MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
|
|
|
- Rhoda Moody
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting the questions: There are SEVEN questions in the paper. Candidates are required to attempt FIVE questions in all. Question no. 1 is compulsory. Out of the remaining SIX questions, attempt any FOUR questions. The number of marks carried by a question/part is indicated against it. Unless otherwise mentioned, symbols and notations have their usual standard meanings. Assume suitable data, if necessary and indicate the same clearly. Neat sketches are to be drawn to illustrate answers, wherever required. All parts and sub-parts of a question are to be attempted together in the answer book. Attempts of questions shall be counted in sequential order. Unless struck off, attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly. Answers must be written in ENGLISH only. Any page or portion of the page left blank in the answer book must be clearly struck off. Values of constants which may be needed: Universal gas constant R = kji kg mole-k. For air R = kj/kg-k, Cp = kj/kg-k, = 1.4, M = kglkg-mole. 1. (a) A rigid tank whose volume is 0.75 m 3 developed a small hole on its wall. Air from the surroundings at 1 bar 25 C leaked in and finally the pressure in the tank reached 1 bar. The process occurred slowly so that heat transfer between the tank and the surroundings kept the temperature of the air inside the tank constant at 25 C. Determine the heat transfer involved in the process: (i) if initially the tank was evacuated, (ii) if it contained air at 0.7 bar and 25 C. 10 (b) (i) Distinguish between skin friction drag and pressure drag. Does the total drag acting on a body necessarily decrease as a result of streamlining? Explain. 5 (ii) With a neat sketch explain the principle and working of a pitot tube. 5 (i) Two concentric spheres have diameters of 0.3 m and 0.8 m and are maintained at uniform temperatures of 700 K and 400 K respectively. The inner and outer spheres have emissivities of 0.5 and 0.7 respectively. The emissivity of the outer surface is The surrounding medium and surrounding surfaces are at a temperature of 30 C. Determine the net radiation heat transfer between the two spheres. Also determine the convective heat transfer coefficient at the outer surface. 5 (ii) Stainless steel ball bearings having diameter of 1.2 cm are to be quenched in water. The balls leave the oven at 900 C and are exposed to air at 30 C for a while before they are dropped in water. If the temperature of the balls is not to fall below 850 C prior to quenching and the heat transfer coefficient in the air is 125 W/m 2 K, determine how long they can stand in the air before being dropped into the water. Following properties of stainless steel may be used: ρ = 8085 kg/m 3, k = 15.1 W/mK, Cp = kj/kg-k, α = m 2 /s 5 (d) A horizontal cylinder is separated into two compartments by an adiabatic frictionless piston. One side contains 0.2 m 3 of nitrogen and the other side contains 0.1 kg of helium both initially at 20 C and 95 kpa. The sides of the cylinder and the helium end are insulated. Now heat is added to the nitrogen side from a reservoir at 500 C until the pressure of the helium rises to 120 kpa. Determine (i) the final temperature of helium, (ii) the final volume of nitrogen, (iii) the heat transferred to nitrogen, and (iv) entropy generated during the process. For more information log on Page 1
2 Following properties of nitrogen and helium are given: Nitrogen: R = kj/kg-k, Cp = kj/kg-k, Cv = kj/kg-k, = 1.4. Helium: R = kj/kg-k, Cp = kj/kg-k, Cv = kj/kg-k, = (e) (i) What is 'dry bulb' temperature and 'wet bulb' temperature? Explain the principle of a sling psychrometer. 5 (ii) How does a natural draft wet cooling tower work? What is a spray pond? How does its performance compare to that of a wet cooling tower? 5 (f) (i) A long water trough of triangular cross-section is formed from two rectangular planks. A gap of 3 mm is maintained at the junction of the two planks. If the water depth initially was 0.6 m, how long does it take for the water depth to reduce to 0.3 m? 5 (ii) Obtain an expression for the reversible work transfer associated with an internally reversible process in a steady flow device in terms of thermodynamic properties of the system. Deduce Bernoulli's equation from it. 5 (g) (i) A two-dimensional incompressible flow of a Newtonian fluid has the following velocity field: u = 2xy, v = y 2 x 2, w = 0. Show that it represents a possible flow field. Find the pressure field p(x, y), if the pressure at point (x = 0, y = 0) is equal to pa. 5 (ii) A 5 cm diameter horizontal jet of water, with a velocity of 30 m/s, strikes the tip of a horizontal cone which deflects the water by 45 from its original direction. How much force is required to hold the cone against the water stream? 5 (h) (i) A centrifugal pump having an impeller diameter of 1 m is to be constructed so that it will supply a head rise of 200 m at a flow rate of water when operating at a speed of 1200 rpm. To study the characteristics of this pump, a geometrically similar model operated at the same speed is to be tested in the laboratory. Determine the required model discharge and head rise. Assume that both model and prototype operate with the same efficiency. 5 (ii) What is cavitation in hydraulic machines? Explain the significance of Thoma cavitation factor (a) A simple steam power cycle uses solar energy for heat input. Water in the cycle enters the pump as saturated liquid at 40 C and is pumped to 2 bar. The water at this pressure evaporates in the steam generator and enters the turbine as saturated vapour. At the exit of the turbine, the condition of steam is 40 C with kg dryness fraction of 0.9. The flow rate is 150 kg/h. The instantaneous solar input is 0.58 kw/m 2 at a specified time. Obtain the isentropic efficiency of the turbine, network output, cycle efficiency and the area of the solar collector needed based on the given solar input. Following properties of steam are given: 10 (b) p T hf hfg hg sf sfg sg (bar) (C) (kj/kg) (kj/kg K) Liquid nitrogen is stored in a spherical thin walled metallic container at 77 K temperature. The container is of 1.0 metre diameter and is covered with evacuated silica powder. The insulation is 20 mm thick and the outer surface is exposed to the surrounding air at 300 K. The convective heat transfer coefficient of the exposed surface is 25 W/m 2 K. The density and latent heat of vaporization of the liquid nitrogen are 804 kg/m 3 and J/kg respectively. Determine the rate of heat transfer to the liquid nitrogen and the rate of liquid boil-off. The thermal conductivity (k) of evacuated silica powder is For more information log on Page 2
3 W/m.K. Neglect the thermal resistance of the metallic container. 10 (i) Explain how draft tubes are advantageous when installed at the exit of Francis and Kaplan turbines. 3 (ii) A sphere of diameter D and density ρs falls at a steady rate through a liquid of density ρ and viscosity. If the Reynolds number is less than 1, 2 gd show that the viscosity can be determined from s where 18U the Reynolds number is evaluated as ρdu/ (a) (i) Compare the governing mechanism of a Pelton turbine with that of a Francis turbine. 4 (ii) Water to run a Pelton wheel is supplied by a penstock of length l and diameter D with a friction factor f. If the only losses associated with the flow in the penstock are due to pipe friction, show that the maximum power output of the turbine occurs when the nozzle diameter D1 is given by D D1 = For more information log on Page 3 1/ fl D (b) A runner of a Francis turbine having 1.5 m outer diameter and 0.75 m inner diameter operates under a head of 150 m with a specific speed of 120 and generates 14 MW power. If the water enters the wheel at an angle of 11 20' and leaves the blade radially with no velocity of whirl, what will be the value of inlet and outlet blade angles? Assume the hydraulic efficiency of the turbine as 92 percent. 10 A room is provided with a sliding glass door (patio door) with a height of 1.8 m and width of 1 m. On a cold winter day, the window glass on the patio door has a uniform temperature of 0 C and the room wall and air temperatures are 15 C. The emissivity of the glass surface is A frost line was observed at the base of the window glass, (i) Explain why the window developed a frost layer at the base and not at the top. (ii) Estimate the heat loss through the window due to free convection and radiation, (iii) If the room is provided with an electric heater, estimate the corresponding daily cost of the window heat loss for an electricity cost of Rs 5/kWh. Assume the following properties of air at 280 K: ν = m 2 /s, k = W/mK, α = m 2 /s, Pr = The following empirical correlation may be useful: 1/ 6 hll 0.387RaL Nu L /16 8/ 27 k / Pr where, RaL is the Rayleigh number (a) (i) A ship with a hull length of 140 metres has to travel with 7.6 m/s velocity. Compute the Froude number. For dynamic similarity, at what velocity should a 1 : 30 scale down model flow through water? 5 (ii) Illustrate the head vs discharge curves for three dissimilar pumps in series and three such pumps in parallel. 5 (b) Carbon dioxide enters an adiabatic nozzle at 1200 K with a velocity of 50 m/s and leaves at 400 K. Determine the Mach number (i) at the inlet of the nozzle, and (ii) at the exit of the nozzle. For CO2, R = kj/kgk, cp = kj/kgk, = On the basis of a cold-air-standard analysis, show that the thermal efficiency of an ideal regenerative gas turbine can be expressed as T k1 1 1 k T3 where, is the compressor pressure ratio and T1, T3 denote the temperatures at the compressor and turbine inlets respectively. 10 2
4 5. (a) The impeller of a centrifugal pump has a diameter of 0.2 m and axial width at outlet of 20 mm. There are 18 blades swept backwards and inclined at 25 to the tangent to the periphery. The flow rate through the impeller is 8.5 m 3 /h when it rotates at 750 rpm. Calculate the head developed by the pump when handling water and assuming one-dimensional ideal flow theory. How can a more realistic estimation of the head developed be carried out? 10 (b) Hot oil is to be cooled in a multi-pass shell and tube heat exchanger by water. The oil flows through the shell with a heat transfer coefficient of h = 35 W/m 2 K and the water flows through the tube with an average velocity of 3 m/s. The tube is made of brass k = 110 W/mK with internal and external diameters of 1.3 cm and 1.5 cm respectively. Determine the overall heat transfer coefficient of this heat exchanger based on the inner surface. Properties of water at 25 C: k = W/mK, ν = m 2 /s, Pr = Given Nu = Re 0.8 Pr A gas turbine engine with regeneration operates with two stages of compression and two stages of expansion. The pressure ratio across each stage of the compressor and turbine is 3.5. The air enters each stage of the compressor at 300 K and each stage of the turbine at 1200 K. The compressor and turbine efficiencies are 78% and 86% respectively and the effectiveness of the regenerator is 72%. Determine the back work ratio and the thermal efficiency of the cycle, assuming constant specific heats for air at room temperature (a) (i) Consider a conical enclosure of height h and base diameter D. Determine the view factor from the conical side surface to a hole of diameter d located at the centre of the base. 5 (ii) Sketch the typical boiling curve for water at 1 atm clearly indicating the salient regimes of boiling. 5 (b) Air at 27 C with a free stream velocity of 10 m/s is used to cool electronic devices mounted on a printed circuit board. Each device, 4 mm 4 mm dissipates 40 mw which is removed from the top surface. A turbulator is located at the leading edge of the board. Estimate the surface temperature of the fourth device located at 15 mm from the leading edge of the board. The following relation may be used: Nu 4 /5 1/ Re Pr x For air at 315 K and 1 atm, k = W/mK, ν = m 2 /s, α = m 2 /s, Pr = An air-conditioner with refrigerant R134a as the working fluid is used to keep a room at 26 C by rejecting the waste heat to the outside air at 34 C. The room is gaining heat through the walls and the windows at a rate of 250 kj/min while the heat generated by the appliances in the room amounts to 900 W. An unknown amount of heat is also generated by the people in the room. The condenser and evaporator pressures are 1200 kpa and 500 kpa respectively. The refrigerant is saturated liquid at the condenser exit and saturated vapour at the compressor inlet. If the refrigerant enters the compressor at a rate of 100 L/min and the isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 75%, determine the (i) temperature of the refrigerant at the compressor exit, (ii) rate of heat generation by the people in the room, (iii) COP of the air-conditioner, and (iv) minimum volume flow rate of the refrigerant at the compressor inlet for the same compressor inlet and exit conditions. Properties of R134a: At 500 kpa : h = kj/kg, vg = m 3 /kg, sg = m 3 /kg, At 1200 kpa: hf = kj/kg (a) Show that the enthalpy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature only and that for an incompressible substance it also depends on pressure, using thermodynamic property relations. 10 x For more information log on Page 4
5 (b) A house built on a riverside is to be cooled in summer by utilizing the cool water of the river which flows at an average temperature of 15 C. A 15 m long section of a circular duct of 20 cm diameter passes through the water. Air enters the underwater section of the duct at 25 C at a velocity of 3 m/s. Assuming the surface of the duct is at the temperature of water, determine the outlet temperature of air as it leaves the underwater portion of the duct. Also, for an overall fan efficiency of 55%, determine the fan power input needed to overcome the flow resistance in this section of the duct. The properties of air at 20 C and 1 atm: ρ = kg/m 3, k = W/mK, ν = m 2 /s, cp = 1.007kJ/kgK, Pr = For fully developed turbulent flow in smooth pipes: f = (0.790 In Re 1.64) 2, where f is the friction factor. 10 A two-cylinder single-acting air compressor is to deliver 20 kg/minute of free air from atmospheric conditions (100 kpa, 20 C). The delivery pressure is 7 bar, clearance is 4% of the stroke and the index for both compression and expansion is 1.3. The compressor is directly coupled to a four-cylinder, four-stroke petrol engine running at 2000 rpm. The BMEP of the engine is 5 bar. Assuming stroke-to-bore ratio of 1.1 for both engine and compressor and mechanical efficiency of 80% for the compressor, calculate the cylinder dimensions for the compressor. 10 For more information log on Page 5
6 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting the questions: There are SEVEN questions divided under THREE sections. Candidates are required to attempt FIVE questions in all. In Section A, Question No.1 is compulsory. In Section B, TWO out of THREE questions are to be attempted. In Section C, TWO out of THREE questions are to be attempted. The number of marks carried by a question/part is indicated against it. Unless otherwise mentioned, symbols and notations have their usual standard meanings. Assume suitable data, if necessary and indicate the same clearly. Neat sketches are to be drawn to illustrate answers, wherever required. All parts and sub-parts of a question are to be attempted together in the answer book. Attempts of questions shall be counted in sequential order. Unless struck off attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly. Answers must be written in ENGLISH only. Any page or portion of the page left blank in the answer book must be clearly struck off. Section - A (Answer all of the following parts) (Each part carries 4 marks) 4 10=40 1. (a) The crank of a crank and slotted lever quick return mechanism is driven at 120 rpm clockwise. The vertical distance between the centres of rotation of the crank and slotted lever is 50 cm. What should be the length of the crank if the quick return ratio is 1:2? Determine the angular velocity of the slotted lever, when the tool-post attains maximum velocity during cutting stroke. (b) Square key of side d/4 and length l is used to transmit torque T from the shaft of diameter d to the hub of a pulley. Assuming the length of the key to be equal to the thickness of the pulley, find the average shear stress and crushing stress developed in the key. A tapering bar having d1, and d2 as diameters of end sections and another bar of uniform cross-section d are of same length l. Both are subjected to the same axial pull P. What should be the value of d in terms of d1, and d2 so that both the bars of same material will have same extension? Evaluate maximum stresses in both the bars. (d) In a cam-follower mechanism the follower needs to rise through 20 mm during 60 of cam rotation, the first 30 with a constant acceleration and then retardation of equal magnitude for next 30. The cam rotates at uniform speed of 300 rpm. Find out the maximum velocity and acceleration of the follower during the rise period. (e) Through the temperature vrs carbon percentage diagram of steel, show the microstructures of various phases of steel. (f) In reference to primary processes of Powder Metallurgy, explain the following: (i) Blending (ii) Compacting (iii) Pre-sintering (iv) Sintering (g) What is centreless grinding? Explain with sketch. What is the difference w.r.t. cylindrical grinding? (h) Illustrate the difference between (i) open die forging and (i) closed die forging with appropriate sketches. (i) (j) Show in a figure location of the surface texture details when used with machining symbols. With sketches describe any four types of point defects in metallic materials. For more information log on Page 6
7 Section - B (Answer any two questions) 2. (a) A machine is driven by a motor, which delivers a constant torque. The resisting torque of the machine increases uniformly from 500 Nm to 1500 Nm through one revolution of the driving shaft and drops suddenly to 500 Nm again at the beginning of the next revolution. The mean speed of the machine shaft is 300 rpm. In order to maintain coefficient fluctuation of speed of the machine as 0.2, a solid circular steel disc of 25 mm thick is used as a flywheel. The mass density of steel is 7800 kg/m 3. Evaluate the diameter of the flywheel disc. 10 (b) A solid shaft of diameter d is used for power transmission. Due to modification of the existing transmission system, it is required to replace the solid shaft by a hollow shaft of the same material and equally strong in torsion. Further the weight of the hollow shaft per metre length should be half that of the solid shaft. Determine the outer and inner diameters of the hollow shaft if diameter of solid shaft, d = 40 mm. 20 A thin cylinder with closed ends has an internal pressure of 6 MN/m 2. The cylinder is of 50 mm internal diameter and 2.5 mm thick. It is also subjected to an axial pull of 10 kn and a torque of 500 Nm. Determine the principal stresses in the cylinder and maximum shear stress (a) The cylinder axes of a V-engine are at 90 to each other. The mass of each piston is 2 kg and that of each connecting rod is 2.8 kg. The mass of rotating parts like crank webs and the crank pin is 1.8 kg. The connecting rod is 400 mm long and its centre of mass is 100 mm from crank pin centre. The stroke of the piston is 160 mm. Find the magnitude of the balancing mass for balancing primary unbalance force and its position, if its centre is placed at 100 mm from crank shaft centre. Whether secondary unbalance force is balanced or not? If not, what is the magnitude of resultant secondary unbalance force for the engine speed of 840 rpm? 10 (b) Design a muff coupling to connect two steel shafts of same diameter in order to transmit 25 kw of power at 360 rpm. The shafts and keys are made of plain carbon steel 30C8 (Syt = Syc = 400 N/mm 2 ). The sleeve is made of grey cast iron FG 200 (Sut = 200 N/mm 2 ). The factor of safety for the shafts and key is 4 and for the sleeve the same is 6 based on yield strengths and ultimate strengths respectively. The standard proportion for the sleeve of muff coupling is usually taken as external diameter = (2 shaft diameter + 13) mm. Axial length of sleeve = (3.5 shaft diameter). Sketch the coupling showing all the dimensions of the shafts, sleeve and keys. Ensure safety of all components. 20 A simply supported beam AB of span L carries a distributed load of varying intensity as shown in figure below. Establish the equation for deflection curve for the beam at a distance x from the origin A of the beam. Determine the deflection of the beam at the mid-section C in terms of W, L, E and I, where EI is the flexural rigidity of the beam. 4. (a) A uniform plank of mass m is resting over two identical rollers rotating in the opposite directions as shown in figure below. The distance between the roller axes is 20 and the rollers are spinning at same speed. The coefficient of friction between the plank and the rollers is. Show that the plank will oscillate when its C.G. is displaced from the mid-point between the rollers. Develop the For more information log on Page 7 10
8 equation of motion of the plank in the direction of oscillation. (i) Determine the frequency of this oscillation. (ii) Investigate the motion of the plank, when the direction of rotation of both the rollers are reversed. 10 (b) A pair of spur gears with 20 full-depth involute teeth consists of a 20 teeth pinion meshing with a 41 teeth gear. The module is 3 mm while the face width is 40 mm. The material for pinion as well as for gear is steel with an ultimate tensile strength of 600 N/mm 2. The gears are heat treated for a surface hardness of 400 BHN. The pinion rotates at 1450 rpm and the service factor for the application is Assume that the velocity factor accounts for the dynamic load and the factor of safety is 1.5. Determine the rated power that the gears can transmit, taking Lewis form factor as A steel rod of 10 cm diameter is forced into a steel ring of 15 cm external diameter and 6 cm wide. Measured strain in the circumferential direction on the external surface of the ring is found to be Assuming coefficient of friction for the mating surfaces to be 0.25, estimate the force required to push the rod out of the ring. Use E = 200 GPa. 10 (d) Describe the properties of the following aluminium alloys: Duralumin, Y-alloy, Magnalium and Hindalium. 10 Section - C (Answer any two questions) 5. (a) Classify gating designs for pouring of metals into the mould cavity in a casting operation. Show them by sketches. A mould of 50 cm 25 cm 10 cm has the provision of a top gating system with pouring height of 15 cm and cross-sectional area of the gate as 5 cm 2. Determine the filling time. 10 (b) Name four types of resistance welding processes. Describe with sketch "Spot welding". 10 Describe with sketches Ultrasonic Machining Process (USM) and the principle of metal removal by this. 15 (d) Write the generalized Taylor's tool life equation. Also write the simplified Taylor's tool life equation. During machining of low carbon steel with HSS tool, the following observations have been made: Cutting speed, m/min Tool life, min Derive the V-T relationship (a) (i) Distinguish between "Simple Moving Average" and "Weighted Moving Average" methods of forecasting. (ii) Demand for an item of a particular size and specification in the past six months, in a firm had been as follows: January February March April May June Compute a weighted 4 months moving average for July. 10 (b) (i) Explain what is "Break Even Analysis"? Demonstrate by a graphical representation. (ii) The Fixed costs of a company are Rs 700,000. The net sales amount is Rs For more information log on Page 8
9 1,200,000 annually. The direct costs are 35% of sales in rupees. Determine the following: (I) "The Break Even Point" in terms of sales Rupees. (II) The sales required to earn a profit of Rs 1,60, (i) With respect to PERT Analysis define the following: Earliest Starting Time (TE) Latest Finish Time (TL) Slack, and critical path (ii) Indicate the Earliest Starting and Latest Finish times on the following network and also indicate the critical path on it. The te values indicated are as per standard deviation. 7. (a) The sales of cars for an automobile manufacturing company for last five years are given below: Year Sales (Y) Demand index (X) (No. of cars) (No. of cars) Find the relation between the demand index (X) and sale of cars (Y). Make a forecast for the year 2016; supposing the demand index rise to Use Least square method. 10 (b) Describe Laser Beam Machining (LBM). Give a detailed schematic diagram. Also discuss the Mechanics of LBM. 10 Explain in detail "Wire Drawing" process. Give a detailed drawing of the set-up. What is the function of "Dog-Gripping tool" for this process? 10 (d) (i) For calculation of simple interest 3 sets of p = principal, n = no. of years and r = rate are given. Simple interest has to be calculated by using C- program. Draw a Flow chart using "Loop Control Structure". (ii) Write a C-code to compute the volume and Area of a sphere using the formulas. 3 r V 4 3 A = 4r For more information log on Page 9
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -11. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before. attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
Set 2 (d) 150 C (a) 0.45 (d) can be positive, negative or zero (C) 8.5 J/K (a) 0.1
 Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
If there is convective heat transfer from outer surface to fluid maintained at T W.
 Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Civil Services Examination-1989
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
Set 1. a. 100 kj/kg b. 110 kj/kg c. 140 kj/kg d. 150 kj/kg
 Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
Civil Services Examination-2013
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 250 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 250 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
SILVER OAK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ADITYA SILVER OAK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 [4062]-186 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B. : (i) Answers
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 [4062]-186 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B. : (i) Answers
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Chapter Four fluid flow mass, energy, Bernoulli and momentum
 4-1Conservation of Mass Principle Consider a control volume of arbitrary shape, as shown in Fig (4-1). Figure (4-1): the differential control volume and differential control volume (Total mass entering
4-1Conservation of Mass Principle Consider a control volume of arbitrary shape, as shown in Fig (4-1). Figure (4-1): the differential control volume and differential control volume (Total mass entering
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems. Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14
 AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Answers to questions in each section should be tied together and handed in separately.
 EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT B.Tech. [SEM V (ME-51, 52, 53, 54)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session: )
![SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT B.Tech. [SEM V (ME-51, 52, 53, 54)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session: ) SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT B.Tech. [SEM V (ME-51, 52, 53, 54)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session: )](/thumbs/78/78353407.jpg) QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1) The inside temperature of a furnace wall ( k=1.35w/m.k), 200mm thick, is 1400 0 C. The heat transfer coefficient
QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1) The inside temperature of a furnace wall ( k=1.35w/m.k), 200mm thick, is 1400 0 C. The heat transfer coefficient
Elements of Mechanical Engineering
 2011 Elements of Mechanical Engineering AMRAT PATEL Asst. Professor 1/17/2011 Smt Shantaben Haribhai Gajera Charitable Trust, Surat LAXMI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, SARIGAM BE I, Sem I (Section: A, B & C)
2011 Elements of Mechanical Engineering AMRAT PATEL Asst. Professor 1/17/2011 Smt Shantaben Haribhai Gajera Charitable Trust, Surat LAXMI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, SARIGAM BE I, Sem I (Section: A, B & C)
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2012 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-187 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2012 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B.
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-187 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2012 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B.
Please welcome for any correction or misprint in the entire manuscript and your valuable suggestions kindly mail us
 Problems of Practices Of Fluid Mechanics Compressible Fluid Flow Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi Bhooshan
Problems of Practices Of Fluid Mechanics Compressible Fluid Flow Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi Bhooshan
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
10 minutes reading time is allowed for this paper.
 EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
TOPIC 2 [A] STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION
![TOPIC 2 [A] STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION TOPIC 2 [A] STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION](/thumbs/96/128741039.jpg) TOPIC 2 [A] STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION CLASS TUTORIAL 1. The walls of a refrigerated truck consist of 1.2 mm thick steel sheet (k=18 W/m-K) at the outer surface, 22 mm thick cork (k=0.04 W/m-K) on the
TOPIC 2 [A] STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION CLASS TUTORIAL 1. The walls of a refrigerated truck consist of 1.2 mm thick steel sheet (k=18 W/m-K) at the outer surface, 22 mm thick cork (k=0.04 W/m-K) on the
S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Examination Heat Transfer
 Examination Heat Transfer code: 4B680 date: 17 january 2006 time: 14.00-17.00 hours NOTE: There are 4 questions in total. The first one consists of independent sub-questions. If necessary, guide numbers
Examination Heat Transfer code: 4B680 date: 17 january 2006 time: 14.00-17.00 hours NOTE: There are 4 questions in total. The first one consists of independent sub-questions. If necessary, guide numbers
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 13 June 2007
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) PART-A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 009 Mechanical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 009 Mechanical
Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Heat and mass transfer
 9210-221 Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Heat and mass transfer 0 You should have the following for this examination one answer book non programmable calculator pen, pencil, drawing instruments
9210-221 Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Heat and mass transfer 0 You should have the following for this examination one answer book non programmable calculator pen, pencil, drawing instruments
GATE 2009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper
 GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
Chapter 7 The Energy Equation
 Chapter 7 The Energy Equation 7.1 Energy, Work, and Power When matter has energy, the matter can be used to do work. A fluid can have several forms of energy. For example a fluid jet has kinetic energy,
Chapter 7 The Energy Equation 7.1 Energy, Work, and Power When matter has energy, the matter can be used to do work. A fluid can have several forms of energy. For example a fluid jet has kinetic energy,
Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology New Delhi II Semester MEL 140 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 PROBLEM SET 1: Review of Basics Problem 1: Define Work. Explain how the force is generated in an automobile. Problem 2: Define and classify Energy and explain the relation between a body and energy. Problem
PROBLEM SET 1: Review of Basics Problem 1: Define Work. Explain how the force is generated in an automobile. Problem 2: Define and classify Energy and explain the relation between a body and energy. Problem
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION. 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance in thermodynamics.
 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA
 Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Problems on Heat Transfer
 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17410 15116 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. (4) Assume
17410 15116 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. (4) Assume
The online of midterm-tests of Fluid Mechanics 1
 The online of midterm-tests of Fluid Mechanics 1 1) The information on a can of pop indicates that the can contains 460 ml. The mass of a full can of pop is 3.75 lbm while an empty can weights 80.5 lbf.
The online of midterm-tests of Fluid Mechanics 1 1) The information on a can of pop indicates that the can contains 460 ml. The mass of a full can of pop is 3.75 lbm while an empty can weights 80.5 lbf.
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
Readings for this homework assignment and upcoming lectures
 Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION B Linear graph paper will be provided.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2016-2017 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2016-2017 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
Heat and Mass Transfer Unit-1 Conduction
 1. State Fourier s Law of conduction. Heat and Mass Transfer Unit-1 Conduction Part-A The rate of heat conduction is proportional to the area measured normal to the direction of heat flow and to the temperature
1. State Fourier s Law of conduction. Heat and Mass Transfer Unit-1 Conduction Part-A The rate of heat conduction is proportional to the area measured normal to the direction of heat flow and to the temperature
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
Objectives. Conservation of mass principle: Mass Equation The Bernoulli equation Conservation of energy principle: Energy equation
 Objectives Conservation of mass principle: Mass Equation The Bernoulli equation Conservation of energy principle: Energy equation Conservation of Mass Conservation of Mass Mass, like energy, is a conserved
Objectives Conservation of mass principle: Mass Equation The Bernoulli equation Conservation of energy principle: Energy equation Conservation of Mass Conservation of Mass Mass, like energy, is a conserved
SATHYABAMA UNIVERISTY. Unit III
 Unit III UNIT III STEAM NOZZLES AND TURBINES Flow of steam through nozzles, shapes of nozzles, effect of friction, critical pressure ratio,supersaturated flow.impulse and reaction principles, compounding,
Unit III UNIT III STEAM NOZZLES AND TURBINES Flow of steam through nozzles, shapes of nozzles, effect of friction, critical pressure ratio,supersaturated flow.impulse and reaction principles, compounding,
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1
 Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
mywbut.com Hydraulic Turbines
 Hydraulic Turbines Hydro-electric power accounts for up to 0% of the world s electrical generation. Hydraulic turbines come in a variety of shapes determined by the available head and a number of sizes
Hydraulic Turbines Hydro-electric power accounts for up to 0% of the world s electrical generation. Hydraulic turbines come in a variety of shapes determined by the available head and a number of sizes
Introduction to Fluid Machines, and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Fluid Machines, and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Introduction to Reaction Type of Hydraulic
Introduction to Fluid Machines, and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 Introduction to Reaction Type of Hydraulic
S.E. (Mech.) (First Sem.) EXAMINATION, (Common to Mech/Sandwich) FLUID MECHANICS (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 8 Seat No. [4262]-113 S.E. (Mech.) (First Sem.) EXAMINATION, 2012 (Common to Mech/Sandwich) FLUID MECHANICS (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 8 Seat No. [4262]-113 S.E. (Mech.) (First Sem.) EXAMINATION, 2012 (Common to Mech/Sandwich) FLUID MECHANICS (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
HYDRAULIC TURBINES. Hydraulics and Hydraulic Machines
 HYDRAULIC TURBINES Introduction: The device which converts h ydraulic energy into mechanical energy or vice versa is known as Hydraulic Machines. The h ydraulic machines which convert h ydraulic energy
HYDRAULIC TURBINES Introduction: The device which converts h ydraulic energy into mechanical energy or vice versa is known as Hydraulic Machines. The h ydraulic machines which convert h ydraulic energy
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
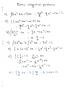 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 00 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 00 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
S6. (a) State what is meant by an ideal gas...
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
2014 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Thermodynamic Processes & Efficiency ME 6101 (2017) 2 / 25 T145 = Q + W cv + i h 2 = h (V2 1 V 2 2)
 Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002
 16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
2 Navier-Stokes Equations
 1 Integral analysis 1. Water enters a pipe bend horizontally with a uniform velocity, u 1 = 5 m/s. The pipe is bended at 90 so that the water leaves it vertically downwards. The input diameter d 1 = 0.1
1 Integral analysis 1. Water enters a pipe bend horizontally with a uniform velocity, u 1 = 5 m/s. The pipe is bended at 90 so that the water leaves it vertically downwards. The input diameter d 1 = 0.1
PHYA5/2C. (JUN15PHYA52C01) WMP/Jun15/PHYA5/2C/E5. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June Section B PMT TOTAL
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2015 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2015 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
(Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION,
 - Printed Pages - 6 TME - 201 (Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I Roll No. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION, 2005-2006 '-" Time: 3 Hours oa:::::t U') om (D om
- Printed Pages - 6 TME - 201 (Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I Roll No. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION, 2005-2006 '-" Time: 3 Hours oa:::::t U') om (D om
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 1 Introduction to Fluid Machines Well, good
Introduction to Fluid Machines and Compressible Flow Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 1 Introduction to Fluid Machines Well, good
TankExampleNov2016. Table of contents. Layout
 Table of contents Task... 2 Calculation of heat loss of storage tanks... 3 Properties ambient air Properties of air... 7 Heat transfer outside, roof Heat transfer in flow past a plane wall... 8 Properties
Table of contents Task... 2 Calculation of heat loss of storage tanks... 3 Properties ambient air Properties of air... 7 Heat transfer outside, roof Heat transfer in flow past a plane wall... 8 Properties
Experiment 1. Measurement of Thermal Conductivity of a Metal (Brass) Bar
 Experiment 1 Measurement of Thermal Conductivity of a Metal (Brass) Bar Introduction: Thermal conductivity is a measure of the ability of a substance to conduct heat, determined by the rate of heat flow
Experiment 1 Measurement of Thermal Conductivity of a Metal (Brass) Bar Introduction: Thermal conductivity is a measure of the ability of a substance to conduct heat, determined by the rate of heat flow
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr.
 Reading Assignments Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr. Sert) Study Set 1 You can find the answers of some of the following
Reading Assignments Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr. Sert) Study Set 1 You can find the answers of some of the following
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Chapter 3 NATURAL CONVECTION
 Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid Sciences, 3rd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Robert H. Turner, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 3 NATURAL CONVECTION Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid Sciences, 3rd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Robert H. Turner, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 3 NATURAL CONVECTION Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM
 First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines
 Contents 1- Introduction. - Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Contents 1- Introduction. - Pumps. Chapter Four Hydraulic Machines (لفرع الميكانيك العام فقط ( Turbines. -3 4- Cavitation in hydraulic machines. 5- Examples. 6- Problems; sheet No. 4 (Pumps) 7- Problems;
Convective Mass Transfer
 Convective Mass Transfer Definition of convective mass transfer: The transport of material between a boundary surface and a moving fluid or between two immiscible moving fluids separated by a mobile interface
Convective Mass Transfer Definition of convective mass transfer: The transport of material between a boundary surface and a moving fluid or between two immiscible moving fluids separated by a mobile interface
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION B Graph paper will be provided.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No.
 *17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
*17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts by Asst. Prof. Channarong Asavatesanupap Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Thammasat University 2 What is Thermodynamics? Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts by Asst. Prof. Channarong Asavatesanupap Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Thammasat University 2 What is Thermodynamics? Thermodynamics
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Q.1 a) any six of the following 6x2= 12. i) Define - ( Each term 01 mark)
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Spring_#7. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
MC 405 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING. Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
 THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question (a, b, etc. ) should
THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question (a, b, etc. ) should
