Nonparametric Bayesian Methods
|
|
|
- Alexis Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nonparametric Bayesian Methods Debdeep Pati Florida State University October 2, 2014
2 Large spatial datasets (Problem of big n) Large observational and computer-generated datasets: Often have spatial and temporal aspects. Goal: Make inference on underlying spatial processes from observations at n locations where n is large.
3 Computational bottleneck The posterior predictive involves (C(X, X ) + σ 2 I ) 1 The covariance matrix C(X, X ) is large: n n for n locations. unstructured: irregular spaced locations. dense: non-negligible correlations. Cholesky decomposition of n n matrices Generally requires O(n 3 ) computations and O(n 2 ) memory.
4 Options for large n Use models that reduce computations and/or storage. Use approximate methods. Compactly supported covariance functions. Reduced rank covariance functions. Leads Statistical and computational efficiency.
5 Covariance Tapering (Furrer et al 2006) Covariance tapering: C(x, x ) = C(x, x ) T (x, x ; γ), T (x, x ; γ): an isotropic correlation function of compact support, i.e., T (x, x ; γ) = 0 for x x γ. Assumptions: The covariance function has compact support. Its range is sufficiently small. The tapered covariance matrix C retains the property of positive definiteness, zero at large distances. Minimal distortion to C for nearby locations. Efficient sparse matrix algorithms can be used. Also saves storage.
6 Reduced Rank approximations Find reduced rank covariance function representation, Banerjee et al. (2008), JRSSB: proposed Gaussian predictive processes f (x) to replace f (x) by projecting f (x) onto a m-dimension (lower) subspace f (x) = E(f (x) f (x 1 ),..., f (x m)). Cressie and Johannesson (2008), JRSSB proposed a reduced rank approach by defining a low rank process f (x) = B T (x)η m 1, where B is a vector consisting of m basis functions and var(η) = G. Have computational advantages but also limitations. (Stein, 2013, Spatial Statistics). Low rank+tapering: Sang and Huang (2011), JRSSB
7 Why Projections help For both predictive process and the basis function truncation approach, C(X, X ) is of the form C(X, X ) = B GB where B is an m n matrix, m n. Need to invert σ 2 I + C(X, X ) = σ 2 I + B GB Use Woodbury Inversion formula (A + UCV ) 1 = A 1 A 1 U ( C 1 + VA 1 U ) 1 VA 1 Requires inverting m m matrices!!!
8 RKHS of Gaussian processes In np Bayes, want priors to place positive probability around arbitrary neighborhoods of a large class of parameter values (large support property) The prior concentration plays a key role in determining the rate of posterior contraction The reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) of a Gaussian process determines the prior support and concentration Intuitively, a space of functions that are similar to the covariance kernel in terms of smoothness
9 Applications of Gaussian processes- Classification Let {(X i, Y i ), i = 1,..., n}, be i.i.d random pairs of observations, where X i [0, 1] d and Y i {0, 1}. Let Z = [0, 1] d {0, 1}. Denote by P X, the probability distribution of X i and by P X,Y the joint distribution of (X i, Y i ) and P n the joint distribution of {(X i, Y i ), i = 1,..., n} and E n denotes the expectation w.r.t P n. The goal of a classification is to predict the label Y given the value of X, i.e. to provide a decision rule f : [0, 1] d {0, 1}. The class of decision rules is denoted by F. The performance of a decision rule f is measured by the misclassification error R(f ) := P(Y f (X )) and corresponding empirical version R n (f ) = 1 n 1 n Yi f (X i ). i=1
10 Applications of Gaussian processes- Classification Of particular interest is the optimal decision rule f (X ) = 1 {η(x ) 1/2} where η(x) = P(Y = 1 X = x). The parameter η is usually estimated from the data necessitating the next definition. An empirical classifier is a random mapping ˆf n : Z n F. Its accuracy can be characterized by excess risk E(ˆf n ) = E n {R(ˆf n ) R(f )}. Theorem The decision rule f is a minimizer of the risk R(f ) over all decision rules f F.
11 Applications of Gaussian processes- Classification Lemma For any empirical decision rule ˆf n, E(ˆf n ) = E n [0,1] d 2η(x) 1 I {ˆfn(x) f (x)} P X (x)dx. We define two metrics on F, d(f, f ) = [0,1] d I {f (x) f (x)}p X (x)dx d η (f, f ) = [0,1] d 2η(x) 1 I {f (x) f (x)}p X (x)dx. d η (f, f ) is actually a pseudo-metric as it satisfies all the axioms except that d(f 1, f 2 ) = 0 = f 1 = f 2.
12 Modeling η(x) We will consider Z = [0, 1] d {0, 1}. For η : [0, 1] d [0, 1], consider y i x i Ber{η(x i )}, Assume η(x) = Φ(f (x)) and f GP(0, c). Consider three different classifiers based on the posterior distribution of η. 1. Plug-in classifiers: ˆf (x) = 1ˆη(x)>1/2, where ˆη(x) is posterior mean / median. 2. Hybrid Plug-in Empirical Risk Minimizer (ERM) classifiers: ˆη ERM is the maximizer of the posterior density R n (f ) Y n, X n, ˆf (x) = 1ˆηERM (x)>1/2 3. Bayes estimate with respect to loss d η (f, f ): ˆf (x) = 1 {Π(η(x)>1/2 Y n,x n )>1/2}.
Fast learning rates for plug-in classifiers under the margin condition
 Fast learning rates for plug-in classifiers under the margin condition Jean-Yves Audibert 1 Alexandre B. Tsybakov 2 1 Certis ParisTech - Ecole des Ponts, France 2 LPMA Université Pierre et Marie Curie,
Fast learning rates for plug-in classifiers under the margin condition Jean-Yves Audibert 1 Alexandre B. Tsybakov 2 1 Certis ParisTech - Ecole des Ponts, France 2 LPMA Université Pierre et Marie Curie,
Geostatistical Modeling for Large Data Sets: Low-rank methods
 Geostatistical Modeling for Large Data Sets: Low-rank methods Whitney Huang, Kelly-Ann Dixon Hamil, and Zizhuang Wu Department of Statistics Purdue University February 22, 2016 Outline Motivation Low-rank
Geostatistical Modeling for Large Data Sets: Low-rank methods Whitney Huang, Kelly-Ann Dixon Hamil, and Zizhuang Wu Department of Statistics Purdue University February 22, 2016 Outline Motivation Low-rank
A full scale, non stationary approach for the kriging of large spatio(-temporal) datasets
 A full scale, non stationary approach for the kriging of large spatio(-temporal) datasets Thomas Romary, Nicolas Desassis & Francky Fouedjio Mines ParisTech Centre de Géosciences, Equipe Géostatistique
A full scale, non stationary approach for the kriging of large spatio(-temporal) datasets Thomas Romary, Nicolas Desassis & Francky Fouedjio Mines ParisTech Centre de Géosciences, Equipe Géostatistique
Econ 2148, fall 2017 Gaussian process priors, reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces, and Splines
 Econ 2148, fall 2017 Gaussian process priors, reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces, and Splines Maximilian Kasy Department of Economics, Harvard University 1 / 37 Agenda 6 equivalent representations of the
Econ 2148, fall 2017 Gaussian process priors, reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces, and Splines Maximilian Kasy Department of Economics, Harvard University 1 / 37 Agenda 6 equivalent representations of the
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017
 ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
Learning gradients: prescriptive models
 Department of Statistical Science Institute for Genome Sciences & Policy Department of Computer Science Duke University May 11, 2007 Relevant papers Learning Coordinate Covariances via Gradients. Sayan
Department of Statistical Science Institute for Genome Sciences & Policy Department of Computer Science Duke University May 11, 2007 Relevant papers Learning Coordinate Covariances via Gradients. Sayan
Bayesian Support Vector Machines for Feature Ranking and Selection
 Bayesian Support Vector Machines for Feature Ranking and Selection written by Chu, Keerthi, Ong, Ghahramani Patrick Pletscher pat@student.ethz.ch ETH Zurich, Switzerland 12th January 2006 Overview 1 Introduction
Bayesian Support Vector Machines for Feature Ranking and Selection written by Chu, Keerthi, Ong, Ghahramani Patrick Pletscher pat@student.ethz.ch ETH Zurich, Switzerland 12th January 2006 Overview 1 Introduction
CS8803: Statistical Techniques in Robotics Byron Boots. Hilbert Space Embeddings
 CS8803: Statistical Techniques in Robotics Byron Boots Hilbert Space Embeddings 1 Motivation CS8803: STR Hilbert Space Embeddings 2 Overview Multinomial Distributions Marginal, Joint, Conditional Sum,
CS8803: Statistical Techniques in Robotics Byron Boots Hilbert Space Embeddings 1 Motivation CS8803: STR Hilbert Space Embeddings 2 Overview Multinomial Distributions Marginal, Joint, Conditional Sum,
Classification objectives COMS 4771
 Classification objectives COMS 4771 1. Recap: binary classification Scoring functions Consider binary classification problems with Y = { 1, +1}. 1 / 22 Scoring functions Consider binary classification
Classification objectives COMS 4771 1. Recap: binary classification Scoring functions Consider binary classification problems with Y = { 1, +1}. 1 / 22 Scoring functions Consider binary classification
Bayesian Modeling and Inference for High-Dimensional Spatiotemporal Datasets
 Bayesian Modeling and Inference for High-Dimensional Spatiotemporal Datasets Sudipto Banerjee University of California, Los Angeles, USA Based upon projects involving: Abhirup Datta (Johns Hopkins University)
Bayesian Modeling and Inference for High-Dimensional Spatiotemporal Datasets Sudipto Banerjee University of California, Los Angeles, USA Based upon projects involving: Abhirup Datta (Johns Hopkins University)
On Gaussian Process Models for High-Dimensional Geostatistical Datasets
 On Gaussian Process Models for High-Dimensional Geostatistical Datasets Sudipto Banerjee Joint work with Abhirup Datta, Andrew O. Finley and Alan E. Gelfand University of California, Los Angeles, USA May
On Gaussian Process Models for High-Dimensional Geostatistical Datasets Sudipto Banerjee Joint work with Abhirup Datta, Andrew O. Finley and Alan E. Gelfand University of California, Los Angeles, USA May
9.520: Class 20. Bayesian Interpretations. Tomaso Poggio and Sayan Mukherjee
 9.520: Class 20 Bayesian Interpretations Tomaso Poggio and Sayan Mukherjee Plan Bayesian interpretation of Regularization Bayesian interpretation of the regularizer Bayesian interpretation of quadratic
9.520: Class 20 Bayesian Interpretations Tomaso Poggio and Sayan Mukherjee Plan Bayesian interpretation of Regularization Bayesian interpretation of the regularizer Bayesian interpretation of quadratic
Least Squares Regression
 CIS 50: Machine Learning Spring 08: Lecture 4 Least Squares Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may or may not cover all the
CIS 50: Machine Learning Spring 08: Lecture 4 Least Squares Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may or may not cover all the
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 4. Gaussian Processes - Regression
 Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 4. Gaussian Processes - Regression Definition (Rep.) Definition: A Gaussian process is a collection of random variables, any finite number of which have a joint Gaussian distribution.
Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 4. Gaussian Processes - Regression Definition (Rep.) Definition: A Gaussian process is a collection of random variables, any finite number of which have a joint Gaussian distribution.
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 9. Gaussian Processes - Regression
 Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 9. Gaussian Processes - Regression Repetition: Regularized Regression Before, we solved for w using the pseudoinverse. But: we can kernelize this problem as well! First step:
Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 9. Gaussian Processes - Regression Repetition: Regularized Regression Before, we solved for w using the pseudoinverse. But: we can kernelize this problem as well! First step:
STAT 518 Intro Student Presentation
 STAT 518 Intro Student Presentation Wen Wei Loh April 11, 2013 Title of paper Radford M. Neal [1999] Bayesian Statistics, 6: 475-501, 1999 What the paper is about Regression and Classification Flexible
STAT 518 Intro Student Presentation Wen Wei Loh April 11, 2013 Title of paper Radford M. Neal [1999] Bayesian Statistics, 6: 475-501, 1999 What the paper is about Regression and Classification Flexible
Stein Variational Gradient Descent: A General Purpose Bayesian Inference Algorithm
 Stein Variational Gradient Descent: A General Purpose Bayesian Inference Algorithm Qiang Liu and Dilin Wang NIPS 2016 Discussion by Yunchen Pu March 17, 2017 March 17, 2017 1 / 8 Introduction Let x R d
Stein Variational Gradient Descent: A General Purpose Bayesian Inference Algorithm Qiang Liu and Dilin Wang NIPS 2016 Discussion by Yunchen Pu March 17, 2017 March 17, 2017 1 / 8 Introduction Let x R d
Nearest Neighbor Gaussian Processes for Large Spatial Data
 Nearest Neighbor Gaussian Processes for Large Spatial Data Abhi Datta 1, Sudipto Banerjee 2 and Andrew O. Finley 3 July 31, 2017 1 Department of Biostatistics, Bloomberg School of Public Health, Johns
Nearest Neighbor Gaussian Processes for Large Spatial Data Abhi Datta 1, Sudipto Banerjee 2 and Andrew O. Finley 3 July 31, 2017 1 Department of Biostatistics, Bloomberg School of Public Health, Johns
Statistical Properties of Large Margin Classifiers
 Statistical Properties of Large Margin Classifiers Peter Bartlett Division of Computer Science and Department of Statistics UC Berkeley Joint work with Mike Jordan, Jon McAuliffe, Ambuj Tewari. slides
Statistical Properties of Large Margin Classifiers Peter Bartlett Division of Computer Science and Department of Statistics UC Berkeley Joint work with Mike Jordan, Jon McAuliffe, Ambuj Tewari. slides
Nonparameteric Regression:
 Nonparameteric Regression: Nadaraya-Watson Kernel Regression & Gaussian Process Regression Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro,
Nonparameteric Regression: Nadaraya-Watson Kernel Regression & Gaussian Process Regression Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro,
STATISTICAL BEHAVIOR AND CONSISTENCY OF CLASSIFICATION METHODS BASED ON CONVEX RISK MINIMIZATION
 STATISTICAL BEHAVIOR AND CONSISTENCY OF CLASSIFICATION METHODS BASED ON CONVEX RISK MINIMIZATION Tong Zhang The Annals of Statistics, 2004 Outline Motivation Approximation error under convex risk minimization
STATISTICAL BEHAVIOR AND CONSISTENCY OF CLASSIFICATION METHODS BASED ON CONVEX RISK MINIMIZATION Tong Zhang The Annals of Statistics, 2004 Outline Motivation Approximation error under convex risk minimization
Least Squares Regression
 E0 70 Machine Learning Lecture 4 Jan 7, 03) Least Squares Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in the lecture. They are not a substitute
E0 70 Machine Learning Lecture 4 Jan 7, 03) Least Squares Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in the lecture. They are not a substitute
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
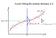 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
MINIMUM EXPECTED RISK PROBABILITY ESTIMATES FOR NONPARAMETRIC NEIGHBORHOOD CLASSIFIERS. Maya Gupta, Luca Cazzanti, and Santosh Srivastava
 MINIMUM EXPECTED RISK PROBABILITY ESTIMATES FOR NONPARAMETRIC NEIGHBORHOOD CLASSIFIERS Maya Gupta, Luca Cazzanti, and Santosh Srivastava University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Seattle,
MINIMUM EXPECTED RISK PROBABILITY ESTIMATES FOR NONPARAMETRIC NEIGHBORHOOD CLASSIFIERS Maya Gupta, Luca Cazzanti, and Santosh Srivastava University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Seattle,
Machine Learning. Bayesian Regression & Classification. Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart
 Machine Learning Bayesian Regression & Classification learning as inference, Bayesian Kernel Ridge regression & Gaussian Processes, Bayesian Kernel Logistic Regression & GP classification, Bayesian Neural
Machine Learning Bayesian Regression & Classification learning as inference, Bayesian Kernel Ridge regression & Gaussian Processes, Bayesian Kernel Logistic Regression & GP classification, Bayesian Neural
Introduction to Systems Analysis and Decision Making Prepared by: Jakub Tomczak
 Introduction to Systems Analysis and Decision Making Prepared by: Jakub Tomczak 1 Introduction. Random variables During the course we are interested in reasoning about considered phenomenon. In other words,
Introduction to Systems Analysis and Decision Making Prepared by: Jakub Tomczak 1 Introduction. Random variables During the course we are interested in reasoning about considered phenomenon. In other words,
Probabilistic Machine Learning. Industrial AI Lab.
 Probabilistic Machine Learning Industrial AI Lab. Probabilistic Linear Regression Outline Probabilistic Classification Probabilistic Clustering Probabilistic Dimension Reduction 2 Probabilistic Linear
Probabilistic Machine Learning Industrial AI Lab. Probabilistic Linear Regression Outline Probabilistic Classification Probabilistic Clustering Probabilistic Dimension Reduction 2 Probabilistic Linear
Kernel-Based Contrast Functions for Sufficient Dimension Reduction
 Kernel-Based Contrast Functions for Sufficient Dimension Reduction Michael I. Jordan Departments of Statistics and EECS University of California, Berkeley Joint work with Kenji Fukumizu and Francis Bach
Kernel-Based Contrast Functions for Sufficient Dimension Reduction Michael I. Jordan Departments of Statistics and EECS University of California, Berkeley Joint work with Kenji Fukumizu and Francis Bach
A first model of learning
 A first model of learning Let s restrict our attention to binary classification our labels belong to (or ) We observe the data where each Suppose we are given an ensemble of possible hypotheses / classifiers
A first model of learning Let s restrict our attention to binary classification our labels belong to (or ) We observe the data where each Suppose we are given an ensemble of possible hypotheses / classifiers
Classification. Chapter Introduction. 6.2 The Bayes classifier
 Chapter 6 Classification 6.1 Introduction Often encountered in applications is the situation where the response variable Y takes values in a finite set of labels. For example, the response Y could encode
Chapter 6 Classification 6.1 Introduction Often encountered in applications is the situation where the response variable Y takes values in a finite set of labels. For example, the response Y could encode
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 10, 2/21/2017
 COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 10, 2/21/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University FEATURE EXPANSIONS FEATURE EXPANSIONS
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 10, 2/21/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University FEATURE EXPANSIONS FEATURE EXPANSIONS
Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes
 Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes Andrew O. Finley 1 and Sudipto Banerjee 2 1 Department of Forestry & Department of Geography, Michigan
Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes Andrew O. Finley 1 and Sudipto Banerjee 2 1 Department of Forestry & Department of Geography, Michigan
Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes
 Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes Alan Gelfand 1 and Andrew O. Finley 2 1 Department of Statistical Science, Duke University, Durham, North
Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes Alan Gelfand 1 and Andrew O. Finley 2 1 Department of Statistical Science, Duke University, Durham, North
Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes
 Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes Andrew O. Finley Department of Forestry & Department of Geography, Michigan State University, Lansing
Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes Andrew O. Finley Department of Forestry & Department of Geography, Michigan State University, Lansing
Recap from previous lecture
 Recap from previous lecture Learning is using past experience to improve future performance. Different types of learning: supervised unsupervised reinforcement active online... For a machine, experience
Recap from previous lecture Learning is using past experience to improve future performance. Different types of learning: supervised unsupervised reinforcement active online... For a machine, experience
Consistency of Nearest Neighbor Methods
 E0 370 Statistical Learning Theory Lecture 16 Oct 25, 2011 Consistency of Nearest Neighbor Methods Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Scribe: Arun Rajkumar 1 Introduction In this lecture we return to the study
E0 370 Statistical Learning Theory Lecture 16 Oct 25, 2011 Consistency of Nearest Neighbor Methods Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Scribe: Arun Rajkumar 1 Introduction In this lecture we return to the study
Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes
 Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes Sudipto Banerjee 1 and Andrew O. Finley 2 1 Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota,
Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space-time weather datasets using Gaussian predictive processes Sudipto Banerjee 1 and Andrew O. Finley 2 1 Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota,
Unsupervised Machine Learning and Data Mining. DS 5230 / DS Fall Lecture 7. Jan-Willem van de Meent
 Unsupervised Machine Learning and Data Mining DS 5230 / DS 4420 - Fall 2018 Lecture 7 Jan-Willem van de Meent DIMENSIONALITY REDUCTION Borrowing from: Percy Liang (Stanford) Dimensionality Reduction Goal:
Unsupervised Machine Learning and Data Mining DS 5230 / DS 4420 - Fall 2018 Lecture 7 Jan-Willem van de Meent DIMENSIONALITY REDUCTION Borrowing from: Percy Liang (Stanford) Dimensionality Reduction Goal:
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771
 Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Overfitting, Bias / Variance Analysis
 Overfitting, Bias / Variance Analysis Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 8, 207 / 40 Outline Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Basic
Overfitting, Bias / Variance Analysis Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 8, 207 / 40 Outline Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Basic
Variable selection and feature construction using methods related to information theory
 Outline Variable selection and feature construction using methods related to information theory Kari 1 1 Intelligent Systems Lab, Motorola, Tempe, AZ IJCNN 2007 Outline Outline 1 Information Theory and
Outline Variable selection and feature construction using methods related to information theory Kari 1 1 Intelligent Systems Lab, Motorola, Tempe, AZ IJCNN 2007 Outline Outline 1 Information Theory and
Instance-based Learning CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2016
 Instance-based Learning CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Outline Non-parametric approach Unsupervised: Non-parametric density estimation Parzen Windows Kn-Nearest
Instance-based Learning CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Outline Non-parametric approach Unsupervised: Non-parametric density estimation Parzen Windows Kn-Nearest
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 2. Regression (cont.)
 Prof. Daniel Cremers 2. Regression (cont.) Regression with MLE (Rep.) Assume that y is affected by Gaussian noise : t = f(x, w)+ where Thus, we have p(t x, w, )=N (t; f(x, w), 2 ) 2 Maximum A-Posteriori
Prof. Daniel Cremers 2. Regression (cont.) Regression with MLE (Rep.) Assume that y is affected by Gaussian noise : t = f(x, w)+ where Thus, we have p(t x, w, )=N (t; f(x, w), 2 ) 2 Maximum A-Posteriori
Machine Learning. Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics. Feng Li. https://funglee.github.io
 Machine Learning Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 207 Overfitting Problem
Machine Learning Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 207 Overfitting Problem
Supervised Learning: Non-parametric Estimation
 Supervised Learning: Non-parametric Estimation Edmondo Trentin March 18, 2018 Non-parametric Estimates No assumptions are made on the form of the pdfs 1. There are 3 major instances of non-parametric estimates:
Supervised Learning: Non-parametric Estimation Edmondo Trentin March 18, 2018 Non-parametric Estimates No assumptions are made on the form of the pdfs 1. There are 3 major instances of non-parametric estimates:
Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II)
 Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II) Hao Helen Zhang Hao Helen Zhang Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II) 1 / 27 Outline of This Note Part I: Statistics Decision Theory (Classical
Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II) Hao Helen Zhang Hao Helen Zhang Lecture 3: Statistical Decision Theory (Part II) 1 / 27 Outline of This Note Part I: Statistics Decision Theory (Classical
Gaussian processes. Chuong B. Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008
 Gaussian processes Chuong B Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008 Many of the classical machine learning algorithms that we talked about during the first half of this course fit the following pattern:
Gaussian processes Chuong B Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008 Many of the classical machine learning algorithms that we talked about during the first half of this course fit the following pattern:
One Picture and a Thousand Words Using Matrix Approximtions October 2017 Oak Ridge National Lab Dianne P. O Leary c 2017
 One Picture and a Thousand Words Using Matrix Approximtions October 2017 Oak Ridge National Lab Dianne P. O Leary c 2017 1 One Picture and a Thousand Words Using Matrix Approximations Dianne P. O Leary
One Picture and a Thousand Words Using Matrix Approximtions October 2017 Oak Ridge National Lab Dianne P. O Leary c 2017 1 One Picture and a Thousand Words Using Matrix Approximations Dianne P. O Leary
A Divide-and-Conquer Bayesian Approach to Large-Scale Kriging
 A Divide-and-Conquer Bayesian Approach to Large-Scale Kriging Cheng Li DSAP, National University of Singapore Joint work with Rajarshi Guhaniyogi (UC Santa Cruz), Terrance D. Savitsky (US Bureau of Labor
A Divide-and-Conquer Bayesian Approach to Large-Scale Kriging Cheng Li DSAP, National University of Singapore Joint work with Rajarshi Guhaniyogi (UC Santa Cruz), Terrance D. Savitsky (US Bureau of Labor
Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Hilary Term 2016
 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Hilary Term 2016 Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford Slides and other materials available at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml Naïve Bayes
Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Hilary Term 2016 Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford Slides and other materials available at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml Naïve Bayes
Class 2 & 3 Overfitting & Regularization
 Class 2 & 3 Overfitting & Regularization Carlo Ciliberto Department of Computer Science, UCL October 18, 2017 Last Class The goal of Statistical Learning Theory is to find a good estimator f n : X Y, approximating
Class 2 & 3 Overfitting & Regularization Carlo Ciliberto Department of Computer Science, UCL October 18, 2017 Last Class The goal of Statistical Learning Theory is to find a good estimator f n : X Y, approximating
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Le Song Machine Learning I CSE 6740, Fall 2013 Naïve Bayes classifier Still use Bayes decision rule for classification P y x = P x y P y P x But assume p x y = 1 is fully factorized
Support Vector Machines Le Song Machine Learning I CSE 6740, Fall 2013 Naïve Bayes classifier Still use Bayes decision rule for classification P y x = P x y P y P x But assume p x y = 1 is fully factorized
Bayesian SAE using Complex Survey Data Lecture 4A: Hierarchical Spatial Bayes Modeling
 Bayesian SAE using Complex Survey Data Lecture 4A: Hierarchical Spatial Bayes Modeling Jon Wakefield Departments of Statistics and Biostatistics University of Washington 1 / 37 Lecture Content Motivation
Bayesian SAE using Complex Survey Data Lecture 4A: Hierarchical Spatial Bayes Modeling Jon Wakefield Departments of Statistics and Biostatistics University of Washington 1 / 37 Lecture Content Motivation
L11: Pattern recognition principles
 L11: Pattern recognition principles Bayesian decision theory Statistical classifiers Dimensionality reduction Clustering This lecture is partly based on [Huang, Acero and Hon, 2001, ch. 4] Introduction
L11: Pattern recognition principles Bayesian decision theory Statistical classifiers Dimensionality reduction Clustering This lecture is partly based on [Huang, Acero and Hon, 2001, ch. 4] Introduction
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II
 STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
12. Structural Risk Minimization. ECE 830 & CS 761, Spring 2016
 12. Structural Risk Minimization ECE 830 & CS 761, Spring 2016 1 / 23 General setup for statistical learning theory We observe training examples {x i, y i } n i=1 x i = features X y i = labels / responses
12. Structural Risk Minimization ECE 830 & CS 761, Spring 2016 1 / 23 General setup for statistical learning theory We observe training examples {x i, y i } n i=1 x i = features X y i = labels / responses
Supervised Learning. Regression Example: Boston Housing. Regression Example: Boston Housing
 Supervised Learning Unsupervised learning: To extract structure and postulate hypotheses about data generating process from observations x 1,...,x n. Visualize, summarize and compress data. We have seen
Supervised Learning Unsupervised learning: To extract structure and postulate hypotheses about data generating process from observations x 1,...,x n. Visualize, summarize and compress data. We have seen
Semi-Supervised Learning by Multi-Manifold Separation
 Semi-Supervised Learning by Multi-Manifold Separation Xiaojin (Jerry) Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Joint work with Andrew Goldberg, Zhiting Xu, Aarti Singh, and Rob
Semi-Supervised Learning by Multi-Manifold Separation Xiaojin (Jerry) Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Joint work with Andrew Goldberg, Zhiting Xu, Aarti Singh, and Rob
Probabilistic classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2016
 Probabilistic classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Topics Probabilistic approach Bayes decision theory Generative models Gaussian Bayes classifier
Probabilistic classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Topics Probabilistic approach Bayes decision theory Generative models Gaussian Bayes classifier
Gaussian Models
 Gaussian Models ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-04-28 Agenda Introduction Gaussian Discriminant Analysis Inference Linear Gaussian Systems The Wishart Distribution Inferring Parameters Introduction Gaussian Density
Gaussian Models ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-04-28 Agenda Introduction Gaussian Discriminant Analysis Inference Linear Gaussian Systems The Wishart Distribution Inferring Parameters Introduction Gaussian Density
Clustering VS Classification
 MCQ Clustering VS Classification 1. What is the relation between the distance between clusters and the corresponding class discriminability? a. proportional b. inversely-proportional c. no-relation Ans:
MCQ Clustering VS Classification 1. What is the relation between the distance between clusters and the corresponding class discriminability? a. proportional b. inversely-proportional c. no-relation Ans:
Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning
 10-715 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning Homework Due Oct 15, 10.30 am Rules Please follow these guidelines. Failure to do so, will result in loss of credit. 1. Homework is due on the due date
10-715 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning Homework Due Oct 15, 10.30 am Rules Please follow these guidelines. Failure to do so, will result in loss of credit. 1. Homework is due on the due date
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Module 3F3: Signal and Pattern Processing Handout 2:. The Multivariate Gaussian & Decision Boundaries
 University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Module 3F3: Signal and Pattern Processing Handout :. The Multivariate Gaussian & Decision Boundaries..15.1.5 1 8 6 6 8 1 Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Module 3F3: Signal and Pattern Processing Handout :. The Multivariate Gaussian & Decision Boundaries..15.1.5 1 8 6 6 8 1 Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Bayes Classification
 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Bayes Classification Class 16. 24 Oct 2017 Instructor: Bhiksha Raj - Abelino Jimenez 11755/18797 1 Recap: KNN A very effective and simple way of performing classification
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Bayes Classification Class 16. 24 Oct 2017 Instructor: Bhiksha Raj - Abelino Jimenez 11755/18797 1 Recap: KNN A very effective and simple way of performing classification
Announcements. Proposals graded
 Announcements Proposals graded Kevin Jamieson 2018 1 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington November 1, 2018 2018 Kevin Jamieson 2 MLE Recap - coin flips Data:
Announcements Proposals graded Kevin Jamieson 2018 1 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington November 1, 2018 2018 Kevin Jamieson 2 MLE Recap - coin flips Data:
Parametric Models. Dr. Shuang LIANG. School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012
 Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
20: Gaussian Processes
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 20: Gaussian Processes Lecturer: Andrew Gordon Wilson Scribes: Sai Ganesh Bandiatmakuri 1 Discussion about ML Here we discuss an introduction
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 20: Gaussian Processes Lecturer: Andrew Gordon Wilson Scribes: Sai Ganesh Bandiatmakuri 1 Discussion about ML Here we discuss an introduction
Statistics: Learning models from data
 DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
Plug-in Approach to Active Learning
 Plug-in Approach to Active Learning Stanislav Minsker Stanislav Minsker (Georgia Tech) Plug-in approach to active learning 1 / 18 Prediction framework Let (X, Y ) be a random couple in R d { 1, +1}. X
Plug-in Approach to Active Learning Stanislav Minsker Stanislav Minsker (Georgia Tech) Plug-in approach to active learning 1 / 18 Prediction framework Let (X, Y ) be a random couple in R d { 1, +1}. X
Lecture 10 February 23
 EECS 281B / STAT 241B: Advanced Topics in Statistical LearningSpring 2009 Lecture 10 February 23 Lecturer: Martin Wainwright Scribe: Dave Golland Note: These lecture notes are still rough, and have only
EECS 281B / STAT 241B: Advanced Topics in Statistical LearningSpring 2009 Lecture 10 February 23 Lecturer: Martin Wainwright Scribe: Dave Golland Note: These lecture notes are still rough, and have only
Data Mining Techniques
 Data Mining Techniques CS 6220 - Section 3 - Fall 2016 Lecture 12 Jan-Willem van de Meent (credit: Yijun Zhao, Percy Liang) DIMENSIONALITY REDUCTION Borrowing from: Percy Liang (Stanford) Linear Dimensionality
Data Mining Techniques CS 6220 - Section 3 - Fall 2016 Lecture 12 Jan-Willem van de Meent (credit: Yijun Zhao, Percy Liang) DIMENSIONALITY REDUCTION Borrowing from: Percy Liang (Stanford) Linear Dimensionality
MIT 9.520/6.860, Fall 2017 Statistical Learning Theory and Applications. Class 19: Data Representation by Design
 MIT 9.520/6.860, Fall 2017 Statistical Learning Theory and Applications Class 19: Data Representation by Design What is data representation? Let X be a data-space X M (M) F (M) X A data representation
MIT 9.520/6.860, Fall 2017 Statistical Learning Theory and Applications Class 19: Data Representation by Design What is data representation? Let X be a data-space X M (M) F (M) X A data representation
Nonparametric Bayesian Methods (Gaussian Processes)
 [70240413 Statistical Machine Learning, Spring, 2015] Nonparametric Bayesian Methods (Gaussian Processes) Jun Zhu dcszj@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn http://bigml.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/~jun State Key Lab of Intelligent
[70240413 Statistical Machine Learning, Spring, 2015] Nonparametric Bayesian Methods (Gaussian Processes) Jun Zhu dcszj@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn http://bigml.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/~jun State Key Lab of Intelligent
Learning Theory. Ingo Steinwart University of Stuttgart. September 4, 2013
 Learning Theory Ingo Steinwart University of Stuttgart September 4, 2013 Ingo Steinwart University of Stuttgart () Learning Theory September 4, 2013 1 / 62 Basics Informal Introduction Informal Description
Learning Theory Ingo Steinwart University of Stuttgart September 4, 2013 Ingo Steinwart University of Stuttgart () Learning Theory September 4, 2013 1 / 62 Basics Informal Introduction Informal Description
Model Selection for Gaussian Processes
 Institute for Adaptive and Neural Computation School of Informatics,, UK December 26 Outline GP basics Model selection: covariance functions and parameterizations Criteria for model selection Marginal
Institute for Adaptive and Neural Computation School of Informatics,, UK December 26 Outline GP basics Model selection: covariance functions and parameterizations Criteria for model selection Marginal
Statistical Approaches to Learning and Discovery. Week 4: Decision Theory and Risk Minimization. February 3, 2003
 Statistical Approaches to Learning and Discovery Week 4: Decision Theory and Risk Minimization February 3, 2003 Recall From Last Time Bayesian expected loss is ρ(π, a) = E π [L(θ, a)] = L(θ, a) df π (θ)
Statistical Approaches to Learning and Discovery Week 4: Decision Theory and Risk Minimization February 3, 2003 Recall From Last Time Bayesian expected loss is ρ(π, a) = E π [L(θ, a)] = L(θ, a) df π (θ)
Approximation Theoretical Questions for SVMs
 Ingo Steinwart LA-UR 07-7056 October 20, 2007 Statistical Learning Theory: an Overview Support Vector Machines Informal Description of the Learning Goal X space of input samples Y space of labels, usually
Ingo Steinwart LA-UR 07-7056 October 20, 2007 Statistical Learning Theory: an Overview Support Vector Machines Informal Description of the Learning Goal X space of input samples Y space of labels, usually
Lecture Notes 15 Prediction Chapters 13, 22, 20.4.
 Lecture Notes 15 Prediction Chapters 13, 22, 20.4. 1 Introduction Prediction is covered in detail in 36-707, 36-701, 36-715, 10/36-702. Here, we will just give an introduction. We observe training data
Lecture Notes 15 Prediction Chapters 13, 22, 20.4. 1 Introduction Prediction is covered in detail in 36-707, 36-701, 36-715, 10/36-702. Here, we will just give an introduction. We observe training data
CSci 8980: Advanced Topics in Graphical Models Gaussian Processes
 CSci 8980: Advanced Topics in Graphical Models Gaussian Processes Instructor: Arindam Banerjee November 15, 2007 Gaussian Processes Outline Gaussian Processes Outline Parametric Bayesian Regression Gaussian
CSci 8980: Advanced Topics in Graphical Models Gaussian Processes Instructor: Arindam Banerjee November 15, 2007 Gaussian Processes Outline Gaussian Processes Outline Parametric Bayesian Regression Gaussian
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
Distributions of Persistence Diagrams and Approximations
 Distributions of Persistence Diagrams and Approximations Vasileios Maroulas Department of Mathematics Department of Business Analytics and Statistics University of Tennessee August 31, 2018 Thanks V. Maroulas
Distributions of Persistence Diagrams and Approximations Vasileios Maroulas Department of Mathematics Department of Business Analytics and Statistics University of Tennessee August 31, 2018 Thanks V. Maroulas
Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function.
 Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
AdaBoost and other Large Margin Classifiers: Convexity in Classification
 AdaBoost and other Large Margin Classifiers: Convexity in Classification Peter Bartlett Division of Computer Science and Department of Statistics UC Berkeley Joint work with Mikhail Traskin. slides at
AdaBoost and other Large Margin Classifiers: Convexity in Classification Peter Bartlett Division of Computer Science and Department of Statistics UC Berkeley Joint work with Mikhail Traskin. slides at
Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces
 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 10th, 2010 Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces Lecturer: Lorenzo Rosasco Scribe: Greg Durrett 1 Introduction In the previous two lectures, we
9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 10th, 2010 Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces Lecturer: Lorenzo Rosasco Scribe: Greg Durrett 1 Introduction In the previous two lectures, we
1. Mathematical Foundations of Machine Learning
 1. Mathematical Foundations of Machine Learning 1.1 Basic Concepts Definition of Learning Definition [Mitchell (1997)] A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of
1. Mathematical Foundations of Machine Learning 1.1 Basic Concepts Definition of Learning Definition [Mitchell (1997)] A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of
Fast learning rates for plug-in classifiers under the margin condition
 arxiv:math/0507180v3 [math.st] 27 May 21 Fast learning rates for plug-in classifiers under the margin condition Jean-Yves AUDIBERT 1 and Alexandre B. TSYBAKOV 2 1 Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées,
arxiv:math/0507180v3 [math.st] 27 May 21 Fast learning rates for plug-in classifiers under the margin condition Jean-Yves AUDIBERT 1 and Alexandre B. TSYBAKOV 2 1 Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées,
Statistical Machine Learning Hilary Term 2018
 Statistical Machine Learning Hilary Term 2018 Pier Francesco Palamara Department of Statistics University of Oxford Slide credits and other course material can be found at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~palamara/sml18.html
Statistical Machine Learning Hilary Term 2018 Pier Francesco Palamara Department of Statistics University of Oxford Slide credits and other course material can be found at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~palamara/sml18.html
5.6 Nonparametric Logistic Regression
 5.6 onparametric Logistic Regression Dmitri Dranishnikov University of Florida Statistical Learning onparametric Logistic Regression onparametric? Doesnt mean that there are no parameters. Just means that
5.6 onparametric Logistic Regression Dmitri Dranishnikov University of Florida Statistical Learning onparametric Logistic Regression onparametric? Doesnt mean that there are no parameters. Just means that
Bayesian Regularization
 Bayesian Regularization Aad van der Vaart Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam International Congress of Mathematicians Hyderabad, August 2010 Contents Introduction Abstract result Gaussian process priors Co-authors
Bayesian Regularization Aad van der Vaart Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam International Congress of Mathematicians Hyderabad, August 2010 Contents Introduction Abstract result Gaussian process priors Co-authors
Bayesian estimation of the discrepancy with misspecified parametric models
 Bayesian estimation of the discrepancy with misspecified parametric models Pierpaolo De Blasi University of Torino & Collegio Carlo Alberto Bayesian Nonparametrics workshop ICERM, 17-21 September 2012
Bayesian estimation of the discrepancy with misspecified parametric models Pierpaolo De Blasi University of Torino & Collegio Carlo Alberto Bayesian Nonparametrics workshop ICERM, 17-21 September 2012
Hilbert Space Methods for Reduced-Rank Gaussian Process Regression
 Hilbert Space Methods for Reduced-Rank Gaussian Process Regression Arno Solin and Simo Särkkä Aalto University, Finland Workshop on Gaussian Process Approximation Copenhagen, Denmark, May 2015 Solin &
Hilbert Space Methods for Reduced-Rank Gaussian Process Regression Arno Solin and Simo Särkkä Aalto University, Finland Workshop on Gaussian Process Approximation Copenhagen, Denmark, May 2015 Solin &
ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning
 ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Sept 27, 2015 Outline Linear regression Ridge regression and Lasso Time complexity (closed form solution) Iterative Solvers Regression Input: training
ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Sept 27, 2015 Outline Linear regression Ridge regression and Lasso Time complexity (closed form solution) Iterative Solvers Regression Input: training
Scalable robust hypothesis tests using graphical models
 Scalable robust hypothesis tests using graphical models Umamahesh Srinivas ipal Group Meeting October 22, 2010 Binary hypothesis testing problem Random vector x = (x 1,...,x n ) R n generated from either
Scalable robust hypothesis tests using graphical models Umamahesh Srinivas ipal Group Meeting October 22, 2010 Binary hypothesis testing problem Random vector x = (x 1,...,x n ) R n generated from either
An introduction to Bayesian inference and model comparison J. Daunizeau
 An introduction to Bayesian inference and model comparison J. Daunizeau ICM, Paris, France TNU, Zurich, Switzerland Overview of the talk An introduction to probabilistic modelling Bayesian model comparison
An introduction to Bayesian inference and model comparison J. Daunizeau ICM, Paris, France TNU, Zurich, Switzerland Overview of the talk An introduction to probabilistic modelling Bayesian model comparison
Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces
 Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces Lorenzo Rosasco 9.520 Class 03 February 9, 2011 About this class Goal To introduce a particularly useful family of hypothesis spaces called Reproducing Kernel Hilbert
Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces Lorenzo Rosasco 9.520 Class 03 February 9, 2011 About this class Goal To introduce a particularly useful family of hypothesis spaces called Reproducing Kernel Hilbert
CMU-Q Lecture 24:
 CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 24: Supervised Learning 2 Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro SUPERVISED LEARNING Hypotheses space Hypothesis function Labeled Given Errors Performance criteria Given a collection of input
CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 24: Supervised Learning 2 Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro SUPERVISED LEARNING Hypotheses space Hypothesis function Labeled Given Errors Performance criteria Given a collection of input
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Bishop Chapter 2: Probability Distributions
 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Chapter 2: Probability Distributions Cécile Amblard Alex Kläser Jakob Verbeek October 11, 27 Probability Distributions: General Density Estimation: given a finite
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Chapter 2: Probability Distributions Cécile Amblard Alex Kläser Jakob Verbeek October 11, 27 Probability Distributions: General Density Estimation: given a finite
The Bayes classifier
 The Bayes classifier Consider where is a random vector in is a random variable (depending on ) Let be a classifier with probability of error/risk given by The Bayes classifier (denoted ) is the optimal
The Bayes classifier Consider where is a random vector in is a random variable (depending on ) Let be a classifier with probability of error/risk given by The Bayes classifier (denoted ) is the optimal
Classification with Reject Option
 Classification with Reject Option Bartlett and Wegkamp (2008) Wegkamp and Yuan (2010) February 17, 2012 Outline. Introduction.. Classification with reject option. Spirit of the papers BW2008.. Infinite
Classification with Reject Option Bartlett and Wegkamp (2008) Wegkamp and Yuan (2010) February 17, 2012 Outline. Introduction.. Classification with reject option. Spirit of the papers BW2008.. Infinite
BINARY CLASSIFICATION
 BINARY CLASSIFICATION MAXIM RAGINSY The problem of binary classification can be stated as follows. We have a random couple Z = X, Y ), where X R d is called the feature vector and Y {, } is called the
BINARY CLASSIFICATION MAXIM RAGINSY The problem of binary classification can be stated as follows. We have a random couple Z = X, Y ), where X R d is called the feature vector and Y {, } is called the
