I. Vrejoiu, E. Pippel, E. Nikulina, and D. Hesse Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics, D Halle, Germany. (Dated: October 18, 2018)
|
|
|
- Letitia Holt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D Leipzig, Germany arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Mar 2011 I. Vrejoiu, E. Pippel, E. Nikulina, and D. Hesse Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics, D Halle, Germany (Dated: October 18, 2018) Abstract High-quality Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 superlattices were fabricated by pulsed laser deposition and were investigated by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and SQUID magnetometry. Superlattices with orthorhombic and tetragonal SrRuO 3 layers were investigated. The superlattices grew coherently; in the growth direction Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 layers were terminated by MnO 2 - and SrRuO 3 layers by RuO 2 -planes. All superlattices showed antiferromagnetic interlayer coupling in low magnetic fields. The coupling strength was significantly higher for orthorhombic than for tetragonal symmetry of the SrRuO 3 layers. The strong interlayer exchange coupling in the superlattice with orthorhombic SrRuO 3 layers led to a magnetization reversal mechanism with a partially inverted hysteresis loop. PACS numbers: d, Ak, d, m, Lx, Gw 1
2 Epitaxial heterostructures and superlattices(sls) of perovskite oxides with different physical properties are an exciting playground, often leading to outstanding physical behavior which cannot be met in the individual compounds. For example, the intriguing magnetic interlayer coupling between manganites, such as La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 (LSMO), and SrRuO 3 (SRO) in epitaxial bilayers and SLs were studied both experimentally and theoretically. 1 From ab initio calculations the antiferromagnetic (AF) interlayer coupling between LSMO and SRO was shown to be mediated by the Mn-O-Ru bond; 1,2 the AF interlayer coupling depended sensitively on interfacial intermixing and could be controlled using the intricate interplay between structure, magnetocrystalline anisotropy, magnitude of the layer magnetization and layer thickness. 1,3 5 Additionally, Weigand et al. reported that the Ru sublattice has antiferromagnetic coupling to the Mn sublattice in the doped Ruddlesden-Popper phase La 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 x Ru x O 7. 6 Having in mind this tendency of antiferromagnetic coupling between the manganese perovskite R 1 x A x MnO 3 systems (R = La or rare earth element, and A = Ca, Sr or Ba) and the ruthenates, we investigated the magnetic interlayer coupling in superlattices in which SRO was combined with Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 (PCMO). Our PCMO films undergo a single magnetic transition into an insulating ferromagnetic or canted antiferromagnetic state 7 9 with a Curie temperature of about 110 K, lower than the Curie temperature of the SRO layers of 160 K. 10 Both SRO and PCMO have orthorhombic structure in the bulk. The present work was mainly motivated by our discovery of a structural transition of the SRO layers from orthorhombic to tetragonal symmetry as a function of PCMO layer thickness, 11 since this opens up the possibility to study exchange coupling in the same system, but for different structural symmetry. Superlattices and single films were fabricated by pulsed laser deposition (248 nm, KrF laser) from polycrystalline targets. Substrate temperature was 650 C and oxygen partial pressure 0.14 mbar. Vicinal SrTiO 3 (001) substrates with a miscut angle of about 0.1, uniform TiO 2 termination and an atomically flat terrace morphology were used. The microstructure of the SLs was investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy and X-ray diffractometry. High-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM), electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) mappings were done in a TITAN FEI microscope with a spherical aberration corrected (c s = 0) probe forming system. The magnetic properties of the SLs were investigated by SQUID magnetometry. The magnetic moments were 2
3 normalized to the volume of the samples and were expressed in Bohr magneton per unit cell using an average unit cell size of (0.39 nm) 3. Three SLs and two single PCMO films were studied, see table I for an overview. Figure 1 shows HAADF-STEM micrographs of PCMO/SRO SLs (a) SL1 and (b) SL3. The interfaces between the PCMO and SRO layers were coherent, no misfit dislocations were found. Closer inspection of the HAADF-STEM micrographs revealed an asymmetry of the interfaces: in the growth direction, the PCMO layers terminate most probably with MnO 2 planes and the SRO layers with RuO 2 planes. As discussed elsewhere 11 the PCMO layers were orthorhombic in all SLs studied here; the SRO layers, however, were orthorhombic in SL1, whereas having mainly tetragonal symmetry in SL2 and SL3. Bulk PCMO and SRO have orthorhombic structures at room temperature, however, for epitaxial films, especially coherent and ultrathin ones, grown on dissimilar substrates, distortions from the orthorhombic bulk structure and formation of particular configurations of crystallographic domains are expected to occur. 12,13 With respect to the cubic SrTiO 3 (001) C substrate the orthorhombic SRO layers had an epitaxial relation with [110] O [001] C, [001] O [100] C, [110] O [010] C, and the tetragonal SRO layers with [001] T [001] C, [110] T [100] C, [110] T [010] C. The PCMO layers grew with [110] O along the substrate normal, but showed two crystallographic domains with the c-axis either along [100] C or [010] C. Figure 2(a) shows the magnetization vs. temperature curves of both the 35 and 5 nm thick PCMO single films. The magnetization was measured on field cooling (FCC) in an in-plane field of 0.01 T, respectively, as well as in remanence during warming after removal of the magnetic field (REM). In the weak magnetic field of 0.01 T both samples show a small ferromagnetic-like magnetic moment below about 115 K, although the magnetization onset is very gradual in case of the 5 nm thick PCMO film. The Curie temperature was determined from the onset of the FCC magnetization measured in 0.01 T and was found to be about 115 K for the 35 nm and in the range between K for the 5 nm thick PCMO film. The remanent magnetization at low temperature is a sizeable fraction of the FCC magnetization, since the magnetically hard axis is along the surface normal. Fig. 2(b) shows the magnetization hysteresis loops of both films after correcting for the diamagnetic substrate contribution and the paramagnetic contribution from the Pr ions. Both films show a ferromagnetic signal; saturation is reached only in large fields of the order of 2 T. Compared to the spin-only moment of Mn of 3.7 µ B /u.c. both films show reduced 3
4 saturation moments in agreement with [8]. In summary, the PCMO films studied here show weak ferromagnetism with a Curie temperature between 110 and 115 K, i.e. lower than the Curie temperature of the SRO layers of about 143 K. The low field (0.001 T) magnetization curves of the SLs are shown in Fig. 3 as a function of temperature. The magnetization curves of SL2 and SL3 with tetragonal SRO layers are similar with a dip at about 110 K. Since this feature is absent in the magnetization of both PCMO single films as well as SRO single films, 14 we interpret this magnetization dip as a signature of AF interlayer coupling between the SRO and PCMO layers. On cooling the SLs, first the SRO layers order ferromagnetically below about 143 K; below about 115 K the PCMO layers also start to order ferromagnetically, but orient their magnetization antiparallel to the SRO magnetization, thus causing a dip in the overall magnetic moment. In Fig. 3(c) the magnetization of SL1 with orthorhombic SRO layers is shown. Here the phenomenology is somewhat different, since a peak is observed in the overall magnetic moment indicating the onset of the AF interlayer coupling. SL1 showed a magnetization maximum both when measured along the magnetically hard [001] O and easy [110] O in-plane direction, albeit the magnetization values were strongly and the maximum temperatures were slightly different. This proves that the maximum is not due to a specific magnetization process. Having observed AF interlayer coupling in the PCMO/SRO superlattices in low magnetic fields, a qualitative measure of the AF coupling strength was obtained by measuring the temperature-dependent magnetization in higher applied fields (not shown). Whereas SL2 and SL3 with tetragonal SRO layers do not show any sign of AF coupling in magnetic fields of 0.1 T and above, the maximum in the magnetization of SL1 persists up to at least 1 T. This indicates that the AF interlayer coupling is stronger in the SL with orthorhombic SRO layers than in those with tetragonal SRO layers. The latter conclusion is corroborated by the magnetization hysteresis loops shown in Fig. 4. The hysteresis loops for in-plane applied fields show a magnetically soft (PCMO) and hard (SRO) component in case of SL2 and SL3; the magnetization reversal occurs in a two-step process with the magnetically soft layer reversing first and with no obvious indication of a strong AF coupling. In contrast, in SL1 with orthorhombic SRO layers the in-plane hysteresis loop has an inverted central part, i.e. the PCMO layer that is reversing first is so strongly exchange coupled to the SRO layers that the reversal already occurs for 4
5 positive fields. This inverted hysteresis loop was also observed for a LSMO/SRO SL 15 and for the exchange-spring system DyFe 2 /YFe The out-of-plane magnetization loops show some hysteresis indicating that the magnetic easy axis lies under some angle with respect to the film plane. In summary, high-quality PCMO/SRO superlattices and single PCMO thin films were grown on SrTiO 3 substrates by pulsed laser deposition. The PCMO single films show ferromagnetic behaviour with a Curie temperature in the range 110 to 115 K depending on film thickness. Antiferromagnetic interlayer exchange coupling was observed in the SLs in low magnetic fields. The strength of the AF interlayer exchange coupling depends on the crystallographic symmetry of the SRO layers and is larger for orthorhombic SRO than for tetragonal SRO layers. This is consistent with the magnetization reversal mechanism observed in the SLs that leads to inverted hysteresis loops in case of strong AF interlayer exchange coupling. The structural transition of the SRO layers changes the magnetocrystalline anisotropy and therefore also the spin structure at the interface. Probably the Ru and Mn spins at the interface are more collinear in case of orthorhombic SRO symmetry leading to a stronger AF exchange coupling. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by the German Science Foundation (DFG) within the Collaborative Research Center SFB 762 Functionality of Oxide Interfaces. We thank Dr. J. Henk for a careful reading of the manuscript. 5
6 1 M. Ziese, I. Vrejoiu, E. Pippel, P. Esquinazi, D. Hesse, C. Etz, J. Henk, A. Ernst, I. V. Maznichenko, W. Hergert, and I. Mertig, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, (2010). 2 Y. Lee, B. Caes, and B. Harmon, Journal of Alloys and Compounds 450, 1 (2008). 3 X. Ke, M. S. Rzchowski, L. J. Belenky, and C. B. Eom, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 5458 (2004). 4 X. Ke, L. J. Belenky, C. B. Eom, and M. S. Rzchowski, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 10K115 (2005). 5 P. Padhan, W. Prellier, and R. C. Budhani, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, (2006). 6 F. Weigand, S. Gold, A. Schmid, J. Geissler, E. Goering, K. Dörr, G. Krabbes, and K. Ruck, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 2035 (2002). 7 Z. Jirák, S. Krupička, Z. Šimša, M. Dlouhá, and S. Vratislav, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 53, 153 (1985). 8 H. Yoshizawa, H. Kawano, Y. Tomioka, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B 52, R13145 (1995). 9 Y. Tomioka, A. Asamitsu, H. Kuwahara, Y. Moritomo, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B 53, R1689 (1996). 10 L.Klein, J.S.Dodge, C.H. Ahn, G.J.Snyder, T.H. Geballe, M. R.Beasley, anda.kapitulnik, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2774 (1996). 11 M. Ziese, I. Vrejoiu, E. Pippel, E. Nikulina, and D. Hesse, arxiv: v1 (2011). 12 M. Fujimoto, H. Koyama, Y. Nishi, T. Suzuki, S. Kobayashi, Y. Tamai, and N. Awaya, J. Am. Ceram Soc. 90, 2205 (2007). 13 Q. Gan, R. A. Rao, C. B. Eom, L. Wu, and F. Tsui, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 5297 (1999). 14 M. Ziese, I. Vrejoiu, and D. Hesse, Phys. Rev. B 81, (2010). 15 M. Ziese, I. Vrejoiu, and D. Hesse, Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, (2010). 16 K. Dumesnil, C. Dufour, P. Mangin, A. Rogalev, and F. Wilhelm, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 17, L215 (2005). 6
7 TABLE I. Layer thicknesses and Curie temperatures of the SLs and single PCMO films. Curie temperatures of the PCMO layers were determined from magnetization, those of the SRO layers from resistivity measurements. Sample [PCMO / SRO] 15 T C (K) T C (K) (SRO) (PCMO) SL1 [1.5 nm / 4.4 nm] SL2 [3.0 nm / 4.0 nm] SL3 [3.8 nm / 4.0 nm] PCMO1 5 nm PCMO2 35 nm 115 7
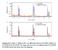
8 FIG. 1. HAADF-STEM images of samples (a) SL1 (1.5 nm/4.4 nm) and (b) SL3 (3.8 nm/4.0 nm). FIG. 2. (a) Magnetization vs. temperature curves of the 35 nm (solid symbols) and 5 nm (open symbols) thick single PCMO films for a field of 0.01 T applied in-plane. Field-cooled (FCC) and remanence (REM) data are shown. (b) In-plane magnetization hysteresis loops of the 35 nm and 5 nm single PCMO films at 10 K. FIG. 3. Low-field (0.001 T) magnetization vs. temperature curves of (a) SL2 and (b) SL3 with tetragonal as well as (c) SL1 with orthorhombic SRO layers. In (a) and (b) the field was applied in-plane along [110] T, in (c) in-plane along [001] O and [110] O. For comparison in (b) the in-plane magnetization of single film PCMO2 is shown. The arrows indicate the onset of AF coupling. Crystallographic directions are indicated schematically. FIG. 4. Magnetization hysteresis loops of SLs (a) SL2, (b) SL3 and (c) SL1 at 10 K for both inplane (solid symbols) and out-of-plane (open symbols) magnetic fields. The arrows in (c) indicate the sweep direction of the in-plane field; note that the central loop of the in-plane magnetization curve is inverted. The field directions are indicated in the figure. 8
9 FIG. 1. 9
10 Temperature T (K) (a) 0.20 µ 0 H = 0.01 T magnetic moment m (µ B / u.c.) (c) T = 10 K 35 nm PCMO FCC REM 5 nm PCMO FCC REM nm PCMO 5 nm PCMO Magnetic Field µ 0 H (T) FIG
11 [001] C [001] T 0.06 [110] T magnetic moment m (µ B / u.c.) (a) (b) SL1 SL2, H [110] T H [110] O H [001] O [110] T SL3, H [110] T PCMO2 [001] C [110] O [110] O [001] O (c) Temperature T (K) FIG
12 2 1 (a) SL2 magnetic moment m (µ B / u.c.) (b) SL3 (c) SL1 H H [110] T [001] T [110] T [001] T 0-1 H [110] O -2 [110] O Magnetic Field µ 0 H (T) FIG
Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic
 Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic (La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 ) superlattices S. Thota, Q. Zhang, F. Guillou, U. Lüders, N. Barrier, W. Prellier * and A. Wahl Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic (La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 ) superlattices S. Thota, Q. Zhang, F. Guillou, U. Lüders, N. Barrier, W. Prellier * and A. Wahl Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study
 Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface
 What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in. manganite multilayers
 Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Chalmers Publication Library
 Chalmers Publication Library Triplet superconductivity in oxide ferromagnetic interlayer of mesa-structure This document has been downloaded from Chalmers Publication Library (CPL). It is the author s
Chalmers Publication Library Triplet superconductivity in oxide ferromagnetic interlayer of mesa-structure This document has been downloaded from Chalmers Publication Library (CPL). It is the author s
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI:.38/NMAT4855 A magnetic heterostructure of topological insulators as a candidate for axion insulator M. Mogi, M. Kawamura, R. Yoshimi, A. Tsukazaki,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI:.38/NMAT4855 A magnetic heterostructure of topological insulators as a candidate for axion insulator M. Mogi, M. Kawamura, R. Yoshimi, A. Tsukazaki,
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 -
 Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE-
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE- NOMENOLOGY In the main text we introduce anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in analogy to ferromagnets where non-crystalline and crystalline contributions
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE- NOMENOLOGY In the main text we introduce anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in analogy to ferromagnets where non-crystalline and crystalline contributions
Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 300 (2006) 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers D. Repetto, A. Enders, K. Kern Max Planck Institut
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 300 (2006) 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers D. Repetto, A. Enders, K. Kern Max Planck Institut
Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional Oxide p-n Heterojunctions
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of
 Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998](/thumbs/78/78285667.jpg) Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource,
Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource,
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Material Science II. d Electron systems
 Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
ELECTRON MAGNETIC RESONANCE OF MANGANESE COMPOUNDS
 ELECTRON MAGNETIC RESONANCE OF MANGANESE COMPOUNDS Peter C Riedi School of Physics and Astronomy, University of St. Andrews, Fife, Scotland KY16 9SS, UK (pcr@st-and.ac.uk) INTRODUCTION This talk will introduce
ELECTRON MAGNETIC RESONANCE OF MANGANESE COMPOUNDS Peter C Riedi School of Physics and Astronomy, University of St. Andrews, Fife, Scotland KY16 9SS, UK (pcr@st-and.ac.uk) INTRODUCTION This talk will introduce
Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties
 Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties Abstract The magnetic properties of a material are the basis of their applications. Specifically, the contrast agents that will be developed in Chaps. 4 and 5 use their magnetic
Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties Abstract The magnetic properties of a material are the basis of their applications. Specifically, the contrast agents that will be developed in Chaps. 4 and 5 use their magnetic
Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Systems, Tanaka-Ohya lab.
 Observation of the room-temperature local ferromagnetism and its nanoscale expansion in the ferromagnetic semiconductor Ge 1 xfe x Yuki K. Wakabayashi 1 and Yukio Takahashi 2 1 Department of Electrical
Observation of the room-temperature local ferromagnetism and its nanoscale expansion in the ferromagnetic semiconductor Ge 1 xfe x Yuki K. Wakabayashi 1 and Yukio Takahashi 2 1 Department of Electrical
Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Te x MnO 3
 phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
The exchange interaction between FM and AFM materials
 Chapter 1 The exchange interaction between FM and AFM materials When the ferromagnetic (FM) materials are contacted with antiferromagnetic (AFM) materials, the magnetic properties of FM materials are drastically
Chapter 1 The exchange interaction between FM and AFM materials When the ferromagnetic (FM) materials are contacted with antiferromagnetic (AFM) materials, the magnetic properties of FM materials are drastically
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/115260649.jpg) 1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
1. 14 August 1996 (final accepted version arxiv:cond-mat/0311297v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 13 Nov 2003 2. Non-collinear magnetism in distorted perovskite compounds 3. I.V.Solovyev a,, N.Hamada b, K.Terakura
Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
Advanced Lab Course. Tunneling Magneto Resistance
 Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems
 Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems By Lina Gunawan (0326114) Supervisor: Dr. Gianluigi Botton November 1, 2006 MSE 702(1) Presentation Outline Literature Review
Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems By Lina Gunawan (0326114) Supervisor: Dr. Gianluigi Botton November 1, 2006 MSE 702(1) Presentation Outline Literature Review
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy & Spectroscopy: A tool for probing electronic inhomogeneities in correlated systems
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy & Spectroscopy: A tool for probing electronic inhomogeneities in correlated systems Anjan K. Gupta Physics Department, I. I. T Kanpur ICTS-GJ, IITK, Feb 2010 Acknowledgements
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy & Spectroscopy: A tool for probing electronic inhomogeneities in correlated systems Anjan K. Gupta Physics Department, I. I. T Kanpur ICTS-GJ, IITK, Feb 2010 Acknowledgements
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in
 Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Role of diffused Co atoms in improving effective exchange coupling in Sm-Co/ Fe spring magnets
 Role of diffused Co atoms in improving effective exchange coupling in Sm-Co/ Fe spring magnets Y. Choi, 1,2 J. S. Jiang, 1 Y. Ding, 3 R. A. Rosenberg, 4 J. E. Pearson, 1 S. D. Bader, 1 A. Zambano, 5 M.
Role of diffused Co atoms in improving effective exchange coupling in Sm-Co/ Fe spring magnets Y. Choi, 1,2 J. S. Jiang, 1 Y. Ding, 3 R. A. Rosenberg, 4 J. E. Pearson, 1 S. D. Bader, 1 A. Zambano, 5 M.
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar
 Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Supplementary Information for Dimensionality-Driven. Insulator-Metal Transition in A-site Excess. Nonstoichiometric Perovskites
 Supplementary Information for Dimensionality-Driven Insulator-Metal Transition in A-site Excess Nonstoichiometric Perovskites Z. Wang, M. Okude, M. Saito, S. Tsukimoto, A. Ohtomo, M. Tsukada, M. Kawasaki,
Supplementary Information for Dimensionality-Driven Insulator-Metal Transition in A-site Excess Nonstoichiometric Perovskites Z. Wang, M. Okude, M. Saito, S. Tsukimoto, A. Ohtomo, M. Tsukada, M. Kawasaki,
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials
 Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Influence of ferromagnetic antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in Ni/Fe x Mn 1 x bilayers
 Influence of ferromagnetic antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in Ni/Fe x Mn 1 x bilayers M. Stampe, P. Stoll, T. Homberg, K. Lenz, and W. Kuch Institut für Experimentalphysik,
Influence of ferromagnetic antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in Ni/Fe x Mn 1 x bilayers M. Stampe, P. Stoll, T. Homberg, K. Lenz, and W. Kuch Institut für Experimentalphysik,
Coexistence of Magnetic Order and Two-dimensional Superconductivity at LaAlO3/SrTiO3 Interfaces
 Coexistence of Magnetic Order and Two-dimensional Superconductivity at LaAlO3/SrTiO3 Interfaces The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Coexistence of Magnetic Order and Two-dimensional Superconductivity at LaAlO3/SrTiO3 Interfaces The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
An alternative to the topological interpretation of the transverse resistivity anomalies in SrRuO 3
 An alternative to the topological interpretation of the transverse resistivity anomalies in SrRuO 3 Daisuke Kan 1,a) Takahiro Moriyama 1, b), Kento Kobayashi 1, and Yuichi Shimakawa 1,2 1 Institute for
An alternative to the topological interpretation of the transverse resistivity anomalies in SrRuO 3 Daisuke Kan 1,a) Takahiro Moriyama 1, b), Kento Kobayashi 1, and Yuichi Shimakawa 1,2 1 Institute for
Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3. Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and
 Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and Dimensionality X. Wang 1,2, W.M Lü 1,2, A. Annadi 1,2, Z.Q. Liu
Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and Dimensionality X. Wang 1,2, W.M Lü 1,2, A. Annadi 1,2, Z.Q. Liu
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Spin pumping in magnetic trilayer structures with an MgO barrier Supplementary Information.
 Spin pumping in magnetic trilayer structures with an MgO barrier Supplementary Information. A. A. Baker, 1, 2 A. I. Figueroa, 2 D. Pingstone, 3 V. K. Lazarov, 3 G. van der Laan, 2 and 1, a) T. Hesjedal
Spin pumping in magnetic trilayer structures with an MgO barrier Supplementary Information. A. A. Baker, 1, 2 A. I. Figueroa, 2 D. Pingstone, 3 V. K. Lazarov, 3 G. van der Laan, 2 and 1, a) T. Hesjedal
Holcomb Group Capabilities
 Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
MnO. Sr x. La 1-x. Temperature (K) Paramagnetic. Metal T C. Paramagnetic Insulator. Ferromagnetic. Metal T N. Ferromagnetic. Spin-canted Insulator
 Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films
 Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007](/thumbs/93/118034102.jpg) Electrical transport properties of polar heterointerface between KTaO 3 and SrTiO 3 A. Kalabukhov, 1, R. Gunnarsson, 1 T. Claeson, 1 and D. Winkler 1 arxiv:0704.1050v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007 1
Electrical transport properties of polar heterointerface between KTaO 3 and SrTiO 3 A. Kalabukhov, 1, R. Gunnarsson, 1 T. Claeson, 1 and D. Winkler 1 arxiv:0704.1050v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007 1
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials
 Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 114107 2006 Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films J. H. Hao a Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 114107 2006 Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films J. H. Hao a Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
of Spontaneous and field-induced
 Magneto-Optics of Spontaneous and field-induced induced Vortices in twinned YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ /La 1-x Sr x MnO 3 bilayers Superconductivity Group (Politecnico di Torino): Roberto Gerbaldo, Gianluca Ghigo,
Magneto-Optics of Spontaneous and field-induced induced Vortices in twinned YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ /La 1-x Sr x MnO 3 bilayers Superconductivity Group (Politecnico di Torino): Roberto Gerbaldo, Gianluca Ghigo,
From 180º stripe domains to more exotic patterns of polarization in ferroelectric nanostructures. A first principles view
 From 180º stripe domains to more exotic patterns of polarization in ferroelectric nanostructures. A first principles view Pablo Aguado-Puente Javier Junquera Ferroelectricity: Basic definitions Existence
From 180º stripe domains to more exotic patterns of polarization in ferroelectric nanostructures. A first principles view Pablo Aguado-Puente Javier Junquera Ferroelectricity: Basic definitions Existence
Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface
 Submitted to Applied Physics Letters 09/22/03 Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface N. Haberkorn Universidad Nacional del Sur, Avda. Alem 1253, Bahía Blanca, 8000 Bs.
Submitted to Applied Physics Letters 09/22/03 Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface N. Haberkorn Universidad Nacional del Sur, Avda. Alem 1253, Bahía Blanca, 8000 Bs.
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase. Alok Banerjee
 Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
Artificially layered structures
 http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
M any functional properties observed in perovskite oxides, ABO3, exhibit close couplings to slight structural
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY CERAMICS CHARACTERIZATION AND ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Atomic level observation of octahedral distortions at the perovskite oxide
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY CERAMICS CHARACTERIZATION AND ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Atomic level observation of octahedral distortions at the perovskite oxide
Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations
 Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations Xavier Batlle, A. Labarta, Ò. Iglesias, M. García del Muro and M. Kovylina Goup of Magnetic Nanomaterials
Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations Xavier Batlle, A. Labarta, Ò. Iglesias, M. García del Muro and M. Kovylina Goup of Magnetic Nanomaterials
J 12 J 23 J 34. Driving forces in the nano-magnetism world. Intra-atomic exchange, electron correlation effects: Inter-atomic exchange: MAGNETIC ORDER
 Driving forces in the nano-magnetism world Intra-atomic exchange, electron correlation effects: LOCAL (ATOMIC) MAGNETIC MOMENTS m d or f electrons Inter-atomic exchange: MAGNETIC ORDER H exc J S S i j
Driving forces in the nano-magnetism world Intra-atomic exchange, electron correlation effects: LOCAL (ATOMIC) MAGNETIC MOMENTS m d or f electrons Inter-atomic exchange: MAGNETIC ORDER H exc J S S i j
Microstructure evolution during BaTiO 3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces
 Journal of the European Ceramic Society 25 (2005) 2201 2206 Microstructure evolution during BaTiO 3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces Andreas Graff a,, Stephan Senz a,
Journal of the European Ceramic Society 25 (2005) 2201 2206 Microstructure evolution during BaTiO 3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces Andreas Graff a,, Stephan Senz a,
doi: /PhysRevLett
 doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2011
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2011 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2011](/thumbs/96/127577148.jpg) Polar Antiferromagnets Produced with Orbital-Order arxiv:1112.0882v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2011 Naoki Ogawa, 1,2, Yasushi Ogimoto, 1,2,3 Yoshiaki Ida, 4 Yusuke Nomura, 4 Ryotaro Arita, 4,5 and Kenjiro
Polar Antiferromagnets Produced with Orbital-Order arxiv:1112.0882v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Dec 2011 Naoki Ogawa, 1,2, Yasushi Ogimoto, 1,2,3 Yoshiaki Ida, 4 Yusuke Nomura, 4 Ryotaro Arita, 4,5 and Kenjiro
Probing Magnetic Order with Neutron Scattering
 Probing Magnetic Order with Neutron Scattering G.J. Mankey, V.V. Krishnamurthy, F.D. Mackey and I. Zoto University of Alabama in collaboration with J.L. Robertson and M.L. Crow Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Probing Magnetic Order with Neutron Scattering G.J. Mankey, V.V. Krishnamurthy, F.D. Mackey and I. Zoto University of Alabama in collaboration with J.L. Robertson and M.L. Crow Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Influence of ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in NiÕFe x Mn 1 x bilayers
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 81, 1442 21 Influence of ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in NiÕFe x Mn 1 x bilayers M. Stampe,* P. Stoll, T. Homberg, K. Lenz, and
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 81, 1442 21 Influence of ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in NiÕFe x Mn 1 x bilayers M. Stampe,* P. Stoll, T. Homberg, K. Lenz, and
Interplay between crystal electric field and magnetic exchange anisotropies in the heavy fermion antiferromagnet YbRhSb under pressure
 24-P-45 TOKIMEKI211, Nov. 24, 211 Interplay between crystal electric field and magnetic exchange anisotropies in the heavy fermion antiferromagnet under pressure K. Umeo N-BARD, Hiroshima University Collaborators
24-P-45 TOKIMEKI211, Nov. 24, 211 Interplay between crystal electric field and magnetic exchange anisotropies in the heavy fermion antiferromagnet under pressure K. Umeo N-BARD, Hiroshima University Collaborators
Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface
 Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface SLAC-PUB-15439 J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation
Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface SLAC-PUB-15439 J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation
Photocarrier Injection and Current Voltage Characteristics of La 0:8 Sr 0:2 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 :Nb Heterojunction at Low Temperature
 Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 44, No. 1, 25, pp. 7367 7371 #25 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Photocarrier Injection and Current Voltage Characteristics of La :8 Sr :2 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 :Nb
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 44, No. 1, 25, pp. 7367 7371 #25 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Photocarrier Injection and Current Voltage Characteristics of La :8 Sr :2 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 :Nb
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.
![Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998. Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.](/thumbs/90/104152266.jpg) Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
Ohoyama., TEM, neutron diffraction, ordered perovskite, CE structure. Abstract An A-site ordered manganese perovskite YBaMn 2
 New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
Tailoring exchange couplings in magnetic topological-insulator/antiferromagnet heterostructures
 Tailoring exchange couplings in magnetic topological-insulator/antiferromagnet heterostructures Qing Lin He 1 *, Xufeng Kou 1, Alexander J. Grutter 2, Gen Yin 1, Lei Pan 1, Xiaoyu Che 1, Yuxiang Liu 1,
Tailoring exchange couplings in magnetic topological-insulator/antiferromagnet heterostructures Qing Lin He 1 *, Xufeng Kou 1, Alexander J. Grutter 2, Gen Yin 1, Lei Pan 1, Xiaoyu Che 1, Yuxiang Liu 1,
with micrometer wide atomic terraces
 Epitaxial growth and properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films with micrometer wide atomic terraces Wei Yuan 1, Yuelei Zhao 1, Chi Tang 2, Tang Su 1, Qi Song 1, Jing Shi 2,a), and Wei Han 1,3,b) 1 International
Epitaxial growth and properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films with micrometer wide atomic terraces Wei Yuan 1, Yuelei Zhao 1, Chi Tang 2, Tang Su 1, Qi Song 1, Jing Shi 2,a), and Wei Han 1,3,b) 1 International
Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors:
 Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite
Materials 218/UCSB: Superconductivity and High T C copper oxide superconductors: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Contents. Acknowledgments
 MAGNETIC MATERIALS Fundamentals and Applications Second edition NICOLA A. SPALDIN University of California, Santa Barbara CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Acknowledgments page xiii I Basics 1 Review
MAGNETIC MATERIALS Fundamentals and Applications Second edition NICOLA A. SPALDIN University of California, Santa Barbara CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Acknowledgments page xiii I Basics 1 Review
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method
 Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Interlayer Exchange Coupling in Semiconductor EuS PbS Ferromagnetic Wedge Multilayers
 Vol. 110 (2006) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the XXXV International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2006 Interlayer Exchange Coupling in Semiconductor EuS PbS Ferromagnetic
Vol. 110 (2006) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the XXXV International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2006 Interlayer Exchange Coupling in Semiconductor EuS PbS Ferromagnetic
Spin correlations in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6+x bulk vs. interface
 Spin correlations in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6+x bulk vs. interface B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline new quantum states in bulk? yes, good evidence for electronic nematic phase new
Spin correlations in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6+x bulk vs. interface B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline new quantum states in bulk? yes, good evidence for electronic nematic phase new
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces
 Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanoparticles of Superconducting materials
 Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanoparticles of Superconducting materials Shipra, A. Gomathi, A. Sundaresan* and C. N. R. Rao* Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit and Department of Science and
Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanoparticles of Superconducting materials Shipra, A. Gomathi, A. Sundaresan* and C. N. R. Rao* Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit and Department of Science and
Temperature dependence of microwave and THz dielectric response
 The 10 th European Meeting on Ferroelectricity, August 2003, Cambridge, UK Ferroelectrics, in press. Temperature dependence of microwave and THz dielectric response in Sr n+1 Ti n O 3n+1 (n=1-4) D. Noujni
The 10 th European Meeting on Ferroelectricity, August 2003, Cambridge, UK Ferroelectrics, in press. Temperature dependence of microwave and THz dielectric response in Sr n+1 Ti n O 3n+1 (n=1-4) D. Noujni
ON THE DOUBLE-EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS IN La 1 _xba x Mn03
 R 712 Philips Res. Repts 25,8-16,1970 ON THE DOUBLE-EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS IN La 1 _xba x Mn03 Abstract 1. Introduetion by F. K. LOTGERING Magnetic and electrical measurements on Lal_",Ba",Mn03 and Lal_",Ba",Mnl_",Ti",03
R 712 Philips Res. Repts 25,8-16,1970 ON THE DOUBLE-EXCHANGE INTERACTIONS IN La 1 _xba x Mn03 Abstract 1. Introduetion by F. K. LOTGERING Magnetic and electrical measurements on Lal_",Ba",Mn03 and Lal_",Ba",Mnl_",Ti",03
Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple perovskite manganite NdMnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple
Temperature Dependent Current-voltage Characteristics of P- type Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Fabricated Using Screenprinting
 Temperature Dependent Current-voltage Characteristics of P- type Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Fabricated Using Screenprinting Process Hyun-Jin Song, Won-Ki Lee, Chel-Jong Choi* School of Semiconductor
Temperature Dependent Current-voltage Characteristics of P- type Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Fabricated Using Screenprinting Process Hyun-Jin Song, Won-Ki Lee, Chel-Jong Choi* School of Semiconductor
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 9 Aug 2006
 Correlation-Driven Charge Order at a Mott Insulator - Band Insulator Digital Interface Rossitza Pentcheva 1 and Warren E. Pickett 2 1 Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Munich,
Correlation-Driven Charge Order at a Mott Insulator - Band Insulator Digital Interface Rossitza Pentcheva 1 and Warren E. Pickett 2 1 Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Munich,
La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 - based Spintronics
 La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 - based Spintronics Investigation on fundamental issues and applications Umberto Scotti di Uccio DiMSAT, Università di Cassino CNR Coherentia Napoli MR (%) 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-50 0 50 µ
La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 - based Spintronics Investigation on fundamental issues and applications Umberto Scotti di Uccio DiMSAT, Università di Cassino CNR Coherentia Napoli MR (%) 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-50 0 50 µ
Onset of the Meissner effect at 65 K in FeSe thin film grown on Nb doped SrTiO 3 substrate
 Onset of the Meissner effect at 65 K in FeSe thin film grown on Nb doped SrTiO 3 substrate Zuocheng Zhang 1,4*, Yihua Wang 2,3*, Qi Song 2,5*, Chang Liu 1,4, Rui Peng 2,5, K.A. Moler 3, Donglai Feng 2,5
Onset of the Meissner effect at 65 K in FeSe thin film grown on Nb doped SrTiO 3 substrate Zuocheng Zhang 1,4*, Yihua Wang 2,3*, Qi Song 2,5*, Chang Liu 1,4, Rui Peng 2,5, K.A. Moler 3, Donglai Feng 2,5
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 May 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 May 2011 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 May 2011](/thumbs/93/114127869.jpg) Coexistence of Magnetic Order and Two-dimensional Superconductivity at LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Interfaces Lu Li 1, C. Richter 2, J. Mannhart 2, R. C. Ashoori 1 arxiv:1105.0235v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 May 2011
Coexistence of Magnetic Order and Two-dimensional Superconductivity at LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Interfaces Lu Li 1, C. Richter 2, J. Mannhart 2, R. C. Ashoori 1 arxiv:1105.0235v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 May 2011
Supplementary Figures:
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Cross-sectional morphology and Chemical composition. (a) A low-magnification dark-field TEM image shows the cross-sectional morphology of the BWO thin film
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Cross-sectional morphology and Chemical composition. (a) A low-magnification dark-field TEM image shows the cross-sectional morphology of the BWO thin film
Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Chemical Vapor Deposition Graphene Grown on Peeled- Off Epitaxial Cu(111) Foil: A Simple Approach to Improved Properties
 Supplementary information Chemical Vapor Deposition Graphene Grown on Peeled- Off Epitaxial Cu(111) Foil: A Simple Approach to Improved Properties Hak Ki Yu 1,2, Kannan Balasubramanian 3, Kisoo Kim 4,
Supplementary information Chemical Vapor Deposition Graphene Grown on Peeled- Off Epitaxial Cu(111) Foil: A Simple Approach to Improved Properties Hak Ki Yu 1,2, Kannan Balasubramanian 3, Kisoo Kim 4,
Soft X-ray Physics DELNOR-WIGGINS PASS STATE PARK
 Soft X-ray Physics Overview of research in Prof. Tonner s group Introduction to synchrotron radiation physics Photoemission spectroscopy: band-mapping and photoelectron diffraction Magnetic spectroscopy
Soft X-ray Physics Overview of research in Prof. Tonner s group Introduction to synchrotron radiation physics Photoemission spectroscopy: band-mapping and photoelectron diffraction Magnetic spectroscopy
8 Summary and outlook
 91 8 Summary and outlook The main task of present work was to investigate the growth, the atomic and the electronic structures of Co oxide as well as Mn oxide films on Ag(001) by means of STM/STS at LT
91 8 Summary and outlook The main task of present work was to investigate the growth, the atomic and the electronic structures of Co oxide as well as Mn oxide films on Ag(001) by means of STM/STS at LT
Bi-directional phase transition of Cu/6H SiC( ) system discovered by positron beam study
 Applied Surface Science 194 (2002) 278 282 Bi-directional phase transition of Cu/6H SiC(0 0 0 1) system discovered by positron beam study J.D. Zhang a,*, H.M. Weng b, Y.Y. Shan a, H.M. Ching a, C.D. Beling
Applied Surface Science 194 (2002) 278 282 Bi-directional phase transition of Cu/6H SiC(0 0 0 1) system discovered by positron beam study J.D. Zhang a,*, H.M. Weng b, Y.Y. Shan a, H.M. Ching a, C.D. Beling
O xide interface attracts great interest since the discovery of high mobility electron gas in the interface of
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS ELECTRONIC DEVICES APPLIED PHYSICS Reversible insulator-metal transition of LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface for nonvolatile memory Hong-Liang Lu 1, Zhi-Min
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS ELECTRONIC DEVICES APPLIED PHYSICS Reversible insulator-metal transition of LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface for nonvolatile memory Hong-Liang Lu 1, Zhi-Min
S emiconductor heterostructures have brought about prominent advances in a variety of mainstream electronics
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: SURFACES, INTERFACES AND THIN FILMS ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS SPINTRONICS MAGNETIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS Tuning the entanglement between orbital reconstruction and charge
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: SURFACES, INTERFACES AND THIN FILMS ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS SPINTRONICS MAGNETIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS Tuning the entanglement between orbital reconstruction and charge
Giant Magnetoresistance
 Giant Magnetoresistance N. Shirato urse: Solid State Physics 2, Spring 2010, Instructor: Dr. Elbio Dagotto Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996
Giant Magnetoresistance N. Shirato urse: Solid State Physics 2, Spring 2010, Instructor: Dr. Elbio Dagotto Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES. J. M. De Teresa
 MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
Electric-field control of magnetic domain wall motion and local magnetization reversal
 Electric-field control of magnetic domain wall motion and local magnetization reversal Tuomas H. E. Lahtinen, Kévin J. A. Franke and Sebastiaan van Dijken* NanoSpin, Department of Applied Physics, Aalto
Electric-field control of magnetic domain wall motion and local magnetization reversal Tuomas H. E. Lahtinen, Kévin J. A. Franke and Sebastiaan van Dijken* NanoSpin, Department of Applied Physics, Aalto
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 25 Apr 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 25 Apr 2011 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 25 Apr 2011](/thumbs/94/121705428.jpg) Metallic characteristics in superlattices composed of insulators, NdMnO 3 /SrMnO 3 /LaMnO 3 J. W. Seo, 1,2 B. T. Phan, 3,4 J. Lee, 4 H.-D. Kim, 5 and C. Panagopoulos 1,2 1) Division of Physics and Applied
Metallic characteristics in superlattices composed of insulators, NdMnO 3 /SrMnO 3 /LaMnO 3 J. W. Seo, 1,2 B. T. Phan, 3,4 J. Lee, 4 H.-D. Kim, 5 and C. Panagopoulos 1,2 1) Division of Physics and Applied
