Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd
|
|
|
- Ira Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH, M. Hervieu, B. Raveau EMAT, University of Antwerp (RUCA) Groenenborgerlaan 171, B2020 Antwerpen, Belgium Laboratoire CRISMAT, ISMRAUMR 6508Universite& de Caen, 6 B du Mare& chal Juin, CAEN Cedex, France Abstract The relationships between incommensurability, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites have been studied by electron di!raction and lattice imaging versus temperature with 0.02)x)0.07. All compositions show an incommensurate superstructure over the whole temperature domain, despite the fact that they are ferromagnetic and conductive below 140 K. The qvector (!δ)ah decreases with increasing temperature for all compositions x. For a given temperature q also decreases with x. Lattice images obtained at low temperature give a clear view of the characteristics of the incommensurate structure. They also provide a better understanding of the charge ordering process. The lowtemperature form of the Crdoped manganites is not a perfectly doubled cell 2a 2 2a a 2, but defects inducing a tripled cell occur pseudoperiodically Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: CMR; Charge ordering; Manganites 1. Introduction * Corresponding author. Tel.: # ; fax: # address: wischud@ruca.ua.ac.be (W. Schuddinck) During the last decade there has been an enormous interest in the properties of the lanthanide manganites Ln A Mn (A"Ca, Sr, Ba, Pb) because of the discovery of &colossal' magnetoresistance (CMR) in one of these compounds [1]. Especially, the charge ordering (CO) phenomena in the Ln Mn manganites have been of considerable interest [2}8]. It has been shown that this charge ordering has an in#uence on the magnetotransport properties of these materials [9}13]. Also, a detailed study of the structure of these manganites is absolutely necessary to understand their behaviour, since tiny structural distortions or modi"cations of their electronic charge distribution may in#uence their transport and magnetic properties dramatically. An earlier study of Chen and Cheong [3] has shown that the antiferro (AFM) to ferromagnetic (FM) transition in La Mn is structurally associated with a commensurate to incommensurate charge ordering phase transition. Another study [14] however, reported that an /00/$ see front matter 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. PII: S ( 9 9 )
2 106 W. Schuddinck et al. / Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 incommensurate modulated structure is also observed for the Sm Mn manganite in spite of the fact that this oxide does not exhibit a FMtoAFM transition. So at this point in time, the relationship between ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism, and charge and orbital ordering in these manganites is not clearly understood. The present article is devoted to an electron microscopy study of structures of the Nd manganites versus temperature. The Nd Mn composition is very interesting because it has been shown that for this material a phase transition takes place below ¹ [15]. When this composition is doped with Cr, the physical properties are altered. The Crdoped materials become conducting at low temperatures (¹(140 K). Conductivity means a mobility of the charges and this is not in agreement with a charge ordering process, which assumes a localisation of the charges. Secondly the Crdoped materials with x'0.02 show strong ferromagnetism at temperatures below 140 K and ferromagnetism suppresses charge ordering. Because of all these properties the Nd manganites are very suitable to study the relationships between ferromagnetism, conductivity, charge ordering and incommensurate structures. 2. Experimental procedure The synthesis of polycrystalline Nd samples (x"0, 0.02, 0.05, 0.07 and 0.12) was carried out, starting from stoichiometric mixtures of Nd, CaO, and Mn. The mixtures were heated at 10003C to achieve decarbonation. Then, the samples were pressed into pellets and sintered, in two steps, at 1200 and 15003C for 12 h. They were slowly cooled down to 8003C and "nally quenched to room temperature. The electron di!raction (ED) versus temperature and the dark "eld lattice images at 150 K were carried out with a Philips CM20 electron microscope operating at 200 kv and equipped with a double tilt liquid N sample holder (tilt $303, $453 and 90 K)¹)300 K). The FFT and inverse FFT were calculated using the Digital Micrograph 2.5 program of Gatan. In the electron di!raction study versus temperature all the patterns were recorded under the same experimental conditions, i.e. increasing the temperature from 90 to 300 K, in steps of 43C(x"0.02) or 103C, waiting for temperature stabilisation during minimum 3 min before each ED recording, made with a constant electron beam adjustment. Resistance measurements were performed from room temperature down to 30 K by the fourprobe method on sintered bars in the earth magnetic "eld. All bars have the same mm dimensions. The magnetisation versus temperature was registered during heating with a vibrating sample magnetometer after a magnetic "eld of 1.4 or 0.01 T was applied at 4.2 K (Fig. 1). 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Charge ordering in Nd 0 5 Ca 0 5 Mn 0 98 Cr 0 02 O 3 When Nd Mn is doped with small amounts of Cr, satellite re#ections appear in the vicinity of the 0 0 superstructure re#ections, i.e. the structure becomes incommensurate. The modulation vector can be written as q"(!δ)ah. The intensity of the incommensurate satellites scales with the intensity of the basic Pnma re#ections as can be clearly seen from the enlarged Fig. 2. This shows that the satellites are not to be considered as a splitting of the 00re#ection, but as satellites of the basic Pnma spots. The 0 0 superstructure re #ections present in the undoped material [15] then have to be considered as the end members of the series with q"0.5ah. Such a modulation is best described using a notation based on four indices hklm: in Fig. 2 the satellite belongs to the 2 02re#ection, whereas the satellite belongs to re#ection In some patterns also the secondorder satellites are visible, indicating that the modulation is not purely sinusoidal. Sometimes the satellites are not exactly along ah, but slightly inclined, i.e. q has a component along ch (indicated by the 3.63 tilt between two satellites in Fig. 2). The origin of this orientation anomaly will be discussed when considering the HREM at low temperature. The position of the satellites changes continuously with temperature. This evolution is visible in the
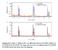
3 W. Schuddinck et al. / Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105} Fig. 2. [0 1 0]ED pattern of Nd Ca Mn Cr O registered at a low temperature (97 K). The intense re#ections are indexed in the a 2 2a a 2 cell. The weaker satellites of this Pnma re#ections are indexed using a notation based on four indices hklm. These satellites sometimes have a component along ch as indicated by the 3.63 tilt angle. Fig. 1. (a) Magnetisation in Nd as a function of temperature. Inset: Magnetisation versus temperature near ¹ ; (b) electric resistance in Nd as a function of temperature; (c) qvalue as a function of temperature for x"0.02, 0.05 and Above ¹+¹ the satellites become streaked along ah and the modulation vector could no longer be measured with enough precision. ED patterns of Fig. 3. The shift of the spot (upper arrow) is visualised with respect to the unsplit position (lower arrow). The evolution of the qvalue for x"0.02 as a function of temperature is sumarised in Fig. 1c. This curve presents the &naked' measurements on a single sample during a heating run from 97 K till room temperature. The curve starts at q"0.472 for ¹"97 K and is then continuously descending till q"0.369 is reached at ¹"244 K. Fig. 3. Evolution with increasing temperature of the position of the 0021 re#ection, indicated by the top white arrow with respect to the unsplit position (bottom white arrow) for the composition Nd. This continuous descent of the qvalue can be correlated with the charge ordering process, similarly it was also done for related compounds [2,3,13,14]. The fact that the intensity of the re#ections drastically drops and becomes streaked at
4 108 W. Schuddinck et al. / Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 ¹+244 K is in good agreement with the CO temperature indicated by the physical measurements at ¹+240 K (inset Fig. 1b). It has to be noted that the conductivity at temperatures below ¹"140 K has no in#uence on the behaviour of the modulation vector q. The descent of q is similar to that measured in the undoped compound [2], which is insulating. It should be noted however, that the resistivity is measured on a large amount of material compared to the amount studied by electron microscopy and that only a slight fraction has to be conductive to give the measured result Evolution of the charge ordering process with increased Crdoping To verify whether charge ordering disappears when the Crdoping is increased * as expected from the M(¹) and R(¹) measurements (Figs. 1a and b) * a systematic exploration of the modulated structure of the doped manganites Nd, following the same process as discribed above, has been carried out for four di!erent xvalues varying from x"0.02 to The results for x"0.02, 0.05 and 0.07 are summarised in Fig. 1c, where the qvalues are drawn versus temperature (97 K)¹)270 K). Based on these results, the following remarks can be made: (1) The structure is incommensurate for all x values in spite of the fact that for ¹(140 K the compounds become strongly ferromagnetic, which is a disadvantage for charge ordering. One would expect that when ferromagnetism becomes stronger charge ordering would be suppressed and the incommensurate re#ections would become weaker; however, such a phenomenon is not observed in any of the crystals studied. (2) In the x"0.05 compound ferromagnetism and CO go together, but apparently this has no in#uence on the behaviour of the qvalue, because a similar descent is observed as that with other xvalues. (3) For each nominal composition, a variation of the modulation vector is observed in di!erent crystals, but within a single crystal the modulation vector is constant. (4) The qvalue is always incommensurate and decreases as the chromium doping (x) is increased. This strongly suggests that the undoped phase has also to be considered as a modulated structure, but with a commensurate qvector (q"0.5), as mentioned in Ref. [14]. (5) The temperature where the re#ections broaden and become streaked along ah is in good agreement with the ¹ obtained by the physical properties for all xvalues. (6) For x"0.12 no clear modulation re#ections were observed, even at ¹"97 K; only a weak streaking along ah with a maximum around q was present Lattice images at 150 K for Nd 0 5 Ca 0 5 Mn 0 98 Cr 0 02 O 3 Lowtemperature (¹ 150 K) HREM was performed for the compound with x"0.02 in order to understand better the character of the charge ordering process and the structure of the incommensurate phase. The [0 1 0] image shown in Fig. 4a shows a fringe system of (0 0 l) planes, similar to that obtained for an overoxidised Sm Mn [14]. To enhance the contrast of this fringe system some processing has been done. A FFT (Fig. 4c) has been obtained from the HREM image of Fig. 4a. Then a mask which only selected a few re#ections (including the satellite re#ections) was applied and an inverse FFT (Fig. 4d) has been calculated using the &masked' FFT. This inverse FFT very clearly shows two characteristic phenomena: The sequence of bright and dark fringes is not regular. No wellordered domains, where one bright fringe alternates with one grey fringe along a over a certain period, are visible. The distance between two bright fringes separated by one grey fringe is approximately 10.8 As ("2 a 2), in agreement with a doubling of the a parameter. But in some regions two adjacent dark or bright fringes appear with an interdistance of 5.4 As ("a 2), as indicated in the "gure by the white arrows. We therefore have a mixing of fringes separated by 2 a 2 and
5 W. Schuddinck et al. / Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105} Fig. 4. (a) Lattice image of a Nd crystal recorded at 150 K. The white arrows indicate the adjacent dark or bright fringes with an interdistance of 5.4 As. The black arrow indicates a shift of a bright fringe along ah. (b) Experimental ED pattern of the same area as (a); (c) ED obtained by FFT of the same area as (a); (d) inverse FFT obtained from (c), by applying a mask which only selected the re#ections visible in (c), white arrows indicate the adjacent dark or bright fringes with an interdistance of 5.4 As. The black arrow indicates a shift of a bright fringe along ah. fringes separated by 3 a 2. Since this mixing tends to be uniform a qvector slightly smaller than 0.5 results. Occasionally, a shift of the fringes along a occurs. This is illustrated by the black arrow in Figs. 4a and c, where a dark fringe is connected to a bright fringe. The amplitude of the translation is a 2. As mentioned in Ref. [2] this shift implies that the modulation vector is no longer parallel to a, but has a small component along c. This explains the inclination of the satellites with respect to ah observed in de ED patterns (see e.g. Fig. 2). The clear presence of these two phenomena strongly support the structural model for the charge ordering process proposed by BarnabeH et al. [2], where such images are interpretated by the presence of an excess Mn (Mn /Mn '1). The additional Mn species are ordered in the form
6 110 W. Schuddinck et al. / Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 of longrange ordered adjacent [Mn O] layers and submitted to a shearing mechanism along a. 4. Conclusion This study of the oxides Nd shows that the charge ordering process is progressive and corresponds to a broad temperature range where the structure is incommensurate. The incommensurability qvector descends continuously as temperature is increased. With increasing temperature also the intensity of the incommensurate satellites reduces and at ¹ the satellite re#ections become streaked along ah. This temperature is in good agreement with the ¹ obtained by physical properties measurements. With increased Crdoping the qvector decreases, but the fact that these Crdoped compounds are ferromagnetic and conductive at low temperature seems to have no in#uence on the behaviour of the modulation vector q. It should be noted, however, that the resistivity is measured on a large amount of material compared to the amount studied by electron microscopy and that only a slight fraction has to be conductive to give the measured result. Lattice images obtained at low temperature allow a better understanding of the characteristics and features of the charge ordering process. However, further investigations with a better direct spacial resolution at lower temperatures and di!raction measurements below 100 K are necessary to obtain a complete image of this complex mechanism and its relationship with phenomena like conductivity and ferromagnetism. Acknowledgements W. Schuddinck is grateful to the FWO for "nancial support. This research has been performed within the framework of IUAP 4/10. References [1] R.M. Kusters, J. Singleton, D.A. Keen et al., Physica B 155 (1989) 362. [2] A. BarnabeH, M. Hervieu, C. Martin et al., J. Appl. Phys. 84 (1998) [3] C.H. Chen, S.W. Cheong, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 (1996) [4] C.H. Chen, S.W. Cheong, H.Y. Hwang, J. Appl. Phys. 81 (1997) [5] P. La!ez, G.V. Tendeloo, F. Millange et al., Mater. Res. Bull. 31 (1996) 905. [6] S. Mori, C.H. Chen, S.W. Cheong, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 (1998) [7] P.G. Radaelli, D.E. Cox, M. Marezio et al., Phys. Rev. B 55 (1997) [8] Y. Tomioka, A. Asamitsu, Y. Moritomo et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 (1995) [9] V. Caignaert, F. Millange, M. Hervieu et al., Solid State Commun. 99 (1996) 173. [10] Y. Tomioka, A. Asamitsu, H. Kuwahara et al., Phys. Rev. B 53 (1996) R1689. [11] Y. Tokura, H. Kuwahara, Y. Moritomo et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 (1996) [12] Z. Jirak, S. Krupicka, Z. Simsa et al., J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 53 (1985) 153. [13] Y. Murakami, D. Shindo, H. Chiba et al., J. Solid State Commun. 140 (1998) 331. [14] A. BarnabeH, M. Hervieu, C. Martin et al., J. Mater. Chem. 8 (1998) [15] O. Richard, W. Schuddinck, G. Van Tendeloo et al., Acta Crystallogr. A 55 (1999) 704.
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
The crucial role of mixed valence in the magnetoresistance properties of manganites and cobaltites
 366, 83 92 doi:10.1098/rsta.2007.2141 Published online 7 September 2007 The crucial role of mixed valence in the magnetoresistance properties of manganites and cobaltites BY B. RAVEAU* Laboratoire CRISMAT,
366, 83 92 doi:10.1098/rsta.2007.2141 Published online 7 September 2007 The crucial role of mixed valence in the magnetoresistance properties of manganites and cobaltites BY B. RAVEAU* Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) La (Sr Ca )MnO x x 3. *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu. a, a b
 International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) 1063 1072 Chemical pressure controlled colossal magnetoresistance effects in q La (Sr Ca )MnO R.S. Liu *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu a, a b a Department of
International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) 1063 1072 Chemical pressure controlled colossal magnetoresistance effects in q La (Sr Ca )MnO R.S. Liu *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu a, a b a Department of
Magnetoelectricity and multiferroics. Charles Simon Laboratoire CRISMAT, CNRS and ENSICAEN, F14050 Caen.
 Magnetoelectricity and multiferroics Charles Simon Laboratoire CRISMAT, CNRS and ENSICAEN, F14050 Caen. Introduction : The possibility for a material to be both ferromagnetic and ferroelectric was predicted
Magnetoelectricity and multiferroics Charles Simon Laboratoire CRISMAT, CNRS and ENSICAEN, F14050 Caen. Introduction : The possibility for a material to be both ferromagnetic and ferroelectric was predicted
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998](/thumbs/78/78285667.jpg) Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Evidence for Jahn-Teller Polarons*
 Zeitschrift fur Physikalische Chemie, Bd. 201, S. 263-269 (1997) by R. Oldenbourg Verlag, München 1997 Giant Oxygen-Isotope Shift of the Ferromagnetic Transition Temperature in the Colossal Magnetoresistive
Zeitschrift fur Physikalische Chemie, Bd. 201, S. 263-269 (1997) by R. Oldenbourg Verlag, München 1997 Giant Oxygen-Isotope Shift of the Ferromagnetic Transition Temperature in the Colossal Magnetoresistive
Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Australian Journal of Physics
 CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
Room temperature charge and orbital ordering and phase coexistence in Bi 0.5 Sr 0.5 MnO 3
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13 (2001) 1071 1078 www.iop.org/journals/cm PII: S0953-8984(01)19607-4 Room temperature charge and orbital
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13 (2001) 1071 1078 www.iop.org/journals/cm PII: S0953-8984(01)19607-4 Room temperature charge and orbital
Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
Ohoyama., TEM, neutron diffraction, ordered perovskite, CE structure. Abstract An A-site ordered manganese perovskite YBaMn 2
 New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5 <= x <= 0.9) manganites
 Title Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5
Title Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase. Alok Banerjee
 Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal
 Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal M. Matsukawa, 1, * A. Tamura, 1 S. Nimori, 2 R. Suryanarayanan, 3 T. Kumagai,
Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal M. Matsukawa, 1, * A. Tamura, 1 S. Nimori, 2 R. Suryanarayanan, 3 T. Kumagai,
Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 (x = 0 and 0.
 Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Material Science II. d Electron systems
 Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES OF THE MAGNETIC FLUCTUATIONS IN YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7¹d
 Pergamon PII: S0022-3697(98)00196-6 J. Phys. Chem Solids Vol 59, No. 10 12, pp. 2140 2144, 1998 0022-3697/98/$ - see front matter 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES
Pergamon PII: S0022-3697(98)00196-6 J. Phys. Chem Solids Vol 59, No. 10 12, pp. 2140 2144, 1998 0022-3697/98/$ - see front matter 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based
 Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7
 J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
Assessment of Variation in Zero Field Hall Constant of Colossal Magnetoresistive Manganites (Re1-x AxMnO3)
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 2018](/thumbs/90/103904416.jpg) Room-temperature Low-field Colossal Magneto-resistance in Double-perovskite Manganite S. Yamada, N. Abe, H. Sagayama,, K. Ogawa, T. Yamagami, and T. Arima Department of Materials System Science, arxiv:8.07596v
Room-temperature Low-field Colossal Magneto-resistance in Double-perovskite Manganite S. Yamada, N. Abe, H. Sagayama,, K. Ogawa, T. Yamagami, and T. Arima Department of Materials System Science, arxiv:8.07596v
COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION
 E. Dagotto et al. / Physics Reports 344 (2001) 1}153 1 COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio DAGOTTO a, Takashi HOTTA b, Adriana MOREO a National High Magnetic Field
E. Dagotto et al. / Physics Reports 344 (2001) 1}153 1 COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio DAGOTTO a, Takashi HOTTA b, Adriana MOREO a National High Magnetic Field
Crystallographic ordering studies of FePt nanoparticles by HREM
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 266 (2003) 215 226 Crystallographic ordering studies of FePt nanoparticles by HREM Mihaela Tanase a, *, Noel T. Nuhfer a, David E. Laughlin a, Timothy J. Klemmer
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 266 (2003) 215 226 Crystallographic ordering studies of FePt nanoparticles by HREM Mihaela Tanase a, *, Noel T. Nuhfer a, David E. Laughlin a, Timothy J. Klemmer
No. 3 An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in MFM results, it is suggested that the PS in LSMO is not a charge seg
 Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered
 Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Ordering phenomena in the diphosphate tungsten bronzes with
 Superstructure Microsc. Mieroanal. Mierostnict. 1 (1990) 41 FEBRUARY 1990, PAGE 41 Classification Physics Abstracts 61.16d S10.15 Ordering phenomena in the diphosphate tungsten bronzes with hexagonal tunnels
Superstructure Microsc. Mieroanal. Mierostnict. 1 (1990) 41 FEBRUARY 1990, PAGE 41 Classification Physics Abstracts 61.16d S10.15 Ordering phenomena in the diphosphate tungsten bronzes with hexagonal tunnels
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in. manganite multilayers
 Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004](/thumbs/72/66676281.jpg) Coexisting charge modulation and ferromagnetism produces long period phases in manganites: new example of electronic soft matter. G.C. Milward, M.J. Calderón, P.B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/0407727v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Coexisting charge modulation and ferromagnetism produces long period phases in manganites: new example of electronic soft matter. G.C. Milward, M.J. Calderón, P.B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/0407727v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
A-site Ordering versus Electronic Inhomogeneity in CMR-Manganite Films
 A-site Ordering versus Electronic Inhomogeneity in CMR-Manganite Films V. Moshnyaga 1*, L. Sudheendra 1, O. I. Lebedev 2, K. Gehrke, O. Shapoval 3, A. Belenchuk 3, S.A. Köster 1, B. Damaschke 1, G. van
A-site Ordering versus Electronic Inhomogeneity in CMR-Manganite Films V. Moshnyaga 1*, L. Sudheendra 1, O. I. Lebedev 2, K. Gehrke, O. Shapoval 3, A. Belenchuk 3, S.A. Köster 1, B. Damaschke 1, G. van
High resolution electron microscopy study of the high Tc superconductor Tl0.5Pb0.5Sr4Cu2CO3O7
 The Microsc. Microanal. Microstruct. 4 (1993) 41 FEBRUARY 1993, PAGE 41 Classification Physics Abstracts 61.16D 61.70 74.70V High resolution electron microscopy study of the high Tc superconductor Tl0.5Pb0.5Sr4Cu2CO3O7
The Microsc. Microanal. Microstruct. 4 (1993) 41 FEBRUARY 1993, PAGE 41 Classification Physics Abstracts 61.16D 61.70 74.70V High resolution electron microscopy study of the high Tc superconductor Tl0.5Pb0.5Sr4Cu2CO3O7
Author's personal copy
 Solid State Sciences 11 (2009) 595 607 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Solid State Sciences journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ssscie Synthesis and structural mechanisms of the 2201-type
Solid State Sciences 11 (2009) 595 607 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Solid State Sciences journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ssscie Synthesis and structural mechanisms of the 2201-type
Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x. O 3 perovskite material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy
 Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Structural and magnetic properties of the colossal magnetoresistance perovskite La 0.85 Ca 0.15 MnO 3
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 13 1 APRIL 2000-I Structural and magnetic properties of the colossal magnetoresistance perovskite La 0.85 Ca 0.15 MnO 3 M. V. Lobanov Department of Chemistry, Moscow
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 13 1 APRIL 2000-I Structural and magnetic properties of the colossal magnetoresistance perovskite La 0.85 Ca 0.15 MnO 3 M. V. Lobanov Department of Chemistry, Moscow
Anomalous Thermal Expansion in (Pr,Ca)MnO 3 due to Orbital Ordering
 Physics Procedia Volume 75, 2015, Pages 475 481 20th International Conference on Magnetism Anomalous Thermal Expansion in (Pr,Ca)MnO 3 due to Orbital Ordering Jussi Tikkanen 12, Simo Kauhala 1, Hannu Huhtinen
Physics Procedia Volume 75, 2015, Pages 475 481 20th International Conference on Magnetism Anomalous Thermal Expansion in (Pr,Ca)MnO 3 due to Orbital Ordering Jussi Tikkanen 12, Simo Kauhala 1, Hannu Huhtinen
Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices
 Physica E 2 (1998) 325 329 Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices D.M. Follstaedt *, R.D. Twesten, J. Mirecki Millunchick, S.R. Lee, E.D. Jones, S.P.
Physica E 2 (1998) 325 329 Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices D.M. Follstaedt *, R.D. Twesten, J. Mirecki Millunchick, S.R. Lee, E.D. Jones, S.P.
Chemistry Institute B6, SUPRATECS, University of Liège, Sart-Tilman, B-4000 Liège, Belgium b
 Synthesis and characterization of Bi 2 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8 ceramics prepared in presence of sodium S. Rahier a*, S. Stassen a, R. Cloots a and M. Ausloos b a Chemistry Institute B6, SUPRATECS, University of
Synthesis and characterization of Bi 2 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8 ceramics prepared in presence of sodium S. Rahier a*, S. Stassen a, R. Cloots a and M. Ausloos b a Chemistry Institute B6, SUPRATECS, University of
PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB
![PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB](/thumbs/84/91030401.jpg) Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties
 Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties Abstract The magnetic properties of a material are the basis of their applications. Specifically, the contrast agents that will be developed in Chaps. 4 and 5 use their magnetic
Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties Abstract The magnetic properties of a material are the basis of their applications. Specifically, the contrast agents that will be developed in Chaps. 4 and 5 use their magnetic
Charge and orbital ordering in Fe and Mn perovskite oxides far from half- doping by resonant x- ray scattering
 Charge and orbital ordering in Fe and Mn perovskite oxides far from half- doping by resonant x- ray scattering J Herrero-Martín 1, J García 2, G Subías 2, J Blasco 2, C Mazzoli 1 and M C Sánchez 2 1 European
Charge and orbital ordering in Fe and Mn perovskite oxides far from half- doping by resonant x- ray scattering J Herrero-Martín 1, J García 2, G Subías 2, J Blasco 2, C Mazzoli 1 and M C Sánchez 2 1 European
Thermopower of single-crystal Nd 1 x Sr,Pb x MnO 3
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 21 1 JUNE 1996-I Thermopower of single-crystal Nd 1 x Sr,Pb x MnO 3 Vincent H. Crespi, Li Lu, Y. X. Jia, K. Khazeni, A. Zettl, and Marvin L. Cohen Department of Physics,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 21 1 JUNE 1996-I Thermopower of single-crystal Nd 1 x Sr,Pb x MnO 3 Vincent H. Crespi, Li Lu, Y. X. Jia, K. Khazeni, A. Zettl, and Marvin L. Cohen Department of Physics,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/NMAT3449 Topological crystalline insulator states in Pb 1 x Sn x Se Content S1 Crystal growth, structural and chemical characterization. S2 Angle-resolved photoemission measurements at various
DOI: 1.138/NMAT3449 Topological crystalline insulator states in Pb 1 x Sn x Se Content S1 Crystal growth, structural and chemical characterization. S2 Angle-resolved photoemission measurements at various
FRACTAL ANALYSIS OF PrFe 1-x Ni x O 3 (0 X 0.3) PERVOSKITE SAMPLES BY USING MICROGRAPHS
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol. 2, Issue 3, July September 2010, p. 161-165 FRACTAL ANALYSIS OF PrFe 1-x Ni x O 3 (0 X 0.3) PERVOSKITE SAMPLES BY USING MICROGRAPHS FEROZ. A. MIR
Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol. 2, Issue 3, July September 2010, p. 161-165 FRACTAL ANALYSIS OF PrFe 1-x Ni x O 3 (0 X 0.3) PERVOSKITE SAMPLES BY USING MICROGRAPHS FEROZ. A. MIR
On conduction mechanism in paramagnetic phase of Gd based manganites
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 41 45. c Indian Academy of Sciences. On conduction mechanism in paramagnetic phase of Gd based manganites S SAGAR 1,2 and M R ANANTHARAMAN 1, 1 Department
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 41 45. c Indian Academy of Sciences. On conduction mechanism in paramagnetic phase of Gd based manganites S SAGAR 1,2 and M R ANANTHARAMAN 1, 1 Department
The (3 + 2)D structure of oxygen deficient LaSrCuO 3.52 {
 PAPER www.rsc.org/materials Journal of Materials Chemistry The (3 + 2)D structure of oxygen deficient LaSrCuO 3.52 { Joke Hadermann,* ab Olivier Pérez, a Nicolas Créon, a Claude Michel a and Maryvonne
PAPER www.rsc.org/materials Journal of Materials Chemistry The (3 + 2)D structure of oxygen deficient LaSrCuO 3.52 { Joke Hadermann,* ab Olivier Pérez, a Nicolas Créon, a Claude Michel a and Maryvonne
Non-linear effects and Joule heating in I-V curves in manganites. Charles Simon, Laboratoire CRISMAT, UMR 6508 ENSICAEN et CNRS, Caen, France.
 Non-linear effects and Joule heating in I-V curves in manganites Silvana Mercone, Raymond Frésard, Vincent Caignaert, Christine Martin, Damien Saurel, Charles Simon, Laboratoire CRISMAT, UMR 6508 ENSICAEN
Non-linear effects and Joule heating in I-V curves in manganites Silvana Mercone, Raymond Frésard, Vincent Caignaert, Christine Martin, Damien Saurel, Charles Simon, Laboratoire CRISMAT, UMR 6508 ENSICAEN
PHASE DIAGRAM AND MAGNETOCALORIC EFFECTS IN Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05
 PHASE DIAGRAM AND MAGNETOCALORIC EFFECTS IN Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 Anil Aryal 1, Abdiel Quetz 1, Sudip Pandey 1, Michael Eubank 1, Tapas Samanta 2, Igor Dubenko 1, Shane Stadler 2, and Naushad Ali 1 1 Department
PHASE DIAGRAM AND MAGNETOCALORIC EFFECTS IN Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 Anil Aryal 1, Abdiel Quetz 1, Sudip Pandey 1, Michael Eubank 1, Tapas Samanta 2, Igor Dubenko 1, Shane Stadler 2, and Naushad Ali 1 1 Department
Polytypism in epitaxially grown gallium nitride
 Journal of Crystal Growth 208 (2000) 57}64 Polytypism in epitaxially grown gallium nitride H. Selke *, V. Kirchner, H. Heinke, S. Einfeldt, P.L. Ryder, D. Hommel Institut fu( r Werkstowphysik und Strukturforschung,
Journal of Crystal Growth 208 (2000) 57}64 Polytypism in epitaxially grown gallium nitride H. Selke *, V. Kirchner, H. Heinke, S. Einfeldt, P.L. Ryder, D. Hommel Institut fu( r Werkstowphysik und Strukturforschung,
Artificially layered structures
 http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6
 Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Nano and micro Hall-effect sensors for room-temperature scanning hall probe microscopy
 Microelectronic Engineering 73 74 (2004) 524 528 www.elsevier.com/locate/mee Nano and micro Hall-effect sensors for room-temperature scanning hall probe microscopy A. Sandhu a, *, A. Okamoto b, I. Shibasaki
Microelectronic Engineering 73 74 (2004) 524 528 www.elsevier.com/locate/mee Nano and micro Hall-effect sensors for room-temperature scanning hall probe microscopy A. Sandhu a, *, A. Okamoto b, I. Shibasaki
Mössbauer studies on FeSe and FeTe
 Mössbauer studies on FeSe and FeTe Yoshikazu Mizuguchi a,b,c, Takao Furubayashi a, Keita Deguchi a,b,c, Shunsuke Tsuda a,b, Takahide Yamaguchi a,b and Yoshihiko Takano a,b,c a Superconducting Materials
Mössbauer studies on FeSe and FeTe Yoshikazu Mizuguchi a,b,c, Takao Furubayashi a, Keita Deguchi a,b,c, Shunsuke Tsuda a,b, Takahide Yamaguchi a,b and Yoshihiko Takano a,b,c a Superconducting Materials
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/117739901.jpg) Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
Hall effect in strongly correlated electron systems
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 24, No. 3, 2006 Hall effect in strongly correlated electron systems V. H. TRAN * Institute of Low Temperature and Structure Research, Polish Academy of Sciences, P. O. Box
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 24, No. 3, 2006 Hall effect in strongly correlated electron systems V. H. TRAN * Institute of Low Temperature and Structure Research, Polish Academy of Sciences, P. O. Box
Magnetic field induced dielectric relaxation in the strain glass state of Pr 0.6 Ca 0.4 MnO 3
 Magnetic field induced dielectric relaxation in the strain glass state of Pr 0.6 Ca 0.4 MnO 3 K Devi Chandrasekhar 1, A K Das 1 and A Venimadhav 2,a) 1 Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian Institute
Magnetic field induced dielectric relaxation in the strain glass state of Pr 0.6 Ca 0.4 MnO 3 K Devi Chandrasekhar 1, A K Das 1 and A Venimadhav 2,a) 1 Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian Institute
lead-free perovskite piezoelectric ceramics Cheuk W. Tai * and Y. Lereah Department of Physical Electronics, School of Electrical Engineering,
 Nano-scale oxygen octahedral tilting in 0.90(Bi 1/2 Na 1/2 )TiO 3-0.05(Bi 1/2 K 1/2 )TiO 3-0.05BaTiO 3 lead-free perovskite piezoelectric ceramics Cheuk W. Tai * and Y. Lereah Department of Physical Electronics,
Nano-scale oxygen octahedral tilting in 0.90(Bi 1/2 Na 1/2 )TiO 3-0.05(Bi 1/2 K 1/2 )TiO 3-0.05BaTiO 3 lead-free perovskite piezoelectric ceramics Cheuk W. Tai * and Y. Lereah Department of Physical Electronics,
Anisotropic magnetic properties of TbNi 2 B 2 C single crystals
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 1996-I Anisotropic magnetic properties of TbNi 2 B 2 C single crystals C. V. Tomy, L. A. Afalfiz, M. R. Lees, J. M. Martin, and D. McK. Paul Department of
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 1996-I Anisotropic magnetic properties of TbNi 2 B 2 C single crystals C. V. Tomy, L. A. Afalfiz, M. R. Lees, J. M. Martin, and D. McK. Paul Department of
YBCO. CuO 2. the CuO 2. planes is controlled. from deviation from. neutron. , blue star for. Hg12011 (this work) for T c = 72
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal structures and joint phase diagram of Hg1201 and YBCO. (a) Hg1201 features tetragonal symmetry and one CuO 2 plane per primitive cell. In the superconducting (SC) doping
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal structures and joint phase diagram of Hg1201 and YBCO. (a) Hg1201 features tetragonal symmetry and one CuO 2 plane per primitive cell. In the superconducting (SC) doping
Phases of Na x CoO 2
 Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Magnetism and Hall effect of the Heusler alloy Co 2 ZrSn synthesized by melt-spinning process
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 299 (2006) 255 259 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Magnetism and Hall effect of the Heusler alloy Co 2 ZrSn synthesized by melt-spinning process Wei Zhang a, Zhengnan
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 299 (2006) 255 259 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Magnetism and Hall effect of the Heusler alloy Co 2 ZrSn synthesized by melt-spinning process Wei Zhang a, Zhengnan
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Fe Co Si. Fe Co Si. Ref. p. 59] d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb Alloys and compounds with Ge
![Fe Co Si. Fe Co Si. Ref. p. 59] d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb Alloys and compounds with Ge Fe Co Si. Fe Co Si. Ref. p. 59] d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb Alloys and compounds with Ge](/thumbs/72/66917236.jpg) Ref. p. 59] 1.5. 3d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb 7 1.75 1.50 Co Si 0.8 0. 3.50 3.5 Co Si 0.8 0. H cr Magnetic field H [koe] 1.5 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.5 C C IF "A" P Frequency ωγ / e [koe] 3.00.75.50.5.00
Ref. p. 59] 1.5. 3d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb 7 1.75 1.50 Co Si 0.8 0. 3.50 3.5 Co Si 0.8 0. H cr Magnetic field H [koe] 1.5 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.5 C C IF "A" P Frequency ωγ / e [koe] 3.00.75.50.5.00
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
Electronic Supplementary Information. Vertically oriented CuO/ZnO nanorod arrays: from plasmaassisted synthesis to photocatalytic H 2 production
 Electronic Supplementary Information Vertically oriented CuO/ZnO nanorod arrays: from plasmaassisted synthesis to photocatalytic H 2 production Quentin Simon, a Davide Barreca,* b Alberto Gasparotto, a
Electronic Supplementary Information Vertically oriented CuO/ZnO nanorod arrays: from plasmaassisted synthesis to photocatalytic H 2 production Quentin Simon, a Davide Barreca,* b Alberto Gasparotto, a
Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La 0.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ) 0.3 CoO 3 System
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
High resolution electron microscopy as a tool for structural investigations
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 6, No. 3, July 1984, pp. 459-475. Printed in India. High resolution electron microscopy as a tool for structural investigations G SINGH and R S RAI Department of Physics, Banaras
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 6, No. 3, July 1984, pp. 459-475. Printed in India. High resolution electron microscopy as a tool for structural investigations G SINGH and R S RAI Department of Physics, Banaras
Superconductivity at 41.0 K in the F-doped LaFeAsO 1-x F x
 Superconductivity at 41.0 K in the F-doped LaFeAsO 1-x F x Wei Lu, Xiao-Li Shen, Jie Yang, Zheng-Cai Li, Wei Yi, Zhi-An Ren*, Xiao-Li Dong, Guang-Can Che, Li-Ling Sun, Fang Zhou, Zhong-Xian Zhao* National
Superconductivity at 41.0 K in the F-doped LaFeAsO 1-x F x Wei Lu, Xiao-Li Shen, Jie Yang, Zheng-Cai Li, Wei Yi, Zhi-An Ren*, Xiao-Li Dong, Guang-Can Che, Li-Ling Sun, Fang Zhou, Zhong-Xian Zhao* National
BNL X-RAY INDUCED INSULATOR-METAL TRANSITIONS IN CMR MANGANITES
 BNL-65316 X-RAY INDUCED INSULATOR-METAL TRANSITIONS IN CMR MANGANITES V KIRYUKHIN1y*, D CASA', B KEIMERl, JP HILL2, A VIGLIANTE2, Y TOMIOKA3, Y TOKURh3y4 1) Dept of Physics, Princeton University, Princeton,
BNL-65316 X-RAY INDUCED INSULATOR-METAL TRANSITIONS IN CMR MANGANITES V KIRYUKHIN1y*, D CASA', B KEIMERl, JP HILL2, A VIGLIANTE2, Y TOMIOKA3, Y TOKURh3y4 1) Dept of Physics, Princeton University, Princeton,
(Me=Mg, Zn) compounds. Solid State Physics, Department of Physics, University of Athens, Zografos, Athens, Greece
 EPR Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. study of the Me14(7) 2 125-129 (Me=Mg, Zn) compounds 125 EPR STUDY OF THE COMPOUNDS (Me = Mg, Zn) Nikolaos Guskos 1,2, Grzegorz Zolnierkiewicz 2, Janusz Typek 2 and Monika Bosacka
EPR Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. study of the Me14(7) 2 125-129 (Me=Mg, Zn) compounds 125 EPR STUDY OF THE COMPOUNDS (Me = Mg, Zn) Nikolaos Guskos 1,2, Grzegorz Zolnierkiewicz 2, Janusz Typek 2 and Monika Bosacka
Transport and magnetic properties in one dimensional A 3 ABO 6 family
 Transport and magnetic properties in one dimensional A 3 ABO 6 family M. Costes 1, J.M. Broto 1, B. Raquet 1, M.N. Baibich 2, H. Rakoto 1, A. Maignan 3, Ch. Martin 3, D. Flahaut 3, S. Hebert 3 1 Laboratoire
Transport and magnetic properties in one dimensional A 3 ABO 6 family M. Costes 1, J.M. Broto 1, B. Raquet 1, M.N. Baibich 2, H. Rakoto 1, A. Maignan 3, Ch. Martin 3, D. Flahaut 3, S. Hebert 3 1 Laboratoire
Double-walled carbon nanotubes in small bundles produced by catalytic vapour deposition: monodispersity in helicity and structural organization
 Double-walled carbon nanotubes in small bundles produced by catalytic vapour deposition: monodispersity in helicity and structural organization P. Launois 1,*, J.-F. Colomer 2, L. Henrard 2, G. Van Tendeloo
Double-walled carbon nanotubes in small bundles produced by catalytic vapour deposition: monodispersity in helicity and structural organization P. Launois 1,*, J.-F. Colomer 2, L. Henrard 2, G. Van Tendeloo
Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7
 The Open Condensed Matter Physics Journal, 2009, 2, 19-24 19 Open Access Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7 Aihua Wang 1,2, Tao Liu 3, Yang Liu 4, Guohui
The Open Condensed Matter Physics Journal, 2009, 2, 19-24 19 Open Access Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7 Aihua Wang 1,2, Tao Liu 3, Yang Liu 4, Guohui
Giant Magnetoresistance
 Giant Magnetoresistance N. Shirato urse: Solid State Physics 2, Spring 2010, Instructor: Dr. Elbio Dagotto Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996
Giant Magnetoresistance N. Shirato urse: Solid State Physics 2, Spring 2010, Instructor: Dr. Elbio Dagotto Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996
Classification of Solids, Fermi Level and Conductivity in Metals Dr. Anurag Srivastava
 Classification of Solids, Fermi Level and Conductivity in Metals Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus
Classification of Solids, Fermi Level and Conductivity in Metals Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Giant frequency dependence of dynamic freezing in nanocrystalline. ferromagnetic LaCo 0.5 Mn 0.5 O 3
 Giant frequency dependence of dynamic freezing in nanocrystalline ferromagnetic LaCo 0.5 Mn 0.5 O 3 R. Mahendiran 1,2,Y. Bréard 2, M. Hervieu 2, B. Raveau 2, and P. Schiffer 1 1 Department of Physics and
Giant frequency dependence of dynamic freezing in nanocrystalline ferromagnetic LaCo 0.5 Mn 0.5 O 3 R. Mahendiran 1,2,Y. Bréard 2, M. Hervieu 2, B. Raveau 2, and P. Schiffer 1 1 Department of Physics and
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/115260649.jpg) 1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 10 Oct 2000
 Mn K-edge XANES studies of La 1 x A x MnO 3 systems (A = Ca, Ba, Pb) arxiv:cond-mat/246v2 1 Oct 2 F. Bridges, 1 C. H. Booth, 2 M. Anderson, 1 G. H. Kwei, 2 J. J. Neumeier 3, J. Snyder, 4 J. Mitchell, 5
Mn K-edge XANES studies of La 1 x A x MnO 3 systems (A = Ca, Ba, Pb) arxiv:cond-mat/246v2 1 Oct 2 F. Bridges, 1 C. H. Booth, 2 M. Anderson, 1 G. H. Kwei, 2 J. J. Neumeier 3, J. Snyder, 4 J. Mitchell, 5
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
Transition Elements. pranjoto utomo
 Transition Elements pranjoto utomo Definition What is transition metal? One of which forms one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. 30Zn? Definition Zink is not transition elements
Transition Elements pranjoto utomo Definition What is transition metal? One of which forms one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. 30Zn? Definition Zink is not transition elements
1.1 Introduction CMR effect in Manganites I - 1
 I - 1 1.1 Introduction The rare-earth perovskites LnTMO 3, with Ln a rare-earth element and TM a transition metal have been intensively studied because of large variety of physical phenomena such as superconductivity,
I - 1 1.1 Introduction The rare-earth perovskites LnTMO 3, with Ln a rare-earth element and TM a transition metal have been intensively studied because of large variety of physical phenomena such as superconductivity,
Title: Magnetic chains of metal formed by assembly of small nanoparticles
 Title: Magnetic chains of metal formed by assembly of small nanoparticles Authors: Chen-Min Liu, Lin Guo*, Rong-Ming Wang*, Yuan Deng, Hui-Bin Xu, Shihe Yang* Supporting Information S1. Sample characterization
Title: Magnetic chains of metal formed by assembly of small nanoparticles Authors: Chen-Min Liu, Lin Guo*, Rong-Ming Wang*, Yuan Deng, Hui-Bin Xu, Shihe Yang* Supporting Information S1. Sample characterization
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE-
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE- NOMENOLOGY In the main text we introduce anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in analogy to ferromagnets where non-crystalline and crystalline contributions
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE- NOMENOLOGY In the main text we introduce anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in analogy to ferromagnets where non-crystalline and crystalline contributions
* Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory, University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford, OX1
 BNL- 6 3833 1 f Crystal chemistry and electronic properties of the n = 2 Ruddlesden-Popper manganates: o f - 6 7 1 0 d r n unconventional C M R materials PD BATTLE* SJ BLUNDELL** DE COX*** MA GREEN* JE
BNL- 6 3833 1 f Crystal chemistry and electronic properties of the n = 2 Ruddlesden-Popper manganates: o f - 6 7 1 0 d r n unconventional C M R materials PD BATTLE* SJ BLUNDELL** DE COX*** MA GREEN* JE
Strong charge ordering above room temperature in B-site disordered electron-doped manganite SrMn Mo O 3-δ
 Strong charge ordering above room temperature in B-site disordered electron-doped manganite SrMn 0.875 Mo 0.125 O 3-δ Aga Shahee* and N. P. Lalla UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, University
Strong charge ordering above room temperature in B-site disordered electron-doped manganite SrMn 0.875 Mo 0.125 O 3-δ Aga Shahee* and N. P. Lalla UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, University
doi: /PhysRevLett
 doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
Charge-order driven multiferroic and magneto-dielectric properties of rare earth manganates
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 33, No. 2, April 2010, pp. 169 178. Indian Academy of Sciences. Charge-order driven multiferroic and magneto-dielectric properties of rare earth manganates CLAUDY RAYAN SERRAO 1,2,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 33, No. 2, April 2010, pp. 169 178. Indian Academy of Sciences. Charge-order driven multiferroic and magneto-dielectric properties of rare earth manganates CLAUDY RAYAN SERRAO 1,2,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/114118020.jpg) Damping and softening of transverse acoustic phonons in colossal magnetoresistive La.7 Ca.3 MnO 3 and La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 Joel S. Helton 1,2,, Yang Zhao 2,3, Dmitry A. Shulyatev 4, and Jeffrey W. Lynn 2, 1
Damping and softening of transverse acoustic phonons in colossal magnetoresistive La.7 Ca.3 MnO 3 and La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 Joel S. Helton 1,2,, Yang Zhao 2,3, Dmitry A. Shulyatev 4, and Jeffrey W. Lynn 2, 1
Orbital ordering in the manganites: Resonant x-ray scattering predictions at the manganese L II and L III edges
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 2 1 JULY 2000-II Orbital ordering in the manganites: Resonant x-ray scattering predictions at the manganese L II and L III edges C. W. M. Castleton* European Synchrotron
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 2 1 JULY 2000-II Orbital ordering in the manganites: Resonant x-ray scattering predictions at the manganese L II and L III edges C. W. M. Castleton* European Synchrotron
Microstructure evolution during BaTiO 3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces
 Journal of the European Ceramic Society 25 (2005) 2201 2206 Microstructure evolution during BaTiO 3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces Andreas Graff a,, Stephan Senz a,
Journal of the European Ceramic Society 25 (2005) 2201 2206 Microstructure evolution during BaTiO 3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces Andreas Graff a,, Stephan Senz a,
Magnetic anisotropy of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 nanopowders
 Magnetic anisotropy of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 nanopowders I. Radelytskyi (1), P. Dłużewski (1), V. Dyakonov (1 and 2), P. Aleshkevych (1), W. Kowalski (1), P. Jarocki (1), H. Szymczak (1) ((1) Institute of
Magnetic anisotropy of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 nanopowders I. Radelytskyi (1), P. Dłużewski (1), V. Dyakonov (1 and 2), P. Aleshkevych (1), W. Kowalski (1), P. Jarocki (1), H. Szymczak (1) ((1) Institute of
Supplementary Note 1 Description of the sample and thin lamella preparation Supplementary Figure 1 FeRh lamella prepared by FIB and used for in situ
 Supplementary Note 1 Description of the sample and thin lamella preparation A 5nm FeRh layer was epitaxially grown on a go (1) substrate by DC sputtering using a co-deposition process from two pure Fe
Supplementary Note 1 Description of the sample and thin lamella preparation A 5nm FeRh layer was epitaxially grown on a go (1) substrate by DC sputtering using a co-deposition process from two pure Fe
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 213 (2000) 271}277
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 213 (2000) 271}277 Low-"eld magnetic properties of La Ca (0)x)0.4) R. Laiho*, K.G. Lisunov, E.LaK hderanta, P. Petrenko, V.N. Stamov, V.S. Zakhvalinskii Wihuri
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 213 (2000) 271}277 Low-"eld magnetic properties of La Ca (0)x)0.4) R. Laiho*, K.G. Lisunov, E.LaK hderanta, P. Petrenko, V.N. Stamov, V.S. Zakhvalinskii Wihuri
