Metamathematics of Elementary Mathematics Lecture 5 Navigation on the Riemann Sphere
|
|
|
- Diana Hodges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Metamathematics of Elementary Mathematics Lecture 5 Navigation on the Riemann Sphere Alexandre Borovik based on ideas of Hovik Khudaverdyan Nesin Mathematics Village Şirince, 26 Jul
2 A heroic era of seafaring with astrolabe and compass. 2
3 A ship compass in a Cardano suspension. A modern replica. 3
4 An astrolabe. 4
5 Loxodrome: a path of constant direction on the globe. 5
6 Rhumb lines: lines of constant direction on a map. How to make them straight? 6
7 Gerard Mercator ( ). 7
8 Mercator s famous map, 1569: rhumb lines are straight. 8
9 Spherical coordinates on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = R 2 : x = R sin θ cos ϕ, y = R sin θ sin ϕ, z = R cos θ 9
10 (θ(t), ϕ(t)) a curve on the sphere tangent vector (x t, y t, z t ) at point (θ, ϕ): R(cos θ cos ϕ θ t sin θ sin ϕ ϕ t, cos θ sin ϕ θ t + sin θ cos ϕ ϕ t, sin θ θ t ), Meridian: θ = t, ϕ = const tangent vector to meridian: R(cos θ cos ϕ, cos θ sin ϕ, sin θ). Cosine of angle α(t) between the curve and the meridian: cos α(t) = θ t (t) θ 2 t + sin 2 θ(t)ϕ 2 t(t) (1) 10
11 Loxodrome: θ t (t) θ 2 t + sin 2 θ(t)ϕ 2 t(t) = const θ t = ± c ϕ t 1 c sin θ 2 Change of variables: t = t(ϕ), θ = θ(ϕ) dϕ dθ ϕ(θ) = k = ±1 c2 c 1 sin θ dθ sin θ = k log tan θ 2 + ϕ 0 11
12 Stereographic projection from the North Pole onto the plane tangent at the South Pole. Invented or known to Apollonius of Perga? 12
13 R r = tan θ 2 Choose polar coordinates r, ϕ in the plane, with ϕ being the same as in spherical coordinates. Then stereographic projection sends (θ, ϕ) ( R tan θ, ϕ) 2 13
14 Since the image of loxodrome tan θ 2 = R r, ϕ(θ) = k log tan θ 2 + ϕ 0 becomes ϕ = k log r R + ϕ 0. This is logarithmic spiral. 14
15 Logarithmic spiral ϕ = k log r R + ϕ 0. 15
16 Logarithmic spiral is characterised by the property that it intersects radial lines at constant angles. Insects fly to a candle along a logarithmic spiral. 16
17 Ommatidia in a facet eye of an insect control bearing at source of light. 17
18 A spider s web. The same principle of constant angles? 18
19 Move to complex variables Z = u + iv = re iϕ Then the map W = s + it = log Z R W = log Z R = log r R + iϕ, sends logarithmic spirals to straight lines t = ks + t 0. ϕ = k log r R + ϕ 0. Meridians ϕ = ϕ 0 are sent to straight lines t = ϕ 0 and parallels θ = θ 0 to segments s = log tan θ
20 A loxodrome, a logarithmic spiral and a rhumb line on a cylinder. (Dr G Megyesi). 20
21 Why cylinder? Bernhard Riemann ( ). Riemann sphere: identified with the complex plane by stereographic projection. 21
22 Leonard Euler ( ). is periodic, because z e z, e z+2πi = e z e 2πi = e z 1 = e z, e πi = 1, 22
23 Now Mercator s projection is nothing else but the logarithm itself: Z Log Z. 23
24 Conformal map: a map from a surface to surface which preserves angles. Map C C z az is conformal. If w = F (z) from C to C is differentiable then w F (z) z, and F is conformal. 24
25 An orientation-preserving conformal map is an analytic function. Indeed, the Jacobian i spositive. The Jacobi matrix: R 2 R 2 (x, y) (u, v) ( u x v x is aproduct of scalar and orthogonal matrices. This is exactly Cauchy-Riemann condition: u x = v y, u y = v x. The rest is the classical theory of the functions of complex variable. u y v y ) 25
26 How all that was done? 26
27 Mercator s globe,
28 Segments of Mercator s globe 28
29 Edward Right, The Correction of Certain Errors in Navigation,
30 c c = 1 cos φ = sec φ. 30
31 Accumulation of corrections: d sec 1,, d sec 2,, d sec 3,... Y (φ) = d(sec 1 + sec 2 + sec sec φ). 31
32 Wright just summed up the table of secants. In modern terminology: Y (φ) = φ 0 sec tdt. 32
33 Suppose a sphericall superficies with meridians, paralels, rumbs, and the whole hydrographicall description drawne thereupon to bee inscribed into a concave cylinder, their axes agreeing in one. Let this sphericall superficies swel like a bladder, (whiles it is in blowing) equally alwayes in euerie part thereof (that is as much in longitude as in latitude) till it apply, and ioyne it selfe (round about, and all alongst also towardes either pole) vnto the concave superficies of the cylinder : each paralel vpon this sphericall superficies increasing successively from the equinoctiall towardes eyther pole, vntil it come to bee of equall diameter with the cylinder, and consequently the meridians stil widening them selves, til they come to be so far distant euery where ech from other as they are at the Equinoctiall. 33
34 Edward Wright was thinking in terms of conformal maps! 34
35 John Napier ( ) 35
36 Henri Bond, 1644: noticed, by looking into tables of logarithm of tangents, that (which is the same as log tan θ 2 ) For years remained an open problem. Y (φ) = log(tan(φ/2 + π/4)) 36
37 Isaac Barrow ( ) Finally proved φ 0 sec(t) dt = log ( ( φ tan 2 + π )) 4 37
38 Is Mercator s projection misleading? 38
39 New look at the changing Earth 39
40 Map of the North Pole, Notice a huge blank space. 40
41 Modern developments: conformal map of the surface of brain on a sphere. 41
42 From cartography to colonoscopy Virtual colonoscopy has some fundamental problems, which it shares with conventional colonoscopy. The most important one is that the navigation using inner views is very challenging... We present a method for mapping the colon onto a flat surface [... ] based on a certain mathematical technique from Riemann surface theory, which allows us to map any highly undulating tubular surface without handles or self-intersections onto a planar rectangle in a conformal manner. [S. Haker et al. Non-distorting Flattening for Virtual Colonoscopy, Lect. Notes Comp. Sci (2000) ] 42
43 Thank you very much for your attention! 43
The Mathematics of Maps Lecture 4. Dennis The The Mathematics of Maps Lecture 4 1/29
 The Mathematics of Maps Lecture 4 Dennis The The Mathematics of Maps Lecture 4 1/29 Mercator projection Dennis The The Mathematics of Maps Lecture 4 2/29 The Mercator projection (1569) Dennis The The Mathematics
The Mathematics of Maps Lecture 4 Dennis The The Mathematics of Maps Lecture 4 1/29 Mercator projection Dennis The The Mathematics of Maps Lecture 4 2/29 The Mercator projection (1569) Dennis The The Mathematics
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
Map Projections. Chapter 3. Emmanuel Stefanakis
 Stefanakis, E., 2014. Geographic Databases and Information Systems. CreateSpace Independent Publ. [In English], pp.386. Get a copy from Amazon Chapter 3 Map Projections Emmanuel Stefanakis http://www2.unb.ca/~estef/
Stefanakis, E., 2014. Geographic Databases and Information Systems. CreateSpace Independent Publ. [In English], pp.386. Get a copy from Amazon Chapter 3 Map Projections Emmanuel Stefanakis http://www2.unb.ca/~estef/
Outline. Shape of the Earth. Geographic Coordinates (φ, λ, z) Ellipsoid or Spheroid Rotate an ellipse around an axis. Ellipse.
 Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Georeferencing. datum. projection. scale. The next few lectures will introduce you to these elements. on the Earth, you ll need to understand how
 Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Notes on Differentiation
 1 The Chain Rule This is the following famous result: Notes on Differentiation 1.1 Theorem. Suppose U and V are open sets with f and g complex-valued functions defined on U and V respectively, where f(u)
1 The Chain Rule This is the following famous result: Notes on Differentiation 1.1 Theorem. Suppose U and V are open sets with f and g complex-valued functions defined on U and V respectively, where f(u)
One a Possible Constructive Geometrical Derivation of Mercator s Conformal Cylindrical Map Projection Based on Some Historical Facts
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 10 (2006), No. 1, 63 71. One a Possible Constructive Geometrical Derivation of Mercator s Conformal Cylindrical Map Projection Based on Some Historical Facts Branislav
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 10 (2006), No. 1, 63 71. One a Possible Constructive Geometrical Derivation of Mercator s Conformal Cylindrical Map Projection Based on Some Historical Facts Branislav
Map Projections 2/4/2013. Map Projections. Rhumb Line (Loxodrome) Great Circle. The GLOBE. Line of constant bearing (e.g., 292.
 The GLOBE ADVANTAGES Directions True Distances True Shapes True Area True DISADVANTAGES Very small scale with little detail. Costly to reproduce and update. Difficult to carry around. Bulky to store. FACTS
The GLOBE ADVANTAGES Directions True Distances True Shapes True Area True DISADVANTAGES Very small scale with little detail. Costly to reproduce and update. Difficult to carry around. Bulky to store. FACTS
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems
 Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
The Prehistory of Conformal Mapping
 The Prehistory of Conformal Mapping Development of Mathematical Cartography in the Eighteenth Century George W. Heine, III The stereographic projection, used in ancient times, and Mercator s projection,
The Prehistory of Conformal Mapping Development of Mathematical Cartography in the Eighteenth Century George W. Heine, III The stereographic projection, used in ancient times, and Mercator s projection,
History of Cartography,
 Maps History of Cartography, the art and science of making maps ~2300 BC ~600 BC Early oldest known maps: Babylonian clay tablets. Greek and Roman Ptolemy s (about AD 85-165) "world map" depicted the Old
Maps History of Cartography, the art and science of making maps ~2300 BC ~600 BC Early oldest known maps: Babylonian clay tablets. Greek and Roman Ptolemy s (about AD 85-165) "world map" depicted the Old
Spatial Data, 16 th Century Dutchmen, GPS and GIS. Martin Charlton, National Centre for Geocomputation National University of Ireland Maynooth
 Spatial Data, 16 th Century Dutchmen, GPS and GIS Martin Charlton, National Centre for Geocomputation National University of Ireland Maynooth Maps as truth Maps are cultural artifacts, comparable in history
Spatial Data, 16 th Century Dutchmen, GPS and GIS Martin Charlton, National Centre for Geocomputation National University of Ireland Maynooth Maps as truth Maps are cultural artifacts, comparable in history
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
Math 396. Map making
 Math 396. Map making 1. Motivation When a cartographer makes a map of part of the surface of the earth, this amounts to choosing a C isomorphism from a 2-submanifold with corners S in the sphere S 2 (r)
Math 396. Map making 1. Motivation When a cartographer makes a map of part of the surface of the earth, this amounts to choosing a C isomorphism from a 2-submanifold with corners S in the sphere S 2 (r)
GIST 3300 / Geographic Information Systems. Last Time. Today
 GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Map Projections (Part 1)
 1 Earth is a round, maps are not. Four projection families. Equivalent (Equal Area) projections Preserves relative areas Commonly used for thematic maps Ex: Albers Conformal projections Preserve angles,
1 Earth is a round, maps are not. Four projection families. Equivalent (Equal Area) projections Preserves relative areas Commonly used for thematic maps Ex: Albers Conformal projections Preserve angles,
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections
 Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Latitude and Longitude Pre Test
 Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
What is a Map Projection?
 What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Projections and Coordinate Systems Overview Projections Examples of different projections Coordinate systems Datums Projections Overview Projections and Coordinate Systems GIS must accurately represent
Projections and Coordinate Systems Overview Projections Examples of different projections Coordinate systems Datums Projections Overview Projections and Coordinate Systems GIS must accurately represent
Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections
 Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Recall: The scale transformation
 Recall: The scale transformation Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 3: Map Projection Basics Professor Keith Clarke 1:400M The real world A representation of the world A cartographic problem
Recall: The scale transformation Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 3: Map Projection Basics Professor Keith Clarke 1:400M The real world A representation of the world A cartographic problem
Dirty REMOTE SENSING : Lecture 8 A mapping interlude..
 Dirty REMOTE SENSING : Lecture 8 A mapping interlude.. Stuart Green Teagasc Spatial Analysis Group Stuart.green@teagasc.ie Web for the Week: http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gps.htm http://www.cstars.ucdavis.edu/classes/ers186-w03/lecture17/lecture17.ppt
Dirty REMOTE SENSING : Lecture 8 A mapping interlude.. Stuart Green Teagasc Spatial Analysis Group Stuart.green@teagasc.ie Web for the Week: http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gps.htm http://www.cstars.ucdavis.edu/classes/ers186-w03/lecture17/lecture17.ppt
The Sphere of the Earth Activities
 The Sphere of the Earth Activities December 20, 2012 Daniel Ramos MMACA (Museu de Matemàtiques de Catalunya) These activities are designed to be done with the materials, posters and software of the exhibit
The Sphere of the Earth Activities December 20, 2012 Daniel Ramos MMACA (Museu de Matemàtiques de Catalunya) These activities are designed to be done with the materials, posters and software of the exhibit
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
Map Projections. Chapter 4 MAP PROJECTION
 Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts.
 MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
A map is a small-scale flat-surface representation of some portion of the earth s surface.
 MAPS AND CHARTS A map is a small-scale flat-surface representation of some portion of the earth s surface. A representation that is designed for plotting navigational information is called a chart. Often
MAPS AND CHARTS A map is a small-scale flat-surface representation of some portion of the earth s surface. A representation that is designed for plotting navigational information is called a chart. Often
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections.
 Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006
 I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
Coordinate Systems. Location on earth is defined by coordinates
 Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet. Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about!
 Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
Map Projections. Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps
 Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity
 Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations
 Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
Plane coordinates ~~~~~~~~~~
 Coordinate Systems & Map Projections Geographic coordinates A Basic Introduction to Coordinate Systems & Map Projections Latitude & longitude Angles Parallels & meridians Lines Plane coordinates ~~~~~~~~~~
Coordinate Systems & Map Projections Geographic coordinates A Basic Introduction to Coordinate Systems & Map Projections Latitude & longitude Angles Parallels & meridians Lines Plane coordinates ~~~~~~~~~~
Mathematics 2203, Test 1 - Solutions
 Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Geographic coordinate systems
 1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
The Elements of GIS. Organizing Data and Information. The GIS Database. MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION
 GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
Tutorial Exercises: Geometric Connections
 Tutorial Exercises: Geometric Connections 1. Geodesics in the Isotropic Mercator Projection When the surface of the globe is projected onto a flat map some aspects of the map are inevitably distorted.
Tutorial Exercises: Geometric Connections 1. Geodesics in the Isotropic Mercator Projection When the surface of the globe is projected onto a flat map some aspects of the map are inevitably distorted.
Georeferencing. Place names Postal addresses Postal codes Coordinate systems (lat/long, UTM, etc.)
 Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006
 Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006 I. Common Projections There are several areas where maps are commonly used and a few projections dominate these fields. An
Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006 I. Common Projections There are several areas where maps are commonly used and a few projections dominate these fields. An
Maths for Map Makers
 SUB Gottingen 7 210 050 861 99 A 2003 Maths for Map Makers by Arthur Allan Whittles Publishing Contents /v Chapter 1 Numbers and Calculation 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14
SUB Gottingen 7 210 050 861 99 A 2003 Maths for Map Makers by Arthur Allan Whittles Publishing Contents /v Chapter 1 Numbers and Calculation 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14
Physics 480/581. Homework No. 10 Solutions: due Friday, 19 October, 2018
 Physics 480/58 Homework No. 0 Solutions: due Friday, 9 October, 208. Using the coordinate bases for -forms, and their reciprocal bases for tangent vectors, and the usual form of the Schwarzschild metric,
Physics 480/58 Homework No. 0 Solutions: due Friday, 9 October, 208. Using the coordinate bases for -forms, and their reciprocal bases for tangent vectors, and the usual form of the Schwarzschild metric,
MATH 423/ Note that the algebraic operations on the right hand side are vector subtraction and scalar multiplication.
 MATH 423/673 1 Curves Definition: The velocity vector of a curve α : I R 3 at time t is the tangent vector to R 3 at α(t), defined by α (t) T α(t) R 3 α α(t + h) α(t) (t) := lim h 0 h Note that the algebraic
MATH 423/673 1 Curves Definition: The velocity vector of a curve α : I R 3 at time t is the tangent vector to R 3 at α(t), defined by α (t) T α(t) R 3 α α(t + h) α(t) (t) := lim h 0 h Note that the algebraic
Final Examination 201-NYA-05 May 18, 2018
 . ( points) Evaluate each of the following limits. 3x x + (a) lim x x 3 8 x + sin(5x) (b) lim x sin(x) (c) lim x π/3 + sec x ( (d) x x + 5x ) (e) lim x 5 x lim x 5 + x 6. (3 points) What value of c makes
. ( points) Evaluate each of the following limits. 3x x + (a) lim x x 3 8 x + sin(5x) (b) lim x sin(x) (c) lim x π/3 + sec x ( (d) x x + 5x ) (e) lim x 5 x lim x 5 + x 6. (3 points) What value of c makes
Navigation. Longitude and Latitude Foundations of Navigation. MTPs:
 Navigation 3.01 Foundations of Navigation References: FTGU pages 177-178, 184-190 Transport Canada Study and Reference Guide Glider Pilot Canada Flight Training Manual Pilot Navigation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/transverse_mercator_projection#spherical_transverse_mercator
Navigation 3.01 Foundations of Navigation References: FTGU pages 177-178, 184-190 Transport Canada Study and Reference Guide Glider Pilot Canada Flight Training Manual Pilot Navigation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/transverse_mercator_projection#spherical_transverse_mercator
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Reference Coordinate Systems (3/3)
 Reference Coordinate Systems (3/3) José E. Sanguino I Instituto de elecomunicações Instituto Superior écnico, v. Rovisco Pais, 049-00 Lisboa, Portugal el: +35.848468, Fax: +35.84847, Email: sanguino@lx.it.pt
Reference Coordinate Systems (3/3) José E. Sanguino I Instituto de elecomunicações Instituto Superior écnico, v. Rovisco Pais, 049-00 Lisboa, Portugal el: +35.848468, Fax: +35.84847, Email: sanguino@lx.it.pt
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography
 EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
Surfaces JWR. February 13, 2014
 Surfaces JWR February 13, 214 These notes summarize the key points in the second chapter of Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces by Manfredo P. do Carmo. I wrote them to assure that the terminology
Surfaces JWR February 13, 214 These notes summarize the key points in the second chapter of Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces by Manfredo P. do Carmo. I wrote them to assure that the terminology
Working with georeferenced data. What is georeferencing? Coordinate Systems. Geographic and Projected Coordinate System
 GIS501 Fundamentals of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Coordinate Systems Working with georeferenced data What is georeferencing? Geographically referenced data which is, in some way, referenced
GIS501 Fundamentals of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Coordinate Systems Working with georeferenced data What is georeferencing? Geographically referenced data which is, in some way, referenced
Chapter 1: The World of Geography
 Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E. Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections
 Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
Map Projections. What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL
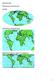 Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017
 Map Projections & Coordinate Sstems Laing the Earth Flat Wh? Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveing instruments measure in meters or
Map Projections & Coordinate Sstems Laing the Earth Flat Wh? Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveing instruments measure in meters or
MERCATOR THE PROJECTIONS THE NORMAL AND TRANSVERSE MERCATOR PROJECTIONS ON THE SPHERE AND THE ELLIPSOID WITH FULL DERIVATIONS OF ALL FORMULAE
 THE MERCATOR PROJECTIONS THE NORMAL AND TRANSVERSE MERCATOR PROJECTIONS ON THE SPHERE AND THE ELLIPSOID WITH FULL DERIVATIONS OF ALL FORMULAE PETER OSBORNE EDINBURGH 2008 The Transverse Mercator projection
THE MERCATOR PROJECTIONS THE NORMAL AND TRANSVERSE MERCATOR PROJECTIONS ON THE SPHERE AND THE ELLIPSOID WITH FULL DERIVATIONS OF ALL FORMULAE PETER OSBORNE EDINBURGH 2008 The Transverse Mercator projection
Introduction to Geographic Information Science. Updates/News. Last Lecture. Geography 4103 / Map Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts. -Coordinate Systems -Datum
 Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Conformal Mapping Lecture 20 Conformal Mapping
 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f (z) be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z). The parametric equation of C is
Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f (z) be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z). The parametric equation of C is
Shape e o f f the e Earth
 1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
Math 461 Homework 8. Paul Hacking. November 27, 2018
 Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 (1) Let S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F :
Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 (1) Let S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F :
Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018
 (1) Let Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 +y 2 +z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F : S
(1) Let Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 +y 2 +z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F : S
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/10/2013. Why? M. Helper GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 2. M. Helper GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 4
 Map Projections & Coordinates Laing the earth flat Wh? Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveing instruments measure in meters or feet,
Map Projections & Coordinates Laing the earth flat Wh? Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveing instruments measure in meters or feet,
Map Projections. Which ones best suit your needs?
 1 z 21 2010-02-20 18:38 Map Projections The Globe Mercator Transverse Mercator Oblique Mercator Space Oblique Mercator Miller Cylindrical Robinson Sinusoidal Equal Area Orthographic Stereographic Gnomonic
1 z 21 2010-02-20 18:38 Map Projections The Globe Mercator Transverse Mercator Oblique Mercator Space Oblique Mercator Miller Cylindrical Robinson Sinusoidal Equal Area Orthographic Stereographic Gnomonic
Map Projections. is about presenting the round Earth on a flat surface.map Projections: Vermeer s Cartographer
 Map Projections is about presenting the round Earth on a flat surface.map Projections: Vermeer s Cartographer What is a map projection? A projection is a way to make a flat representation of the Earth
Map Projections is about presenting the round Earth on a flat surface.map Projections: Vermeer s Cartographer What is a map projection? A projection is a way to make a flat representation of the Earth
Lecture Wise Questions from 23 to 45 By Virtualians.pk. Q105. What is the impact of double integration in finding out the area and volume of Regions?
 Lecture Wise Questions from 23 to 45 By Virtualians.pk Q105. What is the impact of double integration in finding out the area and volume of Regions? Ans: It has very important contribution in finding the
Lecture Wise Questions from 23 to 45 By Virtualians.pk Q105. What is the impact of double integration in finding out the area and volume of Regions? Ans: It has very important contribution in finding the
Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1
 Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1 (a.g.kovalev@dpmms.cam.ac.uk) 1. Suppose that H is a hyperplane in Euclidean n-space R n defined by u x = c for some unit vector u and constant c. The reflection
Part IB GEOMETRY (Lent 2016): Example Sheet 1 (a.g.kovalev@dpmms.cam.ac.uk) 1. Suppose that H is a hyperplane in Euclidean n-space R n defined by u x = c for some unit vector u and constant c. The reflection
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools
 Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
+ dxk. dt 2. dt Γi km dxm. . Its equations of motion are second order differential equations. with intitial conditions
 Homework 7. Solutions 1 Show that great circles are geodesics on sphere. Do it a) using the fact that for geodesic, acceleration is orthogonal to the surface. b ) using straightforwardl equations for geodesics
Homework 7. Solutions 1 Show that great circles are geodesics on sphere. Do it a) using the fact that for geodesic, acceleration is orthogonal to the surface. b ) using straightforwardl equations for geodesics
Part IB Geometry. Theorems. Based on lectures by A. G. Kovalev Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2016
 Part IB Geometry Theorems Based on lectures by A. G. Kovalev Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IB Geometry Theorems Based on lectures by A. G. Kovalev Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester Practice Final Exam
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2010-11 Practice Final Exam 1. A ship is moving northwest at a speed of 50 mi/h. A passenger is walking due southeast on the deck at 4 mi/h. Find the speed of the passenger
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2010-11 Practice Final Exam 1. A ship is moving northwest at a speed of 50 mi/h. A passenger is walking due southeast on the deck at 4 mi/h. Find the speed of the passenger
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping
 Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
2 General Relativity. 2.1 Curved 2D and 3D space
 22 2 General Relativity The general theory of relativity (Einstein 1915) is the theory of gravity. General relativity ( Einstein s theory ) replaced the previous theory of gravity, Newton s theory. The
22 2 General Relativity The general theory of relativity (Einstein 1915) is the theory of gravity. General relativity ( Einstein s theory ) replaced the previous theory of gravity, Newton s theory. The
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere
 The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
Index. Bertrand mate, 89 bijection, 48 bitangent, 69 Bolyai, 339 Bonnet s Formula, 283 bounded, 48
 Index acceleration, 14, 76, 355 centripetal, 27 tangential, 27 algebraic geometry, vii analytic, 44 angle at a corner, 21 on a regular surface, 170 angle excess, 337 angle of parallelism, 344 angular velocity,
Index acceleration, 14, 76, 355 centripetal, 27 tangential, 27 algebraic geometry, vii analytic, 44 angle at a corner, 21 on a regular surface, 170 angle excess, 337 angle of parallelism, 344 angular velocity,
Introduction to Geoinformatics I
 Introduction to Geoinformatics I MAP CONCEPT Definition: 1) A map is a visual representation of an area a symbolic depiction highlighting relationships between elements of that space such as objects, regions,
Introduction to Geoinformatics I MAP CONCEPT Definition: 1) A map is a visual representation of an area a symbolic depiction highlighting relationships between elements of that space such as objects, regions,
Geography 128 Winter Quarter Lecture 4: A Transformational View of Cartography
 Geography 128 Winter Quarter 2017 Lecture 4: A Transformational View of Cartography Tobler, W. R. (1979). A Transformational View of Cartography. American Cartographer, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 101 106. A simplified
Geography 128 Winter Quarter 2017 Lecture 4: A Transformational View of Cartography Tobler, W. R. (1979). A Transformational View of Cartography. American Cartographer, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 101 106. A simplified
CHAPTER 24 THE SAILINGS
 CHAPTER 24 THE SAILINGS INTRODUCTION 2400. Introduction Dead reckoning involves the determination of one s present or future position by projecting the ship s course and distance run from a known position.
CHAPTER 24 THE SAILINGS INTRODUCTION 2400. Introduction Dead reckoning involves the determination of one s present or future position by projecting the ship s course and distance run from a known position.
Pullbacks, Isometries & Conformal Maps
 Pullbacks, Isometries & Conformal Maps Outline 1. Pullbacks Let V and W be vector spaces, and let T : V W be an injective linear transformation. Given an inner product, on W, the pullback of, is the inner
Pullbacks, Isometries & Conformal Maps Outline 1. Pullbacks Let V and W be vector spaces, and let T : V W be an injective linear transformation. Given an inner product, on W, the pullback of, is the inner
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 1/25/2018
 Map Projections & Coordinate Sstems Laing the Earth Flat How? Projections transformation of curved earth to a flat map; sstematic rendering of the lat. & lon. graticule to rectangular coordinate sstem.
Map Projections & Coordinate Sstems Laing the Earth Flat How? Projections transformation of curved earth to a flat map; sstematic rendering of the lat. & lon. graticule to rectangular coordinate sstem.
HOMEWORK 3 - GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES. where ν is the unit normal consistent with the orientation of α (right hand rule).
 HOMEWORK 3 - GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES ANDRÉ NEVES ) If α : I R 2 is a curve on the plane parametrized by arc length and θ is the angle that α makes with the x-axis, show that α t) = dθ dt ν, where
HOMEWORK 3 - GEOMETRY OF CURVES AND SURFACES ANDRÉ NEVES ) If α : I R 2 is a curve on the plane parametrized by arc length and θ is the angle that α makes with the x-axis, show that α t) = dθ dt ν, where
Complex Analysis Math 185A, Winter 2010 Final: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Pedro Nunes and the Retrogression of the Sun
 Irish Math. oc. Bulletin Number 81, ummer 2018, 23 30 IN 0791-5578 Pedro Nunes and the Retrogression of the un PETER LYNCH What has been will be again, what has been done will be done again; there is nothing
Irish Math. oc. Bulletin Number 81, ummer 2018, 23 30 IN 0791-5578 Pedro Nunes and the Retrogression of the un PETER LYNCH What has been will be again, what has been done will be done again; there is nothing
Probability Density (1)
 Probability Density (1) Let f(x 1, x 2... x n ) be a probability density for the variables {x 1, x 2... x n }. These variables can always be viewed as coordinates over an abstract space (a manifold ).
Probability Density (1) Let f(x 1, x 2... x n ) be a probability density for the variables {x 1, x 2... x n }. These variables can always be viewed as coordinates over an abstract space (a manifold ).
Summary for Vector Calculus and Complex Calculus (Math 321) By Lei Li
 Summary for Vector alculus and omplex alculus (Math 321) By Lei Li 1 Vector alculus 1.1 Parametrization urves, surfaces, or volumes can be parametrized. Below, I ll talk about 3D case. Suppose we use e
Summary for Vector alculus and omplex alculus (Math 321) By Lei Li 1 Vector alculus 1.1 Parametrization urves, surfaces, or volumes can be parametrized. Below, I ll talk about 3D case. Suppose we use e
Choosing a Suitable Projection for Navigation in the Arctic
 Choosing a Suitable Projection for Navigation in the Arctic Dr. Andriani Skopeliti, Prof. Lysandros Tsoulos Cartography Laboratory, School of Rural and Surveying Engineering, National Technical University
Choosing a Suitable Projection for Navigation in the Arctic Dr. Andriani Skopeliti, Prof. Lysandros Tsoulos Cartography Laboratory, School of Rural and Surveying Engineering, National Technical University
Mobile Systeme Grundlagen und Anwendungen standortbezogener Dienste. Location Based Services in the Context of Web 2.0
 Mobile Systeme Grundlagen und Anwendungen standortbezogener Dienste Location Based Services in the Context of Web 2.0 Department of Informatics - MIN Faculty - University of Hamburg Lecture Summer Term
Mobile Systeme Grundlagen und Anwendungen standortbezogener Dienste Location Based Services in the Context of Web 2.0 Department of Informatics - MIN Faculty - University of Hamburg Lecture Summer Term
1. For Cosine Rule of any triangle ABC, b² is equal to A. a² - c² 4bc cos A B. a² + c² - 2ac cos B C. a² - c² + 2ab cos A D. a³ + c³ - 3ab cos A
 1. For Cosine Rule of any triangle ABC, b² is equal to A. a² - c² 4bc cos A B. a² + c² - 2ac cos B C. a² - c² + 2ab cos A D. a³ + c³ - 3ab cos A 2. For Cosine Rule of any triangle ABC, c² is equal to A.
1. For Cosine Rule of any triangle ABC, b² is equal to A. a² - c² 4bc cos A B. a² + c² - 2ac cos B C. a² - c² + 2ab cos A D. a³ + c³ - 3ab cos A 2. For Cosine Rule of any triangle ABC, c² is equal to A.
Use your text to define the following term. Use the terms to label the figure below. Define the following term.
 Mapping Our World Section. and Longitude Skim Section of your text. Write three questions that come to mind from reading the headings and the illustration captions.. Responses may include questions about
Mapping Our World Section. and Longitude Skim Section of your text. Write three questions that come to mind from reading the headings and the illustration captions.. Responses may include questions about
Cartographers would certainly find
 WHAT S A by Cynthia Levinson Cartographers would certainly find their job much easier if the earth were like a paper towel roll or an ice cream cone and not like a sphere. Why? Because you can wrap a sheet
WHAT S A by Cynthia Levinson Cartographers would certainly find their job much easier if the earth were like a paper towel roll or an ice cream cone and not like a sphere. Why? Because you can wrap a sheet
Mercator and his Map
 Mercator and his Map UtpalA4ukhopadhyay In this article we present briefly some preliminary ideas of map projection, followed by a detailed account of the Mercator projection. Introduction Utpal Mukhopadhyay
Mercator and his Map UtpalA4ukhopadhyay In this article we present briefly some preliminary ideas of map projection, followed by a detailed account of the Mercator projection. Introduction Utpal Mukhopadhyay
In the 16th century, Gerhardus Mercator ( ) CALCULUS OF THE MERCATOR MAP. Integration L A B
 L A B 10 CALCULUS OF THE MERCATOR MAP Integration In the 16th century, Gerhardus Mercator (1512 1594) designed a map unlike any other standard flat map. While a constant bearing of 45 is a curved line
L A B 10 CALCULUS OF THE MERCATOR MAP Integration In the 16th century, Gerhardus Mercator (1512 1594) designed a map unlike any other standard flat map. While a constant bearing of 45 is a curved line
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE
 MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
Grid-Based Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction
 Structured and Unstructured Grids Grid-Based Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction A majority of modern numerical weather prediction models, particularly those used to obtain forecasts over limited-area
Structured and Unstructured Grids Grid-Based Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction A majority of modern numerical weather prediction models, particularly those used to obtain forecasts over limited-area
Lecture 4. Coordinate Systems & Projections
 Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Index. Excerpt from "Precalculus" 2014 AoPS Inc. Copyrighted Material INDEX
 Index, 29 \, 6, 29 \, 6 [, 5 1, 2!, 29?, 309, 179, 179, 29 30-60-90 triangle, 32 45-45-90 triangle, 32 Agnesi, Maria Gaetana, 191 Airy, Sir George, 180 AMC, vii American Mathematics Competitions, see AMC
Index, 29 \, 6, 29 \, 6 [, 5 1, 2!, 29?, 309, 179, 179, 29 30-60-90 triangle, 32 45-45-90 triangle, 32 Agnesi, Maria Gaetana, 191 Airy, Sir George, 180 AMC, vii American Mathematics Competitions, see AMC
