Civil Services Examination-2013
|
|
|
- David Gerard Sims
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 250 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There are EIGHT questions divided in Two Sections and printed both in HINDI and in ENGLISH. Candidate has to attempt FIVE questions in all. Question no. 1 and 5 are compulsory and out of the remaining, THREE are to be attempted choosing at least ONE from each section. The number of marks carried by a question/part is indicated against it. Answers must be written in the medium authorized in the Admission certificate which must be stated clearly on the cover of this Question-cum-Answer (QCA) booklet in the space provided. No marks will be given for answers written in medium other than the authorized one. Wherever any assumptions are made for answering a question, they must be clearly indicated. Diagrams/Figures, wherever required, shall be drawn in the space provided for answering the question itself. Unless otherwise mentioned, symbols and notations carry their usual standard meaning. Attempts of questions shall be counted in chronological order. Unless struck off, attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly. Any page or portion of the page left blank in the answer book must be clearly struck off. SECTION -A Q. 1(a) In the Figure shown below, block C has a mass of 50 kg and is confined between two walls by smooth rollers. If the block rests on the top of the 40 kg spool, determine the required coefficient of static friction at A and B so that the spool slips at A and B when the magnitude of applied force P is increased to 300 N. 10 OE = 0.4 m OD = 0.2 m Q. 1(b) In the Figure shown, a plate is supported at three positions, A, B and C. A is the ball and socket support, B is the roller support and CD is the cord. Determine the components of reactions at A and B and tension in cord CD. 10 For more information log on Page 1
2 Q. 1(c) The bending moment diagram for a simply supported beam AB is shown in Fig. below. Sketch the loading diagram and S.F. diagram of the beam. 10 Q. 1(d) Distinguish clearly the function of a flywheel used in I.C. Engines and in mechanical punching presses. For the same power output, why flywheels of multi-cylinder inline engines are relatively smaller than that of single cylinder engine? 10 Q. 1(e) Differentiate between (i) annealing, and (ii) tempering. Mark the processes on a TTT diagram and bring out the transformations that take place during the process. 10 Q. 2(a) A compound pendulum of mass 27 kg is suspended from a pivot, such that the distance of pivot from the mass centre of pendulum is 380 mm. When the pendulum swings about its pivot with small oscillation, the period of oscillation is 1.60 second. If the pendulum is now made to swing with amplitude of 45 on each side of the vertical, find the force exerted on the pivot at the extremity of the swing. 25 Q. 2(b) A simply supported beam of 3 m span is subjected to loads as shown below. The beam is of I-section and all its dimensions are shown in mm. Determine the principal stresses at point D in the web. This section is located at a distance of 1 m from the right hand support of the beam. 25 Q. 3(a) In a loaded component principal stresses at a point are 130 MPa and 30 MPa. Using Mohr's stress circle, determine the state of stress at the point with respect to axes x' and y' which are inclined to σ 1 and σ 2 (principal stress) axes at 30 each in anticlockwise direction. Also determine principal strains at the point. Take E = 200 GPa and G = 80 GPa. 20 Q. 3(b) The mass of an electric motor is 100 kg. The mass of the armature alone is 30 kg and its centre of gravity lies 0.5 mm from the axis of rotation. The motor is mounted on five springs of negligible damping and the force transmitted to the floor is oneeleventh of the applied force. Assuming mass of the motor is equally distributed For more information log on Page 2
3 among the five springs, determine the (i) stiffness of each spring (ii) dynamic force transmitted to the floor. The motor is operating at a speed of 1400 rpm. 10 Q. 3(c) In the epicyclic gear train shown in the Figure, S 1 is the driver, A 2 is connected to output. A 1 and A 2 are annulus gears, and S 1 and S 2 are external gears, in which S 2 is fixed gear. Given the tooth numbers of gears are S 1 = 40, S 2 = 30, A 1 = 120 and A 2 = 100, determine the velocity ratio of the co-axial shafts. Determine also the magnitude and direction of the torque required to fix S 2, if a torque of 300 N-m is applied in a clockwise direction to S Q. 4(a) In the figure shown, the end A of a bar AB, is constrained to move along vertical path AD and the bar passes through a swivel bearing pivoted at C. When A has a velocity of 3 m/s towards D and an acceleration of 25 m/s 2 in the opposite direction, determine: (i) Velocity and acceleration of sliding of bar through the swivel, (ii) Angular velocity and angular acceleration of AB. 25 Q. 4(b) What are the desirable properties while selecting a tool material for metal-cutting applications? Compare HSS and ceramic tools with regard to their application in high speed machining. 15 Q. 4(c) What are composite materials? Enumerate the advantages and limitations of the use of composites as engineering materials. 10 SECTION B Q. 5(a) What is underlying philosophy behind JIT systems? Briefly describe the characteristics of JIT systems. 10 Q. 5(b) List the basic principles of plant layout. 10 Q. 5(c) Bars of length 20.05/19.95 mm are in stock. From each, piece of 5.03/4.98 mm are cut. Determine the lengths of the remaining parts. 10 Q. 5(d) A cup, of 50 mm diameter and 100 mm height, is to be drawn from low carbon steel sheet. Neglecting the influence of thickness and corner radii: (i) Calculate the blank diameter For more information log on Page 3
4 (ii) Decide whether it can be drawn in a single draw, if maximum reduction permitted is 40%. 10 Q. 5(e) For a machined surface, show macro and micro-irregularities. What are their causes? What are the various measures of surface finish? Explain any three of them. 10 Q. 6(a) An open loop type NC machine has a stepper motor with a step of 0.9 degree. The lead screw of the machine is of 4 mm pitch. (i) If the tool has to be moved by 2.87 mm, how many pulses will have to be fed? (ii) If the motor is rotating at 15 r.p.m., what is the pulse frequency and the feed rate of the machining operation? 10 Q. 6(b) The process capability of machines manufacturing holes and shafts is ± 0.24 min. The assembly requirements for the hole/shaft, of nominal dimension mm, are of clearance between 0.04 and 0.08 mm. Devise the complete scheme (state what it is?) so that satisfactory assemblies are made. 10 Q. 6(c) Sketch the set-up for spot welding showing details of power input and electrodes (i) Draw the force/time and current/time diagrams. (ii) Explain how heating takes place. (iii) Indicate order of magnitude of current, voltage and time. (iv) How projection -welding is different from spot welding? 10 Q. 6(d) The following table gives the monthwise actual demand of units of some product: Table Month March April May June July August Demand (units) The forecasted demand for the month of March was 400 units. The firm uses exponential smoothing method with smoothing factor 0.2 to forecast demand. (i) Calculate the tracking signal for the model. (ii) Comment on the smoothing factor. 20 Q. 7(a) An assembly line is to produce 40 microwave ovens an hour. The relevant data for the work elements involved in assembly are given below: Work element Time (sec) Immediate Predecessor(s) A 20 None B 55 A C 25 B D 40 B E 05 B F 35 A G 14 D, E H 40 C, F, G (i) Draw the precedence diagram. (ii) Design a balanced assembly line. (iii) Calculate (a) idle time, (b) efficiency, and (c) balance delay. (iv) What can be the maximum output from this assembly line? 25 Q. 7(b) How is the domestic kitchen gas cylinder manufactured? State the raw material, its shape and the processes involved. 10 For more information log on Page 4
5 Q. 7(c) A manufacturer carries stock of an item with an annual demand of 30,000 units. The setup cost (s) and holding cost (h) are not known precisely, though they vary between 100 : 1 and 150 : 1. (i) Calculate EOQ in both conditions. (ii) How sensitive is the optimal Q to s/h ratio? (iii) If s/h doubles or triples, what happens to economic order quantity Q*? 15 Q. 8 (a) A special screw is being produced on a machine. The diameter of screw is critical and the process is to be controlled. Twelve samples of four screws each are drawn chronologically and inspected. The data is tabulated below: Sample Screw Diameter (mm) No The statistical control chart constants for some samples are as under: No. of observations in sample Chart for Average Factors for Control Limits Factor for Central line Chart for ranges of Factors for Control Limits n A 1 A 2 A 3 d 2 D 1 D 2 D 3 D Is the process under statistical control? Justify your answer. 20 Q. 8(b) What is the principle of LBM (Laser Beam Machining)? Draw a sketch and name the salient elements used in LBM. 15 Q. 8(c) Determine the optimum speed, for minimum cost, for a machining operation. The data is as follows: Machine hour rate = Rs. 3,000 Cost of tool = Rs. 3,000 Machining time/job = 6 min. Tool life = 90 min. Taylor's equation constants c = 100; n = 0.5 Handling time/job = 4 min. Tool changing time = 9 min. 15 For more information log on Page 5
6 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 250 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS (Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions) There are EIGHT questions divided in two Sections and printed both in HINDI and in ENGLISH. Candidate has to attempt FIVE questions in all. Question Nos. 1 and 5 are compulsory and out of the remaining, THREE are to be attempted choosing at least ONE question from each Section. The number of marks carried by a question/part is indicated against it. Answers must be written in the medium authorized in the Admission Certificate which must be stated clearly on the cover of this Question-cum-Answer (QCA) Booklet in the space provided. No marks will be given for answers written in medium other than the authorized one. Wherever any assumptions are made for answering a question, they must be clearly indicated. Diagrams/Figures, wherever required, shall be drawn in the space provided for answering the question itself. Unless otherwise mentioned, symbols and notations carry their usual standard meaning. Attempts of questions shall be counted in chronological order. Unless struck off, attempt of a question shall be counted even if attempted partly. Any page or portion of the page left blank in the Question-cum-Answer Booklet must be clearly struck off. Section-A 1. (a) Derive an expression for entropy (S) as given below for a closed system undergoing a reversible process. 10 (b) Write Bernoulli's equation and the conditions for which it is valid. If a fluid ' obeying Bernoulli's equation has elevation, velocity and pressure at a point as 30 m, 50 m/s and 50 bar respectively, calculate the total energy per unit mass of this fluid if its density is 1000 kg/m (c) What is the effect of Mach number on the compressibility? Derive an expression for pressure coefficient in terms of Mach number. 10 (d) Explain Wien's displacement law. Assuming sun to be a blackbody with a constant surface temperature of 5780 K, calculate the wavelength at which it will have the maximum spectral emissive power. 10 (e) In a standard vapour compression refrigeration cycle, the specific enthalpies of refrigerant at the end states of different processes in ascending order are 74.6 kj/kg, kj/kg and kj/kg. If the mass flow rate of refrigerant is 30 kg/min, calculate power consumption and COP of the cycle (a) Prove that the cyclic integral of ratio between heat transfer and temperature of any thermodynamic process is less than or equal to zero. 20 (b) A pipe having 15.4 cm inside diameter and 3.2 m length stands vertically. Another pipe having 10.2 cm inside diameter and 4.8 m length is welded on top of this pipe. Water at 22 C fills the smaller diameter pipe to a depth of 2.24 m. Above the water is air under an absolute pressure of 242 kpa. Determine the total force on the bottom of the larger diameter pipe. 15 For more information log on Page 6
7 (c) Hot gases enter the blades of a gas turbine with a velocity of 550 m/s and leave with a velocity of 120 m/s. There is an increase in the enthalpy of the gases in the blade passages to the extent of 5.1 kj/kg. The rate of gas flow is 98 kg/min. Determine the power produced (a) Derive an expression for entropy change across a normal shock wave occurring in a nozzle. Show the trend of this entropy change (in the form of a diagram), with respect to the Mach number value before the shock. 15 (b) Define availability of a closed and steady-flow system. Atmospheric air is compressed steadily from 100 kpa, 27 C to 500 kpa, 117 C, by a compressor that is cooled only by atmospheric air. Neglecting kinetic energy changes, determine the minimum work required per kg of air compressed. 15 (c) In a balanced counterflow heat exchanger, where, show that (i) ΔT 1 = ΔT 2 = ΔT at any section; (ii) the temperature profiles of two fluids are parallel and linear (a) In a double-pipe heat exchanger,. The inlet temperatures of hot and cold fluids are T h i and T c,i. Determine an expression, in terms of T h,i, T c,i and T h,0, for the ratio of area of counterflow heat exchanger to that of parallel-flow heat exchanger, which will give same hot fluid outlet temperature T h0. Also find out the ratio, if T h,i = 150 C, T ci = 30 C and T h,0 = 90 C. 25 (b) A hot plate of 100 cm height and 25 cm wide is exposed to atmospheric air at 25 C. The surface temperature of the plate is 95 C. Find the heat loss from both the surfaces of the plate. Also find the change in heat loss if the height of the plate is reduced to 50 cm and the width is increased to 40 cm. Use the following relations: Nu = 0.59 (Gr.Pr) 0.25 if Gr.Pr < 10 9 = 0.10 (Gr.Pr) if Gr.Pr > 10 9 The properties of air are: ρ = 1-06 kg/m 3 ; C p =1004 J/kg-K k = W/m-K ν = X l0-6 m 2 /sec 15 (c) Do you think that velocity boundary layer and thermal boundary layer depend on Prandtl number? If yes, explain properly. Also explain, with the help of neat sketches, the significance of relative thickness of velocity boundary layer and thermal boundary layer for the following: (i) Liquid metals (ii) Oils 10 SECTION B 5. (a) Explain Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements of the second law of thermodynamics and prove that both the statements are equivalent. 10 (b) How do the following parameters influence knocking in SI engine combustion? (i) Self-ignition temperature of the fuel (ii) Air-fuel ratio (iii) Dilution by residual gas For more information log on Page 7
8 (iv) Shrouded inlet valve (v) Combustion chamber design 10 (c) Hot gases inside a chimney are at 430 C and the chimney height is 32 metres. The temperature of outside air is 28 C. The furnace is supplied with 17 kg of air per kg of coal burnt. Calculate (i) draught in mm of water; (ii) draught height in metres of hot gases. 10 (d) What is the significance of by-pass factor? For a heating coil, derive an expression of by-pass factor. Find the expression for efficiency also for heating coil. 10 (e) Inner and outer surfaces of a spherical shell are maintained at temperatures T i and T 0 respectively such that T i > T 0. If inner and outer radii of the shell are r i and r 0 and its conductivity is k, derive an expression for the rate of heat conduction through the shell. Assume steady state and no heat generation within the shell (a) In a 4-stroke, 2-cylinder diesel engine, the following data was collected: Piston stroke = 60 cm Diameter of the cylinder = 40 cm Speed of the engine = 250 r.p.m. Indicated mean effective pressure = 8 bar Brake power of the engine = 220 kw Fuel consumption = 80 kg/hr CV of fuel used = kj/kg Hydrogen content in fuel = 13% and remaining is carbon Air consumption = 30 kg/min Cooling water circulated = 90 kg/min Rise in temperature of cooling water = 38 C Piston cooling oil used = 45 kg/min Rise in temperature of cooling oil = 23 C C p of water = 4.18 kj/kg-k C p of cooling oil = 2.2 kj/kg-k C p of exhaust gases = 1.1 kj/kg-k C p of superheated steam = 2 kj/kg-k Latent heat of steam = 2520 kj/kg Exhaust gas temperature = 450 C Ambient temperature = 27 C Find the following quantities per minute: (i) Heat converted to useful brake power (BP) (ii) Heat carried away by cooling water (iii) Heat carried away by cooling oil (iv) Heat carried away by dry exhaust gases (v) Heat carried away by steam formed (vi) Heat supplied by fuel Draw up also a heat balance sheet on minute basis and percentage basis. 40 (b) In the pressure crank angle diagram of normal combustion SI engine, show the point of ignition, point of combustion, angle of advance, ignition lag and combustion period. 10 For more information log on Page 8
9 7. (a) With the help of T-s diagrams, differentiate between Carnot and Rankine vapour cycles. State the advantages of Rankine cycle and derive the expression for its thermal efficiency. 15 (b) A combined cycle power plant operates with mercury and steam cycles. Mercury cycle is superimposed over the steam cycle operating between boiler outlet condition of 40 bar and 400 C (h = kj/kg and s g = kj/kg-k) and condenser temperature of 40 C. The heat released by mercury condensing at 0.2 bar is used to impart the latent heat of vaporization to the water in steam cycle. Mercury turbine receives mercury as saturated vapour at 10 bar. Calculate the mass of mercury circulated per unit mass of water and the efficiency of this binary cycle. 35 Properties of saturated mercury and steam are: P T ( C) Enthalpy (kj/kg) Entropy (kj/kg-k) Sp. vol. (m 3 / kg) (bar) h f h g s f s g v f v g mercury x l x l Steam (a) 100 m 3 of air per minute at 15 C DBT and 80% relative humidity is sensibly heated until its temperature becomes 22 C. Saturation pressures of water vapour at 15 C and 22 C are bar and bar respectively. Find heat added to air per minute. Take atmospheric pressure =1.013 bar. 25 (b) An air refrigerator used for food storage provides 50 tons of refrigeration. The temperature of air entering the compressor is 7 C and the temperature of air before entering into the expander is 27 C. Assuming 30% more power is required than theoretical, find (i) actual COP of the cycle and (ii) kw capacity required to run the compressor. The quantity of air circulated in the system is 100 kg/min. The compression and expansion follow the law pv 1.3 = constant. Take γ = l.4 and C p = 1 kj/kg- C for air. For more information log on Page 9
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -11. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before. attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
(Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION,
 - Printed Pages - 6 TME - 201 (Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I Roll No. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION, 2005-2006 '-" Time: 3 Hours oa:::::t U') om (D om
- Printed Pages - 6 TME - 201 (Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I Roll No. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION, 2005-2006 '-" Time: 3 Hours oa:::::t U') om (D om
Scheme G. Sample Test Paper-I
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time: 1 hour 1) All questions are compulsory 2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary 3) Figures to the right indicate full marks 4) Assume suitable
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time: 1 hour 1) All questions are compulsory 2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary 3) Figures to the right indicate full marks 4) Assume suitable
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
Civil Services Examination-2001
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 00 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 00 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17410 15116 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. (4) Assume
17410 15116 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. (4) Assume
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
Civil Services Examination-1989
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
Elements of Mechanical Engineering
 2011 Elements of Mechanical Engineering AMRAT PATEL Asst. Professor 1/17/2011 Smt Shantaben Haribhai Gajera Charitable Trust, Surat LAXMI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, SARIGAM BE I, Sem I (Section: A, B & C)
2011 Elements of Mechanical Engineering AMRAT PATEL Asst. Professor 1/17/2011 Smt Shantaben Haribhai Gajera Charitable Trust, Surat LAXMI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, SARIGAM BE I, Sem I (Section: A, B & C)
S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
Answers to questions in each section should be tied together and handed in separately.
 EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
Set 2 (d) 150 C (a) 0.45 (d) can be positive, negative or zero (C) 8.5 J/K (a) 0.1
 Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
Set 1. a. 100 kj/kg b. 110 kj/kg c. 140 kj/kg d. 150 kj/kg
 Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION. 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance in thermodynamics.
 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
SILVER OAK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ADITYA SILVER OAK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
Please welcome for any correction or misprint in the entire manuscript and your valuable suggestions kindly mail us
 Problems of Practices Of Fluid Mechanics Compressible Fluid Flow Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi Bhooshan
Problems of Practices Of Fluid Mechanics Compressible Fluid Flow Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi Bhooshan
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Introduction CHAPTER Prime Movers. 1.2 Sources of Energy
 Introduction CHAPTER 1 1.1 Prime Movers Prime mover is a device which converts natural source of energy into mechanical work to drive machines for various applications. In olden days, man had to depend
Introduction CHAPTER 1 1.1 Prime Movers Prime mover is a device which converts natural source of energy into mechanical work to drive machines for various applications. In olden days, man had to depend
THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES
 Chapter 10 THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES It is not the sun to overtake the moon, nor doth the night outstrip theday.theyfloateachinanorbit. The Holy Qur-ān In many engineering applications,
Chapter 10 THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES It is not the sun to overtake the moon, nor doth the night outstrip theday.theyfloateachinanorbit. The Holy Qur-ān In many engineering applications,
PHYA5/2C. (JUN15PHYA52C01) WMP/Jun15/PHYA5/2C/E5. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June Section B PMT TOTAL
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2015 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2015 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology New Delhi II Semester MEL 140 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 PROBLEM SET 1: Review of Basics Problem 1: Define Work. Explain how the force is generated in an automobile. Problem 2: Define and classify Energy and explain the relation between a body and energy. Problem
PROBLEM SET 1: Review of Basics Problem 1: Define Work. Explain how the force is generated in an automobile. Problem 2: Define and classify Energy and explain the relation between a body and energy. Problem
S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2012 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-187 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2012 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B.
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-187 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2012 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B.
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 [4062]-186 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B. : (i) Answers
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 [4062]-186 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B. : (i) Answers
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION
 CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
Unit Workbook 2 - Level 5 ENG U64 Thermofluids 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall 2006
 FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
7. Development of the 2nd Law
 7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
ROLLER BEARING FAILURES IN REDUCTION GEAR CAUSED BY INADEQUATE DAMPING BY ELASTIC COUPLINGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIONS
 ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number:
 ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
PHA7/W PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 7 Nuclear Instability: Applied Physics Option
 Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Level Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) PHA7/W Unit 7 Nuclear
Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Level Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) PHA7/W Unit 7 Nuclear
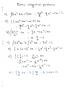 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
ME 200 Final Exam December 12, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
Civil Services Examination-2012
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission
MC 405 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING. Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
 THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question (a, b, etc. ) should
THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question (a, b, etc. ) should
PHYSICS PAPER 1. (THEORY) (Three hours)
 PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) All questions are compulsory. Question number
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) All questions are compulsory. Question number
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002
 16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
wb Thermodynamics 2 Lecture 9 Energy Conversion Systems
 wb1224 - Thermodynamics 2 Lecture 9 Energy Conversion Systems Piero Colonna, Lecturer Prepared with the help of Teus van der Stelt 8-12-2010 Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Content
wb1224 - Thermodynamics 2 Lecture 9 Energy Conversion Systems Piero Colonna, Lecturer Prepared with the help of Teus van der Stelt 8-12-2010 Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Content
Readings for this homework assignment and upcoming lectures
 Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
3. Write a detailed note on the following thrust vector control methods:
 Code No: R05322103 Set No. 1 1. Starting from the first principles and with the help of neatly drawn velocity triangles obtain the following relationship: Ψ = 2 Φ (tan β 2 + tan β 3 ) where Ψ is the blade
Code No: R05322103 Set No. 1 1. Starting from the first principles and with the help of neatly drawn velocity triangles obtain the following relationship: Ψ = 2 Φ (tan β 2 + tan β 3 ) where Ψ is the blade
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : THERMODYNAMICS Course Code : AME00 Regulation : IARE - R1 Year
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : THERMODYNAMICS Course Code : AME00 Regulation : IARE - R1 Year
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT B.Tech. [SEM V (ME-51, 52, 53, 54)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session: )
![SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT B.Tech. [SEM V (ME-51, 52, 53, 54)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session: ) SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT B.Tech. [SEM V (ME-51, 52, 53, 54)] QUIZ TEST-1 (Session: )](/thumbs/78/78353407.jpg) QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1) The inside temperature of a furnace wall ( k=1.35w/m.k), 200mm thick, is 1400 0 C. The heat transfer coefficient
QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1) The inside temperature of a furnace wall ( k=1.35w/m.k), 200mm thick, is 1400 0 C. The heat transfer coefficient
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
12/21/2014 7:39 PM. Chapter 2. Energy and the 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 2 Energy and the 1st Law of Thermodynamics 1 2 Homework Assignment # 2 Problems: 1, 7, 14, 20, 30, 36, 42, 49, 56 Design and open end problem: 2.1D Due Monday 22/12/2014 3 Work and Kinetic Energy
Chapter 2 Energy and the 1st Law of Thermodynamics 1 2 Homework Assignment # 2 Problems: 1, 7, 14, 20, 30, 36, 42, 49, 56 Design and open end problem: 2.1D Due Monday 22/12/2014 3 Work and Kinetic Energy
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
Refrigeration. 05/04/2011 T.Al-Shemmeri 1
 Refrigeration is a process of controlled removal of heat from a substance to keep it at a temperature below the ambient condition, often below the freezing point of water (0 O C) 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
Refrigeration is a process of controlled removal of heat from a substance to keep it at a temperature below the ambient condition, often below the freezing point of water (0 O C) 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
MAE 11. Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018
 MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
B. Tech. (SEM. I) ODD SEMESTER ll-ffiory EXAMINATION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I Roll No. B. Tech. (SEM. I) ODD SEMESTER ll-ffiory EXAMINATION 2010-11 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ' ~Time.- 3 Hours Total Marks.- 100 Note
Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I Roll No. B. Tech. (SEM. I) ODD SEMESTER ll-ffiory EXAMINATION 2010-11 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ' ~Time.- 3 Hours Total Marks.- 100 Note
Topic wise Tests. Complex Variables, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Common Terms, Definitions and Conversion Factors
 1 Common Terms, Definitions and Conversion Factors 1. Force: A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object s interaction with another object. It is defined as Where F = m a F = Force
1 Common Terms, Definitions and Conversion Factors 1. Force: A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object s interaction with another object. It is defined as Where F = m a F = Force
200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 QUESTION PAPER SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. There
Chapter 2: The Physical Properties of Pure Compounds
 Chapter 2: The Physical Properties of Pure Compounds 2-10. The boiler is an important unit operation in the Rankine cycle. This problem further explores the phenomenon of boiling. A. When you are heating
Chapter 2: The Physical Properties of Pure Compounds 2-10. The boiler is an important unit operation in the Rankine cycle. This problem further explores the phenomenon of boiling. A. When you are heating
PHYSICS 111 SPRING FINAL EXAM: May 2, 2017; 2:15pm - 4:15pm
 PHYSICS 111 SPRING 2017 FINAL EXAM: May 2, 2017; 2:15pm - 4:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 30 multiple-choice question, each worth 3 points, for
PHYSICS 111 SPRING 2017 FINAL EXAM: May 2, 2017; 2:15pm - 4:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 30 multiple-choice question, each worth 3 points, for
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Q.1 a) any six of the following 6x2= 12. i) Define - ( Each term 01 mark)
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
ME 200 Final Exam December 14, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel.
 TOM Fly Wheel Mechanical Engineering Department The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel. A heavy-rimmed rotating wheel used to minimize variations
TOM Fly Wheel Mechanical Engineering Department The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel. A heavy-rimmed rotating wheel used to minimize variations
TankExampleNov2016. Table of contents. Layout
 Table of contents Task... 2 Calculation of heat loss of storage tanks... 3 Properties ambient air Properties of air... 7 Heat transfer outside, roof Heat transfer in flow past a plane wall... 8 Properties
Table of contents Task... 2 Calculation of heat loss of storage tanks... 3 Properties ambient air Properties of air... 7 Heat transfer outside, roof Heat transfer in flow past a plane wall... 8 Properties
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
10 minutes reading time is allowed for this paper.
 EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
SATHYABAMA UNIVERISTY. Unit III
 Unit III UNIT III STEAM NOZZLES AND TURBINES Flow of steam through nozzles, shapes of nozzles, effect of friction, critical pressure ratio,supersaturated flow.impulse and reaction principles, compounding,
Unit III UNIT III STEAM NOZZLES AND TURBINES Flow of steam through nozzles, shapes of nozzles, effect of friction, critical pressure ratio,supersaturated flow.impulse and reaction principles, compounding,
Dept of ECE, SCMS Cochin
 B B2B109 Pages: 3 Reg. No. Name: APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2017 Course Code: BE 100 Course Name: ENGINEERING MECHANICS Max. Marks: 100 Duration:
B B2B109 Pages: 3 Reg. No. Name: APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2017 Course Code: BE 100 Course Name: ENGINEERING MECHANICS Max. Marks: 100 Duration:
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON. University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS. For The Following Qualifications:-
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013
 Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
 PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
PTT 277/3 APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (2013/2014)
 PTT 77/3 APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (013/014) 1 Energy can exist in numerous forms: Thermal Mechanical Kinetic Potential Electric Magnetic Chemical Nuclear The total energy of a system on a unit mass:
PTT 77/3 APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (013/014) 1 Energy can exist in numerous forms: Thermal Mechanical Kinetic Potential Electric Magnetic Chemical Nuclear The total energy of a system on a unit mass:
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA
 Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz. EXAM #3 November 21, :00 9:00 PM INSTRUCTIONS
 Seat # Your exam is form 1. Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz EXAM #3 November 21, 2002 7:00 9:00 PM INSTRUTIONS 1. Please indicate which form (1, 2, 3, or 4) exam you have by marking the appropriate bubble
Seat # Your exam is form 1. Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz EXAM #3 November 21, 2002 7:00 9:00 PM INSTRUTIONS 1. Please indicate which form (1, 2, 3, or 4) exam you have by marking the appropriate bubble
