Ohoyama., TEM, neutron diffraction, ordered perovskite, CE structure. Abstract An A-site ordered manganese perovskite YBaMn 2
|
|
|
- Kristina Houston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization Laboratory, Institute for Solid State Physics, University of Tokyo, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba Neutron Scattering Laboratory, Institute for Solid State Physics, The University of Tokyo, Shirakata, Tokai, Ibaraki Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University, Katahira, Aoba-ku, Sendai Keywords: YBaMn 2, TEM, neutron diffraction, ordered perovskite, CE structure Abstract An A-site ordered manganese perovskite YBaMn 2 undergoes unusual and multiple phase transitions; a structural transition at T c1 = 520 K, a metal-insulator transition at T c2 = 480 K and an antiferromagnetic long-range order at T c3 = 195 K. We performed transmission electron microscope (TEM) and powder neutron diffraction experiments, particularly focusing on how charge, orbital and spin degrees of freedom freeze at low temperatures. For the paramagnetic insulating phase (T c3 <T<T c2 ), the so-called CE type of charge and orbital ordered state was observed within the monoclinic a-b plane, which is most commonly observed for the ordinary solid solution of A 3+ 1-x A'2+ MnO x 3 around x = 0.5. However, TEM revealed a 4-fold periodicity along the c axis, suggesting a new stacking pattern, where planes of the CE type are built up according to the sequence [ββ...]. Interestingly, when the system enters into the antiferromagnetic state below T c3, this stacking pattern changes into [...] or [ββ...], suggesting close interplay between spins and orbitals. These features are discussed in terms of inherent structural alternation, i.e., the Y/Ba order along the c axis.
2 Perovskite (ABO 3 ) and its related compounds display interesting electric, magnetic and optical properties. Most well-known examples are the high-t c superconductivity in cuprates (B=Cu) [1] and the colossal magnetoresistance in manganites (B=Mn) [2]. Emergence of various phenomena of interests in the perovskite systems is partly due to the versatility of the A site to form a wide range of solid solution between cations with different valences and ionic sizes. This advantage provides us the opportunity to systematically tune doping level x as well as the Goldschmidt tolerance factor f, as demonstrated by La 2-x Sr x CuO 4 and La 1-x Ca x [3, 4]. It should be stressed, however, that such partial substitution can always be a cause of structural disorder. In A 1-x A' x, the shape, size and tilting angle of each Mn octahedron would depend largely on nearby A/A' ions, so that crystallographic parameters refined usually using X-ray or neutron diffraction data describe nothing but specially averaged ones. A problem is that randomness of the underlying lattice should affect the physical properties more or less. The effect would become more serious when one deals with microscopic phenomena. It is possible that the structural disorder and spacial heterogeneity trigger or accelerate the nucleation of microscopic electronic phase segregations recently observed in La 2-x Sr x CuO 4 [5] and La 0.5 Sr 0.5 [6]. Fortunately, one can tailor a 'clean' system only when x in A 3+ 1-x A'2+ x BO 3 is 1/2. Taking an example of Y 0.5 Ba 0.5 CoO 3-y [7, 8], the A-site metal order takes place in a way that the YO and BaO layers are built up alternatively. Therefore, the composition should be better denoted as YBaCo 2 -y. Recently, we have succeeded to synthesize its manganese analogue, YBaMn 2 (A = Y, A' = Ba, B = Mn) [9, 10], whose structural and physical properties are considerably different from the conventional disordered A 0.5 system with the A/A' ions being randomly distributed [11, 12]. YBaMn 2 undergoes -with descending temperature T- unusual phase transitions; a 1st order structural phase transition at T c1 = 520 K from triclinic P1 to monoclinic P2, a metal-insulator (MI) transition at T c2 = 480 K and an antiferromagnetic ordering at T c3 = 195 K. A peculiar feature is the separation of structural and MI transitions (i.e., T c2 T c1 ), strikingly in contrast to the A 0.5 system, where these transitions occurs simultaneously (i.e., T c1 = T c2 ). Moreover, the value of T c2 is, to the authors
3 knowledge, highest in the manganese perovskite family. Structural considerations [9, 10] naively tell us that these unusual properties in YBaMn 2 are attributable to the absence of lattice disorder, the twodimensionality due to the stacking sequence of -YO-MnO 2 -BaO-MnO 2 -, and rather distorted Mn octahedron from ideal cubic one. However, for the fully understanding of the role of the structure (especially, order/disorder), it is necessary to determine the ordered superstructures of charge, orbital and spin degrees of freedom at low temperatures. In this study, we performed transmission electron microscope (TEM) and neutron powder diffraction for the paramagnetic insulator (PI; T c3 < T < T c2 ) and the antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI; T < T c3 ). It is found that the obtained CO ordered pattern in the PI phase differs from those for the A 0.5 systems. Interestingly, the antiferromagnetic long-range order redesigns the CO ordered pattern. Polycrystalline sample of YBaMn 2 was prepared by a conventional solid state reaction as reported in Ref. [9]. The superlattice originating from the CO order was probed by means of TEM using JEM2010 (JOEL) operating at 200 kv, equipped with a low-temperature sample holder, from the room temperature (RT) down to 24 K. The sample was finely ground under methanol then dispersed on Cu grids coated with holy-carbon support films. The neutron powder diffraction experiments, which allow us to determine the magnetic ordering, were conducted for 25 K < T < 350 K on the Kinken powder diffractometer for high efficiency and high resolution measurements, HERMES, of Institute for Materials Research (IMR), Tohoku University, installed at the JRR-3M reactor in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), Tokai. Neutrons with a wavelength of Å were obtained by the 331 reflection of the Ge monochromator and 12'-blanksample-18' collimation. Shown in Fig. 1 is the crystal structure of YBaMn 2 at 350 K (the PI phase) determined from the Rietveld refinement of both powder X-ray and neutron diffraction patterns. The details of the structural analysis will be reported elsewhere [10]. The structure of the PI phase adopts a monoclinic space group P2 with a unit cell dimension of 2a p 2b p 2c p, where a p, b p and c p denote the cell constants for the simple cubic perovskite. The lattice parameters are determined to be a = Å, b = Å, c = Å, and β =
4 There are two crystallographically inequivalent Mn sites, Mn(1) and Mn(2). There is a sizable difference of the volume of the Mn octahedra (9.56 Å 3 for Mn(1) and Å 3 for Mn(2)), suggesting a charge ordering that the Mn 3+ and Mn 4+ ions occupy the Mn(2) and Mn(1) sites, respectively. Each Mn octahedron is heavily distorted (see Fig. 1) as a result of the A-site order, and the octahedral tilting system is written approximately as a - b - c -. Figure 2 (a) is the [100] p -zone TEM image and corresponding electron diffraction pattern for the PI phase, which clearly reveals a modulation over a wide range of the specimen, originating from the successful alternation of the YO and BO layers along the c axis. In fact, the 7.5 Å-periodicity of the modulation is in good accordance with c = Å. The doubling of the c parameter can be confirmed by the electron diffraction pattern, which contains, in addition to the main reflection spots, relatively strong superlattice reflections with a 2-fold periodicity along [001] p. Furthermore, we observed very weak reflections, the modulation (q) of which is commensurate and can be denoted as q 1 = (0, 0, 1/4) p. The quadruplication along the c axis was invisible from the X-ray and neutron diffraction experiments, and its origin will be discussed later, Direct observation of the CO states can be probed by the TEM investigations [13-15]. In the inset of Fig. 2 (b), we show the [001] p -zone electron diffraction pattern taken at RT, exhibiting the satellite reflections of the CO ordering of a modulation following with the main reflection spots. This modulation appears along [110] p (or [1-10] p ) direction within the a*-b* plane, and the structural modulation can be written as q 2 = (1/4, 1/4, 0) p. The corresponding lattice image (Fig. 2 (b)) indicates the contrast of the q 2 superlattice running diagonally with respect to the a p and b p axes. In addition, one can see the contrast of the lattice constants a p and b p (~5.5 Å). The q 2 superlattice can be ascribed to the CO ordering of the so-called CE type in the a-b plane, namely, the arrangement of the Mn 3+ /Mn 4+ ions into the MnO 2 square lattice accompanied by the alternative arrangement of rows of d 3x 2 -r 2 and d 3y 2 -r 2 orbitals running either along [110] p or [1-10] p. The same pattern has been most frequently obtained for A 1-x A' x when x is around 0.5 [13, 14]. Together with electron diffractions along various directions, we plotted thus obtained superspots on the reciprocal lattice in Fig. 3 (a). The most intriguing
5 feature in the present study is the presence of the modulation vector q 1 = (0, 0, 1/4) p. We interpret the origin of the q 1 modulated structure in terms of stacking sequence of the CE-type layers. By utilizing the interconversion of the Mn 3+ - and Mn 4+ - sublattices or/and the d 3x 2 -r 2- and d 3y 2 -r 2-sublattices, one can pile up the CE-type layers along the c axis so as to satisfy the unit cell 2 2a p 2b p 4c p. However, the crystal structure for the PI state (Fig. 1) excludes models that contain the operation of the interconversion between the Mn 3+ - and Mn 4+ - sublattices. Consequently, one can uniquely obtain a stacking sequence of [ββ...] as depicted in Fig. 4 (a), although there are still two choices that the BaO layers are located between out-of-phase planes, i.e., β and between in-phase planes, i.e., (ββ). This extended three-dimensional (3D) CE pattern is observed for the first time and forms a striking contrast to the half-doped solid solution, where an uniformly stacked pattern (Fig. 4 (b)), the original 3D CE pattern given by Wollan et al. [16] has always been observed [13, 14]. It is noted that the unusual stacking sequence [ββ...] is also observed for the 2D system NaV 2 O 5. In this vanadate, a number of charge stacking patterns appear with increasing pressure, which is successfully mapped onto the ANNNI model (devil's stairscase) [17]. In the manganese perovskite systems, a most probable key in determining the 3D CO ordered structures should lie in the A-site order/disorder. In case of A 0.5, the orbital interlayer interaction that governs stacking form is uniform, thus providing two possible superstructures shown in Figs. 4 (b) and (c), though the real system favors the former as mentioned above. On the other hand, such interlayer interactions should be alternated owing to the fact that the MnO 2 layers are sandwiched by the YO and BaO layers with considerably different ionic radii (r Y 3+ = 1.18 Å, r Ba 2+ = 1.61 Å), thus giving rise to the superlattice in Fig. 4 (a). Finally, we would like to discuss the superstructure in the AFI state below T c3. Figure 5 compares the neutron diffraction patterns taken at 250 K and 20 K. While all of the peaks for the PI phase are of nuclear origin and can be indexed with a monoclinic symmetry with the 2a p 2b p 2c p unit cell, additional peaks of magnetic origin appear when T is decreased below T c3. It is revealed from indexing these magnetic peaks the spin-ordering pattern in the a-b plane is
6 the same as that observed in A 0.5 [18], but that along the c axis has a 4-fold periodicity. A proposed spin structure is shown in Fig. 4 (d). Such quadruplication along the c axis has not been observed for the A 0.5 system. Again, it is quite natural to consider that the Y/Ba order along the c axis quite gives rise to the alternation of the magnetic interlayer interactions and hence leads to such a periodicity. The electron diffraction pattern at 24 K (Fig. 2 (c)) is interpreted as the superimposition of twin domains both having the q 2 modulation. Thus the CE type of the CO ordering is retained within the a-b plane. Figure 2 (d) shows, interestingly enough, the disappearance of the modulation vector of q 1 at 24 K, although the system still has the 4-fold periodicity due to the spin ordering.the superspots at 24K obtained by TEM is summarized in Fig. 3 (b) and possible models of the CO ordering are depicted in Figs. 4 (b) and (c), where layers of the CE type are piled up according to [...] and [ββ...], respectively. The change of the 3D superstructures must be a consequence of the competition between the CO ordering and the spin ordering. This rearrangement across T c3 is partly supported by the nature of the 1st-order phase transition (relatively large hysteretic behavior in magnetic susceptibility and heat absorption/release by a differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurement) [9]. To summarize, we have investigated the superstructures of YBaMn 2 in the charge and orbital ordered states by means of TEM. In addition to the superlattice reflection spots originating from the A-site metal order, those with modulation vectors q 1 = (0, 0, 1/4) p and q 2 = (1/4, 1/4, 0) p appeared in the PI phase. This modulation structure was interpreted taking into account the charge and orbital ordering of the CE type and its stacking arrangement. The stacking sequence according to [ββ...] was first observed among the half-doped manganese perovskite compounds. In the AFI phase, we observed the disappearance of q 1, indicating the uniform [...] or alternative [ββ...] stacking along the c axis. Transformation of the charge/orbital ordering is mediated by the spin ordering with a quadruplicate periodicity along the same axis. This work is partly supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research No , No. 407 and No. 758 and for Creative Scientific Research (No. 13NP0201) from Ministry of Education, Science, Technology, Sports and Culture,
7 Japan. References 1) J. G. Bednorz and K. A. Muller: Z. Phys. B 64 (1986) ) S. Jin et al.: Nature 264 (1994) ) G. M. Luke et al.: Phys. Rev. B 42 (1990) ) C. Martin et al.: Phys. Rev. B 60 (1999) ) J.M. Tranquada et al.: Nature 375 (1995) ) S. Mori et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 (1998) ) W.Z. Zhou: Chem. Mater. 6 (1994) ) D. Akahoshi and Y. Ueda: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 68 (1999) ) T. Nakajima et al.: J. Phys. Chem. Solid 63 (2002) ) T. Nakajima et al.: submitted to J. Solid State Chemistry. 11) P.M. Woodward et al.: Chem. Mater. 10 (1998) ) Colossal Magnetoresistance, Charge Ordering and Related Properties of Manganese Oxides; ed. C.N.R. Rao and B. Raveau, World Scientific (1998). 13) Y. Q. Wang et al.: Mater. Sci. Eng. A 333 (2002) ) N. Fukumoto et al.: Phys. Rev. B 60 (1999) ) T. Asaka et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 (2002) ) E. O. Wollan et al.: Phys. Rev. 100 (1955) ) K. Ohwada et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 (2001) ) Z. Jirák et al.: Phys. Rev. B 61 (2000) Figure Captions Fig. 1: A perspective view of the crystal structure of the monoclinic YBaMn 2 at 350 K (the PI phase) looking down [010] p, where the Mn(1) and Mn(2) octahedra are shown as light and dark polyhedra, respectively, while the Ba 2+ and Y 3+ ions are shown in dark and light balls. Fig. 2: High-resolution TEM images and electron diffraction patterns of YBaMn 2 at RT taken along (a) [100] p -zone and (b) [001] p -zone axes.
8 Electron diffraction patterns at 24 K taken along (c) [001] p -zone and (d) [100] p -zone axes. Fig. 3: The reciprocal lattices with fundamental (closed) and superlattice (open) reflections, obtained from TEM at (a) RT and (b) 24 K. Fig. 4: Schematic representation of charge and orbital ordering patterns (a)-(c) and of spin-ordering pattern (d) for YBaMn 2, where for simplicity only Mn 3+ and Mn 4+ ions are drawn. (a): Proposed model for the PI state. (b) and (c): Proposed models for the AFI state. It is noted that the model (b) having uniform stacking is the original 3D CE structure and is obtained for the metal-disordered A 0.5 system. Fig. 5: Neutron diffraction profiles of YBaMn 2 at 250 K and 20 K, where the peaks are indexed according to the 2a p 2b p 2c p unit cell.
9 c p a p Fig.1 H. Kageyama et al.
10
11 (a) c p * (b) c p * 001* 001* 100* 010* b p * 100* 010* b p * a p * a p * Fig.3 H. Kageyama et al.
12 (a) c p (b) c p β β b p b p a p a p (c) c p (d) c p β β β b p β b p a p a p Fig. 4 H. Kageyama et al.
13 250 K Intensity (arb. units) 20 K (1/2 0 1/2) (0 0 1) (1/2 1/2 1/2) (1 0 0) (1/2 1 1/2) (1/2 0 3/2) (1/2 1/2 3/2) (1 1 0) (0 0 2) (-1 1/2 3/2) (1 1 1) (-3/2 1/2 1/2) (1 0 2) (0 2 0) (1 1 2) (1/2 1/2 5/2) θ ( ) Fig.5 H. Kageyama et al.
Anomalous octahedral distortion and multiple phase transitions in the metal-ordered manganite YBaMn 2 O 6
 Journal of Solid State Chemistry 177 (2004) 987 999 Anomalous octahedral distortion and multiple phase transitions in the metal-ordered manganite YBaMn 2 O 6 T. Nakajima, a H. Kageyama, a, M. Ichihara,
Journal of Solid State Chemistry 177 (2004) 987 999 Anomalous octahedral distortion and multiple phase transitions in the metal-ordered manganite YBaMn 2 O 6 T. Nakajima, a H. Kageyama, a, M. Ichihara,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998](/thumbs/78/78285667.jpg) Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Shigeki Yonezawa*, Yuji Muraoka and Zenji Hiroi Institute for Solid State Physics, University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba
 New β-pyrochlore Oxide Superconductor CsOs 2 O 6 Shigeki Yonezawa*, Yuji Muraoka and Zenji Hiroi Institute for Solid State Physics, University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8581 Abstract The discovery of
New β-pyrochlore Oxide Superconductor CsOs 2 O 6 Shigeki Yonezawa*, Yuji Muraoka and Zenji Hiroi Institute for Solid State Physics, University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8581 Abstract The discovery of
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based
 Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
state, spin-gap and a Böse-Einstein condensation under high fields. (CuBr)LaNb 2 O 7 shows a collinear antiferromagnetic order, (CuBr)Sr 2 Nb 3 O 10 h
 Cédric Tassel (Doctor Course student : 3 rd Kageyama) Department of Chemistry Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan. year)(supervised by Professor Hiroshi Proposal number:
Cédric Tassel (Doctor Course student : 3 rd Kageyama) Department of Chemistry Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan. year)(supervised by Professor Hiroshi Proposal number:
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La 0.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ) 0.3 CoO 3 System
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
BiS 2 - based superconductivity in F-substituted NdOBiS 2
 BiS 2 - based superconductivity in F-substituted NdOBiS 2 Satoshi Demura, 1,2 Yoshikazu Mizuguchi, 1,3 Keita Deguchi, 1,2 Hiroyuki Okazaki, 1 Hiroshi Hara, 1,2 Tohru Watanabe, 1,2 Saleem James Denholme,
BiS 2 - based superconductivity in F-substituted NdOBiS 2 Satoshi Demura, 1,2 Yoshikazu Mizuguchi, 1,3 Keita Deguchi, 1,2 Hiroyuki Okazaki, 1 Hiroshi Hara, 1,2 Tohru Watanabe, 1,2 Saleem James Denholme,
Phthalocyanine-Based Single-Component
 Phthalocyanine-Based Single-Component Molecular Conductor [Mn Ⅲ (Pc)(CN)] 2 O Mitsuo Ikeda, Hiroshi Murakawa, Masaki Matsuda, and Noriaki Hanasaki *, Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science,
Phthalocyanine-Based Single-Component Molecular Conductor [Mn Ⅲ (Pc)(CN)] 2 O Mitsuo Ikeda, Hiroshi Murakawa, Masaki Matsuda, and Noriaki Hanasaki *, Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science,
The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates. Abstract
 The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates Nicola Poccia, Michela Fratini Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome, P. Aldo Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: nicola.poccia@roma1.infn.it
The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates Nicola Poccia, Michela Fratini Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome, P. Aldo Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: nicola.poccia@roma1.infn.it
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction and structural analysis of Eu0.5La0.5FBiS2-xSex
 Synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction and structural analysis of Eu0.5La0.5FBiS2-xSex K. Nagasaka 1, G. Jinno 1, O. Miura 1, A. Miura 2, C. Moriyoshi 3, Y. Kuroiwa 3, Y. Mizuguchi 1 * 1. Department of Electrical
Synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction and structural analysis of Eu0.5La0.5FBiS2-xSex K. Nagasaka 1, G. Jinno 1, O. Miura 1, A. Miura 2, C. Moriyoshi 3, Y. Kuroiwa 3, Y. Mizuguchi 1 * 1. Department of Electrical
Crossbreeding between Experiment and Theory on Orthogonal Dimer Spin System
 Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement No. 4, 7 Crossbreeding between Experiment and Theory on Orthogonal Dimer Spin System Hiroshi Kageyama, Yutaka Ueda, Yasuo Narumi, Koichi Kindo, Masashi Kosaka
Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement No. 4, 7 Crossbreeding between Experiment and Theory on Orthogonal Dimer Spin System Hiroshi Kageyama, Yutaka Ueda, Yasuo Narumi, Koichi Kindo, Masashi Kosaka
MnO. Sr x. La 1-x. Temperature (K) Paramagnetic. Metal T C. Paramagnetic Insulator. Ferromagnetic. Metal T N. Ferromagnetic. Spin-canted Insulator
 Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides. Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625
 Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x. O 3 perovskite material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered
 Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors:
 Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite
Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite
Press Release. Discovery of a New Crystal Structure Family of Oxide-Ion. Conductors NdBaInO 4
 May 16, 2014 Tokyo Institute of Technology(Tokyo Tech) Ibaraki University Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization (ANSTO) Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) SPring-8
May 16, 2014 Tokyo Institute of Technology(Tokyo Tech) Ibaraki University Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization (ANSTO) Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) SPring-8
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials
 Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 2018](/thumbs/90/103904416.jpg) Room-temperature Low-field Colossal Magneto-resistance in Double-perovskite Manganite S. Yamada, N. Abe, H. Sagayama,, K. Ogawa, T. Yamagami, and T. Arima Department of Materials System Science, arxiv:8.07596v
Room-temperature Low-field Colossal Magneto-resistance in Double-perovskite Manganite S. Yamada, N. Abe, H. Sagayama,, K. Ogawa, T. Yamagami, and T. Arima Department of Materials System Science, arxiv:8.07596v
Electronic states of a strongly correlated two-dimensional system, Pd(dmit) 2 salts, controlled by uni-axial strain and counter cations
 J. Phys. IV France 114 (2004) 411-417 EDP Sciences, Les Ulis DOI: 10.1051/jp4:2004114099 411 Electronic states of a strongly correlated two-dimensional system, Pd(dmit) 2 salts, controlled by uni-axial
J. Phys. IV France 114 (2004) 411-417 EDP Sciences, Les Ulis DOI: 10.1051/jp4:2004114099 411 Electronic states of a strongly correlated two-dimensional system, Pd(dmit) 2 salts, controlled by uni-axial
Research Highlights. Salient results from our group. Mixed phosphides in Sn-P and Sn-Mn-P systems
 Research Highlights Dilute magnetic semiconductors and Spintronics Spintronics is a branch of electronics emerged from the dilute magnetic semiconductor in an aspect of utilization of the spin in addition
Research Highlights Dilute magnetic semiconductors and Spintronics Spintronics is a branch of electronics emerged from the dilute magnetic semiconductor in an aspect of utilization of the spin in addition
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/115260649.jpg) 1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Tb 2 Hf 2 O 7 R 2 B 2 7 R B R 3+ T N
 Tb Hf O 7 7 χ ac(t ) χ(t ) M(H) C p(t ) µ χ ac(t ) µ 7 7 7 R B 7 R B R 3+ 111 7 7 7 7 111 θ p = 19 7 7 111 7 15 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 T N.55 3+ 7 µ µ B 7 7 7 3+ 4f 8 S = 3 L = 3 J = 6 J + 1 = 13 7 F 6 3+ 7 7
Tb Hf O 7 7 χ ac(t ) χ(t ) M(H) C p(t ) µ χ ac(t ) µ 7 7 7 R B 7 R B R 3+ 111 7 7 7 7 111 θ p = 19 7 7 111 7 15 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 T N.55 3+ 7 µ µ B 7 7 7 3+ 4f 8 S = 3 L = 3 J = 6 J + 1 = 13 7 F 6 3+ 7 7
Phases of Na x CoO 2
 Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Charge and orbital ordering in Fe and Mn perovskite oxides far from half- doping by resonant x- ray scattering
 Charge and orbital ordering in Fe and Mn perovskite oxides far from half- doping by resonant x- ray scattering J Herrero-Martín 1, J García 2, G Subías 2, J Blasco 2, C Mazzoli 1 and M C Sánchez 2 1 European
Charge and orbital ordering in Fe and Mn perovskite oxides far from half- doping by resonant x- ray scattering J Herrero-Martín 1, J García 2, G Subías 2, J Blasco 2, C Mazzoli 1 and M C Sánchez 2 1 European
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Courtesy of Ray Withers Electron Diffraction and the Structural Characterization of Modulated and Aperiodic Structures
 Courtesy of Ray Withers Electron Diffraction and the Structural Characterization of Modulated and Aperiodic Structures What do we mean by a modulated structure? The standard answer is a material whose
Courtesy of Ray Withers Electron Diffraction and the Structural Characterization of Modulated and Aperiodic Structures What do we mean by a modulated structure? The standard answer is a material whose
Factors Affecting the Magnitude of the Metal-Insulator Transition Temperature Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2004, Vol. 25, No
 Factors Affecting the Magnitude of the Metal-Insulator Transition Temperature Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2004, Vol. 25, No. 7 959 Articles Factors Affecting the Magnitude of the Metal-Insulator Transition
Factors Affecting the Magnitude of the Metal-Insulator Transition Temperature Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2004, Vol. 25, No. 7 959 Articles Factors Affecting the Magnitude of the Metal-Insulator Transition
YBCO. CuO 2. the CuO 2. planes is controlled. from deviation from. neutron. , blue star for. Hg12011 (this work) for T c = 72
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal structures and joint phase diagram of Hg1201 and YBCO. (a) Hg1201 features tetragonal symmetry and one CuO 2 plane per primitive cell. In the superconducting (SC) doping
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal structures and joint phase diagram of Hg1201 and YBCO. (a) Hg1201 features tetragonal symmetry and one CuO 2 plane per primitive cell. In the superconducting (SC) doping
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface
 What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method
 Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7
 J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
Epitaxially stabilized iridium spinel oxide without cations in the tetrahedral site
 Epitaxially stabilized iridium spinel oxide without cations in the tetrahedral site Hiromichi Kuriyama, 1,2 Jobu Matsuno, 2 Seiji Niitaka, 2 Masaya Uchida, 2 Daisuke Hashizume, 2 Aiko Nakao, 2 Kunihisa
Epitaxially stabilized iridium spinel oxide without cations in the tetrahedral site Hiromichi Kuriyama, 1,2 Jobu Matsuno, 2 Seiji Niitaka, 2 Masaya Uchida, 2 Daisuke Hashizume, 2 Aiko Nakao, 2 Kunihisa
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study
 Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
of Spontaneous and field-induced
 Magneto-Optics of Spontaneous and field-induced induced Vortices in twinned YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ /La 1-x Sr x MnO 3 bilayers Superconductivity Group (Politecnico di Torino): Roberto Gerbaldo, Gianluca Ghigo,
Magneto-Optics of Spontaneous and field-induced induced Vortices in twinned YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ /La 1-x Sr x MnO 3 bilayers Superconductivity Group (Politecnico di Torino): Roberto Gerbaldo, Gianluca Ghigo,
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Jun 2009
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Jun 2009 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Jun 2009](/thumbs/81/82959427.jpg) Structural distortion and frustrated magnetic interactions in the layered copper oxychloride (CuCl)LaNb 2 O 7 arxiv:0901.0154v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Jun 2009 Alexander A. Tsirlin 1, 2, and Helge Rosner
Structural distortion and frustrated magnetic interactions in the layered copper oxychloride (CuCl)LaNb 2 O 7 arxiv:0901.0154v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Jun 2009 Alexander A. Tsirlin 1, 2, and Helge Rosner
compound Cs 2 Cu 2 Mo 3 O 12
 133 Cs-NMR study on aligned powder of competing spin chain compound A Yagi 1, K Matsui 1 T Goto 1, M Hase 2 and T Sasaki 3 1 2 Sophia University, Physics Division, Tokyo, 102-8554, Japan National Institute
133 Cs-NMR study on aligned powder of competing spin chain compound A Yagi 1, K Matsui 1 T Goto 1, M Hase 2 and T Sasaki 3 1 2 Sophia University, Physics Division, Tokyo, 102-8554, Japan National Institute
Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Electronic Higher Multipoles in Solids
 Electronic Higher Multipoles in Solids Yoshio Kuramoto Department of Physics, Tohoku University Outline Elementary examples of multiple moments Role of multipole moments in solids Case studies octupole
Electronic Higher Multipoles in Solids Yoshio Kuramoto Department of Physics, Tohoku University Outline Elementary examples of multiple moments Role of multipole moments in solids Case studies octupole
Search for conducting stripes in lightly hole doped YBCO
 Search for conducting stripes in lightly hole doped YBCO András Jánossy 1, Titusz Fehér 1,2 Kálmán Nagy 1 Andreas Erb 3 László Mihály 4 1 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Institute of Physics
Search for conducting stripes in lightly hole doped YBCO András Jánossy 1, Titusz Fehér 1,2 Kálmán Nagy 1 Andreas Erb 3 László Mihály 4 1 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Institute of Physics
Structural and magnetic phase diagram of CeFeAsO 1-x F x and. its relationship to high-temperature superconductivity
 Structural and magnetic phase diagram of CeFeAsO 1-x F x and its relationship to high-temperature superconductivity Jun Zhao 1, Q. Huang 2, Clarina de la Cruz 1,3, Shiliang Li 1, J. W. Lynn 2, Y. Chen
Structural and magnetic phase diagram of CeFeAsO 1-x F x and its relationship to high-temperature superconductivity Jun Zhao 1, Q. Huang 2, Clarina de la Cruz 1,3, Shiliang Li 1, J. W. Lynn 2, Y. Chen
Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds
 Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds M. Suzuki and I.S. Suzuki Department of Physics, State University of New York at Binghamton (October, ) I. INTRODUCTION In recent years
Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds M. Suzuki and I.S. Suzuki Department of Physics, State University of New York at Binghamton (October, ) I. INTRODUCTION In recent years
PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB
![PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB](/thumbs/84/91030401.jpg) Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
Solid State Spectroscopy Problem Set 7
 Solid State Spectroscopy Problem Set 7 Due date: June 29th, 2015 Problem 5.1 EXAFS Study of Mn/Fe substitution in Y(Mn 1-x Fe x ) 2 O 5 From article «EXAFS, XANES, and DFT study of the mixed-valence compound
Solid State Spectroscopy Problem Set 7 Due date: June 29th, 2015 Problem 5.1 EXAFS Study of Mn/Fe substitution in Y(Mn 1-x Fe x ) 2 O 5 From article «EXAFS, XANES, and DFT study of the mixed-valence compound
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials
 Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
SESSION 2. (September 26, 2000) B. Lake Spin-gap and magnetic coherence in a high-temperature superconductor
 SESSION 2 (September 26, 2000) Spin fluctuations and stripes - I S2-I G. Shirane Stripes in Sr doped La 2 CuO 4 insulators and superconductors S2-II B. Lake Spin-gap and magnetic coherence in a high-temperature
SESSION 2 (September 26, 2000) Spin fluctuations and stripes - I S2-I G. Shirane Stripes in Sr doped La 2 CuO 4 insulators and superconductors S2-II B. Lake Spin-gap and magnetic coherence in a high-temperature
Evolution of superconductivity in LaO 1-x F x BiS 2 prepared by high pressure technique
 Evolution of superconductivity in LaO 1-x F x BiS 2 prepared by high pressure technique K. Deguchi 1,2,3, Y. Mizuguchi 1,2,4, S. Demura 1,2,3, H. Hara 1,2,3, T. Watanabe 1,2,3, S. J. Denholme 1,2, M. Fujioka
Evolution of superconductivity in LaO 1-x F x BiS 2 prepared by high pressure technique K. Deguchi 1,2,3, Y. Mizuguchi 1,2,4, S. Demura 1,2,3, H. Hara 1,2,3, T. Watanabe 1,2,3, S. J. Denholme 1,2, M. Fujioka
Hole-concentration dependence of band structure in (Bi,Pb) 2 (Sr,La) 2 CuO 6+δ determined by the angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
 Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena 137 140 (2004) 663 668 Hole-concentration dependence of band structure in (Bi,Pb) 2 (Sr,La) 2 CuO 6+δ determined by the angle-resolved photoemission
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena 137 140 (2004) 663 668 Hole-concentration dependence of band structure in (Bi,Pb) 2 (Sr,La) 2 CuO 6+δ determined by the angle-resolved photoemission
Striping in Cuprates. Michael Bertolli. Solid State II Elbio Dagotto Spring 2008 Department of Physics, Univ. of Tennessee
 Striping in Cuprates Michael Bertolli Solid State II Elbio Dagotto Spring 2008 Department of Physics, Univ. of Tennessee Outline Introduction Basics of Striping Implications to Superconductivity Experimental
Striping in Cuprates Michael Bertolli Solid State II Elbio Dagotto Spring 2008 Department of Physics, Univ. of Tennessee Outline Introduction Basics of Striping Implications to Superconductivity Experimental
SESSION 3. Lattice fluctuations and stripes - I. (September 26, 2000) S3-I S3-II S3-III S3-IV S3-V. E. Kaldis New aspects of Ca doping in 123
 SESSION 3 (September 26, 2000) Lattice fluctuations and stripes - I S3-I E. Kaldis New aspects of Ca doping in 123 S3-II H. Oyanagi Local lattice distortions in YBa 2 Cu 3 O y single crystal: Phase separation
SESSION 3 (September 26, 2000) Lattice fluctuations and stripes - I S3-I E. Kaldis New aspects of Ca doping in 123 S3-II H. Oyanagi Local lattice distortions in YBa 2 Cu 3 O y single crystal: Phase separation
Anisotropic spin-correlations in the Zn-Mg-Ho icosahedral quasicrystal
 Anisotropic spin-correlations in the Zn-Mg-Ho icosahedral quasicrystal Taku J SATO 1, Hiroyuki TAKAKURA 1,, An Pang TSAI 1 and Kaoru SHIBATA 3 1 National Research Institute for Metals, Tsukuba 35-47, JAPAN
Anisotropic spin-correlations in the Zn-Mg-Ho icosahedral quasicrystal Taku J SATO 1, Hiroyuki TAKAKURA 1,, An Pang TSAI 1 and Kaoru SHIBATA 3 1 National Research Institute for Metals, Tsukuba 35-47, JAPAN
High temperature superconductivity
 High temperature superconductivity Applications to the maglev industry Elsa Abreu April 30, 2009 Outline Historical overview of superconductivity Copper oxide high temperature superconductors Angle Resolved
High temperature superconductivity Applications to the maglev industry Elsa Abreu April 30, 2009 Outline Historical overview of superconductivity Copper oxide high temperature superconductors Angle Resolved
Time-Resolved and Momentum-Resolved Resonant Soft X-ray Scattering on Strongly Correlated Systems
 Time-Resolved and Momentum-Resolved Resonant Soft X-ray Scattering on Strongly Correlated Systems Wei-Sheng Lee Stanford Institute of Material and Energy Science (SIMES) SLAC & Stanford University Collaborators
Time-Resolved and Momentum-Resolved Resonant Soft X-ray Scattering on Strongly Correlated Systems Wei-Sheng Lee Stanford Institute of Material and Energy Science (SIMES) SLAC & Stanford University Collaborators
Phase Transitions in Relaxor Ferroelectrics
 Phase Transitions in Relaxor Ferroelectrics Matthew Delgado December 13, 2005 Abstract This paper covers the properties of relaxor ferroelectrics and considers the transition from the paraelectric state
Phase Transitions in Relaxor Ferroelectrics Matthew Delgado December 13, 2005 Abstract This paper covers the properties of relaxor ferroelectrics and considers the transition from the paraelectric state
Effect of Pressure on the Electronic state in Eu- Divalent EuTIn4 (T: Ni, Pd, Pt, Au) Compounds
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Effect of Pressure on the Electronic state in Eu- Divalent EuTIn4 (T: Ni, Pd, Pt, Au) Compounds To cite this article: M Hedo et al 1 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Effect of Pressure on the Electronic state in Eu- Divalent EuTIn4 (T: Ni, Pd, Pt, Au) Compounds To cite this article: M Hedo et al 1 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Material Science II. d Electron systems
 Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6
 Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Observation of quadrupole helix chirality and its domain structure in DyFe 3 (BO 3 ) 4
 Observation of quadrupole helix chirality and its domain structure in DyFe 3 (BO 3 ) 4 T. Usui, Y. Tanaka, H. Nakajima, M. Taguchi, A. Chainani, M. Oura, S. Shin, N. Katayama, H. Sawa, Y. Wakabayashi,
Observation of quadrupole helix chirality and its domain structure in DyFe 3 (BO 3 ) 4 T. Usui, Y. Tanaka, H. Nakajima, M. Taguchi, A. Chainani, M. Oura, S. Shin, N. Katayama, H. Sawa, Y. Wakabayashi,
New Li-Ethylenediamine-Intercalated Superconductor Li x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 with T c = 45 K
 New Li-Ethylenediamine-Intercalated Superconductor Li x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 with T c = 45 K Takehiro Hatakeda, Takashi Noji, Takayuki Kawamata, Masatsune Kato, and Yoji Koike Department of Applied
New Li-Ethylenediamine-Intercalated Superconductor Li x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 with T c = 45 K Takehiro Hatakeda, Takashi Noji, Takayuki Kawamata, Masatsune Kato, and Yoji Koike Department of Applied
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/117739901.jpg) Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
University of Groningen. Orbital ordering and multiferroics Nenert, Gwilherm
 University of Groningen Orbital ordering and multiferroics Nenert, Gwilherm IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Orbital ordering and multiferroics Nenert, Gwilherm IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Neutron Powder Diffraction: a powerful technique for studying structural and magnetic phase transitions
 Neutron Powder Diffraction: a powerful technique for studying structural and magnetic phase transitions A-site ordered perovskite YBaMn 2 O 6 : atomic versus larger scales charge ordering Juan Rodríguez-Carvajal
Neutron Powder Diffraction: a powerful technique for studying structural and magnetic phase transitions A-site ordered perovskite YBaMn 2 O 6 : atomic versus larger scales charge ordering Juan Rodríguez-Carvajal
T. Hatakeda, T. Noji, S. Hosono, T. Kawamata, M. Kato, and Y. Koike
 Resistive superconducting transition and effects of atmospheric exposure in the intercalation superconductor A x (A = Li, Na) T. Hatakeda, T. Noji, S. Hosono, T. Kawamata, M. Kato, and Y. Koike Department
Resistive superconducting transition and effects of atmospheric exposure in the intercalation superconductor A x (A = Li, Na) T. Hatakeda, T. Noji, S. Hosono, T. Kawamata, M. Kato, and Y. Koike Department
Direct observation of electron density reconstruction at the metalinsulator
 Direct observation of electron density reconstruction at the metalinsulator transition in NaOsO3 31 st July 2018 N. Gurung, 1,2 N. Leo, 1,2 S. P. Collins, 3 G. Nisbet, 3 G. Smolentsev 2, M. García-Fernández,
Direct observation of electron density reconstruction at the metalinsulator transition in NaOsO3 31 st July 2018 N. Gurung, 1,2 N. Leo, 1,2 S. P. Collins, 3 G. Nisbet, 3 G. Smolentsev 2, M. García-Fernández,
The Metal-Insulator Transition in Correlated Disordered Systems
 Page 1 of 6 Institution: RUTGERS UNIVERSITY Sign In as Individual FAQ Access Rights Join AAAS The Metal-Insulator Transition in Correlated Disordered Systems Summary of this Article debates: Submit a response
Page 1 of 6 Institution: RUTGERS UNIVERSITY Sign In as Individual FAQ Access Rights Join AAAS The Metal-Insulator Transition in Correlated Disordered Systems Summary of this Article debates: Submit a response
Bipartite magnetic parent phases in the iron oxypnictide superconductor
 M. Hiraishi 1, S. Iimura 2, K. M. Kojima 1,3*, J. Yamaura 4, H. Hiraka 1, K. Ikeda 1, P. Miao 1,3, Y. Ishikawa 1, S. Torii 1, M. Miyazaki 1, I. Yamauchi 1, A. Koda 1,3, K. Ishii 5, M. Yoshida 5,6, J. Mizuki
M. Hiraishi 1, S. Iimura 2, K. M. Kojima 1,3*, J. Yamaura 4, H. Hiraka 1, K. Ikeda 1, P. Miao 1,3, Y. Ishikawa 1, S. Torii 1, M. Miyazaki 1, I. Yamauchi 1, A. Koda 1,3, K. Ishii 5, M. Yoshida 5,6, J. Mizuki
Proceedings of the International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES3) Downloaded from journals.jps.jp by on /6/7 JPS
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES3) Downloaded from journals.jps.jp by 37.44.96.39 on /6/7 Proc. Int. Conf. Strongly Correlated Electron Systems
Proceedings of the International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES3) Downloaded from journals.jps.jp by 37.44.96.39 on /6/7 Proc. Int. Conf. Strongly Correlated Electron Systems
C1.7.2 Neutron Techniques: Crystallography
 C1.7.2 Neutron Techniques: Crystallography Why use Neutrons? Ceramic superconductors are generally heavy metal oxides, and neutron diffraction has long been superior for the precise location of light atoms,
C1.7.2 Neutron Techniques: Crystallography Why use Neutrons? Ceramic superconductors are generally heavy metal oxides, and neutron diffraction has long been superior for the precise location of light atoms,
Lecture 5: Characterization methods
 Lecture 5: Characterization methods X-Ray techniques Single crystal X-Ray Diffration (XRD) Powder XRD Thin film X-Ray Reflection (XRR) Microscopic methods Optical microscopy Electron microscopies (SEM,
Lecture 5: Characterization methods X-Ray techniques Single crystal X-Ray Diffration (XRD) Powder XRD Thin film X-Ray Reflection (XRR) Microscopic methods Optical microscopy Electron microscopies (SEM,
EPR in Kagome Staircase Compound Mg Co V 2 O 8
 Vol. 111 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 1 Proceedings of the Symposium K: Complex Oxide Materials for New Technologies of E-MRS Fall Meeting 2006, Warsaw, September 4 8, 2006 EPR in Kagome Staircase
Vol. 111 (2007) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 1 Proceedings of the Symposium K: Complex Oxide Materials for New Technologies of E-MRS Fall Meeting 2006, Warsaw, September 4 8, 2006 EPR in Kagome Staircase
doi: /PhysRevLett
 doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
Bonding Nature in MgB 2
 Bonding Nature in MgB 2 E.Nishibori, M.Takata*, M.Sakata, H.Tanaka 1, T.Muranaka 2, J.Akimitsu 2 Department of Applied Physics, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8603, Japan 1 Department of Material Science,
Bonding Nature in MgB 2 E.Nishibori, M.Takata*, M.Sakata, H.Tanaka 1, T.Muranaka 2, J.Akimitsu 2 Department of Applied Physics, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8603, Japan 1 Department of Material Science,
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
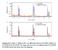 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
X-ray spectroscopy and diffraction experiments by using mini-coils: applications to valence state transitions and frustrated magnets
 X-ray spectroscopy and diffraction experiments by using mini-coils: applications to valence state transitions and frustrated magnets H. Nojiri, IMR Tohoku Univ., Sendai Japan http:spin100.imr.tohoku.ac.jp
X-ray spectroscopy and diffraction experiments by using mini-coils: applications to valence state transitions and frustrated magnets H. Nojiri, IMR Tohoku Univ., Sendai Japan http:spin100.imr.tohoku.ac.jp
Nanostructure Fabrication Using Selective Growth on Nanosize Patterns Drawn by a Scanning Probe Microscope
 Nanostructure Fabrication Using Selective Growth on Nanosize Patterns Drawn by a Scanning Probe Microscope Kentaro Sasaki, Keiji Ueno and Atsushi Koma Department of Chemistry, The University of Tokyo,
Nanostructure Fabrication Using Selective Growth on Nanosize Patterns Drawn by a Scanning Probe Microscope Kentaro Sasaki, Keiji Ueno and Atsushi Koma Department of Chemistry, The University of Tokyo,
The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+±
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
shows the difference between observed (black) and calculated patterns (red). Vertical ticks indicate
 Intensity (arb. unit) a 5 K No disorder Mn-Pt disorder 5 K Mn-Ga disorder 5 K b 5 K Observed Calculated Difference Bragg positions 24 28 32 2 4 6 8 2 4 2θ (degree) 2θ (degree) Supplementary Figure. Powder
Intensity (arb. unit) a 5 K No disorder Mn-Pt disorder 5 K Mn-Ga disorder 5 K b 5 K Observed Calculated Difference Bragg positions 24 28 32 2 4 6 8 2 4 2θ (degree) 2θ (degree) Supplementary Figure. Powder
Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Electrochemical synthesis and properties of CoO 2, the x = 0 phase of the A x CoO 2 systems (A = Li, Na)
 Journal of Applied Physics 103, 07C902 (2008) Proceedings of 52nd Magnetism and Magnetic Materials Conference Electrochemical synthesis and properties of CoO 2, the x = 0 phase of the A x CoO 2 systems
Journal of Applied Physics 103, 07C902 (2008) Proceedings of 52nd Magnetism and Magnetic Materials Conference Electrochemical synthesis and properties of CoO 2, the x = 0 phase of the A x CoO 2 systems
Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies.
 PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ultrathin Spinel-Structured Nanosheets Rich in Oxygen Deficiencies for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation** Jian Bao, Xiaodong Zhang,* Bo Fan, Jiajia Zhang, Min Zhou, Wenlong
Supporting Information Ultrathin Spinel-Structured Nanosheets Rich in Oxygen Deficiencies for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation** Jian Bao, Xiaodong Zhang,* Bo Fan, Jiajia Zhang, Min Zhou, Wenlong
Structural Characterization of Substituted Calcium Titanate Compounds Ca 1-X La X Ti 1-x Fe x O 3
 Egypt. J. Solids, Vol. (27), No. (2), (2004) 213 Structural Characterization of Substituted Calcium Titanate Compounds Ca 1-X La X Ti 1-x Fe x O 3 A.M. Moustafa 1, I.S Ahmed Farag 1 and L.M. Salah 2 1
Egypt. J. Solids, Vol. (27), No. (2), (2004) 213 Structural Characterization of Substituted Calcium Titanate Compounds Ca 1-X La X Ti 1-x Fe x O 3 A.M. Moustafa 1, I.S Ahmed Farag 1 and L.M. Salah 2 1
Refinement of X-ray Fluorescence Holography for Determination of Local Atomic Environment
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 7 (2002) pp. 1464 to 1468 Special Issue on Grain Boundaries, Interfaces, Defects and Localized Quantum Structure in Ceramics c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals Refinement
Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 7 (2002) pp. 1464 to 1468 Special Issue on Grain Boundaries, Interfaces, Defects and Localized Quantum Structure in Ceramics c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals Refinement
Neutron Powder Diffraction Theory and Instrumentation
 NTC, Taiwen Aug. 31, 212 Neutron Powder Diffraction Theory and Instrumentation Qingzhen Huang (qing.huang@nist.gov) NIST Center for Neutron Research (www.ncnr.nist.gov) Definitions E: energy; k: wave vector;
NTC, Taiwen Aug. 31, 212 Neutron Powder Diffraction Theory and Instrumentation Qingzhen Huang (qing.huang@nist.gov) NIST Center for Neutron Research (www.ncnr.nist.gov) Definitions E: energy; k: wave vector;
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2. Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1. Germany.
 Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
Neutron scattering experiments on low-dimensional quantum spin systemsðspin excitations in KCuCl 3 and SrCu 2 (BO 3 ) 2
 Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 62 (2001) 141±147 www.elsevier.nl/locate/jpcs Neutron scattering experiments on low-dimensional quantum spin systemsðspin excitations in KCuCl 3 and SrCu 2 (BO
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 62 (2001) 141±147 www.elsevier.nl/locate/jpcs Neutron scattering experiments on low-dimensional quantum spin systemsðspin excitations in KCuCl 3 and SrCu 2 (BO
NEUTRON SCATTERING STUDY OF ANTIFERROMAGNETIC CORRELATIONS IN THE Zn-Mg-Ho ICOSAHEDRAL QUASICRYSTAL
 NEUTRON SCATTERING STUDY OF ANTIFERROMAGNETIC CORRELATIONS IN THE Zn-Mg-Ho ICOSAHEDRAL QUASICRYSTAL Taku J. SATO, Hiroyuki TAKAKURA,, An Pang TSAI, Kaoru SHIBATA, Kenji OHOYAMA and Ken H. ANDERSEN National
NEUTRON SCATTERING STUDY OF ANTIFERROMAGNETIC CORRELATIONS IN THE Zn-Mg-Ho ICOSAHEDRAL QUASICRYSTAL Taku J. SATO, Hiroyuki TAKAKURA,, An Pang TSAI, Kaoru SHIBATA, Kenji OHOYAMA and Ken H. ANDERSEN National
NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES OF THE MAGNETIC FLUCTUATIONS IN YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7¹d
 Pergamon PII: S0022-3697(98)00196-6 J. Phys. Chem Solids Vol 59, No. 10 12, pp. 2140 2144, 1998 0022-3697/98/$ - see front matter 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES
Pergamon PII: S0022-3697(98)00196-6 J. Phys. Chem Solids Vol 59, No. 10 12, pp. 2140 2144, 1998 0022-3697/98/$ - see front matter 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved NEURON SCATTERING STUDIES
Dielectric and Magnetic Behavior of Polycrystalline Copper Doped Holmium Orthoferrite
 Dielectric and Magnetic Behavior of Polycrystalline Copper Doped Holmium Orthoferrite Fumiya Tsunawaki, Mitsuhiro Matsuo, Hirokazu Shimooka, and Shigemi Kohiki Department of Materials Science, Kyushu Institute
Dielectric and Magnetic Behavior of Polycrystalline Copper Doped Holmium Orthoferrite Fumiya Tsunawaki, Mitsuhiro Matsuo, Hirokazu Shimooka, and Shigemi Kohiki Department of Materials Science, Kyushu Institute
Field-Temperature Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Phases in Ludvigites Ni 3-x Mn x BO 5
 Field-Temperature Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Phases in Ludvigites Ni 3-x Mn x BO 5 L. N. Bezmaternykh, E. M. Kolesnikova*, E. V. Eremin, S. N. Sofronova, N. V. Volkov, and M. S. Molokeev Kirensky Institute
Field-Temperature Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Phases in Ludvigites Ni 3-x Mn x BO 5 L. N. Bezmaternykh, E. M. Kolesnikova*, E. V. Eremin, S. N. Sofronova, N. V. Volkov, and M. S. Molokeev Kirensky Institute
