A-site Ordering versus Electronic Inhomogeneity in CMR-Manganite Films
|
|
|
- Kevin Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A-site Ordering versus Electronic Inhomogeneity in CMR-Manganite Films V. Moshnyaga 1*, L. Sudheendra 1, O. I. Lebedev 2, K. Gehrke, O. Shapoval 3, A. Belenchuk 3, S.A. Köster 1, B. Damaschke 1, G. van Tendeloo 2, K. Samwer 1 1) Erstes Physikalisches Institut, Universität Göttingen, Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, D Göttingen, Germany; 2) EMAT, University of Antwerp (RUCA), Groenenborgerlaan 171, B-2020 Antwerpen, Belgium; 3) Institute of Applied Physics, Academiei Str. 5, MD-2028, Chisinau, Moldova; Epitaxial La 3/4 Ca 1/4 MnO 3 /MgO(100) (LCMO) thin films show unusual rhombohedral (R-3c) structure with a new perovskite superstructure due to unique ordering of La and Ca at the A-site positions. Very sharp insulatormetal and para-ferromagnetic phase transitions at temperatures up to T MI ~T C =295 K were observed. The ordered films were electronically homogeneous down to 1 nm scale as revealed by scanning tunnelling microscopy/spectroscopy. In contrast, orthorhombic and A-site disordered LCMO demonstrate broadened phase transitions as well as mesoscopic phase separation for T<<T C. The unique La/Ca ordering suppresses cation mismatch stress within one super-cell, a~1.55 nm, enhancing electronic homogeneity. Phase separation scenario seems not to be a unique mechanism for CMR as very large CMR=500 % was also observed in A-site ordered films. PACS numbers: Lx, d, h It is commonly believed that the basic physics of colossal magnetoresistant 1 (CMR) perovskite manganites, Ln 1-x Ae x MnO 3 (Ln 3+ =La, Nd, Sm, Pr etc. and Ae 2+ =Ca, Sr, Ba), is governed by the interplay between spin-, charge- and lattice degrees of freedom. The resulting phase diagram contains a number of competing electronic and structural phases 2-4. The Curie temperature, T C, and metal-insulator transition temperature, T MI, is controlled by A-site substitutions in the perovskite lattice with corresponding changing of the average ionic radius of the A-site cation, <r A >, and the tolerance factor, t = r + r ) / 2( r + r ) 2-4. Two types of A-site ( A O B O occupancy are reported for perovskite manganites. First, random distribution of A-site cations like in a solid solution is shown for CMR manganites 5, like LCMO. The disorder not only reduces T 5 C due to size mismatch strain fields and corresponding Jahn-Teller (JT) distortions of the MnO 6 octahedra 6 but also causes electronic inhomogeneity or phase separation (PS) PS has been modelled both for cation disorder 11 and stress 12. CMR effect was attributed to the disorder induced PS, imposed on the first order phase transition 13. Secondly, the A-site ordered configuration was reported for half-doped manganites, Ln 0.5 Ba 0.5 MnO The LnO and BaO layers, alternatively stacked along the c-axis, provide the absence of random Coulomb potential and/or local strain in the MnO 2 sheets. Such an ordering stabilizes the long-range charge/orbital ordered (COO) insulating phase at high temperatures up to T CO =500 K (for Ln=Y). 1
2 To the best of our knowledge there are no reports on the A-site ordered and optimally doped (0.2<x<0.4) CMR manganites. Prototypic middle bandwidth manganite as La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 with relatively small average radius of A-site cation, <r A >=1.205 Å, and tolerance factor, t=0.97<1, possesses orthorhombic (P nma ) structure at room temperature and transforms to a rhombohedral (R-3c) structure at 700 K 6. In this letter we report LCMO films with pseudo-cubic (R-3c) structure and new type of perovskite superstructure due to La/Ca ordering. We show that a unique ordering at the A-site positions not only brings about long range Coulomb order, but also suppresses cation mismatch strain within the superstructure unit cell. LCMO films with nominal Ca-doping level x=0.25 were epitaxially grown on MgO(100) substrates by a metalorganic aerosol deposition (MAD) technique 17,18. The thickness of the films were d=80-90 nm as determined from small angle X-ray scattering (XRD). XRD analysis shows cube-on-cube epitaxy of LCMO on MgO(100) and indicates a stress-free state of the film: the film lattice parameter, a p = nm, is very close to bulk value 19. Remarkably, in LCMO films a pseudo-cubic or rhombohedral (R-3c) crystalline structure was observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and electron diffraction (ED) analysis, shown in Fig. 1. The brighter basic reflections in both patterns show a square arrangement with a a p. Weak satellite reflections on both ED patterns suggest a modulated structure with a modulation vector q 1 1/4 [011]* C in the cross-section (Fig. 1c) and q 2 1/2 ([001]* C in plain-view ED pattern (Fig. 1a). High resolution (HREM) plain-view and cross-section images are shown in Fig. 1b & 1d, respectively. In the plain view a twinned structure was seen; therefore the modulation in the ED patterns is only one- dimensional, but appears in two symmetry related directions. The La(Ca)O layers (indicated by arrows in Fig. 1b & 1d are imaged as rows of brighter dots, whereas LaO layers are imaged as rows of less brightness dots in Fig. 1b. The cross-section HREM image in Fig. 1d gives even more evidence for this modulated structure. The Fourier transform (not shown here) of this modulated area exhibits a pattern very similar to the corresponding ED pattern in Fig. 1c. The modulation shows up as alternative blocks of 2a p x a p size of a different brightness, indicating an ordering of La and Ca-columns. In Fig. 2 a model for the La/Ca ordering is shown, which is in agreement with the measured ED and HREM. The La-Ca ordering involves an alternating stacking of La-O and La(Ca)-O layers along the [010] c direction. The La and Ca are ordered within the La(Ca)-O layer along the [100] c direction: two La atoms alternate with two Ca atoms (see [001] c view in Fig. 2b). The layering of LaO and (La,Ca)O planes becomes evident along the [011] c direction. In this direction the film can be viewed as composed of two repeating La-Mn-O (LMO) layers followed 2
3 by the two layers of La-Mn-Ca-Mn-O (LMCMO). Both layers together form the body-centred cubic superstructure unit cell. The theoretical cation stoichiometry, La 3/4 Ca 1/4 Mn 1 O 3, agrees with nominal composition. The simulated ED patterns in Fig. 2 correlate very well with those measured (Fig. 1). The image simulations (the insets in Fig. 2a, and 2b), based on the proposed model, are also in agreement with the experimental images. We also checked for PS in cation ordered LCMO (O-film) in comparison with disordered a orthorhombic LCMO (D-film) 20 using scanning tunnelling microscopy/spectroscopy (STM/STS) 9. The surface of the O-film (Fig. 3a) looks very smooth and flat with average surface roughness, RMS=0.2 nm. One-unit cell height steps are clearly seen in between nm wide terraces. The D-film (Fig. 3b) shows crystalline grains with diameter ~50 nm and RMS=2 nm. In Fig. 3c, & 3d we present the distribution of the local tunnelling conductance, σ=(di/dv) V=0, measured in the ferromagnetic state for T=115 K<<T C for the O- and D-films, respectively. The O-film (Fig. 3c) shows spatially homogenous, at least down to 1 nm scale (the limit of our STS setup), tunnelling conductance of metallic type i.e. σ 0. The conductance map of the D-film (Fig. 3d) is inhomogeneous insulating regions, σ 0, of about 5-20 nm size ( black clouds in Fig. 3d) are intermixed with metallic (red) regions. Thus, even for T<<T C the D-film shows a mesoscopic PS, whereas the O-film does not. In Fig. 4a we compared temperature dependence of the resistivity, ρ(t), for the O-film with T MI =272 K and T C =264 K and that for a bulk orthorhombic LCMO 3 with the same doping level x=0.25. The metal-insulator transition, characterized by the temperature coefficient of the resistance TCR max =100%*(1/R)(dR/dT) 21, is very sharp for the cation ordered LCMO film, yielding TCR max =37 %/K. In contrast the bulk orthorhombic LCMO possesses broadened MI- transition, TCR max =12 %, and significantly lower T MI ~240 K. We have observed a new perovskite superstructure due to A-site cation ordering in LCMO films. A more symmetric pseudo-cubic (R-3c) crystalline structure builds up with enlarged super-lattice cell in [001] direction i.e. a s =4a p =1.55 nm. We analysed the projections of perovskite unit cells from the cross-section HREM pictures by assuming the positions for La- (shown as blue spheres), Ca- (red) and Mn- (white) atoms and superpose them on the crosssection HREM in Fig. 2c. Remarkably, the local stresses due to La/Ca cation size mismatch, which are crucial for PS and magnetotransport phenomena, are compensated within one supercell. Basic LMO and CMO cells, approximated as quadrangles around La (B-cell) and Ca (Rcell) atoms, respectively, are evidently not equal: their lengths relate exactly to their lattice parameters, i.e. a LMO =0.390 nm and a CMO =0.373 nm. This indicates a stress-free state of R- and 3
4 B-cells. Along [001]- and [010]-axes basic cells are linked by the intermediate, B1-cells, which accommodate LMO/CMO local stresses via axial deformation with intervening tensile, B1 +, and compressive, B1 -, strains of (Mn-Mn)-distances, probably due to the change of (Mn-O-Mn)- angle. The sequence of strained domains is the following: [R-(B1 + )-B-(B1 - )]-[(R-(B1 + )-B-(B1 - )]- (1) Along the diagonals of super-cell, the local stress has rather biaxial nature resulting in parallelogram-like deformation, (B1 +- ), with the following sequence of strain domains: [R-(B1 +- )-R-(B1 +- )]-[(R-(B1 +- )-R-(B1 +- )]- (2) The resulting distribution of local stresses within one super-cell is shown in Fig. 2d. One can see tensile-like (blue) and the compressive-like (red) stressed perovskite cells arranged in a zigzagstripe fashion along the [011] diagonal of the super-cell. The overall stress, being the sum of red and blue regions, is fully compensated within one super-cell. In another words, the ordered LCMO film along the [011]-direction looks as infinite superlattice, [2 LMO /2 La 0.5 Ca 0.5 MnO 3 ] N, in which small lattice misfit ε=(a LMO -a LCMO )/a LMO =1.5 % can be accommodated by the above shown mechanism. Such a layering looks energetically more favourable than a simple [LMO/CMO] N layering, which would result in a significantly larger lattice misfit, ε=4.5 %. We believe that the revealed very short scale stress accommodation mechanism drives the formation of a cation-ordered perovskite superstructure with enlarged super-cell, a s =4a p. This modifies the crystalline structure of the film from the bulk orthorhombic to a more symmetric R- 3c structure, which diminishes lattice distortions. Moreover, it provides a natural link between the disorder 11 and stress 12 in computational models for the phase separation problem (Fig. 3). Short scale stress relaxation within (R-3c) structure in the A-site ordered LCMO films yields very sharp phase transition and homogeneous ferromagnetic (FM) metallic ground state for T<T C. In contrast, cation disorder within orthorhombic LCMO exerts stress on a much larger, presumably, mesoscopic scale. This results in a structurally correlated nano-scale regions with cooperative Jahn-Teller (JT) effect 22,23 and localized charge carriers in accordance with observed broadening of phase transitions and metallic and insulating domains for T<T C in Fig. 3d. Interestingly, very large CMR=100%[(R(0)-R(5T)]/R(5T) 500 %, observed for A-site ordered LCMO (see Fig. 4), means that mescoscopic phase separation 11 seems to be not necessary attribute for the CMR effect at the FM/paramagnetic transition. This appears to be in accordance with CMR1 effect 24, which occurs in the absence of quenched disorder close to antiferromagnetic(af)/charge ordering phase boundary as field induced AF/FM transition. 4
5 Our experimental results allow to formulate a common superlattice rule to search for the A-site ordered manganite films: [(mln-mn-o)/(2(ln-mn-b-mn-o)] N (4) with m=0,1,2,3,..; Ln=Y, La, Nd, Pr ; and B=Ca, Sr, Ba. The ordered variants of LCMO films for different numbers of LMO layers m can be obtained as following: for m=1 we get La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 ; for m=2 La 3/4 Ca 1/4 MnO 3 ; m=3 La 4/5 Ca 1/5 MnO 3 ; m=4 La 5/6 Ca 1/6 MnO 3. Such a growth strategy provides a tool to check the relevance of earlier estimations 5 that the disorder-free manganite with large average cation radius (Ba) would possess very high T C =530 K. Interestingly, the layer-by-layer MAD-grown La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 films show an increase of the T MI of about 40 K (shown in Fig. 4b) as compared to the bulk samples 3, reaching room temperature, T MI =295 K. There are few earlier reports 25,26 on the possibility to increase the transition temperature for La-Ca-Mn-O films, prepared by pulsed laser ablation, up to room temperature region. However, there was no evidence on the origin of the observed effect. Our results indicate that the increase of the transition temperature could be achieved by controlling the structure and cation ordering in optimally doped manganite films, showing CMR effect. The authors thank Ch. Renner for the help in STM/STS and E. Dagotto for valuable comments. Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft via SFB 602, TPA2 is acknowledged. L.S. thanks the A. von Humboldt Foundation for the fellowship. REFERENCES 1. R. von Helmolt, J. Wecker, B. Holzapfel, L. Schultz, and K. Samwer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 2331 (1993). 2. H. Y. Hwang, S-W. Cheong, P. G. Radaelli, M. Marezio, and B. Batlogg, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, (1995). 3. P. Schiffer, A.P. Ramirez, W. Bao, and S-W. Cheong, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, (1995). 4. A.J. Millis, Nature 392, (1998). 5. L.M. Rodriguez and J.P. Attfield, Phys. Rev. B 54, (1996). 6. P.G. Radaelli, M. Marezio, H.Y. Hwang, S-W. Cheong and B. Batlogg, Phys. Rev. B 54, (1996). 7. M. Uehara, S. Mori, C.H. Chen, and S-W. Cheong, Nature 399, (1999). 8. M. Fäth, S. Freisem, A. A. Menovsky, Y. Tomioka, J. Aarts, and J. A. Mydosh, Science 285, 1540 (1999). 9. T. Becker, C. Streng, Y. Luo, V. Moshnyaga, B. Damaschke, N. Schannon, and K. Samwer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, (2002). 10. Ch. Renner, G. Aeppli, B.-G. Kim, Y.-A. Soh, S.-W. Cheong, Nature 416, 518 (2002). 11. E. Dagotto, T. Hotta, A. Moreo, Physics Reports 344, (2001). 12. K. Ahn, T. Lookman, and A.R. Bishop, Nature 428, (2004). 13. J. Burgy, M. Mayr, V. Martin-Mayor, A. Moreo, and E. Dagotto, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, (2001). 14. T. Arima, D. Akahoshi, K. Oikawa, T. Kamiyama, M. Uchida, T. Arima and Y. Tokura, Phys.Rev. B 66, (R) (2002). 15. D. Akahoshi, M. Uchida,Y. Tomioka, T. Arima, T. Arima, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, (2003). 16. F. Millange, V. Caignart, B. Domenges, B. Raveau, E. Magnan and E. Suard, Chem. Mater. 10,
6 (1998). 17. V. Moshnyaga, I. Khoroshun, A. Sidorenko, P.A. Petrenko, A. Weidinger, M. Zeitler, B. Rauschenbach, R. Tidecks, K. Samwer, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 2842 (1999). 18. V. Moshnyaga et al., Nature Materials 2 (4), (2003). 19. P. G. Radaelli, G. Iannone, M. Marezio, H. Y. Hwang, S -W. Cheong, J. D. Jorgensen, D.N. Argyriou, Phys. Rev. B 56, 8265 (1997). 20. Detailed comparison of the characteristics of O - and D-films are available on Phys. Rev. Lett. Online. 21. M. Rajeswari, et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 (18), (1998). 22. V. Kiryukhin, T.Y. Koo, H. Ishibashi, J.P. Hill, and S-W. Cheong Phys. Rev. B 67, (2003). 23. J.W. Linn, R.W. Erwin, J.A. Borchers, Q. Huang, A. Santoro, J-L. Peng J-L. and Z.Y. Li, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 4046 (1996). 24. H. Aliaga, D. Magnoux, A. Moreo, D. Poilblanc, S. Yunoki, and E. Dagotto, Phys. Rev. B 68, (2003). 25. J. Y. Gu, K. H. Kim, T. W. Noh, and K.-S. Suh, J. Appl. Phys. 78, 6151 (1995). 26. R. Shreekala et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 1886 (1999). 6
7 FIG. 1 Plan-view (a) and cross-section (c) electron diffraction (ED) patterns of the cation ordered La 0.75 Ca 0.25 MnO 3 film with modulated structure. The ED pattern obtained from the MgO substrate indicated by white square in (c). The white rectangles in (a) correspond to the twinned LCMO structure. Plan-view (b) and cross-section (d) HREM images of the same film. The Fourier transforms from single domain of the modulated area given as insert and exhibit a pattern similar to the corresponding ED patterns in Fig. 1a) and 1c). 7
8 FIG. 2 Structural model of the La-Ca ordered La 0.75 Ca 0.25 MnO 3 phase, taking into account experimental evidence: (a) - represents the projection along [100] c direction and (b) represents the projection along [001] c direction. The corresponding calculated ED patterns and simulated HREM images obtained at a defocus value f = - 30 nm and thickness t = 18 nm based on the proposed model (given as inset in HREM images) show a good agreement with an experimental ones. In (c) a fragment of HREM image (b) is shown with superimposed single perovskite cells, containing A-cations (red - Ca and blue - La) and Mn (white). The distribution of local stress is shown in (d) with compressive-like (red stripes) and tensile-like (blue stripes). The overall stress is compensated within one super-cell, a S =4a p =1.55 nm 8
9 FIG. 3 Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) morphology image (500x500 nm 2 ) of a pseudo-cubic LCMO ( O-film ) (a) and 250x250 nm 2 STM morphology scan of the orthorhombic D-film (b). The tunneling conductivity map of O-film (c)- and D-films (d), obtained from the same regions as in Fig. 1(a) and (b), respectively. Electronically homogeneous behaviour in O-film and metal-like (red) and insulator-like (black) coexistence in D-film are evident. Scale represents the conductance in na/v. 9
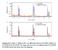
10 ρ (mωcm) a) B= T T (K) b) CMR (%) T MI (K) x MI =0.175 in Bulk 180 0,15 0,20 0,25 0,30 0,35 0,40 0,45 0,50 Ca concentration, x FIG. 4. (a) - Temperature dependence of the resistivity, ρ(t), for cation ordered film (red curve by B=0 and the blue one for B=5 T) and for a bulk sample (redrawn from Ref. 3, open quadrates) of the same La 0.75 Ca 0.25 MnO 3 composition. The right scale relates to the evaluated temperature dependence of CMR=100%(R(0)-R(5T))/R(5T); (b) Metal-insulator transition temperatures, T MI, for MAD layer-bylayer grown LCMO/MgO films (red quadrates) for bulk samples (redrawn from Ref. 3, black quadrates) as a function of Ca-doping level. The connecting lines are drawn as guide to the eye. 10
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in. manganite multilayers
 Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Evidence for Jahn-Teller Polarons*
 Zeitschrift fur Physikalische Chemie, Bd. 201, S. 263-269 (1997) by R. Oldenbourg Verlag, München 1997 Giant Oxygen-Isotope Shift of the Ferromagnetic Transition Temperature in the Colossal Magnetoresistive
Zeitschrift fur Physikalische Chemie, Bd. 201, S. 263-269 (1997) by R. Oldenbourg Verlag, München 1997 Giant Oxygen-Isotope Shift of the Ferromagnetic Transition Temperature in the Colossal Magnetoresistive
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 23 Jul 2007
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 23 Jul 2007 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 23 Jul 2007](/thumbs/77/75146340.jpg) Polaronic signature in the metallic phase of La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 films detected by scanning tunneling spectroscopy S. Seiro, Y. Fasano, I. Maggio-Aprile, E. Koller, O. Kuffer, and Ø. Fischer Département
Polaronic signature in the metallic phase of La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 films detected by scanning tunneling spectroscopy S. Seiro, Y. Fasano, I. Maggio-Aprile, E. Koller, O. Kuffer, and Ø. Fischer Département
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered
 Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Manipulation of the magnetic order parameter and the metal-insulatortransition. of a manganite thin film with applied elastic stress
 Manipulation of the magnetic order parameter and the metal-insulatortransition of a manganite thin film with applied elastic stress Surendra Singh, 1 M. R. Fitzsimmons, 2 T. Lookman, 2 H. Jeen 3,4 and
Manipulation of the magnetic order parameter and the metal-insulatortransition of a manganite thin film with applied elastic stress Surendra Singh, 1 M. R. Fitzsimmons, 2 T. Lookman, 2 H. Jeen 3,4 and
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Te x MnO 3
 phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
Australian Journal of Physics
 CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
No. 3 An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in MFM results, it is suggested that the PS in LSMO is not a charge seg
 Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) La (Sr Ca )MnO x x 3. *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu. a, a b
 International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) 1063 1072 Chemical pressure controlled colossal magnetoresistance effects in q La (Sr Ca )MnO R.S. Liu *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu a, a b a Department of
International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) 1063 1072 Chemical pressure controlled colossal magnetoresistance effects in q La (Sr Ca )MnO R.S. Liu *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu a, a b a Department of
PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB
![PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB PROOF COPY [LD9110BJ] PRB](/thumbs/84/91030401.jpg) Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
Effect of oxygen stoichiometry on spin, charge, and orbital ordering in manganites R. Vidya,* P. Ravindran, P. Vajeeston, A. Kjekshus, and H. Fjellvåg Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, P.O.
Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 (x = 0 and 0.
 Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5 <= x <= 0.9) manganites
 Title Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5
Title Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5
Accepted in Applied Physics Letters. Atomic-scale electrochemistry on the surface of a manganite by scanning tunneling microscopy
 Accepted in Applied Physics Letters Atomic-scale electrochemistry on the surface of a manganite by scanning tunneling microscopy Rama K. Vasudevan 1,2,*, Alexander Tselev 1,2, Anthony G. Gianfrancesco
Accepted in Applied Physics Letters Atomic-scale electrochemistry on the surface of a manganite by scanning tunneling microscopy Rama K. Vasudevan 1,2,*, Alexander Tselev 1,2, Anthony G. Gianfrancesco
Ohoyama., TEM, neutron diffraction, ordered perovskite, CE structure. Abstract An A-site ordered manganese perovskite YBaMn 2
 New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
New Stacking Variations of the CE-type Structure in the Metal-Ordered Manganite YBaMn 2 1 H. Kageyama, 1 T. Nakajima, 1 M. Ichihara, 1 Y. Ueda, and 2 H. Yoshizawa, 3 K. Ohoyama 1 Material Design and Characterization
Assessment of Variation in Zero Field Hall Constant of Colossal Magnetoresistive Manganites (Re1-x AxMnO3)
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study
 Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
SEEING Phase Transitions with. Magnetic Force Microscopy. Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin. Alex de Lozanne
 SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/114118020.jpg) Damping and softening of transverse acoustic phonons in colossal magnetoresistive La.7 Ca.3 MnO 3 and La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 Joel S. Helton 1,2,, Yang Zhao 2,3, Dmitry A. Shulyatev 4, and Jeffrey W. Lynn 2, 1
Damping and softening of transverse acoustic phonons in colossal magnetoresistive La.7 Ca.3 MnO 3 and La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 Joel S. Helton 1,2,, Yang Zhao 2,3, Dmitry A. Shulyatev 4, and Jeffrey W. Lynn 2, 1
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Complexity in Transition Metal Oxides
 Complexity in Transition Metal Oxides Adriana Moreo Dept. of Physics and ORNL University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA. Supported by NSF grants DMR-0443144 and 0454504. Collaborators G. Alvarez (ORNL)
Complexity in Transition Metal Oxides Adriana Moreo Dept. of Physics and ORNL University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA. Supported by NSF grants DMR-0443144 and 0454504. Collaborators G. Alvarez (ORNL)
Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 Specific heat of Pr 0.6 Ca 1 x Sr x 0.4 MnO 3 0 x 1 M. R. Lees, O. A. Petrenko, G. Balakrishnan, and D. McK. Paul Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry
Intrinsic chemical and structural inhomogeneity in lightly doped La 1-x Sr x MnO 3
 Intrinsic chemical and structural inhomogeneity in lightly doped La 1-x x MnO 3 Tomohiro Shibata, a Bruce Bunker, a John Mitchell, b and Peter Schiffer c a) Department of Physics, University of Notre Dame,
Intrinsic chemical and structural inhomogeneity in lightly doped La 1-x x MnO 3 Tomohiro Shibata, a Bruce Bunker, a John Mitchell, b and Peter Schiffer c a) Department of Physics, University of Notre Dame,
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
ANALYSIS OF CATION VALENCES AND OXYGEN VACANCIES IN MAGNETORESISTIVE OXIDES BY ELECTRON ENERGY-LOSS SPECTROSCOPY
 ANALYSIS OF CATION VALENCES AND OXYGEN VACANCIES IN MAGNETORESISTIVE OXIDES BY ELECTRON ENERGY-LOSS SPECTROSCOPY Z.L. WANGa, J.S. YIN, Y. BERTA, J. ZHANG* School of Material Science and Engineering, Georgia
ANALYSIS OF CATION VALENCES AND OXYGEN VACANCIES IN MAGNETORESISTIVE OXIDES BY ELECTRON ENERGY-LOSS SPECTROSCOPY Z.L. WANGa, J.S. YIN, Y. BERTA, J. ZHANG* School of Material Science and Engineering, Georgia
Thermopower of single-crystal Nd 1 x Sr,Pb x MnO 3
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 21 1 JUNE 1996-I Thermopower of single-crystal Nd 1 x Sr,Pb x MnO 3 Vincent H. Crespi, Li Lu, Y. X. Jia, K. Khazeni, A. Zettl, and Marvin L. Cohen Department of Physics,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 21 1 JUNE 1996-I Thermopower of single-crystal Nd 1 x Sr,Pb x MnO 3 Vincent H. Crespi, Li Lu, Y. X. Jia, K. Khazeni, A. Zettl, and Marvin L. Cohen Department of Physics,
Coherent optical and acoustic phonon generation correlated with the charge-ordering phase transition in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3
 Coherent optical and acoustic phonon generation correlated with the charge-ordering phase transition in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 D. Lim, 1 V. K. Thorsmølle, 1 R. D. Averitt, 1 Q. X. Jia, 1 K. H. Ahn, 2 M. J.
Coherent optical and acoustic phonon generation correlated with the charge-ordering phase transition in La 1 x Ca x MnO 3 D. Lim, 1 V. K. Thorsmølle, 1 R. D. Averitt, 1 Q. X. Jia, 1 K. H. Ahn, 2 M. J.
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79,
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79, 17442 29 Ferroelectric poling and converse-piezoelectric-effect-induced strain effects in La.7 Ba.3 MnO 3 thin films grown on ferroelectric single-crystal substrates R. K. Zheng,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79, 17442 29 Ferroelectric poling and converse-piezoelectric-effect-induced strain effects in La.7 Ba.3 MnO 3 thin films grown on ferroelectric single-crystal substrates R. K. Zheng,
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy & Spectroscopy: A tool for probing electronic inhomogeneities in correlated systems
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy & Spectroscopy: A tool for probing electronic inhomogeneities in correlated systems Anjan K. Gupta Physics Department, I. I. T Kanpur ICTS-GJ, IITK, Feb 2010 Acknowledgements
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy & Spectroscopy: A tool for probing electronic inhomogeneities in correlated systems Anjan K. Gupta Physics Department, I. I. T Kanpur ICTS-GJ, IITK, Feb 2010 Acknowledgements
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides. Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625
 Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Magnetic coupling in the insulating and metallic ferromagnetic La 1Àx Ca x MnO 3
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 224429 Magnetic coupling in the insulating and metallic ferromagnetic La 1Àx Ca x MnO 3 Pengcheng Dai, 1,2 J. A. Fernandez-Baca, 2 E. W. Plummer, 1,2 Y. Tomioka, 3,4 and Y.
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 224429 Magnetic coupling in the insulating and metallic ferromagnetic La 1Àx Ca x MnO 3 Pengcheng Dai, 1,2 J. A. Fernandez-Baca, 2 E. W. Plummer, 1,2 Y. Tomioka, 3,4 and Y.
The crucial role of mixed valence in the magnetoresistance properties of manganites and cobaltites
 366, 83 92 doi:10.1098/rsta.2007.2141 Published online 7 September 2007 The crucial role of mixed valence in the magnetoresistance properties of manganites and cobaltites BY B. RAVEAU* Laboratoire CRISMAT,
366, 83 92 doi:10.1098/rsta.2007.2141 Published online 7 September 2007 The crucial role of mixed valence in the magnetoresistance properties of manganites and cobaltites BY B. RAVEAU* Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy
 Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of
 Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7
 J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
Direct measurement of charge transfer phenomena at ferromagnetic/superconducting oxide interfaces Spain. One Shields Ave. Davis, CA
 Direct measurement of charge transfer phenomena at ferromagnetic/superconducting oxide interfaces M. Varela 1,, A.R. Lupini 1, V. Peña 2, Z. Sefrioui 2, I. Arslan 3,4,, N.D. Browning 3,4, J. Santamaria
Direct measurement of charge transfer phenomena at ferromagnetic/superconducting oxide interfaces M. Varela 1,, A.R. Lupini 1, V. Peña 2, Z. Sefrioui 2, I. Arslan 3,4,, N.D. Browning 3,4, J. Santamaria
Mössbauer study of the relationship between magnetic properties and Jahn Teller distortion in La 1 x Ba x (Mn,Fe)O 3 perovskites
 phys. stat. sol. (b) 242, No. 14, 293 2937 (25) / DOI 1.12/pssb.25412 Mössbauer study of the relationship between magnetic properties and Jahn Teller distortion in La 1 x Ba x (Mn,Fe)O 3 perovskites Zhi-qi
phys. stat. sol. (b) 242, No. 14, 293 2937 (25) / DOI 1.12/pssb.25412 Mössbauer study of the relationship between magnetic properties and Jahn Teller distortion in La 1 x Ba x (Mn,Fe)O 3 perovskites Zhi-qi
Structural and magnetic properties of the colossal magnetoresistance perovskite La 0.85 Ca 0.15 MnO 3
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 13 1 APRIL 2000-I Structural and magnetic properties of the colossal magnetoresistance perovskite La 0.85 Ca 0.15 MnO 3 M. V. Lobanov Department of Chemistry, Moscow
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 13 1 APRIL 2000-I Structural and magnetic properties of the colossal magnetoresistance perovskite La 0.85 Ca 0.15 MnO 3 M. V. Lobanov Department of Chemistry, Moscow
Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems
 Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems By Lina Gunawan (0326114) Supervisor: Dr. Gianluigi Botton November 1, 2006 MSE 702(1) Presentation Outline Literature Review
Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems By Lina Gunawan (0326114) Supervisor: Dr. Gianluigi Botton November 1, 2006 MSE 702(1) Presentation Outline Literature Review
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport. Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR)
 Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Jul 2004](/thumbs/72/66676281.jpg) Coexisting charge modulation and ferromagnetism produces long period phases in manganites: new example of electronic soft matter. G.C. Milward, M.J. Calderón, P.B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/0407727v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Coexisting charge modulation and ferromagnetism produces long period phases in manganites: new example of electronic soft matter. G.C. Milward, M.J. Calderón, P.B. Littlewood arxiv:cond-mat/0407727v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998](/thumbs/78/78285667.jpg) Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 213 (2000) 271}277
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 213 (2000) 271}277 Low-"eld magnetic properties of La Ca (0)x)0.4) R. Laiho*, K.G. Lisunov, E.LaK hderanta, P. Petrenko, V.N. Stamov, V.S. Zakhvalinskii Wihuri
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 213 (2000) 271}277 Low-"eld magnetic properties of La Ca (0)x)0.4) R. Laiho*, K.G. Lisunov, E.LaK hderanta, P. Petrenko, V.N. Stamov, V.S. Zakhvalinskii Wihuri
Material Science II. d Electron systems
 Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
Phase Diagram of Spin States and Magnetic Interactions in Isotope Substituted (Pr,Eu) 0.7 Ca 0.3 CoO 3
 Solid State Phenomena Vols. 168-169 (2011) pp 465-468 Online available since 2010/Dec/30 at www.scientific.net (2011) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.168-169.465
Solid State Phenomena Vols. 168-169 (2011) pp 465-468 Online available since 2010/Dec/30 at www.scientific.net (2011) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.168-169.465
Signatures of electronic phase separation in the Hall effect of anisotropically strained La 0.67 Ca 0.33 MnO 3 films
 Signatures of electronic phase separation in the Hall effect of anisotropically strained La 0.67 Ca 0.33 MnO 3 films Liuqi Yu 1, Lingfei Wang 2, Xiaohang Zhang 3, W.B. Wu 2, S. von Molnár 1, Z. Fisk 4
Signatures of electronic phase separation in the Hall effect of anisotropically strained La 0.67 Ca 0.33 MnO 3 films Liuqi Yu 1, Lingfei Wang 2, Xiaohang Zhang 3, W.B. Wu 2, S. von Molnár 1, Z. Fisk 4
The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates. Abstract
 The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates Nicola Poccia, Michela Fratini Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome, P. Aldo Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: nicola.poccia@roma1.infn.it
The Misfit Strain Critical Point in the 3D Phase Diagrams of Cuprates Nicola Poccia, Michela Fratini Department of Physics, Sapienza University of Rome, P. Aldo Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: nicola.poccia@roma1.infn.it
Manganites: phenonmenology, present understanding and future prospects
 Manganites: phenonmenology, present understanding and future prospects Sandeep Pathak Materials Research Center, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore - 560 012, India (Dated:) Manganites are mixed-valence
Manganites: phenonmenology, present understanding and future prospects Sandeep Pathak Materials Research Center, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore - 560 012, India (Dated:) Manganites are mixed-valence
Uncorrelated and correlated nanoscale lattice distortions in the paramagnetic phase of magnetoresistive manganites
 Uncorrelated and correlated nanoscale lattice distortions in the paramagnetic phase of magnetoresistive manganites V. Kiryukhin 1, A. Borissov 1, J. S. Ahn 1, Q. Huang 2, J. W. Lynn 2, and S-W. Cheong
Uncorrelated and correlated nanoscale lattice distortions in the paramagnetic phase of magnetoresistive manganites V. Kiryukhin 1, A. Borissov 1, J. S. Ahn 1, Q. Huang 2, J. W. Lynn 2, and S-W. Cheong
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface
 What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
Magnon-phonon effects in ferromagnetic manganites
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 65, 04409 Magnon-phonon effects in ferromagnetic manganites L. M. Woods* Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Tennessee 37996 and Oak Ridge
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 65, 04409 Magnon-phonon effects in ferromagnetic manganites L. M. Woods* Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Tennessee 37996 and Oak Ridge
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method
 Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Electronic structure calculations results from LDA+U method Vladimir I. Anisimov Institute of Metal Physics Ekaterinburg, Russia LDA+U method applications Mott insulators Polarons and stripes in cuprates
Si, X. X. Xi, and Q. X. JIA
 LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6
 Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Linear temperature dependence of electron spin resonance linewidths in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and YBaMn 2 O 6 Abstract D. L. Huber Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53706
Charge-order driven multiferroic and magneto-dielectric properties of rare earth manganates
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 33, No. 2, April 2010, pp. 169 178. Indian Academy of Sciences. Charge-order driven multiferroic and magneto-dielectric properties of rare earth manganates CLAUDY RAYAN SERRAO 1,2,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 33, No. 2, April 2010, pp. 169 178. Indian Academy of Sciences. Charge-order driven multiferroic and magneto-dielectric properties of rare earth manganates CLAUDY RAYAN SERRAO 1,2,
Magneto-electronic phase separation in doped cobaltites
 Magneto-electronic phase separation in doped cobaltites A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Chunyong He IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
Magneto-electronic phase separation in doped cobaltites A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Chunyong He IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in
 Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Magnetic anisotropy of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 nanopowders
 Magnetic anisotropy of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 nanopowders I. Radelytskyi (1), P. Dłużewski (1), V. Dyakonov (1 and 2), P. Aleshkevych (1), W. Kowalski (1), P. Jarocki (1), H. Szymczak (1) ((1) Institute of
Magnetic anisotropy of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 nanopowders I. Radelytskyi (1), P. Dłużewski (1), V. Dyakonov (1 and 2), P. Aleshkevych (1), W. Kowalski (1), P. Jarocki (1), H. Szymczak (1) ((1) Institute of
Magnetization reversal and nanoscopic magnetic-phase separation in La 1 x Sr x CoO 3
 Magnetization reversal and nanoscopic magnetic-phase separation in La 1 x Sr x CoO 3 Joseph E. Davies, 1 J. Wu, 2 C. Leighton, 2, * and Kai Liu 1, 1 Department of Physics, University of California, Davis,
Magnetization reversal and nanoscopic magnetic-phase separation in La 1 x Sr x CoO 3 Joseph E. Davies, 1 J. Wu, 2 C. Leighton, 2, * and Kai Liu 1, 1 Department of Physics, University of California, Davis,
Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x. O 3 perovskite material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 24 Nov 2003](/thumbs/88/117739901.jpg) Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
Soft x-ray resonant diffraction study of magnetic and orbital correlations in a manganite near half-doping arxiv:cond-mat/0311553v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Nov 003 K. J. Thomas 1, J. P. Hill 1, Y-J. Kim 1,
Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices
 Physica E 2 (1998) 325 329 Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices D.M. Follstaedt *, R.D. Twesten, J. Mirecki Millunchick, S.R. Lee, E.D. Jones, S.P.
Physica E 2 (1998) 325 329 Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices D.M. Follstaedt *, R.D. Twesten, J. Mirecki Millunchick, S.R. Lee, E.D. Jones, S.P.
1.1 Introduction CMR effect in Manganites I - 1
 I - 1 1.1 Introduction The rare-earth perovskites LnTMO 3, with Ln a rare-earth element and TM a transition metal have been intensively studied because of large variety of physical phenomena such as superconductivity,
I - 1 1.1 Introduction The rare-earth perovskites LnTMO 3, with Ln a rare-earth element and TM a transition metal have been intensively studied because of large variety of physical phenomena such as superconductivity,
Lecture contents. Stress and strain Deformation potential. NNSE 618 Lecture #23
 1 Lecture contents Stress and strain Deformation potential Few concepts from linear elasticity theory : Stress and Strain 6 independent components 2 Stress = force/area ( 3x3 symmetric tensor! ) ij ji
1 Lecture contents Stress and strain Deformation potential Few concepts from linear elasticity theory : Stress and Strain 6 independent components 2 Stress = force/area ( 3x3 symmetric tensor! ) ij ji
Structure and properties of artificial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 m SrTiO 3 n 15 superlattices on 001 SrTiO 3.
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 94, NUMBER 12 15 DECEMBER 2003 Structure and properties of artificial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 m SrTiO 3 n 15 superlattices on 001 SrTiO 3. O. I. Lebedev, a) J. Verbeeck, and
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 94, NUMBER 12 15 DECEMBER 2003 Structure and properties of artificial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 m SrTiO 3 n 15 superlattices on 001 SrTiO 3. O. I. Lebedev, a) J. Verbeeck, and
Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal
 Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal M. Matsukawa, 1, * A. Tamura, 1 S. Nimori, 2 R. Suryanarayanan, 3 T. Kumagai,
Anomalous pressure effect on the remanent lattice striction of a La,Pr 1.2 Sr 1.8 Mn 2 O 7 bilayered manganite single crystal M. Matsukawa, 1, * A. Tamura, 1 S. Nimori, 2 R. Suryanarayanan, 3 T. Kumagai,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 26 Feb 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 26 Feb 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 26 Feb 2003](/thumbs/93/118020191.jpg) OPEN QUESTIONS IN CMR MANGANITES, RELEVANCE OF CLUSTERED STATES, AND ANALOGIES WITH OTHER COMPOUNDS arxiv:cond-mat/0302550v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 26 Feb 2003 ELBIO DAGOTTO 1 1 National High Magnetic Field
OPEN QUESTIONS IN CMR MANGANITES, RELEVANCE OF CLUSTERED STATES, AND ANALOGIES WITH OTHER COMPOUNDS arxiv:cond-mat/0302550v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 26 Feb 2003 ELBIO DAGOTTO 1 1 National High Magnetic Field
Strong charge ordering above room temperature in B-site disordered electron-doped manganite SrMn Mo O 3-δ
 Strong charge ordering above room temperature in B-site disordered electron-doped manganite SrMn 0.875 Mo 0.125 O 3-δ Aga Shahee* and N. P. Lalla UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, University
Strong charge ordering above room temperature in B-site disordered electron-doped manganite SrMn 0.875 Mo 0.125 O 3-δ Aga Shahee* and N. P. Lalla UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, University
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces
 Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Supplementary Figure 1: Projected density of states (DOS) of the d states for the four titanium ions in the SmSr superlattice (Ti 1 -Ti 4 as defined
 Supplementary Figure 1: Projected density of states (DOS) of the d states for the four titanium ions in the SmSr superlattice (Ti 1 -Ti 4 as defined in the main text). Supplementary Table 1: Comparison
Supplementary Figure 1: Projected density of states (DOS) of the d states for the four titanium ions in the SmSr superlattice (Ti 1 -Ti 4 as defined in the main text). Supplementary Table 1: Comparison
C. D. Lee and R. M. Feenstra Dept. Physics, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213
 Morphology and surface reconstructions of GaN(1 1 00) surfaces C. D. Lee and R. M. Feenstra Dept. Physics, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 J. E. Northrup Palo Alto Research Center, 3333
Morphology and surface reconstructions of GaN(1 1 00) surfaces C. D. Lee and R. M. Feenstra Dept. Physics, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 J. E. Northrup Palo Alto Research Center, 3333
CORRELATED ELECTRON OXIDES AS THE COMPLEX SYSTEM. Yoshinori Tokura
 CORRELATED ELECTRON OXIDES AS THE COMPLEX SYSTEM Yoshinori Tokura When electron-electron Coulomb repulsion interaction is strong in a solid, electrons are almost localized on the respective atomic sites
CORRELATED ELECTRON OXIDES AS THE COMPLEX SYSTEM Yoshinori Tokura When electron-electron Coulomb repulsion interaction is strong in a solid, electrons are almost localized on the respective atomic sites
Bangmin Zhang. (B. Sci., Lanzhou University, China) (M. Sci., Lanzhou University, China) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY
 Properties of strain modulated manganite Pr 0.67 Sr 0.33 MnO 3 thin films Bangmin Zhang (B. Sci., Lanzhou University, China) (M. Sci., Lanzhou University, China) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR
Properties of strain modulated manganite Pr 0.67 Sr 0.33 MnO 3 thin films Bangmin Zhang (B. Sci., Lanzhou University, China) (M. Sci., Lanzhou University, China) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR
Room temperature charge and orbital ordering and phase coexistence in Bi 0.5 Sr 0.5 MnO 3
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13 (2001) 1071 1078 www.iop.org/journals/cm PII: S0953-8984(01)19607-4 Room temperature charge and orbital
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF PHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13 (2001) 1071 1078 www.iop.org/journals/cm PII: S0953-8984(01)19607-4 Room temperature charge and orbital
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 22 Jul 1999
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 22 Jul 1999 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 22 Jul 1999](/thumbs/71/65805847.jpg) Charge carrier density collapse in La 067 Ca 033 and La 067 Sr 033 epitaxial thin films W Westerburg, F Martin, and G Jakob Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, D-55099 Mainz, Germany
Charge carrier density collapse in La 067 Ca 033 and La 067 Sr 033 epitaxial thin films W Westerburg, F Martin, and G Jakob Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, D-55099 Mainz, Germany
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002](/thumbs/73/69440848.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0209089v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002 Double exchange and orbital correlations in electron doped manganites Tulika Maitra 1 and A. Taraphder 2 Department of Physics & Meteorology and Centre
arxiv:cond-mat/0209089v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 4 Sep 2002 Double exchange and orbital correlations in electron doped manganites Tulika Maitra 1 and A. Taraphder 2 Department of Physics & Meteorology and Centre
Presented by: Göteborg University, Sweden
 SMR 1760-3 COLLEGE ON PHYSICS OF NANO-DEVICES 10-21 July 2006 Nanoelectromechanics of Magnetic and Superconducting Tunneling Devices Presented by: Robert Shekhter Göteborg University, Sweden * Mechanically
SMR 1760-3 COLLEGE ON PHYSICS OF NANO-DEVICES 10-21 July 2006 Nanoelectromechanics of Magnetic and Superconducting Tunneling Devices Presented by: Robert Shekhter Göteborg University, Sweden * Mechanically
Evolution of microstructure, strain and physical properties in oxide nanocomposite films
 Intensity(a.u.) LSMO(002) ZnO(110) LAO(002) Supporting Information for Evolution of microstructure, strain and physical properties in oxide nanocomposite films Aiping Chen 1, *, Marcus Weigand 1, Zhenxing
Intensity(a.u.) LSMO(002) ZnO(110) LAO(002) Supporting Information for Evolution of microstructure, strain and physical properties in oxide nanocomposite films Aiping Chen 1, *, Marcus Weigand 1, Zhenxing
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES. J. M. De Teresa
 MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
Revisiting the Role of Vacancies in Manganese Related Perovskites
 The Open Inorganic Chemistry Journal, 2007, 1, 37-46 37 Revisiting the Role of Vacancies in Manganese Related Perovskites Luisa Ruiz-González 1, Raquel Cortés-Gil 1,2, José M. Alonso 2,3, José M. González-Calbet
The Open Inorganic Chemistry Journal, 2007, 1, 37-46 37 Revisiting the Role of Vacancies in Manganese Related Perovskites Luisa Ruiz-González 1, Raquel Cortés-Gil 1,2, José M. Alonso 2,3, José M. González-Calbet
Microstructure evolution during BaTiO 3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces
 Journal of the European Ceramic Society 25 (2005) 2201 2206 Microstructure evolution during BaTiO 3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces Andreas Graff a,, Stephan Senz a,
Journal of the European Ceramic Society 25 (2005) 2201 2206 Microstructure evolution during BaTiO 3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces Andreas Graff a,, Stephan Senz a,
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar
 Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 174415 Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect H. C. Yang Department of Physics, National Taiwan
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 174415 Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect H. C. Yang Department of Physics, National Taiwan
When transition metals are incorporated into a certain site of the BiT, some of BiT-LaTMO 3
 Band gap tuning in ferroelectric Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 by alloying LaTMO 3 (TM = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, and Al) Woo Seok Choi and Ho Nyung Lee Materials Science and Technology Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Band gap tuning in ferroelectric Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 by alloying LaTMO 3 (TM = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, and Al) Woo Seok Choi and Ho Nyung Lee Materials Science and Technology Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional Oxide p-n Heterojunctions
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Newcastle University eprints
 Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
Magnetic field induced dielectric relaxation in the strain glass state of Pr 0.6 Ca 0.4 MnO 3
 Magnetic field induced dielectric relaxation in the strain glass state of Pr 0.6 Ca 0.4 MnO 3 K Devi Chandrasekhar 1, A K Das 1 and A Venimadhav 2,a) 1 Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian Institute
Magnetic field induced dielectric relaxation in the strain glass state of Pr 0.6 Ca 0.4 MnO 3 K Devi Chandrasekhar 1, A K Das 1 and A Venimadhav 2,a) 1 Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian Institute
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 2019](/thumbs/95/123272699.jpg) Effect of A-site ionic radius on metamagnetic transition in charge ordered Sm.5 (Ca.5 y Sr y )MnO 3 compounds arxiv:193.11348v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 219 Sanjib Banik, 1, Kalpataru Pradhan, 1, and
Effect of A-site ionic radius on metamagnetic transition in charge ordered Sm.5 (Ca.5 y Sr y )MnO 3 compounds arxiv:193.11348v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 27 Mar 219 Sanjib Banik, 1, Kalpataru Pradhan, 1, and
