Study on river-discharge measurements with a bottom-mounted ADCP
|
|
|
- Edwina Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Study on river-discharge measurements with a bottom-mounted ADCP Y. Nihei & T. Sakai Tokyo University of Science, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Chiba, Japan ABSTRACT: To examine the accuracy of discharge measurements in rivers, continuous measurements of flood flows were conducted with a bottom-mounted ADCP. The observed data indicates that the vertical distribution of the velocity varied considerably in the rising and falling stages of a hydrologic event, in which the unsteadiness parameterα and H.W.L. were relatively larger. It should be noted from the observed data that the averaged coefficients of float were in good agreements with well-known empirical values, while the coefficients of float varied appreciably in each hydrologic event. The accuracy for evaluating river discharge is investigated by using the rating curves with H-Q and V-Q, showing that the rating curves with H-Q and V-Q are appropriate for the evaluation of discharge in the upper and lower reaches of the river, respectively. Oohori River 5m Stn.1 Stn.2 1 INTRODUCTION River discharge is essential for river planning and management. In measuring river discharge, rod-float measurements are widely adopted under flood-flow conditions. Using a rating curve between the observed discharge Q and water elevation H at a crosssection of a river, so called an H-Q curve, the continuous data for river discharge Q can be obtained from the observed water elevation H. Therefore a huge number of gauging stations recording water elevation have been developed. However, under flood-flow conditions, the discharge in a rising stage tends to be higher than that in a falling stage at a same water elevation, producing a looped rating curve. Further the discharge monitoring with floats may have measuring errors due to various hydraulic phenomenon. From the above viewpoints, it is necessary to evaluate the accuracy and applicability of previous methods for discharge measurements. Moreover it is expected to develop a more accurate technique for measuring river discharge. For this purpose, the continuous measurements of flood flows were conducted with a bottommounted ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler) which can record a vertical distribution of velocity. An ADCP has already been used as a standard current meter of physical oceanography and coastal environments (e.g., Pettigrew et al. 1986). The recent ADCP technology can realize to measure the threedimensional velocity with fine vertical resolution in which the minimum cell size is 1cm. Then the potential for applying the ADCP into current measurements in shallow-water flow like river flow has been increasing. In the present paper, the field measurements were done in the Oohori River in Japan, an urban small river. The analysis of the observed data was employed to examine the vertical distribution of velocity in rising and falling stages and then evaluate a coefficient of float which is the ratio of depthaveraged velocity to velocity in surface layer. In addition, the accuracy of rating curves with H-Q and V- Q (Huang 24) is discussed, in which V means a depth-averaged velocity. 2 OUTLINE OF FIELD MEASUREMENTS The Oohori River chosen as a field site inflows into the western part of Lake Teganuma, one of typical eutrophied lakes in Japan. As shown in Fig.1, the measuring stations were in lower reach of the Oohori River at Stns.1 and 2 which were located at 1.5 km and.9 km upstream from the river mouth, respec- N Lake Teganuma Figure 1. Field site and location of measuring stations.
2 4. 2. H.W.L. L.W.L. ADCP vegetation.4cm Transducer.14m Wooden flame (a) Stn.1 Pile Figure 3. Schematic view of the bottom-mounted ADCP in the field measurements. 4. ADCP Table 1. Configuration of the ADCP used in the field measurements. 2. vegetation H.W.L. L.W.L (b) Stn.2 Figure 2. Cross-sectional view at both the measuring stations. Cell size Cell number Sampling interval Blank zone tively. The backwater from the lake was known to affect time variations of the water elevation at both the stations. The influence from the lake appeared more appreciably at Stn.2 than at Stn.1. Figure 2 describes the cross-sectional view at both the stations. The Oohori River is a compound channel and the width of the flood plane with vegetation layer at Stn.1 is much larger than that at Stn.2. The ADCP is bottom-mounted in the center of the main channel. The instrument used in the present study was a 12 khz WorkHorse Sentinel ADCP (RD Instruments, Inc.). The ADCP was installed on the river bed looking upward, to give the vertical profile of velocity, as indicated in Fig.3. The configuration parameters of the ADCP are summarized in Table 1. In the configuration, the blank zone, in which no measurements were taken near the head of the ADCP, was.14 m. The measurements of water elevation were also conducted with the pressure gauge (Diver, Eijikelkamp Co.). The ADCP was installed at Stn.1 in 24 and at Stn.2 in 25, respectively. From these field measurements, the observed data in five hydrologic events were selected to perform the analysis of observed data. The information for the events are detailed in Table 2, in which the unsteadiness parameter α proposed by Nezu et al. (1997) is defined as h 1 = T d U c.2m 15 5 minutes.14m α, (1) Table 2. Outline of the hydrologic events. Event Station Period T d [s] h U c [m/s] Rising stage A May 2 to 21, 24 Falling stage B C-1 C-2 D E Stn.1 Stn.2 June 11 to 12, 24 November 12, 24 November 12, 24 November 15, 24 July 3 to 4, 25 Rising stage Falling stage Rising stage Falling stage Rising stage Falling stage Rising stage Falling stage Rising stage Falling stage
3 1.2 z h =.87m 1.2 z rising stage h = 1.2m falling stage 1.2 z h = 2m (a) Event A (Peak depth=1.66m) 1.2 z h =.77m 1.2 z h =.96m 1.2 z h = 1.6m (b) Event D (Peak depth=1.2m) Figure 4. Vertical distribution of streamwise velocity in the rising and falling stages (h: water depth) where h is the difference of maximum flow depth and the base flow depth, T d means the time duration of the rising or falling stage in the hydrograph and U c represents the average of peak flow and base flow depth-averaged velocity. In Table 2, these parameters are displayed in the rising and falling stages of each event. Since two peaks of the hydrograph appeared in the event C, the period of the event is separately denoted as event C-1 and C-2 in Table 2. 3 VERTICAL FLOW STRUCTURE IN FLOOD EVENTS 3.1 Vertical distribution of streamwise velocity To examine the fundamental vertical flow structure in the rising and falling stages, Fig.4 indicates the vertical distribution of streamwise velocity in the events A and D. The horizontal axis in the figure means the streamwise velocity v normalized by the depth-averaged velocity V. For evaluating the depthaveraged velocity V, the velocity in the blank zone near the riverbed are estimated with the approxima- b = az tion described as v (z: the height from the riverbed; a, b: constants). The observed results in the event A shows that, in shallower water depth (h=.87 m), the velocity distributions in the rising and falling stages almost coincided with each other. However, in deeper depth (h=1.2 m and 2 m), the velocity in the rising stage tended to be uniform vertically, while the velocity distribution in the falling stage was inclined in the vertical direction. The results in the event A demonstrate that the vertical distribution of the velocity varied considerably in the rising and falling stages of the hydrologic event. On the other hand, the observed results in the event D reveal that the velocity distributions in the rising stage were almost agreements with those in the falling stage at three depth conditions. The observed results for the vertical flow structure indicate that the appreciable differences of the vertical distribution of the velocity were found only in the event A. It is noted from Table 2 that the unsteadiness parameter α and depth difference h in the event A were larger than those in the other events. These parameters may be closely related to the difference of the vertical flow structure in the hydrograph. In near future, hence, it is necessary to collect further ADCP data to clarify the vertical flow structure under various flow conditions. It is also 5 noteworthy that α = in the event A may be regarded as a weak unsteadiness condition in the laboratory experiments done by Nezu et al. (1997). 3.2 Coefficient of float In discharge measurements with rod floats flowing near water surface, it is necessary to convert measured surface velocity with rod floats into a depthaveraged velocity V. In the evaluation for the river discharge, one needs to use a coefficient of floats
4 Rising stage Falling stage Obs. Approximation.9.7 Event A v s25[m/s] v s5[m/s].9 Event D v s25[m/s] v s5 [m/s] (a) V and v s25 (b) V and v s5 Figure 5. Comparison between the depth-averaged velocity V and the surface velocity v s25 and v s5. which is a ratio of the depth-averaged velocity to the surface velocity. The ADCP can monitor the vertical distribution of velocity. It is therefore possible to confirm the validity of well-known coefficients of float by using the vertical distribution of velocity obtained by the bottom-mounted ADCP. In general float measurements, a surface float and a.5 m long rod are adopted in h <.7 m and.7 m < h < 1.3 m, where h is water depth, respectively. The relationship between the depth-averaged velocity and surface velocity in the events A and D are illustrated in Fig.5. Here two surface velocities v s25 and v s5 are introduced as the velocity averaged in the surface layer with the thickness of 25 cm and 5 cm, respectively. The surface velocities v s25 and v s5 corresponds to the velocities measured by surface float and a.5 m long rod, respectively. The observed results are separately depicted in the rising and falling stages in the figure. The correlations between the depth-averaged velocity V and the surface velocities v s25 and v s5 in the event A indicate that, under the same surface velocity, the depth-averaged velocity V in the rising stage was larger than that in the falling stage. These tendencies were found in both the surface velocities. On the other hand, the difference of the depthaveraged velocity in the rising and falling stages was not observed in the event D. The relations between the depth-averaged and surface velocities are almost Table 3. Coefficients of float in each hydrologic event. Event Rising Falling Rising Falling stage stage stage stage A B C D E Average similar to the vertical flow structure mentioned in the above. In Fig.5, linear approximations for the correlations between the depth-averaged and surface velocities are also exhibited. The slopes of the linear approximations correspond to the coefficients of float (=V/ v s25 or V/ v s5 ). The evaluated coefficients of float in each hydrologic event are summarized in Table 3. In the event A, the difference of the coefficients of float in the rising and falling stages was.4-.5, while, in the other events, the coefficient in the rising stage was comparable to that in the falling stage. The results are also similar to those shown in Figs.4 & 5. The averaged coefficients for v s25 and v s5 were.83 and.87, respectively, almost corresponding to well-known empirical values for the coeffi-
5 2. Event A Event B Event C Event D Stn.1 2. Event A Event B Event C Event D H Event E Stn V[m/s] Event E H (a) H-Q Figure 6. H-Q and V-Q curves at Stns.1 and V[m/s] (b) V-Q cients of float (=.85 and.88, respectively). In each hydrologic event, however, the coefficients of float for the surface velocities v s25 and v s5 varied appreciably. The coefficients for v s25 and v s5 were from.75 to.92 and from.78 to.93, respectively. 4 ACCURACY OF DISCHARGE EVALUATION WITH H-Q AND V-Q CURVES 4.1 Procedure of discharge evaluation Accuracy of discharge evaluation with rating curves is examined using the observed data with the ADCP. For this purpose, it is necessary to evaluate river discharge with the depth-averaged velocity obtained by the ADCP mounted at a point in a cross section. To obtain the transverse distribution of velocity in a cross section from the ADCP data, a dynamic interpolation method presented by Nihei & Kimizu (26) is introduced, in which observed velocities can be spatially interpolated in the cross section with satisfying the fundamental dynamic principle of fluid motion. With the dynamic interpolation method, the time sequence of the discharge can be calculated from the depth-averaged velocity and water elevation. 4.2 H-Q and V-Q curves The correlations of H-Q and V-Q at Stns.1 and 2 are displayed in Fig.6. Approximations for the correlations are also depicted in the figures. At Stn.1, both the rating curves of H-Q and V-Q were looped in the hydrograph. The loop of the V-Q curve was larger than that of the H-Q curve. In contrast, at Stn.2, the H-Q rating curve was looped more largely than the V-Q curve. The influences of the backwater from Lake Teganuma appeared more appreciably for water elevation at Stn.2 than that at Stn.1 due to the difference of the distance from the river mouth. Therefore larger loop of the H-Q curve was found at Stn Results and discussion The discharge can be evaluated by using the approximations for H-Q and V-Q as shown in Fig.6. Table 4 reveals the observed and evaluated discharges averaged during a hydrologic event. In the table, the observed discharge Q obs and the ratio of the evaluated discharge Q cal to Q obs are separately expressed in the rising and falling stages and total period of each event. The results for the total periods of events A, B, C and D at Stn.1 illustrate that the ratio Q cal Qobs with the H-Q curve was from 89 to 124%, while Q cal Qobs with the V-Q curve was from 67 to 143 %. This fact exhibits that
6 Table 4. Comparison of the observed and evaluated discharge in each hydrologic event. Event [m 3 /s] H-Q V-Q Total A Rising stage Falling stage Total B Rising stage Falling stage Total C Rising stage Falling stage Total D Rising stage Falling stage Total E Rising stage Falling stage the accuracy of the V-Q curve was lower than that of the H-Q curve due to larger loop of the V-Q curve at Stn.1 as mentioned in Fig. 6. Furthermore the accuracy of the H-Q and V-Q curves was lower in the rising stage or falling stage because of the existence of the loop of the rating curves. Then the temporal variations of discharge may not be accurately evaluated with H-Q and V-Q curves. On the other hand, Qcal Qobs in the event E at Stn.2 suggests that the accuracy of the H-Q curve was lower than that of the V-Q curve. It should be noted from the result that at measuring stations with significant backwater influences from lakes like Stn.2, a V-Q curve is more appropriate to accurately evaluate river discharge than an H-Q curve. v s25 and v s5 were from.75 to.92 and from.78 to.93, respectively. 3) The H-Q and V-Q curves are appropriate for the evaluation of discharge in the upper and lower reaches of the river, respectively, due to the difference of the backwater effect from the lake. 4) The temporal variations of discharge may not be accurately evaluated with the H-Q and V-Q curves. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This study was partially supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (2) (no ), the River Fund in charge of the FOREM and Academic Frontier Project (25) of MEXT. The authors would like to express their deep thanks to students in hydraulics laboratory, Department of Civil Eng., Tokyo University of Science, for their help in conducting field observations in the present study. REFERENCES Huang, H. 24. Index-velocity rating development for rapidly changing flows in an irrigation canal using broadband StreamPro ADCP and ChannelMaster H-ADCP, Proc. of River 4 : Nezu, I., Kadota., A., Nakagawa, H Turbulent structure in unsteady depth-varying open-channel flows, J. Hydraul. Eng. 123(9): Nihei, Y. & Kimizu, A. 26. Evaluation of river velocity and discharge with a new assimilated method, J. River Basin Management 4(1): 1-4. Pettigrew, N. R., Beardsley, R. C. and Irish, J. D Field evaluations of bottom-mounted acoustic Doppler profiler and conventional current meter moorings, IEEE: CONCLUSIONS The flood-flow measurements were done with the bottom-mounted ADCP. With the observed data, the vertical flow structure and the evaluation of the discharge with the H-Q and V-Q curves are discussed. Main conclusions in the present study are as follows: 1) In the event A with relatively larger unsteadiness parameter α and stage variation h, the vertical flow structure and the coefficient of floats were found to be different appreciably in the rising and falling stages. 2) The averaged values of the float coefficients for v s25 and v s5 were.83 and.87, respectively, almost corresponding to the well-known empirical values. In each hydrologic event, however, the coefficients of float varied considerably. The coefficients for the surface velocities
A TIPPING-BUCKET SEDIMENT TRAP FOR CONTINUOUS MONITORING OF SEDIMENT DEPOSITION RATE
 A TIPPING-BUCKET SEDIMENT TRAP FOR CONTINUOUS MONITORING OF SEDIMENT DEPOSITION RATE YASUO NIHEI AND YUICHI IMASHIMIZU Department of Civil Eng., Tokyo University of Science, 2641 Yamazaki, Noda-shi 278-851,
A TIPPING-BUCKET SEDIMENT TRAP FOR CONTINUOUS MONITORING OF SEDIMENT DEPOSITION RATE YASUO NIHEI AND YUICHI IMASHIMIZU Department of Civil Eng., Tokyo University of Science, 2641 Yamazaki, Noda-shi 278-851,
A DYNAMIC INTERPOLATION AND EXTRAPOLATION METHOD TO EVALUATE CROSS-SECTIONAL VELOCITY FROM POINT VELOCITY
 A DYNAMIC INTERPOLATION AND EXTRAPOLATION METHOD TO EVALUATE CROSS-SECTIONAL VELOCITY FROM POINT VELOCITY J. KASHIWADA, 1 Y. NIHEI, 2 E. TAKASHIMA, 3 Y. YAMASAKI, 4 and M. ICHIYAMA 5 1 Engineer, River
A DYNAMIC INTERPOLATION AND EXTRAPOLATION METHOD TO EVALUATE CROSS-SECTIONAL VELOCITY FROM POINT VELOCITY J. KASHIWADA, 1 Y. NIHEI, 2 E. TAKASHIMA, 3 Y. YAMASAKI, 4 and M. ICHIYAMA 5 1 Engineer, River
A DYNAMIC INTERPOLATION AND EXTRAPOLATION METHOD TO EVALUATE CROSS-SECTIONAL VELOCITY FROM POINT VELOCITY
 A DYNAMIC INTERPOLATION AND EXTRAPOLATION METHOD TO EVALUATE CROSS-SECTIONAL VELOCITY FROM POINT VELOCITY J. Kashiwada, 1 Y. Nihei, 2 E. Takashima, 3 Y. Yamasaki, 4 and M. Ichiyama 5 1 Engineer, River
A DYNAMIC INTERPOLATION AND EXTRAPOLATION METHOD TO EVALUATE CROSS-SECTIONAL VELOCITY FROM POINT VELOCITY J. Kashiwada, 1 Y. Nihei, 2 E. Takashima, 3 Y. Yamasaki, 4 and M. Ichiyama 5 1 Engineer, River
ADCP MEASUREMENTS OF VERTICAL FLOW STRUCTURE AND COEFFICIENTS OF FLOAT IN FLOOD FLOWS
 ADCP MEASUREMENTS OF VERTICAL FLOW STRUCTURE AND COEFFICIENTS OF FLOAT IN FLOOD FLOWS Yasuo NIHEI (1) and Takeiro SAKAI (2) (1) Department of Civil Engineering, Tokyo University of Science, 2641 Yamazaki,
ADCP MEASUREMENTS OF VERTICAL FLOW STRUCTURE AND COEFFICIENTS OF FLOAT IN FLOOD FLOWS Yasuo NIHEI (1) and Takeiro SAKAI (2) (1) Department of Civil Engineering, Tokyo University of Science, 2641 Yamazaki,
Measurements of In Situ Pick-up Rate of Nutrients on Riverbed
 1th International Conference on Integrated Diffuse Pollution Management (IWA DIPCON 8). Research Center for Environmental and Hazardous Substance Management (EHSM), Khon Kaen University, Thailand; 5-9
1th International Conference on Integrated Diffuse Pollution Management (IWA DIPCON 8). Research Center for Environmental and Hazardous Substance Management (EHSM), Khon Kaen University, Thailand; 5-9
IMPROVEMENT OF DISCHARGE OBSERVATION ACCURACY IN ICE-COVERED RIVERS FOR RIVER MANAGEMENT
 in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research IMPROVEMENT OF DISCHARGE
in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research IMPROVEMENT OF DISCHARGE
New computation method for flood flows and bed variations in a low-lying river with complex river systems
 River Flow 2014 Schleiss et al. (Eds) 2014 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02674-2 New computation method for flood flows and bed variations in a low-lying river with complex river systems
River Flow 2014 Schleiss et al. (Eds) 2014 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02674-2 New computation method for flood flows and bed variations in a low-lying river with complex river systems
Tanjung Priok GFPPEP. Presentation and discussion, 22 October 2009 PT. PLN (Persero) Jasa Enjiniring Office Jl. KS Tubun I/2 Petamburan, Jakarta
 Tanjung Priok GFPPEP Presentation and discussion, 22 October 2009 PT. PLN (Persero) Jasa Enjiniring Office Jl. KS Tubun I/2 Petamburan, Jakarta prepared by Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Tanjung Priok GFPPEP Presentation and discussion, 22 October 2009 PT. PLN (Persero) Jasa Enjiniring Office Jl. KS Tubun I/2 Petamburan, Jakarta prepared by Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Experimental Study for Investigating the Impact Force on a Wooden House by Driftwood in Steady and Unsteady Surge-type Flow
 Experimental Study for Investigating the Impact Force on a Wooden House by Driftwood in Steady and Unsteady Surge-type Flow K. Miyahara 1 and N. Tanaka 2 1 Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Saitama
Experimental Study for Investigating the Impact Force on a Wooden House by Driftwood in Steady and Unsteady Surge-type Flow K. Miyahara 1 and N. Tanaka 2 1 Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Saitama
Evaluation of flood discharge hydrographs and bed variations in a channel network on the Ota River delta, Japan
 3 Floods: From Risk to Opportunity (IAHS Publ. 357, 3). Evaluation of flood discharge hydrographs and bed variations in a channel network on the Ota River delta, Japan T. GOTOH, S. FUKUOKA & R. TANAKA
3 Floods: From Risk to Opportunity (IAHS Publ. 357, 3). Evaluation of flood discharge hydrographs and bed variations in a channel network on the Ota River delta, Japan T. GOTOH, S. FUKUOKA & R. TANAKA
Study about Velocity Index in Actual River during Flooding
 Study about Velocity Index in Actual River during Flooding Atsuhiro Yorozuya 1, Kazuhiko Fukami 1 1 International Centre for Water Hazard and Risk Management (ICHARM) under the auspices of UNESCO, Public
Study about Velocity Index in Actual River during Flooding Atsuhiro Yorozuya 1, Kazuhiko Fukami 1 1 International Centre for Water Hazard and Risk Management (ICHARM) under the auspices of UNESCO, Public
An Intensive Field Survey of Physical Environments in a Mangrove Forest
 An Intensive Field Survey of Physical Environments in a Mangrove Forest Yasuo ihei ), Kazuo adaoka 2), Yasunori Aoki ), Kensui Wakaki 2), Hideaki Yai 3) and Keita Furukawa 4) ) Department of Civil Engineering,
An Intensive Field Survey of Physical Environments in a Mangrove Forest Yasuo ihei ), Kazuo adaoka 2), Yasunori Aoki ), Kensui Wakaki 2), Hideaki Yai 3) and Keita Furukawa 4) ) Department of Civil Engineering,
VARIATION OF MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT WITH SEEPAGE IN SAND-BED CHANNEL *Satish Patel 1 and Bimlesh Kumar 2
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 3678 3685 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) VARIATION OF MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT WITH SEEPAGE IN SAND-BED CHANNEL
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 3678 3685 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) VARIATION OF MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT WITH SEEPAGE IN SAND-BED CHANNEL
9. Flood Routing. chapter Two
 9. Flood Routing Flow routing is a mathematical procedure for predicting the changing magnitude, speed, and shape of a flood wave as a function of time at one or more points along a watercourse (waterway
9. Flood Routing Flow routing is a mathematical procedure for predicting the changing magnitude, speed, and shape of a flood wave as a function of time at one or more points along a watercourse (waterway
HORIZONTAL TURBULENT DIFFUSION AT SEA SURFACE FOR OIL TRANSPORT SIMULATION
 HORIZONTAL TURBULENT DIFFUSION AT SEA SURFACE FOR OIL TRANSPORT SIMULATION Yoshitaka Matsuzaki 1, Isamu Fujita 2 In numerical simulations of oil transport at the sea surface, it is not known how to determine
HORIZONTAL TURBULENT DIFFUSION AT SEA SURFACE FOR OIL TRANSPORT SIMULATION Yoshitaka Matsuzaki 1, Isamu Fujita 2 In numerical simulations of oil transport at the sea surface, it is not known how to determine
DYNAMICS OF FLOOD FLOWS AND BED VARIATIONS IN RIVER SECTIONS REPAIRED TO SHIP-BOTTOM SHAPED CHANNELS FROM COMPOUND CHANNLS
 E-proceedings of the 36 th IAHR World Congress DYNAMICS OF FLOOD FLOWS AND BED VARIATIONS IN RIVER SECTIONS REPAIRED TO SHIP-BOTTOM SHAPED CHANNELS FROM COMPOUND CHANNLS TAKUMA SASAKI (1) & SHOJI FUKUOKA
E-proceedings of the 36 th IAHR World Congress DYNAMICS OF FLOOD FLOWS AND BED VARIATIONS IN RIVER SECTIONS REPAIRED TO SHIP-BOTTOM SHAPED CHANNELS FROM COMPOUND CHANNLS TAKUMA SASAKI (1) & SHOJI FUKUOKA
Countermeasures for Preserving Riverine Tidal Flats in a Ship-Bottom Shaped Channel of the Lower Ota River Floodway
 ICHE 214, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 214 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-939232-8 Countermeasures for Preserving Riverine Tidal Flats in a Ship-Bottom Shaped Channel of the Lower Ota River
ICHE 214, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 214 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-939232-8 Countermeasures for Preserving Riverine Tidal Flats in a Ship-Bottom Shaped Channel of the Lower Ota River
Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FOUR. Stream flow measurement. Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib
 Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FOUR Stream flow measurement Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib -١ 4.1 Introduction - Surface water hydrology deals with the movement of water
Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FOUR Stream flow measurement Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib -١ 4.1 Introduction - Surface water hydrology deals with the movement of water
Investigation of Flow Profile in Open Channels using CFD
 Investigation of Flow Profile in Open Channels using CFD B. K. Gandhi 1, H.K. Verma 2 and Boby Abraham 3 Abstract Accuracy of the efficiency measurement of a hydro-electric generating unit depends on the
Investigation of Flow Profile in Open Channels using CFD B. K. Gandhi 1, H.K. Verma 2 and Boby Abraham 3 Abstract Accuracy of the efficiency measurement of a hydro-electric generating unit depends on the
Factors affecting confluence scour
 & Wang (eds) River Sedimentation 1999., Balkema, Rotterdam. ISBN 9 9 3. 17 19 Factors affecting confluence scour R. B. Rezaur & A. W. Jayawardena. Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Hong
& Wang (eds) River Sedimentation 1999., Balkema, Rotterdam. ISBN 9 9 3. 17 19 Factors affecting confluence scour R. B. Rezaur & A. W. Jayawardena. Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Hong
A Comparison of Predicted Along-channel Eulerian Flows at Cross- Channel Transects from an EFDC-based Model to ADCP Data in South Puget Sound
 A Comparison of Predicted Along-channel Eulerian Flows at Cross- Channel Transects from an EFDC-based Model to ADCP Data in South Puget Sound Skip Albertson, J. A. Newton and N. Larson Washington State
A Comparison of Predicted Along-channel Eulerian Flows at Cross- Channel Transects from an EFDC-based Model to ADCP Data in South Puget Sound Skip Albertson, J. A. Newton and N. Larson Washington State
COMPARISON OF LABORATORY AND FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF BRIDGE PIER SCOUR
 COMPARISON OF LABORATORY AND FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF BRIDGE PIER SCOUR LEE, SEUNGOH, STURM, T. W., School of Civil and Environ. Engrg., Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332-0512 USA GOTVALD,
COMPARISON OF LABORATORY AND FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF BRIDGE PIER SCOUR LEE, SEUNGOH, STURM, T. W., School of Civil and Environ. Engrg., Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA 30332-0512 USA GOTVALD,
Effect of River Levee with Geosynthetic- Reinforced Soil against Overflow Erosion and Infiltration
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU International Symposium on Hydraulic Structures Jun 28th, 4:00 PM - 6:00 PM Effect of River Levee with Geosynthetic- Reinforced Soil against Overflow Erosion and
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU International Symposium on Hydraulic Structures Jun 28th, 4:00 PM - 6:00 PM Effect of River Levee with Geosynthetic- Reinforced Soil against Overflow Erosion and
Laboratory Investigation of Submerged Vane Shapes Effect on River Banks Protection
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 1402-1407, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Laboratory Investigation of Submerged Vane Shapes Effect on River Banks Protection Touraj Samimi Behbahan Department
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 1402-1407, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Laboratory Investigation of Submerged Vane Shapes Effect on River Banks Protection Touraj Samimi Behbahan Department
Technical Memorandum No
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. Case study of reservoir sedimentation
 Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. HR Wallingford, Wallingford, UK Published in the proceedings of River Flow 2012, 5-7 September 2012 Abstract Reservoir sedimentation is a main concern in the Tarbela reservoir
Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. HR Wallingford, Wallingford, UK Published in the proceedings of River Flow 2012, 5-7 September 2012 Abstract Reservoir sedimentation is a main concern in the Tarbela reservoir
Lecture 10: River Channels
 GEOG415 Lecture 10: River Channels 10-1 Importance of channel characteristics Prediction of flow was the sole purpose of hydrology, and still is a very important aspect of hydrology. - Water balance gives
GEOG415 Lecture 10: River Channels 10-1 Importance of channel characteristics Prediction of flow was the sole purpose of hydrology, and still is a very important aspect of hydrology. - Water balance gives
Influence of Two-line Emergent Floodplain Vegetation on A Straight Compound Channel Flow
 International Journal of Integrated Engineering, Vol. 5 No. 1 (2013) p. 58-63 Influence of Two-line Emergent Floodplain Vegetation on A Straight Compound Channel Flow Mazlin Jumain 1,*, Zulkiflee Ibrahim
International Journal of Integrated Engineering, Vol. 5 No. 1 (2013) p. 58-63 Influence of Two-line Emergent Floodplain Vegetation on A Straight Compound Channel Flow Mazlin Jumain 1,*, Zulkiflee Ibrahim
Canal Velocity Indexing at Colorado River Indian Tribes (CRIT) Irrigation Project in Parker, Arizona using the SonTek Argonaut SL
 Canal Velocity Indexing at Colorado River Indian Tribes (CRIT) Irrigation Project in Parker, Arizona using the SonTek Argonaut SL Authors: Dr. Stuart Styles P.E., Mark Niblack, Beau Freeman Abstract An
Canal Velocity Indexing at Colorado River Indian Tribes (CRIT) Irrigation Project in Parker, Arizona using the SonTek Argonaut SL Authors: Dr. Stuart Styles P.E., Mark Niblack, Beau Freeman Abstract An
Control of saline water intrusion by vane-like barrier
 Control of saline water intrusion by vane-like barrier M. Ifuku Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ehime University, Japan. Abstract There have been many studies on density current in estuary
Control of saline water intrusion by vane-like barrier M. Ifuku Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ehime University, Japan. Abstract There have been many studies on density current in estuary
CHANGES IN RIVER BED AROUND THE FUKAWA CONTRACTION AREA BY FLOODS AND CHANNEL IMPROVEMENT WORKS IN THE LOWER TONE RIVER
 The 1 th Int. Conf. on Hydroscience and Engineering (ICHE-212), Nov. 4 Nov. 7, Orlando, USA 1 CHANGES IN RIVER BED AROUND THE FUKAWA CONTRACTION AREA BY FLOODS AND CHANNEL IMPROVEMENT WORKS IN THE LOWER
The 1 th Int. Conf. on Hydroscience and Engineering (ICHE-212), Nov. 4 Nov. 7, Orlando, USA 1 CHANGES IN RIVER BED AROUND THE FUKAWA CONTRACTION AREA BY FLOODS AND CHANNEL IMPROVEMENT WORKS IN THE LOWER
Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Arup Kumar Sarma Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Arup Kumar Sarma Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 04 Gradually Varied Flow Lecture No. # 07 Rapidly Varied Flow: Hydraulic Jump
Hydraulics Prof. Dr. Arup Kumar Sarma Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 04 Gradually Varied Flow Lecture No. # 07 Rapidly Varied Flow: Hydraulic Jump
SEDIMENT TRANSPORT IN RIVER MOUTH ESTUARY
 SEDIMENT TRANSPORT IN RIVER MOUTH ESTUARY Katsuhide YOKOYAMA, Dr.Eng. dredge Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering Tokyo Metropolitan University 1-1 Minami-Osawa Osawa, Hachioji,, Tokyo,
SEDIMENT TRANSPORT IN RIVER MOUTH ESTUARY Katsuhide YOKOYAMA, Dr.Eng. dredge Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering Tokyo Metropolitan University 1-1 Minami-Osawa Osawa, Hachioji,, Tokyo,
EFFECTS OF ICE ON THE HYDRAULICS OF INNER MONGOLIA REACH OF THE YELLOW RIVER
 Ice in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Ice Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research EFFECTS OF
Ice in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Ice Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research EFFECTS OF
Birecik Dam & HEPP Downstream River Arrangement R. Naderer, G. Scharler Verbundplan GmbH, 5021 Salzburg, Austria
 Birecik Dam & HEPP Downstream River Arrangement R. Naderer, G. Scharler Verbundplan GmbH, 5021 Salzburg, Austria e-mail: scharlerg@verbund.co.at Abstract Birecik Dam & HEPP on the Euphrates river in Turkey
Birecik Dam & HEPP Downstream River Arrangement R. Naderer, G. Scharler Verbundplan GmbH, 5021 Salzburg, Austria e-mail: scharlerg@verbund.co.at Abstract Birecik Dam & HEPP on the Euphrates river in Turkey
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF BACKWATER RISE DUE TO BRIDGE PIERS AS FLOW OBSTRUCTIONS
 Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC1 6, Alexandria, Egypt 19 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF BACKWATER RISE DUE TO BRIDGE PIERS AS FLOW OBSTRUCTIONS Kassem Salah El-Alfy Associate Prof., Irrigation
Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC1 6, Alexandria, Egypt 19 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF BACKWATER RISE DUE TO BRIDGE PIERS AS FLOW OBSTRUCTIONS Kassem Salah El-Alfy Associate Prof., Irrigation
Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped outer bank
 River Sedimentation Wieprecht et al. (Eds) 2017 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02945-3 Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped
River Sedimentation Wieprecht et al. (Eds) 2017 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02945-3 Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped
Diego Burgos. Geology 394. Advisors: Dr. Prestegaard. Phillip Goodling
 Sediment Transport into an Urban Tributary Junction Diego Burgos Geology 394 Advisors: Dr. Prestegaard Phillip Goodling 1 Abstract Tributary junctions are an important component of stream morphology and
Sediment Transport into an Urban Tributary Junction Diego Burgos Geology 394 Advisors: Dr. Prestegaard Phillip Goodling 1 Abstract Tributary junctions are an important component of stream morphology and
Flood River Discharge Measurement Method in Japan
 Flood River Discharge Measurement Method in Japan Hydrologic Engineering Research Team Hydraulic Engineering Research Group Public Work Research Institute (PWRI) Contents 1. Overview of River Discharge
Flood River Discharge Measurement Method in Japan Hydrologic Engineering Research Team Hydraulic Engineering Research Group Public Work Research Institute (PWRI) Contents 1. Overview of River Discharge
A NONLINEAR OPTIMIZATION MODEL FOR ESTIMATING MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT
 Twelfth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC2 2008, Alexandria, Egypt 299 A NONLINEAR OPTIMIZATION MODEL FOR ESTIMATING MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT Maysoon Kh. Askar and K. K. Al-Jumaily
Twelfth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC2 2008, Alexandria, Egypt 299 A NONLINEAR OPTIMIZATION MODEL FOR ESTIMATING MANNING S ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT Maysoon Kh. Askar and K. K. Al-Jumaily
Prediction of landslide-induced debris flow hydrograph: the Atsumari debris flow disaster in Japan
 Monitoring, Simulation, Prevention and Remediation of Dense and Debris Flows 27 Prediction of landslide-induced debris flow hydrograph: the Atsumari debris flow disaster in Japan H. Takaoka 1, H. Hashimoto
Monitoring, Simulation, Prevention and Remediation of Dense and Debris Flows 27 Prediction of landslide-induced debris flow hydrograph: the Atsumari debris flow disaster in Japan H. Takaoka 1, H. Hashimoto
Analysis of flow around impermeable groynes on one side of symmetrical compound channel: An experimental study
 Water Science and Engineering, 2010, 3(1): 56-66 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2010.01.006 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com Analysis of flow around impermeable groynes on one side
Water Science and Engineering, 2010, 3(1): 56-66 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2010.01.006 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com Analysis of flow around impermeable groynes on one side
Evaluation of the Potential for Hysteresis in Index-Velocity Ratings for the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal near Lemont, Illinois
 Prepared in cooperation with the Chicago District of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Evaluation of the Potential for Hysteresis in Index-Velocity Ratings for the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal near Lemont,
Prepared in cooperation with the Chicago District of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Evaluation of the Potential for Hysteresis in Index-Velocity Ratings for the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal near Lemont,
A distributed runoff model for flood prediction in ungauged basins
 Predictions in Ungauged Basins: PUB Kick-off (Proceedings of the PUB Kick-off meeting held in Brasilia, 2 22 November 22). IAHS Publ. 39, 27. 267 A distributed runoff model for flood prediction in ungauged
Predictions in Ungauged Basins: PUB Kick-off (Proceedings of the PUB Kick-off meeting held in Brasilia, 2 22 November 22). IAHS Publ. 39, 27. 267 A distributed runoff model for flood prediction in ungauged
FAILURES IN THE AMAZON RIVERBANKS, IQUITOS, PERU
 FAILURES IN THE AMAZON RIVERBANKS, IQUITOS, PERU A.Carrillo-Gil University of Engineering & A.Carrillo Gil S.A.,Consulting Engineering,Lima,Peru L. Dominguez University of Engineering,Lima & The Maritime
FAILURES IN THE AMAZON RIVERBANKS, IQUITOS, PERU A.Carrillo-Gil University of Engineering & A.Carrillo Gil S.A.,Consulting Engineering,Lima,Peru L. Dominguez University of Engineering,Lima & The Maritime
Free Flow Below Skew Sluice Gate
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-67X, p-issn: 2278-8X, www.ijerd.com Volume, Issue 3 (March 24), PP.44-52 Talib Mansoor Civil Engineering Department, Aligarh Muslim
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-67X, p-issn: 2278-8X, www.ijerd.com Volume, Issue 3 (March 24), PP.44-52 Talib Mansoor Civil Engineering Department, Aligarh Muslim
B-1. Attachment B-1. Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling
 Attachment B-1 Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling 1 October 2012 Lower Susquehanna River Watershed Assessment Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications
Attachment B-1 Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling 1 October 2012 Lower Susquehanna River Watershed Assessment Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications
Multi-variate hydrological data assimilation opportunities and challenges. Henrik Madsen DHI, Denmark
 Multi-variate hydrological data assimilation opportunities and challenges Henrik Madsen DHI, Denmark Outline Introduction to multi-variate hydrological data assimilation Opportunities and challenges Data
Multi-variate hydrological data assimilation opportunities and challenges Henrik Madsen DHI, Denmark Outline Introduction to multi-variate hydrological data assimilation Opportunities and challenges Data
MODELING FLUID FLOW IN OPEN CHANNEL WITH HORSESHOE CROSS SECTION
 July. 2. Vol. 7. No. 2 MODELING FLUID FLOW IN OPEN CHANNEL WITH HORSESHOE CROSS SECTION 1 J. JOMBA, 2 D.M.THEURI, 2 E. MWENDA, 2 C. CHOMBA ABSTRACT Flow in a closed conduit is regarded as open channel
July. 2. Vol. 7. No. 2 MODELING FLUID FLOW IN OPEN CHANNEL WITH HORSESHOE CROSS SECTION 1 J. JOMBA, 2 D.M.THEURI, 2 E. MWENDA, 2 C. CHOMBA ABSTRACT Flow in a closed conduit is regarded as open channel
Analysis of Physical Oceanographic Data from Bonne Bay, September 2002 September 2004
 Physics and Physical Oceanography Data Report -1 Analysis of Physical Oceanographic Data from Bonne Bay, September September Clark Richards and Brad deyoung Nov. 9 Department of Physics and Physical Oceanography
Physics and Physical Oceanography Data Report -1 Analysis of Physical Oceanographic Data from Bonne Bay, September September Clark Richards and Brad deyoung Nov. 9 Department of Physics and Physical Oceanography
Closed duct flows are full of fluid, have no free surface within, and are driven by a pressure gradient along the duct axis.
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open channel flow is a flow of liquid, basically water in a conduit with a free surface. The open channel flows are driven by gravity alone, and the pressure gradient at the atmospheric
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open channel flow is a flow of liquid, basically water in a conduit with a free surface. The open channel flows are driven by gravity alone, and the pressure gradient at the atmospheric
Discharge. Discharge (Streamflow) is: Q = Velocity (L T -1 ) x Area (L 2 ) Units: L 3 T -1 e.g., m 3 s -1. Velocity. Area
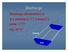 Discharge Discharge (Streamflow) is: Q = Velocity (L T -1 ) x Area (L 2 ) Units: L 3 T -1 e.g., m 3 s -1 Velocity Area Where is the average velocity?? 3 Source: Brooks et al., Hydrology and the Management
Discharge Discharge (Streamflow) is: Q = Velocity (L T -1 ) x Area (L 2 ) Units: L 3 T -1 e.g., m 3 s -1 Velocity Area Where is the average velocity?? 3 Source: Brooks et al., Hydrology and the Management
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 One-dimensional unsteady flow computation in channels with floodplains D. Bousmar, R. Scherer & Y. Zech Civil Engineering Dept., Universite Catholique de Louvain, Place du Levant, 1, B-1348 Louvain-la-Neuve,
One-dimensional unsteady flow computation in channels with floodplains D. Bousmar, R. Scherer & Y. Zech Civil Engineering Dept., Universite Catholique de Louvain, Place du Levant, 1, B-1348 Louvain-la-Neuve,
Calibration of Manning s Friction Factor for Rivers in Iraq Using Hydraulic Model (Al-Kufa River as Case study)
 Calibration of Manning s Friction Factor for Rivers in Iraq Using Hydraulic Model (Al-Kufa River as Case study) Luay Kadhim Hameed, Civil Engineering Dept./ University of Kufa Hayder Sami Mohammed, Structure
Calibration of Manning s Friction Factor for Rivers in Iraq Using Hydraulic Model (Al-Kufa River as Case study) Luay Kadhim Hameed, Civil Engineering Dept./ University of Kufa Hayder Sami Mohammed, Structure
!"#$%&&'()*+#$%(,-./0*)%(!
 8:30 Sign in Hoosic River Revival Coalition!"#$%&&'()*+#$%(,-./0*)%(! 12-#30+4/#"5-(60 9:00 Welcome and Introductions 9:15 Goals for Today s Program: A Description of the Planning Process 9:30 First Session:
8:30 Sign in Hoosic River Revival Coalition!"#$%&&'()*+#$%(,-./0*)%(! 12-#30+4/#"5-(60 9:00 Welcome and Introductions 9:15 Goals for Today s Program: A Description of the Planning Process 9:30 First Session:
Opanuku Stream Benchmark Validation 1. Introduction. 2. The Opanuku Stream Model
 Opanuku Stream Benchmark Validation 1. Introduction The model accuracy benchmark published by the Flood Risk Management Committee of the IAHR in http://members.iahr.org/imis/communitymanagement/communitylayouts/flood_risk_manageme
Opanuku Stream Benchmark Validation 1. Introduction The model accuracy benchmark published by the Flood Risk Management Committee of the IAHR in http://members.iahr.org/imis/communitymanagement/communitylayouts/flood_risk_manageme
Sediment trapping efficiency of modular steel check dam in laboratory experiment and field observation
 Sediment trapping efficiency of modular steel check dam in laboratory experiment and field observation Su-Chin CHEN 1, Hiroshi KOKURYO 2, Shuan-Pei AN 1, Sheng-Jui LU 1, and Hui-Kai HUANG 1* 1 Department
Sediment trapping efficiency of modular steel check dam in laboratory experiment and field observation Su-Chin CHEN 1, Hiroshi KOKURYO 2, Shuan-Pei AN 1, Sheng-Jui LU 1, and Hui-Kai HUANG 1* 1 Department
Detailed Investigation of Velocity Distributions in Compound Channels for both Main Channel and Flood Plain
 Detailed Investigation of Velocity Distributions in Compound Channels for both Main Channel and Flood Plain Jarmina Nake 1, Dr. Mimi Das Saikia 2 M.Tech Student, Dept. of Civil engineering, ADTU, Guwahati,
Detailed Investigation of Velocity Distributions in Compound Channels for both Main Channel and Flood Plain Jarmina Nake 1, Dr. Mimi Das Saikia 2 M.Tech Student, Dept. of Civil engineering, ADTU, Guwahati,
Study on Flushing Mechanism of Dam Reservoir Sedimentation and Recovery of Riffle-Pool in Downstream Reach by a Flushing Bypass Tunnel
 Study on Flushing Mechanism of Dam Reservoir Sedimentation and Recovery of -Pool in Downstream Reach by a Flushing Bypass Tunnel Tomoo Fukuda Department of Science and Engineering, Chuo University, Tokyo,
Study on Flushing Mechanism of Dam Reservoir Sedimentation and Recovery of -Pool in Downstream Reach by a Flushing Bypass Tunnel Tomoo Fukuda Department of Science and Engineering, Chuo University, Tokyo,
Behavior of radioactive cesium accumulation in water bodies in contaminated area by FDNPP accident
 Behavior of radioactive cesium accumulation in water bodies in contaminated area by FDNPP accident Seiji HAYASHI Center for Regional Environmental Research National Institute for Environmental Studies
Behavior of radioactive cesium accumulation in water bodies in contaminated area by FDNPP accident Seiji HAYASHI Center for Regional Environmental Research National Institute for Environmental Studies
EFFECT OF BAFFLE BLOCKS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF RADIAL HYDRAULIC JUMP
 Fourth International Water Technology Conference IWTC 99, Alexandria, Egypt 255 EFFECT OF BAFFLE BLOCKS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF RADIAL HYDRAULIC JUMP O. S. Rageh Irrigation & Hydraulics Dept., Faculty of
Fourth International Water Technology Conference IWTC 99, Alexandria, Egypt 255 EFFECT OF BAFFLE BLOCKS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF RADIAL HYDRAULIC JUMP O. S. Rageh Irrigation & Hydraulics Dept., Faculty of
CHAPTER 07 CANAL DESIGN
 CHAPTER 07 CANAL DESIGN Dr. M. R. Kabir Professor and Head, Department of Civil Engineering University of Asia Pacific (UAP), Dhaka LECTURE 17 Canal Design Types Canal Design Drainage Channel Design Irrigation
CHAPTER 07 CANAL DESIGN Dr. M. R. Kabir Professor and Head, Department of Civil Engineering University of Asia Pacific (UAP), Dhaka LECTURE 17 Canal Design Types Canal Design Drainage Channel Design Irrigation
Flow estimations through spillways under submerged tidal conditions
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIII 137 Flow estimations through spillways under submerged tidal conditions P. D. Scarlatos 1, M. Ansar 2 & Z. Chen 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIII 137 Flow estimations through spillways under submerged tidal conditions P. D. Scarlatos 1, M. Ansar 2 & Z. Chen 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering
Formation Of Hydraulic Jumps On Corrugated Beds
 International Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering IJCEE-IJENS Vol:10 No:01 37 Formation Of Hydraulic Jumps On Corrugated Beds Ibrahim H. Elsebaie 1 and Shazy Shabayek Abstract A study of the effect
International Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering IJCEE-IJENS Vol:10 No:01 37 Formation Of Hydraulic Jumps On Corrugated Beds Ibrahim H. Elsebaie 1 and Shazy Shabayek Abstract A study of the effect
Process-based Long Term Morphological Modelling the present state-of-the-art and the way ahead. Dirk-Jan Walstra
 Process-based Long Term Morphological Modelling the present state-of-the-art and the way ahead Dirk-Jan Walstra Deltares Delft Hydraulics Delft University of Technology Les littoraux à l heure du changement
Process-based Long Term Morphological Modelling the present state-of-the-art and the way ahead Dirk-Jan Walstra Deltares Delft Hydraulics Delft University of Technology Les littoraux à l heure du changement
FORMATION OF HYDRAULIC JUMPS ON CORRUGATED BEDS
 International Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering IJCEE-IJENS Vol: 10 No: 01 40 FORMATION OF HYDRAULIC JUMPS ON CORRUGATED BEDS Ibrahim H. Elsebaie 1 and Shazy Shabayek Abstract A study of the
International Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering IJCEE-IJENS Vol: 10 No: 01 40 FORMATION OF HYDRAULIC JUMPS ON CORRUGATED BEDS Ibrahim H. Elsebaie 1 and Shazy Shabayek Abstract A study of the
Evaluation of Scour Depth around Bridge Piers with Various Geometrical Shapes
 Evaluation of Scour Depth around Bridge Piers with Various Geometrical Shapes Dr. P. D. Dahe * Department of Civil Engineering, SGGSIE&T, Vishnupuri, Nanded (Maharashtra) S. B. Kharode Department of Civil
Evaluation of Scour Depth around Bridge Piers with Various Geometrical Shapes Dr. P. D. Dahe * Department of Civil Engineering, SGGSIE&T, Vishnupuri, Nanded (Maharashtra) S. B. Kharode Department of Civil
Sediment Transport Mechanism and Grain Size Distributions in Stony Bed Rivers. S.FUKUOKA 1 and K.OSADA 2
 Sediment Transport Mechanism and Grain Size Distributions in Stony Bed Rivers S.FUKUOKA 1 and K.OSADA 1 Professor, Research and Development Initiative, Chuo-University, 1-13-7 Kasuga Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo,
Sediment Transport Mechanism and Grain Size Distributions in Stony Bed Rivers S.FUKUOKA 1 and K.OSADA 1 Professor, Research and Development Initiative, Chuo-University, 1-13-7 Kasuga Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo,
Field Observations and One-Dimensional Flow Modeling of Summit Creek in Mack Park, Smithfield, Utah
 Intermountain Center for River Rehabilitation and Restoration, Utah State University 31 July 2018 Field Observations and One-Dimensional Flow Modeling of Summit Creek in Mack Park, Smithfield, Utah I.
Intermountain Center for River Rehabilitation and Restoration, Utah State University 31 July 2018 Field Observations and One-Dimensional Flow Modeling of Summit Creek in Mack Park, Smithfield, Utah I.
The Hydraulics of Open Channel Flow: An Introduction
 The Hydraulics of Open Channel Flow: An Introduction Basic principles, sediment motion, hydraulic modelling, design of hydraulic structures Second Edition Hubert Chanson Department of Civil Engineering
The Hydraulics of Open Channel Flow: An Introduction Basic principles, sediment motion, hydraulic modelling, design of hydraulic structures Second Edition Hubert Chanson Department of Civil Engineering
Keywords: flow characteristics, compound straight channel, bed morphology, floodplain
 Flow Characteristics on Floodplain Vegetation in Compound Straight Channels Nur Amirah Nabilah Mohd Zamri 1, a, Zulhilmi Ismail 1,b,Zulkiflee Ibrahim 1,c 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi
Flow Characteristics on Floodplain Vegetation in Compound Straight Channels Nur Amirah Nabilah Mohd Zamri 1, a, Zulhilmi Ismail 1,b,Zulkiflee Ibrahim 1,c 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi
On variational data assimilation for 1D and 2D fluvial hydraulics
 On variational data assimilation for D and D fluvial hydraulics I. Gejadze, M. Honnorat, FX Le Dimet, and J. Monnier LJK - MOISE project-team, Grenoble, France. Contact: Jerome.Monnier@imag.fr Civil Engineering
On variational data assimilation for D and D fluvial hydraulics I. Gejadze, M. Honnorat, FX Le Dimet, and J. Monnier LJK - MOISE project-team, Grenoble, France. Contact: Jerome.Monnier@imag.fr Civil Engineering
Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics in a Compound Meandering River
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-07, pp-136-140 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-07, pp-136-140 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA
 A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
SEDIMENT TRANSPORT ANALYSIS FOR SECURING WATER (CASE STUDY : UPPER JENEBERANG RIVER)
 : Integrated Solution to Overcome the Climate Change Impact on Coastal Area Semarang, Indonesia November 19th, 2015 Paper No. A-I-069 SEDIMENT TRANSPORT ANALYSIS FOR SECURING WATER (CASE STUDY : UPPER
: Integrated Solution to Overcome the Climate Change Impact on Coastal Area Semarang, Indonesia November 19th, 2015 Paper No. A-I-069 SEDIMENT TRANSPORT ANALYSIS FOR SECURING WATER (CASE STUDY : UPPER
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 9, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 A study of turbulence characteristics in open channel transitions as a function of Froude and Reynolds numbers using Laser technique M.I.A. El-shewey, S.G. Joshi Department of Civil Engineering, Indian
A study of turbulence characteristics in open channel transitions as a function of Froude and Reynolds numbers using Laser technique M.I.A. El-shewey, S.G. Joshi Department of Civil Engineering, Indian
Large-Scale Sediment Inflow and Bed-Variation from 12th Typhoon (2011) in the Asahi River Basin
 ICHE 214, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 214 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-93923-32-8 Large-Scale Sediment Inflow and Bed-Variation from 12th Typhoon (211) in the Asahi River Basin Y. Tsukamoto
ICHE 214, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 214 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-93923-32-8 Large-Scale Sediment Inflow and Bed-Variation from 12th Typhoon (211) in the Asahi River Basin Y. Tsukamoto
Kinetic energy and momentum correction factors in a stream
 Kinetic energy and momentum correction factors in a stream Mehmet Ardıçlıoğlu, Mücella Vapur, 2Onur Genç, University of Erciyes, Department of Civil Engineering, Kayseri, Turkey 2 Melikşah University,
Kinetic energy and momentum correction factors in a stream Mehmet Ardıçlıoğlu, Mücella Vapur, 2Onur Genç, University of Erciyes, Department of Civil Engineering, Kayseri, Turkey 2 Melikşah University,
Lecture Note for Open Channel Hydraulics
 Chapter -one Introduction to Open Channel Hydraulics 1.1 Definitions Simply stated, Open channel flow is a flow of liquid in a conduit with free space. Open channel flow is particularly applied to understand
Chapter -one Introduction to Open Channel Hydraulics 1.1 Definitions Simply stated, Open channel flow is a flow of liquid in a conduit with free space. Open channel flow is particularly applied to understand
Technical Memorandum No Sediment Model
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
Numerical Hydraulics
 ETH Zurich, Fall 2017 Numerical Hydraulics Assignment 2 Numerical solution of shallow water wave propagation (www.surfertoday.com) 1 Introduction 1.1 Equations Understanding the propagation of shallow
ETH Zurich, Fall 2017 Numerical Hydraulics Assignment 2 Numerical solution of shallow water wave propagation (www.surfertoday.com) 1 Introduction 1.1 Equations Understanding the propagation of shallow
EFFECT OF CHANNEL BENDS ON TRANSVERSE MIXING
 NIJOTECH VOL. 10. NO. 1 SEPTEMBER 1986 ENGMANN 57 EFFECT OF CHANNEL BENDS ON TRANSVERSE MIXING BY E. O. ENGMANN ABSTRACT Velocity and tracer concentration measurements made in a meandering channel are
NIJOTECH VOL. 10. NO. 1 SEPTEMBER 1986 ENGMANN 57 EFFECT OF CHANNEL BENDS ON TRANSVERSE MIXING BY E. O. ENGMANN ABSTRACT Velocity and tracer concentration measurements made in a meandering channel are
8. Hydrometry - measurement and analysis
 130 8. Hydrometry - measurement and analysis 8.1 Definitions In English, the traditional word used to describe the measurement of water levels and flow volumes is Hydrography. That is ambiguous, for that
130 8. Hydrometry - measurement and analysis 8.1 Definitions In English, the traditional word used to describe the measurement of water levels and flow volumes is Hydrography. That is ambiguous, for that
COMPARISON BETWEEN EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL RESULTS OF FLOOD FLOW IN A COMPOUND MEANDERING CHANNEL
 COMPARISON BETWEEN EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL RESULTS OF FLOOD FLOW IN A COMPOUND MEANDERING CHANNEL Alex George Mutasingwa, Graduate student, Hiroshima University Shoji Fukuoka, Professor, Department
COMPARISON BETWEEN EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL RESULTS OF FLOOD FLOW IN A COMPOUND MEANDERING CHANNEL Alex George Mutasingwa, Graduate student, Hiroshima University Shoji Fukuoka, Professor, Department
Modelling of flow and sediment transport in rivers and freshwater deltas Peggy Zinke
 1 Modelling of flow and sediment transport in rivers and freshwater deltas Peggy Zinke with contributions from Norwegian and international project partners 2 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Basic ideas of flow
1 Modelling of flow and sediment transport in rivers and freshwater deltas Peggy Zinke with contributions from Norwegian and international project partners 2 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Basic ideas of flow
STREAM GAUGING TECHNIQUES
 World Meteorological Organization -- Working together in weather, climate and water STREAM GAUGING TECHNIQUES Presentation based on the WMO Manual on streamgauging (2010), Volume II Chapter 2, with additional
World Meteorological Organization -- Working together in weather, climate and water STREAM GAUGING TECHNIQUES Presentation based on the WMO Manual on streamgauging (2010), Volume II Chapter 2, with additional
Measurements of lateral flow from the Mississippi River at Mardi Gras Pass in the Bohemia Spillway using synoptic ADCP
 Measurements of lateral flow from the Mississippi River at Mardi Gras Pass in the Bohemia Spillway using synoptic ADCP A Technical Report Submitted to: The Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation Submitted
Measurements of lateral flow from the Mississippi River at Mardi Gras Pass in the Bohemia Spillway using synoptic ADCP A Technical Report Submitted to: The Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation Submitted
Sediment Extraction and Flow Structure of Vortex Settling Basin
 Sediment Extraction and Flow Structure of Vortex Settling Basin J. Chapokpour 1, J. Farhoudi 2 1- Post Graduate Student, Hyd. Structures, Dept. of Irrigation Eng., Faculty of agricultural technology and
Sediment Extraction and Flow Structure of Vortex Settling Basin J. Chapokpour 1, J. Farhoudi 2 1- Post Graduate Student, Hyd. Structures, Dept. of Irrigation Eng., Faculty of agricultural technology and
Complete Velocity Distribution in River Cross-sections Measured by Acoustic Instruments
 Complete Velocity Distribution in River Cross-sections Measured by Acoustic Instruments Ralph T. Cheng and Jeffrey W. Gartner U. S. Geological Survey Menlo Park, California (650) 329-4500 rtcheng@usgs.gov
Complete Velocity Distribution in River Cross-sections Measured by Acoustic Instruments Ralph T. Cheng and Jeffrey W. Gartner U. S. Geological Survey Menlo Park, California (650) 329-4500 rtcheng@usgs.gov
UPPER COSUMNES RIVER FLOOD MAPPING
 UPPER COSUMNES RIVER FLOOD MAPPING DRAFT BASIC DATA NARRATIVE FLOOD INSURANCE STUDY SACRAMENTO COUTY, CALIFORNIA Community No. 060262 November 2008 Prepared By: CIVIL ENGINEERING SOLUTIONS, INC. 1325 Howe
UPPER COSUMNES RIVER FLOOD MAPPING DRAFT BASIC DATA NARRATIVE FLOOD INSURANCE STUDY SACRAMENTO COUTY, CALIFORNIA Community No. 060262 November 2008 Prepared By: CIVIL ENGINEERING SOLUTIONS, INC. 1325 Howe
Appendix O. Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum
 Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
Summary Results from Horizontal ADCP tests in the Indiana Harbor Canal and the White River
 Summary Results from Horizontal ADCP tests in the Indiana Harbor Canal and the White River This report summarizes results of tests of horizontally deployed ADCPs in the Indiana Harbor Canal and the White
Summary Results from Horizontal ADCP tests in the Indiana Harbor Canal and the White River This report summarizes results of tests of horizontally deployed ADCPs in the Indiana Harbor Canal and the White
LAB-SCALE INVESTIGATION ONBAR FORMATION COORDINATES IN RIVER BASED ON FLOW AND SEDIMENT
 LAB-SCALE INVESTIGATION ONBAR FORMATION COORDINATES IN RIVER BASED ON FLOW AND SEDIMENT Mat Salleh M. Z., Ariffin J., Mohd-Noor M. F. and Yusof N. A. U. Faculty of Civil Engineering, University Technology
LAB-SCALE INVESTIGATION ONBAR FORMATION COORDINATES IN RIVER BASED ON FLOW AND SEDIMENT Mat Salleh M. Z., Ariffin J., Mohd-Noor M. F. and Yusof N. A. U. Faculty of Civil Engineering, University Technology
An experimental study of longitudinal velocity distribution at cross-over and bend section of a compound meandering channel
 American Journal of Civil Engineering 2013; 1(3): 124-128 Published online November 20, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce) doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.20130103.16 An experimental study of longitudinal
American Journal of Civil Engineering 2013; 1(3): 124-128 Published online November 20, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajce) doi: 10.11648/j.ajce.20130103.16 An experimental study of longitudinal
 http://water.usgs.gov/waterwatch/ Stream Flow Measurement: Velocity-Area method Stream discharge = Q = U * A Q = volumetric flow rate in [L 3 T -1 ] U= average stream velocity [L 2 T -1 ] A = cross sectional
http://water.usgs.gov/waterwatch/ Stream Flow Measurement: Velocity-Area method Stream discharge = Q = U * A Q = volumetric flow rate in [L 3 T -1 ] U= average stream velocity [L 2 T -1 ] A = cross sectional
Groundwater dynamics and surface water-groundwater interaction in a prograding delta island, Louisiana, USA
 Supplementary Information Groundwater dynamics and surface water-groundwater interaction in a prograding delta island, Louisiana, USA Michael T. O Connor 1* and Kevan B. Moffett 1,2 1 Department of Geological
Supplementary Information Groundwater dynamics and surface water-groundwater interaction in a prograding delta island, Louisiana, USA Michael T. O Connor 1* and Kevan B. Moffett 1,2 1 Department of Geological
FLOOD ROUTING FOR A SPECIFIC ORIENTATION OF PLANNED DEVELOPMENTS FOR AL-SHAMIYA RIVER IN IRAQ AS CASE STUDY
 Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (JCIET) Volume 4, Issue 2, July-December 2017, pp. 1 12, Article ID: JCIET_04_02_001 Available online at http: //www.iaeme.com/jciet/issues.asp?jtype=jciet&vtype=4&itype=2
Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (JCIET) Volume 4, Issue 2, July-December 2017, pp. 1 12, Article ID: JCIET_04_02_001 Available online at http: //www.iaeme.com/jciet/issues.asp?jtype=jciet&vtype=4&itype=2
Advanced /Surface Hydrology Dr. Jagadish Torlapati Fall 2017 MODULE 2 - ROUTING METHODS
 Routing MODULE - ROUTING METHODS Routing is the process of find the distribution of flow rate and depth in space and time along a river or storm sewer. Routing is also called Flow routing or flood routing.
Routing MODULE - ROUTING METHODS Routing is the process of find the distribution of flow rate and depth in space and time along a river or storm sewer. Routing is also called Flow routing or flood routing.
DOMINANT DISCHARGE IN THE KOR RIVER, FARS PROVINCE, IRAN
 Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt 299 DOMINANT DISCHARGE IN THE KOR RIVER, FARS PROVINCE, IRAN Keshavarzi Ali Reza 1 and Nabavi, S. H. 2 1 Associate Prof.,
Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt 299 DOMINANT DISCHARGE IN THE KOR RIVER, FARS PROVINCE, IRAN Keshavarzi Ali Reza 1 and Nabavi, S. H. 2 1 Associate Prof.,
Growing and decaying processes and resistance of sand waves in the vicinity of the Tone River mouth
 Advances in River Sediment Research Fukuoka et al. (eds) 2013 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-00062-9 Growing and decaying processes and resistance of sand waves in the vicinity of the Tone
Advances in River Sediment Research Fukuoka et al. (eds) 2013 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-00062-9 Growing and decaying processes and resistance of sand waves in the vicinity of the Tone
