arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998
|
|
|
- Shauna Gibbs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo, H. ujioka, 3 K. Hirota, 3 and Y. Endoh 3 1 Neutron Scattering Laboratory, I. S. S. P., University of Tokyo, Tokai, Ibaraki, , Japan PRESTO, Center for Integrated Research in Science and Engineering (CIRSE) Nagoya University, Nagoya, , Japan 3 CREST, Department of Physics, Tohoku University, oba-ku, Sendai, , Japan (ebruary 6, 018) We demonstrate that the half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn exhibits -type chargeordered and spin-orderedstates below TN,CO=Kand belowtn 1 K, respectively. However, the volume fraction of the -type ordering is relatively small, and the system is dominated by the -type spin ordering. The coexistence of the two types of ordering is essential to understand its transport properties, and we argue that it can be viewed as an effective phase separation between the metallic d(x y ) orbital ordering and the charge-localized d(3x r )/d(3y r ) orbital ordering. 7..+z, a, h It is well known that a Mn-based Ruddlesden-Popper compound (La,Sr) n+1 Mn n O 3n+1 has a unique layeredtype structure in which every n MnO layers are separated by an additional ( x Sr x ) O blocking bilayer along the c axis. 1 One of the attractive features of this family of compounds is that, by changing the number of MnO layers (n), effective dimensionality can be artificially controlled. The change of effective dimensionality have the strong influence on the magnetism as well as transport properties. 1 or instance, the 3d n = system x Sr x is a ferromagnetic metal for 0.17 < x < 0.6duetothedouble-exchangemechanism, whereas the d n = 1 compound +x Sr 1 x MnO is a good insulator for 0 x < 0.7 and exhibits spin glass behavior for a wide range of the hole concentration. 3 or the n = bilayer La x Sr 1+x Mn system, we have very recently reported that a canted -type antiferromagnetic (M) structure is stabilized for the hole concentration of 0.0 < x < 0.8 (Ref. ). One of the important aspects of perovskite manganites is the charge ordering which is frequently observed at a commensurate hole concentration. In the vicinity of x = 1/, a number of the 3d n = manganite systems including Pr 1/ Ca 1/ (Ref. 6, 7) shows the so-called -type charge and spin ordering, in which Mn 3+ and Mn + ions are aligned alternately. 8 Neutron and X-ray diffraction experiments revealed that this unique -type charge/spin ordering is also realized in the n = 1 / Sr 3/ MnO system. 9, Very recently, an electron diffraction measurement suggested that the -type charge ordering is also formed in the n = Sr Mn system. 11 To see the influence of the -type charge ordering, the typical examples of the resistivity of several manganites with x = 0.0 are depicted in ig. 1. The resistivity of the 3d n = system Pr 1/ Ca 1/ (Ref. 1) and that of the d n = 1 system / Sr 3/ MnO are insulating over the whole temperature range, and they exhibit a sharp increase below T CO. By contrast, the resistivity of Pr 1/ Sr 1/ is considerably small. 1,1 This is because a relatively wide one-electron bandwidth W in Pr 1/ Sr 1/ suppresses the -type chargeordering, and leads to the -type M spin ordering with very small resistivity (ρ 7 3 Ωcm) below 138 K. Interestingly, the ab-plane resistivity in Sr Mn below T CO shows a rather flat temperature dependence similar to that of Pr 1/ Sr 1/, although it is two order of magnitude larger (ρ 1 Ωcm) than that of Pr 1/ Sr 1/. Resistivity [Ωcm] Resistivity of 0% hole-doped Manganites Pr 1/ Ca 1/ -type Nd 1/ Sr 1/ -type + (-type) Sr Mn -type + (-type) Pr 1/ Sr 1/ -type / Sr 3/ MnO -type Temperature [K] IG. 1. Resistivity of 0 % hole-doped d and 3d manganite samples: Pr 1/ Ca 1/ from Ref. 1, Nd 1/ Sr 1/ from Ref. 13, Pr 1/ Sr 1/ from Ref. 1, the ab-plane resistivities in Sr Mn and in / Sr 3/ MnO by the present work. It would be of great interest to elucidate what sort of mechanism could possibly cause such a drastic difference of the resistivity among 0% hole-doped manganite samples, and why only a difference of one MnO layer leads to totally different behavior in the resistivity between two good d systems n = 1 / Sr 3/ MnO and n = Sr Mn. In order to obtain some insights on these issues, we have performed neutron diffraction studies on the high quality large single crystal sample of the 0 % 1
2 hole-doped bilayer system Sr Mn. or the present neutron diffraction study, we have prepared high quality single crystal samples by floating zone method as reported elsewhere. The sample quality was checked by powder x-ray diffraction measurements to confirm that all the crystals were in a single phase. The resistivity was measured for several crystals including the pieces taken from the same single crystal used in the present neutron diffraction studies, and the results are in excellent accord with the preceding work. 11,16 Neutron diffraction measurements were carried out on triple-axis spectrometers GPTS, TOPN, and HQR in the JRR-3M research reactor at the Japan tomic Energy Research Institute. The spectrometers were operated in their double axis mode, and the (00) reflection of pyrolytic graphite (PG) was used to monochromate the neutron beam. t GPTS, the measurements were carried out on both the (h,h,l) and (h,0,l) reciprocal zones with an incident momentum of k i =.667Å 1, together with PG filters to eliminate higher order contaminations, and with a typical combination of collimators of The lattice constants of the sample at room temperature are a = 3.87Å, and c = Å, respectively. Intensity (counts/0 sec x ) Intensity (counts/ sec x 3 ) (c) (0,0,.) Sr Mn (a) (0,0,3) 1 (1/,1/,3) Temperature ( K ) Temperature ( K ) IG.. Temperature dependence of selected positions for Sr Mn : (a) -type M Bragg, (b) -type charge order, (c) magnetic diffuse scattering, (d) -type M Bragg. (b) heating cooling 1 (3/,3/,1) We first describe the ordering process observed in Sr Mn. igure shows the temperature dependences of Bragg and diffuse peaks in Sr Mn. The moststrikingresultofthebilayersystem Sr Mn is the coexistence of the -type M spin ordering and the -type charge ordering. The intensity at Q = (0,0,3) corresponds to the squared moment of the -type M spin ordering, while the intensity at Q = ( 3, 3,1) gives a measure of the order parameter of the -type charge ordering. t TN,CO = K, the -type M spin ordering and the -type charge ordering are formed simultaneously, as seen in ig. (a) and (b). With decreasing temperature, the intensity of Q = (0,0,3) increasesmonotonically, while that of Q = ( 3, 3,1) reaches (d) Intensity (counts/30 sec x ) Intensity (counts/min x ) a maximum at TN 1 K, and turns to decrease, and almost vanishes at 7 K. By contrast, the intensity of the -type spin ordering emerges at TN 1 K, and exhibits a peak at 11 K, and drastically decreases below as shown in ig. (d). or all known manganites such as Pr 1 x Ca x, / Sr 3/ MnO, and Nd 1/ Sr 1/, the -type charge/spin ordering is stable at low temperatures. 7,9,13 By contrast, the type charge/spin-orderedstatein Sr Mn is unstable at low temperatures, and transforms to the metallic -type M state. It should be noted, however, that the substantial intensity for the -type charge/spin ordering is still discernible below 7 K in ig. (b) and (d). s was seen in the resistivity shown in ig. 1, salient hysteresis was also observed in the temperature dependences of the -type and -type charge/spin orderings in ig. for a wide temperature region of < T < TN,CO. Clearly, the hysteresis should be attributed to the onset and the suppression of the -type charge/spin ordering. The temperature dependence of the magnetic diffuse scattering in ig. (c) observed at Q= (0, 0,.) demonstrates that the strong M spin correlations have alreadybeen welldeveloped within the MnO layersfrom room temperature down to TN,CO. The observed structure for the -type charge and spin ordering in the bilayer system Sr Mn is essentially the same with the known -type ordering except for the stacking along the c axis. The -type spin pattern in the ab plane is depicted in ig. 3(a), and the observed Bragg spots on the (h,h,l) reciprocal plane is illustrated in ig. 3(d). The superlattice reflections due to the lattice distortion accompanied with the -type charge ordering are observed at (h,h,l) = ( n+1, n+1,m), while those for the -type M spin ordering are observed at (h,h,l) = ( n+1, n+1,l) with n,m = integer, and l = integer or half integer. In the (h,h,l) zone, however, all the magnetic reflections are originated from the Mn 3+ ions. Since the reflections which are originated from the Mn + sites in the -type spin ordering can be observed on the (h,0,l) zone, we have performed a survey of the (h,0,l) zone as well, and confirmedthat the reflectionsby Mn + sites are observed at the ( 1,0,l) positions with l = integer, and half integer. igure shows the typical profiles for the -type charge and spin ordering observed along the l direction in the (h,h,l) zone. The measurements were carried out at 10 K and at 11 K, respectively, where the each scattering intensity exhibited the maxima, and the data measured at room temperature were subtracted as a back ground. 17 We confirmed that the peaks for the charge ordering on the ( 3, 3,l) line were stronger than those on the ( 1, 1,l) line, whereas the peaks for the -type M spin ordering on the ( 3, 3,l) line were weaker than those on the ( 1, 1,l) line, being consistent with the magnetic form factor. We therefore identify that the former scattering is originated from the charge ordering, but the latter from the magnetic scattering.
3 (0,0,l) (0,0,) (0,0,) magnetic unit cell Mn 3+ Mn + La -x Sr 1+x Mn (x=0.0) y S S (b) Type-I stacking z (a) -type M S S magnetic unit cell (d) (h,h,l) zone I/mmm cell (c) Type-II stacking (0,0,0) (1/,1/, 0) (1,1,0) (3/,3/, 0) (,,0) (h,h,0) IG. 3. (a): -type spin arrangement in the ab plane. The dashed square indicates the offset pattern at the z = 1/ layer by a displacement vector d = ( 1,0,0)M. (b), (c): two stacking patterns along the c axis. and denote the ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic coupling between adjacent bilayers, respectively. (See the text in details) (d): (h, h, l) reciprocal plane for Sr Mn. x x -type CO -type M -type M Nuclear Reflecting a bilayer structure of the n = +x Sr x Mn system, the Bragg intensities for both charge and spin ordering are modulated along the l direction as, I( n+1 I( n+1, n+1,l) 1+cosπlz for charge, (1), n+1,l) 1 cosπlz for spin, () where z is the Mn-Mn distance between MnO layers within bilayers. Note that, due to the M coupling of two MnO layers within bilayers, the sign of the cosine term for the magnetic Bragg reflections becomes minus in eq. (). lthough the peaks of the charge ordering are observed only at l = integer, those of the spin ordering are observed both at l = integer and half integer. This difference is caused by the fact that there exist two kinds of coupling of bilayers along the c axis as depicted in ig. 3(b) and (c). rom a straight forward analysis, we found that the peaks given by l = integer correspond to the ferromagnetic stacking of bilayers along the c axis (Type- I stacking) as indicated by - in ig. 3(b). On the other hand, the peaks observed at l = half integer correspond to a stacking sequence of --- (Type-II stacking). In addition, the profile shown in ig. (b) has a broad component beneath the Bragg reflections, which corresponds to the magnetic diffuse scattering and is again modulated as I(l) 1 cosπlz. This indicates that, in addition to the regular Type-I and Type-II stackings, there are some bilayers which are randomly stacked along the c axis, reflecting a good d character of Sr Mn. Intensity (counts/30sec) Intensity (counts/0sec) Sr Mn (3/,3/,l) 10 K-RT (1/,1/,l) 11 K-RT IG.. (a) Profile of structural scattering observed along q = ( 3, 3,l), and (b) profile of -type spin order observed along q = ( 1, 1,l). or details, see the text. The analysis further revealed a shift of the -type spin patterns relative to the next bilayers. By going to the adjacent bilayers, the -type spin arrangement has to shift by either d = (± 1,0,0) M, (0,± 1,0) M or their linear combination, reflecting the body-centered tetragonal structure of the crystal. The case of d = ( 1,0,0) M in the units of the magnetic unit cell is illustrated by a dashed line in ig. 3(a), and our analysis yielded that the observed magnetic structure is consistent with d = (± 1,0,0) M for both the Type-I and Type-II stackings. mong the half-doped manganites with the -type charge/spin ordering, Sr Mn is very unusual. The preceding resistivity measurements and the electron diffraction study lead the speculation that Sr Mn hasanintermediate-temperaturecharge-orderedphase. 11 We found that it is correct, but the -type charge ordering coexists with the -type M ordering. One can see from ig. that the scattering from the -type ordering is weak, and that the scattering is dominated by the -type M ordering even in the intermediate temperature phase for < T <. This observation is corroborated by the analysis of the observed magnetic moments. We obtained the magnetic moments for the -type spin ordering at 11 K µ = 0.70()µ B /Mn for the Type-I stacking and µ = 0.6(6)µ B /Mn for the Type-II stacking, respectively, whereas the -type (a) (b) 3
4 moment was µ =.3(1)µ B /Mn at 11 K. Clearly the apparently small moment for the -type spin ordering is an artifact and is a strong indication of a small volume of the -type region. By assuming that the magnetic moments in the -type and -type spin ordering are approximately equal, we estimated that the volume fraction of the -type spin ordering is 18% at 11 K. Examining the resistivity of the half-doped manganites in ig. 1, one can notice that the resistivity has a clear correlation with the relative stability of the -type charge-ordered state against the metallic -type M state. Pr 1 x Ca x and / Sr 3/ MnO show no - type M state, and they exhibit very large resistivity at low temperatures. Unlike these -type charge-ordered systems, Nd 1/ Sr 1/ shows rather small resistivity of Ωcm, and it was recently discovered that this system exhibits a parasitic -type M state in the -type charge-ordered phase. 18 The resistivity of Sr Mn is an order of 0 Ωcm, 16 and we have demonstrated in the present work that Sr Mn is dominated by the -type ordering both in the intermediate temperature phase for < T < and at low temperatures with the remnant -type charge-ordered region. inally the metallic -type M Pr 1/ Sr 1/ has the resistivity of Ωcm. This trend of the resistivity should be attributed to a metallic character of the -type M spin ordering. 1 Since spins are aligned ferromagnetically within MnO planes in the -type ordering, the double-exchange interaction is actuated, and yields the metallic in-plane conductivity. Recently, the metallic conductivity of the -type M state is reported in several heavily-doped manganite systems. 1,19 igure 1 indicates that, as the fraction of the -type state increases, the low temperature resistivity decreases. It is intriguing to examine whether these results can be understood on analogy of phase separation, which is recently proposed for the less-doped manganite case. 0 The fluctuation of charge density is essential in the phase separation model, and it is naturally built-in in a less-doped manganite system because the charge-density fluctuation may drive the system to split into a low hole-density insulating M region or into a high holedensity metallic M region. 0 or the 0 % hole-doped systems, such charge fluctuation is unlikely. On the other hand, the present results indicate that there can be two stable phases near 0 % hole-doping due to the orbital and charge ordering. In the -type M state of Sr Mn, the e g electrons supposedly occupy the d(x y ) orbital, whereas in the -type chargeordered state, the e g electrons occupy d(3x r ) and d(3y r ) orbitals alternately. The d(x y ) orbital is isotropic and charges are delocalized, while the d(3x r ) and d(3y r ) orbitals are accompanied with large Jahn-Teller distortions of MnO 6 octahedra, and clearly the charges are localized in the -type charge/spin ordering. Combining the existing results on the half-doped manganites with our present observations, we suggest that, in general, the -type charge/spin ordering coexists with the -type spin ordering at any desired ratio in nearly 0 % hole-doped systems, and such a coexistence between two orbital-ordered states could be viewed as an effective phase separation. We note that somewhat different case of microscopic phase separation is observed in x Ca x. 1 In conclusion, we have demonstrated that the bilayer manganite Sr Mn exhibits a-typecharge/spin ordered state at intermediate temperature, but this state coexists with the dominant -type antiferromagnetic state. With decreasing temperature, the -type state is suppressed through a first order transition. Strong hysteresis was observed for < T <. Reflecting the dominant -type orbital and spin ordering, however, the resistivity of Sr Mn is extremely low, and the anomaly in the resistivity around the -type charge ordering is weak. These results indicate the importance of the competition between the metallic -type d(x y ) orbital ordering and the insulating -type d(3x r )/d(3y r ) orbital ordering near half-doped manganites. Wethank N.urukawa, E.DaggotoandH. Kawanofor valuable discussions, and Y. Tokura for providing numericaldatain Ref. 1, 13, 1. Thisworkwassupportedbya Grant-In-id for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Japan, and the work in Nagoya was supported by Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology (PRESTO), Japan Science and Technology Cooperation (JST), Japan. 1 Y. Moritomo, Y. Tomioka,. samitsu, Y. Tokura, and Y. Matsui, Nature (London) 380, 11 (1996); T. Kimura,. samitsu, Y. Tomioka, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 370 (1997).. Urushibara, Y. Moritomo, T. rima,. samitsu, G. Kido, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B 1, 13 (199). 3 Y. Moritomo, Y. Tomioka,. samitsu, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B 1, 397 (199). K. Hirota, Y. Moritomo, H. ujioka, M. Kubota, H. Yoshizawa, and Y. Endoh, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 67, 3380 (1998). S-W. Cheong and C. H. Chen, pp.1, in Colossal Magnetoresistance, Charge Ordering and Related Properties of Manganese Oxides ed. by C. N. R. Rao and B. Raveau (World Scientific). 6 Z.Jirák, S.Krupička, Z.Šimša, M.DlouháandS.Vratislav, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 3, 13 (198). 7 H. Yoshizawa, H. Kawano, Y. Tomioka, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B, R131 (199); J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 6 3 (1996). 8 E. O. Wollan and W. C. Koehler, Phys. Rev. 0, (19). 9 B. J. Sternlieb, J. P. Hill, U. C. Wildgruber, G. M. Luke, B. Nachumi, Y. Moritomo, and Y. Tokura Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 169 (1996). Y. Murakami, H. Kawada, M. Tanaka, T. rima, Y. Moritomo, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 193 (1998).
5 11 J. Q. Li, Y. Matsui, T. Kimura, Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B 7, R30 (1998). 1 Y. Tomioka et al., J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 6, 366 (199). 13 H. Kuwahara, Y. Tomioka,. samitsu, Y. Moritomo, and Y. Tokura, Science, (199). 1 Y. Tomioka et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 7, 8 (199). 1 H.Kawanoet al., Phys.Rev.Lett.78, 3 (1997); Physica B1-3, 89 (1998);H. Yoshizawa et al., Phys. Rev. B 8, R71 (1998). 16 Y. Moritomo,. Nakamura, K.Ohoyama, M. Ohashi, K. Hirota, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., in press. 17 romthehysteresis, wesuspectthepossibleexistenceofthe structural transition between T N 1 K and 7 K. However, because there is no influence of the nuclear Bragg points on these lines and the change of the lattice constants is negligible, we substract the room temperature data as a back ground. 18 H. Kawano et al., cond-mat/ Y. Moritomo et al., Phys. Rev. B, 79 (1997); Phys. Rev. B 7, R9 (1998). 0 S. Yunoki et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 8 (1998); condmat/980719; S. Yunoki and. Moreo, Phys. Rev. B 8, 603 (1998); E. Daggoto et al., Phys. Rev. B 8, 61 (1998). 1 S. Mori et al., Nature (London) 39, 73 (1998); Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 397 (1998).
MnO. Sr x. La 1-x. Temperature (K) Paramagnetic. Metal T C. Paramagnetic Insulator. Ferromagnetic. Metal T N. Ferromagnetic. Spin-canted Insulator
 Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
Ohoyama., TEM, neutron diffraction, ordered perovskite, CE structure. Abstract An A-site ordered manganese perovskite YBaMn 2
 New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 Feb 1999
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 Feb 1999 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 Feb 1999](/thumbs/93/112651486.jpg) NEUTRON SCATTERING STUDY OF ELASTIC MAGNETIC SIGNALS IN SUPERCONDUCTING La 1.94 Sr 0.06 CuO 4 arxiv:cond-mat/9902319v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 Feb 1999 S. Wakimoto, K. Yamada, S. Ueki, G. Shirane, Y. S.
NEUTRON SCATTERING STUDY OF ELASTIC MAGNETIC SIGNALS IN SUPERCONDUCTING La 1.94 Sr 0.06 CuO 4 arxiv:cond-mat/9902319v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 Feb 1999 S. Wakimoto, K. Yamada, S. Ueki, G. Shirane, Y. S.
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/117739901.jpg) Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based
 Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides. Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625
 Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Australian Journal of Physics
 CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered
 Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/115260649.jpg) 1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
Material Science II. d Electron systems
 Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Apr 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Apr 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Apr 2007](/thumbs/80/81932493.jpg) TbMn 2O 5 Non-resonant and Resonant X-ray Scattering Studies on Multiferroic TbMn 2 O 5 arxiv:0704.0533v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Apr 2007 J. Koo 1, C. Song 1, S. Ji 1, J.-S. Lee 1, J. Park 1, T.-H. Jang 1,
TbMn 2O 5 Non-resonant and Resonant X-ray Scattering Studies on Multiferroic TbMn 2 O 5 arxiv:0704.0533v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Apr 2007 J. Koo 1, C. Song 1, S. Ji 1, J.-S. Lee 1, J. Park 1, T.-H. Jang 1,
Assessment of Variation in Zero Field Hall Constant of Colossal Magnetoresistive Manganites (Re1-x AxMnO3)
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES OF THE MAGNETIC FLUCTUATIONS IN YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7¹d
 Pergamon PII: S0022-3697(98)00196-6 J. Phys. Chem Solids Vol 59, No. 10 12, pp. 2140 2144, 1998 0022-3697/98/$ - see front matter 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES
Pergamon PII: S0022-3697(98)00196-6 J. Phys. Chem Solids Vol 59, No. 10 12, pp. 2140 2144, 1998 0022-3697/98/$ - see front matter 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Anisotropic spin-correlations in the Zn-Mg-Ho icosahedral quasicrystal
 Anisotropic spin-correlations in the Zn-Mg-Ho icosahedral quasicrystal Taku J SATO 1, Hiroyuki TAKAKURA 1,, An Pang TSAI 1 and Kaoru SHIBATA 3 1 National Research Institute for Metals, Tsukuba 35-47, JAPAN
Anisotropic spin-correlations in the Zn-Mg-Ho icosahedral quasicrystal Taku J SATO 1, Hiroyuki TAKAKURA 1,, An Pang TSAI 1 and Kaoru SHIBATA 3 1 National Research Institute for Metals, Tsukuba 35-47, JAPAN
Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal
 Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal M. Matsukawa, 1, * A. Tamura, 1 S. Nimori, 2 R. Suryanarayanan, 3 T. Kumagai,
Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal M. Matsukawa, 1, * A. Tamura, 1 S. Nimori, 2 R. Suryanarayanan, 3 T. Kumagai,
Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Orbital ordering in the manganites: Resonant x-ray scattering predictions at the manganese L II and L III edges
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 2 1 JULY 2000-II Orbital ordering in the manganites: Resonant x-ray scattering predictions at the manganese L II and L III edges C. W. M. Castleton* European Synchrotron
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 2 1 JULY 2000-II Orbital ordering in the manganites: Resonant x-ray scattering predictions at the manganese L II and L III edges C. W. M. Castleton* European Synchrotron
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004](/thumbs/72/66676281.jpg) Coexisting charge modulation and ferromagnetism produces long period phases in manganites: new example of electronic soft matter. G.C. Milward, M.J. Calderón, P.B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/0407727v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Coexisting charge modulation and ferromagnetism produces long period phases in manganites: new example of electronic soft matter. G.C. Milward, M.J. Calderón, P.B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/0407727v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Phases of Na x CoO 2
 Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials
 Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
Neutron Scattering in Transition Metal Oxides
 Neutron Scattering in Transition Metal Oxides C. Ulrich Department Prof. B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung, Stuttgart, Germany physics of the 3d electrons strongly correlated electrons
Neutron Scattering in Transition Metal Oxides C. Ulrich Department Prof. B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung, Stuttgart, Germany physics of the 3d electrons strongly correlated electrons
YBCO. CuO 2. the CuO 2. planes is controlled. from deviation from. neutron. , blue star for. Hg12011 (this work) for T c = 72
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal structures and joint phase diagram of Hg1201 and YBCO. (a) Hg1201 features tetragonal symmetry and one CuO 2 plane per primitive cell. In the superconducting (SC) doping
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal structures and joint phase diagram of Hg1201 and YBCO. (a) Hg1201 features tetragonal symmetry and one CuO 2 plane per primitive cell. In the superconducting (SC) doping
Spin waves throughout the Brillouin zone and magnetic exchange coupling in the ferromagnetic metallic manganites La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x=0.25,0.
 Spin waves throughout the Brillouin zone and magnetic exchange coupling in the ferromagnetic metallic manganites La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x=0.25,0.30 F. Ye, 1, * Pengcheng Dai, 2,1 J. A. Fernandez-Baca, 1,2 D.
Spin waves throughout the Brillouin zone and magnetic exchange coupling in the ferromagnetic metallic manganites La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x=0.25,0.30 F. Ye, 1, * Pengcheng Dai, 2,1 J. A. Fernandez-Baca, 1,2 D.
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5 <= x <= 0.9) manganites
 Title Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5
Title Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5
I. Vrejoiu, E. Pippel, E. Nikulina, and D. Hesse Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics, D Halle, Germany. (Dated: October 18, 2018)
 Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
University of Groningen. Orbital ordering and multiferroics Nenert, Gwilherm
 University of Groningen Orbital ordering and multiferroics Nenert, Gwilherm IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Orbital ordering and multiferroics Nenert, Gwilherm IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Charge and orbital ordering in Fe and Mn perovskite oxides far from half- doping by resonant x- ray scattering
 Charge and orbital ordering in Fe and Mn perovskite oxides far from half- doping by resonant x- ray scattering J Herrero-Martín 1, J García 2, G Subías 2, J Blasco 2, C Mazzoli 1 and M C Sánchez 2 1 European
Charge and orbital ordering in Fe and Mn perovskite oxides far from half- doping by resonant x- ray scattering J Herrero-Martín 1, J García 2, G Subías 2, J Blasco 2, C Mazzoli 1 and M C Sánchez 2 1 European
Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x. O 3 perovskite material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Tuning order in cuprate superconductors
 Tuning order in cuprate superconductors arxiv:cond-mat/0201401 v1 23 Jan 2002 Subir Sachdev 1 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 2 1 Department of Physics, Yale University, P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120,
Tuning order in cuprate superconductors arxiv:cond-mat/0201401 v1 23 Jan 2002 Subir Sachdev 1 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 2 1 Department of Physics, Yale University, P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/114118020.jpg) Damping and softening of transverse acoustic phonons in colossal magnetoresistive La.7 Ca.3 MnO 3 and La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 Joel S. Helton 1,2,, Yang Zhao 2,3, Dmitry A. Shulyatev 4, and Jeffrey W. Lynn 2, 1
Damping and softening of transverse acoustic phonons in colossal magnetoresistive La.7 Ca.3 MnO 3 and La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 Joel S. Helton 1,2,, Yang Zhao 2,3, Dmitry A. Shulyatev 4, and Jeffrey W. Lynn 2, 1
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
doi: /PhysRevLett
 doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 2018](/thumbs/90/103904416.jpg) Room-temperature Low-field Colossal Magneto-resistance in Double-perovskite Manganite S. Yamada, N. Abe, H. Sagayama,, K. Ogawa, T. Yamagami, and T. Arima Department of Materials System Science, arxiv:8.07596v
Room-temperature Low-field Colossal Magneto-resistance in Double-perovskite Manganite S. Yamada, N. Abe, H. Sagayama,, K. Ogawa, T. Yamagami, and T. Arima Department of Materials System Science, arxiv:8.07596v
Metal-Insulator Transition in Mn Perovskite Compounds
 Metal-Insulator Transition in Mn Perovskite Compounds arxiv:cond-mat/9811221v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 16 Nov 1998 Yukitoshi Motome 1), Hiroki Nakano 2) and Masatoshi Imada 2), 1) Department of Physics, Tokyo
Metal-Insulator Transition in Mn Perovskite Compounds arxiv:cond-mat/9811221v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 16 Nov 1998 Yukitoshi Motome 1), Hiroki Nakano 2) and Masatoshi Imada 2), 1) Department of Physics, Tokyo
Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7
 The Open Condensed Matter Physics Journal, 2009, 2, 19-24 19 Open Access Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7 Aihua Wang 1,2, Tao Liu 3, Yang Liu 4, Guohui
The Open Condensed Matter Physics Journal, 2009, 2, 19-24 19 Open Access Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7 Aihua Wang 1,2, Tao Liu 3, Yang Liu 4, Guohui
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
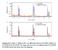 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Proceedings of the International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES3) Downloaded from journals.jps.jp by on /6/7 JPS
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES3) Downloaded from journals.jps.jp by 37.44.96.39 on /6/7 Proc. Int. Conf. Strongly Correlated Electron Systems
Proceedings of the International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES3) Downloaded from journals.jps.jp by 37.44.96.39 on /6/7 Proc. Int. Conf. Strongly Correlated Electron Systems
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/e151117/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Quantum Hall effect in a bulk antiferromagnet EuMni2 with magnetically confined two-dimensional Dirac fermions Hidetoshi
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/e151117/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Quantum Hall effect in a bulk antiferromagnet EuMni2 with magnetically confined two-dimensional Dirac fermions Hidetoshi
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase. Alok Banerjee
 Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION
 E. Dagotto et al. / Physics Reports 344 (2001) 1}153 1 COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio DAGOTTO a, Takashi HOTTA b, Adriana MOREO a National High Magnetic Field
E. Dagotto et al. / Physics Reports 344 (2001) 1}153 1 COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio DAGOTTO a, Takashi HOTTA b, Adriana MOREO a National High Magnetic Field
NEUTRON SCATTERING STUDY OF ANTIFERROMAGNETIC CORRELATIONS IN THE Zn-Mg-Ho ICOSAHEDRAL QUASICRYSTAL
 NEUTRON SCATTERING STUDY OF ANTIFERROMAGNETIC CORRELATIONS IN THE Zn-Mg-Ho ICOSAHEDRAL QUASICRYSTAL Taku J. SATO, Hiroyuki TAKAKURA,, An Pang TSAI, Kaoru SHIBATA, Kenji OHOYAMA and Ken H. ANDERSEN National
NEUTRON SCATTERING STUDY OF ANTIFERROMAGNETIC CORRELATIONS IN THE Zn-Mg-Ho ICOSAHEDRAL QUASICRYSTAL Taku J. SATO, Hiroyuki TAKAKURA,, An Pang TSAI, Kaoru SHIBATA, Kenji OHOYAMA and Ken H. ANDERSEN National
Artificially layered structures
 http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002](/thumbs/73/69440848.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0209089v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002 Double exchange and orbital correlations in electron doped manganites Tulika Maitra 1 and A. Taraphder 2 Department of Physics & Meteorology and Centre
arxiv:cond-mat/0209089v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002 Double exchange and orbital correlations in electron doped manganites Tulika Maitra 1 and A. Taraphder 2 Department of Physics & Meteorology and Centre
Strong interplay between stripe spin fluctuations, nematicity and superconductivity in FeSe
 Strong interplay between stripe spin fluctuations, nematicity and superconductivity in FeSe Qisi Wang 1, Yao Shen 1, Bingying Pan 1, Yiqing ao 1, Mingwei Ma 2, Fang Zhou 2, P. Steens 3,. Schmalzl 4, T.
Strong interplay between stripe spin fluctuations, nematicity and superconductivity in FeSe Qisi Wang 1, Yao Shen 1, Bingying Pan 1, Yiqing ao 1, Mingwei Ma 2, Fang Zhou 2, P. Steens 3,. Schmalzl 4, T.
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method
 Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7
 J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
Exchange interactions
 Exchange interactions Tomasz Dietl Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, PL-02-668Warszawa, Poland Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw, PL-00-681Warszawa, Poland 1. POTENTIAL
Exchange interactions Tomasz Dietl Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, PL-02-668Warszawa, Poland Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw, PL-00-681Warszawa, Poland 1. POTENTIAL
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. A, Schematic of a Au/SRO113/SRO214 junction. A 15-nm thick SRO113 layer was etched along with 30-nm thick SRO214 substrate layer. To isolate the top Au electrodes
Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. A, Schematic of a Au/SRO113/SRO214 junction. A 15-nm thick SRO113 layer was etched along with 30-nm thick SRO214 substrate layer. To isolate the top Au electrodes
COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION
 COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio Dagotto 1, Takashi Hotta 2, Adriana Moreo 1 1 National High Magnetic Field Lab and Department of Physics, Florida State University,
COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio Dagotto 1, Takashi Hotta 2, Adriana Moreo 1 1 National High Magnetic Field Lab and Department of Physics, Florida State University,
PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB
![PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB](/thumbs/84/91030401.jpg) Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) La (Sr Ca )MnO x x 3. *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu. a, a b
 International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) 1063 1072 Chemical pressure controlled colossal magnetoresistance effects in q La (Sr Ca )MnO R.S. Liu *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu a, a b a Department of
International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) 1063 1072 Chemical pressure controlled colossal magnetoresistance effects in q La (Sr Ca )MnO R.S. Liu *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu a, a b a Department of
arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2000
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2000 arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2000](/thumbs/75/71950529.jpg) Electronic Structure of La 2 x Sr x CuO 4 in the Vicinity of the Superconductor-Insulator Transition arxiv:cond-mat/99248v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2 A. Ino, C. Kim 2, M. Nakamura 3, T. Yoshida, T.
Electronic Structure of La 2 x Sr x CuO 4 in the Vicinity of the Superconductor-Insulator Transition arxiv:cond-mat/99248v3 [cond-mat.supr-con] 23 May 2 A. Ino, C. Kim 2, M. Nakamura 3, T. Yoshida, T.
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport. Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR)
 Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Island phases and charge order in two-dimensional manganites
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 024422 Island phases and charge order in two-dimensional manganites H. Aliaga, 1 B. Normand, 2 K. Hallberg, 1 M. Avignon, 3 and B. Alascio 1 1 Instituto Balseiro and Centro
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 024422 Island phases and charge order in two-dimensional manganites H. Aliaga, 1 B. Normand, 2 K. Hallberg, 1 M. Avignon, 3 and B. Alascio 1 1 Instituto Balseiro and Centro
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2004](/thumbs/92/110261985.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0412124v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2004 Transient differential reflectivity of ferromagnetic and paramagnetic phases in the bilayered manganite La 1.24 Sr 1.76 Mn 2 O 7 Y. Hirobe, Y. Kubo,
arxiv:cond-mat/0412124v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2004 Transient differential reflectivity of ferromagnetic and paramagnetic phases in the bilayered manganite La 1.24 Sr 1.76 Mn 2 O 7 Y. Hirobe, Y. Kubo,
Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6
 Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
BNL X-RAY INDUCED INSULATOR-METAL TRANSITIONS IN CMR MANGANITES
 BNL-65316 X-RAY INDUCED INSULATOR-METAL TRANSITIONS IN CMR MANGANITES V KIRYUKHIN1y*, D CASA', B KEIMERl, JP HILL2, A VIGLIANTE2, Y TOMIOKA3, Y TOKURh3y4 1) Dept of Physics, Princeton University, Princeton,
BNL-65316 X-RAY INDUCED INSULATOR-METAL TRANSITIONS IN CMR MANGANITES V KIRYUKHIN1y*, D CASA', B KEIMERl, JP HILL2, A VIGLIANTE2, Y TOMIOKA3, Y TOKURh3y4 1) Dept of Physics, Princeton University, Princeton,
Role of Incommensuration in the charge density wave and superconducting states of 1T-TiSe 2
 Role of Incommensuration in the charge density wave and superconducting states of 1T-TiSe 2 Astha Sethi May 10, 2017 Abstract A brief review of some of the most recent experiments on the charge density
Role of Incommensuration in the charge density wave and superconducting states of 1T-TiSe 2 Astha Sethi May 10, 2017 Abstract A brief review of some of the most recent experiments on the charge density
EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS: SUPER-EXCHANGE, DOUBLE EXCHANGE, RKKY; MAGNETIC ORDERS. Tomasz Dietl
 Analele Universităţii de Vest din Timişoara Vol. LIII, 2009 Seria Fizică EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS: SUPER-EXCHANGE, DOUBLE EXCHANGE, RKKY; MAGNETIC ORDERS Tomasz Dietl Institute of Physics, Polish Academy
Analele Universităţii de Vest din Timişoara Vol. LIII, 2009 Seria Fizică EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS: SUPER-EXCHANGE, DOUBLE EXCHANGE, RKKY; MAGNETIC ORDERS Tomasz Dietl Institute of Physics, Polish Academy
Ferroelectricity, Magnetism, and Multiferroicity. Kishan K. Sinha Xu Lab Department of Physics and astronomy University of Nebraska-Lincoln
 Ferroelectricity, Magnetism, and Multiferroicity Kishan K. Sinha Xu Lab Department of Physics and astronomy University of Nebraska-Lincoln Magnetism, Ferroelectricity, and Multiferroics Magnetism o Spontaneous
Ferroelectricity, Magnetism, and Multiferroicity Kishan K. Sinha Xu Lab Department of Physics and astronomy University of Nebraska-Lincoln Magnetism, Ferroelectricity, and Multiferroics Magnetism o Spontaneous
Osaka University, 2-1, Yamada-oka, Suita, Osaka , Japan. Naka-gun, Ibaraki , Japan
 Materials Science Forum Online: 2009-12-03 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vol. 635, pp 49-54 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.635.49 2010 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Structural Relation Between the X-Phase
Materials Science Forum Online: 2009-12-03 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vol. 635, pp 49-54 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.635.49 2010 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Structural Relation Between the X-Phase
CDW phase of TiSe 2. Young Il Joe. May 5, 2008
 CDW phase of TiSe 2 Young Il Joe May 5, 2008 Structural phase transsition and the soft phonon mode[1, 2] Disalvo and his collaborators[1] carried out a neutron scattering experiment on TiSe 2 and showed
CDW phase of TiSe 2 Young Il Joe May 5, 2008 Structural phase transsition and the soft phonon mode[1, 2] Disalvo and his collaborators[1] carried out a neutron scattering experiment on TiSe 2 and showed
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in. manganite multilayers
 Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Electronic Higher Multipoles in Solids
 Electronic Higher Multipoles in Solids Yoshio Kuramoto Department of Physics, Tohoku University Outline Elementary examples of multiple moments Role of multipole moments in solids Case studies octupole
Electronic Higher Multipoles in Solids Yoshio Kuramoto Department of Physics, Tohoku University Outline Elementary examples of multiple moments Role of multipole moments in solids Case studies octupole
Good Vibrations Studying phonons with momentum resolved spectroscopy. D.J. Voneshen 20/6/2018
 Good Vibrations Studying phonons with momentum resolved spectroscopy D.J. Voneshen 20/6/2018 Overview What probe to use? Types of instruments. Single crystals example Powder example Thing I didn t talk
Good Vibrations Studying phonons with momentum resolved spectroscopy D.J. Voneshen 20/6/2018 Overview What probe to use? Types of instruments. Single crystals example Powder example Thing I didn t talk
University of Bristol. 1 Naval Research Laboratory 2 II. Physikalisches Institut, Universität zu Köln
 Charge ordering as alternative to Jahn-Teller distortion In collaboration with Michelle Johannes 1, Daniel Khomskii 2 (theory) and Mohsen Abd-Elmeguid et al 2, Radu Coldea et al 3 (experiment) 1 Naval
Charge ordering as alternative to Jahn-Teller distortion In collaboration with Michelle Johannes 1, Daniel Khomskii 2 (theory) and Mohsen Abd-Elmeguid et al 2, Radu Coldea et al 3 (experiment) 1 Naval
Charge-order driven multiferroic and magneto-dielectric properties of rare earth manganates
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 33, No. 2, April 2010, pp. 169 178. Indian Academy of Sciences. Charge-order driven multiferroic and magneto-dielectric properties of rare earth manganates CLAUDY RAYAN SERRAO 1,2,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 33, No. 2, April 2010, pp. 169 178. Indian Academy of Sciences. Charge-order driven multiferroic and magneto-dielectric properties of rare earth manganates CLAUDY RAYAN SERRAO 1,2,
ON THE DOUBLE-EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS IN La 1 _xba x Mn03
 R 712 Philips Res. Repts 25,8-16,1970 ON THE DOUBLE-EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS IN La 1 _xba x Mn03 Abstract 1. Introduetion by F. K. LOTGERING Magnetic and electrical measurements on Lal_",Ba",Mn03 and Lal_",Ba",Mnl_",Ti",03
R 712 Philips Res. Repts 25,8-16,1970 ON THE DOUBLE-EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS IN La 1 _xba x Mn03 Abstract 1. Introduetion by F. K. LOTGERING Magnetic and electrical measurements on Lal_",Ba",Mn03 and Lal_",Ba",Mnl_",Ti",03
Orbital Engineering of Pulsed Laser Deposited Single-layered Manganite Thin Films
 Orbital Engineering of Pulsed Laser Deposited Single-layered Manganite Thin Films Fachbereich Material- und Geowissenschaften genehmigte Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades eines Doktors
Orbital Engineering of Pulsed Laser Deposited Single-layered Manganite Thin Films Fachbereich Material- und Geowissenschaften genehmigte Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades eines Doktors
CHARGE ORDERING AND PHASE COMPETITION IN THE LAYERED PEROVSKITE LaSr 2 Mn 2 O 7
 CHARGE ORDERING AND PHASE COMPETITION IN THE LAYERED PEROVSKITE LaSr Mn O 7 D. N Argyriou 1, H. N. Bordallo 1, B. J. Campbell, A. K. Cheetham. D. E. Cox 3, J. S. Gardner 4, K. Hanif 5, A. dos Santos, G.
CHARGE ORDERING AND PHASE COMPETITION IN THE LAYERED PEROVSKITE LaSr Mn O 7 D. N Argyriou 1, H. N. Bordallo 1, B. J. Campbell, A. K. Cheetham. D. E. Cox 3, J. S. Gardner 4, K. Hanif 5, A. dos Santos, G.
Origin of the anomalous low temperature upturn in resistivity in the electron-doped cuprates.
 Origin of the anomalous low temperature upturn in resistivity in the electron-doped cuprates. Y. Dagan 1, A. Biswas 2, M. C. Barr 1, W. M. Fisher 1, and R. L. Greene 1. 1 Center for Superconductivity Research,
Origin of the anomalous low temperature upturn in resistivity in the electron-doped cuprates. Y. Dagan 1, A. Biswas 2, M. C. Barr 1, W. M. Fisher 1, and R. L. Greene 1. 1 Center for Superconductivity Research,
Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors:
 Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite
Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite
Magnetic neutron diffraction. Rob McQueeney, Ames Laboratory and Iowa State University
 Magnetic neutron diffraction Rob McQueeney, Ames Laboratory and Iowa State University September 19, 2018 Magnetic moment-rare earths Progressive filling of 4f levels Strong Hund s rules Strong spin-orbit
Magnetic neutron diffraction Rob McQueeney, Ames Laboratory and Iowa State University September 19, 2018 Magnetic moment-rare earths Progressive filling of 4f levels Strong Hund s rules Strong spin-orbit
Lattice effects in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x 0 1 : Relationships between distortions, charge distribution, and magnetism
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 57, NUMBER 17 1 MAY 1998-I Lattice effects in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x 0 1 : Relationships between distortions, charge distribution, and magnetism C. H. Booth* Department of Physics
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 57, NUMBER 17 1 MAY 1998-I Lattice effects in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x 0 1 : Relationships between distortions, charge distribution, and magnetism C. H. Booth* Department of Physics
Incommensurate Magnetic Order in PrNiAl 4
 Incommensurate Magnetic Order in PrNiAl 4 R. White a, W.D. Hutchison a, M. Avdeev b and K. Nishimura c a School of Physical, Environmental and Mathematical Sciences, The University of New South Wales,
Incommensurate Magnetic Order in PrNiAl 4 R. White a, W.D. Hutchison a, M. Avdeev b and K. Nishimura c a School of Physical, Environmental and Mathematical Sciences, The University of New South Wales,
Anisotropic Magnetic Structures in Iron-Based Superconductors
 Anisotropic Magnetic Structures in Iron-Based Superconductors Chi-Cheng Lee, Weiguo Yin & Wei Ku CM-Theory, CMPMSD, Brookhaven National Lab Department of Physics, SUNY Stony Brook Another example of SC
Anisotropic Magnetic Structures in Iron-Based Superconductors Chi-Cheng Lee, Weiguo Yin & Wei Ku CM-Theory, CMPMSD, Brookhaven National Lab Department of Physics, SUNY Stony Brook Another example of SC
Geometrical frustration, phase transitions and dynamical order
 Geometrical frustration, phase transitions and dynamical order The Tb 2 M 2 O 7 compounds (M = Ti, Sn) Yann Chapuis PhD supervisor: Alain Yaouanc September 2009 ann Chapuis (CEA/Grenoble - Inac/SPSMS)
Geometrical frustration, phase transitions and dynamical order The Tb 2 M 2 O 7 compounds (M = Ti, Sn) Yann Chapuis PhD supervisor: Alain Yaouanc September 2009 ann Chapuis (CEA/Grenoble - Inac/SPSMS)
* Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory, University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford, OX1
 BNL- 6 3833 1 f Crystal chemistry and electronic properties of the n = 2 Ruddlesden-Popper manganates: o f - 6 7 1 0 d r n unconventional C M R materials PD BATTLE* SJ BLUNDELL** DE COX*** MA GREEN* JE
BNL- 6 3833 1 f Crystal chemistry and electronic properties of the n = 2 Ruddlesden-Popper manganates: o f - 6 7 1 0 d r n unconventional C M R materials PD BATTLE* SJ BLUNDELL** DE COX*** MA GREEN* JE
Room temperature charge and orbital ordering and phase coexistence in Bi 0.5 Sr 0.5 MnO 3
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13 (2001) 1071 1078 www.iop.org/journals/cm PII: S0953-8984(01)19607-4 Room temperature charge and orbital
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13 (2001) 1071 1078 www.iop.org/journals/cm PII: S0953-8984(01)19607-4 Room temperature charge and orbital
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 18 May 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 18 May 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 18 May 2005](/thumbs/90/103872584.jpg) Extracting d-orbital occupancy from magnetic Compton scattering in bilayer manganites arxiv:cond-mat/55435v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 18 May 25 B. Barbiellini 1, P. E. Mijnarends 1,2, S. Kaprzyk 1,3, A. Bansil
Extracting d-orbital occupancy from magnetic Compton scattering in bilayer manganites arxiv:cond-mat/55435v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 18 May 25 B. Barbiellini 1, P. E. Mijnarends 1,2, S. Kaprzyk 1,3, A. Bansil
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 A11046W1 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2015 Wednesday, 17 June, 2.30
A11046W1 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2015 Wednesday, 17 June, 2.30
Institute of Physics ASCR, Na Slovance 2, Prague, Czech Republic
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 802 2004 Materials Research Society DD6.10.1 Pressure Dependence of Magnetic States of UGe 2 Alexander B. Shick 1, Václav Janiš 1, Václav Drchal 1 and Warren E. Pickett
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 802 2004 Materials Research Society DD6.10.1 Pressure Dependence of Magnetic States of UGe 2 Alexander B. Shick 1, Václav Janiš 1, Václav Drchal 1 and Warren E. Pickett
Neutron Powder Diffraction Theory and Instrumentation
 NTC, Taiwen Aug. 31, 212 Neutron Powder Diffraction Theory and Instrumentation Qingzhen Huang (qing.huang@nist.gov) NIST Center for Neutron Research (www.ncnr.nist.gov) Definitions E: energy; k: wave vector;
NTC, Taiwen Aug. 31, 212 Neutron Powder Diffraction Theory and Instrumentation Qingzhen Huang (qing.huang@nist.gov) NIST Center for Neutron Research (www.ncnr.nist.gov) Definitions E: energy; k: wave vector;
Two-Staged Magnetoresistance Driven by Ising-like
 1 Two-Staged Magnetoresistance Driven by Ising-like Spin Sublattice in SrCo 6 O 11 S. Ishiwata 1,2*, I. Terasaki 2, F. Ishii 3, N. Nagaosa 3,4, H. Mukuda 5, Y. Kitaoka 5, T. Saito 1, and M. Takano 1 1
1 Two-Staged Magnetoresistance Driven by Ising-like Spin Sublattice in SrCo 6 O 11 S. Ishiwata 1,2*, I. Terasaki 2, F. Ishii 3, N. Nagaosa 3,4, H. Mukuda 5, Y. Kitaoka 5, T. Saito 1, and M. Takano 1 1
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2. Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1. Germany.
 Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
T. Hatakeda, T. Noji, S. Hosono, T. Kawamata, M. Kato, and Y. Koike
 Resistive superconducting transition and effects of atmospheric exposure in the intercalation superconductor A x (A = Li, Na) T. Hatakeda, T. Noji, S. Hosono, T. Kawamata, M. Kato, and Y. Koike Department
Resistive superconducting transition and effects of atmospheric exposure in the intercalation superconductor A x (A = Li, Na) T. Hatakeda, T. Noji, S. Hosono, T. Kawamata, M. Kato, and Y. Koike Department
X-ray spectroscopy and diffraction experiments by using mini-coils: applications to valence state transitions and frustrated magnets
 X-ray spectroscopy and diffraction experiments by using mini-coils: applications to valence state transitions and frustrated magnets H. Nojiri, IMR Tohoku Univ., Sendai Japan http:spin100.imr.tohoku.ac.jp
X-ray spectroscopy and diffraction experiments by using mini-coils: applications to valence state transitions and frustrated magnets H. Nojiri, IMR Tohoku Univ., Sendai Japan http:spin100.imr.tohoku.ac.jp
Effect of randomness on anomalous Hall coefficient in antiferromagnet U 2 PdGa 3
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 26, No. 4, 2008 Effect of randomness on anomalous Hall coefficient in antiferromagnet U 2 PdGa 3 V. H. TRAN * Institute of Low Temperature and Structure Research, Polish
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 26, No. 4, 2008 Effect of randomness on anomalous Hall coefficient in antiferromagnet U 2 PdGa 3 V. H. TRAN * Institute of Low Temperature and Structure Research, Polish
Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies.
 PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
