Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
|
|
|
- Justin Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL* Department of Physics, University of Kalyani, Nadia , India MS received 23 May 2013; revised 12 July 2013 Abstract. Detailed magnetic properties of Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7) have been reported. All the samples crystallize in orthorhombic perovskite structure with Pnma space group. Magnetization measurements under field cooled (FC) protocal reveal magnetization reversal at low temperatures and low magnetic field. This indicates clear evidence of two magnetic sublattices aligned opposite to each other. There is a well-defined maximum around 48 K in the x = 0 7 sample (i.e. Pr 0 3 Nd 0 7 MnO 3 ) in the χ value which is identified as paramagnetic to ferrimagnetic transition. The peak value shifts to higher temperature with decrease of x and width of the maximum broadened. It is also observable that with decrease of Nd, both the value of χ and χ decrease. An attempt is made to explain the magnetization reversal within the framework of available models. Keywords. Manganites; magnetic transition; exchange interaction; magnetization reversal. 1. Introduction The subject of magnetization reversal in rare earth oxides has received considerable attention in recent years. The magnetic moments of rare earth ions are polarized due to the coupling with the Mn subsystem resulting in a noticeable anisotropic contribution to the low-temperature magnetic and thermodynamic properties of the manganites as observed in PrMnO 3 and NdMnO 3 (Hemberger et al 2004; Hong et al 2012). In rare earth manganites, if rare earth ion is replaced by another rare earth ion, interesting changes in transport and magnetic properties occur. In Nd 1 x Ce x MnO 3, Nd is substituted by Ce and these types of manganites contain Mn 3+ and Mn 2+ sublattices. DE interaction between these sublattices explains the FM, AFM nature with temperature and low-temperature magnetization reversal phenomena (Zhang et al 2005). This kind of magnetic phenomena have also been observed in GdCrO 3 (Yoshii 2001), Gd 0 7 Ca 0 3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 (Biswas et al 2013), Bi 0 3 Ca 0 7 Mn 0 75 Cr 0 25 O 3 (Zhang et al 2012), Sr 2 YbRuO 6 (Singh and Tomy 2008), La 1 x Gd x MnO 3 (Hemberger et al 2004), La 0 5 Gd 0 5 CrO 3 (Sharma et al 2010), La 1 x Pr x CrO 3 (Yoshii et al 2001) and La 1 x Ce x CrO 3 (Manna et al 2010). In GdCrO 3, rare earth Gd and transition metal Cr are canted or aligned in opposite direction. Again in Gd 0 7 Ca 0 3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3, Gd is aligned against Cr and Mn ions. In Bi 0 3 Ca 0 7 Mn 0 75 Cr 0 25 O 3, Mn and Cr are canted in opposite direction and Ru and Yb are canted in opposite direction in Sr 2 YbRuO 6. Again for being La 3+ non-magnetic, reversal of magnetization in *Author for correspondence (sudipta.pal@rediffmail.com) La 0 5 Gd 0 5 CrO 3 is due to canted opposite direction magnetic moment of Gd and Cr. For all these compounds, reversal of magnetization phenomena are explained considering two sublattice systems which are aligned antiparallel to each other. The magnetization reversal phenomena in YFe 1 x Mn x O 3 (Mandal et al 2013) can be explained by random occupation of magnetic ions and different magnetic interactions like Fe O Fe, Fe O Mn and Mn O Mn. Again in NdMnO 3 (Hong et al 2012), the negative magnetization phenomena has been explained by considering Nd 3+ and Mn 3+ are canted in opposite direction. In this report, we have investigated Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 compounds and it is interesting to observe how the magnetic properties change with doping of Nd ions in place of Pr. 2. Experimental Polycrystalline samples of the composition, Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7) were prepared in air via solid state reaction method. The precursors Pr 6 O 11, Nd 2 O 3 and MnO 2 were mixed in proper stoichiometric ratio. They were heated at 900 C for 24 h. Then, the powder was pelletized and fired in air at 1500 C for 24 h and the furnace was cooled down to room temperature at a rate of 100 C/h. The room temperature crystal structure was determined by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements using CuKα radiation (Philips diffractometer). The lattice parameters were obtained from the Rietveld analysis of XRD data using FULLPROF program (Rodrigues-Carvajal et al 1993). Quantum design magnetometer was used to collect the a.c. magnetic susceptibility and d.c. magnetization data. 809
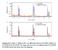
2 810 Sanjay Biswas, Momin Hossain Khan and Sudipta Pal Figure 1. X-ray diffraction spectrum of Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7). Table 1. Values of lattice parameters of Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3. Compounds a ± 10 3 (Å) b ± 10 3 (Å) c ± 10 3 (Å) V ± 10 3 (Å 3 ) Pr 0 7 Nd 0 3 MnO Pr 0 5 Nd 0 5 MnO Pr 0 3 Nd 0 7 MnO Results and discussion Powder X-ray diffraction pattern, taken at room temperature and shown in figure 1, revealed a single phase orthorhombic Pbnm structure for all the samples. The lattice parameters are tabulated in table 1. For all concentrations, we obtained b > a > c/ 2 indicative of a static JT distortion. The values of lattice parameters of present Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7) solid solution are observed in between the values of end members PrMnO 3 and NdMnO 3 (Hemberger et al 2004). Very small change in the lattice parameters is observed with change of x. The lattice parameters decrease with the increase of x, which results from the substitution of smaller Nd 3+ (1 08 Å) in place of Pr 3+ (1 09 Å). The temperature dependence of the a.c. susceptibility has been shown in figures 2(a and b). The in-phase and quadrature components of a.c. susceptibility (χ and χ ) show a number of features. A well-defined peak is observed for all the compounds. There is well-defined maximum around 48 K in the x = 0 7 sample (i.e. Pr 0 3 Nd 0 7 MnO 3 ), which is assumed as a paramagnetic to ferrimagnetic transition according to earlier reports (Snyder et al 1997; Pena et al 2002). The width of the maximum broadened as well as shifted to the higher temperature with decrease of x and an additional maximum around 20 K is observed for x = 0 3 compound. It is remarkable to note that the anomalies associated with the magnetic ordering starts building at temperature around K in the compounds. It is also observable that with decrease of Nd, both the values of χ and χ decrease. In χ value, sharp peak is observed around K depending on the composition of the compounds. Similar peak in χ has been reported in NdMnO 3 compound and it was
3 Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO ascribed as the orientation of Mn spins (Wu et al 2000). The two anomalies, both in the real and imaginary susceptbility data for x = 0 3 sample indicate that Mn orders at first antiferromagnetically with canted spin configuration and the rare earth moments subsequently couple antiferromagnetically with the canted moments of Mn. It is interesting to note that due to the magnetic anisotropy in the sample at low temperature, the values of χ slightly deviated from Curie Weiss behaviour. Above the transition temperature (T max ), χ shows a ferromagnetic character (as shown in figure 3) and follows a Curie Weiss behaviour as for ferromagnetic system, χ = μ 2 eff/[8(t Θ], with Θ positive. The value of Θ has been obtained as 54, 58 and 71 for x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7, respectively. Positive paramagnetic temperature, Θ, is obtained for all the compounds by extrapolating (χ) 1 to 0 indicating the presence of ferromagnetic interaction in all the compounds. Now, from quantum mechanical spins μ eff per mole for Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7) are 5 839, and μ B, respectively. The Curie Weiss law gives μ eff per mole for Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7) which are 5 548, and μ B, respectively. So, the experimental value agrees well with the theoretical estimation. Small deviation from the theoretical value could be explained considering that some of the ions Pr + Nd in the ferromagnetic network are aligned or canted in the direction of Mn ions due to the magnetic anisotropy in the compounds for doping. Figure 4 provides temperature dependence d.c. magnetization of Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7). The d.c. magnetization has been measured in the external Figure 3. Temperature-dependent inverse d.c. susceptibility of Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7). Solid line is the high temperature fit using χ = μ 2 eff /[8(T Θ)]. Figure 2. (a) Plot of T-dependent real a.c. susceptibility (χ ) of Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7) compounds recorded at 10 Oe a.c. field and (b) plot of T-dependent imaginary a.c. susceptibility (χ ) of Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7) compounds. Figure 4. D.C. magnetization M vs temperature in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 (x = 0 3, 0 5 and 0 7) in FC mode. Solid line shows Curie Weiss type fitting of M T data recorded in FC mode under 50 Oe.
4 812 Sanjay Biswas, Momin Hossain Khan and Sudipta Pal Table 2. Fitting parameters for M T curves recorded in FC mode. Compounds M Mn ± 10 3 (μ B /mol) H int ± 10 2 (Oe) θ w ± 10 2 (K) Pr 0 7 Nd 0 3 MnO Pr 0 5 Nd 0 5 MnO Pr 0 3 Nd 0 7 MnO Figure 5. M H curves recorded for Pr 0 5 Nd 0 5 MnO 3 : (a) at 2 K, (b) at 20 K, (c) at 50 K and (d) at 80 K. applied field 50 Oe in ZFC and FC processes. Interesting features can be observed in FC magnetization properties. In the sample, x = 0 3 and 0 5, FC magnetization becomes zero around 18 and 22 K, respectively. This can be considered as compensation point. FC magnetization goes through a positive maximum, before reaching the compensation point. The temperature at the maximum is considered as T max. Upon further decrease of temperature, the magnetization becomes negative. At 5 K, the value of magnetization reaches 0 1 and 0 14 μ B /mol for x = 0 3 and 0 5, respectively. FC magnetization in x = 0 7 sample does not show negative value up to 5 K. The negative FC magnetization observed only in the solid solutions may have a correlation with the weakening of anisotropy around Pr 3+, arising from the substitution of Nd 3+. With decreasing temperatures, the Pr and Nd spins are more and more aligned in the opposite direction of the exchange field of the manganese moments, following a Curie-type temperature dependence and finally, yielding a negative magnetization at the lowest temperatures, when the polarization of the Pr + Nd spins exceeds FM component of Mn moments. The solid lines in figure 4(b) shows that the negative magnetization, M, can well be approximated by (Manna et al 2010; Sharma et al 2010): CNd ( Hint + Hext ) M = MMn +, T θ W where M Mn is the canted moment of Mn, H int the internal field due to the canted Mn moment, H ext the applied field, C Nd the Curie constant (1 59) and θ w the Weiss constant. The limitation of this analysis is the assumption that M Mn and H int are independent of temperature, which is usually true, if T << T N. In the present case, this may not be true and hence the value obtained will only be an approximation. The parameters obtained from the fitting using (1) are given in table 2. Similar results have been observed for GdCrO 3 (Yoshii 2001), Bi 0 3 Ca 0 7 Mn 0 75 Cr 0 25 O 3 (Zhang et al 2012), Sr 2 YbRuO 6 (Singh and Tomy 2008) and La 0 5 Gd 0 5 CrO 3 (Sharma et al 2010). In these samples, negative magnetization is explained considering two (1)
5 Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO sublattices in opposite direction. The positive value of M Mn is consistent with the result that FC magnetization goes through a positive maximum before reaching the compensation point and M Mn was used as a fitting parameter and considered to be constant well below the temperature T max. Actually, in our samples, the reversal of magnetization can easily be understood considering M Mn is parallel to the applied field, while M Pr+Nd are antiparallel to it. As the temperature decreases, the disordered Pr + Nd ions begin to polarize against the canted field of M Mn moments. As a result, the net magnetization of the system is M S = M Mn M Pr+Nd. As the temperature decreases from T max, M Pr+Nd increases much faster than M Mn. At the compensation point of magnetization, the two sublattices are equal and net magnetization becomes zero. And below the compensation temperature, the net magnetization becomes negative. For better understanding of the magnetic property, field-dependent magnetization measurement has been performed at some particular temperature, signifying each magnetic phase identified from the M T curve on one of the samples with x = 0 5. The measurements were performed after cooling the sample in zero field and the results have been shown in figure 5. It is observed that at 80 K, the M H curve does not show hysteresis, however, it shows a nonlinear nature, indicating a ferrimagnetic behaviour. M H curve at 50 K, where the maximum in FC magnetization occurs, is similar to the earlier one, with small increase in magnetization value. A small hysteresis is observed at 20 K with coercive field (H C ) of 800 Oe. The hysteresis increases with lowering of temperature and at 2 K, a better hysteresis curve formed with coercive field (H C ) of 3600 Oe. The hysteresis loops in figure 5 clearly shows that these loops are symmetric about the origin. This indicates absence of the exchange bias field for the sample in zero field cooled condition. Similar magnetization behaviours have been observed earlier in Nd based manganites (Hong et al 2012). It is noticeable that magnetization does not reach to saturation value in the M H curve. This may be due to the spin canting of ions in the magnetic sublattice along with large magnetic anisotropy in the sample. 4. Conclusions The low-temperature magnetization reversal in the compound Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 has been investigated. The interaction between two interacting networks of Pr/Nd and Mn ion largely changes, this may be due to the spin canting of ions in the magnetic sublattice along with large magnetic anisotropy in the sample. The relative effect of each sublattice s magnetization due to local internal field at the Mn site and negatively aligned Mn spins with respect to the Pr + Nd ferromagnetic moments varies with temperature and leads to a spin reversal when the magnetic moment of the ferromagnetic network sublattice is larger than the Mn moment. Acknowledgements The authors acknowledge experimental assistance from Laboratoire CRISMAT, UMR 6508, CNRS/ ENSICAEN, Caen Cedex, France and DST FAST TRACK project no. SR/FTP/PS-101/2010, Govt. of India. References Biswas S, Khan M H, Pal S and Bose E 2013 J. Magn. Magn. Mater Hemberger J, Lobina S, von Nidda H A K, Ivanov V Y, Mukhin A A, Balbashov A M and Loidl A 2004 Phys. Rev. B Hong F, Cheng Z, Wang J, Wang X and Dou S 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett Hemberger J et al 2004 Phys. Rev. B Mandal P, Serrao C R, Suard E, Caignaert V, Raveau B, Sundaresan A and Rao C N R 2013 J. Solid State Chem Manna P K et al 2010 J. Phys: Conf. Series Pena O, Bahout M, Ghanimi K, Duran P, Gutierrez D and Moure C 2002 J. Mater. Chem Rodrigues-Carvajal J 1993 Physica B Sharma N, Srivastava B K, Krishnamurthy A and Nigam A K 2010 Solid State Sci Singh R P and Tomy C V 2008 J. Phys.: Condensed Matter Snyder G J, Booth C H, Bridges F, Hiskes R, Dicarolis S, Beasley M R and Geballe T H 1997 Phys. Rev. B55 10 Wu et al 2000 J. Appl. Phys Yoshii K 2001 J. Solid State Chem Yoshii K, Nakamura A, Ishii Y and Morri Y 2001 J. Solid State Chem Zhang R R et al 2012 J. Alloys Compd Zhang S, Tan S, Tong W and Zhang Y 2005 Phys. Rev. B
Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple perovskite manganite NdMnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple
Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x. O 3 perovskite material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La 0.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ) 0.3 CoO 3 System
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7
 J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
CHAPTER 2 MAGNETISM. 2.1 Magnetic materials
 CHAPTER 2 MAGNETISM Magnetism plays a crucial role in the development of memories for mass storage, and in sensors to name a few. Spintronics is an integration of the magnetic material with semiconductor
CHAPTER 2 MAGNETISM Magnetism plays a crucial role in the development of memories for mass storage, and in sensors to name a few. Spintronics is an integration of the magnetic material with semiconductor
Supporting Information (Online Material) for
 Supporting Information (Online Material) for Five-Fold Ordering in High-Pressure Perovskites RMn 3 O 6 (R = Gd-Tm and Y) Lei Zhang,, Yoshitaka Matsushita, Kazunari Yamaura,, Alexei A. Belik, *, Research
Supporting Information (Online Material) for Five-Fold Ordering in High-Pressure Perovskites RMn 3 O 6 (R = Gd-Tm and Y) Lei Zhang,, Yoshitaka Matsushita, Kazunari Yamaura,, Alexei A. Belik, *, Research
Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds
 Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds M. Suzuki and I.S. Suzuki Department of Physics, State University of New York at Binghamton (October, ) I. INTRODUCTION In recent years
Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds M. Suzuki and I.S. Suzuki Department of Physics, State University of New York at Binghamton (October, ) I. INTRODUCTION In recent years
Field-Temperature Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Phases in Ludvigites Ni 3-x Mn x BO 5
 Field-Temperature Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Phases in Ludvigites Ni 3-x Mn x BO 5 L. N. Bezmaternykh, E. M. Kolesnikova*, E. V. Eremin, S. N. Sofronova, N. V. Volkov, and M. S. Molokeev Kirensky Institute
Field-Temperature Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Phases in Ludvigites Ni 3-x Mn x BO 5 L. N. Bezmaternykh, E. M. Kolesnikova*, E. V. Eremin, S. N. Sofronova, N. V. Volkov, and M. S. Molokeev Kirensky Institute
Magnetic Structure of TbRu 2 Al 10
 Magnetic Structure of TbRu 2 Al 10 R. White a, W.D. Hutchison a and T. Mizushima b a School of Physical, Environmental and Mathematical Sciences, The University of New South Wales, Canberra ACT 2600, Australia.
Magnetic Structure of TbRu 2 Al 10 R. White a, W.D. Hutchison a and T. Mizushima b a School of Physical, Environmental and Mathematical Sciences, The University of New South Wales, Canberra ACT 2600, Australia.
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2. Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1. Germany.
 Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
Magnetism. Ram Seshadri MRL 2031, x6129, Some basics:
 Magnetism Ram Seshadri MRL 2031, x6129, seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu Some basics: A magnet is associated with magnetic lines of force, and a north pole and a south pole. he lines of force come out of the north
Magnetism Ram Seshadri MRL 2031, x6129, seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu Some basics: A magnet is associated with magnetic lines of force, and a north pole and a south pole. he lines of force come out of the north
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties
 Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties Abstract The magnetic properties of a material are the basis of their applications. Specifically, the contrast agents that will be developed in Chaps. 4 and 5 use their magnetic
Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties Abstract The magnetic properties of a material are the basis of their applications. Specifically, the contrast agents that will be developed in Chaps. 4 and 5 use their magnetic
Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a. [Co 24 ] cluster
![Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a. [Co 24 ] cluster Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a. [Co 24 ] cluster](/thumbs/76/73822148.jpg) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a [Co 24 ] cluster Guang-Ming Liang, Qing-Ling
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a [Co 24 ] cluster Guang-Ming Liang, Qing-Ling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Materials and Methods Single crystals of Pr 2 Ir 2 O 7 were grown by a flux method [S1]. Energy dispersive x-ray analysis found no impurity phases, no inhomogeneities and a ratio between Pr and Ir of 1:1.03(3).
Materials and Methods Single crystals of Pr 2 Ir 2 O 7 were grown by a flux method [S1]. Energy dispersive x-ray analysis found no impurity phases, no inhomogeneities and a ratio between Pr and Ir of 1:1.03(3).
Transition Elements. pranjoto utomo
 Transition Elements pranjoto utomo Definition What is transition metal? One of which forms one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. 30Zn? Definition Zink is not transition elements
Transition Elements pranjoto utomo Definition What is transition metal? One of which forms one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. 30Zn? Definition Zink is not transition elements
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6
 Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
复习题. 2 Calculate the intensity of magnetic field in the air gap of the magnetic circuit shown in the figure. Use the values N=200,
 复习题 1 Calculate the magnetic moment of a sphere of radius R made from a magnetic material with magnetic susceptibility, when it is magnetized by an external magnetic field H. How is the value of the moment
复习题 1 Calculate the magnetic moment of a sphere of radius R made from a magnetic material with magnetic susceptibility, when it is magnetized by an external magnetic field H. How is the value of the moment
ON THE DOUBLE-EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS IN La 1 _xba x Mn03
 R 712 Philips Res. Repts 25,8-16,1970 ON THE DOUBLE-EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS IN La 1 _xba x Mn03 Abstract 1. Introduetion by F. K. LOTGERING Magnetic and electrical measurements on Lal_",Ba",Mn03 and Lal_",Ba",Mnl_",Ti",03
R 712 Philips Res. Repts 25,8-16,1970 ON THE DOUBLE-EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS IN La 1 _xba x Mn03 Abstract 1. Introduetion by F. K. LOTGERING Magnetic and electrical measurements on Lal_",Ba",Mn03 and Lal_",Ba",Mnl_",Ti",03
Anomalous magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in Ho Ni,Fe 2 compounds
 Anomalous magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in Ho Ni,Fe 2 compounds Niraj K. Singh, S. Agarwal, and K. G. Suresh* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India-400076 R.
Anomalous magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in Ho Ni,Fe 2 compounds Niraj K. Singh, S. Agarwal, and K. G. Suresh* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India-400076 R.
Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic
 Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic sublattices Y. Sun, 1,a) J.-Z. Cong, 1 Y.-S. Chai, 1 L.-Q. Yan, 1 Y.-L. Zhao, 1 S.-G. Wang, 1 W. Ning, 2 and Y.-H Zhang 2 1 Beijing National
Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic sublattices Y. Sun, 1,a) J.-Z. Cong, 1 Y.-S. Chai, 1 L.-Q. Yan, 1 Y.-L. Zhao, 1 S.-G. Wang, 1 W. Ning, 2 and Y.-H Zhang 2 1 Beijing National
J 12 J 23 J 34. Driving forces in the nano-magnetism world. Intra-atomic exchange, electron correlation effects: Inter-atomic exchange: MAGNETIC ORDER
 Driving forces in the nano-magnetism world Intra-atomic exchange, electron correlation effects: LOCAL (ATOMIC) MAGNETIC MOMENTS m d or f electrons Inter-atomic exchange: MAGNETIC ORDER H exc J S S i j
Driving forces in the nano-magnetism world Intra-atomic exchange, electron correlation effects: LOCAL (ATOMIC) MAGNETIC MOMENTS m d or f electrons Inter-atomic exchange: MAGNETIC ORDER H exc J S S i j
Observation of giant magnetocaloric effect in HoCoSi
 Materials Letters 113, 195 (2013) Observation of giant magnetocaloric effect in ocosi Sachin Gupta and K.G. Suresh * Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai-400076, India Abstract
Materials Letters 113, 195 (2013) Observation of giant magnetocaloric effect in ocosi Sachin Gupta and K.G. Suresh * Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai-400076, India Abstract
Research Highlights. Salient results from our group. Mixed phosphides in Sn-P and Sn-Mn-P systems
 Research Highlights Dilute magnetic semiconductors and Spintronics Spintronics is a branch of electronics emerged from the dilute magnetic semiconductor in an aspect of utilization of the spin in addition
Research Highlights Dilute magnetic semiconductors and Spintronics Spintronics is a branch of electronics emerged from the dilute magnetic semiconductor in an aspect of utilization of the spin in addition
Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Raman Studies on Functional Perovskite Oxides
 Raman Studies on Functional Perovskite Oxides Venkata S. Bhadram Postdoctoral Research Associate Geophysical Laboratory Carnegie Institution for Science Bangalore Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific
Raman Studies on Functional Perovskite Oxides Venkata S. Bhadram Postdoctoral Research Associate Geophysical Laboratory Carnegie Institution for Science Bangalore Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific
NEW ROUTES TO MULTIFERROICS
 NEW ROUTES TO MULTIFERROICS C. N. R. RAO Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research & Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India 1 MULTIFERROICS Ferromagnetic Ferroelectric Ferroelastic
NEW ROUTES TO MULTIFERROICS C. N. R. RAO Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research & Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India 1 MULTIFERROICS Ferromagnetic Ferroelectric Ferroelastic
PHASE DIAGRAM AND MAGNETOCALORIC EFFECTS IN Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05
 PHASE DIAGRAM AND MAGNETOCALORIC EFFECTS IN Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 Anil Aryal 1, Abdiel Quetz 1, Sudip Pandey 1, Michael Eubank 1, Tapas Samanta 2, Igor Dubenko 1, Shane Stadler 2, and Naushad Ali 1 1 Department
PHASE DIAGRAM AND MAGNETOCALORIC EFFECTS IN Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 Anil Aryal 1, Abdiel Quetz 1, Sudip Pandey 1, Michael Eubank 1, Tapas Samanta 2, Igor Dubenko 1, Shane Stadler 2, and Naushad Ali 1 1 Department
Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic
 Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic (La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 ) superlattices S. Thota, Q. Zhang, F. Guillou, U. Lüders, N. Barrier, W. Prellier * and A. Wahl Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic (La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 ) superlattices S. Thota, Q. Zhang, F. Guillou, U. Lüders, N. Barrier, W. Prellier * and A. Wahl Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Electromagnetism II. Instructor: Andrei Sirenko Spring 2013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm. Spring 2013, NJIT 1
 Electromagnetism II Instructor: Andrei Sirenko sirenko@njit.edu Spring 013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm Spring 013, NJIT 1 PROBLEMS for CH. 6 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/phys433/phys433eandm013.htm Can obtain
Electromagnetism II Instructor: Andrei Sirenko sirenko@njit.edu Spring 013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm Spring 013, NJIT 1 PROBLEMS for CH. 6 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/phys433/phys433eandm013.htm Can obtain
Studying the Magnetic Properties of CoSi Single Crystals 1
 ORDER, DISORDER, AND PHASE TRANSITION IN CONDENSED SYSTEM Studying the Magnetic Properties of CoSi Single Crystals 1 V. N. Narozhnyi* and V. N. Krasnorussky Vereshchagin Institute for High Pressure Physics,
ORDER, DISORDER, AND PHASE TRANSITION IN CONDENSED SYSTEM Studying the Magnetic Properties of CoSi Single Crystals 1 V. N. Narozhnyi* and V. N. Krasnorussky Vereshchagin Institute for High Pressure Physics,
Design and fabrication of an experimental set. up for ac Susceptibility measurement of
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue1, January-2013 1 Design and fabrication of an experimental set up for ac Susceptibility measurement of La x Sr 1-x MnO 3
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue1, January-2013 1 Design and fabrication of an experimental set up for ac Susceptibility measurement of La x Sr 1-x MnO 3
Ferromagnetic and spin-glass properties of single-crystalline U 2 NiSi 3
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 25, No. 4, 2007 Ferromagnetic and spin-glass properties of single-crystalline U 2 NiSi 3 * M. SZLAWSKA **, A. PIKUL, D. KACZOROWSKI Institute of Low Temperature and Structure
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 25, No. 4, 2007 Ferromagnetic and spin-glass properties of single-crystalline U 2 NiSi 3 * M. SZLAWSKA **, A. PIKUL, D. KACZOROWSKI Institute of Low Temperature and Structure
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 9 Dec 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 9 Dec 2015 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 9 Dec 2015](/thumbs/87/97379003.jpg) : A Model Molecular-Field Helical Heisenberg Antiferromagnet N. S. Sangeetha, Abhishek Pandey, and D. C. Johnston Ames Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa
: A Model Molecular-Field Helical Heisenberg Antiferromagnet N. S. Sangeetha, Abhishek Pandey, and D. C. Johnston Ames Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa
Reduction of hysteresis losses in the magnetic refrigerant La0.8Ce0.2Fe11.4Si1.6 by the addition of boron
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Reduction of hysteresis losses in the magnetic refrigerant La0.8Ce0.2Fe11.4Si1.6
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Reduction of hysteresis losses in the magnetic refrigerant La0.8Ce0.2Fe11.4Si1.6
Dielectric and Magnetic Behavior of Polycrystalline Copper Doped Holmium Orthoferrite
 Dielectric and Magnetic Behavior of Polycrystalline Copper Doped Holmium Orthoferrite Fumiya Tsunawaki, Mitsuhiro Matsuo, Hirokazu Shimooka, and Shigemi Kohiki Department of Materials Science, Kyushu Institute
Dielectric and Magnetic Behavior of Polycrystalline Copper Doped Holmium Orthoferrite Fumiya Tsunawaki, Mitsuhiro Matsuo, Hirokazu Shimooka, and Shigemi Kohiki Department of Materials Science, Kyushu Institute
Phases of Na x CoO 2
 Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Phases of Na x CoO 2 by Aakash Pushp (pushp@uiuc.edu) Abstract This paper deals with the various phases of Na x CoO 2 ranging from charge ordered insulator to Curie-Weiss metal to superconductor as the
Correlations among magnetic, magnetocaloric and magneto-transport properties in HoNiSi
 Correlations among magnetic, magnetocaloric and magneto-transport properties in HoNiSi Sachin Gupta and K. G. Suresh* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai-400076, India
Correlations among magnetic, magnetocaloric and magneto-transport properties in HoNiSi Sachin Gupta and K. G. Suresh* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai-400076, India
Interplay of 4f-3d Magnetism and Ferroelectricity in DyFeO 3
 Interplay of 4f-3d Magnetism and rroelectricity in O 3 B. RAJESWARAN 1, D.SANYAL 2, MAHUYA CHAKRABARTI 3, Y. SUNDARAYYA 1, A. SUNDARESAN 1 and C.N.R. RAO 1 1 Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit, Jawaharlal
Interplay of 4f-3d Magnetism and rroelectricity in O 3 B. RAJESWARAN 1, D.SANYAL 2, MAHUYA CHAKRABARTI 3, Y. SUNDARAYYA 1, A. SUNDARESAN 1 and C.N.R. RAO 1 1 Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit, Jawaharlal
Structural Analysis and Dielectric Properties of Cobalt Incorporated Barium Titanate
 AMANTULLA MANSURI, ASHUTOSH MISHRA School of Physics, Devi Ahilya University, Khandwa road campus, Indore, 452001, India Corresponding author: a.mansuri14@gmail.com Abstract The polycrystalline samples
AMANTULLA MANSURI, ASHUTOSH MISHRA School of Physics, Devi Ahilya University, Khandwa road campus, Indore, 452001, India Corresponding author: a.mansuri14@gmail.com Abstract The polycrystalline samples
Magnetic properties and magnetic entropy changes of La 1 x Pr x Fe 11.5 Si 1.5 compounds with 0 x 0.5
 Vol 16 No 12, December 2007 c 2007 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2007/16(12)/3848-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Magnetic properties and magnetic entropy changes of La 1 x Pr x Fe 11.5 Si 1.5 compounds
Vol 16 No 12, December 2007 c 2007 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2007/16(12)/3848-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Magnetic properties and magnetic entropy changes of La 1 x Pr x Fe 11.5 Si 1.5 compounds
Ferroelectricity at the Néel Temperature of Chromium in Rare-earth. Orthochromites: Magnetic Jahn-Teller Effect
 Ferroelectricity at the Néel Temperature of Chromium in Rare-earth Orthochromites: Magnetic Jahn-Teller Effect B. Rajeswaran 1, D. I. Khomskii 2, A. Sundaresan 1 and C. N. R. Rao 1 1 Chemistry and Physics
Ferroelectricity at the Néel Temperature of Chromium in Rare-earth Orthochromites: Magnetic Jahn-Teller Effect B. Rajeswaran 1, D. I. Khomskii 2, A. Sundaresan 1 and C. N. R. Rao 1 1 Chemistry and Physics
Dielectric behaviour and a.c. conductivity in Cu x Fe 3 x O 4 ferrite
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 23, No. 5, October 2000, pp. 447 452. Indian Academy of Sciences. Dielectric behaviour and a.c. conductivity in Cu x Fe 3 x O 4 ferrite A N PATIL, M G PATIL, K K PATANKAR, V L MATHE,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 23, No. 5, October 2000, pp. 447 452. Indian Academy of Sciences. Dielectric behaviour and a.c. conductivity in Cu x Fe 3 x O 4 ferrite A N PATIL, M G PATIL, K K PATANKAR, V L MATHE,
Lecture contents. Magnetic properties Diamagnetism Band paramagnetism Atomic paramagnetism Ferromagnetism. Molecular field theory Exchange interaction
 1 Lecture contents Magnetic properties Diamagnetism and paramagnetism Atomic paramagnetism Ferromagnetism Molecular field theory Exchange interaction NNSE 58 EM Lecture #1 [SI] M magnetization or magnetic
1 Lecture contents Magnetic properties Diamagnetism and paramagnetism Atomic paramagnetism Ferromagnetism Molecular field theory Exchange interaction NNSE 58 EM Lecture #1 [SI] M magnetization or magnetic
On conduction mechanism in paramagnetic phase of Gd based manganites
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 41 45. c Indian Academy of Sciences. On conduction mechanism in paramagnetic phase of Gd based manganites S SAGAR 1,2 and M R ANANTHARAMAN 1, 1 Department
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 1, February 2012, pp. 41 45. c Indian Academy of Sciences. On conduction mechanism in paramagnetic phase of Gd based manganites S SAGAR 1,2 and M R ANANTHARAMAN 1, 1 Department
Interaction of matter with magnetic fields
 LN07-1 Interaction of matter with magnetic fields All substances have magnetic properties, which can be determined by examining their behaviour in the presence of an external magnetic field, H. N S When
LN07-1 Interaction of matter with magnetic fields All substances have magnetic properties, which can be determined by examining their behaviour in the presence of an external magnetic field, H. N S When
XRD spectra of new YBaCuO superconductors
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 34, No. 5, August 11, pp. 1053 1057. c Indian Academy of Sciences. XRD spectra of new YBaCuO superconductors S SUJINNAPRAM c, P UDOMSAMUTHIRUN a,b,, T KRUAEHONG a, T NILKAMJON a,b
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 34, No. 5, August 11, pp. 1053 1057. c Indian Academy of Sciences. XRD spectra of new YBaCuO superconductors S SUJINNAPRAM c, P UDOMSAMUTHIRUN a,b,, T KRUAEHONG a, T NILKAMJON a,b
YFe 2 Al 10. unravelling the origin of quantum criticality
 YFe Al unravelling the origin of quantum criticality André Strydom Physics Department, University of Johannesburg Acknowledgements Frank Steglich (MPI CPfS, Dresden) Michael Baenitz and co workers (MPI
YFe Al unravelling the origin of quantum criticality André Strydom Physics Department, University of Johannesburg Acknowledgements Frank Steglich (MPI CPfS, Dresden) Michael Baenitz and co workers (MPI
shows the difference between observed (black) and calculated patterns (red). Vertical ticks indicate
 Intensity (arb. unit) a 5 K No disorder Mn-Pt disorder 5 K Mn-Ga disorder 5 K b 5 K Observed Calculated Difference Bragg positions 24 28 32 2 4 6 8 2 4 2θ (degree) 2θ (degree) Supplementary Figure. Powder
Intensity (arb. unit) a 5 K No disorder Mn-Pt disorder 5 K Mn-Ga disorder 5 K b 5 K Observed Calculated Difference Bragg positions 24 28 32 2 4 6 8 2 4 2θ (degree) 2θ (degree) Supplementary Figure. Powder
Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 (x = 0 and 0.
 Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
L S VAIDHYANATHAN, C K SUBRAMANIAM and G RANGARAJAN Physics Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras , India
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 14, No. 4, August 1991, pp. 931 935. ~-~ Printed in India. DC magnetization studies of (PrxY 1 - x)ua2cu307 - r L S VAIDHYANATHAN, C K SUBRAMANIAM and G RANGARAJAN Physics Department,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 14, No. 4, August 1991, pp. 931 935. ~-~ Printed in India. DC magnetization studies of (PrxY 1 - x)ua2cu307 - r L S VAIDHYANATHAN, C K SUBRAMANIAM and G RANGARAJAN Physics Department,
Incommensurate Magnetic Order in PrNiAl 4
 Incommensurate Magnetic Order in PrNiAl 4 R. White a, W.D. Hutchison a, M. Avdeev b and K. Nishimura c a School of Physical, Environmental and Mathematical Sciences, The University of New South Wales,
Incommensurate Magnetic Order in PrNiAl 4 R. White a, W.D. Hutchison a, M. Avdeev b and K. Nishimura c a School of Physical, Environmental and Mathematical Sciences, The University of New South Wales,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.1067 Light-induced spin-crossover magnet Shin-ichi Ohkoshi, 1,2, * Kenta Imoto, 1 Yoshihide Tsunobuchi, 1 Shinjiro Takano, 1 and Hiroko Tokoro 1 1 Department of Chemistry, School of
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.1067 Light-induced spin-crossover magnet Shin-ichi Ohkoshi, 1,2, * Kenta Imoto, 1 Yoshihide Tsunobuchi, 1 Shinjiro Takano, 1 and Hiroko Tokoro 1 1 Department of Chemistry, School of
Structural and magnetic properties of Ni doped CeO 2 nanoparticles
 *E-mail: shailuphy@gmail.com Abstract: We report room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni doped CeO 2 nanoparticles using X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM),
*E-mail: shailuphy@gmail.com Abstract: We report room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni doped CeO 2 nanoparticles using X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM),
Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanoparticles of Superconducting materials
 Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanoparticles of Superconducting materials Shipra, A. Gomathi, A. Sundaresan* and C. N. R. Rao* Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit and Department of Science and
Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanoparticles of Superconducting materials Shipra, A. Gomathi, A. Sundaresan* and C. N. R. Rao* Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit and Department of Science and
Critical behavior near the ferromagnetic Curie phase transition in CeCuGe
 Critical behavior near the ferromagnetic Curie phase transition in CeCuGe B.M. Sondezi-Mhlungu, A.M. Strydom Physics Department, University of Johannesburg,P.O. Box 524, Auckland Park, 2006,South Africa
Critical behavior near the ferromagnetic Curie phase transition in CeCuGe B.M. Sondezi-Mhlungu, A.M. Strydom Physics Department, University of Johannesburg,P.O. Box 524, Auckland Park, 2006,South Africa
Competition between Ferrimagnetism and Magnetic Frustration in Zinc Substituted YBaFe 4 O 7
 Competition between Ferrimagnetism and Magnetic Frustration in Zinc Substituted YBaFe 4 O 7 Tapati Sarkar *, V. Pralong, V. Caignaert and B. Raveau Laboratoire CRISMAT, UMR 6508 CNRS ENSICAEN, 6 bd Maréchal
Competition between Ferrimagnetism and Magnetic Frustration in Zinc Substituted YBaFe 4 O 7 Tapati Sarkar *, V. Pralong, V. Caignaert and B. Raveau Laboratoire CRISMAT, UMR 6508 CNRS ENSICAEN, 6 bd Maréchal
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar
 Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Exotic phase transitions in RERhSn compounds
 NUKLEONIKA 2003;48(Supplement 1):S35 S40 PROCEEDINGS Exotic phase transitions in RERhSn compounds Kazimierz Łątka, Roman Kmieć, Robert Kruk, Andrzej W. Pacyna, Michał Rams, Tobias Schmidt, Rainer Pöttgen
NUKLEONIKA 2003;48(Supplement 1):S35 S40 PROCEEDINGS Exotic phase transitions in RERhSn compounds Kazimierz Łątka, Roman Kmieć, Robert Kruk, Andrzej W. Pacyna, Michał Rams, Tobias Schmidt, Rainer Pöttgen
Interplay between crystal electric field and magnetic exchange anisotropies in the heavy fermion antiferromagnet YbRhSb under pressure
 24-P-45 TOKIMEKI211, Nov. 24, 211 Interplay between crystal electric field and magnetic exchange anisotropies in the heavy fermion antiferromagnet under pressure K. Umeo N-BARD, Hiroshima University Collaborators
24-P-45 TOKIMEKI211, Nov. 24, 211 Interplay between crystal electric field and magnetic exchange anisotropies in the heavy fermion antiferromagnet under pressure K. Umeo N-BARD, Hiroshima University Collaborators
This is an author -deposited version published in: Eprints ID: 4761
 Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author
Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author
Superconductivity at 41.0 K in the F-doped LaFeAsO 1-x F x
 Superconductivity at 41.0 K in the F-doped LaFeAsO 1-x F x Wei Lu, Xiao-Li Shen, Jie Yang, Zheng-Cai Li, Wei Yi, Zhi-An Ren*, Xiao-Li Dong, Guang-Can Che, Li-Ling Sun, Fang Zhou, Zhong-Xian Zhao* National
Superconductivity at 41.0 K in the F-doped LaFeAsO 1-x F x Wei Lu, Xiao-Li Shen, Jie Yang, Zheng-Cai Li, Wei Yi, Zhi-An Ren*, Xiao-Li Dong, Guang-Can Che, Li-Ling Sun, Fang Zhou, Zhong-Xian Zhao* National
Temperature and frequency dependent giant magnetodielectric coupling in DyMn0.33Fe0.67O3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Temperature and frequency dependent giant magnetodielectric
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Temperature and frequency dependent giant magnetodielectric
ISSN: ISO 9001:2008 Certified International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT) Volume 4, Issue 1, July 2014
 Structural and Electrical Properties of Sr - Substituted Perovskites Nano crystalline Lamno 3 G.N.Chaudhari, A.B.Bodade, D.K.Burghate Department of Chemistry, Shri Shivaji Science College, Amravati-444603
Structural and Electrical Properties of Sr - Substituted Perovskites Nano crystalline Lamno 3 G.N.Chaudhari, A.B.Bodade, D.K.Burghate Department of Chemistry, Shri Shivaji Science College, Amravati-444603
Magnetic Phase Diagrams of Manganites in the Electron Doping Region
 Physics of the Solid State, Vol. 46, No., 4, pp. 93. Translated from Fizika Tverdogo Tela, Vol. 46, No., 4, pp. 93. Original Russian Text Copyright 4 by Dunaevskiœ. REVIEWS Magnetic Phase Diagrams of Manganites
Physics of the Solid State, Vol. 46, No., 4, pp. 93. Translated from Fizika Tverdogo Tela, Vol. 46, No., 4, pp. 93. Original Russian Text Copyright 4 by Dunaevskiœ. REVIEWS Magnetic Phase Diagrams of Manganites
Structural and magnetic properties of the (Ca1-xNax)(Fe2-xTix)O4 solid solution (0 x 1)
 Structural and magnetic properties of the (Ca1-xNax)(Fe2-xTix)O4 solid solution (0 x 1) Siwar Zouari, Laurent Ranno, Abdelwaheb Cheikh-Rouhou, Olivier Isnard, Pierre Wolfers, Pierre Bordet, Pierre Strobel
Structural and magnetic properties of the (Ca1-xNax)(Fe2-xTix)O4 solid solution (0 x 1) Siwar Zouari, Laurent Ranno, Abdelwaheb Cheikh-Rouhou, Olivier Isnard, Pierre Wolfers, Pierre Bordet, Pierre Strobel
Observation of slow relaxation of the magnetization and hysteresis. loop in antiferromagnetic ordered phase of a 2D framework based on
 Observation of slow relaxation of the magnetization and hysteresis loop in antiferromagnetic ordered phase of a 2D framework based on Co II magnetic chains Shi-Yuan Zhang, a Wei Shi,* a Yanhua Lan, b Na
Observation of slow relaxation of the magnetization and hysteresis loop in antiferromagnetic ordered phase of a 2D framework based on Co II magnetic chains Shi-Yuan Zhang, a Wei Shi,* a Yanhua Lan, b Na
Magnetic ordering, magnetic anisotropy and the mean-field theory
 Magnetic ordering, magnetic anisotropy and the mean-field theory Alexandra Kalashnikova kalashnikova@mail.ioffe.ru Ferromagnets Mean-field approximation Curie temperature and critical exponents Magnetic
Magnetic ordering, magnetic anisotropy and the mean-field theory Alexandra Kalashnikova kalashnikova@mail.ioffe.ru Ferromagnets Mean-field approximation Curie temperature and critical exponents Magnetic
Evolution of superconductivity in LaO 1-x F x BiS 2 prepared by high pressure technique
 Evolution of superconductivity in LaO 1-x F x BiS 2 prepared by high pressure technique K. Deguchi 1,2,3, Y. Mizuguchi 1,2,4, S. Demura 1,2,3, H. Hara 1,2,3, T. Watanabe 1,2,3, S. J. Denholme 1,2, M. Fujioka
Evolution of superconductivity in LaO 1-x F x BiS 2 prepared by high pressure technique K. Deguchi 1,2,3, Y. Mizuguchi 1,2,4, S. Demura 1,2,3, H. Hara 1,2,3, T. Watanabe 1,2,3, S. J. Denholme 1,2, M. Fujioka
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Chapter 6 Antiferromagnetism and Other Magnetic Ordeer
 Chapter 6 Antiferromagnetism and Other Magnetic Ordeer 6.1 Mean Field Theory of Antiferromagnetism 6.2 Ferrimagnets 6.3 Frustration 6.4 Amorphous Magnets 6.5 Spin Glasses 6.6 Magnetic Model Compounds TCD
Chapter 6 Antiferromagnetism and Other Magnetic Ordeer 6.1 Mean Field Theory of Antiferromagnetism 6.2 Ferrimagnets 6.3 Frustration 6.4 Amorphous Magnets 6.5 Spin Glasses 6.6 Magnetic Model Compounds TCD
Assessment of Variation in Zero Field Hall Constant of Colossal Magnetoresistive Manganites (Re1-x AxMnO3)
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
b-cu 3 V 2 O 8 : Magnetic ordering in a spin-½ kagomé-staircase lattice
 b-cu 3 V 2 O 8 : Magnetic ordering in a spin-½ kagomé-staircase lattice N. Rogado 1, M. K. Haas 1, G. Lawes 2, D. A. Huse 3, A. P. Ramirez 2, and R. J. Cava 1 1 Department of Chemistry and Princeton Materials
b-cu 3 V 2 O 8 : Magnetic ordering in a spin-½ kagomé-staircase lattice N. Rogado 1, M. K. Haas 1, G. Lawes 2, D. A. Huse 3, A. P. Ramirez 2, and R. J. Cava 1 1 Department of Chemistry and Princeton Materials
Arnab Pariari & Prabhat Mandal Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics, 1/AF Bidhannagar, Calcutta , India
 Supplementary information for Coexistence of topological Dirac fermions on the surface and three-dimensional Dirac cone state in the bulk of ZrTe 5 single crystal Arnab Pariari & Prabhat Mandal Saha Institute
Supplementary information for Coexistence of topological Dirac fermions on the surface and three-dimensional Dirac cone state in the bulk of ZrTe 5 single crystal Arnab Pariari & Prabhat Mandal Saha Institute
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Magnetic Properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 Mn 1-x Ni x O 3 Perovskites
 Magnetic Properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 Mn 1-x Ni x O 3 Perovskites Ruben Medina 2011 NSF/REU Program Physics Department, University of Notre Dame Advisor: Prof. Howard A. Blackstead Abstract: Using the SQUID
Magnetic Properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 Mn 1-x Ni x O 3 Perovskites Ruben Medina 2011 NSF/REU Program Physics Department, University of Notre Dame Advisor: Prof. Howard A. Blackstead Abstract: Using the SQUID
Fe Co Si. Fe Co Si. Ref. p. 59] d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb Alloys and compounds with Ge
![Fe Co Si. Fe Co Si. Ref. p. 59] d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb Alloys and compounds with Ge Fe Co Si. Fe Co Si. Ref. p. 59] d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb Alloys and compounds with Ge](/thumbs/72/66917236.jpg) Ref. p. 59] 1.5. 3d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb 7 1.75 1.50 Co Si 0.8 0. 3.50 3.5 Co Si 0.8 0. H cr Magnetic field H [koe] 1.5 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.5 C C IF "A" P Frequency ωγ / e [koe] 3.00.75.50.5.00
Ref. p. 59] 1.5. 3d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb 7 1.75 1.50 Co Si 0.8 0. 3.50 3.5 Co Si 0.8 0. H cr Magnetic field H [koe] 1.5 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.5 C C IF "A" P Frequency ωγ / e [koe] 3.00.75.50.5.00
Exchange bias phenomenon in (Nd 1-x Y x ) 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 (x = 0, 0.1) perovskites
 Exchange bias phenomenon in (Nd 1-x Y x ) 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 (x = 0, 0.1) perovskites E. L. FertmanA. V. FedorchenkoA. V. Kotlyar and V. A. DesnenkoE. ČižmárA. BaranD. D. KhalyavinA. N. SalakV. V. ShvartsmanA.
Exchange bias phenomenon in (Nd 1-x Y x ) 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 (x = 0, 0.1) perovskites E. L. FertmanA. V. FedorchenkoA. V. Kotlyar and V. A. DesnenkoE. ČižmárA. BaranD. D. KhalyavinA. N. SalakV. V. ShvartsmanA.
Crossing point phenomena () in specific heat curves of superconducting ferromagnets
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2012 Crossing point phenomena () in specific heat curves of superconducting
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2012 Crossing point phenomena () in specific heat curves of superconducting
Phase Diagram of Spin States and Magnetic Interactions in Isotope Substituted (Pr,Eu) 0.7 Ca 0.3 CoO 3
 Solid State Phenomena Vols. 168-169 (2011) pp 465-468 Online available since 2010/Dec/30 at www.scientific.net (2011) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.168-169.465
Solid State Phenomena Vols. 168-169 (2011) pp 465-468 Online available since 2010/Dec/30 at www.scientific.net (2011) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.168-169.465
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase. Alok Banerjee
 Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method
 Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Anisotropic magnetic properties of TbNi 2 B 2 C single crystals
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 1996-I Anisotropic magnetic properties of TbNi 2 B 2 C single crystals C. V. Tomy, L. A. Afalfiz, M. R. Lees, J. M. Martin, and D. McK. Paul Department of
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 1996-I Anisotropic magnetic properties of TbNi 2 B 2 C single crystals C. V. Tomy, L. A. Afalfiz, M. R. Lees, J. M. Martin, and D. McK. Paul Department of
Magnetic properties in a partially oxidized nanocomposite of Cu-CuCl
 Magnetic properties in a partially oxidized nanocomposite of Cu-CuCl Qi Li 1, Shi-Wei Zhang 1,3, Yan Zhang 2 and Chinping Chen 2,4 1 State Key Laboratory for Structural Chemistry of Unstable and Stable
Magnetic properties in a partially oxidized nanocomposite of Cu-CuCl Qi Li 1, Shi-Wei Zhang 1,3, Yan Zhang 2 and Chinping Chen 2,4 1 State Key Laboratory for Structural Chemistry of Unstable and Stable
Observation of magnetism in Au thin films.
 Observation of magnetism in Au thin films. S. Reich*, G. Leitus and Y. Feldman. Department of Materials and Interfaces, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovoth, Israel. *e-mail: shimon.reich@weizmann.ac.il
Observation of magnetism in Au thin films. S. Reich*, G. Leitus and Y. Feldman. Department of Materials and Interfaces, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovoth, Israel. *e-mail: shimon.reich@weizmann.ac.il
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Tunable temperature induced magnetization jump. in a GdVO 3 single crystal
 Tunable temperature induced magnetization jump in a GdVO 3 single crystal L D Tung * Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL, United Kingdom. (dated: 20 Dec. 05, accepted to be published
Tunable temperature induced magnetization jump in a GdVO 3 single crystal L D Tung * Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL, United Kingdom. (dated: 20 Dec. 05, accepted to be published
I. Vrejoiu, E. Pippel, E. Nikulina, and D. Hesse Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics, D Halle, Germany. (Dated: October 18, 2018)
 Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based
 Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
New Li-Ethylenediamine-Intercalated Superconductor Li x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 with T c = 45 K
 New Li-Ethylenediamine-Intercalated Superconductor Li x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 with T c = 45 K Takehiro Hatakeda, Takashi Noji, Takayuki Kawamata, Masatsune Kato, and Yoji Koike Department of Applied
New Li-Ethylenediamine-Intercalated Superconductor Li x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 with T c = 45 K Takehiro Hatakeda, Takashi Noji, Takayuki Kawamata, Masatsune Kato, and Yoji Koike Department of Applied
Structure-Property Relationships in Pr 1-x Sr 1+x CoO 4, (0 x 0.40)
 American Journal of Condensed Matter Physics 2012, 2(4): 93-100 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajcmp.20120204.04 Structure-Property Relationships in Pr 1-x Sr 1+x CoO 4, (0 x 0.40) A. Hassen 1,*, A. I. Ali 2, Bog G. Kim
American Journal of Condensed Matter Physics 2012, 2(4): 93-100 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajcmp.20120204.04 Structure-Property Relationships in Pr 1-x Sr 1+x CoO 4, (0 x 0.40) A. Hassen 1,*, A. I. Ali 2, Bog G. Kim
Novel Field-Induced Phases in HoMnO 3 at Low Temperatures
 Novel Field-Induced Phases in HoMnO 3 at Low Temperatures B. Lorenz 1, F. Yen 1, M. M. Gospodinov 2, and C. W. Chu 1,3,4 1 Department of Physics and TCSAM, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204-5002
Novel Field-Induced Phases in HoMnO 3 at Low Temperatures B. Lorenz 1, F. Yen 1, M. M. Gospodinov 2, and C. W. Chu 1,3,4 1 Department of Physics and TCSAM, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204-5002
magnetic ordering from Cr K. Mukherjee, Kartik K Iyer and E.V. Sampathkumaran *
 Magnetic behavior of bulk and fine particles of RCr 2 Si 2 C (R= La, Ce) compounds: Possible magnetic ordering from Cr K. Mukherjee, Kartik K Iyer and E.V. Sampathkumaran * Tata Institute of Fundamental
Magnetic behavior of bulk and fine particles of RCr 2 Si 2 C (R= La, Ce) compounds: Possible magnetic ordering from Cr K. Mukherjee, Kartik K Iyer and E.V. Sampathkumaran * Tata Institute of Fundamental
Superconductivity in nickel-based compound GdONiBi and hole doped Gd 0.9 Sr 0.1 ONiBi
 Superconductivity in nickel-based compound GdONiBi and hole doped Gd 0.9 Sr 0.1 ONiBi Junyi Ge, Shixun Cao, Jincang Zhang Department of Physics,Shanghai University,Shanghai 200444, China We successfully
Superconductivity in nickel-based compound GdONiBi and hole doped Gd 0.9 Sr 0.1 ONiBi Junyi Ge, Shixun Cao, Jincang Zhang Department of Physics,Shanghai University,Shanghai 200444, China We successfully
Transport and magnetic properties in one dimensional A 3 ABO 6 family
 Transport and magnetic properties in one dimensional A 3 ABO 6 family M. Costes 1, J.M. Broto 1, B. Raquet 1, M.N. Baibich 2, H. Rakoto 1, A. Maignan 3, Ch. Martin 3, D. Flahaut 3, S. Hebert 3 1 Laboratoire
Transport and magnetic properties in one dimensional A 3 ABO 6 family M. Costes 1, J.M. Broto 1, B. Raquet 1, M.N. Baibich 2, H. Rakoto 1, A. Maignan 3, Ch. Martin 3, D. Flahaut 3, S. Hebert 3 1 Laboratoire
