Use your text to define the following term. Use the terms to label the figure below. Define the following term.
|
|
|
- Katherine Blankenship
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mapping Our World Section. and Longitude Skim Section of your text. Write three questions that come to mind from reading the headings and the illustration captions.. Responses may include questions about latitude,. longitude, and time zones.. New cartography Use your text to define the following term. the science of mapmaking Use the terms to label the figure below. equator line of latitude line of longitude prime meridian International Line 0 0 Academic parallel Define the following term. lines that lie in a common plane and do not intersect Section. and Longitude
2 Section. and Longitude (continued) Use with pages. Organize information about latitude by completing this graphic organizer. Use Figure - and other information in your text. They run parallel to the equator. Distances are in degrees north or south of the equator. Lines of The equator is at 0 latitude. The poles are at 0 latitude. Summarize the information about degrees of latitude by completing the table. Degrees of Symbol Actual Distance Degree km Minute. km Longitude Use with page. Complete each sentence to help you remember information about longitude. Lines of longitude are also known as meridians. Longitude is distance in degrees east or west of the prime meridian. The prime meridian is the reference point for meridians. It represents 0 longitude. The prime meridian goes through Greenwich, England. Points west of the prime meridian are numbered from 0 to 0 west longitude. Points east of the prime meridian are numbered from 0 to 0 east longitude. Mapping Our World
3 Name Section. and Longitude (continued) Use with pages. Compare and contrast information about latitude and longitude. Place each statement in the Venn diagram to show whether it is true for latitude, longitude, or both. Two statements have already been written in for you. Lines are parallel. Lines converge at a point. Lines form circles. Lines form semicircles. Degrees cover consistent distances. Degrees do not cover consistent distances. Necessary to precisely locate positions on Earth Longitude Both Lines converge Necessary to at a point. precisely locate Degrees do not positions on cover consistent Earth distances. Lines form semicircles. Lines form circles. Lines are parallel. Degrees cover consistent distances. Time Zones Use with page. Analyze the figure below showing U.S. time zones. Assume that it is :00 in the Mountain time zone. Draw the hands on the other clocks to show the time it would be in each of the other U.S. time zones. Alaska Standard Time 0 0 Pacific Mountain Central Eastern Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time 0 AK HI WA OR ID NV UT CA AZ MT WY CO NM VT NH ME ND MN WI NY MA SD RI MI IA IL IN OH PA NJ CT NE DE WV VA MO MD KS KY NC TN OK AR SC GA MS AL TX LA FL SYNTHESIZE Write the instructions you would give a classmate to locate the point N, E on a globe. Responses should demonstrate an understanding of using latitude and longitude to locate points. Section. and Longitude
4 Mapping Our World Section. Types of Maps Skim Section of your text. List the three map projections mentioned in the headings and illustration captions.. Mercator projection. conic projection. gnomonic projection New In the left column, write the terms defined below. gnomonic projection a map made by projecting points and lines onto a piece of paper that touches a globe at a single point Mercator projection a map that has parallel lines of latitude and longitude topographic map a map that shows changes in elevation of Earth s surface conic projection a map made by projecting points and lines from a globe onto a cone map scale the ratio between distances on a map and actual distances on the surface of Earth contour interval the difference in elevation between two side-by-side contour lines on a map map legend a table that explains what the symbols on a map represent contour line Academic distort a line on a map that connects points of equal elevation Define the following term. to twist out of the true meaning or proportion Mapping Our World
5 Section. Types of Maps (continued) Mercator Use with page. Complete the table to organize information about Mercator projections. Made by Advantages Disadvantages Uses Mercator parallel lines of latitude and longitude show the correct shape of landmasses; indicate directon in straight lines distort areas of landmasses navigation of ships and planes Conic Use with page. Organize information about conic projections by filling in the graphic organizer. Made by: projecting points and lines from a globe onto a cone Advantages: highly accurate for limited areas Conic Disadvantages: distortion near top and bottom of projection Uses: road maps, weather maps Gnomonic Use with page. Complete the following sentences to help you understand gnomonic projections. Gnomonic projections are made by projecting points and lines from a globe onto a piece of paper that touches the globe at a single point. The advantage of these projections is that they plot the shortest distance between two points. The disadvantage of gnomonic projections is that they distort direction and distance between landmasses. They are used by air and sea navigators to plot great-circle routes. Section. Types of Maps
Lecture 26 Section 8.4. Mon, Oct 13, 2008
 Lecture 26 Section 8.4 Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Oct 13, 2008 Outline 1 2 3 4 Exercise 8.12, page 528. Suppose that 60% of all students at a large university access course information using the Internet.
Lecture 26 Section 8.4 Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Oct 13, 2008 Outline 1 2 3 4 Exercise 8.12, page 528. Suppose that 60% of all students at a large university access course information using the Internet.
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Analyzing Severe Weather Data
 Chapter Weather Patterns and Severe Storms Investigation A Analyzing Severe Weather Data Introduction Tornadoes are violent windstorms associated with severe thunderstorms. Meteorologists carefully monitor
Chapter Weather Patterns and Severe Storms Investigation A Analyzing Severe Weather Data Introduction Tornadoes are violent windstorms associated with severe thunderstorms. Meteorologists carefully monitor
Your Galactic Address
 How Big is the Universe? Usually you think of your address as only three or four lines long: your name, street, city, and state. But to address a letter to a friend in a distant galaxy, you have to specify
How Big is the Universe? Usually you think of your address as only three or four lines long: your name, street, city, and state. But to address a letter to a friend in a distant galaxy, you have to specify
Nursing Facilities' Life Safety Standard Survey Results Quarterly Reference Tables
 Nursing Facilities' Life Safety Standard Survey Results Quarterly Reference Tables Table of Contents Table 1: Summary of Life Safety Survey Results by State Table 2: Ten Most Frequently Cited Life Safety
Nursing Facilities' Life Safety Standard Survey Results Quarterly Reference Tables Table of Contents Table 1: Summary of Life Safety Survey Results by State Table 2: Ten Most Frequently Cited Life Safety
Sample Statistics 5021 First Midterm Examination with solutions
 THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA Statistics 5021 February 12, 2003 Sample First Midterm Examination (with solutions) 1. Baseball pitcher Nolan Ryan played in 20 games or more in the 24 seasons from 1968 through
THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA Statistics 5021 February 12, 2003 Sample First Midterm Examination (with solutions) 1. Baseball pitcher Nolan Ryan played in 20 games or more in the 24 seasons from 1968 through
Smart Magnets for Smart Product Design: Advanced Topics
 Smart Magnets for Smart Product Design: Advanced Topics Today s Presenter Jason Morgan Vice President Engineering Correlated Magnetics Research 6 Agenda Brief overview of Correlated Magnetics Research
Smart Magnets for Smart Product Design: Advanced Topics Today s Presenter Jason Morgan Vice President Engineering Correlated Magnetics Research 6 Agenda Brief overview of Correlated Magnetics Research
Evolution Strategies for Optimizing Rectangular Cartograms
 Evolution Strategies for Optimizing Rectangular Cartograms Kevin Buchin 1, Bettina Speckmann 1, and Sander Verdonschot 2 1 TU Eindhoven, 2 Carleton University September 20, 2012 Sander Verdonschot (Carleton
Evolution Strategies for Optimizing Rectangular Cartograms Kevin Buchin 1, Bettina Speckmann 1, and Sander Verdonschot 2 1 TU Eindhoven, 2 Carleton University September 20, 2012 Sander Verdonschot (Carleton
Drought Monitoring Capability of the Oklahoma Mesonet. Gary McManus Oklahoma Climatological Survey Oklahoma Mesonet
 Drought Monitoring Capability of the Oklahoma Mesonet Gary McManus Oklahoma Climatological Survey Oklahoma Mesonet Mesonet History Commissioned in 1994 Atmospheric measurements with 5-minute resolution,
Drought Monitoring Capability of the Oklahoma Mesonet Gary McManus Oklahoma Climatological Survey Oklahoma Mesonet Mesonet History Commissioned in 1994 Atmospheric measurements with 5-minute resolution,
Teachers Curriculum Institute Map Skills Toolkit 411
 Map kills Toolkit To the Teacher tudents encounter maps every day inside and outside their classes in books and on handheld devices, computers, or television screens. Whether they re navigating cities
Map kills Toolkit To the Teacher tudents encounter maps every day inside and outside their classes in books and on handheld devices, computers, or television screens. Whether they re navigating cities
2 Mapping Earth Reading Essentials. 2. Contrast What is the difference between a map view and a profile view?
 Mapping Earth Maps What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree.
Mapping Earth Maps What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree.
EXST 7015 Fall 2014 Lab 08: Polynomial Regression
 EXST 7015 Fall 2014 Lab 08: Polynomial Regression OBJECTIVES Polynomial regression is a statistical modeling technique to fit the curvilinear data that either shows a maximum or a minimum in the curve,
EXST 7015 Fall 2014 Lab 08: Polynomial Regression OBJECTIVES Polynomial regression is a statistical modeling technique to fit the curvilinear data that either shows a maximum or a minimum in the curve,
Parametric Test. Multiple Linear Regression Spatial Application I: State Homicide Rates Equations taken from Zar, 1984.
 Multiple Linear Regression Spatial Application I: State Homicide Rates Equations taken from Zar, 984. y ˆ = a + b x + b 2 x 2K + b n x n where n is the number of variables Example: In an earlier bivariate
Multiple Linear Regression Spatial Application I: State Homicide Rates Equations taken from Zar, 984. y ˆ = a + b x + b 2 x 2K + b n x n where n is the number of variables Example: In an earlier bivariate
What Lies Beneath: A Sub- National Look at Okun s Law for the United States.
 What Lies Beneath: A Sub- National Look at Okun s Law for the United States. Nathalie Gonzalez Prieto International Monetary Fund Global Labor Markets Workshop Paris, September 1-2, 2016 What the paper
What Lies Beneath: A Sub- National Look at Okun s Law for the United States. Nathalie Gonzalez Prieto International Monetary Fund Global Labor Markets Workshop Paris, September 1-2, 2016 What the paper
Cartography the art of making maps
 Cartography the art of making maps A map is a drawing or a picture of the earths surface, showing how things are related to each other by distance, direction and size. Maps are used for: Navigation Distance
Cartography the art of making maps A map is a drawing or a picture of the earths surface, showing how things are related to each other by distance, direction and size. Maps are used for: Navigation Distance
Mapping Our World Chapter 2
 Mapping Our World Chapter 2 Section 2.1: Latitude and Longitude Maps are flat models of threedimensional objects. For thousands of years people have used maps to define borders and to find places. With
Mapping Our World Chapter 2 Section 2.1: Latitude and Longitude Maps are flat models of threedimensional objects. For thousands of years people have used maps to define borders and to find places. With
Appendix 5 Summary of State Trademark Registration Provisions (as of July 2016)
 Appendix 5 Summary of State Trademark Registration Provisions (as of July 2016) App. 5-1 Registration Renewal Assignments Dates Term # of of 1st # of Use # of Form Serv. Key & State (Years) Fee Spec. Use
Appendix 5 Summary of State Trademark Registration Provisions (as of July 2016) App. 5-1 Registration Renewal Assignments Dates Term # of of 1st # of Use # of Form Serv. Key & State (Years) Fee Spec. Use
Summary of Natural Hazard Statistics for 2008 in the United States
 Summary of Natural Hazard Statistics for 2008 in the United States This National Weather Service (NWS) report summarizes fatalities, injuries and damages caused by severe weather in 2008. The NWS Office
Summary of Natural Hazard Statistics for 2008 in the United States This National Weather Service (NWS) report summarizes fatalities, injuries and damages caused by severe weather in 2008. The NWS Office
Introduction to Geography
 Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
Meteorology 110. Lab 1. Geography and Map Skills
 Meteorology 110 Name Lab 1 Geography and Map Skills 1. Geography Weather involves maps. There s no getting around it. You must know where places are so when they are mentioned in the course it won t be
Meteorology 110 Name Lab 1 Geography and Map Skills 1. Geography Weather involves maps. There s no getting around it. You must know where places are so when they are mentioned in the course it won t be
SAMPLE AUDIT FORMAT. Pre Audit Notification Letter Draft. Dear Registrant:
 Pre Audit Notification Letter Draft Dear Registrant: The Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (PennDOT) is a member of the Federally Mandated International Registration Plan (IRP). As part of this
Pre Audit Notification Letter Draft Dear Registrant: The Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (PennDOT) is a member of the Federally Mandated International Registration Plan (IRP). As part of this
Multiway Analysis of Bridge Structural Types in the National Bridge Inventory (NBI) A Tensor Decomposition Approach
 Multiway Analysis of Bridge Structural Types in the National Bridge Inventory (NBI) A Tensor Decomposition Approach By Offei A. Adarkwa Nii Attoh-Okine (Ph.D) (IEEE Big Data Conference -10/27/2014) 1 Presentation
Multiway Analysis of Bridge Structural Types in the National Bridge Inventory (NBI) A Tensor Decomposition Approach By Offei A. Adarkwa Nii Attoh-Okine (Ph.D) (IEEE Big Data Conference -10/27/2014) 1 Presentation
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools
 Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map
 What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY
 MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY BYOD BRING YOUR OWN DEVICE IN SMALL GROUPS (3-4), USE YOUR ELECTRONIC DEVICE(S) AND DEFINE THE FOLLOWING VOCAB. WORDS 1. GEOGRAPHY 2.
MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY BYOD BRING YOUR OWN DEVICE IN SMALL GROUPS (3-4), USE YOUR ELECTRONIC DEVICE(S) AND DEFINE THE FOLLOWING VOCAB. WORDS 1. GEOGRAPHY 2.
CHAPTER EXIT CHAPTER. Models of Earth. 3.1 Modeling the Planet. 3.2 Mapmaking and Technology. 3.3 Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE
 EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
Earth Science: Chapter 2 Assessment
 Earth Science: Chapter 2 Assessment Do not write on this text booklet. Write the letter of the correct answer on your answer sheet. SECTION 1: Multiple Choice (50 points) Choose the letter of the BEST
Earth Science: Chapter 2 Assessment Do not write on this text booklet. Write the letter of the correct answer on your answer sheet. SECTION 1: Multiple Choice (50 points) Choose the letter of the BEST
Latitude and Longitude Pre Test
 Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
Name Class Date. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. 1. true north and magnetic north 2. latitude and longitude 3. equator and prime meridian
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. 1. true north and magnetic north 2. latitude and longitude 3. equator and prime meridian
2. What does the map scale tell the map reader? a ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the length given to that distance on a map
 AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
History of Cartography,
 Maps History of Cartography, the art and science of making maps ~2300 BC ~600 BC Early oldest known maps: Babylonian clay tablets. Greek and Roman Ptolemy s (about AD 85-165) "world map" depicted the Old
Maps History of Cartography, the art and science of making maps ~2300 BC ~600 BC Early oldest known maps: Babylonian clay tablets. Greek and Roman Ptolemy s (about AD 85-165) "world map" depicted the Old
Cluster Analysis. Part of the Michigan Prosperity Initiative
 Cluster Analysis Part of the Michigan Prosperity Initiative 6/17/2010 Land Policy Institute Contributors Dr. Soji Adelaja, Director Jason Ball, Visiting Academic Specialist Jonathon Baird, Research Assistant
Cluster Analysis Part of the Michigan Prosperity Initiative 6/17/2010 Land Policy Institute Contributors Dr. Soji Adelaja, Director Jason Ball, Visiting Academic Specialist Jonathon Baird, Research Assistant
Forecasting the 2012 Presidential Election from History and the Polls
 Forecasting the 2012 Presidential Election from History and the Polls Drew Linzer Assistant Professor Emory University Department of Political Science Visiting Assistant Professor, 2012-13 Stanford University
Forecasting the 2012 Presidential Election from History and the Polls Drew Linzer Assistant Professor Emory University Department of Political Science Visiting Assistant Professor, 2012-13 Stanford University
Annual Performance Report: State Assessment Data
 Annual Performance Report: 2005-2006 State Assessment Data Summary Prepared by: Martha Thurlow, Jason Altman, Damien Cormier, and Ross Moen National Center on Educational Outcomes (NCEO) April, 2008 The
Annual Performance Report: 2005-2006 State Assessment Data Summary Prepared by: Martha Thurlow, Jason Altman, Damien Cormier, and Ross Moen National Center on Educational Outcomes (NCEO) April, 2008 The
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, and Wealth
 Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, and Wealth Victor M. Yakovenko Adrian A. Dragulescu and A. Christian Silva Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA http://www2.physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics.html
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, and Wealth Victor M. Yakovenko Adrian A. Dragulescu and A. Christian Silva Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA http://www2.physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics.html
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
Class business PS is due Wed. Lecture 20 (QPM 2016) Multivariate Regression November 14, / 44
 Multivariate Regression Prof. Jacob M. Montgomery Quantitative Political Methodology (L32 363) November 14, 2016 Lecture 20 (QPM 2016) Multivariate Regression November 14, 2016 1 / 44 Class business PS
Multivariate Regression Prof. Jacob M. Montgomery Quantitative Political Methodology (L32 363) November 14, 2016 Lecture 20 (QPM 2016) Multivariate Regression November 14, 2016 1 / 44 Class business PS
Module 19: Simple Linear Regression
 Module 19: Simple Linear Regression This module focuses on simple linear regression and thus begins the process of exploring one of the more used and powerful statistical tools. Reviewed 11 May 05 /MODULE
Module 19: Simple Linear Regression This module focuses on simple linear regression and thus begins the process of exploring one of the more used and powerful statistical tools. Reviewed 11 May 05 /MODULE
2006 Supplemental Tax Information for JennisonDryden and Strategic Partners Funds
 2006 Supplemental Information for JennisonDryden and Strategic Partners s We have compiled the following information to help you prepare your 2006 federal and state tax returns: Percentage of income from
2006 Supplemental Information for JennisonDryden and Strategic Partners s We have compiled the following information to help you prepare your 2006 federal and state tax returns: Percentage of income from
A. Spatial Sense (Working with Maps, Globes, and Other Geographic Tools)
 A. Spatial Sense (Working with Maps, Globes, and Other Geographic Tools) Measuring Distance Using Map Scale All maps are drawn to scale; that is, they are smaller than the things they represent. Scale
A. Spatial Sense (Working with Maps, Globes, and Other Geographic Tools) Measuring Distance Using Map Scale All maps are drawn to scale; that is, they are smaller than the things they represent. Scale
C Further Concepts in Statistics
 Appendix C.1 Representing Data and Linear Modeling C1 C Further Concepts in Statistics C.1 Representing Data and Linear Modeling Use stem-and-leaf plots to organize and compare sets of data. Use histograms
Appendix C.1 Representing Data and Linear Modeling C1 C Further Concepts in Statistics C.1 Representing Data and Linear Modeling Use stem-and-leaf plots to organize and compare sets of data. Use histograms
Introduction to Geography
 Introduction to Geography What is geography? Geography comes from the Greek word Geographia. Geo means earth and graphia means to describe or chart. Geographers study the earth in relation to space and
Introduction to Geography What is geography? Geography comes from the Greek word Geographia. Geo means earth and graphia means to describe or chart. Geographers study the earth in relation to space and
Swine Enteric Coronavirus Disease (SECD) Situation Report June 30, 2016
 Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Veterinary Services Swine Enteric Coronavirus Disease (SECD) Situation Report June 30, 2016 Information current as of 12:00 pm MDT, 06/29/2016 This report provides
Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Veterinary Services Swine Enteric Coronavirus Disease (SECD) Situation Report June 30, 2016 Information current as of 12:00 pm MDT, 06/29/2016 This report provides
Mapping Earth. How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled?
 Name Mapping Earth How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about maps Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Name Mapping Earth How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about maps Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections
 Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. In your textbook, read about latitude and longitude. Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B.
 Name Cass Date Mapping Our Word SECTION 2.1 Latitude and Longitude In your textbook, read about atitude and ongitude. Match the definition in Coumn A with the term in Coumn B. c d e b a Coumn A 1. Science
Name Cass Date Mapping Our Word SECTION 2.1 Latitude and Longitude In your textbook, read about atitude and ongitude. Match the definition in Coumn A with the term in Coumn B. c d e b a Coumn A 1. Science
STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Greenwich, England, and represents 0
 Name Cass Date Mapping Our Word SECTION 2.1 Latitude and Longitude In your textbook, read about atitude and ongitude. Match the definition in Coumn A with the term in Coumn B. Coumn A 1. Science of mapmaking
Name Cass Date Mapping Our Word SECTION 2.1 Latitude and Longitude In your textbook, read about atitude and ongitude. Match the definition in Coumn A with the term in Coumn B. Coumn A 1. Science of mapmaking
Final Exam. 1. Definitions: Briefly Define each of the following terms as they relate to the material covered in class.
 Name Answer Key Economics 170 Spring 2003 Honor pledge: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam including the preparation of my one page formula list and the preparation of the Stata assignment
Name Answer Key Economics 170 Spring 2003 Honor pledge: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam including the preparation of my one page formula list and the preparation of the Stata assignment
Geographic Grid. Locations Feature 1 Feature 2 Feature 3
 Geographic Grid Name The geographic grid refers to the internationally-recognized system of latitude and longitude used to location positions on Earth's surface. Accurate use of this coordinate system
Geographic Grid Name The geographic grid refers to the internationally-recognized system of latitude and longitude used to location positions on Earth's surface. Accurate use of this coordinate system
AIR FORCE RESCUE COORDINATION CENTER
 AIR FORCE RESCUE COORDINATION CENTER 2006 ANNUAL REPORT 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS AFRCC CHARTER & MISSION STATEMENT 3 AFRCC ORGANIZATION 4 TABLE 1 10 YEAR LOOKBACK 5 TABLE 2 ACTIVITY BY MISSION TYPE 6 TABLE
AIR FORCE RESCUE COORDINATION CENTER 2006 ANNUAL REPORT 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS AFRCC CHARTER & MISSION STATEMENT 3 AFRCC ORGANIZATION 4 TABLE 1 10 YEAR LOOKBACK 5 TABLE 2 ACTIVITY BY MISSION TYPE 6 TABLE
APPENDIX A GLOSSARY. Appendix A.1
 APPENDIX A GLOSSARY Appendix A.1 Appendix A.2 Back Bearing A back bearing is measured from the object to your position. It is the exact opposite of a direct bearing. Base Line An imaginary line on the
APPENDIX A GLOSSARY Appendix A.1 Appendix A.2 Back Bearing A back bearing is measured from the object to your position. It is the exact opposite of a direct bearing. Base Line An imaginary line on the
Latitude and Longitude:
 Latitude and Longitude: Finding Locations on Planet Earth. With thanks and credit to Step.com Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line.
Latitude and Longitude: Finding Locations on Planet Earth. With thanks and credit to Step.com Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line.
Map Skills Lesson 1. Materials: maps, pencils, Lesson 1 Worksheet, strips of paper, grid paper
 Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
Combinatorics. Problem: How to count without counting.
 Combinatorics Problem: How to count without counting. I How do you figure out how many things there are with a certain property without actually enumerating all of them. Sometimes this requires a lot of
Combinatorics Problem: How to count without counting. I How do you figure out how many things there are with a certain property without actually enumerating all of them. Sometimes this requires a lot of
Chapter 3 SECTION 1 OBJECTIVES
 Chapter 3 SECTION 1 OBJECTIVES Distinguish between latitude and longitude and locate coordinates on maps. Explain how latitude and longitude can be used to locate places on Earth s surface. Explain the
Chapter 3 SECTION 1 OBJECTIVES Distinguish between latitude and longitude and locate coordinates on maps. Explain how latitude and longitude can be used to locate places on Earth s surface. Explain the
What are Latitude and Longitude?
 What are Latitude and Longitude? By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.29.17 Word Count 959 Level 950L A few miles from Quito, Ecuador's capital, is the equator line. It is located
What are Latitude and Longitude? By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.29.17 Word Count 959 Level 950L A few miles from Quito, Ecuador's capital, is the equator line. It is located
AFRCC AIR FORCE RESCUE COORDINATION CENTER
 AFRCC AIR FORCE RESCUE COORDINATION CENTER 2003 ANNUAL REPORT AFRCC ANNUAL REPORT TABLE OF CONTENTS AFRCC Mission Statement and Charter... 3 Organizational Chart... 4 Commander's Comments... 5 2003 AFRCC
AFRCC AIR FORCE RESCUE COORDINATION CENTER 2003 ANNUAL REPORT AFRCC ANNUAL REPORT TABLE OF CONTENTS AFRCC Mission Statement and Charter... 3 Organizational Chart... 4 Commander's Comments... 5 2003 AFRCC
Data Visualization (CIS 468)
 Data Visualization (CIS 468) Tables & Maps Dr. David Koop Discriminability What is problematic here? File vtkdatasetreader PythonSource vtkimageclip vtkimagedatageometryfilter vtkimageresample vtkimagereslice
Data Visualization (CIS 468) Tables & Maps Dr. David Koop Discriminability What is problematic here? File vtkdatasetreader PythonSource vtkimageclip vtkimagedatageometryfilter vtkimageresample vtkimagereslice
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
Regression Diagnostics
 Diag 1 / 78 Regression Diagnostics Paul E. Johnson 1 2 1 Department of Political Science 2 Center for Research Methods and Data Analysis, University of Kansas 2015 Diag 2 / 78 Outline 1 Introduction 2
Diag 1 / 78 Regression Diagnostics Paul E. Johnson 1 2 1 Department of Political Science 2 Center for Research Methods and Data Analysis, University of Kansas 2015 Diag 2 / 78 Outline 1 Introduction 2
page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #1 - Introduction to Latitude and Longitude Northern Hemisphere Southern Hemisphere
 page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #1 - Introduction to Latitude and Longitude A. Introduction There are many methods that can be used to locate ones position on the surface of the earth. A common method for
page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #1 - Introduction to Latitude and Longitude A. Introduction There are many methods that can be used to locate ones position on the surface of the earth. A common method for
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
Data Visualization (DSC 530/CIS )
 Data Visualization (DSC 530/CIS 602-01) Tables Dr. David Koop Visualization of Tables Items and attributes For now, attributes are not known to be positions Keys and values - key is an independent attribute
Data Visualization (DSC 530/CIS 602-01) Tables Dr. David Koop Visualization of Tables Items and attributes For now, attributes are not known to be positions Keys and values - key is an independent attribute
Using Map and Compass Together
 Using Map and Compass Together In situations where you foresee a potential evacuation on foot, where there are no roads, and no indication as to the direction of travel (i.e., road signs), it is recommended
Using Map and Compass Together In situations where you foresee a potential evacuation on foot, where there are no roads, and no indication as to the direction of travel (i.e., road signs), it is recommended
Map Skills and Geographic Tools
 Name: Period: Map Skills and Geographic Tools TEKS: 8.9C interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering
Name: Period: Map Skills and Geographic Tools TEKS: 8.9C interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering
Kari Lock. Department of Statistics, Harvard University Joint Work with Andrew Gelman (Columbia University)
 Bayesian Combinaion of Sae Polls and Elecion Forecass Kari Lock Deparmen of Saisics, Harvard Universiy Join Work wih Andrew Gelman (Columbia Universiy Harvard Insiue for Quaniaive Social Science Feb 4
Bayesian Combinaion of Sae Polls and Elecion Forecass Kari Lock Deparmen of Saisics, Harvard Universiy Join Work wih Andrew Gelman (Columbia Universiy Harvard Insiue for Quaniaive Social Science Feb 4
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab
 Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
Topographic Maps and Landforms Geology Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Today s Lab Activities 1) Discussion of Last Week s Lab 2) Lecture on Topo Maps and Elevation Contours 3) Construct Topographic Maps and
The veto as electoral stunt
 The veto as eectora stunt EITM and a test with comparative data Eric ITAM, Mexico City Apr. 2, 203 eitm@mpsa Motivation A Form: see EITM in action forma mode 2 comparative statics 3 fasifiabe impications
The veto as eectora stunt EITM and a test with comparative data Eric ITAM, Mexico City Apr. 2, 203 eitm@mpsa Motivation A Form: see EITM in action forma mode 2 comparative statics 3 fasifiabe impications
Spatial locations. Spatial locations. Spatial locations. Spatial locations
 Where am I? sounds simple, but definitely not huge amount of picky detail Cartographers make a career from the details focus on the minimum you need to know c Philip M. Dixon (Iowa State Univ.) Spatial
Where am I? sounds simple, but definitely not huge amount of picky detail Cartographers make a career from the details focus on the minimum you need to know c Philip M. Dixon (Iowa State Univ.) Spatial
Lab#3: GIS Projections and Coordinate Systems. Start Arcmap and create a data frame for each of the above coordinate systems.
 NRM338 Fall 2017 Lab#3 Page#1 of 18 In this lab, you will Lab#3: GIS Projections and Coordinate Systems 1) Define the geographic coordinate system of two GIS themes. 2) Determine the geographic coordinates
NRM338 Fall 2017 Lab#3 Page#1 of 18 In this lab, you will Lab#3: GIS Projections and Coordinate Systems 1) Define the geographic coordinate system of two GIS themes. 2) Determine the geographic coordinates
Cardinal and Intermediate Directions:
 Name Period Parent Signature Due Date: (TBA) Geography/Map Skills Study Guide Continents and Oceans of the World: Label the continents (7) and oceans (4) on the lines below the map. 1 11 3 5 4 8 2 9 10
Name Period Parent Signature Due Date: (TBA) Geography/Map Skills Study Guide Continents and Oceans of the World: Label the continents (7) and oceans (4) on the lines below the map. 1 11 3 5 4 8 2 9 10
Discontinuation of Support for Field Chemistry Measurements in the National Atmospheric Deposition Program National Trends Network (NADP/NTN)
 Discontinuation of Support for Field Chemistry Measurements in the National Atmospheric Deposition Program National Trends Network (NADP/NTN) Christopher Lehmann, NADP Program Office, Illinois State Water
Discontinuation of Support for Field Chemistry Measurements in the National Atmospheric Deposition Program National Trends Network (NADP/NTN) Christopher Lehmann, NADP Program Office, Illinois State Water
Key Issue #1. How do geographers describe where things are? 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Key Issue #1 How do geographers describe where things are? Learning Outcomes 1.1.1: Explain differences between early maps and contemporary maps. 1.1.2: Describe the role of map scale and projections and
Key Issue #1 How do geographers describe where things are? Learning Outcomes 1.1.1: Explain differences between early maps and contemporary maps. 1.1.2: Describe the role of map scale and projections and
Chapter 1: The World of Geography
 Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Mapping Our World. To find out more about maps, visit the Earth Science Web Site at earthgeu.com
 2 What You ll Learn How latitude and longitude are used to locate places on Earth. How maps are made, and what types of maps are best suited to particular purposes. What technology is used to map Earth
2 What You ll Learn How latitude and longitude are used to locate places on Earth. How maps are made, and what types of maps are best suited to particular purposes. What technology is used to map Earth
What is a Map Projection?
 What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
Introduction to Mathematical Statistics and Its Applications Richard J. Larsen Morris L. Marx Fifth Edition
 Introduction to Mathematical Statistics and Its Applications Richard J. Larsen Morris L. Marx Fifth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies
Introduction to Mathematical Statistics and Its Applications Richard J. Larsen Morris L. Marx Fifth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies
Name Date Class. a. High elevation and high relief b. High elevation and level surface c. Flat land and low relief
 Exploring Earth s Surface (pp. 21 27) This section describes factors that determine the shape of Earth s land surface. The section also describes how scientists divide Earth into four spheres. Use Target
Exploring Earth s Surface (pp. 21 27) This section describes factors that determine the shape of Earth s land surface. The section also describes how scientists divide Earth into four spheres. Use Target
Map Skills Unit. Note taking unit
 Map Skills Unit Note taking unit Introduction To learn about the Earth, we are going to learn about two geographic tools you can use.globes and maps. Globe A globe is a round model of the planet Earth
Map Skills Unit Note taking unit Introduction To learn about the Earth, we are going to learn about two geographic tools you can use.globes and maps. Globe A globe is a round model of the planet Earth
Swine Enteric Coronavirus Disease (SECD) Situation Report Sept 17, 2015
 Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Veterinary Services Swine Enteric Coronavirus Disease (SECD) Situation Report Sept 17, 2015 Information current as of 12:00 pm MDT, 09/16/2015 This report provides
Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Veterinary Services Swine Enteric Coronavirus Disease (SECD) Situation Report Sept 17, 2015 Information current as of 12:00 pm MDT, 09/16/2015 This report provides
Analysis of the USDA Annual Report (2015) of Animal Usage by Research Facility. July 4th, 2017
 Analysis of the USDA Annual Report (2015) of Animal Usage by Research Facility July 4th, 2017 Author's information: Jorge Sigler, Catherine Perry, Amanda Gray, James Videle For inquiries contact James
Analysis of the USDA Annual Report (2015) of Animal Usage by Research Facility July 4th, 2017 Author's information: Jorge Sigler, Catherine Perry, Amanda Gray, James Videle For inquiries contact James
 Name Period Parent Signature Geography/Map Skills Study Guide *For extra practice with these skills, check out Mr. Kath s website: http://rkath.weebly.com/activities--links.html Continents and Oceans of
Name Period Parent Signature Geography/Map Skills Study Guide *For extra practice with these skills, check out Mr. Kath s website: http://rkath.weebly.com/activities--links.html Continents and Oceans of
Week 3 Linear Regression I
 Week 3 Linear Regression I POL 200B, Spring 2014 Linear regression is the most commonly used statistical technique. A linear regression captures the relationship between two or more phenomena with a straight
Week 3 Linear Regression I POL 200B, Spring 2014 Linear regression is the most commonly used statistical technique. A linear regression captures the relationship between two or more phenomena with a straight
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections.
 Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
MAPPING THE EARTH HOW DO YOU FIND A LOCATION ON THE EARTH?
 MAPPING THE EARTH HOW DO YOU FIND A LOCATION ON THE EARTH? UNIT TOPICS TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE TOPIC 2: FIELD MAPS TOPIC 3: TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS TOPIC 4: NYS LANDSCAPES TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE
MAPPING THE EARTH HOW DO YOU FIND A LOCATION ON THE EARTH? UNIT TOPICS TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE TOPIC 2: FIELD MAPS TOPIC 3: TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS TOPIC 4: NYS LANDSCAPES TOPIC 1: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE
Map Projections. Chapter 4 MAP PROJECTION
 Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Navigation. Longitude and Latitude Foundations of Navigation. MTPs:
 Navigation 3.01 Foundations of Navigation References: FTGU pages 177-178, 184-190 Transport Canada Study and Reference Guide Glider Pilot Canada Flight Training Manual Pilot Navigation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/transverse_mercator_projection#spherical_transverse_mercator
Navigation 3.01 Foundations of Navigation References: FTGU pages 177-178, 184-190 Transport Canada Study and Reference Guide Glider Pilot Canada Flight Training Manual Pilot Navigation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/transverse_mercator_projection#spherical_transverse_mercator
AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are?
 AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are? Studying Human Geography Physical Geography Physical geography deals with Earth s natural
AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are? Studying Human Geography Physical Geography Physical geography deals with Earth s natural
1. Label a few examples of lines of latitude and lines of longitude on the globe above left.
 Oceanography 2 Location, Direction, and Distance on Nautical Charts Please read Appendix III in the textbook for reference. Learning Objectives for the first nautical chart Lab 1. Use the latitude-longitude
Oceanography 2 Location, Direction, and Distance on Nautical Charts Please read Appendix III in the textbook for reference. Learning Objectives for the first nautical chart Lab 1. Use the latitude-longitude
Test Bank Chapter 2: Representations of Earth
 Multiple Choice Test Bank Chapter 2: Representations of Earth 1. A rhumb line on a Mercator projection is a line of. a. true size b. true shape c. true compass bearing d. true location 2. Maximum longitude
Multiple Choice Test Bank Chapter 2: Representations of Earth 1. A rhumb line on a Mercator projection is a line of. a. true size b. true shape c. true compass bearing d. true location 2. Maximum longitude
Map Making. Chapter 2 Section 1
 Map Making Chapter 2 Section 1 Latitude and Longitude Objectives Compare and contrast latitude and longitude. Describe how time zones vary. Vocabulary cartography equator latitude longitude prime meridian
Map Making Chapter 2 Section 1 Latitude and Longitude Objectives Compare and contrast latitude and longitude. Describe how time zones vary. Vocabulary cartography equator latitude longitude prime meridian
Draft Report. Prepared for: Regional Air Quality Council 1445 Market Street, Suite 260 Denver, Colorado Prepared by:
 Draft Report Evaluation of Preliminary MM5 Meteorological Model Simulation for the June-July 2006 Denver Ozone SIP Modeling Period Focused on Colorado Prepared for: Regional Air Quality Council 1445 Market
Draft Report Evaluation of Preliminary MM5 Meteorological Model Simulation for the June-July 2006 Denver Ozone SIP Modeling Period Focused on Colorado Prepared for: Regional Air Quality Council 1445 Market
Chapter 02 Maps. Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 02 Maps Multiple Choice Questions 1. Every projection has some degree of distortion because A. a curved surface cannot be represented on a flat surface without distortion. B. parallels and meridians
Chapter 02 Maps Multiple Choice Questions 1. Every projection has some degree of distortion because A. a curved surface cannot be represented on a flat surface without distortion. B. parallels and meridians
Latitude and Longitude. Begin
 Latitude and Longitude Begin The Earth is divided in two halves, the top half is called the northern hemisphere, and the bottom half is called the southern hemisphere. The dividing line between the two
Latitude and Longitude Begin The Earth is divided in two halves, the top half is called the northern hemisphere, and the bottom half is called the southern hemisphere. The dividing line between the two
Latitude and Longitude
 Latitude and Longitude Finding Your Location on a Sphere Coordinate Systems n When you are locating a point on a flat surface you can use Cartesian coordinates of x and y. n The point 2, 3 is plotted on
Latitude and Longitude Finding Your Location on a Sphere Coordinate Systems n When you are locating a point on a flat surface you can use Cartesian coordinates of x and y. n The point 2, 3 is plotted on
Resources. Amusement Park Physics With a NASA Twist EG GRC
 Resources 141 EG-2003-03-010-GRC 142 EG-2003-03-01o-GRC Vocabulary acceleration-the rate of change of velocity displacement-change in position of an object force-a push or a pull exerted on some object
Resources 141 EG-2003-03-010-GRC 142 EG-2003-03-01o-GRC Vocabulary acceleration-the rate of change of velocity displacement-change in position of an object force-a push or a pull exerted on some object
Unit I: Earth Dimensions. Review Book pp.19-30
 Unit I: Earth Dimensions Review Book pp.19-30 Objective #1 Describe the actual shape of the Earth and explain 3 pieces of evidence for its actual shape. Earth s Shape The Earth appears to be the shape
Unit I: Earth Dimensions Review Book pp.19-30 Objective #1 Describe the actual shape of the Earth and explain 3 pieces of evidence for its actual shape. Earth s Shape The Earth appears to be the shape
Module 2: Mapping Topic 2 Content: Determining Latitude and Longitude Notes
 Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Although the changing position of the Sun throughout the day
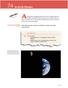 74 As Earth Rotates R E A D I N G Although the changing position of the throughout the day makes it look like the is moving, you now know that it is really Earth that moves. The rotation of Earth around
74 As Earth Rotates R E A D I N G Although the changing position of the throughout the day makes it look like the is moving, you now know that it is really Earth that moves. The rotation of Earth around
Empirical Application of Panel Data Regression
 Empirical Application of Panel Data Regression 1. We use Fatality data, and we are interested in whether rising beer tax rate can help lower traffic death. So the dependent variable is traffic death, while
Empirical Application of Panel Data Regression 1. We use Fatality data, and we are interested in whether rising beer tax rate can help lower traffic death. So the dependent variable is traffic death, while
