Diffusion in Solid State
|
|
|
- Rosalind Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (Diffusion in Solid State): - Diffusion in Solid State Diffusion Mechanism It is known that at high temperature, the Amplitude of vibrations of atoms leads to expansion, while keeping the (Frequency of Vibration) constant in general form
2 Diffusion by voids Nv Na exp Hf / RT The percentage of voids in metal lines of F. C. C to % at high temperatures Wo, is the vibrations between the void and solvent A very far from the solute B W1, is the vibrations between the void and solvent A away, the closest distance from the void and solute B W, are the frequencies between the void and solute B W3, are the frequencies between the void and solvent atoms A, where A is the closest distance
3 from the void. W4, are the frequencies between the void and solvent A away from the solute B. The relationship between these vibrations known (Correlation factor) (f). f Wo W 1 + 7( ) W W4 Wo W 1 + W + 7( W 4 3 W 4 Wo ) W 3 f 7 W1 + W3 7 W1 + W + W 3 Diffusion by Interstitial atoms Q / RT D νa exp Vibration frequency,, Q the activation energy necessary for diffusion, ΔHm ν enthalpy
4 Fick,s first Law dc J D dx Expressed in this law the following equation: Where each of: J, is called flux. C, concentration of solute in the solvent D, diffusion coefficient To derive the law, we assume the existence of two surfaces adjacent the lattice A and B (each an alloy of copper and zinc), where the concentration of zinc in A, more than in the B,
5 The sum of the number of atoms of zinc, which can jump over the energy barrier per second, is: This is a net movement of atoms of zinc, down to include the focus from A to B. And therefore: Where J is, flux. The A, sectional area, from the definition of C: C A na A. a C J ν a[ C A CB ] b C A CB dc a dx B nb A. a وبما ان : () J ν ( n 6 And CA, CB is composition of zinc in both A and B. νa dc J. :. νa D b dc J D dx b dx The negative sign indicates that the flux direction is the direction of decreasing n. In comparison with equation (1) we get: - A n B 1 ). A Fick,s second Law
6 Δv A. Δx Where Δv is the size of the piece. The number of atoms inside the volume at a certain moment nδv n. A. Δx dj J A J A A. x dx dc J A J A. A. x dt dc dj dt dx dc J D dx dc dc D dt dx Solution of Fick,s second Law dc dt x u Dt dc du dc u. ( ) du dt du t dc dx dc du. du dx 1 dc. Dt du dc dx dc du du ) dx dc 1. du 4Dt dc d( ) du du ( dc dc u. du du
7 dc du y dc du :But dy udu y ln y - u + cte y Be u B is a constant dc y du Be u u اذن بما ان u C B e du + A 0 A is anther constant. erf (u) u e 0 u du u x Dt C A + Bref ( x ) Dt erf (u) function erf ( u) π u e 0 u du
8 π u e 0 u du. 0 erf (u) u + u e 0 u du 0 u 0 and π erf ( ) ( ) 1 π π erf ( ) ( ) 1 π erf (-u) -erf (u) Q-1
9 Q-
10
11
12 Q-3 Q-4
13 Q-5 Q-6
14
15 D D e Q / RT o (15).. "D": Diffusion coefficient Where Q represents the activation energy. The Do- diffusion constant, and be equal to ( ν a ). Table some of the values of D, Do, Q, for some metals and alloys. 3 x Q جول / مول D o متر / ثانیة D متر / ثانیة o 00 م x x 118 7, x 0, x 0,7 4, x x,6 9, x 0, x 0.5 منصھر Which can be written as the following: متر / ثانیة o 500 م , ,5 عملیة الانتشار المذیب D في المذاب Cu في Cu Fe (α ) في Fe Fe (α ) في C Fe (γ ) في C Fe (γ ) في Mn Fe (γ ) في Ni Cu في Zn Al في Cu ln D ln D o Q 1. R T k If a line chart decreed between ln D and inverted absolute temperature as in Figure () will get a straight line equal to his inclination, and since R is the gas constant, we will have a Q value easily. Since the intersection with the vertical coordinates, represents a ln Do, logarithmic tables, and we can get the value of Do.
16 معامل الانتشار الذاتي D سم / ثانیة 11- x 1.9 x 5 9 x x 5 7- x,68 Log D / كالفن /T k x 1.4 x 1.5 x 1.11 x 1 x درجة الحرارة T o K كالفن Figure () shows the relationship between the diffusion coefficient and the absolute temperature in some metals and alloys.
17 Q-7
18 Q-9 Q-8
19
20 types of transactions diffusion: - 1-Self-diffution It is intended that the diffusion of radioactive metal dissolved in the same non-radioactive metal, such as Ni * in Ni, and Ag * in Ag. in general,the self-diffusion equation as follows: D * self D * 0 self e * Q / RT 1- grain boundaries Diffusion The diffusion in fine g,b is greater than large g,b. Equation can be written as follows: D g. b D og. b e Qg. b / RT 1- grain boundaries Diffusion In general, the value of activation energy for the grain boundaries diffusion is half of the value of the Self-diffusion.
21 1 Q g. b Q From this we can deduce that the diffusion coefficient in the g.b will be larger than the diffusion coefficient of Self-diffusion. self D > D g. b self 3 - surface diffusion: - Which is diffusion along the surface of crystals and is usually faster than the g.b diffusion and the Self-diffusion We note that: Ds D s o Q / RT s Q < Q s < Qg. b self s > Dg, b D > D self
22 Phenomenon of Krkindal: -
23
24 pair diffusible of( copper nickel) alloy, was heated at 900 o c for a period of 40 hours,. If one of alloys was containing 40% a% nickel in place is located to the right of the surface interval, and the other alloy was containing 50% b% nickel in place is located to the left of the interface,find A The diffusion equation of copper nickel alloy B - the diffusion coefficient ( note that at a point about 0. cm from the boundary is 4.5% )? C - the time required to get the same concentration, but just 0.4 cm from the boundary? A - The first condition, at the beginning of the experiment time will be zero, and the concentration, is % b when X is negative., So the diffusion equation would be: x b% A + Berf ~ D 0 b% A + Berf ( ) b% A B The second condition, at the beginning of the experiment also be time zero, and the concentration is% a when X is positive, so the diffusion equation would be:
25 a% A + Berf + x D 0 a% A + Berf ( ) a % A + B a% + b% A a% b% B ~ N Ni a % + b% + a% b% N Ni 45% - 5% erf erf x ~ x ~ D. t D. t B - Upon passage of 40 hours, the concentration became 4.5%) at distance of 0. cm from the boundary. So: 4.5% 45% 5% erf x ~ D. t erf x D. t erf ( ) 0.5 D x cm D.563x sec
26 C - Since the concentration is fixed, 4.5% 45% 5% erf 4.5% 45% 5% erf x 1 ~ D. t x ~ 1 D. t x 1 t 1 1 erf ~ D. t D. t x t x 1 erf x ~ اذا :
Module 16. Diffusion in solids II. Lecture 16. Diffusion in solids II
 Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
Introduction To Materials Science FOR ENGINEERS, Ch. 5. Diffusion. MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5
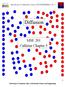 Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at
 Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS. IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5
 DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5 Diffusion The mechanism by which matter is transported through matter. It is related to internal atomic movement. Atomic movement;
DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5 Diffusion The mechanism by which matter is transported through matter. It is related to internal atomic movement. Atomic movement;
Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion
 Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion Mass transport in a gas or liquid generally involves the flow of fluid (e.g. convection
Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion Mass transport in a gas or liquid generally involves the flow of fluid (e.g. convection
Kinetics. Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces
 Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
EMA5001 Lecture 2 Interstitial Diffusion & Fick s 1 st Law. Prof. Zhe Cheng Mechanical & Materials Engineering Florida International University
 EMA500 Lecture Interstitial Diffusion & Fick s st Law Prof. Zhe Cheng Mechanical & Materials Engineering Florida International University Substitutional Diffusion Different possibilities Exchange Mechanis
EMA500 Lecture Interstitial Diffusion & Fick s st Law Prof. Zhe Cheng Mechanical & Materials Engineering Florida International University Substitutional Diffusion Different possibilities Exchange Mechanis
MSE 360 Exam 1 Spring Points Total
 MSE 360 Exam 1 Spring 011 105 Points otal Name(print) ID number No notes, books, or information stored in calculator memories may be used. he NCSU academic integrity policies apply to this exam. As such,
MSE 360 Exam 1 Spring 011 105 Points otal Name(print) ID number No notes, books, or information stored in calculator memories may be used. he NCSU academic integrity policies apply to this exam. As such,
water adding dye partial mixing homogenization time
 iffusion iffusion is a process of mass transport that involves the movement of one atomic species into another. It occurs by ranom atomic jumps from one position to another an takes place in the gaseous,
iffusion iffusion is a process of mass transport that involves the movement of one atomic species into another. It occurs by ranom atomic jumps from one position to another an takes place in the gaseous,
Appendix 4. Appendix 4A Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases
 Appendix 4 W-143 Appendix 4A Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases We can determine the heat capacity from the energy content of materials as a function of temperature. The simplest material to model is an ideal
Appendix 4 W-143 Appendix 4A Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases We can determine the heat capacity from the energy content of materials as a function of temperature. The simplest material to model is an ideal
Interfacial Defects. Grain Size Determination
 Interfacial Defects 4.27 For an FCC single crystal, would you expect the surface energy for a (00) plane to be greater or less than that for a () plane? Why? (Note: You may want to consult the solution
Interfacial Defects 4.27 For an FCC single crystal, would you expect the surface energy for a (00) plane to be greater or less than that for a () plane? Why? (Note: You may want to consult the solution
Diffusion. Diffusion = the spontaneous intermingling of the particles of two or more substances as a result of random thermal motion
 Diffusion Diffusion = the spontaneous intermingling of the particles of two or more substances as a result of random thermal motion Fick s First Law Γ ΔN AΔt Γ = flux ΔN = number of particles crossing
Diffusion Diffusion = the spontaneous intermingling of the particles of two or more substances as a result of random thermal motion Fick s First Law Γ ΔN AΔt Γ = flux ΔN = number of particles crossing
Diffusion. Diffusion. Diffusion in Solid Materials
 Atoms movements in materials Diffusion Movement of atoms in solids, liquids and gases is very important Eamples: Hardening steel, chrome-plating, gas reactions, Si wafers.. etc. We will study: Atomic mechanisms
Atoms movements in materials Diffusion Movement of atoms in solids, liquids and gases is very important Eamples: Hardening steel, chrome-plating, gas reactions, Si wafers.. etc. We will study: Atomic mechanisms
Diffusion in Dilute Alloys
 Chapter 3 Diffusion in Dilute Alloys Our discussion of the atomistic mechanisms for diffusion has been confined to the situations where the diffusing species is chemically identical to the host atom. We
Chapter 3 Diffusion in Dilute Alloys Our discussion of the atomistic mechanisms for diffusion has been confined to the situations where the diffusing species is chemically identical to the host atom. We
Oxidation & Reduction II. Suggested reading: Chapter 5
 Lecture 1 Oxidation & Reduction II Suggested reading: Chapter 5 Recall from Last time: Redox Potentials The Nernst equation: E cell E 0 RT F ln Q Cell Potential and ph For the H + /H couple at 1 bar and
Lecture 1 Oxidation & Reduction II Suggested reading: Chapter 5 Recall from Last time: Redox Potentials The Nernst equation: E cell E 0 RT F ln Q Cell Potential and ph For the H + /H couple at 1 bar and
= π + sin π = π + 0 = π, so the object is moving at a speed of π feet per second after π seconds. (c) How far does it go in π seconds?
 Mathematics 115 Professor Alan H. Stein April 18, 005 SOLUTIONS 1. Define what is meant by an antiderivative or indefinite integral of a function f(x). Solution: An antiderivative or indefinite integral
Mathematics 115 Professor Alan H. Stein April 18, 005 SOLUTIONS 1. Define what is meant by an antiderivative or indefinite integral of a function f(x). Solution: An antiderivative or indefinite integral
Physical Pharmacy. Diffusion
 Physical Pharmacy Diffusion Diffusion Diffusion is defined as a process of mass transfer of individual molecules of a substance brought about by random molecular motion and associated with a driving force
Physical Pharmacy Diffusion Diffusion Diffusion is defined as a process of mass transfer of individual molecules of a substance brought about by random molecular motion and associated with a driving force
Surface Physics Surface Diffusion. Assistant: Dr. Enrico Gnecco NCCR Nanoscale Science
 Surface Physics 008 8. Surface Diffusion Assistant: Dr. Enrico Gnecco NCCR Nanoscale Science Random-Walk Motion Thermal motion of an adatom on an ideal crystal surface: - Thermal excitation the adatom
Surface Physics 008 8. Surface Diffusion Assistant: Dr. Enrico Gnecco NCCR Nanoscale Science Random-Walk Motion Thermal motion of an adatom on an ideal crystal surface: - Thermal excitation the adatom
Module 17. Diffusion in solids III. Lecture 17. Diffusion in solids III
 Module 17 Diffusion in solids III Lecture 17 Diffusion in solids III 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Numerical problems in
Module 17 Diffusion in solids III Lecture 17 Diffusion in solids III 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Numerical problems in
Extrinsic Point Defects: Impurities
 Extrinsic Point Defects: Impurities Substitutional and interstitial impurities Sol solutions, solubility limit Entropy of ing, eal solution model Enthalpy of ing, quasi-chemical model Ideal and regular
Extrinsic Point Defects: Impurities Substitutional and interstitial impurities Sol solutions, solubility limit Entropy of ing, eal solution model Enthalpy of ing, quasi-chemical model Ideal and regular
Answers to Assigned Problems from Chapter 2
 Answers to Assigned Problems from Chapter 2 2.2. 1 mol of ice has a volume of 18.01 g/0.9168 g cm 3 = 19.64 cm 3 1 mol of water has a volume of 18.01 g/0.9998 g cm 3 = 18.01 cm 3 V(ice water) = 1.63 cm
Answers to Assigned Problems from Chapter 2 2.2. 1 mol of ice has a volume of 18.01 g/0.9168 g cm 3 = 19.64 cm 3 1 mol of water has a volume of 18.01 g/0.9998 g cm 3 = 18.01 cm 3 V(ice water) = 1.63 cm
MECH6661 lectures 6/1 Dr. M. Medraj Mech. Eng. Dept. - Concordia University. Fe3C (cementite)
 Outline Solid solution Gibbs free energy of binary solutions Ideal solution Chemical potential of an ideal solution Regular solutions Activity of a component Real solutions Equilibrium in heterogeneous
Outline Solid solution Gibbs free energy of binary solutions Ideal solution Chemical potential of an ideal solution Regular solutions Activity of a component Real solutions Equilibrium in heterogeneous
Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing
 Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing 1 APPENDIX A: H f, G f, BUT S (no Δ, no sub f ) Hº f Gº f Sº 2 Third Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of any perfect crystalline substance approaches
Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing 1 APPENDIX A: H f, G f, BUT S (no Δ, no sub f ) Hº f Gº f Sº 2 Third Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of any perfect crystalline substance approaches
Dopant Diffusion. (1) Predeposition dopant gas. (2) Drive-in Turn off dopant gas. dose control. Doped Si region
 Dopant Diffusion (1) Predeposition dopant gas dose control SiO Si SiO Doped Si region () Drive-in Turn off dopant gas or seal surface with oxide profile control (junction depth; concentration) SiO SiO
Dopant Diffusion (1) Predeposition dopant gas dose control SiO Si SiO Doped Si region () Drive-in Turn off dopant gas or seal surface with oxide profile control (junction depth; concentration) SiO SiO
100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals.
 2.21 Ionic Bonding 100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals. Forming ions Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. Non-metal
2.21 Ionic Bonding 100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals. Forming ions Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. Non-metal
Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction
 Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
Physical Chemistry I CHEM 4641 Final Exam 13 questions, 30 points
 Physical Chemistry I CHEM 4641 Final Exam 13 questions, 30 points Name: KEY Gas constant: R = 8.314 J mol -1 K -1 = 0.008314 kj mol -1 K -1. Boltzmann constant k = 1.381 10-23 J/K = 0.6950 cm -1 /K h =
Physical Chemistry I CHEM 4641 Final Exam 13 questions, 30 points Name: KEY Gas constant: R = 8.314 J mol -1 K -1 = 0.008314 kj mol -1 K -1. Boltzmann constant k = 1.381 10-23 J/K = 0.6950 cm -1 /K h =
EE 143 Microfabrication Technology Fall 2014
 EE 143 Microfabrication Technology Fall 2014 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 EE 143: Microfabrication
EE 143 Microfabrication Technology Fall 2014 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 EE 143: Microfabrication
Transport of Chemicals, Kinetics, and Equilibrium
 Transport of Chemicals, Kinetics, and Equilibrium Module 1: Basic Concepts, Lecture Chemical Fate and Transport in the Environment, nd edition. H.F. Hemond and E.J. Fechner-Levy. Academic Press. London.
Transport of Chemicals, Kinetics, and Equilibrium Module 1: Basic Concepts, Lecture Chemical Fate and Transport in the Environment, nd edition. H.F. Hemond and E.J. Fechner-Levy. Academic Press. London.
5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible. 26 Fe Cu Ni Co Pd Ag Ru 101.
 Physical Chemistry II Lab CHEM 4644 spring 2017 final exam KEY 5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible h = 6.626 10-34 J s c = 3.00 10 8 m/s 1 GHz = 10 9 s -1. B= h 8π 2 I ν= 1 2 π k μ 6 P
Physical Chemistry II Lab CHEM 4644 spring 2017 final exam KEY 5 questions, 3 points each, 15 points total possible h = 6.626 10-34 J s c = 3.00 10 8 m/s 1 GHz = 10 9 s -1. B= h 8π 2 I ν= 1 2 π k μ 6 P
The relevant half cell reactions and potentials are: Calculate the equilibrium constant, K, for the reaction at 25 C. lnk
 CHEM1405 2004-J-3 June 2004 Calculate the initial cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction at 25 C from the standard electrode potentials. Assume the concentration of all species is initially
CHEM1405 2004-J-3 June 2004 Calculate the initial cell potential for the following unbalanced reaction at 25 C from the standard electrode potentials. Assume the concentration of all species is initially
1.1 Atomic Structure Details of the three Sub-atomic (fundamental) Particles
 1.1 Atomic Structure Details of the three Sub-atomic (fundamental) Particles Particle Position Relative Mass Relative Charge Proton Nucleus 1 +1 Neutron Nucleus 1 0 Electron Orbitals 1/1840-1 An atom of
1.1 Atomic Structure Details of the three Sub-atomic (fundamental) Particles Particle Position Relative Mass Relative Charge Proton Nucleus 1 +1 Neutron Nucleus 1 0 Electron Orbitals 1/1840-1 An atom of
1 Electrons and Chemical Bonding
 CHAPTER 13 1 Electrons and Chemical Bonding SECTION Chemical Bonding BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is chemical bonding? What are valence
CHAPTER 13 1 Electrons and Chemical Bonding SECTION Chemical Bonding BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is chemical bonding? What are valence
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II. Partial Properties of Solutions
 MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Partial Properties of Solutions A total property of a system consisting of multiple substances is represented as nm = n i M i If the system consists of a liquid
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Partial Properties of Solutions A total property of a system consisting of multiple substances is represented as nm = n i M i If the system consists of a liquid
MATSCI 204 Thermodynamics and Phase Equilibria Winter Chapter #4 Practice problems
 MATSCI 204 Thermodynamics and Phase Equilibria Winter 2013 Chapter #4 Practice problems Problem: 1-Show that for any extensive property Ω of a binary system A-B: d ( "# ) "# B, = "# + 1$ x B 2- If "# has
MATSCI 204 Thermodynamics and Phase Equilibria Winter 2013 Chapter #4 Practice problems Problem: 1-Show that for any extensive property Ω of a binary system A-B: d ( "# ) "# B, = "# + 1$ x B 2- If "# has
Electrochemical Cells at Non-Standard Conditions
 Electrochemical Cells at Non-Standard Conditions Oxidation-reduction reactions in the real world rarely occur under standard conditions. Even if the cell started out with all dissolved species at 1M concentration,
Electrochemical Cells at Non-Standard Conditions Oxidation-reduction reactions in the real world rarely occur under standard conditions. Even if the cell started out with all dissolved species at 1M concentration,
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions Reactions in which electrons are transferred from one reactant to another oxidation the loss of electrons reduction the gainof electrons LEO the lion says GER Oxidation
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions Reactions in which electrons are transferred from one reactant to another oxidation the loss of electrons reduction the gainof electrons LEO the lion says GER Oxidation
CHEM 4641 Fall questions worth a total of 32 points. Show your work, except on multiple-choice questions. 1 V α=
 Physical Chemistry I Final Exam Name: KEY CHEM 4641 Fall 017 15 questions worth a total of 3 points. Show your work, except on multiple-choice questions. 1 V 1 V α= κt = V T P V P T Gas constant R = 8.314
Physical Chemistry I Final Exam Name: KEY CHEM 4641 Fall 017 15 questions worth a total of 3 points. Show your work, except on multiple-choice questions. 1 V 1 V α= κt = V T P V P T Gas constant R = 8.314
3. APLICATION OF GIBBS-DUHEM EQUATION
 3. APLICATION OF GIBBS-DUHEM EQUATION Gibbs-Duhem Equation When extensive property of a solution is given by; Q' = Q'(T,P,n,n...) The change in extensive property with composition was; dq Q n dn Q n dn
3. APLICATION OF GIBBS-DUHEM EQUATION Gibbs-Duhem Equation When extensive property of a solution is given by; Q' = Q'(T,P,n,n...) The change in extensive property with composition was; dq Q n dn Q n dn
Part I.
 Part I bblee@unimp . Introduction to Mass Transfer and Diffusion 2. Molecular Diffusion in Gasses 3. Molecular Diffusion in Liquids Part I 4. Molecular Diffusion in Biological Solutions and Gels 5. Molecular
Part I bblee@unimp . Introduction to Mass Transfer and Diffusion 2. Molecular Diffusion in Gasses 3. Molecular Diffusion in Liquids Part I 4. Molecular Diffusion in Biological Solutions and Gels 5. Molecular
Statistical and Thermal Physics. Problem Set 5
 Statistical and Thermal Physics xford hysics Second year physics course Dr A. A. Schekochihin and Prof. A. T. Boothroyd (with thanks to Prof. S. J. Blundell Problem Set 5 Some useful constants Boltzmann
Statistical and Thermal Physics xford hysics Second year physics course Dr A. A. Schekochihin and Prof. A. T. Boothroyd (with thanks to Prof. S. J. Blundell Problem Set 5 Some useful constants Boltzmann
Long-Term Atomistic Simulation of Heat and Mass Transport
 Long-Term Atomistic Simulation of Heat and Mass Transport Kevin G. Wang 1, Mauricio Ponga 2, Michael Ortiz 2 1 Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Long-Term Atomistic Simulation of Heat and Mass Transport Kevin G. Wang 1, Mauricio Ponga 2, Michael Ortiz 2 1 Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Experiment 7: Understanding Crystal Structures
 Experiment 7: Understanding Crystal Structures To do well in this laboratory experiment you need to be familiar with the concepts of lattice, crystal structure, unit cell, coordination number, the different
Experiment 7: Understanding Crystal Structures To do well in this laboratory experiment you need to be familiar with the concepts of lattice, crystal structure, unit cell, coordination number, the different
Theory of Electromigration
 Theory of Electromigration Electromigration is the transport of material in a conductor under the influence of an applied electric field. All conductors are susceptible to electromigration, therefore it
Theory of Electromigration Electromigration is the transport of material in a conductor under the influence of an applied electric field. All conductors are susceptible to electromigration, therefore it
III.6. METAL SEMICONDUCTOR CONTACT BIAS
 .6. MEAL SEMCONUCOR CONAC BAS 1. Work purpose he determination of the potential difference that appears at the contact surface between a metal and a semiconductor, potential difference that is known under
.6. MEAL SEMCONUCOR CONAC BAS 1. Work purpose he determination of the potential difference that appears at the contact surface between a metal and a semiconductor, potential difference that is known under
12-8 Taking the oxidation state of H as + 1 and that of O as - 2, the order of increasing oxidation state of the carbon atoms is
 12-1 idation occurs when an atom or molecule loses electrons in the course of a reaction. Reduction occurs when an atom or molecule gains electrons in the course of a reaction. 12-4 (a) The Zn 2+ is reduced
12-1 idation occurs when an atom or molecule loses electrons in the course of a reaction. Reduction occurs when an atom or molecule gains electrons in the course of a reaction. 12-4 (a) The Zn 2+ is reduced
UNIT VIII d & f Block Elements ( 5 : MARKS)
 TEACHER RIENTED UNIT VIII d & f Block Elements ( 5 : MARKS) 1) Electronic configuration ) ccurrence and General characteristics of transition elements ) General trends in properties ) Preparation and properties
TEACHER RIENTED UNIT VIII d & f Block Elements ( 5 : MARKS) 1) Electronic configuration ) ccurrence and General characteristics of transition elements ) General trends in properties ) Preparation and properties
1. The accumulated net change function or area-so-far function
 Name: Section: Names of collaborators: Main Points: 1. The accumulated net change function ( area-so-far function) 2. Connection to antiderivative functions: the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 3. Evaluating
Name: Section: Names of collaborators: Main Points: 1. The accumulated net change function ( area-so-far function) 2. Connection to antiderivative functions: the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 3. Evaluating
CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Concepts of Stress and Strain 6.1 Using mechanics of materials principles (i.e., equations of mechanical equilibrium applied to a free-body diagram),
CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Concepts of Stress and Strain 6.1 Using mechanics of materials principles (i.e., equations of mechanical equilibrium applied to a free-body diagram),
Diffusion and Ion implantation Reference: Chapter 4 Jaeger or Chapter 3 Ruska N & P Dopants determine the resistivity of material Note N lower
 Diffusion and Ion implantation Reference: Chapter 4 Jaeger or Chapter 3 Ruska N & P Dopants determine the resistivity of material Note N lower resistavity than p: due to higher carrier mobility Near linear
Diffusion and Ion implantation Reference: Chapter 4 Jaeger or Chapter 3 Ruska N & P Dopants determine the resistivity of material Note N lower resistavity than p: due to higher carrier mobility Near linear
Prelim 2 Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 90 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck!
 April 4, Prelim Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Trigonometric Formulas sin x sin x cos x cos (u + v) cos
April 4, Prelim Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Trigonometric Formulas sin x sin x cos x cos (u + v) cos
Electrochemistry. To use principles of electrochemistry to understand the properties of electrochemical cells and electrolysis.
 Electrochemistry Objectives: To use principles of electrochemistry to understand the properties of electrochemical cells and electrolysis. Background: Part I: Galvanic Cells: A Galvanic cell is a device
Electrochemistry Objectives: To use principles of electrochemistry to understand the properties of electrochemical cells and electrolysis. Background: Part I: Galvanic Cells: A Galvanic cell is a device
Topics in the November 2014 Exam Paper for CHEM1101
 November 2014 Topics in the November 2014 Exam Paper for CHEM1101 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2014-N-2: 2014-N-3: 2014-N-4: 2014-N-5: 2014-N-7: 2014-N-8: 2014-N-9: 2014-N-10: 2014-N-11:
November 2014 Topics in the November 2014 Exam Paper for CHEM1101 Click on the links for resources on each topic. 2014-N-2: 2014-N-3: 2014-N-4: 2014-N-5: 2014-N-7: 2014-N-8: 2014-N-9: 2014-N-10: 2014-N-11:
which has an equilibrium constant of Which of the following diagrams represents a mixture of the reaction at equilibrium?
 Chapter 9 Quiz: Chemical Equilibria 1. Which of the following statements is true regarding chemical equilibrium? I. The concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium are constant, which means
Chapter 9 Quiz: Chemical Equilibria 1. Which of the following statements is true regarding chemical equilibrium? I. The concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium are constant, which means
UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
Investigations of the effects of 7 TeV proton beams on LHC collimator materials and other materials to be used in the LHC
 Russian Research Center Kurchatov Institute Investigations of the effects of 7 ev proton beams on LHC collimator materials and other materials to be used in the LHC A.I.Ryazanov Aims of Investigations:
Russian Research Center Kurchatov Institute Investigations of the effects of 7 ev proton beams on LHC collimator materials and other materials to be used in the LHC A.I.Ryazanov Aims of Investigations:
t = no of steps of length s
 s t = no of steps of length s Figure : Schematic of the path of a diffusing molecule, for example, one in a gas or a liquid. The particle is moving in steps of length s. For a molecule in a liquid the
s t = no of steps of length s Figure : Schematic of the path of a diffusing molecule, for example, one in a gas or a liquid. The particle is moving in steps of length s. For a molecule in a liquid the
1.1 Atomic Structure Details of the three Sub-atomic (fundamental) Particles
 1.1 Atomic Structure Details of the three Sub-atomic (fundamental) Particles Particle Position Relative Mass Relative Charge Proton Nucleus 1 +1 Neutron Nucleus 1 0 Electron Orbitals 1/1800-1 An atom of
1.1 Atomic Structure Details of the three Sub-atomic (fundamental) Particles Particle Position Relative Mass Relative Charge Proton Nucleus 1 +1 Neutron Nucleus 1 0 Electron Orbitals 1/1800-1 An atom of
Thermodynamic and Stochiometric Principles in Materials Balance
 Thermodynamic and Stochiometric Principles in Materials Balance Typical metallurgical engineering problems based on materials and energy balance NiO is reduced in an open atmosphere furnace by excess carbon
Thermodynamic and Stochiometric Principles in Materials Balance Typical metallurgical engineering problems based on materials and energy balance NiO is reduced in an open atmosphere furnace by excess carbon
OCN 623: Thermodynamic Laws & Gibbs Free Energy. or how to predict chemical reactions without doing experiments
 OCN 623: Thermodynamic Laws & Gibbs Free Energy or how to predict chemical reactions without doing experiments Definitions Extensive properties Depend on the amount of material e.g. # of moles, mass or
OCN 623: Thermodynamic Laws & Gibbs Free Energy or how to predict chemical reactions without doing experiments Definitions Extensive properties Depend on the amount of material e.g. # of moles, mass or
Diffusione nei solidi: teoria e applicazioni a materiali avanzati
 Università Ca Foscari Venezia Diffusione nei solidi: teoria e applicazioni a materiali avanzati Prof. Elti Cattaruzza Department of Molecular Sciences and Nanosystems, Università Ca Foscari Venezia, via
Università Ca Foscari Venezia Diffusione nei solidi: teoria e applicazioni a materiali avanzati Prof. Elti Cattaruzza Department of Molecular Sciences and Nanosystems, Università Ca Foscari Venezia, via
4. Thermal properties of solids. Time to study: 4 hours. Lecture Oscillations of the crystal lattice
 4. Thermal properties of solids Time to study: 4 hours Objective After studying this chapter you will get acquainted with a description of oscillations of atoms learn how to express heat capacity for different
4. Thermal properties of solids Time to study: 4 hours Objective After studying this chapter you will get acquainted with a description of oscillations of atoms learn how to express heat capacity for different
Diffusion in multicomponent solids. Anton Van der Ven Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI
 Diffusion in multicomponent solids nton Van der Ven Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Michigan nn rbor, MI Coarse graining time Diffusion in a crystal Two levels of time coarse
Diffusion in multicomponent solids nton Van der Ven Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Michigan nn rbor, MI Coarse graining time Diffusion in a crystal Two levels of time coarse
Name: SOLUTIONS Date: 11/9/2017. M20550 Calculus III Tutorial Worksheet 8
 Name: SOLUTIONS Date: /9/7 M55 alculus III Tutorial Worksheet 8. ompute R da where R is the region bounded by x + xy + y 8 using the change of variables given by x u + v and y v. Solution: We know R is
Name: SOLUTIONS Date: /9/7 M55 alculus III Tutorial Worksheet 8. ompute R da where R is the region bounded by x + xy + y 8 using the change of variables given by x u + v and y v. Solution: We know R is
Lab #14: Electrochemical Cells
 Lab #14: Electrochemical Cells Objectives: 1. To understand the nature of electrochemical cells. 2. To construct a table listing the reduction potentials of a series of metal ions, in order of ease of
Lab #14: Electrochemical Cells Objectives: 1. To understand the nature of electrochemical cells. 2. To construct a table listing the reduction potentials of a series of metal ions, in order of ease of
Distinguish between. and non-thermal energy sources.
 Distinguish between System & Surroundings We also distinguish between thermal We also distinguish between thermal and non-thermal energy sources. P Work The gas in the cylinder is the system How much work
Distinguish between System & Surroundings We also distinguish between thermal We also distinguish between thermal and non-thermal energy sources. P Work The gas in the cylinder is the system How much work
Atoms, electrons and Solids
 Atoms, electrons and Solids Shell model of an atom negative electron orbiting a positive nucleus QM tells that to minimize total energy the electrons fill up shells. Each orbit in a shell has a specific
Atoms, electrons and Solids Shell model of an atom negative electron orbiting a positive nucleus QM tells that to minimize total energy the electrons fill up shells. Each orbit in a shell has a specific
1.8 Thermodynamics. Lattice formation enthalpy Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions
 1.8 Thermodynamics Review: In 1.3 we looked at ionic bonding and learned that: Giant ionic lattice structure Ionic bonding: Strong electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions that
1.8 Thermodynamics Review: In 1.3 we looked at ionic bonding and learned that: Giant ionic lattice structure Ionic bonding: Strong electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions that
Diffusion of a density in a static fluid
 Diffusion of a density in a static fluid u(x, y, z, t), density (M/L 3 ) of a substance (dye). Diffusion: motion of particles from places where the density is higher to places where it is lower, due to
Diffusion of a density in a static fluid u(x, y, z, t), density (M/L 3 ) of a substance (dye). Diffusion: motion of particles from places where the density is higher to places where it is lower, due to
Chapter 5: Diffusion (2)
 Chapter 5: Diffusin () ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Nn-steady state diffusin and Fick s nd Law Hw des diffusin depend n structure? Chapter 5-1 Class Eercise (1) Put a sugar cube inside a cup f pure water, rughly
Chapter 5: Diffusin () ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Nn-steady state diffusin and Fick s nd Law Hw des diffusin depend n structure? Chapter 5-1 Class Eercise (1) Put a sugar cube inside a cup f pure water, rughly
MATH 2433 Homework 1
 MATH 433 Homework 1 1. The sequence (a i ) is defined recursively by a 1 = 4 a i+1 = 3a i find a closed formula for a i in terms of i.. In class we showed that the Fibonacci sequence (a i ) defined by
MATH 433 Homework 1 1. The sequence (a i ) is defined recursively by a 1 = 4 a i+1 = 3a i find a closed formula for a i in terms of i.. In class we showed that the Fibonacci sequence (a i ) defined by
Chapter 1 -- Introduction to Qualitative Analysis. NAME: Lab Section: Date: Sign-Off:
 Chapter 1 -- Introduction to Qualitative Analysis NAME: Lab Section: Date: Sign-Off: Chapter 1 -- Introduction to Qualitative Analysis Introduction Qualitative analysis is a way inorganic chemists have
Chapter 1 -- Introduction to Qualitative Analysis NAME: Lab Section: Date: Sign-Off: Chapter 1 -- Introduction to Qualitative Analysis Introduction Qualitative analysis is a way inorganic chemists have
1. Electronic configuration of a transition element X in +3 oxidation state is [Ar]3d 5. What is its atomic number? (i) 25 (ii) 26 (iii) 27 (iv) 24
![1. Electronic configuration of a transition element X in +3 oxidation state is [Ar]3d 5. What is its atomic number? (i) 25 (ii) 26 (iii) 27 (iv) 24 1. Electronic configuration of a transition element X in +3 oxidation state is [Ar]3d 5. What is its atomic number? (i) 25 (ii) 26 (iii) 27 (iv) 24](/thumbs/84/89512424.jpg) Unit 8 The d- and f- Block Elements I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Electronic configuration of a transition element X in +3 oxidation state is [Ar]3d 5. What is its atomic number? 25 26 27 24
Unit 8 The d- and f- Block Elements I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Electronic configuration of a transition element X in +3 oxidation state is [Ar]3d 5. What is its atomic number? 25 26 27 24
ChemGGuru. JEE Main Online Exam 2019 [Memory Based Paper] Questions & Answer. Morning 9 th January 2019 CHEMISTRY
![ChemGGuru. JEE Main Online Exam 2019 [Memory Based Paper] Questions & Answer. Morning 9 th January 2019 CHEMISTRY ChemGGuru. JEE Main Online Exam 2019 [Memory Based Paper] Questions & Answer. Morning 9 th January 2019 CHEMISTRY](/thumbs/95/126342984.jpg) CAREER PINT ChemGGuru JEE Main nline Exam 019 [Memory Based Paper] Questions & Answer Morning 9 th January 019 CHEMISTRY Q.1 What is the correct order of acidic-strength? N CH CH ( I) NC CH( CH II) F CH
CAREER PINT ChemGGuru JEE Main nline Exam 019 [Memory Based Paper] Questions & Answer Morning 9 th January 019 CHEMISTRY Q.1 What is the correct order of acidic-strength? N CH CH ( I) NC CH( CH II) F CH
Inspection Documents for Type 2.1 Coverage:
 Inspection Documents for Type 2.1 Coverage: Python Chemical Injection Pumps Date: Size: Description: Table of contents: March 8th, 2018 13 (1/8 Plunger) PCI-xxx-13x-xx-x Certificate of Material Test Certification
Inspection Documents for Type 2.1 Coverage: Python Chemical Injection Pumps Date: Size: Description: Table of contents: March 8th, 2018 13 (1/8 Plunger) PCI-xxx-13x-xx-x Certificate of Material Test Certification
- A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of electron density, making it have ends (poles) that are slightly charged.
 POLARITY and shape: - A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of electron density, making it have ends (poles) that are slightly charged. POLARITY influences several easily observable properties. -
POLARITY and shape: - A polar molecule has an uneven distribution of electron density, making it have ends (poles) that are slightly charged. POLARITY influences several easily observable properties. -
TRANSPORT PHENOMENON FICK S LAW OF DIFFUSION ATP-POWERED PUMPS -II-
 TRANSPORT PHENOMENON FICK S LAW OF DIFFUSION ATP-POWERED PUMPS -II- Yalçın İŞLER, PhD Izmir Katip Celebi University Department of Biomedical Engineering islerya@yahoo.com DIFFUSION Diffusion describes
TRANSPORT PHENOMENON FICK S LAW OF DIFFUSION ATP-POWERED PUMPS -II- Yalçın İŞLER, PhD Izmir Katip Celebi University Department of Biomedical Engineering islerya@yahoo.com DIFFUSION Diffusion describes
Inspection Documents for Type 2.1 Coverage:
 Inspection Documents for Type 2.1 Coverage: Python XL Chemical Injection Pumps Date: Size: Description: Table of contents: September 8th, 2017 19 (3/16 Plunger) PCI-xxx-25x-xx-x Certificate of Material
Inspection Documents for Type 2.1 Coverage: Python XL Chemical Injection Pumps Date: Size: Description: Table of contents: September 8th, 2017 19 (3/16 Plunger) PCI-xxx-25x-xx-x Certificate of Material
Properties of Error Function erf(z) And Complementary Error Function erfc(z)
 Properties of Error Function erf(z) And Complementary Error Function erfc(z) z erf (z) π e -y dy erfc (z) 1 - erf (z) erf () erf( ) 1 erf(- ) - 1 erf (z) d erf(z) dz π z for z
Properties of Error Function erf(z) And Complementary Error Function erfc(z) z erf (z) π e -y dy erfc (z) 1 - erf (z) erf () erf( ) 1 erf(- ) - 1 erf (z) d erf(z) dz π z for z
Exam Thermodynamics 12 April 2018
 1 Exam Thermodynamics 12 April 2018 Please, hand in your answers to problems 1, 2, 3 and 4 on separate sheets. Put your name and student number on each sheet. The examination time is 12:30 until 15:30.
1 Exam Thermodynamics 12 April 2018 Please, hand in your answers to problems 1, 2, 3 and 4 on separate sheets. Put your name and student number on each sheet. The examination time is 12:30 until 15:30.
The critical temperature of superconductor and its electronic specific heat
 arxiv:1008.1446v1 [physics.gen-ph] 9 Aug 2010 The critical temperature of superconductor and its electronic specific heat 1 Introduction B.V.Vasiliev The task of the critical parameters of a superconductor
arxiv:1008.1446v1 [physics.gen-ph] 9 Aug 2010 The critical temperature of superconductor and its electronic specific heat 1 Introduction B.V.Vasiliev The task of the critical parameters of a superconductor
Convective Mass Transfer
 Convective Mass Transfer Definition of convective mass transfer: The transport of material between a boundary surface and a moving fluid or between two immiscible moving fluids separated by a mobile interface
Convective Mass Transfer Definition of convective mass transfer: The transport of material between a boundary surface and a moving fluid or between two immiscible moving fluids separated by a mobile interface
collisions of electrons. In semiconductor, in certain temperature ranges the conductivity increases rapidly by increasing temperature
 1.9. Temperature Dependence of Semiconductor Conductivity Such dependence is one most important in semiconductor. In metals, Conductivity decreases by increasing temperature due to greater frequency of
1.9. Temperature Dependence of Semiconductor Conductivity Such dependence is one most important in semiconductor. In metals, Conductivity decreases by increasing temperature due to greater frequency of
Chapter 6: Messy Integrals
 Chapter 6: Messy Integrals Review: Solve the following integrals x 4 sec x tan x 0 0 Find the average value of 3 1 x 3 3 Evaluate 4 3 3 ( x 1), then find the area of ( x 1) 4 Section 6.1: Slope Fields
Chapter 6: Messy Integrals Review: Solve the following integrals x 4 sec x tan x 0 0 Find the average value of 3 1 x 3 3 Evaluate 4 3 3 ( x 1), then find the area of ( x 1) 4 Section 6.1: Slope Fields
Series solutions of second order linear differential equations
 Series solutions of second order linear differential equations We start with Definition 1. A function f of a complex variable z is called analytic at z = z 0 if there exists a convergent Taylor series
Series solutions of second order linear differential equations We start with Definition 1. A function f of a complex variable z is called analytic at z = z 0 if there exists a convergent Taylor series
Supporting Information. DFT Study of Methane Synthesis from Syngas on Ce Doped Ni(111) Surface
 Supporting Information DFT Study of Methane Synthesis from Syngas on Ce Doped Ni(111) Surface Kai Li, 1 Cong Yin, 2 Yi Zheng, 3 Feng He, 1 Ying Wang, 1 Menggai Jiao, 1 Hao Tang, 2,* Zhijian Wu 1,* 1 State
Supporting Information DFT Study of Methane Synthesis from Syngas on Ce Doped Ni(111) Surface Kai Li, 1 Cong Yin, 2 Yi Zheng, 3 Feng He, 1 Ying Wang, 1 Menggai Jiao, 1 Hao Tang, 2,* Zhijian Wu 1,* 1 State
Lecture 15: Optoelectronic devices: Introduction
 Lecture 15: Optoelectronic devices: Introduction Contents 1 Optical absorption 1 1.1 Absorption coefficient....................... 2 2 Optical recombination 5 3 Recombination and carrier lifetime 6 3.1
Lecture 15: Optoelectronic devices: Introduction Contents 1 Optical absorption 1 1.1 Absorption coefficient....................... 2 2 Optical recombination 5 3 Recombination and carrier lifetime 6 3.1
Math 212-Lecture 20. P dx + Qdy = (Q x P y )da. C
 15. Green s theorem Math 212-Lecture 2 A simple closed curve in plane is one curve, r(t) : t [a, b] such that r(a) = r(b), and there are no other intersections. The positive orientation is counterclockwise.
15. Green s theorem Math 212-Lecture 2 A simple closed curve in plane is one curve, r(t) : t [a, b] such that r(a) = r(b), and there are no other intersections. The positive orientation is counterclockwise.
Analysis of the simulation
 Analysis of the simulation Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař January 7, 2014 Thermodynamic properties time averages of thermodynamic quantites correspond to ensemble averages (ergodic theorem) some quantities
Analysis of the simulation Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař January 7, 2014 Thermodynamic properties time averages of thermodynamic quantites correspond to ensemble averages (ergodic theorem) some quantities
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *4711189762* CEMISTRY 5070/41 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical October/November 2013 1 hour Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *4711189762* CEMISTRY 5070/41 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical October/November 2013 1 hour Candidates
So far changes in the state of systems that occur within the restrictions of the first law of thermodynamics were considered:
 Entropy So far changes in the state of systems that occur within the restrictions of the first law of thermodynamics were considered: Energy is transferred from one state to another by any possible forms,
Entropy So far changes in the state of systems that occur within the restrictions of the first law of thermodynamics were considered: Energy is transferred from one state to another by any possible forms,
PHOTOELECTRON SPECTROSCOPY PROBLEMS:
 PHOTOELECTRON SPECTROSCOPY PROBLEMS: 1. A hydrogen atom in its ground state is irradiated with 80 nm radiation. What is the kinetic energy (in ev) of the ejected photoelectron? Useful formulae: ν = c/λ
PHOTOELECTRON SPECTROSCOPY PROBLEMS: 1. A hydrogen atom in its ground state is irradiated with 80 nm radiation. What is the kinetic energy (in ev) of the ejected photoelectron? Useful formulae: ν = c/λ
CHEM J-14 June 2014
 CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
Introduction to Semiconductor Physics. Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India
 Introduction to Semiconductor Physics 1 Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India http://folk.uio.no/ravi/cmp2013 Review of Semiconductor Physics Semiconductor fundamentals
Introduction to Semiconductor Physics 1 Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India http://folk.uio.no/ravi/cmp2013 Review of Semiconductor Physics Semiconductor fundamentals
Chemistry STD-XII-Science-Top concepts and Notes on d and f block elements. The d and f-block Elements Top 15 Concepts
 The d and f-block Elements Top 15 Concepts 1. d -Block elements: The elements lying in the middle of periodic table belonging to groups 3 to 12 are known as d block elements. Their general electronic configuration
The d and f-block Elements Top 15 Concepts 1. d -Block elements: The elements lying in the middle of periodic table belonging to groups 3 to 12 are known as d block elements. Their general electronic configuration
Review for Chapter 4: Structures and Properties of Substances
 Review for Chapter 4: Structures and Properties of Substances You are responsible for the following material: 1. Terms: You should be able to write definitions for the following terms. A complete definition
Review for Chapter 4: Structures and Properties of Substances You are responsible for the following material: 1. Terms: You should be able to write definitions for the following terms. A complete definition
Spring 2011 solutions. We solve this via integration by parts with u = x 2 du = 2xdx. This is another integration by parts with u = x du = dx and
 Math - 8 Rahman Final Eam Practice Problems () We use disks to solve this, Spring solutions V π (e ) d π e d. We solve this via integration by parts with u du d and dv e d v e /, V π e π e d. This is another
Math - 8 Rahman Final Eam Practice Problems () We use disks to solve this, Spring solutions V π (e ) d π e d. We solve this via integration by parts with u du d and dv e d v e /, V π e π e d. This is another
CHEM J-14 June 2014
 CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
Hydrated nickel(ii) salts are green in colour. Give the electron configuration of a nickel(ii) ion and hence state why the ion is coloured.
 1. This question is about nickel compounds. (a) Hydrated nickel(ii) salts are green in colour. Give the electron configuration of a nickel(ii) ion and hence state why the ion is coloured.......... (b)
1. This question is about nickel compounds. (a) Hydrated nickel(ii) salts are green in colour. Give the electron configuration of a nickel(ii) ion and hence state why the ion is coloured.......... (b)
The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4)
 The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4) First Law: Energy of universe is constant: ΔE system = - ΔE surroundings Second Law: New variable, S, entropy. Changes in S, ΔS, tell us which processes made
The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4) First Law: Energy of universe is constant: ΔE system = - ΔE surroundings Second Law: New variable, S, entropy. Changes in S, ΔS, tell us which processes made
