Theory of Electromigration
|
|
|
- Daniel Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Theory of Electromigration Electromigration is the transport of material in a conductor under the influence of an applied electric field. All conductors are susceptible to electromigration, therefore it is important to consider the effects the electrical current resulting from the applied field may have on the conductor. The net force exerted on a single metal ion in a conductor has two opposing contributions: a direct force and wind force. Direct Force Application of an electric field results in an electrostatic pull being exerted on the metal ion core. The direction and magnitude of the electrostatic pull depend on the charge on the ion core, modified by screening effects. Positively charged ion cores (cations) are pulled towards the cathode, whilst negatively charged ion cores (anions) are pulled towards the anode. The direct force, F d, is given by: F d = azee = azejρ where a = factor accounting for screening (a<<1); Z = actual valence of the atom; e = electron charge (1.6 x C); j = current density (A m -2 );ρ = resistivity (Ω m). When electromigration in conductors was discovered, it was thought that the migration effects would be analogous to those in liquid electrolysis. Consider for example, the electrolysis of the molten salt, NaCl. The Na + ions move towards the cathode, whilst the Cl ions move towards the anode (as shown in the diagram below), as the electric field is applied.
2 It was thought that the metal ions within a wire would always move towards the cathode as in electrolysis. While this is found in some cases, in the metallization of interest for ICs (which are based on good metal conductors) the migration was observed to be in the opposite direction towards the anode. This startling effect results from the wind force. Wind Force Electrons move along the metallization line, carrying the current. These electrons tend to scatter. Electron scattering takes place at imperfections within the lattice: vacancies, impurities, grain boundaries, dislocations and even phonon vibrations of the metal ions from their ideal positions! The scattering of electrons gives us electrical resistance but it also results in a force exerted on the metal ion core. An electron changes direction as a result of a scattering event. This change in direction is accompanied by an acceleration, which results in a force. The electrons are also accelerated within the electric field. When the overall electron drift velocity is established, the force on the
3 ions due to electron scattering is in the direction of the electron flow this is known as the wind force, F w, which can be described as: F w = en e λσ i E where n e = density of electrons;σ i = cross-section for collision; λ = mean free path. The term electron wind comes from an analogy with, for example, a tree being blown in the wind. The wind is analogous to the electron current, the leaves on the tree to the metal ions in a conductor. Net Force In good conductors, such as the ones used in IC metallization, the electron wind force is the dominant force felt by the ion cores, resulting in atomic migration towards the anode. The net force on the ions can be represented as: F net = F wind +F direct = ( Z w + Z d ) ejρ = Z * ejρ where Z wind, Z direct and Z * respectively refer to the effective valences for the wind force, direct force and the net force. Diffusion The migration of the metal ion cores occurs by diffusive jumps. In the cases of interest in metallization, this is self-diffusion or substitutional diffusion by the vacancy mechanism. To find out more about diffusion, refer to Diffusion in the MATTER Software.
4 The rate of diffusion is described by the diffusion coefficient (or diffusivity) with units of m 2 s 1. The diffusivity, D, has an Arrhenius dependence on temperature according to: D = D 0 exp ( Q/RT) where D 0 = constant (m 2 s 1 ); Q = activation energy for diffusion (J mol 1 ); R = gas constant (8.314 J mol 1 K 1 ); T = absolute temperature (K). The diffusion coefficient and the activation energy are dependent on the nature of the material. We depict above a 2-D section through a simple cubic metallic lattice showing a single vacant site. The vacancy can jump into either position 1, 2, 3 or 4 (i.e. it can exchange position with the atom in position 1, 2, 3 or 4). Without any external influence, the probability of the vacancy jumping into each site is equal, as its energy on every site is the same and the activation energy for a jump from site to site is always the same. When an electric field is applied, the activation energies for a jump into sites 1 and 2 remain identical, whereas the activation energy for a jump into site 4 is smaller than that into site 3. This results in a biasing of vacancy diffusion jumps towards the cathode. This net flux of vacancies towards the cathode corresponds to the net flux of atoms (or ions) towards the anode. This flux of metal ions can be considered to be due to the effective charge, Z *, on the ion and the associated net force as described above. J = CDF net /RT = CDZ * eρj/rt where J = atomic flux (atoms m 2 s 1 ) ; C = atomic concentration (atoms m 3 ); D = diffusivity (m 2 s 1 ). Note that this overall net flux is exceedingly minute. There is only a very slight biasing of atomic movement e.g. in 1000 atoms 499 would diffuse towards the anode whilst 501 diffuse towards
5 the cathode, resulting in a net of 2 atoms migrating towards the cathode. Electromigration is a very slow process, taking time.
Energy Losses in the Electrical Circuits
 Energy Losses in the Electrical Circuits Motors, lighting systems, wiring, mechanical terminations, distribution panels, protective devices, transformers, switchgear, and all end of circuit equipment experience
Energy Losses in the Electrical Circuits Motors, lighting systems, wiring, mechanical terminations, distribution panels, protective devices, transformers, switchgear, and all end of circuit equipment experience
Atoms, electrons and Solids
 Atoms, electrons and Solids Shell model of an atom negative electron orbiting a positive nucleus QM tells that to minimize total energy the electrons fill up shells. Each orbit in a shell has a specific
Atoms, electrons and Solids Shell model of an atom negative electron orbiting a positive nucleus QM tells that to minimize total energy the electrons fill up shells. Each orbit in a shell has a specific
Kinetics. Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces
 Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
Electrolytic processes Notes
 Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 3: Chemical changes Electrolytic processes Notes 3.22 Recall that electrolytes are ionic compounds in the molten state or dissolved in water When an ionic substance is melted
Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 3: Chemical changes Electrolytic processes Notes 3.22 Recall that electrolytes are ionic compounds in the molten state or dissolved in water When an ionic substance is melted
16EC401 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES UNIT I PN JUNCTION DIODE. Energy Band Diagram of Conductor, Insulator and Semiconductor:
 16EC401 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES UNIT I PN JUNCTION DIODE Energy bands in Intrinsic and Extrinsic silicon: Energy Band Diagram of Conductor, Insulator and Semiconductor: 1 2 Carrier transport: Any motion
16EC401 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES UNIT I PN JUNCTION DIODE Energy bands in Intrinsic and Extrinsic silicon: Energy Band Diagram of Conductor, Insulator and Semiconductor: 1 2 Carrier transport: Any motion
Electrical Conduction in Ceramic Materials 1 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch7, McGraw-Hill, 2000
 MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 19 Electrical Conduction in Ceramic Materials 1 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch7, McGraw-Hill, 2000 Prof. A. K. M. B. Rashid Department of
MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 19 Electrical Conduction in Ceramic Materials 1 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch7, McGraw-Hill, 2000 Prof. A. K. M. B. Rashid Department of
Electrical Conduction. Electrical conduction is the flow of electric charge produced by the movement of electrons in a conductor. I = Q/t.
 Electrical Conduction e- in wire e- out Electrical conduction is the flow of electric charge produced by the movement of electrons in a conductor. The rate of electron flow (called the current, I, in amperes)
Electrical Conduction e- in wire e- out Electrical conduction is the flow of electric charge produced by the movement of electrons in a conductor. The rate of electron flow (called the current, I, in amperes)
collisions of electrons. In semiconductor, in certain temperature ranges the conductivity increases rapidly by increasing temperature
 1.9. Temperature Dependence of Semiconductor Conductivity Such dependence is one most important in semiconductor. In metals, Conductivity decreases by increasing temperature due to greater frequency of
1.9. Temperature Dependence of Semiconductor Conductivity Such dependence is one most important in semiconductor. In metals, Conductivity decreases by increasing temperature due to greater frequency of
 Electrochem 1 Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force (potential in volts) Electrode
Electrochem 1 Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force (potential in volts) Electrode
18.3 Electrolysis. Dr. Fred Omega Garces. Chemistry 201. Driving a non-spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction Reaction. Miramar College.
 18.3 Electrolysis Driving a non-spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction Reaction Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Electrolysis Voltaic Vs. Electrolytic Cells Voltaic Cell Energy is released
18.3 Electrolysis Driving a non-spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction Reaction Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Electrolysis Voltaic Vs. Electrolytic Cells Voltaic Cell Energy is released
DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS. IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5
 DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5 Diffusion The mechanism by which matter is transported through matter. It is related to internal atomic movement. Atomic movement;
DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5 Diffusion The mechanism by which matter is transported through matter. It is related to internal atomic movement. Atomic movement;
Chemistry Lecture #36: Properties of Ionic Compounds and Metals
 Chemistry Lecture #36: Properties of Ionic Compounds and Metals Ionic compounds are made of anions (negative ions) and cations (positive ions). The compound sticks together because opposite charges attract
Chemistry Lecture #36: Properties of Ionic Compounds and Metals Ionic compounds are made of anions (negative ions) and cations (positive ions). The compound sticks together because opposite charges attract
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications. CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications
 CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications Band Theory Fermi-Dirac Function f(e) = 1/[1 + e (E-E F)/kT ] Where the Fermi Energy, E F, is defined as the energy where f(e) = 1/2. That is to say
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications Band Theory Fermi-Dirac Function f(e) = 1/[1 + e (E-E F)/kT ] Where the Fermi Energy, E F, is defined as the energy where f(e) = 1/2. That is to say
GLASS Asst. Lect. Shireen Hasan
 Collage of Engineering Materials Department Third Class Lecture (13) GLASS Asst. Lect. Shireen Hasan 6-3 transport properties: The transport property of glasses is controlled by the diffusion, or transport
Collage of Engineering Materials Department Third Class Lecture (13) GLASS Asst. Lect. Shireen Hasan 6-3 transport properties: The transport property of glasses is controlled by the diffusion, or transport
Types of Cells Chemical transformations to produce electricity- Galvanic cell or Voltaic cell (battery)
 Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force Electrode Potentials Gibbs Free Energy Gibbs
Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force Electrode Potentials Gibbs Free Energy Gibbs
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction
 9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Electrostatics Review
 NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. An electron orbits a nucleus which carries a charge of +9.6 x10-19 C. If the electron s orbital radius is 2.0 x10-10 m, what is its electric potential energy? A. -6.9 x10-18
NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. An electron orbits a nucleus which carries a charge of +9.6 x10-19 C. If the electron s orbital radius is 2.0 x10-10 m, what is its electric potential energy? A. -6.9 x10-18
Electrolysis and Faraday's laws of Electrolysis
 Electrolysis and Faraday's laws of Electrolysis Electrolysis is defined as the passage of an electric current through an electrolyte with subsequent migration of positively and negatively charged ions
Electrolysis and Faraday's laws of Electrolysis Electrolysis is defined as the passage of an electric current through an electrolyte with subsequent migration of positively and negatively charged ions
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS. SEMESTER 2 July, 2012
 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 July, 2012 COURSE NAME: CODE: CHEMISTRY FOR ENGINEEERS CHY-1008 GROUP: ADET 2 DATE: July 2, 2011 TIME: DURATION: 1:00 pm 2 HOURS
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 July, 2012 COURSE NAME: CODE: CHEMISTRY FOR ENGINEEERS CHY-1008 GROUP: ADET 2 DATE: July 2, 2011 TIME: DURATION: 1:00 pm 2 HOURS
Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at
 Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 12. Chem 4631
 Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 12 Chem 4631 What is a fuel cell? An electro-chemical energy conversion device A factory that takes fuel as input and produces electricity as output. O 2 (g) H 2 (g)
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 12 Chem 4631 What is a fuel cell? An electro-chemical energy conversion device A factory that takes fuel as input and produces electricity as output. O 2 (g) H 2 (g)
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry. Notes.
 Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 12: Electrical Properties School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 12-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How are electrical conductance and resistance
Chapter 12: Electrical Properties School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 12-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How are electrical conductance and resistance
Introduction To Materials Science FOR ENGINEERS, Ch. 5. Diffusion. MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5
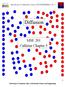 Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
11.3. Electrolytic Cells. Electrolysis of Molten Salts. 524 MHR Unit 5 Electrochemistry
 11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
Fernando O. Raineri. Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby).
 Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). P1) What is the reduction potential of the hydrogen electrode g bar H O aq Pt(s) H,1 2 3 when the aqueous solution
Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). P1) What is the reduction potential of the hydrogen electrode g bar H O aq Pt(s) H,1 2 3 when the aqueous solution
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000. Dr.Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 18: Electrical Properties Dr.Coates 18.2 Ohm s Law V = IR where R is the resistance of the material, V is the voltage and I is the current. l R A
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 18: Electrical Properties Dr.Coates 18.2 Ohm s Law V = IR where R is the resistance of the material, V is the voltage and I is the current. l R A
lect 26:Electrolytic Cells
 lect 26:Electrolytic Cells Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis
lect 26:Electrolytic Cells Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis
1. Ionic bonding - chemical bond resulting from the attraction of positive and negative ions
 Bonding Bonding can occur in 2 ways: 1. Electron transfer (ionic) 2. Electron sharing (covalent) 1. Ionic bonding - chemical bond resulting from the attraction of positive and negative ions Cation- positive
Bonding Bonding can occur in 2 ways: 1. Electron transfer (ionic) 2. Electron sharing (covalent) 1. Ionic bonding - chemical bond resulting from the attraction of positive and negative ions Cation- positive
EECS 117 Lecture 13: Method of Images / Steady Currents
 EECS 117 Lecture 13: Method of Images / Steady Currents Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS 217 Lecture 13 p. 1/21 Point Charge Near Ground Plane Consider
EECS 117 Lecture 13: Method of Images / Steady Currents Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley EECS 217 Lecture 13 p. 1/21 Point Charge Near Ground Plane Consider
Chemistry Objective. Warm-Up What do the following atoms have to do to become stable? a. barium b. nitrogen c. fluorine
 Chemistry Objective Students will: 1. describe how a covalent bond is formed. 2. describe properties of a covalently bonded substance. 3. describe the difference between a polar covalent and nonpolar covalent
Chemistry Objective Students will: 1. describe how a covalent bond is formed. 2. describe properties of a covalently bonded substance. 3. describe the difference between a polar covalent and nonpolar covalent
Electrochemistry SYBSc 2017
 Electrochemistry SYBSc 2017 Definition It is a branch in chemistry which deals with the qualitative and quantitative studies of chemical changes brought about by the passage of electricity. It is also
Electrochemistry SYBSc 2017 Definition It is a branch in chemistry which deals with the qualitative and quantitative studies of chemical changes brought about by the passage of electricity. It is also
Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures
 Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures In Chapter 2, the reduction of the extent of a solid in one or more dimensions was shown to lead to a dramatic alteration of the overall behavior of the solids. Generally,
Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures In Chapter 2, the reduction of the extent of a solid in one or more dimensions was shown to lead to a dramatic alteration of the overall behavior of the solids. Generally,
PN Junction
 P Junction 2017-05-04 Definition Power Electronics = semiconductor switches are used Analogue amplifier = high power loss 250 200 u x 150 100 u Udc i 50 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 i,u dc i,u u
P Junction 2017-05-04 Definition Power Electronics = semiconductor switches are used Analogue amplifier = high power loss 250 200 u x 150 100 u Udc i 50 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 i,u dc i,u u
Chem 321 Lecture 17 - Potentiometry 10/24/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 17 - Potentiometry 10/24/13 Electrodes The cell described in the potentiometric chloride titration (see 10/22/13 posting) consists of a Ag/AgCl reference electrode
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 17 - Potentiometry 10/24/13 Electrodes The cell described in the potentiometric chloride titration (see 10/22/13 posting) consists of a Ag/AgCl reference electrode
AR-7781 (Physical Chemistry)
 Model Answer: B.Sc-VI th Semester-CBT-602 AR-7781 (Physical Chemistry) One Mark Questions: 1. Write a nuclear reaction for following Bethe s notation? 35 Cl(n, p) 35 S Answer: 35 17Cl + 1 1H + 35 16S 2.
Model Answer: B.Sc-VI th Semester-CBT-602 AR-7781 (Physical Chemistry) One Mark Questions: 1. Write a nuclear reaction for following Bethe s notation? 35 Cl(n, p) 35 S Answer: 35 17Cl + 1 1H + 35 16S 2.
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding
 Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic 7.3 Bonding in Metals 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY & YOU Where does table
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic 7.3 Bonding in Metals 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. CHEMISTRY & YOU Where does table
States of Matter SM VI. Liquids & Solids. Liquids. Description of. Vapor Pressure. if IMF then VP, b.p.
 chem101/3, wi2010 po 20 1 States of Matter SM VI Description of Liquids & Solids chem101/3, wi2010 po 20 2 Liquids molecules slide along in close contact attraction due to various IMF s can diffuse, but
chem101/3, wi2010 po 20 1 States of Matter SM VI Description of Liquids & Solids chem101/3, wi2010 po 20 2 Liquids molecules slide along in close contact attraction due to various IMF s can diffuse, but
EE301 Electronics I , Fall
 EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
2015 EdExcel A-Level Physics Topic 3. Resistivity and I=nAqv
 2015 EdExcel A-Level Physics Topic 3 Resistivity and I=nAqv 10/25/2017 Factors affecting the resistance of a wire The resistance of a wire depends on 3 things: the length of the wire, the width of the
2015 EdExcel A-Level Physics Topic 3 Resistivity and I=nAqv 10/25/2017 Factors affecting the resistance of a wire The resistance of a wire depends on 3 things: the length of the wire, the width of the
Unit 3: Chemical Bonds. IB Chemistry SL Ms. Kiely Coral Gables Senior High
 Unit 3: Chemical Bonds IB Chemistry SL Ms. Kiely Coral Gables Senior High Bell Ringer What is the name of Ag₂SO₃? Quiz next class! Answer Silver(I) sulfite Physical Properties of Ionic Compounds 1. Ionic
Unit 3: Chemical Bonds IB Chemistry SL Ms. Kiely Coral Gables Senior High Bell Ringer What is the name of Ag₂SO₃? Quiz next class! Answer Silver(I) sulfite Physical Properties of Ionic Compounds 1. Ionic
Electrical Resistance
 Electrical Resistance I + V _ W Material with resistivity ρ t L Resistance R V I = L ρ Wt (Unit: ohms) where ρ is the electrical resistivity 1 Adding parts/billion to parts/thousand of dopants to pure
Electrical Resistance I + V _ W Material with resistivity ρ t L Resistance R V I = L ρ Wt (Unit: ohms) where ρ is the electrical resistivity 1 Adding parts/billion to parts/thousand of dopants to pure
CH5715 Energy Conversion and Storage. Electrolytes. For lecture notes: energy-conversion-and-storage/
 CH5715 Energy Conversion and Storage Electrolytes For lecture notes: http://jtsigroup.wp.st-andrews.ac.uk/ch5715- energy-conversion-and-storage/ Textbook Solid State Electrochemistry Cambridge - P. G.
CH5715 Energy Conversion and Storage Electrolytes For lecture notes: http://jtsigroup.wp.st-andrews.ac.uk/ch5715- energy-conversion-and-storage/ Textbook Solid State Electrochemistry Cambridge - P. G.
Electrochemical Cells Homework Unit 11 - Topic 4
 Electrochemical Cell Vocabulary Electrochemical Cells Homework Unit 11 - Topic 4 Electrode Anode Voltaic Cell Oxidation Electrolytic Cell Cathode Salt Bridge Reduction Half Reaction Refer to Table J: For
Electrochemical Cell Vocabulary Electrochemical Cells Homework Unit 11 - Topic 4 Electrode Anode Voltaic Cell Oxidation Electrolytic Cell Cathode Salt Bridge Reduction Half Reaction Refer to Table J: For
Lewis Dot Symbols. The Octet Rule ATOMS TEND TO GAIN, LOSE, or SHARE ELECTRONS to ATTAIN A FILLED OUTER SHELL of 8 ELECTRONS.
 Chapter 9, Part 1 Models of Chemical Bonding Recall Chapter 2: Chemical bonds hold atoms together in a compound. transfer of electrons, forming cations and anions, results in ionic bonding sharing of electron
Chapter 9, Part 1 Models of Chemical Bonding Recall Chapter 2: Chemical bonds hold atoms together in a compound. transfer of electrons, forming cations and anions, results in ionic bonding sharing of electron
Session 5: Solid State Physics. Charge Mobility Drift Diffusion Recombination-Generation
 Session 5: Solid State Physics Charge Mobility Drift Diffusion Recombination-Generation 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 Mobile Charge Carriers in Semiconductors Three primary types of carrier action occur
Session 5: Solid State Physics Charge Mobility Drift Diffusion Recombination-Generation 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 Mobile Charge Carriers in Semiconductors Three primary types of carrier action occur
Population inversion occurs when there are more atoms in the excited state than in the ground state. This is achieved through the following:
 Lasers and SemiconductorsTutorial Lasers 1. Fill in the table the differences between spontaneous emission and stimulated emission in atoms: External stimulus Direction of emission Phase & coherence of
Lasers and SemiconductorsTutorial Lasers 1. Fill in the table the differences between spontaneous emission and stimulated emission in atoms: External stimulus Direction of emission Phase & coherence of
Mass transfer by migration & diffusion (Ch. 4)
 Mass transfer by migration & diffusion (Ch. 4) Mass transfer equation Migration Mixed migration & diffusion near an electrode Mass transfer during electrolysis Effect of excess electrolyte Diffusion Microscopic
Mass transfer by migration & diffusion (Ch. 4) Mass transfer equation Migration Mixed migration & diffusion near an electrode Mass transfer during electrolysis Effect of excess electrolyte Diffusion Microscopic
SEMICONDUCTORS. Conductivity lies between conductors and insulators. The flow of charge in a metal results from the
 SEMICONDUCTORS Conductivity lies between conductors and insulators The flow of charge in a metal results from the movement of electrons Electros are negatively charged particles (q=1.60x10-19 C ) The outermost
SEMICONDUCTORS Conductivity lies between conductors and insulators The flow of charge in a metal results from the movement of electrons Electros are negatively charged particles (q=1.60x10-19 C ) The outermost
12/10/09. Chapter 18: Electrical Properties. View of an Integrated Circuit. Electrical Conduction ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 18: Electrical Properties ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How are electrical conductance and resistance characterized? What are the physical phenomena that distinguish? For metals, how is affected by and
Chapter 18: Electrical Properties ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How are electrical conductance and resistance characterized? What are the physical phenomena that distinguish? For metals, how is affected by and
Overview of electrochemistry
 Overview of electrochemistry 1 Homogeneous Heterogeneous Equilibrium electrochemistry (no current flows) Thermodynamics of electrolyte solutions: electrolytic dissociation thermodynamics and activities
Overview of electrochemistry 1 Homogeneous Heterogeneous Equilibrium electrochemistry (no current flows) Thermodynamics of electrolyte solutions: electrolytic dissociation thermodynamics and activities
If a sodium atom gives an electron to a chlorine atom, both become more stable.
 3. STRUCTURE AND BONDING IONIC (ELECTROVALENT) BONDING Noble gases like neon or argon have eight electrons in their outer shells (or two in the case of helium). These noble gas structures are thought of
3. STRUCTURE AND BONDING IONIC (ELECTROVALENT) BONDING Noble gases like neon or argon have eight electrons in their outer shells (or two in the case of helium). These noble gas structures are thought of
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
KNOWLEDGE AREA MATTER AND MATERIALS
 Unit INDEX Bladsy KNOWLEDGE AREA MATTER AND MATERIALS 15 Unit 1 MACROSCOPIC PROPERTIES OF MATTER 15 Unit 2 Unit 3 Activity 1 17 Case study: Mopani worms 18 1.1 Mixtures 18 Practical activity 1 20 1.2 Pure
Unit INDEX Bladsy KNOWLEDGE AREA MATTER AND MATERIALS 15 Unit 1 MACROSCOPIC PROPERTIES OF MATTER 15 Unit 2 Unit 3 Activity 1 17 Case study: Mopani worms 18 1.1 Mixtures 18 Practical activity 1 20 1.2 Pure
Lecture 3 Semiconductor Physics (II) Carrier Transport
 Lecture 3 Semiconductor Physics (II) Carrier Transport Thermal Motion Carrier Drift Carrier Diffusion Outline Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini; Chapter 2, Sect. 2.4-2.6 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture 3 1
Lecture 3 Semiconductor Physics (II) Carrier Transport Thermal Motion Carrier Drift Carrier Diffusion Outline Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini; Chapter 2, Sect. 2.4-2.6 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture 3 1
Chapter 5. Carrier Transport Phenomena
 Chapter 5 Carrier Transport Phenomena 1 We now study the effect of external fields (electric field, magnetic field) on semiconducting material 2 Objective Discuss drift and diffusion current densities
Chapter 5 Carrier Transport Phenomena 1 We now study the effect of external fields (electric field, magnetic field) on semiconducting material 2 Objective Discuss drift and diffusion current densities
Chapter 5. Early Atomic Theory and Structure
 Chapter 5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure 1 5.1 Early thoughts ~ 400 B.C. Greek philosophers Empedocles all matter was composed of four elements earth, air, water, fire Democritus all forms of matter
Chapter 5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure 1 5.1 Early thoughts ~ 400 B.C. Greek philosophers Empedocles all matter was composed of four elements earth, air, water, fire Democritus all forms of matter
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain
 Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain Chapter 3: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Slide 2 Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 3 Not at rest
Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain Chapter 3: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Slide 2 Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 3 Not at rest
1 Written and composed by: Prof. Muhammad Ali Malik (M. Phil. Physics), Govt. Degree College, Naushera
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Q # 1. What do you know about electric current? Ans. Electric Current The amount of electric charge that flows through a cross section of a conductor per unit time is known as electric
CURRENT ELECTRICITY Q # 1. What do you know about electric current? Ans. Electric Current The amount of electric charge that flows through a cross section of a conductor per unit time is known as electric
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
7.1 Electrolyte and electrolytic solution
 Out-class reading: Levine, pp. 294-310 Section 10.6 solutions of electrolytes Section 10.9 ionic association pp. 512-515 Section 16.6 electrical conductivity of electrolyte solutions. Contents of solution
Out-class reading: Levine, pp. 294-310 Section 10.6 solutions of electrolytes Section 10.9 ionic association pp. 512-515 Section 16.6 electrical conductivity of electrolyte solutions. Contents of solution
Metallic and Ionic Structures and Bonding
 Metallic and Ionic Structures and Bonding Ionic compounds are formed between elements having an electronegativity difference of about 2.0 or greater. Simple ionic compounds are characterized by high melting
Metallic and Ionic Structures and Bonding Ionic compounds are formed between elements having an electronegativity difference of about 2.0 or greater. Simple ionic compounds are characterized by high melting
Contents. 2. Fluids. 1. Introduction
 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
ADVANCED UNDERGRADUATE LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 20. Semiconductor Resistance, Band Gap, and Hall Effect
 ADVANCED UNDERGRADUATE LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 20 Semiconductor Resistance, Band Gap, and Hall Effect Revised: November 1996 by David Bailey March 1990 by John Pitre & Taek-Soon Yoon Introduction Solid materials
ADVANCED UNDERGRADUATE LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 20 Semiconductor Resistance, Band Gap, and Hall Effect Revised: November 1996 by David Bailey March 1990 by John Pitre & Taek-Soon Yoon Introduction Solid materials
The Electromagnetic Properties of Materials
 The lectromagnetic Properties of Materials lectrical conduction Metals Semiconductors Insulators (dielectrics) Superconductors Magnetic materials Ferromagnetic materials Others Photonic Materials (optical)
The lectromagnetic Properties of Materials lectrical conduction Metals Semiconductors Insulators (dielectrics) Superconductors Magnetic materials Ferromagnetic materials Others Photonic Materials (optical)
Electrochemistry. Michael Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction says that whenever a conductor is
 Surname 1 Name Course Instructor Date Electrochemistry 1. Faraday s Law Michael Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction says that whenever a conductor is positioned in a changeable magnetic field emf
Surname 1 Name Course Instructor Date Electrochemistry 1. Faraday s Law Michael Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction says that whenever a conductor is positioned in a changeable magnetic field emf
470 Lecture #7 of 18
 Lecture #7 of 18 470 471 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: Introduction, Review, and B&F Chapter 1, 15 & 4 main concepts: Section 1.1: Redox reactions Chapter 15: Electrochemical instrumentation Section
Lecture #7 of 18 470 471 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: Introduction, Review, and B&F Chapter 1, 15 & 4 main concepts: Section 1.1: Redox reactions Chapter 15: Electrochemical instrumentation Section
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Defect Ch em Ch istry 1
 Defect Chemistry 1 What is a defect? Fundamental definition Any deviation from the perfect crystal lattice is a defect! Macroscopic defects like porosities and cracks have an overall negative influence
Defect Chemistry 1 What is a defect? Fundamental definition Any deviation from the perfect crystal lattice is a defect! Macroscopic defects like porosities and cracks have an overall negative influence
INTRODUCTION TO THE DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS DEFECTS, DEFECTS, DEFECTS CAN T LIVE WITH THEM!!! CAN T LIVE WITHOUT THEM!!! INTRODUCTION TO DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS DEFECTS, DEFECTS, DEFECTS Perfect crystals
INTRODUCTION TO THE DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS DEFECTS, DEFECTS, DEFECTS CAN T LIVE WITH THEM!!! CAN T LIVE WITHOUT THEM!!! INTRODUCTION TO DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS DEFECTS, DEFECTS, DEFECTS Perfect crystals
Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds
 Main Ideas Ionic bonds form from attractions between positive and negative ions Differences in attraction strength give ionic and molecular compounds different properties Multiple atoms can bond covalently
Main Ideas Ionic bonds form from attractions between positive and negative ions Differences in attraction strength give ionic and molecular compounds different properties Multiple atoms can bond covalently
Faraday s Law. Current (Amperes)
 Faraday s Law How can one predict the amount of product made in an electrolytic reaction? Why? In an electrolytic reaction, an electrical current is used to run a nonspontaneous redox reaction. This might
Faraday s Law How can one predict the amount of product made in an electrolytic reaction? Why? In an electrolytic reaction, an electrical current is used to run a nonspontaneous redox reaction. This might
CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials. Compiled by. Dr. A.O. Oladebeye
 CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr. A.O. Oladebeye Department of Chemistry University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria Electrochemical Cell Electrochemical
CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr. A.O. Oladebeye Department of Chemistry University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria Electrochemical Cell Electrochemical
Chapter 11. Intermolecular Forces and Liquids & Solids
 Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids & Solids The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids & Solids Gases vs. Liquids & Solids difference is distance between molecules Liquids Molecules close together;
Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces and Liquids & Solids The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids & Solids Gases vs. Liquids & Solids difference is distance between molecules Liquids Molecules close together;
General Physics II. Electromagnetic Induction and Electromagnetic Waves
 General Physics II Electromagnetic Induction and Electromagnetic Waves 1 Induced emf We have seen that an electric current produces a magnetic field. Michael Faraday demonstrated that a magnetic field
General Physics II Electromagnetic Induction and Electromagnetic Waves 1 Induced emf We have seen that an electric current produces a magnetic field. Michael Faraday demonstrated that a magnetic field
Electrochemistry C020. Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy
 Electrochemistry C020 Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy Using chemistry to generate electricity involves using a Voltaic Cell or Galvanic Cell (battery)
Electrochemistry C020 Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy Using chemistry to generate electricity involves using a Voltaic Cell or Galvanic Cell (battery)
Chapter 4: Bonding in Solids and Electronic Properties. Free electron theory
 Chapter 4: Bonding in Solids and Electronic Properties Free electron theory Consider free electrons in a metal an electron gas. regards a metal as a box in which electrons are free to move. assumes nuclei
Chapter 4: Bonding in Solids and Electronic Properties Free electron theory Consider free electrons in a metal an electron gas. regards a metal as a box in which electrons are free to move. assumes nuclei
PHY102 Electricity Course Summary
 TOPIC 1 ELECTOSTTICS PHY1 Electricity Course Summary Coulomb s Law The magnitude of the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional
TOPIC 1 ELECTOSTTICS PHY1 Electricity Course Summary Coulomb s Law The magnitude of the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional
Electro - Principles I
 Electro - Principles I Page 10-1 Atomic Theory It is necessary to know what goes on at the atomic level of a semiconductor so the characteristics of the semiconductor can be understood. In many cases a
Electro - Principles I Page 10-1 Atomic Theory It is necessary to know what goes on at the atomic level of a semiconductor so the characteristics of the semiconductor can be understood. In many cases a
Semiconductor Physics
 Semiconductor Physics Motivation Is it possible that there might be current flowing in a conductor (or a semiconductor) even when there is no potential difference supplied across its ends? Look at the
Semiconductor Physics Motivation Is it possible that there might be current flowing in a conductor (or a semiconductor) even when there is no potential difference supplied across its ends? Look at the
Electrical conduction in solids
 Equations of motion Electrical conduction in solids Electrical conduction is the movement of electrically charged particles through a conductor or semiconductor, which constitutes an electric current.
Equations of motion Electrical conduction in solids Electrical conduction is the movement of electrically charged particles through a conductor or semiconductor, which constitutes an electric current.
2. Conductometry. Introduction This is a method of analysis based on measuring electrolytic conductance
 2. Conductometry Introduction This is a method of analysis based on measuring electrolytic conductance Conductance: is the ability of the medium to carry the electric current. Electric current passes through
2. Conductometry Introduction This is a method of analysis based on measuring electrolytic conductance Conductance: is the ability of the medium to carry the electric current. Electric current passes through
Metallic & Ionic Solids. Crystal Lattices. Properties of Solids. Network Solids. Types of Solids. Chapter 13 Solids. Chapter 13
 1 Metallic & Ionic Solids Chapter 13 The Chemistry of Solids Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Crystal Lattices Properties of Solids Regular 3-D arrangements of equivalent LATTICE POINTS
1 Metallic & Ionic Solids Chapter 13 The Chemistry of Solids Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Crystal Lattices Properties of Solids Regular 3-D arrangements of equivalent LATTICE POINTS
HALL EFFECT IN SEMICONDUCTORS
 Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics Physics Laboratory I P Andrzej Kubiaczyk 30 HALL EFFECT IN SEMICONDUCTORS 1. ackground 1.1. Electron motion in electric and magnetic fields A particle
Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics Physics Laboratory I P Andrzej Kubiaczyk 30 HALL EFFECT IN SEMICONDUCTORS 1. ackground 1.1. Electron motion in electric and magnetic fields A particle
Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop
 Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Oxidation Historically, oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn
Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Oxidation Historically, oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn
Test ID B 1. C 2. C 3. E 4. A 5. E 6. B 7. C 8. D 9. E 10. E 11. E 12. B 13. D 14. B 15. A 16. C 17. B 18. E 19. D 20. D 21. B
 Multiple Choice Answers Test ID A 1. D 2. D 3. C 4. A 5. D 6. E 7. B 8. A 9. B 10. E 11. B 12. D 13. B 14. D 15. C 16. E 17. B 18. D 19. B 20. A 21. A Test ID B 1. C 2. C 3. E 4. A 5. E 6. B 7. C 8. D
Multiple Choice Answers Test ID A 1. D 2. D 3. C 4. A 5. D 6. E 7. B 8. A 9. B 10. E 11. B 12. D 13. B 14. D 15. C 16. E 17. B 18. D 19. B 20. A 21. A Test ID B 1. C 2. C 3. E 4. A 5. E 6. B 7. C 8. D
Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas OL
 Name: Chemical Bonding 5. Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forces Objectives -understand that compounds can be
Name: Chemical Bonding 5. Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forces Objectives -understand that compounds can be
Nasser S. Alzayed.
 Lecture #4 Nasser S. Alzayed nalzayed@ksu.edu.sa ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY AND OHM'S LAW The momentum of a free electron is related to the wavevector by mv = ћk. In an electric field E and magnetic field
Lecture #4 Nasser S. Alzayed nalzayed@ksu.edu.sa ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY AND OHM'S LAW The momentum of a free electron is related to the wavevector by mv = ћk. In an electric field E and magnetic field
We can use chemistry to generate electricity... this is termed a Voltaic (or sometimes) Galvanic Cell
 Unit 6 Electrochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin Electrochemistry Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy. We can use chemistry to generate electricity...
Unit 6 Electrochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin Electrochemistry Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy. We can use chemistry to generate electricity...
SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS REVIEW BONDS,
 SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS REVIEW BONDS, BANDS, EFFECTIVE MASS, DRIFT, DIFFUSION, GENERATION, RECOMBINATION February 3, 2011 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles
SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS REVIEW BONDS, BANDS, EFFECTIVE MASS, DRIFT, DIFFUSION, GENERATION, RECOMBINATION February 3, 2011 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles
2. Electric Current. E.M.F. of a cell is defined as the maximum potential difference between the two electrodes of the
 2. Electric Current The net flow of charges through a etallic wire constitutes an electric current. Do you know who carries current? Current carriers In solid - the electrons in outerost orbit carries
2. Electric Current The net flow of charges through a etallic wire constitutes an electric current. Do you know who carries current? Current carriers In solid - the electrons in outerost orbit carries
Chapter 27. Current And Resistance
 Chapter 27 Current And Resistance Electric Current Electric current is the rate of flow of charge through some region of space The SI unit of current is the ampere (A) 1 A = 1 C / s The symbol for electric
Chapter 27 Current And Resistance Electric Current Electric current is the rate of flow of charge through some region of space The SI unit of current is the ampere (A) 1 A = 1 C / s The symbol for electric
Superconductivity. The Discovery of Superconductivity. Basic Properties
 Superconductivity Basic Properties The Discovery of Superconductivity Using liquid helium, (b.p. 4.2 K), H. Kamerlingh Onnes found that the resistivity of mercury suddenly dropped to zero at 4.2 K. H.
Superconductivity Basic Properties The Discovery of Superconductivity Using liquid helium, (b.p. 4.2 K), H. Kamerlingh Onnes found that the resistivity of mercury suddenly dropped to zero at 4.2 K. H.
Electrochemistry. Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts
 Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Conducting surface - equipotential. Potential varies across the conducting surface. Lecture 9: Electrical Resistance.
 Lecture 9: Electrical Resistance Electrostatics (time-independent E, I = 0) Stationary Currents (time-independent E and I 0) E inside = 0 Conducting surface - equipotential E inside 0 Potential varies
Lecture 9: Electrical Resistance Electrostatics (time-independent E, I = 0) Stationary Currents (time-independent E and I 0) E inside = 0 Conducting surface - equipotential E inside 0 Potential varies
Chapter 3: Electric Current And Direct-Current Circuits
 Chapter 3: Electric Current And Direct-Current Circuits 3.1 Electric Conduction 3.1.1 Describe the microscopic model of current Mechanism of Electric Conduction in Metals Before applying electric field
Chapter 3: Electric Current And Direct-Current Circuits 3.1 Electric Conduction 3.1.1 Describe the microscopic model of current Mechanism of Electric Conduction in Metals Before applying electric field
Revision Pack CHEMISTRY
 Revision Pack CHEMISTRY CC1 States of Matter CC2 Separating Mixtures CC3 Atomic Structure CC4 Elements and Periodic Table CC5 Ionic Bonding CC6 Covalent bonding When we tackle obstacles, we find hidden
Revision Pack CHEMISTRY CC1 States of Matter CC2 Separating Mixtures CC3 Atomic Structure CC4 Elements and Periodic Table CC5 Ionic Bonding CC6 Covalent bonding When we tackle obstacles, we find hidden
Topics to discuss...
 MME 467: Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 18 Defects in Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch6, McGraw-Hill, 2000 Prof. A. K. M. B. Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka Topics
MME 467: Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 18 Defects in Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch6, McGraw-Hill, 2000 Prof. A. K. M. B. Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka Topics
3. What type of force is the woman applying to cart in the illustration below?
 Name: Forces and Motion STUDY GUIDE Directions: Answer the following questions. 1. What is a force? a. A type of energy b. The rate at which an object performs work c. A push or a pull d. An object that
Name: Forces and Motion STUDY GUIDE Directions: Answer the following questions. 1. What is a force? a. A type of energy b. The rate at which an object performs work c. A push or a pull d. An object that
Pushes and Pulls. Example- an apple falling on a tree exerts a downward force with a magnitude of about 1 newton.
 What are Forces? Pushes and Pulls Force- a push or pull that acts on an object. Forces make a moving object speed up, slow down, or change direction. Forces have both magnitude and direction. Magnitude
What are Forces? Pushes and Pulls Force- a push or pull that acts on an object. Forces make a moving object speed up, slow down, or change direction. Forces have both magnitude and direction. Magnitude
