabat where an air parcel is lifted rapidly causing the air parcel to expand as the environmental pressure decreases and the air parcel does work
ATMO 551a Fall 08. Equivalent Potential Temperature
 Equivalent Potential emperature he equivalent potential temperature, θ e, is the potential temperature that would result if all of the water in the air parcel were condensed and rained out by raising the
Equivalent Potential emperature he equivalent potential temperature, θ e, is the potential temperature that would result if all of the water in the air parcel were condensed and rained out by raising the
Kelvin Effect. Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics
 Kelvin Effect Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Vapor Pressure (e) e < e # e = e # Vapor Pressure e > e # Relative humidity RH =
Kelvin Effect Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Vapor Pressure (e) e < e # e = e # Vapor Pressure e > e # Relative humidity RH =
Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes)
 10/12/06 ATS 541 - Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Cloud Physics 1 Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes) ATS 541 students: Answer all questions ATS 441 students: You may delete problem 3 or problem 5 1. [10
10/12/06 ATS 541 - Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Cloud Physics 1 Exam 1 (Chaps. 1-6 of the notes) ATS 541 students: Answer all questions ATS 441 students: You may delete problem 3 or problem 5 1. [10
ATMOS 5130 Lecture 9. Enthalpy Conservation Property The Second Law and Its Consequences Entropy
 ATMOS 5130 Lecture 9 Enthalpy Conservation Property The Second Law and Its Consequences Entropy CLASS Presentation Form group of 2 students Present ~20 minute presentation (~ 10 minute each person) Focus
ATMOS 5130 Lecture 9 Enthalpy Conservation Property The Second Law and Its Consequences Entropy CLASS Presentation Form group of 2 students Present ~20 minute presentation (~ 10 minute each person) Focus
Parcel Model. Meteorology September 3, 2008
 Parcel Model Meteorology 5210 September 3, 2008 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature, θ, mixing
Parcel Model Meteorology 5210 September 3, 2008 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature, θ, mixing
Parcel Model. Atmospheric Sciences September 30, 2012
 Parcel Model Atmospheric Sciences 6150 September 30, 2012 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature,
Parcel Model Atmospheric Sciences 6150 September 30, 2012 1 Governing Equations for Precipitating Convection For precipitating convection, we have the following set of equations for potential temperature,
Lecture Ch. 6. Condensed (Liquid) Water. Cloud in a Jar Demonstration. How does saturation occur? Saturation of Moist Air. Saturation of Moist Air
 Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
Step 1. Step 2. g l = g v. dg = 0 We have shown that over a plane surface of water. g v g l = ρ v R v T ln e/e sat. this can be rewritten
 The basic question is what makes the existence of a droplet thermodynamically preferable to the existence only of water vapor. We have already derived an expression for the saturation vapor pressure over
The basic question is what makes the existence of a droplet thermodynamically preferable to the existence only of water vapor. We have already derived an expression for the saturation vapor pressure over
Köhler Curve. Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics
 Köhler Curve Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Review of Kelvin Effect Gibbs Energy for formation of a drop G = G &'()*+, G ).'+
Köhler Curve Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Review of Kelvin Effect Gibbs Energy for formation of a drop G = G &'()*+, G ).'+
Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 Atmospheric Thermodynamics Atmospheric Composition What is the composition of the Earth s atmosphere? Gaseous Constituents of the Earth s atmosphere (dry air) Constituent Molecular Weight Fractional Concentration
Atmospheric Thermodynamics Atmospheric Composition What is the composition of the Earth s atmosphere? Gaseous Constituents of the Earth s atmosphere (dry air) Constituent Molecular Weight Fractional Concentration
df dz = dp dt Essentially, this is just a statement of the first law in one of the forms we derived earlier (expressed here in W m 3 ) dq p dt dp
 A problem with using entropy as a variable is that it is not a particularly intuitive concept. The mechanics of using entropy for evaluating system evolution is well developed, but it sometimes feels a
A problem with using entropy as a variable is that it is not a particularly intuitive concept. The mechanics of using entropy for evaluating system evolution is well developed, but it sometimes feels a
Diabatic Processes. Diabatic processes are non-adiabatic processes such as. entrainment and mixing. radiative heating or cooling
 Diabatic Processes Diabatic processes are non-adiabatic processes such as precipitation fall-out entrainment and mixing radiative heating or cooling Parcel Model dθ dt dw dt dl dt dr dt = L c p π (C E
Diabatic Processes Diabatic processes are non-adiabatic processes such as precipitation fall-out entrainment and mixing radiative heating or cooling Parcel Model dθ dt dw dt dl dt dr dt = L c p π (C E
Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics
 Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics Reference Peixoto and Oort, Sec. 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5 (but skip the discussion of oceans until next week); Ch. 10 Thermodynamic
Today s Lecture: Atmosphere finish primitive equations, mostly thermodynamics Reference Peixoto and Oort, Sec. 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5 (but skip the discussion of oceans until next week); Ch. 10 Thermodynamic
Quasi-equilibrium transitions
 Quasi-equilibrium transitions We have defined a two important equilibrium conditions. he first is one in which there is no heating, or the system is adiabatic, and dh/ =0, where h is the total enthalpy
Quasi-equilibrium transitions We have defined a two important equilibrium conditions. he first is one in which there is no heating, or the system is adiabatic, and dh/ =0, where h is the total enthalpy
Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere
![Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium. Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere](/thumbs/72/66535634.jpg) Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Vertical temperature profile Total atmospheric mass: ~5.15x10
Radiative equilibrium Some thermodynamics review Radiative-convective equilibrium Goal: Develop a 1D description of the [tropical] atmosphere Vertical temperature profile Total atmospheric mass: ~5.15x10
Measuring State Parameters of the Atmosphere
 Measuring State Parameters of the Atmosphere Some Applications of Atmospheric Thermodynamics Earth Observing Laboratory, NCAR IDEAS-4 Tutorial Introduction Goals of This Presentation Present two complementary
Measuring State Parameters of the Atmosphere Some Applications of Atmospheric Thermodynamics Earth Observing Laboratory, NCAR IDEAS-4 Tutorial Introduction Goals of This Presentation Present two complementary
1. Heterogeneous Systems and Chemical Equilibrium
 1. Heterogeneous Systems and Chemical Equilibrium The preceding section involved only single phase systems. For it to be in thermodynamic equilibrium, a homogeneous system must be in thermal equilibrium
1. Heterogeneous Systems and Chemical Equilibrium The preceding section involved only single phase systems. For it to be in thermodynamic equilibrium, a homogeneous system must be in thermal equilibrium
1. Water Vapor in Air
 1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
Chapter 17. Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling
 Overhead Slides for Chapter 17 of Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling by Mark Z. Jacobson Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-4020 August 21, 1998 Mass
Overhead Slides for Chapter 17 of Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling by Mark Z. Jacobson Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-4020 August 21, 1998 Mass
The Tropical Atmosphere: Hurricane Incubator
 The Tropical Atmosphere: Hurricane Incubator Images from journals published by the American Meteorological Society are copyright AMS and used with permission. A One-Dimensional Description of the Tropical
The Tropical Atmosphere: Hurricane Incubator Images from journals published by the American Meteorological Society are copyright AMS and used with permission. A One-Dimensional Description of the Tropical
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]
![Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic]](/thumbs/81/83694823.jpg) Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
Thermodynamics Review [?] Entropy & thermodynamic potentials Hydrostatic equilibrium & buoyancy Stability [dry & moist adiabatic] Entropy 1. (Thermodynamics) a thermodynamic quantity that changes in a
π (r 1 + r 2 ) 2 πr 2 1 v T1 v T2 v T1
 How do we get rain? So far we ve discussed droplet growth by vapor diffusion, but this is not the process that by itself is primarily responsible for precipitation in warm clouds. The primary production
How do we get rain? So far we ve discussed droplet growth by vapor diffusion, but this is not the process that by itself is primarily responsible for precipitation in warm clouds. The primary production
Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 2
 Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 2 Topics Some aspects of advection and the Coriolis-effect (1.7) Composition of the atmosphere (figure 1.6) Equation of state (1.8&1.9) Water vapour in the atmosphere (1.10)
Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 2 Topics Some aspects of advection and the Coriolis-effect (1.7) Composition of the atmosphere (figure 1.6) Equation of state (1.8&1.9) Water vapour in the atmosphere (1.10)
Physics 360 Review 3
 Physics 360 Review 3 The test will be similar to the second test in that calculators will not be allowed and that the Unit #2 material will be divided into three different parts. There will be one problem
Physics 360 Review 3 The test will be similar to the second test in that calculators will not be allowed and that the Unit #2 material will be divided into three different parts. There will be one problem
Exam 2: Cloud Physics April 16, 2008 Physical Meteorology Questions 1-10 are worth 5 points each. Questions are worth 10 points each.
 Exam : Cloud Physics April, 8 Physical Meteorology 344 Name Questions - are worth 5 points each. Questions -5 are worth points each.. Rank the concentrations of the following from lowest () to highest
Exam : Cloud Physics April, 8 Physical Meteorology 344 Name Questions - are worth 5 points each. Questions -5 are worth points each.. Rank the concentrations of the following from lowest () to highest
GEF2200 Atmosfærefysikk 2012
 GEF2200 Atmosfærefysikk 2012 Løsningsforslag til oppgavesett 4 WH06 3.46 (WH 2.49) The air parcel has the properties p = 1000hPa, T = 15 C and T d = 4 C. b Lifting the air parcel to p 2 = 900hPa, T 2 we
GEF2200 Atmosfærefysikk 2012 Løsningsforslag til oppgavesett 4 WH06 3.46 (WH 2.49) The air parcel has the properties p = 1000hPa, T = 15 C and T d = 4 C. b Lifting the air parcel to p 2 = 900hPa, T 2 we
Terminal velocity. 1. The collision cross-sectional area is. π (r 1 + r 2 ) 2 πr The relative collection velocity is.
 How do we get rain? So far we ve discussed droplet growth by vapor diffusion, but this is not the process that by itself is primarily responsible for precipitation in warm clouds. The primary production
How do we get rain? So far we ve discussed droplet growth by vapor diffusion, but this is not the process that by itself is primarily responsible for precipitation in warm clouds. The primary production
1/2 and e0 e s ' 1+ imm w 4 M s 3 πρ0 r 3 m. n 0 ktr. .Also,since n 0 ktr 1,wehave. 4 3 M sπρ 0 r 3. ktr. 3 M sπρ 0
 Chapter 6 6.1 Shw that fr a very weak slutin drplet (m 4 3 πr3 ρ 0 M s ), (6.8) can be written as e 0 ' 1+ a r b r 3 where a σ 0 /n 0 kt and b imm w / 4 3 M sπρ 0. What is yur interpretatin f thecnd and
Chapter 6 6.1 Shw that fr a very weak slutin drplet (m 4 3 πr3 ρ 0 M s ), (6.8) can be written as e 0 ' 1+ a r b r 3 where a σ 0 /n 0 kt and b imm w / 4 3 M sπρ 0. What is yur interpretatin f thecnd and
SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2009/2010. MAPH Physical Meteorology
 SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2009/2010 MAPH 40240 Physical Meteorology Extern examiner: Professor Keith Shine Head of School: Professor Micheal O Searcoid Examiner: Dr. Rodrigo Caballero Time Allowed: 2 hours
SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2009/2010 MAPH 40240 Physical Meteorology Extern examiner: Professor Keith Shine Head of School: Professor Micheal O Searcoid Examiner: Dr. Rodrigo Caballero Time Allowed: 2 hours
The Clausius-Clapeyron and the Kelvin Equations
 PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics The Clausius-Clapeyron and the Kelvin Equations by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
PhD Environmental Fluid Mechanics Physics of the Atmosphere University of Trieste International Center for Theoretical Physics The Clausius-Clapeyron and the Kelvin Equations by Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio
Liquid water static energy page 1/8
 Liquid water static energy age 1/8 1) Thermodynamics It s a good idea to work with thermodynamic variables that are conserved under a known set of conditions, since they can act as assive tracers and rovide
Liquid water static energy age 1/8 1) Thermodynamics It s a good idea to work with thermodynamic variables that are conserved under a known set of conditions, since they can act as assive tracers and rovide
First Law of Thermodynamics
 First Law of Thermodynamics September 11, 2013 The first law of thermodynamics is the conservation of energy applied to thermal systems. Here, we develop the principles of thermodynamics for a discrete
First Law of Thermodynamics September 11, 2013 The first law of thermodynamics is the conservation of energy applied to thermal systems. Here, we develop the principles of thermodynamics for a discrete
1. Droplet Growth by Condensation
 1. Droplet Growth by Condensation It was shown before that a critical size r and saturation ratio S must be exceeded for a small solution droplet to become a cloud droplet. Before the droplet reaches the
1. Droplet Growth by Condensation It was shown before that a critical size r and saturation ratio S must be exceeded for a small solution droplet to become a cloud droplet. Before the droplet reaches the
Buoyancy and Coriolis forces
 Chapter 2 Buoyancy and Coriolis forces In this chapter we address several topics that we need to understand before starting on our study of geophysical uid dynamics. 2.1 Hydrostatic approximation Consider
Chapter 2 Buoyancy and Coriolis forces In this chapter we address several topics that we need to understand before starting on our study of geophysical uid dynamics. 2.1 Hydrostatic approximation Consider
Convection and buoyancy oscillation
 Convection and buoyancy oscillation Recap: We analyzed the static stability of a vertical profile by the "parcel method"; For a given environmental profile (of T 0, p 0, θ 0, etc.), if the density of an
Convection and buoyancy oscillation Recap: We analyzed the static stability of a vertical profile by the "parcel method"; For a given environmental profile (of T 0, p 0, θ 0, etc.), if the density of an
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
Precipitation Processes METR σ is the surface tension, ρ l is the water density, R v is the Gas constant for water vapor, T is the air
 Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
Chemistry. Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations. NC State University
 Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON VERY IMPORTANT NOTE. Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2011/12 ENERGY AND MATTER SOLUTIONS Duration: 120 MINS VERY IMPORTANT NOTE Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2011/12 ENERGY AND MATTER SOLUTIONS Duration: 120 MINS VERY IMPORTANT NOTE Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
Sample Final Questions: Solutions Math 21B, Winter y ( y 1)(1 + y)) = A y + B
 Sample Final Questions: Solutions Math 2B, Winter 23. Evaluate the following integrals: tan a) y y dy; b) x dx; c) 3 x 2 + x dx. a) We use partial fractions: y y 3 = y y ) + y)) = A y + B y + C y +. Putting
Sample Final Questions: Solutions Math 2B, Winter 23. Evaluate the following integrals: tan a) y y dy; b) x dx; c) 3 x 2 + x dx. a) We use partial fractions: y y 3 = y y ) + y)) = A y + B y + C y +. Putting
Simplified Microphysics. condensation evaporation. evaporation
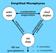 Simplified Microphysics water vapor condensation evaporation cloud droplets evaporation condensation collection rain drops fall out (precipitation) = 0 (reversible) = (irreversible) Simplified Microphysics
Simplified Microphysics water vapor condensation evaporation cloud droplets evaporation condensation collection rain drops fall out (precipitation) = 0 (reversible) = (irreversible) Simplified Microphysics
From the last time, we ended with an expression for the energy equation. u = ρg u + (τ u) q (9.1)
 Lecture 9 9. Administration None. 9. Continuation of energy equation From the last time, we ended with an expression for the energy equation ρ D (e + ) u = ρg u + (τ u) q (9.) Where ρg u changes in potential
Lecture 9 9. Administration None. 9. Continuation of energy equation From the last time, we ended with an expression for the energy equation ρ D (e + ) u = ρg u + (τ u) q (9.) Where ρg u changes in potential
Initiation of rain in nonfreezing clouds
 Collision-coalescence Topics: Initiation of rain in nonfreezing clouds ( warm rain process) Droplet terminal fall speed Collision efficiency Growth equations Initiation of rain in nonfreezing clouds We
Collision-coalescence Topics: Initiation of rain in nonfreezing clouds ( warm rain process) Droplet terminal fall speed Collision efficiency Growth equations Initiation of rain in nonfreezing clouds We
Outline. Aim. Gas law. Pressure. Scale height Mixing Column density. Temperature Lapse rate Stability. Condensation Humidity.
 Institute of Applied Physics University of Bern Outline A planetary atmosphere consists of different gases hold to the planet by gravity The laws of thermodynamics hold structure as vertical coordinate
Institute of Applied Physics University of Bern Outline A planetary atmosphere consists of different gases hold to the planet by gravity The laws of thermodynamics hold structure as vertical coordinate
Ay123 Set 1 solutions
 Ay13 Set 1 solutions Mia de los Reyes October 18 1. The scale of the Sun a Using the angular radius of the Sun and the radiant flux received at the top of the Earth s atmosphere, calculate the effective
Ay13 Set 1 solutions Mia de los Reyes October 18 1. The scale of the Sun a Using the angular radius of the Sun and the radiant flux received at the top of the Earth s atmosphere, calculate the effective
P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C.
![P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C. P sat = A exp [B( 1/ /T)] B= 5308K. A=6.11 mbar=vapor press. 0C.](/thumbs/79/79184286.jpg) Lecture 5. Water and water vapor in the atmosphere 14 Feb 2008 Review of buoyancy, with an unusual demonstration of Archimedes principle. Water is a polar molecule that forms hydrogen bonds. Consequently
Lecture 5. Water and water vapor in the atmosphere 14 Feb 2008 Review of buoyancy, with an unusual demonstration of Archimedes principle. Water is a polar molecule that forms hydrogen bonds. Consequently
Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
Temperature and Thermodynamics, Part II. Topics to be Covered
 Teperature and Therodynaics, Part II Topics to be Covered Profiles of Teperature in the Boundary Layer Potential teperature Adiabatic Lapse Rate Theral Stratification 1/8/17 Why are We Interested in Theral
Teperature and Therodynaics, Part II Topics to be Covered Profiles of Teperature in the Boundary Layer Potential teperature Adiabatic Lapse Rate Theral Stratification 1/8/17 Why are We Interested in Theral
Solutions Ph 236b Week 1
 Solutions Ph 236b Week 1 Page 1 of 7 Solutions Ph 236b Week 1 Kevin Barkett and Mark Scheel January 19, 216 Contents Problem 1................................... 2 Part (a...................................
Solutions Ph 236b Week 1 Page 1 of 7 Solutions Ph 236b Week 1 Kevin Barkett and Mark Scheel January 19, 216 Contents Problem 1................................... 2 Part (a...................................
ρ x + fv f 'w + F x ρ y fu + F y Fundamental Equation in z coordinate p = ρrt or pα = RT Du uv tanφ Dv Dt + u2 tanφ + vw a a = 1 p Dw Dt u2 + v 2
 Fundamental Equation in z coordinate p = ρrt or pα = RT Du uv tanφ + uw Dt a a = 1 p ρ x + fv f 'w + F x Dv Dt + u2 tanφ + vw a a = 1 p ρ y fu + F y Dw Dt u2 + v 2 = 1 p a ρ z g + f 'u + F z Dρ Dt + ρ
Fundamental Equation in z coordinate p = ρrt or pα = RT Du uv tanφ + uw Dt a a = 1 p ρ x + fv f 'w + F x Dv Dt + u2 tanφ + vw a a = 1 p ρ y fu + F y Dw Dt u2 + v 2 = 1 p a ρ z g + f 'u + F z Dρ Dt + ρ
GEF2200 atmospheric physics 2018
 GEF2200 atmospheric physics 208 Solutions: thermodynamics 3 Oppgaver hentet fra boka Wallace and Hobbs (2006) er merket WH06 WH06 3.8r Unsaturated air is lifted (adiabatically): The first pair of quantities
GEF2200 atmospheric physics 208 Solutions: thermodynamics 3 Oppgaver hentet fra boka Wallace and Hobbs (2006) er merket WH06 WH06 3.8r Unsaturated air is lifted (adiabatically): The first pair of quantities
Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics. Monday, January 6, 14
 Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Molecular Simulations Molecular dynamics: solve equations of motion Monte Carlo: importance sampling r 1 r 2 r n MD MC r 1 r 2 2 r n 2 3 3 4 4 Questions How can
Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Molecular Simulations Molecular dynamics: solve equations of motion Monte Carlo: importance sampling r 1 r 2 r n MD MC r 1 r 2 2 r n 2 3 3 4 4 Questions How can
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Monday 7 October 2013, Class #15
 Monday 7 October 2013, Class #15 Concepts for Today (Basics for Thermodynamics) Weather versus climate Lapse Rate (Adiabatic Lapse Rate) Ideal Gas Law Adiabatic Processes Potential Temperature Hydrostatic
Monday 7 October 2013, Class #15 Concepts for Today (Basics for Thermodynamics) Weather versus climate Lapse Rate (Adiabatic Lapse Rate) Ideal Gas Law Adiabatic Processes Potential Temperature Hydrostatic
Answer Key. Calculus I Math 141 Fall 2003 Professor Ben Richert. Exam 2
 Answer Key Calculus I Math 141 Fall 2003 Professor Ben Richert Exam 2 November 18, 2003 Please do all your work in this booklet and show all the steps. Calculators and note-cards are not allowed. Problem
Answer Key Calculus I Math 141 Fall 2003 Professor Ben Richert Exam 2 November 18, 2003 Please do all your work in this booklet and show all the steps. Calculators and note-cards are not allowed. Problem
Meteorology 6150 Cloud System Modeling
 Meteorology 6150 Cloud System Modeling Steve Krueger Spring 2009 1 Fundamental Equations 1.1 The Basic Equations 1.1.1 Equation of motion The movement of air in the atmosphere is governed by Newton s Second
Meteorology 6150 Cloud System Modeling Steve Krueger Spring 2009 1 Fundamental Equations 1.1 The Basic Equations 1.1.1 Equation of motion The movement of air in the atmosphere is governed by Newton s Second
Final Exam for Physics 176. Professor Greenside Wednesday, April 29, 2009
 Print your name clearly: Signature: I agree to neither give nor receive aid during this exam Final Exam for Physics 76 Professor Greenside Wednesday, April 29, 2009 This exam is closed book and will last
Print your name clearly: Signature: I agree to neither give nor receive aid during this exam Final Exam for Physics 76 Professor Greenside Wednesday, April 29, 2009 This exam is closed book and will last
Clouds and turbulent moist convection
 Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
Chapter 5. On-line resource
 Chapter 5 The water-air heterogeneous system On-line resource on-line analytical system that portrays the thermodynamic properties of water vapor and many other gases http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/
Chapter 5 The water-air heterogeneous system On-line resource on-line analytical system that portrays the thermodynamic properties of water vapor and many other gases http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/fluid/
where p oo is a reference level constant pressure (often 10 5 Pa). Since θ is conserved for adiabatic motions, a prognostic temperature equation is:
 1 Appendix C Useful Equations Purposes: Provide foundation equations and sketch some derivations. These equations are used as starting places for discussions in various parts of the book. C.1. Thermodynamic
1 Appendix C Useful Equations Purposes: Provide foundation equations and sketch some derivations. These equations are used as starting places for discussions in various parts of the book. C.1. Thermodynamic
( ) = 1005 J kg 1 K 1 ;
 Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
Problem Set 3 1. A parcel of water is added to the ocean surface that is denser (heavier) than any of the waters in the ocean. Suppose the parcel sinks to the ocean bottom; estimate the change in temperature
Calculus Math 21B, Winter 2009 Final Exam: Solutions
 Calculus Math B, Winter 9 Final Exam: Solutions. (a) Express the area of the region enclosed between the x-axis and the curve y = x 4 x for x as a definite integral. (b) Find the area by evaluating the
Calculus Math B, Winter 9 Final Exam: Solutions. (a) Express the area of the region enclosed between the x-axis and the curve y = x 4 x for x as a definite integral. (b) Find the area by evaluating the
3 Hydrostatic Equilibrium
 3 Hydrostatic Equilibrium Reading: Shu, ch 5, ch 8 31 Timescales and Quasi-Hydrostatic Equilibrium Consider a gas obeying the Euler equations: Dρ Dt = ρ u, D u Dt = g 1 ρ P, Dɛ Dt = P ρ u + Γ Λ ρ Suppose
3 Hydrostatic Equilibrium Reading: Shu, ch 5, ch 8 31 Timescales and Quasi-Hydrostatic Equilibrium Consider a gas obeying the Euler equations: Dρ Dt = ρ u, D u Dt = g 1 ρ P, Dɛ Dt = P ρ u + Γ Λ ρ Suppose
Phase Changes and Latent Heat
 Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
2 Equations of Motion
 2 Equations of Motion system. In this section, we will derive the six full equations of motion in a non-rotating, Cartesian coordinate 2.1 Six equations of motion (non-rotating, Cartesian coordinates)
2 Equations of Motion system. In this section, we will derive the six full equations of motion in a non-rotating, Cartesian coordinate 2.1 Six equations of motion (non-rotating, Cartesian coordinates)
ln( P vap(s) / torr) = T / K ln( P vap(l) / torr) = T / K
 Chem 4501 Introduction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Fall Semester 2017 Homework Problem Set Number 9 Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 9-4. Paraphrase: Given expressions
Chem 4501 Introduction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Fall Semester 2017 Homework Problem Set Number 9 Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 9-4. Paraphrase: Given expressions
Tropical Cyclones: Steady State Physics
 Tropical Cyclones: Steady State Physics Energy Production Carnot Theorem: Maximum efficiency results from a particular energy cycle: Isothermal expansion Adiabatic expansion Isothermal compression Adiabatic
Tropical Cyclones: Steady State Physics Energy Production Carnot Theorem: Maximum efficiency results from a particular energy cycle: Isothermal expansion Adiabatic expansion Isothermal compression Adiabatic
Physics 161 Homework 7 - Solutions Wednesday November 16, 2011
 Physics 161 Homework 7 - s Wednesday November 16, 2011 Make sure your name is on every page, and please box your final answer Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attempt all the problems,
Physics 161 Homework 7 - s Wednesday November 16, 2011 Make sure your name is on every page, and please box your final answer Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attempt all the problems,
We can see from the gas phase form of the equilibrium constant that pressure of species depend on pressure. For the general gas phase reaction,
 Pressure dependence Equilibrium constant We can see from the gas phase form of the equilibrium constant that the equilibrium concentrations of species depend on pressure. This dependence is inside the
Pressure dependence Equilibrium constant We can see from the gas phase form of the equilibrium constant that the equilibrium concentrations of species depend on pressure. This dependence is inside the
Outline Review Example Problem 1. Thermodynamics. Review and Example Problems: Part-2. X Bai. SDSMT, Physics. Fall 2014
 Review and Example Problems: Part- SDSMT, Physics Fall 014 1 Review Example Problem 1 Exponents of phase transformation : contents 1 Basic Concepts: Temperature, Work, Energy, Thermal systems, Ideal Gas,
Review and Example Problems: Part- SDSMT, Physics Fall 014 1 Review Example Problem 1 Exponents of phase transformation : contents 1 Basic Concepts: Temperature, Work, Energy, Thermal systems, Ideal Gas,
Naraine Persaud, Entry Code ME-11 1
 Naraine Persaud, Entry Code ME-11 1 Persaud, N. 2005. Adiabatic cooling. In: Water Encyclopedia Volume 4: Oceanography; Meteorology; Physics and Chemistry; Water Law; and Water History, Art, and Culture.
Naraine Persaud, Entry Code ME-11 1 Persaud, N. 2005. Adiabatic cooling. In: Water Encyclopedia Volume 4: Oceanography; Meteorology; Physics and Chemistry; Water Law; and Water History, Art, and Culture.
HONOUR SCHOOL OF NATURAL SCIENCE. Final Examination GENERAL PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY I. Answer FIVE out of nine questions
 HONOUR SCHOOL OF NATURAL SCIENCE Final Examination GENERAL PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY I Monday, 12 th June 2000, 9.30 a.m. - 12.30 p.m. Answer FIVE out of nine questions The numbers in square brackets indicate
HONOUR SCHOOL OF NATURAL SCIENCE Final Examination GENERAL PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY I Monday, 12 th June 2000, 9.30 a.m. - 12.30 p.m. Answer FIVE out of nine questions The numbers in square brackets indicate
Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 Atmospheric Thermodynamics R. Wordsworth February 12, 2015 1 Objectives Derive hydrostatic equation Derive dry and moist adiabats Understand how the theory relates to observed properties of real atmospheres
Atmospheric Thermodynamics R. Wordsworth February 12, 2015 1 Objectives Derive hydrostatic equation Derive dry and moist adiabats Understand how the theory relates to observed properties of real atmospheres
Goal: Use understanding of physically-relevant scales to reduce the complexity of the governing equations
 Scale analysis relevant to the tropics [large-scale synoptic systems]* Goal: Use understanding of physically-relevant scales to reduce the complexity of the governing equations *Reminder: Midlatitude scale
Scale analysis relevant to the tropics [large-scale synoptic systems]* Goal: Use understanding of physically-relevant scales to reduce the complexity of the governing equations *Reminder: Midlatitude scale
Solutions to questions from chapter 8 in GEF Cloud Physics
 Solutions to questions from chapter 8 in GEF4310 - Cloud Physics i.h.h.karset@geo.uio.no Problem 1 a) What is expressed by the equation below? Answer: The left side is the time rate of change of the mass
Solutions to questions from chapter 8 in GEF4310 - Cloud Physics i.h.h.karset@geo.uio.no Problem 1 a) What is expressed by the equation below? Answer: The left side is the time rate of change of the mass
Stellar structure Conservation of mass Conservation of energy Equation of hydrostatic equilibrium Equation of energy transport Equation of state
 Stellar structure For an isolated, static, spherically symmetric star, four basic laws / equations needed to describe structure: Conservation of mass Conservation of energy (at each radius, the change
Stellar structure For an isolated, static, spherically symmetric star, four basic laws / equations needed to describe structure: Conservation of mass Conservation of energy (at each radius, the change
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II. Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition
 MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition Thermodynamics addresses two types of problems: 1- Computation of energy difference between two
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition Thermodynamics addresses two types of problems: 1- Computation of energy difference between two
Math 113/113H Winter 2006 Departmental Final Exam
 Name KEY Instructor Section No. Student Number Math 3/3H Winter 26 Departmental Final Exam Instructions: The time limit is 3 hours. Problems -6 short-answer questions, each worth 2 points. Problems 7 through
Name KEY Instructor Section No. Student Number Math 3/3H Winter 26 Departmental Final Exam Instructions: The time limit is 3 hours. Problems -6 short-answer questions, each worth 2 points. Problems 7 through
THERMODYNAMICS 1 /43
 THERMODYNAMICS 1 Atmosphere A multi-component Multi-Phase System The gas phase atmospheric cons1tuents; major gases; fixed propor1ons by volume (dry air) Nitrogen (N 2 ) 78,08 % Oxygen (O 2 ) 29,05 % Argon
THERMODYNAMICS 1 Atmosphere A multi-component Multi-Phase System The gas phase atmospheric cons1tuents; major gases; fixed propor1ons by volume (dry air) Nitrogen (N 2 ) 78,08 % Oxygen (O 2 ) 29,05 % Argon
Practice Final Solutions
 Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
1 Thermodynamics: some Preliminaries
 1 Thermodynamics: some Preliminaries Beforewebegintoconsider thetransfer ofradiation through an atmosphere, let s consider the structure of an atmosphere with a little thermodynamics. This material hopefully
1 Thermodynamics: some Preliminaries Beforewebegintoconsider thetransfer ofradiation through an atmosphere, let s consider the structure of an atmosphere with a little thermodynamics. This material hopefully
What is thermodynamics? and what can it do for us?
 What is thermodynamics? and what can it do for us? The overall goal of thermodynamics is to describe what happens to a system (anything of interest) when we change the variables that characterized the
What is thermodynamics? and what can it do for us? The overall goal of thermodynamics is to describe what happens to a system (anything of interest) when we change the variables that characterized the
MATH2321, Calculus III for Science and Engineering, Fall Name (Printed) Print your name, the date, and then sign the exam on the line
 MATH2321, Calculus III for Science and Engineering, Fall 218 1 Exam 2 Name (Printed) Date Signature Instructions STOP. above. Print your name, the date, and then sign the exam on the line This exam consists
MATH2321, Calculus III for Science and Engineering, Fall 218 1 Exam 2 Name (Printed) Date Signature Instructions STOP. above. Print your name, the date, and then sign the exam on the line This exam consists
First law of thermodynamics (Jan 12, 2016) page 1/7. Here are some comments on the material in Thompkins Chapter 1
 First law of thermodynamics (Jan 12, 2016) age 1/7 Here are some comments on the material in Thomkins Chater 1 1) Conservation of energy Adrian Thomkins (eq. 1.9) writes the first law as: du = d q d w
First law of thermodynamics (Jan 12, 2016) age 1/7 Here are some comments on the material in Thomkins Chater 1 1) Conservation of energy Adrian Thomkins (eq. 1.9) writes the first law as: du = d q d w
Thermodynamic Energy Equation
 Thermodynamic Energy Equation The temperature tendency is = u T x v T y w T z + dt dt (1) where dt/dt is the individual derivative of temperature. This temperature change experienced by the air parcel
Thermodynamic Energy Equation The temperature tendency is = u T x v T y w T z + dt dt (1) where dt/dt is the individual derivative of temperature. This temperature change experienced by the air parcel
Math 221 Examination 2 Several Variable Calculus
 Math Examination Spring Instructions These problems should be viewed as essa questions. Before making a calculation, ou should explain in words what our strateg is. Please write our solutions on our own
Math Examination Spring Instructions These problems should be viewed as essa questions. Before making a calculation, ou should explain in words what our strateg is. Please write our solutions on our own
Generating cloud drops from CCN. Wallace & Hobbs (1977)
 Generating cloud drops from CCN Wallace & Hobbs (1977) Cloud Drops and Equilibrium Considera3ons: review We discussed how to compute the equilibrium vapor pressure over a pure water drop, or a solu3on
Generating cloud drops from CCN Wallace & Hobbs (1977) Cloud Drops and Equilibrium Considera3ons: review We discussed how to compute the equilibrium vapor pressure over a pure water drop, or a solu3on
Outline Review Example Problem 1 Example Problem 2. Thermodynamics. Review and Example Problems. X Bai. SDSMT, Physics. Fall 2013
 Review and Example Problems SDSMT, Physics Fall 013 1 Review Example Problem 1 Exponents of phase transformation 3 Example Problem Application of Thermodynamic Identity : contents 1 Basic Concepts: Temperature,
Review and Example Problems SDSMT, Physics Fall 013 1 Review Example Problem 1 Exponents of phase transformation 3 Example Problem Application of Thermodynamic Identity : contents 1 Basic Concepts: Temperature,
Radiative Transfer Chapter 3, Hartmann
 Radiative Transfer Chapter 3, Hartmann Shortwave Absorption: Clouds, H 2 0, O 3, some CO 2 Shortwave Reflection: Clouds, surface, atmosphere Longwave Absorption: Clouds, H 2 0, CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O Planck
Radiative Transfer Chapter 3, Hartmann Shortwave Absorption: Clouds, H 2 0, O 3, some CO 2 Shortwave Reflection: Clouds, surface, atmosphere Longwave Absorption: Clouds, H 2 0, CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O Planck
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 27 May, 2004 1.30 to 3.30 PAPER 64 ASTROPHYSICAL FLUID DYNAMICS Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. Candidates
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 27 May, 2004 1.30 to 3.30 PAPER 64 ASTROPHYSICAL FLUID DYNAMICS Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. Candidates
Geometry and Motion Selected answers to Sections A and C Dwight Barkley 2016
 MA34 Geometry and Motion Selected answers to Sections A and C Dwight Barkley 26 Example Sheet d n+ = d n cot θ n r θ n r = Θθ n i. 2. 3. 4. Possible answers include: and with opposite orientation: 5..
MA34 Geometry and Motion Selected answers to Sections A and C Dwight Barkley 26 Example Sheet d n+ = d n cot θ n r θ n r = Θθ n i. 2. 3. 4. Possible answers include: and with opposite orientation: 5..
Math 162: Calculus IIA
 Math 62: Calculus IIA Final Exam ANSWERS December 9, 26 Part A. (5 points) Evaluate the integral x 4 x 2 dx Substitute x 2 cos θ: x 8 cos dx θ ( 2 sin θ) dθ 4 x 2 2 sin θ 8 cos θ dθ 8 cos 2 θ cos θ dθ
Math 62: Calculus IIA Final Exam ANSWERS December 9, 26 Part A. (5 points) Evaluate the integral x 4 x 2 dx Substitute x 2 cos θ: x 8 cos dx θ ( 2 sin θ) dθ 4 x 2 2 sin θ 8 cos θ dθ 8 cos 2 θ cos θ dθ
Exercise 1: Vertical structure of the lower troposphere
 EARTH SCIENCES SCIENTIFIC BACKGROUND ASSESSMENT Exercise 1: Vertical structure of the lower troposphere In this exercise we will describe the vertical thermal structure of the Earth atmosphere in its lower
EARTH SCIENCES SCIENTIFIC BACKGROUND ASSESSMENT Exercise 1: Vertical structure of the lower troposphere In this exercise we will describe the vertical thermal structure of the Earth atmosphere in its lower
Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 3
 Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 3 Moist convection Dew point temperature/lapse rate/lcl Equivalent potential temperature Conditional and potential instability Thermodynamic diagram CAPE Introduction to Python
Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 3 Moist convection Dew point temperature/lapse rate/lcl Equivalent potential temperature Conditional and potential instability Thermodynamic diagram CAPE Introduction to Python
Dynamic Meteorology: lecture 2
 Dynamic Meteorology: lecture 2 Sections 1.3-1.5 and Box 1.5 Potential temperature Radiatively determined temperature (boxes 1.1-1.4) Buoyancy (-oscillations) and static instability, Brunt-Vaisala frequency
Dynamic Meteorology: lecture 2 Sections 1.3-1.5 and Box 1.5 Potential temperature Radiatively determined temperature (boxes 1.1-1.4) Buoyancy (-oscillations) and static instability, Brunt-Vaisala frequency
