Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5 <= x <= 0.9) manganites
|
|
|
- Horace Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5 <= x <= 0.9) manganites Author(s) Li, XG; Zheng, RK; Li, G; Zhou, HD; Huang, RX; Xie, JQ; Wang, Z Citation Europhysics Letters, 00, v. 60 n. 5, p Issued Date 00 URL Rights This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivatives.0 International License.; Europhysics Letters. Copyright E D P Sciences.; The original publication is available at
2 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 December 00 Europhys. Lett., 60 (5), pp (00) Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.9) manganites X. G. Li 1 ( ),R.K.Zheng 1,G.Li 1,H.D.Zhou 1, R. X. Huang 1, J. Q. Xie and Z. D. Wang 1,3 1 Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Science and Technology of China -Hefei, Anhui, 3006, PRC Laboratory of Internal Friction and Defects in Solids, University of Science and Technology of China -Hefei, Anhui, 3006, PRC 3 Department of Physics, University of Hong Kong -Hong Kong, PRC (received May 00; accepted in final form 1 September 00) PACS d Ultrasonics, quantum acoustics, and physical effects of sound. PACS Kb Solid-solid transitions. PACS k Polarons and electron-phonon interactions. Abstract. The longitudinal ultrasonic sound velocity and attenuation, the resistivity, and lattice parameters were studied as a function of temperature from 30 K to 300 K in La 1 x Ca xmno 3 (0.5 x 0.9). For all the samples, a dramatic stiffening of the sound velocity belowthe charge ordering transition temperature was directly driven by distinct changes of the lattice parameters due to the formation of long-range ordering of Jahn-Teller distorted MnO 6 octahedra. The relative change of the sound velocity ( /)below depends on the Ca concentration x and reaches the maximum at x = 0.75, implying that the effective strength of the electron-lattice interaction with the Jahn-Teller distortion is the strongest at x =0.75 and hence the charge-ordered state is mostly stabilized near x =0.75 and insensitive to the application of a magnetic field, which is supported by the charge transport properties under high magnetic fields up to 1 T. Recently, the real-space charge ordering (CO) in perovskite-based manganites R 1 x D x MnO 3 (R and D are trivalent rare-earth and divalent alkaline-earth ions, respectively) has been studied extensively [1 ]. The La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 compound is a well-known system showing both metal-insulator transition and CO phenomenon at different doping levels [5]. For instance, the compound is ferromagnetic metal-like at low temperature for 0. x 0.5, while it shows a charge ordering transition and becomes a charge-ordered insulator at low temperature for 0.5 x [5]. Above the charge ordering transition temperature, Mn 3+ and Mn + ions are randomly distributed within the MnO plane in the lattice. With decreasing temperature the thermally activated charge carriers are gradually localized, and finally become ordered throughout the crystal structure (i.e. charge ordering) in the presence of a sufficiently strong long-range Coulomb interaction and/or an appropriate electron-lattice interaction with the Jahn-Teller distortion [6 10]. Neutron diffraction measurements [,11] on ( ) lixg@ustc.edu.cn c EDP Sciences
3 X. G. Li et al.: Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered etc. 671 the charge-ordered La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 (x =1/, /3) revealed that the distinct changes of the lattice parameters near are closely related to the development of a strong Jahn-Teller type lattice distortion, implying that the Jahn-Teller effect plays an important role in the lattice instabilities and the CO state. On the other hand, the CO state can be dramatically suppressed or even melted by application of external magnetic fields via enhanced doubleexchange (DE) interaction [1, 13], which pinpoints that the stability of the CO state is also related to the effective strength of the DE interaction. Besides, a lot of experimental data have shown that the stability of the CO state is sensitive to the commensurability of the doping concentration [1, 1]. These features indicate that the stability of the CO state depends on the interactions and competitions among the spin, charge, and lattice degree of freedoms. The ultrasonic responses to the formation of the CO state in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 system have been theoretically and experimentally studied by several groups. Based on the Hamiltonian of small polarons with strong nearest-neighbor repulsion and the electron-lattice interaction, it was theoretically found that a dramatic renormalization of the sound velocity around arises from the strong coupling of the acoustic phonons to the CO state for the half-doped R 0.5 D 0.5 MnO 3 systems [15]. On the other hand, it was observed experimentally that the formation of the CO state in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 system is accompanied by a dramatic stiffening in the sound velocity below [, 16, 17], which was attributed to a strong electron-lattice interaction. Despite these ultrasonic studies on the CO state, a systematic ultrasonic study and a comprehensive understanding on the stability of the CO state and its relationship to the electron-lattice interaction with Jahn-Teller distortion, the external magnetic field, and the concentration of the Mn 3+ ions is still incomplete. In this letter, we present a systematic study of the ultrasonic sound velocity and attenuation, the lattice parameters, and the resistivity as functions of temperature and Ca concentration x in order to get more insight into the CO state and the electron-lattice interaction with Jahn-Teller distortion. The polycrystalline La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 (x =0.5, 0.55, 0.6, 0.65, 0.7, 0.75, 0.8, 0.83, 0.85, 0.87, 0.9) samples were prepared by a coprecipitation method using ammonium carbonate. The lattice parameters of the La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 samples were determined by a Japan MXP18AHF powder X-ray diffractometer (MAC Science Co. Ltd.) using Cu K α radiation (λ = Å) from 30 K to 300 K. The resistivity ρ(t ) was measured by a standard four-probe technique from 30 K to 300 K under external magnetic fields up to 1 T. The ultrasonic sound velocity and attenuation were measured on the Matec-7700 series equipment (Matec Instrument Companies, USA) using a pulse-echo-overlap technique [18]. The relative change of the sound velocity / in fig. 3 below was defined according to the following equation: / =( max min )/ min =( max TCO )/ TCO, where max and min (= TCO ) are the maximal and minimum sound velocity in the temperature range from 5 K to 300 K, respectively. In fig. 1 we show the temperature dependencies of the lattice parameters from 30 K to 300 K for the selected La 1 x Ca x MnO 3. Near the charge ordering transition temperature of the system [,11], the distinct changes of lattice parameters of the a-axis, b-axis and c-axis can be observed. We note that the ratios of the orthorhombic lattice (b/ )/a are smaller than 1for0.5 x 0.75, while those for x>0.75 are larger than 1, suggesting a compression (or elongation) of the b-axis and an elongation (or compression) of the a and c axes. The difference in the orthorhombic lattice for x 0.75 and x>0.75 suggests that there exist different types of orbital orderings due to different types of Jahn-Teller distortions for 0.5 x 0.75 and x>0.75. In fact, the orbital ordering below for the half-doped La 0.5 Ca 0.5 MnO 3 is of (3x r )/(3y r ) type, while that for La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 (x>0.75) is of (3z r )
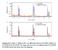
4 67 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Lattice Parameters (Å) 5. a c b/ 5.35 b/ x =0.55 c x =0.75 a b/ x=0.85 a c x =0.7 b/ c c 5.8 a a T (K) T (K) Fig. 1 Temperature dependence of the lattice parameters for La 1 xca xmno 3 (x =0.55,0.7,0.75, 0.8, 0.85, 0.87). The solid lines are guides to the eyes. b/ a c b/ x =0.8 x= type [19]. The former obviously originates from the Q -mode Jahn-Teller distortion, and the latter is due tothe Q 3 -mode [0]. These crossovers of different types of orbital orderings as well as crystal structures from tetragonal compressed orthorhombic one to tetragonal elongated orthorhombic one between 0.5 x 0.75 and x>0.75 are related tothe change of Jahn-Teller vibration modes from Q to Q 3. We note here that these distinct changes of the lattice parameters were shown tobe related tothe effect of cooperative static Jahn-Teller distortion near [, 11]. It is therefore expected that there are dramatic anomalies of a particular phonon mode near [1]. Figure plots the temperature dependence of the longitudinal ultrasonic sound velocity ( ) and attenuation (α) at zeromagnetic field for the selected La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 samples. With decreasing temperature from room temperature to the sound velocities soften conspicuously and then stiffen dramatically below. These substantial sound velocity softening and stiffening accompanied by an attenuation peak around indicate the dramatic instabilities of a particular phonon mode related to the CO transition in these charge-ordered La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 manganites. Since many theoretical and experimental results including our previous ultrasonic measurement on the CaMnO 3 showed that a typical / caused by antiferromagnetic (AFM) spin fluctuations near an AFM phase transition is merely of the order 0.1% [16,, 3], it is undoubtful that the large stiffening of the sound velocity (for example, / =7%atx =0.5 and 9% at x =0.75, see fig. 3) in the present charge-ordered system below is closely related to the formation of the CO state in the presence of the strong electron-lattice interaction with the static Jahn-Taller distortion. Figure 3 shows the relative change of the sound velocity / as a function of the Ca concentration x below. One can find that /, which directly reflects the contribution of the formation of the CO state to the stiffening of the sound velocity, is strongly x-dependent. With increasing Ca concentration from x = 0.5 to x = 0.75, / increases monotonously, suggesting an increasing effect of electron-lattice interaction with the Jahn-Teller distortion. When the Ca concentration increases further from x = 0.75, / decreases slightly at
5 X. G. Li et al.: Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered etc. 673 (km/s) α x = α x = α (db/cm) (km/s) (km/s) x =0.7 x = α 3 5. α x =0.8 x = α.5 α T(K) T(K) α (db/cm) α (db/cm) Fig. Temperature dependence of the longitudinal ultrasonic sound velocities and attenuations for La 1 xca xmno 3 (x =0.55, 0.65,0.7, 0.75, 0.8, 0.87). x<0.83, and then drops rapidly to a low value at x =0.9. From the /-x relationship (fig. 3), one may conclude that the effective strength of electron-lattice interaction with the static Jahn-Teller distortion is the strongest near x = Recently, Yunoki et al. [] demonstrated theoretically that a charge-ordered state can easily be stabilized for half-doped (x = 0.5) manganites in the presence of a relatively strong electron-lattice interaction with Jahn-Teller distortion. Therefore, despite the fact that the CO states can be of bi-stripe type or Wigner-crystal type [5], their stability is expected to be the most robust near x =0.75 because of the largest effective strength of the electron-lattice interaction with the Jahn-Teller distortion near x =0.75, as determined from the magnitude of / in fig. 3. Moreover, this robustness can also be seen from figs. and 5 to be addressed below. 30 /= ( max - TCO )/ TCO 5 / % Ca concentration x Fig. 3 The relative change of longitudinal sound velocity / vs. Ca concentration x in the CO state.
6 67 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS La 1-x Ca x Mn O 10 0 T 3 (a) T x=0.5 6 T T 10 T T 1 T T 1 T T (b) 10 x=0.55 T 6 T T 10 T T 1 T T 1 T x=0.6( 10) x=0.65 x=0.7 x=0.75 (d) 10 1 x=0.9 + x=0.8 x=0.87 x=0.83 (c) T(K) Fig. ariations of resistivity with temperature under different external magnetic fields up to 1 T for La 1 xca xmno 3 (x =0.5, 0.55, 0.6, 0.65, 0.7, 0.75, 0.8, 0.83, 0.87, 0.9). Figure shows the temperature dependence of the resistivity ρ(t ) under magnetic fields up to1 T for La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 (x = 0.5, 0.55, 0.6, 0.65, 0.7, 0.75, 0.8, 0.83, 0.87, 0.9). With decreasing temperature the zero-field ρ(t ) curve at x = 0.5 shows a semiconductorlike behavior, but with a discernible change in the slope near signaling the onset of the formation of the CO state [11, 5]. When the magnetic field H increases from 0 T to 6 T, the resistivity reduces slightly, but for 6 T <H 11 T the resistivity decreases dramatically 100 = ()- (H) (K) x =0.5 x =0.55 x =0.75 x =0.8 x =0.83 x = H (T) Fig. 5 Magnetic-field dependence of for La 1 xca xmno 3 (x =0.5, 0.55, 0.75, 0.8, 0.83, 0.87).
7 X. G. Li et al.: Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered etc. 675 although it still remains semiconductor-like. For H > 1 T, a distinct change of ρ(t ) induced by the magnetic field appears, and a metal-insulator transition occurs around 150 K, which can be viewed as a sign of the collapse of the CO state. Furthermore, the, determined from the peak temperature of the d ln ρ/dt 1 -T curve [] (see fig. 5), shifts dramatically toa lower temperature as the magnetic field increases. The field-dependent resistivity behaviors at x = 0.5 (fig. (a)), together with the electronic phase separation (i.e., the coexistence of metallic ferromagnetic (FM) phase and the insulating CO phase) reported earlier in darkfield image and X-ray diffraction experiments by Radaelli et al. [11] and Mori et al. [6], unambiguously demonstrate that there is a particular strong competition between the electronlattice interaction and the DE interaction. All these results may be understood based on this competition picture. As is well known, the strong electron-lattice interaction favors the localization of charge carriers, while the DE-induced ferromagnetism demands the active hopping of charge carriers. Therefore, it is the competition between these two interactions (i.e. the electron-lattice and the DE) that is mainly responsible for the charge transport properties and the stability of the CO state. An external magnetic field tends to align electron spins along its direction and thus results in the increase of the effective strength of DE interaction, which in turn enhances the FM coupling between neighboring Mn spins as well as the mobility of charge carriers, increasing the total size of the FM domains and reducing that of the insulating CO domains. Above a percolation threshold the metallic FM domains are connected in the whole sample, leading to a dramatic reduction of the resistivity. Similar to that observed at x = 0.5, ρ(t )and at x =0.55 were alsosignificantly suppressed by the external magnetic field (see figs. (b) and 5). Nevertheless, we noticed that the magnetic-field effect on the resistivity and the CO state becomes less effective as x increases from 0.5 to 0.55 because of a stronger effective electron-lattice interaction at x =0.55 which has a larger / than that at x =0.5. In contrast with those observed for x =0.5and 0.55, ρ(t )and at x =0.75 are independent of external magnetic fields up to 1 T, as shown in figs. (c) and 5. The field-independent ρ(t ) behavior is consistent with the fact that the effective electron-lattice interaction with the Jahn-Teller distortion is very strong at (or near) x = 0.75, and indicates the robustness of the ordered state of the Jahn-Teller distortion at (or near) this x. As for the samples (x =0.65, 0.7, 0.8 and 0.83) with large / below (see fig. 3), ρ(t )and are alsoalmost field independent as the CO states may be considered as mixtures of some very stable CO states (like x = /3 and 3/ etc.) via a phase separation scenario [1, 5]. Nevertheless, with further increasing Ca concentration (x > 0.83) ρ(t ) becomes weakly field dependent. This weak field dependence of ρ(t ) may be related to the emergence of weak ferromagnetism [7] and the decrease of the effective electron-lattice interaction with the Jahn-Teller distortion for x>0.83. In summary, the above ultrasonic, resistivity and crystal structure changes in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.9) demonstrate that the stability of the CO state is closely related to the effective strength of the electron-lattice interaction with the Jahn-Teller distortion, which are consistent with the theoretical results in refs. [5, 19,, 8]. It was found that in the CO state the effective strength of the electron-lattice interaction with the Jahn-Teller distortion is rather strong, particularly near Ca concentration x = 0.75, where the CO state is mostly stabilized and insensitive to external magnetic fields. This work was supported by the Chinese National Nature Science Fund, the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, and a CRCG grant at the University of Hong Kong.
8 676 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS REFERENCES [1] Mori S., Chen C. H. and Cheong S.-W., Nature, 39 (1998) 73. [] Ramirez A. P., Schiffer P., Cheong S.-W., Chen C. H., Bao W., Palstra T. T. M., Gammel P. L., Bishop D. J. and Zegarski B., Phys. Rev. Lett., 76 (1996) [3] Wagner P., Gordon I., Mangin S., Moshchalkov.., Bruynseraede Y., Pinsard L. and Revcolevschi A., Phys. Rev. B, 61 (000) 59. [] Fernández-Díaz M. T., Martínez J. L., Alonso J. M. and Herrero E., Phys. Rev. B, 59 (1999) 177. [5] Dagotto E., Hotta T. and Moreo A., Phys. Rep., 3 (001) 1. [6] Mishra S. K., Pandit R. and Satpathy S., Phys. Rev. B, 56 (1997) 316. [7] Mutou T. and Kontani H., Phys. Rev. Lett., 83 (1999) [8] Li J. Q., Uehara M., Tsuruta C., Matsui Y. and Zhao Z. X., Phys. Rev. Lett., 8 (1999) 386. [9] Yamada Y., Suzuki J., Oikawa K., Katano S. and Fernandez-Baca J. A., Pyhs. Rev. B, 6 (000) [10] Mukhin A. A., Ivanov. Y., Travkin. D., Lebedev S. P., Pimenov A., Loidl A. and Balbashov A. M., JETP Lett., 68 (1998) 356. [11] Radaelli P. G., Cox D. E., Marezio M. and Cheong S.-W., Phys. Rev. B, 55 (1997) [1] Tomioka Y., Asamitsu A., Moritomo Y., Kuwahara H. and Tokura Y., Phys. Rev. Lett., 7 (1995) [13] Tomioka Y., Asamitsu A., Kuwahara H., Moritomo Y. and Tokura Y., Phys. Rev. Lett., 53 (1996) R1689. [1] Tomioka Y. and Tokura Y., in Colossal Magnetoresistive Oxides, editedbytokura Y. (Gordon and Breach Science Publishers) 000, pp [15] Lee J. D. and Min B. I., Phys. Rev. B, 55 (1996) R1713. [16] Zheng R. K., Zhu C. F., Xie J. Q. and Li X. G., Phys. Rev. B, 63 (001) 07. [17] Fujishiro H., Fukase T. and Ikebe M., J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 70 (001) 68. [18] Papadakis E. P., Physical Acoustics, editedbymason W. P. and Thurston R. N., ol. 1 (Academic Press, NewYork) 1976, p [19] Hotta T., Malvezzi A. L. and Dagotto E., Phys. Rev. B, 6 (000) 93. [0] Sawada H., Moritkawa Y., Terakura K. and Hamada N., Phys. Rev. B, 56 (1997) 115. [1] Ibarra M. I., Teresa J. M. De., Blasco J., Algarabel P. A., Marquina C., García J., Stankiewicz J. and Ritter C., Phys. Rev. B, 56 (1997) 85. [] Leisure R. G. and Moss R. W., Phys. Rev., 188 (1969) 80. [3] Golding B., Phys. Rev. Lett., 0 (1968) 5. [] Yunoki S., Hotta T. and Dagotto E., Phys. Rev. Lett., 8 (000) 371. [5] Murakami Y., Shindo D., Chiba H., Kikuchi M. and Syono, J. Solid State Chem., 10 (1997) 331. [6] Mori S., Chen C. H. and Cheong S.-W., Phys. Rev. Lett., 81 (1998) 397. [7] Fujishiro H., Ikebe M., Ohshiden S. and Noto K., J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 69 (000) [8] Hotta T., Takada Y., Koizumi H. and Dagotto E., Phys. Rev. Lett., 8 (000) 77.
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered
 Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal
 Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal M. Matsukawa, 1, * A. Tamura, 1 S. Nimori, 2 R. Suryanarayanan, 3 T. Kumagai,
Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal M. Matsukawa, 1, * A. Tamura, 1 S. Nimori, 2 R. Suryanarayanan, 3 T. Kumagai,
Assessment of Variation in Zero Field Hall Constant of Colossal Magnetoresistive Manganites (Re1-x AxMnO3)
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998](/thumbs/78/78285667.jpg) Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Room temperature charge and orbital ordering and phase coexistence in Bi 0.5 Sr 0.5 MnO 3
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13 (2001) 1071 1078 www.iop.org/journals/cm PII: S0953-8984(01)19607-4 Room temperature charge and orbital
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13 (2001) 1071 1078 www.iop.org/journals/cm PII: S0953-8984(01)19607-4 Room temperature charge and orbital
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
Australian Journal of Physics
 CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/114118020.jpg) Damping and softening of transverse acoustic phonons in colossal magnetoresistive La.7 Ca.3 MnO 3 and La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 Joel S. Helton 1,2,, Yang Zhao 2,3, Dmitry A. Shulyatev 4, and Jeffrey W. Lynn 2, 1
Damping and softening of transverse acoustic phonons in colossal magnetoresistive La.7 Ca.3 MnO 3 and La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 Joel S. Helton 1,2,, Yang Zhao 2,3, Dmitry A. Shulyatev 4, and Jeffrey W. Lynn 2, 1
Material Science II. d Electron systems
 Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
MnO. Sr x. La 1-x. Temperature (K) Paramagnetic. Metal T C. Paramagnetic Insulator. Ferromagnetic. Metal T N. Ferromagnetic. Spin-canted Insulator
 Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Complexity in Transition Metal Oxides
 Complexity in Transition Metal Oxides Adriana Moreo Dept. of Physics and ORNL University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA. Supported by NSF grants DMR-0443144 and 0454504. Collaborators G. Alvarez (ORNL)
Complexity in Transition Metal Oxides Adriana Moreo Dept. of Physics and ORNL University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA. Supported by NSF grants DMR-0443144 and 0454504. Collaborators G. Alvarez (ORNL)
Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x. O 3 perovskite material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Magnon-phonon effects in ferromagnetic manganites
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 65, 04409 Magnon-phonon effects in ferromagnetic manganites L. M. Woods* Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Tennessee 37996 and Oak Ridge
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 65, 04409 Magnon-phonon effects in ferromagnetic manganites L. M. Woods* Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Tennessee 37996 and Oak Ridge
Island phases and charge order in two-dimensional manganites
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 024422 Island phases and charge order in two-dimensional manganites H. Aliaga, 1 B. Normand, 2 K. Hallberg, 1 M. Avignon, 3 and B. Alascio 1 1 Instituto Balseiro and Centro
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 024422 Island phases and charge order in two-dimensional manganites H. Aliaga, 1 B. Normand, 2 K. Hallberg, 1 M. Avignon, 3 and B. Alascio 1 1 Instituto Balseiro and Centro
BNL X-RAY INDUCED INSULATOR-METAL TRANSITIONS IN CMR MANGANITES
 BNL-65316 X-RAY INDUCED INSULATOR-METAL TRANSITIONS IN CMR MANGANITES V KIRYUKHIN1y*, D CASA', B KEIMERl, JP HILL2, A VIGLIANTE2, Y TOMIOKA3, Y TOKURh3y4 1) Dept of Physics, Princeton University, Princeton,
BNL-65316 X-RAY INDUCED INSULATOR-METAL TRANSITIONS IN CMR MANGANITES V KIRYUKHIN1y*, D CASA', B KEIMERl, JP HILL2, A VIGLIANTE2, Y TOMIOKA3, Y TOKURh3y4 1) Dept of Physics, Princeton University, Princeton,
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based
 Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
University of Groningen. Orbital ordering and multiferroics Nenert, Gwilherm
 University of Groningen Orbital ordering and multiferroics Nenert, Gwilherm IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Orbital ordering and multiferroics Nenert, Gwilherm IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
No. 3 An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in MFM results, it is suggested that the PS in LSMO is not a charge seg
 Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 68,
 Electronic structure of La 1Àx Ca x MnO 3 determined by spin-polarized x-ray absorption spectroscopy: Comparison of experiments with band-structure computations Q. Qian, 1 T. A. Tyson, 1 S. Savrassov,
Electronic structure of La 1Àx Ca x MnO 3 determined by spin-polarized x-ray absorption spectroscopy: Comparison of experiments with band-structure computations Q. Qian, 1 T. A. Tyson, 1 S. Savrassov,
Structural and magnetic phase diagram of CeFeAsO 1-x F x and. its relationship to high-temperature superconductivity
 Structural and magnetic phase diagram of CeFeAsO 1-x F x and its relationship to high-temperature superconductivity Jun Zhao 1, Q. Huang 2, Clarina de la Cruz 1,3, Shiliang Li 1, J. W. Lynn 2, Y. Chen
Structural and magnetic phase diagram of CeFeAsO 1-x F x and its relationship to high-temperature superconductivity Jun Zhao 1, Q. Huang 2, Clarina de la Cruz 1,3, Shiliang Li 1, J. W. Lynn 2, Y. Chen
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/115260649.jpg) 1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 22 Jul 1999
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 22 Jul 1999 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 22 Jul 1999](/thumbs/71/65805847.jpg) Charge carrier density collapse in La 067 Ca 033 and La 067 Sr 033 epitaxial thin films W Westerburg, F Martin, and G Jakob Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, D-55099 Mainz, Germany
Charge carrier density collapse in La 067 Ca 033 and La 067 Sr 033 epitaxial thin films W Westerburg, F Martin, and G Jakob Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, D-55099 Mainz, Germany
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides. Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625
 Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Te x MnO 3
 phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/117739901.jpg) Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
Review of typical behaviours observed in strongly correlated systems. Charles Simon Laboratoire CRISMAT, CNRS and ENSICAEN, F14050 Caen.
 Review of typical behaviours observed in strongly correlated systems Charles Simon Laboratoire CRISMAT, CNRS and ENSICAEN, F14050 Caen. Introduction : Major part of solid state physics of the second part
Review of typical behaviours observed in strongly correlated systems Charles Simon Laboratoire CRISMAT, CNRS and ENSICAEN, F14050 Caen. Introduction : Major part of solid state physics of the second part
Ferroelectricity, Magnetism, and Multiferroicity. Kishan K. Sinha Xu Lab Department of Physics and astronomy University of Nebraska-Lincoln
 Ferroelectricity, Magnetism, and Multiferroicity Kishan K. Sinha Xu Lab Department of Physics and astronomy University of Nebraska-Lincoln Magnetism, Ferroelectricity, and Multiferroics Magnetism o Spontaneous
Ferroelectricity, Magnetism, and Multiferroicity Kishan K. Sinha Xu Lab Department of Physics and astronomy University of Nebraska-Lincoln Magnetism, Ferroelectricity, and Multiferroics Magnetism o Spontaneous
Magnetic coupling in the insulating and metallic ferromagnetic La 1Àx Ca x MnO 3
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 224429 Magnetic coupling in the insulating and metallic ferromagnetic La 1Àx Ca x MnO 3 Pengcheng Dai, 1,2 J. A. Fernandez-Baca, 2 E. W. Plummer, 1,2 Y. Tomioka, 3,4 and Y.
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 224429 Magnetic coupling in the insulating and metallic ferromagnetic La 1Àx Ca x MnO 3 Pengcheng Dai, 1,2 J. A. Fernandez-Baca, 2 E. W. Plummer, 1,2 Y. Tomioka, 3,4 and Y.
Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 174415 Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect H. C. Yang Department of Physics, National Taiwan
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 174415 Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect H. C. Yang Department of Physics, National Taiwan
CHARGE ORDERING AND PHASE COMPETITION IN THE LAYERED PEROVSKITE LaSr 2 Mn 2 O 7
 CHARGE ORDERING AND PHASE COMPETITION IN THE LAYERED PEROVSKITE LaSr Mn O 7 D. N Argyriou 1, H. N. Bordallo 1, B. J. Campbell, A. K. Cheetham. D. E. Cox 3, J. S. Gardner 4, K. Hanif 5, A. dos Santos, G.
CHARGE ORDERING AND PHASE COMPETITION IN THE LAYERED PEROVSKITE LaSr Mn O 7 D. N Argyriou 1, H. N. Bordallo 1, B. J. Campbell, A. K. Cheetham. D. E. Cox 3, J. S. Gardner 4, K. Hanif 5, A. dos Santos, G.
Anisotropic Magnetic Structures in Iron-Based Superconductors
 Anisotropic Magnetic Structures in Iron-Based Superconductors Chi-Cheng Lee, Weiguo Yin & Wei Ku CM-Theory, CMPMSD, Brookhaven National Lab Department of Physics, SUNY Stony Brook Another example of SC
Anisotropic Magnetic Structures in Iron-Based Superconductors Chi-Cheng Lee, Weiguo Yin & Wei Ku CM-Theory, CMPMSD, Brookhaven National Lab Department of Physics, SUNY Stony Brook Another example of SC
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004](/thumbs/72/66676281.jpg) Coexisting charge modulation and ferromagnetism produces long period phases in manganites: new example of electronic soft matter. G.C. Milward, M.J. Calderón, P.B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/0407727v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Coexisting charge modulation and ferromagnetism produces long period phases in manganites: new example of electronic soft matter. G.C. Milward, M.J. Calderón, P.B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/0407727v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Spin waves throughout the Brillouin zone and magnetic exchange coupling in the ferromagnetic metallic manganites La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x=0.25,0.
 Spin waves throughout the Brillouin zone and magnetic exchange coupling in the ferromagnetic metallic manganites La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x=0.25,0.30 F. Ye, 1, * Pengcheng Dai, 2,1 J. A. Fernandez-Baca, 1,2 D.
Spin waves throughout the Brillouin zone and magnetic exchange coupling in the ferromagnetic metallic manganites La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x=0.25,0.30 F. Ye, 1, * Pengcheng Dai, 2,1 J. A. Fernandez-Baca, 1,2 D.
PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB
![PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB](/thumbs/84/91030401.jpg) Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 (x = 0 and 0.
 Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Magneto-electronic phase separation in doped cobaltites
 Magneto-electronic phase separation in doped cobaltites A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Chunyong He IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
Magneto-electronic phase separation in doped cobaltites A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Chunyong He IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6
 Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Metal-Insulator Transition in Mn Perovskite Compounds
 Metal-Insulator Transition in Mn Perovskite Compounds arxiv:cond-mat/9811221v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 16 Nov 1998 Yukitoshi Motome 1), Hiroki Nakano 2) and Masatoshi Imada 2), 1) Department of Physics, Tokyo
Metal-Insulator Transition in Mn Perovskite Compounds arxiv:cond-mat/9811221v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 16 Nov 1998 Yukitoshi Motome 1), Hiroki Nakano 2) and Masatoshi Imada 2), 1) Department of Physics, Tokyo
The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+±
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION
 COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio Dagotto 1, Takashi Hotta 2, Adriana Moreo 1 1 National High Magnetic Field Lab and Department of Physics, Florida State University,
COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio Dagotto 1, Takashi Hotta 2, Adriana Moreo 1 1 National High Magnetic Field Lab and Department of Physics, Florida State University,
Signatures of electronic phase separation in the Hall effect of anisotropically strained La 0.67 Ca 0.33 MnO 3 films
 Signatures of electronic phase separation in the Hall effect of anisotropically strained La 0.67 Ca 0.33 MnO 3 films Liuqi Yu 1, Lingfei Wang 2, Xiaohang Zhang 3, W.B. Wu 2, S. von Molnár 1, Z. Fisk 4
Signatures of electronic phase separation in the Hall effect of anisotropically strained La 0.67 Ca 0.33 MnO 3 films Liuqi Yu 1, Lingfei Wang 2, Xiaohang Zhang 3, W.B. Wu 2, S. von Molnár 1, Z. Fisk 4
Influence of magnetic field on the paramagnetic-ferromagnetic transition inala 1 x Ca x MnO 3 xé0.25 crystal: Ultrasonic and transport studies
 Influence of magnetic field on the paramagnetic-ferromagnetic transition inala 1 x Ca x MnO 3 xé.5 crystal: Ultrasonic and transport studies B. I. Belevtsev, 1, * G. A. Zvyagina, 1 K. R. Zhekov, 1 I. G.
Influence of magnetic field on the paramagnetic-ferromagnetic transition inala 1 x Ca x MnO 3 xé.5 crystal: Ultrasonic and transport studies B. I. Belevtsev, 1, * G. A. Zvyagina, 1 K. R. Zhekov, 1 I. G.
The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates. Abstract
 The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates Nicola Poccia, Michela Fratini Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome, P. Aldo Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: nicola.poccia@roma1.infn.it
The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates Nicola Poccia, Michela Fratini Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome, P. Aldo Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: nicola.poccia@roma1.infn.it
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 9 Jan 1995
 Double Exchange Alone Does Not Explain the Resistivity of La 1 x Sr x MnO 3 A. J. Millis P. B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/9501034v1 9 Jan 1995 B. I. Shraiman AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 07974
Double Exchange Alone Does Not Explain the Resistivity of La 1 x Sr x MnO 3 A. J. Millis P. B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/9501034v1 9 Jan 1995 B. I. Shraiman AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 07974
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Intrinsic chemical and structural inhomogeneity in lightly doped La 1-x Sr x MnO 3
 Intrinsic chemical and structural inhomogeneity in lightly doped La 1-x x MnO 3 Tomohiro Shibata, a Bruce Bunker, a John Mitchell, b and Peter Schiffer c a) Department of Physics, University of Notre Dame,
Intrinsic chemical and structural inhomogeneity in lightly doped La 1-x x MnO 3 Tomohiro Shibata, a Bruce Bunker, a John Mitchell, b and Peter Schiffer c a) Department of Physics, University of Notre Dame,
Electronic and vibrational Raman spectroscopy of Nd 0.5 Sr 0.5 MnO 3 through the phase transitions
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 64, No. 1 journal of January 2005 physics pp. 119 128 Electronic and vibrational Raman spectroscopy of Nd 0.5 Sr 0.5 MnO 3 through the phase transitions Md MOTIN
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 64, No. 1 journal of January 2005 physics pp. 119 128 Electronic and vibrational Raman spectroscopy of Nd 0.5 Sr 0.5 MnO 3 through the phase transitions Md MOTIN
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials
 Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Ultrashort Lifetime Expansion for Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering. Luuk Ament
 Ultrashort Lifetime Expansion for Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering Luuk Ament In collaboration with Jeroen van den Brink and Fiona Forte What is RIXS? Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering Synchrotron
Ultrashort Lifetime Expansion for Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering Luuk Ament In collaboration with Jeroen van den Brink and Fiona Forte What is RIXS? Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering Synchrotron
Lattice effects in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x 0 1 : Relationships between distortions, charge distribution, and magnetism
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 57, NUMBER 17 1 MAY 1998-I Lattice effects in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x 0 1 : Relationships between distortions, charge distribution, and magnetism C. H. Booth* Department of Physics
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 57, NUMBER 17 1 MAY 1998-I Lattice effects in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 x 0 1 : Relationships between distortions, charge distribution, and magnetism C. H. Booth* Department of Physics
Polarons in linear chains of fullerenes
 Polarons in linear chains of fullerenes V. A. Levashov, A. A. Remova, and V. R. Belosludov a) Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, 630090 Novosibirsk, Russia Submitted 6 September 1996 Pis ma Zh. Éksp. Teor.
Polarons in linear chains of fullerenes V. A. Levashov, A. A. Remova, and V. R. Belosludov a) Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, 630090 Novosibirsk, Russia Submitted 6 September 1996 Pis ma Zh. Éksp. Teor.
New Hamiltonian and Cooper pair s origin of pseudogap and colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 New Hamiltonian and Cooper pair s origin of pseudogap and colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Fu-sui Liu Department of Physics, Beijing University, Beijing 100871, China E-mail: fsliu@pku.edu.cn Abstract
New Hamiltonian and Cooper pair s origin of pseudogap and colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Fu-sui Liu Department of Physics, Beijing University, Beijing 100871, China E-mail: fsliu@pku.edu.cn Abstract
Thermopower of single-crystal Nd 1 x Sr,Pb x MnO 3
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 21 1 JUNE 1996-I Thermopower of single-crystal Nd 1 x Sr,Pb x MnO 3 Vincent H. Crespi, Li Lu, Y. X. Jia, K. Khazeni, A. Zettl, and Marvin L. Cohen Department of Physics,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 21 1 JUNE 1996-I Thermopower of single-crystal Nd 1 x Sr,Pb x MnO 3 Vincent H. Crespi, Li Lu, Y. X. Jia, K. Khazeni, A. Zettl, and Marvin L. Cohen Department of Physics,
CORRELATED ELECTRON OXIDES AS THE COMPLEX SYSTEM. Yoshinori Tokura
 CORRELATED ELECTRON OXIDES AS THE COMPLEX SYSTEM Yoshinori Tokura When electron-electron Coulomb repulsion interaction is strong in a solid, electrons are almost localized on the respective atomic sites
CORRELATED ELECTRON OXIDES AS THE COMPLEX SYSTEM Yoshinori Tokura When electron-electron Coulomb repulsion interaction is strong in a solid, electrons are almost localized on the respective atomic sites
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
The crucial role of mixed valence in the magnetoresistance properties of manganites and cobaltites
 366, 83 92 doi:10.1098/rsta.2007.2141 Published online 7 September 2007 The crucial role of mixed valence in the magnetoresistance properties of manganites and cobaltites BY B. RAVEAU* Laboratoire CRISMAT,
366, 83 92 doi:10.1098/rsta.2007.2141 Published online 7 September 2007 The crucial role of mixed valence in the magnetoresistance properties of manganites and cobaltites BY B. RAVEAU* Laboratoire CRISMAT,
COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION
 E. Dagotto et al. / Physics Reports 344 (2001) 1}153 1 COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio DAGOTTO a, Takashi HOTTA b, Adriana MOREO a National High Magnetic Field
E. Dagotto et al. / Physics Reports 344 (2001) 1}153 1 COLOSSAL MAGNETORESISTANT MATERIALS: THE KEY ROLE OF PHASE SEPARATION Elbio DAGOTTO a, Takashi HOTTA b, Adriana MOREO a National High Magnetic Field
Magnons in Ferromagnetic Metallic Manganites
 Magnons in Ferromagnetic Metallic Manganites Jiandi Zhang 1,* F. Ye 2, Hao Sha 1, Pengcheng Dai 3,2, J. A. Fernandez-Baca 2, and E.W. Plummer 3,4 1 Department of physics, Florida International University,
Magnons in Ferromagnetic Metallic Manganites Jiandi Zhang 1,* F. Ye 2, Hao Sha 1, Pengcheng Dai 3,2, J. A. Fernandez-Baca 2, and E.W. Plummer 3,4 1 Department of physics, Florida International University,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 2019](/thumbs/95/123272699.jpg) Effect of A-site ionic radius on metamagnetic transition in charge ordered Sm.5 (Ca.5 y Sr y )MnO 3 compounds arxiv:193.11348v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 219 Sanjib Banik, 1, Kalpataru Pradhan, 1, and
Effect of A-site ionic radius on metamagnetic transition in charge ordered Sm.5 (Ca.5 y Sr y )MnO 3 compounds arxiv:193.11348v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 219 Sanjib Banik, 1, Kalpataru Pradhan, 1, and
Jim Freericks (Georgetown University) Veljko Zlatic (Institute of Physics, Zagreb)
 Theoretical description of the hightemperature phase of YbInCu 4 and EuNi 2 (Si 1-x Ge x ) 2 Jim Freericks (Georgetown University) Veljko Zlatic (Institute of Physics, Zagreb) Funding: National Science
Theoretical description of the hightemperature phase of YbInCu 4 and EuNi 2 (Si 1-x Ge x ) 2 Jim Freericks (Georgetown University) Veljko Zlatic (Institute of Physics, Zagreb) Funding: National Science
A New Electronic Orbital Order Identified in Parent Compound of Fe-Based High-Temperature Superconductors
 A New Electronic Orbital Order Identified in Parent Compound of Fe-Based High-Temperature Superconductors Cooperative Research Team on Predictive Capability for Strongly Correlated Systems Summary: The
A New Electronic Orbital Order Identified in Parent Compound of Fe-Based High-Temperature Superconductors Cooperative Research Team on Predictive Capability for Strongly Correlated Systems Summary: The
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002](/thumbs/73/69440848.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0209089v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002 Double exchange and orbital correlations in electron doped manganites Tulika Maitra 1 and A. Taraphder 2 Department of Physics & Meteorology and Centre
arxiv:cond-mat/0209089v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002 Double exchange and orbital correlations in electron doped manganites Tulika Maitra 1 and A. Taraphder 2 Department of Physics & Meteorology and Centre
doi: /PhysRevLett
 doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
Exact diagonalization study of spin, orbital, and lattice correlations in CMR manganites
 Exact diagonalization study of spin, orbital, and lattice correlations in CMR manganites Alexander Weiße 1, Gerhard Wellein 2, and Holger Fehske 3,1 1 Physikalisches Institut, Universität Bayreuth, D-9544
Exact diagonalization study of spin, orbital, and lattice correlations in CMR manganites Alexander Weiße 1, Gerhard Wellein 2, and Holger Fehske 3,1 1 Physikalisches Institut, Universität Bayreuth, D-9544
Neutron Scattering in Transition Metal Oxides
 Neutron Scattering in Transition Metal Oxides C. Ulrich Department Prof. B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung, Stuttgart, Germany physics of the 3d electrons strongly correlated electrons
Neutron Scattering in Transition Metal Oxides C. Ulrich Department Prof. B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung, Stuttgart, Germany physics of the 3d electrons strongly correlated electrons
Electrical Resistivity Measurements under High Pressure for Nd3.5Sm0.5Ni3O8
 Proc. 17th Int. Conf. on High Pressure in Semiconductor Physics & Workshop on High-pressure Study on Superconducting JJAP Conf. Proc. 6, https://doi.org/10.7567/jjapcp.6.011106 Electrical Resistivity Measurements
Proc. 17th Int. Conf. on High Pressure in Semiconductor Physics & Workshop on High-pressure Study on Superconducting JJAP Conf. Proc. 6, https://doi.org/10.7567/jjapcp.6.011106 Electrical Resistivity Measurements
Tuning order in cuprate superconductors
 Tuning order in cuprate superconductors arxiv:cond-mat/0201401 v1 23 Jan 2002 Subir Sachdev 1 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 2 1 Department of Physics, Yale University, P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120,
Tuning order in cuprate superconductors arxiv:cond-mat/0201401 v1 23 Jan 2002 Subir Sachdev 1 and Shou-Cheng Zhang 2 1 Department of Physics, Yale University, P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120,
Introduction to Heisenberg model. Javier Junquera
 Introduction to Heisenberg model Javier Junquera Most important reference followed in this lecture Magnetism in Condensed Matter Physics Stephen Blundell Oxford Master Series in Condensed Matter Physics
Introduction to Heisenberg model Javier Junquera Most important reference followed in this lecture Magnetism in Condensed Matter Physics Stephen Blundell Oxford Master Series in Condensed Matter Physics
Exchange interactions
 Exchange interactions Tomasz Dietl Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, PL-02-668Warszawa, Poland Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw, PL-00-681Warszawa, Poland 1. POTENTIAL
Exchange interactions Tomasz Dietl Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, PL-02-668Warszawa, Poland Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw, PL-00-681Warszawa, Poland 1. POTENTIAL
Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7
 The Open Condensed Matter Physics Journal, 2009, 2, 19-24 19 Open Access Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7 Aihua Wang 1,2, Tao Liu 3, Yang Liu 4, Guohui
The Open Condensed Matter Physics Journal, 2009, 2, 19-24 19 Open Access Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7 Aihua Wang 1,2, Tao Liu 3, Yang Liu 4, Guohui
Hole dispersions in the G- and C-type orbital ordering backgrounds: Doped manganese oxides. Fan, XJ; Shen, SQ; Wang, ZD; Li, XG; Wang, QH
 Title Hole dispersions in the G- and C-type orbital ordering bacgrounds: Doped manganese oxides Author(s) Fan, XJ; Shen, SQ; Wang, ZD; Li, XG; Wang, QH Citation Physical Review B - Condensed Matter And
Title Hole dispersions in the G- and C-type orbital ordering bacgrounds: Doped manganese oxides Author(s) Fan, XJ; Shen, SQ; Wang, ZD; Li, XG; Wang, QH Citation Physical Review B - Condensed Matter And
On conduction mechanism in paramagnetic phase of Gd based manganites
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 41 45. c Indian Academy of Sciences. On conduction mechanism in paramagnetic phase of Gd based manganites S SAGAR 1,2 and M R ANANTHARAMAN 1, 1 Department
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 41 45. c Indian Academy of Sciences. On conduction mechanism in paramagnetic phase of Gd based manganites S SAGAR 1,2 and M R ANANTHARAMAN 1, 1 Department
Instabilities and insulator-metal transitions in half-doped manganites induced by magnetic-field and doping
 Instabilities and insulator-metal transitions in half-doped manganites induced by magnetic-field and doping O. Cépas, 1,2, * H. R. Krishnamurthy, 1,3 and T. V. Ramakrishnan 1,3,4 1 Department of Physics,
Instabilities and insulator-metal transitions in half-doped manganites induced by magnetic-field and doping O. Cépas, 1,2, * H. R. Krishnamurthy, 1,3 and T. V. Ramakrishnan 1,3,4 1 Department of Physics,
Ohoyama., TEM, neutron diffraction, ordered perovskite, CE structure. Abstract An A-site ordered manganese perovskite YBaMn 2
 New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
SEEING Phase Transitions with. Magnetic Force Microscopy. Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin. Alex de Lozanne
 SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport. Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR)
 Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Electron State and Lattice Effects in Cuprate High Temperature Superconductors
 Electron State and Lattice Effects in Cuprate High Temperature Superconductors - The True Story Revealed by Fermi Surface and Unconventional Lattice Effects- October 27-28, 2005 Headquarters and Information
Electron State and Lattice Effects in Cuprate High Temperature Superconductors - The True Story Revealed by Fermi Surface and Unconventional Lattice Effects- October 27-28, 2005 Headquarters and Information
Magnetic field induced dielectric relaxation in the strain glass state of Pr 0.6 Ca 0.4 MnO 3
 Magnetic field induced dielectric relaxation in the strain glass state of Pr 0.6 Ca 0.4 MnO 3 K Devi Chandrasekhar 1, A K Das 1 and A Venimadhav 2,a) 1 Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian Institute
Magnetic field induced dielectric relaxation in the strain glass state of Pr 0.6 Ca 0.4 MnO 3 K Devi Chandrasekhar 1, A K Das 1 and A Venimadhav 2,a) 1 Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian Institute
compound Cs 2 Cu 2 Mo 3 O 12
 133 Cs-NMR study on aligned powder of competing spin chain compound A Yagi 1, K Matsui 1 T Goto 1, M Hase 2 and T Sasaki 3 1 2 Sophia University, Physics Division, Tokyo, 102-8554, Japan National Institute
133 Cs-NMR study on aligned powder of competing spin chain compound A Yagi 1, K Matsui 1 T Goto 1, M Hase 2 and T Sasaki 3 1 2 Sophia University, Physics Division, Tokyo, 102-8554, Japan National Institute
Synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction and structural analysis of Eu0.5La0.5FBiS2-xSex
 Synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction and structural analysis of Eu0.5La0.5FBiS2-xSex K. Nagasaka 1, G. Jinno 1, O. Miura 1, A. Miura 2, C. Moriyoshi 3, Y. Kuroiwa 3, Y. Mizuguchi 1 * 1. Department of Electrical
Synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction and structural analysis of Eu0.5La0.5FBiS2-xSex K. Nagasaka 1, G. Jinno 1, O. Miura 1, A. Miura 2, C. Moriyoshi 3, Y. Kuroiwa 3, Y. Mizuguchi 1 * 1. Department of Electrical
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 7 May 1996
 Electronic Hamiltonian for Transition Metal Oxide Compounds Erwin Müller-Hartmann 1 and Elbio Dagotto 2 1. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität zu Köln, Zülpicher Str. 77, D-50937 Köln, Germany.
Electronic Hamiltonian for Transition Metal Oxide Compounds Erwin Müller-Hartmann 1 and Elbio Dagotto 2 1. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität zu Köln, Zülpicher Str. 77, D-50937 Köln, Germany.
University of Bristol. 1 Naval Research Laboratory 2 II. Physikalisches Institut, Universität zu Köln
 Charge ordering as alternative to Jahn-Teller distortion In collaboration with Michelle Johannes 1, Daniel Khomskii 2 (theory) and Mohsen Abd-Elmeguid et al 2, Radu Coldea et al 3 (experiment) 1 Naval
Charge ordering as alternative to Jahn-Teller distortion In collaboration with Michelle Johannes 1, Daniel Khomskii 2 (theory) and Mohsen Abd-Elmeguid et al 2, Radu Coldea et al 3 (experiment) 1 Naval
EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS: SUPER-EXCHANGE, DOUBLE EXCHANGE, RKKY; MAGNETIC ORDERS. Tomasz Dietl
 Analele Universităţii de Vest din Timişoara Vol. LIII, 2009 Seria Fizică EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS: SUPER-EXCHANGE, DOUBLE EXCHANGE, RKKY; MAGNETIC ORDERS Tomasz Dietl Institute of Physics, Polish Academy
Analele Universităţii de Vest din Timişoara Vol. LIII, 2009 Seria Fizică EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS: SUPER-EXCHANGE, DOUBLE EXCHANGE, RKKY; MAGNETIC ORDERS Tomasz Dietl Institute of Physics, Polish Academy
Superconductivity at 41.0 K in the F-doped LaFeAsO 1-x F x
 Superconductivity at 41.0 K in the F-doped LaFeAsO 1-x F x Wei Lu, Xiao-Li Shen, Jie Yang, Zheng-Cai Li, Wei Yi, Zhi-An Ren*, Xiao-Li Dong, Guang-Can Che, Li-Ling Sun, Fang Zhou, Zhong-Xian Zhao* National
Superconductivity at 41.0 K in the F-doped LaFeAsO 1-x F x Wei Lu, Xiao-Li Shen, Jie Yang, Zheng-Cai Li, Wei Yi, Zhi-An Ren*, Xiao-Li Dong, Guang-Can Che, Li-Ling Sun, Fang Zhou, Zhong-Xian Zhao* National
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method
 Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Novel Magnetic Properties of Carbon Nanotubes. Abstract
 Novel Magnetic Properties of Carbon Nanotubes Jian Ping Lu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599 jpl@physics.unc.edu arxiv:cond-mat/94779v1
Novel Magnetic Properties of Carbon Nanotubes Jian Ping Lu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599 jpl@physics.unc.edu arxiv:cond-mat/94779v1
Effects of boson dispersion in fermion-boson coupled systems
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 19 15 NOVEMBER 2000-I Effects of boson dispersion in fermion-boson coupled systems Yukitoshi Motome Institute of Materials Science, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 19 15 NOVEMBER 2000-I Effects of boson dispersion in fermion-boson coupled systems Yukitoshi Motome Institute of Materials Science, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
Effect of Bivalent Cation Ca-Doping on Magnetic Properties in Multiferroic YMnO 3 Manganites
 J Supercond Nov Magn (2010) 23: 501 506 DOI 10.1007/s10948-009-0623-1 ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of Bivalent Cation Ca-Doping on Magnetic Properties in Multiferroic YMnO 3 Manganites Yuling Su Zhenping Chen
J Supercond Nov Magn (2010) 23: 501 506 DOI 10.1007/s10948-009-0623-1 ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of Bivalent Cation Ca-Doping on Magnetic Properties in Multiferroic YMnO 3 Manganites Yuling Su Zhenping Chen
